AGE AND MINERALOGY OF THE STEAMBOAT SPRINGS SILICA SINTER DEPOSIT, NEVADA, A PRELIMINARY REPORT ON CORE SNLG 87-29
|
|
|
- Ambrose Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings NZ Geothermal Workshop 2003 AGE AND MINERALOGY OF THE STEAMBOAT SPRINGS SILICA SINTER DEPOSIT, NEVADA, A PRELIMINARY REPORT ON CORE SNLG B. Y. LYNNE, J. MOORE, P.R.L. BROWNE K. A. CAMPBELL University of Auckland, Geology Department, Private Bag 92109, Auckland, New Zealand 2 University of Utah,Energy and Geoscience Institute, Salt Lake City, Utah,U.S.A. SUMMARY - In 1993, a geothermal exploration slim hole, SNLG 87-29, was drilled to m at Steamboat Springs, Nevada, U.S.A. The purpose of the drilling was to develop a fast, cost-effective method of drilling continuously cored, small diameter exploration holes in hard geothermal reservoir rock. Three principal lithologies were penetrated and all were fractured: Quaternary hot spring siliceous sinter with intercalated alluvium, Tertiary volcanic breccias and lahars, and an underlying Cretaceous granodiorite. The well only produced hot water from Sinter occurs at depths from 2.62 m to m, with metres of continuous sinter core recovered. The objectives of this study were to: (1) utilise silica sinter deposits to assess past climates and environments; (2) evaluate the influence of depositional and post-depositional conditions on silica mineral phases and their maturation pathways; (3) identify the paragenetic sequence associated with Steamboat Springs sinter diagenesis; and (4) determine the factors that produce coloured, metal-rich sinters. Radiocarbon dating of three core samples (6283 +/- 60 BP to /- 70 BP) and X-ray powder diffraction analysis reveal that an unknown mechanism has influenced both the silica maturation profile as well as the signature because neither reflect a stratigraphictrend. 1. INTRODUCTION Where near-neutral alkali-chloride waters discharge at the surface and cool below 100 C, silica precipitates to deposit silica sinter (Fournier and Rowe, 1966). Its precipitation occurs rapidly and preserves many biotic and abiotic features, which become trapped, silicified and fossilised plants, pollen, microbes, sinter fragments), leaving fingerprints of the conditions at the time of entrapment. Siliceous hot-spring deposits change in mineralogy during maturation. When initially deposited, sinter consists of noncrystalline opaline silica (opal-a) which transforms to paracrystalline opal-ct +/- opal-c and eventually to microcrystalline quartz (cf. White et al., 1964, Smith, 1998, Herdianita et al.,2000, Campbell et al., 2001, Lynne and Campbell, in press). Depositional and post-depositional conditions, such as weathering or heating nearby also affect mineralogical maturation pathways and preservation of biotic and abiotic inclusions in sinter (Lynne and Campbell in review). Cores of sinter from a drillhole at Steamboat Springs, Nevada, U.S.A. (Fig. at depths to m, to m, and to were radiocarbon-dated (Figs. 2A, 3A, 3E). Their mineralogy was determined by X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) analysis. The textural and morphological characteristics of the samples were examined petrographically and by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). 2. GEOLOGY AND GEOTHERMAL ACTIVITY The Steamboat Springs geothermal area is located in Washoe County (latitude longitude on the eastern side of the Sierra Nevada Mountains. The thermal area covers and includes active fumaroles and ancient silica sinter deposits. Currently the geothermal field generates 62 Mw per year of electric power from binary and steam-flash plants. The oldest rocks in the area,. south and west of the site, are Triassic-Jurassic metamorphosed sediments, which are intruded by Cretaceous plutonic rocks. Younger pumiceous rhyolite domes and basaltic andesites outcrop along a 65
2 northeast trend within the site. Granites occur west of the thermal area. The present thermal activity occurs on a northeast-trending fault indicating structural control of fluid flow. Normal faults occur regionally. Older Miocene faults strike whereas younger Quaternary faults strike Ancient sinter deposits form the High, Low and Main terraces. Drill hole SNLG is located at the base of the High terrace (Fig. 1). North \ North t Reno I 120' 45' Figure 1- Location of Steamboat Springs drill site SNLG METHODS -- Sections of the core were dated by AMs at Rafter Radiocarbon Laboratory, Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences Ltd, Lower Hutt, New Zealand. The following chemical pretreatment was carried out on each bulk sample; HCI, HF, oxidation with 10% nitric, 5% KOH, sieved at 150 and then at 6 The fiaction between 6 and 150 was then subjected to sodium polytungstate (SPT) centrifuging to separate plant remains fiom the remaining material. The initial specific gravity used was 2.4 with sample m requiring further SPT with specific graivities of 2.1 and 1.8 After this procedure enough pollen and plant fragments were collected to radiocarbon date. The material was transferred into a quartz combustion tube containing and Ag wire, then evacuated and flame sealed before combusting overnight at 900 The resulting was converted to graphite by mixing with over a Fe catalyst at 700 "C. The graphite was measured on the tandem accelerator at Geological and Nuclear SciencesLtd. The structural state of the silica sinter was measured by its degree of lattice order, following X-ray Powder (XRPD) techniques of Herdianita et al. (2000). The band width at half maximum peak height (FWHM)is used to determine the degree of lattice brder, or mineralogical maturation, of the silica structure. Individual horizons up to 10 thick within each core were analysed by XRPD (Table 1). Thin section microscopy was used to determine the microscale features and textures of the sinter, and to various inclusions. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) enabled examination of the ultrastructural morphology. Samples were mounted on aluminium stubs, powder coated for 10 minutes at with platinum and examined using a Phillips SEM field emission gun at an accelerating voltage of Trace elements in distinctive coloured horizons within the sinter core were analysed by electron diffraction spectroscopy (EDS). Polished sections were mounted on the SEM and analysed by EDS with a back scatter detector at operating conditions of 20 and a spot size of pin. 4. RESULTS Three sections from the core of drill hole SNLG yielded ages that were inconsistent with their stratigraphic positions. The shallowest sample from a depth of to m (Fig. yielded an age of /- 64 years BP. Sinter from intermediate depths, to m (Fig. 3A-B) revealed the oldest age of 11,493 +/- 70 years BP. The deepest sample from to m yielded the youngest age of /- 60 years BP (Fig. 3E). The mineralogical maturation of each core section, as indicated by decreasing FWHM values, has been reported to increase with age (cf. Herdianita et which generally increases with depth in structurally undisturbed strata. Not all horizons from thethree Steamboat cores show an increase in mineralogical maturation with age as expected (cf. Campbell et al., 2001). White et al. (1964) recognized that chalcedonization of opaline sinter was controlled in part by depth and in part by age, and recorded in some Steamboat drillholes, that the degree of chalcedonization was clearly not related to depth alone.
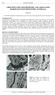
3 Figure 2-Core sinter sample from SNLG at a depth of m to m. (A) Hand specimen of core showing individual sub-sample horizons analysed by XRPD. Individual horizons consist of; A and F breccia in a cream silica matrix, D cream vitreous silica, E = porous friable silica, H brown and orange finely laminated smooth silica. (B- D) Thin section photomicrographs. (B) Iron-rich laminae, horizon H. (C) Sub-angular quartz phenocryst inside rounded, laminated sinter fragment, horizon F. (D)Cracked, iron-stained sinter horizon A, possibly from dessication of paleosurface, (E - F) Scanning electron microscope images of; (E) welded opal-a spheres in a smooth sinter matrix determined by EDS to be ironrich, (F) opal-a spheres in iron-poor sinter. 67
4 I E m I Figure 3- Core sinter samples fiom SNLG (A - D) m to m. (A-B) Hand specimen of core sample shows individual sub-sample analysed by XRPD. Horizons consist of; A breccia zone with matrix around clasts, B = cream vitreous clasts in a white sinter which show reverse grading, C breccia zone in an matrix. Breccia fragment without matrix analysed, D vein of silica with minimal fragmental inclusions. (C) Electron diffraction spectroscopy (EDS) scan across coloured fracture infill shown in D (0= oxygen, Si = silica, Fe iron, W =tungsten, Hg mercury). (D) Polished mount which shows location of EDS scan. (E) Hand specimen of core sample fiom depths m to m which show sub-sample horizons analysed by XRPD. Horizons consist of; A cream vitreous silica zone, B = mixture of clasts and grey sinter matrix, C = large white fragment. LO
5 Table 1 - Core sub-sample depths, ages and mineralogy. Core depth Core FWHM horizon horizon (years) BP 8684 A I D I A / B I C +I A I B 1 +I C I-60 Many of the horizons in the three core samples examined consisted of breccia (Figs. 2A, 3A, 3E). XRPD analysis of individual sinter clasts within the breccia horizons indicates that they have a different mineralogical state compared to the matrix. Other clasts within breccia zones reveal quartz phenocrysts within sinter clasts (Fig. 2C). Therefore, XRPD results also record multiple episodes of hot-spring discharge, and local weathering and transport of sinter and alluvium. Thin section microscopy and SEM analyses document a variety of clast morphologies and textures within the breccia. These include rounded sinter clasts (Fig. sub-angular quartz inside rounded sinter clasts (Fig. angular quartz detritus, equant interlocking quartz grains inside sub-rounded sinter clasts, and fragments of rhyolite and alkali feldspar. Evidence of fossilised cracking at the original depositional surface is also recorded in thin section (Fig. 2D). Reverse grading occurs at depths of m and m (Figs. 2A zone F, 3A zone B). SEM observations show domains of dissolution forming etched surfaces and voids. Reprecipitation of opal-a spheres has occurred in these voids. Jarosite crystals (10-15 diameter) also are present in some voids. Silicified microbial filaments diameter tubular filament mould) dominate these core horizons, implying a low-temperature depositional regime. EDS analysis revealed the presence of iron, antimony, arsenic and titanium in all coloured samples analysed; whereas tungsten and mercury were detected only in some coloured horizons. XRPD analysis of sinter core samples from a depth of m to m yielded an age of 11,493 years BP. Analysis of white (zones B and C) and brown (zones A and D) sub-sample horizons (Fig. 3A and B) produced different XRPD results. The white sinter areas exhibit FWHM values of 1.9 to 2.0 whereas the brown sinter areas revealed higher FWHM values of 2.2 to 2.85 SEM observations reveal that a distinctly different morphology of opal-a spheres forms in iron-rich areas as compared to iron-poor areas (Fig. 2E-F). Iron-rich zones contain individual opal-a spheres protruding from a dense smooth matrix in which they are cemented. EDS analysis of the smooth matrix revealed silica, oxygen and iron. Iron-poor zones are characterized by a matrix of coalesced opal-a spheres. 5. CONCLUSIONS Unlike some other sinter deposits, neither the ages nor the mineralogical maturation of sinter from the Steamboat Springs core samples follow stratigraphy White et al., 1964, Kano, 1983, Campbell et al., 2001.) Orientations of filamentous horizons indicate that these sinter deposits have not been overturned. Furthermore, many of the individual sinter layers record evidence of more than one depositional period. For example, detrital quartz, alkali feldspar and rhyolite inclusions within rounded sinter clasts in a silica matrix suggest that sinter deposited around the inclusions, followed by their transport and then precipitation of additional silica laminae. Brecciation in surface sinter around the drill site and in thin section a mechanism for sinter breccia formation. The reverse grading may be due to sieve settling that allowed finer grained material to filter to the base of a horizon, possibly during an earthquake, or via down-slopemovement of older eroded material.
6 Dissolution textures, jarosite crystals and the presence of a second generation of opal-a spheres suggest that steam overprinting remobilized silica within the deposit. Strongly coloured laminae, patchy coloured areas and fracture infill are common in the Steamboat Springs cores where iron is a constituent (Fig. 3C-D). XRPD shows consistently higher less mature) FWHM values for sinter that is rich in iron, and therefore this metal may retard silica maturation. Furthermore, many cross-cutting fractures are infilled with breccia in an iron-rich sinter matrix. The FWHM values of this heterogenous matrix are considerably higher than in the surrounding sinter and hence may indicate a younger infill. If so, the AMS radiocarbon dates do not represent the age of the original sinter but reflect an influx of younger that infused and overprinted the older silica. 6.ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank the following: University of Utah and the Energy and Geoscience Institute, Utah, for allowing access to Steamboat Springs core; Stu Johnson for devoting unlimited time and guidance in the field; David Langton and Gary Smith for assistance with core cutting; Catherine Hobbis for technical assistance with the SEM and EDS; Ritchie Sims and Louise - Cotterall for assistance with photography. 7. REFERENCES Campbell, K.A., Sannazzaro, K., Rodgers, K.A., Herdianita, N.R., and Browne, P.R.L. (2001). Sedimentary facies and mineralogy of the Late Pleistocene Umukuri silica sinter, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. Journal SedimentaryResearch, Vol. 71, Fournier, R.O., and Rowe, J.J. (1966). Estimation of underground temperatures from the silica content of water hot springs and wet-steam wells, American Journal Science, Herdianita, N.R., Rodgers, K.A., and Browne, P.R.L. (2000). Routine instrumental procedures to characterize the mineralogy of modem and ancient silica sinters. Geothermics, Vol. 29, 81. Kano, K. (1983). Ordering of opal-ct in diagenesis. Geochemical Journal, Vol. 17, 93. Lynne, and Campbell, K.A. (in press). Diagenetic transformations (opal-a to opal-ct) of low- and mid- temperature microbial textures in siliceous hot-spring deposits, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. Canadian Journal Earth Sciences. Lynne, B.Y. and Campbell, K.A. (in review). Morphologic and mineralogic transitions from opal-a to opal-ct in low-temperature silica sinter diagenesis, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. Smith, D.K. (1998). Opal, cristobalite and tridymite: Noncrystallinity versus crystallinity, nomenclature of the silica minerals and bibliography. Powder Diffraction, Vol. 13, 19. White, D.E., Thompson, G.A., and Sandberg, C.H. (1964). Rocks, structure, and geologic history of Steamboat Springs thermal area, Washoe County, Nevada. Geological Survey, Professionalpaper p.
SILICEOUS SINTER DIAGENESIS AT THE OPAL MOUND, ROOSEVELT HOT SPRINGS, UTAH, USA
 Proceedings 26 th NZ Geothermal Workshop 24 SILIEOUS SINTER DIAGENESIS AT THE OPAL MOUND, ROOSEVELT HOT SPRINGS, UTAH, USA B.Y. LYNNE 1, K.A. AMPBELL 1, J. MOORE 2 & P.R.L. BROWNE 1 1 Department of Geology,
Proceedings 26 th NZ Geothermal Workshop 24 SILIEOUS SINTER DIAGENESIS AT THE OPAL MOUND, ROOSEVELT HOT SPRINGS, UTAH, USA B.Y. LYNNE 1, K.A. AMPBELL 1, J. MOORE 2 & P.R.L. BROWNE 1 1 Department of Geology,
A Closer Look At Hydrothermal Alteration and Fluid-Rock Interaction Using Scanning Electron Microscopy
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 A Closer Look At Hydrothermal Alteration and Fluid-Rock Interaction Using Scanning Electron Microscopy Bridget Y. Lynne
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia, 19-25 April 2015 A Closer Look At Hydrothermal Alteration and Fluid-Rock Interaction Using Scanning Electron Microscopy Bridget Y. Lynne
WAMUNYU EDWARD MUREITHI I13/2358/2007
 WAMUNYU EDWARD MUREITHI I13/2358/2007 Olkaria geothermal area is situated south of Lake Naivasha on the floor of the southern segment of the Kenya rift. The geology of the Olkaria Geothermal area is subdivided
WAMUNYU EDWARD MUREITHI I13/2358/2007 Olkaria geothermal area is situated south of Lake Naivasha on the floor of the southern segment of the Kenya rift. The geology of the Olkaria Geothermal area is subdivided
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
Habitable Environments of Ancient Mars: Deciphering the Rock Record. John Grotzinger
 Habitable Environments of Ancient Mars: Deciphering the Rock Record John Grotzinger Modern Mars: Recurring Slope Lineae McEwan et al., 2014 Mars Timeline: Water-related environments Ehlmann et al., 2011,
Habitable Environments of Ancient Mars: Deciphering the Rock Record John Grotzinger Modern Mars: Recurring Slope Lineae McEwan et al., 2014 Mars Timeline: Water-related environments Ehlmann et al., 2011,
Supporting Information Appendix
 Supporting Information Appendix 1. Supporting Text. Silica-rich terrestrial deposits without tridymite. 2. Table S1. Chemical compositions from Rietveld analysis and chemical composition of minerals used
Supporting Information Appendix 1. Supporting Text. Silica-rich terrestrial deposits without tridymite. 2. Table S1. Chemical compositions from Rietveld analysis and chemical composition of minerals used
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS. Subtitle
 THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Chapter 10. Chapter Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Rocks. Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Name. GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks
 Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety
Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety
9/4/2015. Feldspars White, pink, variable Clays White perfect Quartz Colourless, white, red, None
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Engineering Geology. Igneous rocks. Hussien Al - deeky
 Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
A Regional Diagenetic and Petrophysical Model for the Montney Formation, Western Canada Sedimentary Basin*
 A Regional Diagenetic and Petrophysical Model for the Montney Formation, Western Canada Sedimentary Basin* Noga Vaisblat 1, Nicholas B. Harris 1, Vincent Crombez 2, Tristan Euzen 3, Marta Gasparrini 2,
A Regional Diagenetic and Petrophysical Model for the Montney Formation, Western Canada Sedimentary Basin* Noga Vaisblat 1, Nicholas B. Harris 1, Vincent Crombez 2, Tristan Euzen 3, Marta Gasparrini 2,
Geology 252, Historical Geology, California State University, Los Angeles - professor: Dr. Alessandro Grippo
 LAB # 1 - CLASTIC ROCKS Background: - Mechanical and Chemical Weathering - Production of Clastic Sediment - Classification of Sediment according to size: Gravel, Sand, Silt, Clay - Erosion, Transportation
LAB # 1 - CLASTIC ROCKS Background: - Mechanical and Chemical Weathering - Production of Clastic Sediment - Classification of Sediment according to size: Gravel, Sand, Silt, Clay - Erosion, Transportation
23/9/2013 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY. Chapter 2: Rock classification:
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
ES Chap 5 & 6: Rocks
 ES Chap 5 & 6: Rocks Objectives 1. Identify and explain characteristics of igneous rocks. This means that if I am given an igneous rock I: a. Can use grain size to identify a rock as intrusive, extrusive,
ES Chap 5 & 6: Rocks Objectives 1. Identify and explain characteristics of igneous rocks. This means that if I am given an igneous rock I: a. Can use grain size to identify a rock as intrusive, extrusive,
ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION
 Name: Miramar College Grade: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory SEDIMENTARY ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The
Name: Miramar College Grade: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory SEDIMENTARY ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The
Sedimentary Rocks. Weathering. Mechanical & Chemical Weathering. Sediments. Lithification. Deposition. Transport. Erosion.
 Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
 UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Evolution of the Earth
 Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
Minerals Give Clues To Their Environment Of Formation. Also. Rocks: Mixtures of Minerals
 Minerals Give Clues To Their Environment Of Formation!!Can be a unique set of conditions to form a particular mineral or rock!!temperature and pressure determine conditions to form diamond or graphite
Minerals Give Clues To Their Environment Of Formation!!Can be a unique set of conditions to form a particular mineral or rock!!temperature and pressure determine conditions to form diamond or graphite
B) color B) Sediment must be compacted and cemented before it can change to sedimentary rock. D) igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks
 1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way.
 Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way. All rocks fit into one of three categories: Igneous- formed by the cooling and hardening of hot molten rock Sedimentary- formed
Rocks Rock- A group of minerals, glass, mineroid bound together in some way. All rocks fit into one of three categories: Igneous- formed by the cooling and hardening of hot molten rock Sedimentary- formed
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
Rocks Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3
 Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification VI. Additional sub-classes
Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification VI. Additional sub-classes
Rocks Environmental Significance. Rocks Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3. Rocks Definition of a rock
 Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 Environmental Significance I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification
Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 Environmental Significance I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 100. Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification. Thomas Doe
 CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Igneous Origins Intrusive Batholithic or plutonic: phaneritic Dikes or sills that chill rapidly: aphanitic Extrusive deposition as melt (lava) pyroclastic
CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Igneous Origins Intrusive Batholithic or plutonic: phaneritic Dikes or sills that chill rapidly: aphanitic Extrusive deposition as melt (lava) pyroclastic
Sediment. Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface
 Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
K.A. Campbell, D.M. Guido, J.D. Farmer, M.J. Van Kranendonk, S.W. Ruff, F. Westall
 Tracing hot-spring facies and their geothermally silicified microbial textures into the terrestrial geologic record: Relevance for Mars biosignature recognition K.A. Campbell, D.M. Guido, J.D. Farmer,
Tracing hot-spring facies and their geothermally silicified microbial textures into the terrestrial geologic record: Relevance for Mars biosignature recognition K.A. Campbell, D.M. Guido, J.D. Farmer,
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy. Thanks to Rob Viens for slides
 Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
8 th Earth Science Chapter 4 Rocks Name Section 1 The Rock Cycle:
 8 th Earth Science Chapter 4 Rocks Name Section 1 The Rock Cycle: Most rock used for stone contains one or more common minerals, called rock-forming minerals, such as, feldspar,, or. When you look closely,
8 th Earth Science Chapter 4 Rocks Name Section 1 The Rock Cycle: Most rock used for stone contains one or more common minerals, called rock-forming minerals, such as, feldspar,, or. When you look closely,
FIREPLACE GEOLOGY. Dining Hall
 FIREPLACE GEOLOGY Dining Hall The Dining Hall fireplace represents a slice through a Cascade Mountain volcano. Volcanoes are formed from molten magma rising up from within the Earth s crust. Magma that
FIREPLACE GEOLOGY Dining Hall The Dining Hall fireplace represents a slice through a Cascade Mountain volcano. Volcanoes are formed from molten magma rising up from within the Earth s crust. Magma that
Case Study: Tauhara New Zealand. Santiago de Chile, May 2014
 Case Study: Tauhara New Zealand The Geothermal Institute University of Auckland Bridget Lynne Santiago de Chile, 26-29 May 2014 Bridget Y. Lynne Mick Pender Trystan Glynn-Morris Tauhara Subsidence Case
Case Study: Tauhara New Zealand The Geothermal Institute University of Auckland Bridget Lynne Santiago de Chile, 26-29 May 2014 Bridget Y. Lynne Mick Pender Trystan Glynn-Morris Tauhara Subsidence Case
Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
 1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle Bell Ringer Name the 3 types of rock. Is one type of rock able to change into a different
To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle Bell Ringer Name the 3 types of rock. Is one type of rock able to change into a different
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Clastic Textures. I. What is the sorting of sample numbers 60, 61, and 62? Answers on last page.
 Sed Rock s Sel f-instruction N ame Geology 100 Harbor Secti on Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering, which originates by the successive deposition of
Sed Rock s Sel f-instruction N ame Geology 100 Harbor Secti on Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering, which originates by the successive deposition of
Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8
 Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8 Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of
Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8 Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
EARTH SCIENCE. Geology, the Environment and the Universe. Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks
 EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
1. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a part of the crystal structure of the mineral kaolinite.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a part of the crystal structure of the mineral kaolinite. An arrangement of atoms such as the one shown in the diagram determines
1. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a part of the crystal structure of the mineral kaolinite. An arrangement of atoms such as the one shown in the diagram determines
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter
 A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter Rocks are classified by how they are formed, their composition, and texture Rocks change over time through the rock
A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter Rocks are classified by how they are formed, their composition, and texture Rocks change over time through the rock
A. IGNEOUS Rocks formed by cooling and hardening of hot molten rock called magma (within crust or at its surface).
 EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
WEATHERING. Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions 10/22/2012
 WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
Characterization of Montana Grow Product David Mogk January 16, 2014
 Characterization of Montana Grow Product David Mogk January 16, 2014 Samples of the raw material that is used in the production of Montana Grow products were characterized using X- ray Powder Diffraction
Characterization of Montana Grow Product David Mogk January 16, 2014 Samples of the raw material that is used in the production of Montana Grow products were characterized using X- ray Powder Diffraction
Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
 Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
ORE MICROSCOPY AND ORE PETROGRAPHY
 >...- ORE MICROSCOPY AND ORE PETROGRAPHY Second Edition JAMES R. CRAIG Department of Geological Sciences Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg, Virginia DAVID J. VAUGHAN Department
>...- ORE MICROSCOPY AND ORE PETROGRAPHY Second Edition JAMES R. CRAIG Department of Geological Sciences Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg, Virginia DAVID J. VAUGHAN Department
Quartz Cementation in Mudrocks: How Common Is It?
 Quartz Cementation in Mudrocks: How Common Is It? Kitty L. Milliken Barnett Shale SE/CL image Woodford Shale SE/CL image Cements are Pore-filling Precipitates Specific definition differs with research
Quartz Cementation in Mudrocks: How Common Is It? Kitty L. Milliken Barnett Shale SE/CL image Woodford Shale SE/CL image Cements are Pore-filling Precipitates Specific definition differs with research
Rocks and Minerals. Tillery, Chapter 19. Solid Earth Materials
 Rocks and Minerals Tillery, Chapter 19 Science 330 Summer 2007 No other planet in the solar system has the unique combination of fluids of Earth. Earth has a surface that is mostly covered with liquid
Rocks and Minerals Tillery, Chapter 19 Science 330 Summer 2007 No other planet in the solar system has the unique combination of fluids of Earth. Earth has a surface that is mostly covered with liquid
Crust Elements. Elements of Earth. Minerals. Crystals. Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air
 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways.
 A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
Chapter: Earth Materials
 Table of Contents Chapter: Earth Materials Section 1: Minerals Section 2: Igneous Rocks Section 3: Sedimentary Rocks Section 4: Metamorphic Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1 Minerals Common Elements Composition
Table of Contents Chapter: Earth Materials Section 1: Minerals Section 2: Igneous Rocks Section 3: Sedimentary Rocks Section 4: Metamorphic Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1 Minerals Common Elements Composition
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks
 Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
 Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
I m good. Thank you.
 I m good. Thank you. The Rock Cycle Ag Earth Science Chapter 3.1 A natural occurring, inorganic crystalline material with a unique chemical composition. mineral A consolidated mixture of minerals rock
I m good. Thank you. The Rock Cycle Ag Earth Science Chapter 3.1 A natural occurring, inorganic crystalline material with a unique chemical composition. mineral A consolidated mixture of minerals rock
Why is quartz one of the most weathering-resistant minerals?
 Why is it a poor idea to use limestone for tombstones in a wet hot area like the Amazon rainforest? A) Because limestone weathers at a very fast rate B) Because limestone weathers at a very low rate C)
Why is it a poor idea to use limestone for tombstones in a wet hot area like the Amazon rainforest? A) Because limestone weathers at a very fast rate B) Because limestone weathers at a very low rate C)
Geology 229 Engineering Geology. Lecture 7. Rocks and Concrete as Engineering Material (West, Ch. 6)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 7 Rocks and Concrete as Engineering Material (West, Ch. 6) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock mass properties Weakness planes control rock mass strength; Rock textures;
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 7 Rocks and Concrete as Engineering Material (West, Ch. 6) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock mass properties Weakness planes control rock mass strength; Rock textures;
Recognising Igneous Rocks Teacher Notes
 Minerals are the building blocks of rocks Minerals are inorganic crystals with constant structure and composition Classification of igneous rocks Igneous (Latin ig = fire, neous = born) rocks are formed
Minerals are the building blocks of rocks Minerals are inorganic crystals with constant structure and composition Classification of igneous rocks Igneous (Latin ig = fire, neous = born) rocks are formed
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Laboratory 5 Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks a.
 Laboratory 5 Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks a. LAB 5 provides samples of all three principal groupings of rocks including: 1) Igneous (plutonic and extrusive felsic, intermediate, and mafic varieties)
Laboratory 5 Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks a. LAB 5 provides samples of all three principal groupings of rocks including: 1) Igneous (plutonic and extrusive felsic, intermediate, and mafic varieties)
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Stratigraphy. Stratigraphy deals with the study of any layered (stratified) rock, but primarily with sedimentary rocks and their
 Stratigraphy Stratigraphy deals with the study of any layered (stratified) rock, but primarily with sedimentary rocks and their composition origin age relationships geographic extent Stratified Sedimentary
Stratigraphy Stratigraphy deals with the study of any layered (stratified) rock, but primarily with sedimentary rocks and their composition origin age relationships geographic extent Stratified Sedimentary
Big Island Field Trip
 Big Island Field Trip Space Still Available Group Airline Tickets May be available if enough people sign on If interested send email to Greg Ravizza Planning Meeting Next Week Will
Big Island Field Trip Space Still Available Group Airline Tickets May be available if enough people sign on If interested send email to Greg Ravizza Planning Meeting Next Week Will
Mud Sand Gravel. Clastic Textures
 Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Please see the questions online before you begin. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Please see the questions online before you begin. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Mud Sand Gravel. Clastic Textures
 Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Read the sedimentary rocks chapter before you start. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Read the sedimentary rocks chapter before you start. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Liz LaRosa Images from Geology.com unless otherwise noted
 Liz LaRosa http://www.middleschoolscience.com 2010 Images from Geology.com unless otherwise noted A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter Rocks are classified
Liz LaRosa http://www.middleschoolscience.com 2010 Images from Geology.com unless otherwise noted A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter Rocks are classified
Geogenic versus Anthropogenic Metals and Metalloids
 Geogenic versus Anthropogenic Metals and Metalloids Geochemical methods for evaluating whether metals and metalloids are from geogenic versus anthropogenic sources 1 Definitions Geogenic from natural geological
Geogenic versus Anthropogenic Metals and Metalloids Geochemical methods for evaluating whether metals and metalloids are from geogenic versus anthropogenic sources 1 Definitions Geogenic from natural geological
I. Uniformitarianism- James Hutton s 2-part theory states: A. The geologic processes now at work were also active in the past B. The present physical
 How Earth s Rocks Were Formed I. Uniformitarianism- James Hutton s 2-part theory states: A. The geologic processes now at work were also active in the past B. The present physical features of Earth were
How Earth s Rocks Were Formed I. Uniformitarianism- James Hutton s 2-part theory states: A. The geologic processes now at work were also active in the past B. The present physical features of Earth were
Bog Hot Valley. (updated 2012)
 Bog Hot Valley (updated 2012) Geologic setting: Bog Hot Valley is located along a major fault lineament between Soldier Meadows Hot Springs and Oregon (figure; Hose and Taylor, 1974). This lineament can
Bog Hot Valley (updated 2012) Geologic setting: Bog Hot Valley is located along a major fault lineament between Soldier Meadows Hot Springs and Oregon (figure; Hose and Taylor, 1974). This lineament can
SUB-SURFACE GEOLOGY AND HYDROTHERMAL ALTERATION OF WELLS LA-9D AND LA-10D OF ALUTO LANGANO GEOTHERMAL FIELD, ETHIOPIA
 Proceedings, 6 th African Rift Geothermal Conference Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2 nd -4 th November 2016 SUB-SURFACE GEOLOGY AND HYDROTHERMAL ALTERATION OF WELLS LA-9D AND LA-10D OF ALUTO LANGANO GEOTHERMAL
Proceedings, 6 th African Rift Geothermal Conference Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2 nd -4 th November 2016 SUB-SURFACE GEOLOGY AND HYDROTHERMAL ALTERATION OF WELLS LA-9D AND LA-10D OF ALUTO LANGANO GEOTHERMAL
ENVI.2030L Rock Identification
 ENVI.2030L Rock Identification Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety of rocks - aggregates
ENVI.2030L Rock Identification Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety of rocks - aggregates
GEOL FORENSIC GEOLOGY ROCK IDENTIFICATION
 GEOL.2150 - FORENSIC GEOLOGY ROCK IDENTIFICATION Name I. Introduction There are three basic types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic: Igneous. Igneous rocks have solidified from molten matter
GEOL.2150 - FORENSIC GEOLOGY ROCK IDENTIFICATION Name I. Introduction There are three basic types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic: Igneous. Igneous rocks have solidified from molten matter
GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA
 254 GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA Sam Lee CRC LEME, Department of Applied Geology, Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Western Australia, 6485 INTRODUCTION
254 GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA Sam Lee CRC LEME, Department of Applied Geology, Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Western Australia, 6485 INTRODUCTION
1. Gravel-size 2. Sand-size 3. Silt-size 4. Clay-size 5. Microcrystalline 6. Macrocrystalline
 Name: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Lab Grade: SEDIMENTARY & METAMORPHIC ROCK CLASSIFICATION and IDENTIFICATION SEDIMENTARY PRE-ID SECTION To be completed before observing hand samples: I. Introduction &
Name: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Lab Grade: SEDIMENTARY & METAMORPHIC ROCK CLASSIFICATION and IDENTIFICATION SEDIMENTARY PRE-ID SECTION To be completed before observing hand samples: I. Introduction &
Earth Materials Unit: Sedimen ntary Rocks and Processes Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Five and Six Lab: Laboratorry Six Name
 Earth Materi ials Unit: Sedimentary Rocks and Proces sses Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Fivee and Six Lab: Laboratory Six Name Page 1 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Purpose: To classify sedimentary rocks
Earth Materi ials Unit: Sedimentary Rocks and Proces sses Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Fivee and Six Lab: Laboratory Six Name Page 1 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Purpose: To classify sedimentary rocks
Name: Grade: GEOL Physical Geology Laboratory Sedimentaryand Metamorphic Rocks Lab #6
 Name: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory Sedimentaryand Metamorphic Rocks Lab #6 Grade: PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory
Name: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory Sedimentaryand Metamorphic Rocks Lab #6 Grade: PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory
Aggregates for Concrete
 Fine Aggregate Sand and/or crushed stone < 5 mm (0.2 in.) F.A. content usually 35% to 45% by mass or volume of total aggregate Coarse Aggregate Gravel and crushed stone 5 mm (0.2 in.) typically between
Fine Aggregate Sand and/or crushed stone < 5 mm (0.2 in.) F.A. content usually 35% to 45% by mass or volume of total aggregate Coarse Aggregate Gravel and crushed stone 5 mm (0.2 in.) typically between
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals
 Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
Igneous, Metamorphic & Sedimentary. Chapter 5 & Chapter 6
 Igneous, Metamorphic & Sedimentary Chapter 5 & Chapter 6 Section 5.1 What are Igneous Rocks? Compare and contrast intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks. Describe the composition of magma Discuss the factors
Igneous, Metamorphic & Sedimentary Chapter 5 & Chapter 6 Section 5.1 What are Igneous Rocks? Compare and contrast intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks. Describe the composition of magma Discuss the factors
Rock Cycle and Rock Types Homework
 Rock Cycle and Rock Types Homework Completion Complete each statement. 1. A(n) is a solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally. 2. Rocks are generally classified as igneous,, or
Rock Cycle and Rock Types Homework Completion Complete each statement. 1. A(n) is a solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally. 2. Rocks are generally classified as igneous,, or
The 3 types of rocks:
 Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Igneous Activity The 3 types of rocks:! Sedimentary! Igneous! Metamorphic Marble 1 10/7/15 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Come from rocks sediments (rock fragments, sand, silt, etc.) Fossils
Practice Test Rocks and Minerals. Name. Page 1
 Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
KS3 Chemistry. 8H The Rock Cycle. 8H The Rock Cycle. Sedimentary rocks. Metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks. The rock cycle. Summary activities
 KS3 Chemistry 1of 20 38 12of 20 38 Examples of sedimentary rocks How can you describe sandstone? limestone chalk Sandstone is sandstone sandstone an orangey-coloured rock which looks like lots of sand
KS3 Chemistry 1of 20 38 12of 20 38 Examples of sedimentary rocks How can you describe sandstone? limestone chalk Sandstone is sandstone sandstone an orangey-coloured rock which looks like lots of sand
City of Fort Collins: Geology Staff Training, June 2012
 1 City of Fort Collins: Geology Staff Training, June 2012 Levels of Analysis Descriptive (What do you see, feel, hear, etc..) This rock is made of round grains of quartz. Interpretive-- (The detective
1 City of Fort Collins: Geology Staff Training, June 2012 Levels of Analysis Descriptive (What do you see, feel, hear, etc..) This rock is made of round grains of quartz. Interpretive-- (The detective
Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
 Chapter 2 Lecture Outline Foundations of Earth Science Seventh Edition Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Natalie Bursztyn Utah State University Focus Question 2.1 What processes can transform a rock
Chapter 2 Lecture Outline Foundations of Earth Science Seventh Edition Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Natalie Bursztyn Utah State University Focus Question 2.1 What processes can transform a rock
Sedimentary Geology. Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1
 Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Pacific Northwest Rock Lab, Part II. Igneous Rocks. Name Per.
 Name Per. Pacific Northwest Rock Lab, Part II After you ve classified all your rocks, place their numbers next to the names and read the information about the rock. Check the classifications here (igneous,
Name Per. Pacific Northwest Rock Lab, Part II After you ve classified all your rocks, place their numbers next to the names and read the information about the rock. Check the classifications here (igneous,
