The Gibbs Phenomenon
|
|
|
- Victoria Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Gibbs Phenomenon Eli Dean & Britton Girard Math 572, Fall 2013 December 4, 2013
2 1. Introduction 1 S N f(x) := f(n)e inx := 1 2π n N n N denotes the partial Fourier sum for f at the point x f(x)e inx dx e inx Can use Fourier Sums to approximate f : T R under the appropriate conditions
3 1. Introduction 2 Def n : Pointwise Convergence of Functions: A series of functions {f n } n N converges pointwise to f on the set D if ɛ > 0 and x D, N N such that f n (x) f(x) < ɛ n N. Def n : Uniform Convergence of Functions: A series of functions {f n } n N converges uniformly to f on the set D if ɛ > 0, N N such that f n (x) f(x) < ɛ n N and x D Figure : Pointwise Conv Figure : Uniform Conv.
4 1. Introduction 3 Some movies to illustrate the difference. (First Uniform then Pointwise)
5 1. Introduction 3 Some movies to illustrate the difference. (First Uniform then Pointwise) Persistent bump in second illustrates Gibbs Phenomenon.
6 2. Gibbs Phenomenon: A Brief History 1 Basic Background 1848: Property of overshooting discovered by Wilbraham 1899: Gibbs brings attention to behavior of Fourier Series (Gibbs observed same behavior as Wilbraham but by studying a different function) 1906: Maxime Brocher shows that the phenomenon occurs for general Fourier Series around a jump discontinuity
7 2. Gibbs Phenomenon: A Brief History 2 Key Players and Contributions Lord Kelvin: Constructed two machines while studying tide heights as a function of time, h(t). Machine capable of computing periodic function h(t) using Fourier Coefficients Constructed a Harmonic Analyzer capable of computing Fourier coefficients of past tide height functions, h(t). A. A. Michelson: Elaborated on Kelvin s device and constructed a machine which would save considerable time and labour involved in calculations... of the resultant of a large number of simple harmonic motions. Using first 80 coefficients of sawtooth wave, Michelson s machine closely approximated the sawtooth function except for two blips near the points of discontinuity
8 2. Gibbs Phenomenon: A Brief History 3 Key Players and Contributions Cont. Wilbraham 1848: Wilbraham investigated the equation: y = cos(x) + cos(3x) 3 + cos(5x) cos((2n 1)x) 2n Discovered that at a distance of π 4 alternately above and below it, joined by perpendiculars which are themselves part of the locus the equation overshoots π 4 by a distance of: 1 2 sin(x) π x dx Also suggested ( that similar analysis of ) y = 2 sin(x) sin(2x) 2 + sin(3x) ( 1) n+1 sin(nx) n (An equation explored later on) would lead to an analogous result These discoveries gained little attention at the time
9 2. Gibbs Phenomenon: A Brief History 4 Key Players and Contributions Cont. J. Willard Gibbs 1898: Published and article in Nature investigating the behavior of the function given by: ( y = 2 sin(x) sin(2x) + sin(3x) ) n+1 sin(nx)... + ( 1) 2 3 n Gibbs observed in this first article that the limiting behavior of the function (sawtooth) had vertical portions, which are bisected the axis of X, [extending] beyond the points where they meet the inclined portions, their total lengths being express by four times the definite integral 0 sin(u) u du.
10 2. Gibbs Phenomenon: A Brief History 5 Key Players and Contributions Cont. Brocher 1906: In an article in Annals of Mathematics, Brocher demonstrated that Gibbs Phenomenon will be observed in any Fourier Series of a function f with a jump discontinuity saying that the limiting curve of the approximating curves has a vertical line that has to be produced beyond these points by an amount that bears a devinite ratio to the magnitude of the jump. Before Brocher, Gibbs Phenomenon had only been observed in specific series without any generalization of the concept
11 3. Gibbs Phenomenon: An Example 1 Consider the square wave function given by: { 1 if π x < 0 g(x) := 1 if 0 x < π Goal: Analytically prove that Gibbs Phenomenon occurs at jump discontinuities of this 2π-periodic function
12 3. Gibbs Phenomenon: An Example 2 Using the definition a n := 1 2π S N f(x) = = 4 π N n= N M m=1 f(x)e inx dx, basic Calculus yields a n e inθ = 1 π n N n is odd sin((2m 1)θ) 2m 1 ( ) 2 e inθ n i where M is the largest integer such that 2M 1 N.
13 3. Gibbs Phenomenon: An Example 3 Here we notice that sin((2m 1)θ) 2m 1 which yields the following identity: S 2M 1 g(x) = 4 π = 4 π = 4 π = M x 0 m=1 x M m=1 x 0 cos((2m 1)θ) dθ sin((2m 1)x) 2m 1 0 cos((2m 1)θ) dθ M cos((2m 1)θ) dθ m=1
14 3. Gibbs Phenomenon: An Example 4 Now using the identity we get the following: M m=1 S 2M 1 g(x) = 4 π cos((2m 1)x) = sin(2mx) 2 sin(x) = 4 π x 0 m=1 x 0 M cos((2m 1)θ) dθ sin(2m θ) 2 sin(θ) dθ
15 3. Gibbs Phenomenon: An Example 5 At this point, using basic analysis of the derivative of S 2M 1 g(x), we see that there are local maximum and minimum values at x M,+ = π and x M, = π 2M 2M Here, using the substitution u = 2Mθ and the fact that for u 0, sin(u) u, we get that for large M Further, the value 2 π S 2M 1 g(x m,+ ) 2 π and S 2M 1 g(x m, ) 2 π 0 sin(θ) θ 0 0 sin(θ) θ dθ sin(θ) θ dθ dθ Have shown that M >> 1, M N, x = x M,+ such that S 2M 1 g(x m,+ ) is always a blip near the jump discontinuity, namely at x = where the value S 2M 1 g(x) is not near 1! π 2M,
16 3. Gibbs Phenomenon: An Example 6 Have shown analytically that a blip persists for all S 2M 1 g near the jump discontinuity. Demonstrated again by square wave
17 3. Gibbs Phenomenon: An Example 6 Have shown analytically that a blip persists for all S 2M 1 g near the jump discontinuity. Demonstrated again by square wave We can also see the same behavior in the 2π-periodic sawtooth function given by f(x) = x on the interval [, π).
18 3. Gibbs Phenomenon: An Example 7 For both of the square wave and sawtooth functions, we have shown that a blip of constant size persists while S M g g pointwise, we now know that S M g g uniformly since for small enough neighborhoods, the blip is always outside the boundaries. (revisit square wave animation)
19 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 1 Kernels And Convolutions Kernels: Def n : (Good Kernel) A family {K n } n N real-valued integrable functions on the circle is a family of good kernels if the following hold: (i) n N, 1 2π K n(θ) dθ = 1. (ii) M > 0 such that n N, (iii) δ > 0, δ θ <π K n(θ) dθ M. K n(θ) dθ 0 as n.
20 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 1 Kernels And Convolutions Kernels: Def n : (Good Kernel) A family {K n } n N real-valued integrable functions on the circle is a family of good kernels if the following hold: (i) n N, 1 2π K n(θ) dθ = 1. (ii) M > 0 such that n N, (iii) δ > 0, δ θ <π Dirichlet: D N (θ) = K n(θ) dθ M. K n(θ) dθ 0 as n. n N e inθ
21 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 1 Kernels And Convolutions Kernels: Def n : (Good Kernel) A family {K n } n N real-valued integrable functions on the circle is a family of good kernels if the following hold: (i) n N, 1 2π K n(θ) dθ = 1. (ii) M > 0 such that n N, (iii) δ > 0, δ θ <π Dirichlet: D N (θ) = D N (θ) dθ = K n(θ) dθ M. K n(θ) dθ 0 as n. n N n N e inθ e inθ dθ
22 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 1 Kernels And Convolutions Kernels: Def n : (Good Kernel) A family {K n } n N real-valued integrable functions on the circle is a family of good kernels if the following hold: (i) n N, 1 2π K n(θ) dθ = 1. (ii) M > 0 such that n N, (iii) δ > 0, δ θ <π Dirichlet: D N (θ) = D N (θ) dθ = K n(θ) dθ M. K n(θ) dθ 0 as n. n N n N e inθ e inθ dθ Fejér: F N (θ) = [D 0 (θ) + D 1 (θ) D N 1 (θ)]/n
23 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 1 Kernels And Convolutions Kernels: Def n : (Good Kernel) A family {K n } n N real-valued integrable functions on the circle is a family of good kernels if the following hold: (i) n N, 1 2π K n(θ) dθ = 1. (ii) M > 0 such that n N, (iii) δ > 0, δ θ <π Dirichlet: D N (θ) = D N (θ) dθ = K n(θ) dθ M. K n(θ) dθ 0 as n. n N n N e inθ e inθ dθ Fejér: F N (θ) = [D 0 (θ) + D 1 (θ) D N 1 (θ)]/n Recall: Dirichlet Kernel is NOT a good kernel and Fejér Kernel is.
24 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 2 Kernels And Convolutions Cont. Convolution: Def n : The convolution of two functions, f and g is given by: (f g)(θ) = 1 2π f(y)g(θ y) dy (1)
25 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 2 Kernels And Convolutions Cont. Convolution: Def n : The convolution of two functions, f and g is given by: S M f = (D M f)(θ) (f g)(θ) = 1 2π f(y)g(θ y) dy (1)
26 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 2 Kernels And Convolutions Cont. Convolution: Def n : The convolution of two functions, f and g is given by: S M f = (D M f)(θ) (f g)(θ) = 1 2π f(y)g(θ y) dy (1) Def n : σ M f(θ) := [S 0 f(θ) + S 1 f(θ) S M 1 f(θ)]/m
27 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 2 Kernels And Convolutions Cont. Convolution: Def n : The convolution of two functions, f and g is given by: S M f = (D M f)(θ) (f g)(θ) = 1 2π f(y)g(θ y) dy (1) Def n : σ M f(θ) := [S 0 f(θ) + S 1 f(θ) S M 1 f(θ)]/m From a previous homework, we also know that F M f = σ M f
28 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 2 Kernels And Convolutions Cont. Convolution: Def n : The convolution of two functions, f and g is given by: S M f = (D M f)(θ) (f g)(θ) = 1 2π f(y)g(θ y) dy (1) Def n : σ M f(θ) := [S 0 f(θ) + S 1 f(θ) S M 1 f(θ)]/m From a previous homework, we also know that F M f = σ M f F M f is of sort an averaging of the Dirichlet kernels, or more importantly, the partial Fourier sums.
29 4. Gibbs Phenomenon: General Principles 3 The Problem is Quite General Brocher showed Gibbs Phenomenon occurs with any 2π-periodic piecewise-continuous function with a jump discontinuity Overshoot is proportional to height of jump: Square Wave: Overshoot = k(2) k = Overshoot/Undershoot given by (f(x + d ) f(x d ) where x d is point of discontinuity Suggests an overshoot of (2π) for a maximum height of Thus, need a way to resolve this for modeling of periodic phenomena to be practical Using Fejér Kernel averages Dirichlet kernels and could therefore be a way of eliminating this phenomenon animation experiment
30 5. Conclusion 1 Gibbs Phenomenon observed in all 2π-periodic functions with a jump discontinuity In some cases, it is quite basic to show it s persistence analytically Causes nastiness in approximations of functions by Fourier series, but is easily remedied with averaging using Fejér Kernel
Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 2008
 Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 8 Contents Fourier Series. The coefficients........................................ Convergence......................................... 4.3 Convergence
Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 8 Contents Fourier Series. The coefficients........................................ Convergence......................................... 4.3 Convergence
Math 5587 Midterm II Solutions
 Math 5587 Midterm II Solutions Prof. Jeff Calder November 3, 2016 Name: Instructions: 1. I recommend looking over the problems first and starting with those you feel most comfortable with. 2. Unless otherwise
Math 5587 Midterm II Solutions Prof. Jeff Calder November 3, 2016 Name: Instructions: 1. I recommend looking over the problems first and starting with those you feel most comfortable with. 2. Unless otherwise
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration
 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
Fourier series A periodic function f(x) with period T = 2π can be represented by a Fourier series: sinnx dx = sinnxsinmx dx =
 Periodic functions and boundary conditions Afunctionisperiodic,withperiodT,ifitrepeatsitselfexactlyafteranintervaloflengthT. i.e. y(x = y(x+ T for any x. Evidently, the derivatives of y(x are also periodic
Periodic functions and boundary conditions Afunctionisperiodic,withperiodT,ifitrepeatsitselfexactlyafteranintervaloflengthT. i.e. y(x = y(x+ T for any x. Evidently, the derivatives of y(x are also periodic
CONVERGENCE OF THE FOURIER SERIES
 CONVERGENCE OF THE FOURIER SERIES SHAW HAGIWARA Abstract. The Fourier series is a expression of a periodic, integrable function as a sum of a basis of trigonometric polynomials. In the following, we first
CONVERGENCE OF THE FOURIER SERIES SHAW HAGIWARA Abstract. The Fourier series is a expression of a periodic, integrable function as a sum of a basis of trigonometric polynomials. In the following, we first
Computer Problems for Fourier Series and Transforms
 Computer Problems for Fourier Series and Transforms 1. Square waves are frequently used in electronics and signal processing. An example is shown below. 1 π < x < 0 1 0 < x < π y(x) = 1 π < x < 2π... and
Computer Problems for Fourier Series and Transforms 1. Square waves are frequently used in electronics and signal processing. An example is shown below. 1 π < x < 0 1 0 < x < π y(x) = 1 π < x < 2π... and
Math 1102: Calculus I (Math/Sci majors) MWF 3pm, Fulton Hall 230 Homework 4 Solutions
 Math 0: Calculus I (Math/Sci majors) MWF 3pm, Fulton Hall 30 Homework 4 Solutions Please write neatly, and show all work. Caution: An answer with no work is wrong! Problem A. Use Weierstrass (ɛ,δ)-definition
Math 0: Calculus I (Math/Sci majors) MWF 3pm, Fulton Hall 30 Homework 4 Solutions Please write neatly, and show all work. Caution: An answer with no work is wrong! Problem A. Use Weierstrass (ɛ,δ)-definition
22. Periodic Functions and Fourier Series
 November 29, 2010 22-1 22. Periodic Functions and Fourier Series 1 Periodic Functions A real-valued function f(x) of a real variable is called periodic of period T > 0 if f(x + T ) = f(x) for all x R.
November 29, 2010 22-1 22. Periodic Functions and Fourier Series 1 Periodic Functions A real-valued function f(x) of a real variable is called periodic of period T > 0 if f(x + T ) = f(x) for all x R.
Examples of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 10.3). The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case.
 s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
Advanced Calculus Math 127B, Winter 2005 Solutions: Final. nx2 1 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x
 . Define f n, g n : [, ] R by f n (x) = Advanced Calculus Math 27B, Winter 25 Solutions: Final nx2 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x 2 + n 2 x. 2 Show that the sequences (f n ), (g n ) converge pointwise on [, ],
. Define f n, g n : [, ] R by f n (x) = Advanced Calculus Math 27B, Winter 25 Solutions: Final nx2 + n 2 x, g n(x) = n2 x 2 + n 2 x. 2 Show that the sequences (f n ), (g n ) converge pointwise on [, ],
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYSIS II MATH 4332 BLECHER NOTES
 INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYSIS II MATH 433 BLECHER NOTES. As in earlier classnotes. As in earlier classnotes (Fourier series) 3. Fourier series (continued) (NOTE: UNDERGRADS IN THE CLASS ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYSIS II MATH 433 BLECHER NOTES. As in earlier classnotes. As in earlier classnotes (Fourier series) 3. Fourier series (continued) (NOTE: UNDERGRADS IN THE CLASS ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE
Math 54: Mock Final. December 11, y y 2y = cos(x) sin(2x). The auxiliary equation for the corresponding homogeneous problem is
 Name: Solutions Math 54: Mock Final December, 25 Find the general solution of y y 2y = cos(x) sin(2x) The auxiliary equation for the corresponding homogeneous problem is r 2 r 2 = (r 2)(r + ) = r = 2,
Name: Solutions Math 54: Mock Final December, 25 Find the general solution of y y 2y = cos(x) sin(2x) The auxiliary equation for the corresponding homogeneous problem is r 2 r 2 = (r 2)(r + ) = r = 2,
Week 6 Lectures, Math 6451, Tanveer
 Fourier Series Week 6 Lectures, Math 645, Tanveer In the context of separation of variabe to find soutions of PDEs, we encountered or and in other cases f(x = f(x = a 0 + f(x = a 0 + b n sin nπx { a n
Fourier Series Week 6 Lectures, Math 645, Tanveer In the context of separation of variabe to find soutions of PDEs, we encountered or and in other cases f(x = f(x = a 0 + f(x = a 0 + b n sin nπx { a n
Math 152 Take Home Test 1
 Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
Time-Frequency Analysis
 Time-Frequency Analysis Basics of Fourier Series Philippe B. aval KSU Fall 015 Philippe B. aval (KSU) Fourier Series Fall 015 1 / 0 Introduction We first review how to derive the Fourier series of a function.
Time-Frequency Analysis Basics of Fourier Series Philippe B. aval KSU Fall 015 Philippe B. aval (KSU) Fourier Series Fall 015 1 / 0 Introduction We first review how to derive the Fourier series of a function.
Convergence of Fourier series
 Convergence of Fourier series Final Degree Dissertation Degree in Mathematics Javier Canto Llorente Supervisor: Javier Duoandikoetxea Zuazo Leioa, June 26 Contents Introduction v rigonometric Fourier
Convergence of Fourier series Final Degree Dissertation Degree in Mathematics Javier Canto Llorente Supervisor: Javier Duoandikoetxea Zuazo Leioa, June 26 Contents Introduction v rigonometric Fourier
Problem set 5, Real Analysis I, Spring, otherwise. (a) Verify that f is integrable. Solution: Compute since f is even, 1 x (log 1/ x ) 2 dx 1
 Problem set 5, Real Analysis I, Spring, 25. (5) Consider the function on R defined by f(x) { x (log / x ) 2 if x /2, otherwise. (a) Verify that f is integrable. Solution: Compute since f is even, R f /2
Problem set 5, Real Analysis I, Spring, 25. (5) Consider the function on R defined by f(x) { x (log / x ) 2 if x /2, otherwise. (a) Verify that f is integrable. Solution: Compute since f is even, R f /2
ELEMENTARY APPLICATIONS OF FOURIER ANALYSIS
 ELEMENTARY APPLICATIONS OF FOURIER ANALYSIS COURTOIS Abstract. This paper is intended as a brief introduction to one of the very first applications of Fourier analysis: the study of heat conduction. We
ELEMENTARY APPLICATIONS OF FOURIER ANALYSIS COURTOIS Abstract. This paper is intended as a brief introduction to one of the very first applications of Fourier analysis: the study of heat conduction. We
1 x 7/6 + x dx. Solution: We begin by factoring the denominator, and substituting u = x 1/6. Hence, du = 1/6x 5/6 dx, so dx = 6x 5/6 du = 6u 5 du.
 Circle One: Name: 7:45-8:35 (36) 8:5-9:4 (36) Math-4, Spring 7 Quiz #3 (Take Home): 6 7 Due: 9 7 You may discuss this quiz solely with me or other students in my discussion sessions only. Use a new sheet
Circle One: Name: 7:45-8:35 (36) 8:5-9:4 (36) Math-4, Spring 7 Quiz #3 (Take Home): 6 7 Due: 9 7 You may discuss this quiz solely with me or other students in my discussion sessions only. Use a new sheet
Methods of Mathematical Physics X1 Homework 3 Solutions
 Methods of Mathematical Physics - 556 X Homework 3 Solutions. (Problem 2.. from Keener.) Verify that l 2 is an inner product space. Specifically, show that if x, y l 2, then x, y x k y k is defined and
Methods of Mathematical Physics - 556 X Homework 3 Solutions. (Problem 2.. from Keener.) Verify that l 2 is an inner product space. Specifically, show that if x, y l 2, then x, y x k y k is defined and
Theta Functions MAΘ National Convention 2018
 Theta Functions MAΘ National Convention 018 Note that choice stands for None of the above answers is correct 1. How many times do y = x and y = x 3 intersect? A) 0 B) 1 C) D) 3. Let f(x) = x + 19 and g(x)
Theta Functions MAΘ National Convention 018 Note that choice stands for None of the above answers is correct 1. How many times do y = x and y = x 3 intersect? A) 0 B) 1 C) D) 3. Let f(x) = x + 19 and g(x)
y = x 3 and y = 2x 2 x. 2x 2 x = x 3 x 3 2x 2 + x = 0 x(x 2 2x + 1) = 0 x(x 1) 2 = 0 x = 0 and x = (x 3 (2x 2 x)) dx
 Millersville University Name Answer Key Mathematics Department MATH 2, Calculus II, Final Examination May 4, 2, 8:AM-:AM Please answer the following questions. Your answers will be evaluated on their correctness,
Millersville University Name Answer Key Mathematics Department MATH 2, Calculus II, Final Examination May 4, 2, 8:AM-:AM Please answer the following questions. Your answers will be evaluated on their correctness,
Convergence of Fourier Series
 MATH 454: Analysis Two James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April, 8 MATH 454: Analysis Two Outline The Cos Family MATH 454: Analysis
MATH 454: Analysis Two James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April, 8 MATH 454: Analysis Two Outline The Cos Family MATH 454: Analysis
(x 3)(x + 5) = (x 3)(x 1) = x + 5. sin 2 x e ax bx 1 = 1 2. lim
 SMT Calculus Test Solutions February, x + x 5 Compute x x x + Answer: Solution: Note that x + x 5 x x + x )x + 5) = x )x ) = x + 5 x x + 5 Then x x = + 5 = Compute all real values of b such that, for fx)
SMT Calculus Test Solutions February, x + x 5 Compute x x x + Answer: Solution: Note that x + x 5 x x + x )x + 5) = x )x ) = x + 5 x x + 5 Then x x = + 5 = Compute all real values of b such that, for fx)
Outline of Fourier Series: Math 201B
 Outline of Fourier Series: Math 201B February 24, 2011 1 Functions and convolutions 1.1 Periodic functions Periodic functions. Let = R/(2πZ) denote the circle, or onedimensional torus. A function f : C
Outline of Fourier Series: Math 201B February 24, 2011 1 Functions and convolutions 1.1 Periodic functions Periodic functions. Let = R/(2πZ) denote the circle, or onedimensional torus. A function f : C
DRAFT - Math 102 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 Math02 - Term72 - Guides and Exercises - DRAFT 7 Techniques of Integration A summery for the most important integrals that we have learned so far: 7. Integration by Parts The Product Rule states that if
Math02 - Term72 - Guides and Exercises - DRAFT 7 Techniques of Integration A summery for the most important integrals that we have learned so far: 7. Integration by Parts The Product Rule states that if
Math 3150 HW 3 Solutions
 Math 315 HW 3 Solutions June 5, 18 3.8, 3.9, 3.1, 3.13, 3.16, 3.1 1. 3.8 Make graphs of the periodic extensions on the region x [ 3, 3] of the following functions f defined on x [, ]. Be sure to indicate
Math 315 HW 3 Solutions June 5, 18 3.8, 3.9, 3.1, 3.13, 3.16, 3.1 1. 3.8 Make graphs of the periodic extensions on the region x [ 3, 3] of the following functions f defined on x [, ]. Be sure to indicate
Continuity. MATH 161 Calculus I. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics
 Continuity MATH 161 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Intuitive Idea A process or an item can be described as continuous if it exists without interruption. The mathematical
Continuity MATH 161 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Intuitive Idea A process or an item can be described as continuous if it exists without interruption. The mathematical
Math 115 ( ) Yum-Tong Siu 1. Derivation of the Poisson Kernel by Fourier Series and Convolution
 Math 5 (006-007 Yum-Tong Siu. Derivation of the Poisson Kernel by Fourier Series and Convolution We are going to give a second derivation of the Poisson kernel by using Fourier series and convolution.
Math 5 (006-007 Yum-Tong Siu. Derivation of the Poisson Kernel by Fourier Series and Convolution We are going to give a second derivation of the Poisson kernel by using Fourier series and convolution.
Physics 250 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations
 Physics 25 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations Peter Young November 25, 27 Homogeneous Equations We have already discussed second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which
Physics 25 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations Peter Young November 25, 27 Homogeneous Equations We have already discussed second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which
Last Update: April 4, 2011
 Math ES Winter Last Update: April 4, Introduction to Partial Differential Equations Disclaimer: his lecture note tries to provide an alternative approach to the material in Sections..6 in the textbook.
Math ES Winter Last Update: April 4, Introduction to Partial Differential Equations Disclaimer: his lecture note tries to provide an alternative approach to the material in Sections..6 in the textbook.
Vectors in Function Spaces
 Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
PLEASE MARK YOUR ANSWERS WITH AN X, not a circle! 1. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 4. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)...
 Math, Exam III November 6, 7 The Honor Code is in effect for this examination. All work is to be your own. No calculators. The exam lasts for hour and min. Be sure that your name is on every page in case
Math, Exam III November 6, 7 The Honor Code is in effect for this examination. All work is to be your own. No calculators. The exam lasts for hour and min. Be sure that your name is on every page in case
Fourier Series. Now we need to take a theoretical excursion to build up the mathematics that makes separation of variables possible.
 Fourier Series Now we need to take a theoretical excursion to build up the mathematics that makes separation of variables possible Periodic functions Definition: A function f is periodic with period p
Fourier Series Now we need to take a theoretical excursion to build up the mathematics that makes separation of variables possible Periodic functions Definition: A function f is periodic with period p
A1. Let r > 0 be constant. In this problem you will evaluate the following integral in two different ways: r r 2 x 2 dx
 Math 6 Summer 05 Homework 5 Solutions Drew Armstrong Book Problems: Chap.5 Eercises, 8, Chap 5. Eercises 6, 0, 56 Chap 5. Eercises,, 6 Chap 5.6 Eercises 8, 6 Chap 6. Eercises,, 30 Additional Problems:
Math 6 Summer 05 Homework 5 Solutions Drew Armstrong Book Problems: Chap.5 Eercises, 8, Chap 5. Eercises 6, 0, 56 Chap 5. Eercises,, 6 Chap 5.6 Eercises 8, 6 Chap 6. Eercises,, 30 Additional Problems:
GRE Math Subject Test #5 Solutions.
 GRE Math Subject Test #5 Solutions. 1. E (Calculus) Apply L Hôpital s Rule two times: cos(3x) 1 3 sin(3x) 9 cos(3x) lim x 0 = lim x 2 x 0 = lim 2x x 0 = 9. 2 2 2. C (Geometry) Note that a line segment
GRE Math Subject Test #5 Solutions. 1. E (Calculus) Apply L Hôpital s Rule two times: cos(3x) 1 3 sin(3x) 9 cos(3x) lim x 0 = lim x 2 x 0 = lim 2x x 0 = 9. 2 2 2. C (Geometry) Note that a line segment
4.10 Dirichlet problem in the circle and the Poisson kernel
 220 CHAPTER 4. FOURIER SERIES AND PDES 4.10 Dirichlet problem in the circle and the Poisson kernel Note: 2 lectures,, 9.7 in [EP], 10.8 in [BD] 4.10.1 Laplace in polar coordinates Perhaps a more natural
220 CHAPTER 4. FOURIER SERIES AND PDES 4.10 Dirichlet problem in the circle and the Poisson kernel Note: 2 lectures,, 9.7 in [EP], 10.8 in [BD] 4.10.1 Laplace in polar coordinates Perhaps a more natural
Math 101 Fall 2006 Exam 1 Solutions Instructor: S. Cautis/M. Simpson/R. Stong Thursday, October 5, 2006
 Math 101 Fall 2006 Exam 1 Solutions Instructor: S. Cautis/M. Simpson/R. Stong Thursday, October 5, 2006 Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. Use of calculators is not permitted. You
Math 101 Fall 2006 Exam 1 Solutions Instructor: S. Cautis/M. Simpson/R. Stong Thursday, October 5, 2006 Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. Use of calculators is not permitted. You
7: FOURIER SERIES STEVEN HEILMAN
 7: FOURIER SERIES STEVE HEILMA Contents 1. Review 1 2. Introduction 1 3. Periodic Functions 2 4. Inner Products on Periodic Functions 3 5. Trigonometric Polynomials 5 6. Periodic Convolutions 7 7. Fourier
7: FOURIER SERIES STEVE HEILMA Contents 1. Review 1 2. Introduction 1 3. Periodic Functions 2 4. Inner Products on Periodic Functions 3 5. Trigonometric Polynomials 5 6. Periodic Convolutions 7 7. Fourier
Section 5.6. Integration By Parts. MATH 126 (Section 5.6) Integration By Parts The University of Kansas 1 / 10
 Section 5.6 Integration By Parts MATH 126 (Section 5.6) Integration By Parts The University of Kansas 1 / 10 Integration By Parts Manipulating the Product Rule d dx (f (x) g(x)) = f (x) g (x) + f (x) g(x)
Section 5.6 Integration By Parts MATH 126 (Section 5.6) Integration By Parts The University of Kansas 1 / 10 Integration By Parts Manipulating the Product Rule d dx (f (x) g(x)) = f (x) g (x) + f (x) g(x)
This practice exam is intended to help you prepare for the final exam for MTH 142 Calculus II.
 MTH 142 Practice Exam Chapters 9-11 Calculus II With Analytic Geometry Fall 2011 - University of Rhode Island This practice exam is intended to help you prepare for the final exam for MTH 142 Calculus
MTH 142 Practice Exam Chapters 9-11 Calculus II With Analytic Geometry Fall 2011 - University of Rhode Island This practice exam is intended to help you prepare for the final exam for MTH 142 Calculus
MATH 3150: PDE FOR ENGINEERS FINAL EXAM (VERSION D) 1. Consider the heat equation in a wire whose diffusivity varies over time: u k(t) 2 x 2
 MATH 35: PDE FOR ENGINEERS FINAL EXAM (VERSION D). Consider the heat equation in a wire whose diffusivity varies over time: u t = u k(t) x where k(t) is some positive function of time. Assume the wire
MATH 35: PDE FOR ENGINEERS FINAL EXAM (VERSION D). Consider the heat equation in a wire whose diffusivity varies over time: u t = u k(t) x where k(t) is some positive function of time. Assume the wire
x 2 y = 1 2. Problem 2. Compute the Taylor series (at the base point 0) for the function 1 (1 x) 3.
 MATH 8.0 - FINAL EXAM - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS 8.0 Calculus, Fall 207 Professor: Jared Speck Problem. Consider the following curve in the plane: x 2 y = 2. Let a be a number. The portion of
MATH 8.0 - FINAL EXAM - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS 8.0 Calculus, Fall 207 Professor: Jared Speck Problem. Consider the following curve in the plane: x 2 y = 2. Let a be a number. The portion of
Exercises given in lecture on the day in parantheses.
 A.Miller M22 Fall 23 Exercises given in lecture on the day in parantheses. The ɛ δ game. lim x a f(x) = L iff Hero has a winning strategy in the following game: Devil plays: ɛ > Hero plays: δ > Devil plays:
A.Miller M22 Fall 23 Exercises given in lecture on the day in parantheses. The ɛ δ game. lim x a f(x) = L iff Hero has a winning strategy in the following game: Devil plays: ɛ > Hero plays: δ > Devil plays:
There are some trigonometric identities given on the last page.
 MA 114 Calculus II Fall 2015 Exam 4 December 15, 2015 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: No books or notes may be used. Turn off all your electronic devices and do not wear ear-plugs during
MA 114 Calculus II Fall 2015 Exam 4 December 15, 2015 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: No books or notes may be used. Turn off all your electronic devices and do not wear ear-plugs during
f(s) e -i n π s/l d s
 Pointwise convergence of complex Fourier series Let f(x) be a periodic function with period l defined on the interval [,l]. The complex Fourier coefficients of f( x) are This leads to a Fourier series
Pointwise convergence of complex Fourier series Let f(x) be a periodic function with period l defined on the interval [,l]. The complex Fourier coefficients of f( x) are This leads to a Fourier series
3. Use absolute value notation to write an inequality that represents the statement: x is within 3 units of 2 on the real line.
 PreCalculus Review Review Questions 1 The following transformations are applied in the given order) to the graph of y = x I Vertical Stretch by a factor of II Horizontal shift to the right by units III
PreCalculus Review Review Questions 1 The following transformations are applied in the given order) to the graph of y = x I Vertical Stretch by a factor of II Horizontal shift to the right by units III
Mathematical Economics: Lecture 2
 Mathematical Economics: Lecture 2 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University September 25, 2012 Outline 1 Number Line The number line, origin (Figure 2.1 Page 11) Number Line Interval (a, b) = {x R 1 : a < x < b}
Mathematical Economics: Lecture 2 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University September 25, 2012 Outline 1 Number Line The number line, origin (Figure 2.1 Page 11) Number Line Interval (a, b) = {x R 1 : a < x < b}
(p) p(y) = (e) g(t) = (t + t 2 )(1 5t + 4t 2 ) (r) x(t) = sin(t) cos(t) tan(t) (s) f(x) = x ( 3 x + 5 x) (t) f(x) = 1 2 (x ) (u) f(x) = 4x3 3x 2
 1. Find the derivative! (a) f(x) = x + x 2 x 3 + 1 (o) g(t) = sin(t) cos(t) tan(t) (b) f(x) = x + x 2 3 x 2 (c) f(x) = 1 x + 2 x 2 2 x + 312 (p) p(y) = 2 cos(y) + tan(y) sin(y) (d) h(t) = 2 t 3 + t 4 +
1. Find the derivative! (a) f(x) = x + x 2 x 3 + 1 (o) g(t) = sin(t) cos(t) tan(t) (b) f(x) = x + x 2 3 x 2 (c) f(x) = 1 x + 2 x 2 2 x + 312 (p) p(y) = 2 cos(y) + tan(y) sin(y) (d) h(t) = 2 t 3 + t 4 +
A Singular Integral Transform for the Gibbs-Wilbraham Effect in Inverse Fourier Transforms
 Universal Journal of Integral Equations 4 (2016), 54-62 www.papersciences.com A Singular Integral Transform for the Gibbs-Wilbraham Effect in Inverse Fourier Transforms N. H. S. Haidar CRAMS: Center for
Universal Journal of Integral Equations 4 (2016), 54-62 www.papersciences.com A Singular Integral Transform for the Gibbs-Wilbraham Effect in Inverse Fourier Transforms N. H. S. Haidar CRAMS: Center for
be the set of complex valued 2π-periodic functions f on R such that
 . Fourier series. Definition.. Given a real number P, we say a complex valued function f on R is P -periodic if f(x + P ) f(x) for all x R. We let be the set of complex valued -periodic functions f on
. Fourier series. Definition.. Given a real number P, we say a complex valued function f on R is P -periodic if f(x + P ) f(x) for all x R. We let be the set of complex valued -periodic functions f on
NOTES ON FOURIER SERIES and FOURIER TRANSFORM
 NOTES ON FOURIER SERIES and FOURIER TRANSFORM Physics 141 (2003) These are supplemental math notes for our course. The first part, (Part-A), provides a quick review on Fourier series. I assume that you
NOTES ON FOURIER SERIES and FOURIER TRANSFORM Physics 141 (2003) These are supplemental math notes for our course. The first part, (Part-A), provides a quick review on Fourier series. I assume that you
Math 121A: Homework 6 solutions
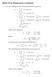 Math A: Homework 6 solutions. (a) The coefficients of the Fourier sine series are given by b n = π f (x) sin nx dx = x(π x) sin nx dx π = (π x) cos nx dx nπ nπ [x(π x) cos nx]π = n ( )(sin nx) dx + π n
Math A: Homework 6 solutions. (a) The coefficients of the Fourier sine series are given by b n = π f (x) sin nx dx = x(π x) sin nx dx π = (π x) cos nx dx nπ nπ [x(π x) cos nx]π = n ( )(sin nx) dx + π n
Calculus II Practice Test 1 Problems: , 6.5, Page 1 of 10
 Calculus II Practice Test Problems: 6.-6.3, 6.5, 7.-7.3 Page of This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on the actual test. To prepare for the test: review homework,
Calculus II Practice Test Problems: 6.-6.3, 6.5, 7.-7.3 Page of This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on the actual test. To prepare for the test: review homework,
If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy. du du. If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u
 Section 3 4B The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then f (u) u The Chain Rule with the Power
Section 3 4B The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then f (u) u The Chain Rule with the Power
Math 321 Final Examination April 1995 Notation used in this exam: N. (1) S N (f,x) = f(t)e int dt e inx.
 Math 321 Final Examination April 1995 Notation used in this exam: N 1 π (1) S N (f,x) = f(t)e int dt e inx. 2π n= N π (2) C(X, R) is the space of bounded real-valued functions on the metric space X, equipped
Math 321 Final Examination April 1995 Notation used in this exam: N 1 π (1) S N (f,x) = f(t)e int dt e inx. 2π n= N π (2) C(X, R) is the space of bounded real-valued functions on the metric space X, equipped
1.1 Appearance of Fourier series
 Chapter Fourier series. Appearance of Fourier series The birth of Fourier series can be traced back to the solutions of wave equation in the work of Bernoulli and the heat equation in the work of Fourier.
Chapter Fourier series. Appearance of Fourier series The birth of Fourier series can be traced back to the solutions of wave equation in the work of Bernoulli and the heat equation in the work of Fourier.
If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy. du du. If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u
 Section 3 4B Lecture The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u The Chain Rule
Section 3 4B Lecture The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u The Chain Rule
10.12 INTRODUCTION TO FOURIER SERIES
 10.12 Fourier Series Contemporary Calculus 1 10.12 INTRODUCTION TO FOURIER SERIES When we discussed Maclaurin series in earlier sections we used information about the derivatives of a function f(x) to
10.12 Fourier Series Contemporary Calculus 1 10.12 INTRODUCTION TO FOURIER SERIES When we discussed Maclaurin series in earlier sections we used information about the derivatives of a function f(x) to
Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm III B (Solutions)
 Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm III B (Solutions). Set up (but do not evaluate) an integral for the surface area of the surface f(x, y) x 2 y y over the region x, y 4. We have that the surface are is
Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm III B (Solutions). Set up (but do not evaluate) an integral for the surface area of the surface f(x, y) x 2 y y over the region x, y 4. We have that the surface are is
A glimpse of Fourier analysis
 Chapter 7 A glimpse of Fourier analysis 7.1 Fourier series In the middle of the 18th century, mathematicians and physicists started to study the motion of a vibrating string (think of the strings of a
Chapter 7 A glimpse of Fourier analysis 7.1 Fourier series In the middle of the 18th century, mathematicians and physicists started to study the motion of a vibrating string (think of the strings of a
3 a = 3 b c 2 = a 2 + b 2 = 2 2 = 4 c 2 = 3b 2 + b 2 = 4b 2 = 4 b 2 = 1 b = 1 a = 3b = 3. x 2 3 y2 1 = 1.
 MATH 222 LEC SECOND MIDTERM EXAM THU NOV 8 PROBLEM ( 5 points ) Find the standard-form equation for the hyperbola which has its foci at F ± (±2, ) and whose asymptotes are y ± 3 x The calculations b a
MATH 222 LEC SECOND MIDTERM EXAM THU NOV 8 PROBLEM ( 5 points ) Find the standard-form equation for the hyperbola which has its foci at F ± (±2, ) and whose asymptotes are y ± 3 x The calculations b a
MATH 20B MIDTERM #2 REVIEW
 MATH 20B MIDTERM #2 REVIEW FORMAT OF MIDTERM #2 The format will be the same as the practice midterms. There will be six main questions worth 0 points each. These questions will be similar to problems you
MATH 20B MIDTERM #2 REVIEW FORMAT OF MIDTERM #2 The format will be the same as the practice midterms. There will be six main questions worth 0 points each. These questions will be similar to problems you
FOURIER TRANSFORMS. 1. Fourier series 1.1. The trigonometric system. The sequence of functions
 FOURIER TRANSFORMS. Fourier series.. The trigonometric system. The sequence of functions, cos x, sin x,..., cos nx, sin nx,... is called the trigonometric system. These functions have period π. The trigonometric
FOURIER TRANSFORMS. Fourier series.. The trigonometric system. The sequence of functions, cos x, sin x,..., cos nx, sin nx,... is called the trigonometric system. These functions have period π. The trigonometric
The Fourier series for a 2π-periodic function
 The Fourier series for a 2π-periodic function Let f : ( π, π] R be a bounded piecewise continuous function which we continue to be a 2π-periodic function defined on R, i.e. f (x + 2π) = f (x), x R. The
The Fourier series for a 2π-periodic function Let f : ( π, π] R be a bounded piecewise continuous function which we continue to be a 2π-periodic function defined on R, i.e. f (x + 2π) = f (x), x R. The
Fourier Series. Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta
 1 Lecture Notes on Partial Differential Equations Chapter IV Fourier Series Ilyasse Aksikas Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta aksikas@ualberta.ca DEFINITIONS 2 Before
1 Lecture Notes on Partial Differential Equations Chapter IV Fourier Series Ilyasse Aksikas Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta aksikas@ualberta.ca DEFINITIONS 2 Before
HARMONIC ANALYSIS TERENCE TAO
 HARMONIC ANALYSIS TERENCE TAO Analysis in general tends to revolve around the study of general classes of functions (often real-valued or complex-valued) and operators (which take one or more functions
HARMONIC ANALYSIS TERENCE TAO Analysis in general tends to revolve around the study of general classes of functions (often real-valued or complex-valued) and operators (which take one or more functions
MATH 131P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER 12, 2012
 MATH 3P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER, This is a closed ook, closed notes, no calculators/computers exam. There are 6 prolems. Write your solutions to Prolems -3 in lue ook #, and your solutions to
MATH 3P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER, This is a closed ook, closed notes, no calculators/computers exam. There are 6 prolems. Write your solutions to Prolems -3 in lue ook #, and your solutions to
CALCULUS II ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS. (v) (vi) x arctan(x) dx, (vii) (viii) e u du = e u = e arctan(y).
 CALCULUS II ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS. Evaluate the integrals e arctan(y) (i) + y dy, (ii) (iii) (iv) t cos(t)dt, ( + x ) 8 dx, ue u du, (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) sec(θ) tan(θ) 6 dθ, φtan(φ) dφ, x arctan(x) dx,
CALCULUS II ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS. Evaluate the integrals e arctan(y) (i) + y dy, (ii) (iii) (iv) t cos(t)dt, ( + x ) 8 dx, ue u du, (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) sec(θ) tan(θ) 6 dθ, φtan(φ) dφ, x arctan(x) dx,
Math 5440 Problem Set 7 Solutions
 Math 544 Math 544 Problem Set 7 Solutions Aaron Fogelson Fall, 13 1: (Logan, 3. # 1) Verify that the set of functions {1, cos(x), cos(x),...} form an orthogonal set on the interval [, π]. Next verify that
Math 544 Math 544 Problem Set 7 Solutions Aaron Fogelson Fall, 13 1: (Logan, 3. # 1) Verify that the set of functions {1, cos(x), cos(x),...} form an orthogonal set on the interval [, π]. Next verify that
Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS : Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Integrals / 7 The Substitution Method Idea: To replace a relatively
Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS : Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Integrals / 7 The Substitution Method Idea: To replace a relatively
0 3 x < x < 5. By continuing in this fashion, and drawing a graph, it can be seen that T = 2.
 04 Section 10. y (π) = c = 0, and thus λ = 0 is an eigenvalue, with y 0 (x) = 1 as the eigenfunction. For λ > 0 we again have y(x) = c 1 sin λ x + c cos λ x, so y (0) = λ c 1 = 0 and y () = -c λ sin λ
04 Section 10. y (π) = c = 0, and thus λ = 0 is an eigenvalue, with y 0 (x) = 1 as the eigenfunction. For λ > 0 we again have y(x) = c 1 sin λ x + c cos λ x, so y (0) = λ c 1 = 0 and y () = -c λ sin λ
MA 201: Differentiation and Integration of Fourier Series Applications of Fourier Series Lecture - 10
 MA 201: Differentiation and Integration of Fourier Series Applications of Fourier Series ecture - 10 Fourier Series: Orthogonal Sets We begin our treatment with some observations: For m,n = 1,2,3,... cos
MA 201: Differentiation and Integration of Fourier Series Applications of Fourier Series ecture - 10 Fourier Series: Orthogonal Sets We begin our treatment with some observations: For m,n = 1,2,3,... cos
2003 Mathematics. Advanced Higher. Finalised Marking Instructions
 2003 Mathematics Advanced Higher Finalised Marking Instructions 2003 Mathematics Advanced Higher Section A Finalised Marking Instructions Advanced Higher 2003: Section A Solutions and marks A. (a) Given
2003 Mathematics Advanced Higher Finalised Marking Instructions 2003 Mathematics Advanced Higher Section A Finalised Marking Instructions Advanced Higher 2003: Section A Solutions and marks A. (a) Given
Fourier Series and Recent Developments in Analysis
 Fourier Series and Recent Developments in Analysis Karlstad, June 2003 Javier Soria (U. Barcelona) 1 Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier (1768-1830) It was around 1804 that Fourier did his important mathematical
Fourier Series and Recent Developments in Analysis Karlstad, June 2003 Javier Soria (U. Barcelona) 1 Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier (1768-1830) It was around 1804 that Fourier did his important mathematical
Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 12: 3.3 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation
 Lecture Notes for Math 21: ODE and PDE. Lecture 12: 3.3 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation Shawn D. Ryan Spring 2012 1 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation Last Time: We considered the
Lecture Notes for Math 21: ODE and PDE. Lecture 12: 3.3 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation Shawn D. Ryan Spring 2012 1 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation Last Time: We considered the
Fast Fourier Transform
 Fast Fourier Transform December 8, 2016 FFT JPEG RGB Y C B C R (luma (brightness), chroma 2 (color)) chroma resolution is reduced image is split in blocks 8 8 pixels JPEG RGB Y C B C R (luma (brightness),
Fast Fourier Transform December 8, 2016 FFT JPEG RGB Y C B C R (luma (brightness), chroma 2 (color)) chroma resolution is reduced image is split in blocks 8 8 pixels JPEG RGB Y C B C R (luma (brightness),
Analysis II: Fourier Series
 .... Analysis II: Fourier Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American May 3, 011 K.Maruno (UT-Pan American) Analysis II May 3, 011 1 / 16 Fourier series were
.... Analysis II: Fourier Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American May 3, 011 K.Maruno (UT-Pan American) Analysis II May 3, 011 1 / 16 Fourier series were
b n x n + b n 1 x n b 1 x + b 0
 Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Final Exam SOLUTIONS MAT 131 Fall 2011
 1. Compute the following its. (a) Final Exam SOLUTIONS MAT 131 Fall 11 x + 1 x 1 x 1 The numerator is always positive, whereas the denominator is negative for numbers slightly smaller than 1. Also, as
1. Compute the following its. (a) Final Exam SOLUTIONS MAT 131 Fall 11 x + 1 x 1 x 1 The numerator is always positive, whereas the denominator is negative for numbers slightly smaller than 1. Also, as
Fall 2013 Hour Exam 2 11/08/13 Time Limit: 50 Minutes
 Math 8 Fall Hour Exam /8/ Time Limit: 5 Minutes Name (Print): This exam contains 9 pages (including this cover page) and 7 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter all requested information
Math 8 Fall Hour Exam /8/ Time Limit: 5 Minutes Name (Print): This exam contains 9 pages (including this cover page) and 7 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter all requested information
Calculus & Analytic Geometry I
 TQS 124 Autumn 2008 Quinn Calculus & Analytic Geometry I The Derivative: Analytic Viewpoint Derivative of a Constant Function. For c a constant, the derivative of f(x) = c equals f (x) = Derivative of
TQS 124 Autumn 2008 Quinn Calculus & Analytic Geometry I The Derivative: Analytic Viewpoint Derivative of a Constant Function. For c a constant, the derivative of f(x) = c equals f (x) = Derivative of
Math 5051 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis I Homework Assignment 2
 Math 551 Measure Theory and Functional nalysis I Homework ssignment 2 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Friday, September 25th, 215 Please do Exercises 1, 4*, 7, 9*, 11, 12, 13, 16, 21*, 26, 28, 31, 32, 33, 36, 37.
Math 551 Measure Theory and Functional nalysis I Homework ssignment 2 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Friday, September 25th, 215 Please do Exercises 1, 4*, 7, 9*, 11, 12, 13, 16, 21*, 26, 28, 31, 32, 33, 36, 37.
0. Mathematical Functions
 0. Mathematical Functions This is a course on complex methods in the physical sciences. Before dealing with complex numbers, however, let us undertake a brief review of real mathematical functions and
0. Mathematical Functions This is a course on complex methods in the physical sciences. Before dealing with complex numbers, however, let us undertake a brief review of real mathematical functions and
MATH 124B: HOMEWORK 2
 MATH 24B: HOMEWORK 2 Suggested due date: August 5th, 26 () Consider the geometric series ( ) n x 2n. (a) Does it converge pointwise in the interval < x
MATH 24B: HOMEWORK 2 Suggested due date: August 5th, 26 () Consider the geometric series ( ) n x 2n. (a) Does it converge pointwise in the interval < x
n=0 ( 1)n /(n + 1) converges, but not
 Math 07H Topics for the third exam (and beyond) (Technically, everything covered on the first two exams plus...) Absolute convergence and alternating series A series a n converges absolutely if a n converges.
Math 07H Topics for the third exam (and beyond) (Technically, everything covered on the first two exams plus...) Absolute convergence and alternating series A series a n converges absolutely if a n converges.
Topics in Fourier analysis - Lecture 2.
 Topics in Fourier analysis - Lecture 2. Akos Magyar 1 Infinite Fourier series. In this section we develop the basic theory of Fourier series of periodic functions of one variable, but only to the extent
Topics in Fourier analysis - Lecture 2. Akos Magyar 1 Infinite Fourier series. In this section we develop the basic theory of Fourier series of periodic functions of one variable, but only to the extent
Mathematics for Engineers II. lectures. Power series, Fourier series
 Power series, Fourier series Power series, Taylor series It is a well-known fact, that 1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + = n=0 x n = 1 1 x if 1 < x < 1. On the left hand side of the equation there is sum containing
Power series, Fourier series Power series, Taylor series It is a well-known fact, that 1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + = n=0 x n = 1 1 x if 1 < x < 1. On the left hand side of the equation there is sum containing
Solutions to Exam 1, Math Solution. Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists. Recall that (f 1 ) (a) =
 Solutions to Exam, Math 56 The function f(x) e x + x 3 + x is one-to-one (there is no need to check this) What is (f ) ( + e )? Solution Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists
Solutions to Exam, Math 56 The function f(x) e x + x 3 + x is one-to-one (there is no need to check this) What is (f ) ( + e )? Solution Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists
More on Fourier Series
 More on Fourier Series R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations Lecture 6.1 New Fourier series from old Recall: Given a function f (x, we can dilate/translate its graph via multiplication/addition,
More on Fourier Series R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations Lecture 6.1 New Fourier series from old Recall: Given a function f (x, we can dilate/translate its graph via multiplication/addition,
C-N M151 Lecture Notes (part 1) Based on Stewart s Calculus (2013) B. A. Starnes
 Lecture Calculus is the study of infinite Mathematics. In essence, it is the extension of algebraic concepts to their limfinity(l). What does that even mean? Well, let's begin with the notion of functions
Lecture Calculus is the study of infinite Mathematics. In essence, it is the extension of algebraic concepts to their limfinity(l). What does that even mean? Well, let's begin with the notion of functions
MATH 162. FINAL EXAM ANSWERS December 17, 2006
 MATH 6 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS December 7, 6 Part A. ( points) Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating about the y-axis the region under the curve y x, for / x. Using the shell method, the radius
MATH 6 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS December 7, 6 Part A. ( points) Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating about the y-axis the region under the curve y x, for / x. Using the shell method, the radius
Math 230 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution
 Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
Math 321 Final Exam 8:30am, Tuesday, April 20, 2010 Duration: 150 minutes
 Math 321 Final Exam 8:30am, Tuesday, April 20, 2010 Duration: 150 minutes Name: Student Number: Do not open this test until instructed to do so! This exam should have 17 pages, including this cover sheet.
Math 321 Final Exam 8:30am, Tuesday, April 20, 2010 Duration: 150 minutes Name: Student Number: Do not open this test until instructed to do so! This exam should have 17 pages, including this cover sheet.
Chapter 5: Bases in Hilbert Spaces
 Orthogonal bases, general theory The Fourier basis in L 2 (T) Applications of Fourier series Chapter 5: Bases in Hilbert Spaces I-Liang Chern Department of Applied Mathematics National Chiao Tung University
Orthogonal bases, general theory The Fourier basis in L 2 (T) Applications of Fourier series Chapter 5: Bases in Hilbert Spaces I-Liang Chern Department of Applied Mathematics National Chiao Tung University
Convergence for periodic Fourier series
 Chapter 8 Convergence for periodic Fourier series We are now in a position to address the Fourier series hypothesis that functions can realized as the infinite sum of trigonometric functions discussed
Chapter 8 Convergence for periodic Fourier series We are now in a position to address the Fourier series hypothesis that functions can realized as the infinite sum of trigonometric functions discussed
SECTION A. f(x) = ln(x). Sketch the graph of y = f(x), indicating the coordinates of any points where the graph crosses the axes.
 SECTION A 1. State the maximal domain and range of the function f(x) = ln(x). Sketch the graph of y = f(x), indicating the coordinates of any points where the graph crosses the axes. 2. By evaluating f(0),
SECTION A 1. State the maximal domain and range of the function f(x) = ln(x). Sketch the graph of y = f(x), indicating the coordinates of any points where the graph crosses the axes. 2. By evaluating f(0),
M412 Assignment 5 Solutions
 M41 Assignment 5 Solutions 1. [1 pts] Haberman.5.1 (a). Solution. Setting u(x, y) =X(x)Y(y), we find that X and Y satisfy X + λx = Y λy =, X () = X () = Y() =. In this case, we find from the X equation
M41 Assignment 5 Solutions 1. [1 pts] Haberman.5.1 (a). Solution. Setting u(x, y) =X(x)Y(y), we find that X and Y satisfy X + λx = Y λy =, X () = X () = Y() =. In this case, we find from the X equation
2.8 Linear Approximation and Differentials
 2.8 Linear Approximation Contemporary Calculus 1 2.8 Linear Approximation and Differentials Newton's method used tangent lines to "point toward" a root of the function. In this section we examine and use
2.8 Linear Approximation Contemporary Calculus 1 2.8 Linear Approximation and Differentials Newton's method used tangent lines to "point toward" a root of the function. In this section we examine and use
1 Taylor-Maclaurin Series
 Taylor-Maclaurin Series Writing x = x + n x, x = (n ) x,.., we get, ( y ) 2 = y ( x) 2... and letting n, a leap of logic reduces the interpolation formula to: y = y + (x x )y + (x x ) 2 2! y +... Definition...
Taylor-Maclaurin Series Writing x = x + n x, x = (n ) x,.., we get, ( y ) 2 = y ( x) 2... and letting n, a leap of logic reduces the interpolation formula to: y = y + (x x )y + (x x ) 2 2! y +... Definition...
