Introduction: Advancing Simulations of Sequences of Earthquakes and Aseismic Slip (SEAS)
|
|
|
- Chloe King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction: Advancing Simulations of Sequences of Earthquakes and Aseismic Slip (SEAS) Brittany Erickson (Portland State University) Junle Jiang (University of California, San Diego) SCEC DR-SEAS Workshop, Apr , 2018
2 Outline! Motivation! Objectives! Current activities! Benchmarks for code verification! Timeline for future activities! Workshop agenda 2
3 Motivation! SEAS (aka seismic cycle ) simulations are now prevalent in earthquake research addressing key SCEC objectives but remain untested! Dynamic rupture (DR) group Simulating detailed single-event earthquake ruptures Successful code verification exercises and ongoing validation efforts Imposed artificial prestress conditions and ad hoc nucleation procedures! Earthquake Simulators (ES) Simulating millennium-scale seismicity patterns in fault systems Quasi-static approximation and some key physical features missing! A new generation of verified SEAS models is needed Simulating longer periods of earthquake activity than single-event ruptures Computational rigor and physically sound approaches 3
4 Ingredients & output of SEAS models seismogenic zone slow tectonic loading 4
5 Problems that set SEAS models apart from DR! The use of variable time stepping and possible switching between different computational schemes to capture inter- and co-seismic phases.! The interaction between nonlinear nature of the problem and accumulation of roundoff errors.! The need to distinguish between legitimate solution differences and those due to improper choices of algorithm, model resolution, and modeling procedures.! The importance of numerical efficiency and computational performance for feasibility of even the most basic problems. 5
6 Examples of SEAS modeling velocity-weakening region velocity-weakening patches velocity-strengthening region logarithmic slip rate A planar fault in a 3D homogenous half-space Jiang and Lapusta, Science,
7 (a) (b) coseismic rupture Complex interactions between earthquakes and aseismic slip! Fully dynamic rupture! Postseismic stress relaxation (c) Depth (km) 20 microseismicity interseismic aftershocks interseismic events Along-strike distance (km) logrithmic slip rate (m/s) coseismic slip (m)! Microseismicity! Complexity in large events! Interseismic fault coupling! Compare with seismological, geodetic, and geological data Jiang and Lapusta (Science, 2016; JGR, 2017) 7
8 How rheology and structure influence earthquake sequences cumulative fault slip along depth! Quasi-dynamic earthquake ruptures in 2D antiplane models! Heterogeneous bulk material properties! Off-fault plasticity Erickson and Dunham (JGR, 2014) Erickson et al. (JMPS, 2017) 8
9 Complexities in SEAS problems! Transition from slow, quasi-static to dynamic, wave-producing slip! Stress transfer due to dynamic waves! Transition to postseismic slip! Postseismic and interseismic slip and the associated stress redistribution! Interaction with the deep visco-elasto-plastic response and the associated stress redistribution! Interaction with fluids throughout the cycle! Interaction with off-fault damage and healing! The role of geometrical complexities Investigated in a number of studies (e.g., Jiang and Lapusta, 2016; Erickson and Dunham, 2014; Luo and Ampuero, 2011; Barbot et al., 2012; Liu, 2013; Wei, 2013; Segall and Bradley, 2012; Kaneko et al., 2011; van Dinther et al., 2013; Hajarolasvadi and Elbanna, 2017; Kroll et al., 2017; Tal et al., 2018) 9
10 Some outstanding questions! How do these physical factors influence the earthquake cycle? Do they matter? How to implement them with efficiency in 3D, larger scale simulations (e.g., Earthquake Simulators at SCEC)?! Do our numerical models resolve the true fault behavior and its complexity? What features in models may arise from numerical approximation and resolution issues?! What are the best practices and significant issues for SEAS modeling? 10
11 Objectives of SEAS working group! Lead the efforts on code verification of SEAS models! Explore important issues in SEAS modeling and further advance our computational capabilities! Promote robust and reproducible earthquake science! Lend experience and tools to the community! Provide synergy with other SCEC working groups such as the Dynamic Rupture group, Earthquake Simulators, Community Rheology Model, etc 11
12 Past & current activities! Submitted SCEC proposals for working group and workshop (Nov.)! Developed the first Benchmark Problem BP1 (Mar.)! Established online platform with basic model comparison tools (Mar.)! Received and analyzed 23 submissions from 11 modelers! The current workshop for science talks, benchmark results, & discussions 12
13 Benchmarks for code verification! Guidelines Start simple & incrementally increase model complexity Take advantage of experience and tools from the dynamic rupture group Design benchmarks that maximize participations Develop the web platform based on comparison needs! Tasks What model features should we compare? How do we assess agreements and discrepancies? What constitute successful code verifications for SEAS models? 13
14 1 st benchmark BP1 2D anti-plane shear motion. The fault is a vertical strike-slip fault in a homogeneous half-space. Friction is regularized rate-and-state friction with the aging law. (readily adaptable to a 3D benchmark) 14
15 Online platform! Code verification web server installed and maintained by Michael Barall ( Using existing architecture/tools from dynamic rupture group 15
16 coseismic processes (manual) Benchmark results abrahaps cattania erickson Miang kozdon lapbert liu luo wei xpa SliS rate (P/s) Shear Stress (03a) 11 models and model submissions lapbert liu luo wei xpa Jiang: SBIM,0.0 time stepping from Lapusta et al., dz = abrahaps cattania erickson Miang kozdon iPe (s) iPe (s) Fault length 80km: No. of events: 35 0 Depth (km) long-term evolution of slip/rate/stress (online platform) Cumulative Slip (m) Slip evolution along depth (manual) Fault length 160km: 16
17 Benchmark design! Ingredients in benchmark design 2D anti-plane/in-plane or 3D problems State evolution in friction laws (aging vs. slip formulations) Complexity in structure, geometry, or frictional properties Fluid processes, inelastic effects, etc.! The next benchmark(s) 3D problem similar to BP1 (with a lower resolution) 2D problem with viscoelasticity 2D problem with different evolution laws! Future benchmarks? 17
18 Timelines for future activities! Proposals for 2018 SEAS verification exercises in SCEC5: Pending Co-PIs: Erickson, Jiang, and Barall Other modelers to request separate funding from SCEC or others One-day SEAS-themed workshop (2019 Spring): Pending! Conference presentations 2018 SCEC and AGU annual meetings, and others.! Group meetings 2018 SCEC meeting and potential 2019 workshop! Publications Development of an initial set of 2D/3D benchmarks and significant SEAS issues 18
19 Workshop agenda Monday afternoon: SEAS modeling and its connections to dynamic rupture problems 14:30-15:00 Introduction to SEAS activities 15:00-15:15 SEAS: on resolution, complexity, and dynamic effects 15:15-15:30 Modeling of the nucleation process of laboratory and crustal earthquakes 15:30-15:45 Coupling spectral boundary integral and volume-based models for high resolution fault zone physics 15:45-16:00 Modeling the rupture process on rough faults during multiple slip events wit hte mortar finite element method 16:00-16:15 Break 16:15-16:30 Discontinuous Galerkin methods for earthquake cycle simulations 16:30-16:45 RSQSim modeling and applications 16:45-17:30 Discussions Brittany Erickson / Junle Jiang Nadia Lapusta Yoshihiro Kaneko Ahmed Elbanna Yuval Tal Jeremy Kozdon Kayla Kroll 19
20 Tuesday morning: Multi-physics and diverse observables in SEAS models 08:30-08:45 The effect of shear heating on the earthquake cycle 08:45-09:00 Time stepping for earthquake cycles with plasticity 09:00-09:15 Modelling frictional faults as plastic shear bands in nonlinear media 09:15-09:30 FDRA - Fault dynamics with radition damping approximation: history and capabilities 09:30-09:45 The spectrum of rupture styles at subduction zone governed by the geometry and rheology of the upper plate 09:45-10:00 Modeling of slow slip events on a non-planar subduction fault 10:00-10:15 Numerical simulation of dynamic triggering of slow slip events in California and New Zealand 10:15-10:30 Break 10:30-12:00 Benchmark results and discussions 12:00-13:00 Lunch 13:00-14:30 Workshop wrap-up and future plans Kali Allison Brittany Erickson Casper Pranger Paul Segall Sylvain Barbot Yajing Liu Matt Wei Brittany Erickson / Junle Jiang Brittany Erickson / Junle Jiang 20
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta. California Institute of Technology
 Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip
 Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
March 2017 SCEC Rupture Dynamics Code Validation Workshop
 Presentation for March 1, 2017 SCEC Boardroom Los Angeles, CA March 2017 SCEC Rupture Dynamics Code Validation Workshop Ruth A. Harris (U.S. Geological Survey) Ralph J. Archuleta (UC Santa Barbara) INTRODUCTION
Presentation for March 1, 2017 SCEC Boardroom Los Angeles, CA March 2017 SCEC Rupture Dynamics Code Validation Workshop Ruth A. Harris (U.S. Geological Survey) Ralph J. Archuleta (UC Santa Barbara) INTRODUCTION
Earthquake and Volcano Deformation
 Earthquake and Volcano Deformation Paul Segall Stanford University Draft Copy September, 2005 Last Updated Sept, 2008 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: To be published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, c
Earthquake and Volcano Deformation Paul Segall Stanford University Draft Copy September, 2005 Last Updated Sept, 2008 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: To be published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, c
A new hybrid numerical scheme for modelling elastodynamics in unbounded media with near-source heterogeneities
 A new hybrid numerical scheme for modelling elastodynamics in unbounded media with near-source heterogeneities Setare Hajarolasvadi Ahmed E. Elbanna https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bltx92tuwha MOTIVATION
A new hybrid numerical scheme for modelling elastodynamics in unbounded media with near-source heterogeneities Setare Hajarolasvadi Ahmed E. Elbanna https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bltx92tuwha MOTIVATION
Aspects of a Discontinuous Galerkin Approach for 3D Dynamic Rupture Modeling in the Case of a Complex Fault System
 AGU Fall Meeting 2011 S54C-08 Aspects of a Discontinuous Galerkin Approach for 3D Dynamic Rupture Modeling in the Case of a Complex Fault System Christian Pelties Josep de la Puente (BSC), Jean Paul Ampuero
AGU Fall Meeting 2011 S54C-08 Aspects of a Discontinuous Galerkin Approach for 3D Dynamic Rupture Modeling in the Case of a Complex Fault System Christian Pelties Josep de la Puente (BSC), Jean Paul Ampuero
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area. Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC
 Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Overview of the PyLith Finite Element Code
 Overview of the PyLith Finite Element Code www.geodynamics.org Charles Williams (GNS Science) Brad Aagaard (USGS) Matt Knepley (University of Chicago) CIG Software PyLith is a Tool for Crustal Deformation
Overview of the PyLith Finite Element Code www.geodynamics.org Charles Williams (GNS Science) Brad Aagaard (USGS) Matt Knepley (University of Chicago) CIG Software PyLith is a Tool for Crustal Deformation
Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications for aftershock rates
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Abstract
 Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Challenges in earthquake physics and source imaging
 Challenges in earthquake physics and source imaging Jean-Paul Ampuero and Nadia Lapusta (Caltech Seismolab) Main goals and current issues in earthquake dynamics The source imaging inverse problem Parallels
Challenges in earthquake physics and source imaging Jean-Paul Ampuero and Nadia Lapusta (Caltech Seismolab) Main goals and current issues in earthquake dynamics The source imaging inverse problem Parallels
EFFECTS OF NON-LINEAR WEAKENING ON EARTHQUAKE SOURCE SCALINGS
 Extended abstract for the 11th International Conference on Fracture 2005 1 EFFECTS OF NON-LINEAR WEAKENING ON EARTHQUAKE SOURCE SCALINGS J.-P. Ampuero Geosciences Department, Princeton University, USA
Extended abstract for the 11th International Conference on Fracture 2005 1 EFFECTS OF NON-LINEAR WEAKENING ON EARTHQUAKE SOURCE SCALINGS J.-P. Ampuero Geosciences Department, Princeton University, USA
The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory and Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University 2nd edition CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory and Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University 2nd edition CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
Earthquake nucleation. Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab
 Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures
 Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Using deformation rates in Northern Cascadia to constrain time-dependent stress- and slip-rate on the megathrust
 Using deformation rates in Northern Cascadia to constrain time-dependent stress- and slip-rate on the megathrust Lucile Bruhat Paul Segall Stanford University 1 50 Interseismic period for the Cascadia
Using deformation rates in Northern Cascadia to constrain time-dependent stress- and slip-rate on the megathrust Lucile Bruhat Paul Segall Stanford University 1 50 Interseismic period for the Cascadia
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II
 Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Final Report. Submitted by Ruth Harris to SCEC March 27, 2017
 Final Report Submitted by Ruth Harris to SCEC March 27, 2017 A Collaborative Project: Rupture Dynamics, Validation of the Numerical Simulation Method (SCEC Project 16056) Coordinating Principal Investigator:
Final Report Submitted by Ruth Harris to SCEC March 27, 2017 A Collaborative Project: Rupture Dynamics, Validation of the Numerical Simulation Method (SCEC Project 16056) Coordinating Principal Investigator:
A hierarchy of tremor migration patterns induced by the interaction of brittle asperities mediated by aseismic slip transients
 A hierarchy of tremor migration patterns induced by the interaction of brittle asperities mediated by aseismic slip transients J.-P. Ampuero (Caltech Seismolab), H. Perfettini (IRD), H. Houston and B.
A hierarchy of tremor migration patterns induced by the interaction of brittle asperities mediated by aseismic slip transients J.-P. Ampuero (Caltech Seismolab), H. Perfettini (IRD), H. Houston and B.
Fault-Zone Properties arid Earthquake Rupture Dynamics
 Fault-Zone Properties arid Earthquake Rupture Dynamics Eiichi Fukuyama National Research Institute for Earth Science,and Disaster Prevention Tsukuba, Japan i ':-> i' ' -':'.." \,' " '' L VH ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM
Fault-Zone Properties arid Earthquake Rupture Dynamics Eiichi Fukuyama National Research Institute for Earth Science,and Disaster Prevention Tsukuba, Japan i ':-> i' ' -':'.." \,' " '' L VH ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM
Rheology III. Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep
 Rheology III Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep Ideal materials fall into one of the following categories:
Rheology III Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep Ideal materials fall into one of the following categories:
Scaling of small repeating earthquakes explained by interaction of seismic and aseismic slip in a rate and state fault model
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005749, 2009 Scaling of small repeating earthquakes explained by interaction of seismic and aseismic slip in a
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005749, 2009 Scaling of small repeating earthquakes explained by interaction of seismic and aseismic slip in a
Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation. Luis A. Dalguer
 Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation Luis A. Dalguer Computational Seismology Group Swiss Seismological Service (SED) ETH-Zurich July 12-18, 2011 2 st QUEST Workshop,
Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation Luis A. Dalguer Computational Seismology Group Swiss Seismological Service (SED) ETH-Zurich July 12-18, 2011 2 st QUEST Workshop,
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities
 Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics
 Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Regional Geodesy. Shimon Wdowinski. MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region. University of Miami
 MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
Megathrust earthquakes: How large? How destructive? How often? Jean-Philippe Avouac California Institute of Technology
 Megathrust earthquakes: How large? How destructive? How often? Jean-Philippe Avouac California Institute of Technology World seismicity (data source: USGS) and velocities relative to ITRF1997 (Sella et
Megathrust earthquakes: How large? How destructive? How often? Jean-Philippe Avouac California Institute of Technology World seismicity (data source: USGS) and velocities relative to ITRF1997 (Sella et
A possible mechanism of M 9 earthquake generation cycles in the area of repeating M 7 8 earthquakes surrounded by aseismic sliding
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 63, 773 777, 2011 A possible mechanism of M 9 earthquake generation cycles in the area of repeating M 7 8 earthquakes surrounded by aseismic sliding Takane Hori 1 and Shin ichi
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 63, 773 777, 2011 A possible mechanism of M 9 earthquake generation cycles in the area of repeating M 7 8 earthquakes surrounded by aseismic sliding Takane Hori 1 and Shin ichi
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
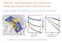 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA
 3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent faults
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2011) 186, 1389 1403 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05117.x Shallow slip deficit due to large strike-slip earthquakes in dynamic rupture simulations with
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2011) 186, 1389 1403 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05117.x Shallow slip deficit due to large strike-slip earthquakes in dynamic rupture simulations with
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA
 Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding
 Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 168, 797 808 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03255.x Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding Naoyuki Kato Earthquake Research Institute, University
Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 168, 797 808 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03255.x Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding Naoyuki Kato Earthquake Research Institute, University
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller
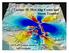 Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
Estimating fault slip rates, locking distribution, elastic/viscous properites of lithosphere/asthenosphere. Kaj M. Johnson Indiana University
 3D Viscoelastic Earthquake Cycle Models Estimating fault slip rates, locking distribution, elastic/viscous properites of lithosphere/asthenosphere Kaj M. Johnson Indiana University In collaboration with:
3D Viscoelastic Earthquake Cycle Models Estimating fault slip rates, locking distribution, elastic/viscous properites of lithosphere/asthenosphere Kaj M. Johnson Indiana University In collaboration with:
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ).
 Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Hitoshi Hirose (1), and Kazuro Hirahara (2) Abstract. Introduction
 Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Secondary Project Proposal
 Secondary Project Proposal Post-seismic deformation of Chi-chi earthquake Yunyue (Elita) Li 11:, Wednesday, June 2, 21 Li 2 Secondary project proposal Personal prospective MOTIVATION My interests for earthquake
Secondary Project Proposal Post-seismic deformation of Chi-chi earthquake Yunyue (Elita) Li 11:, Wednesday, June 2, 21 Li 2 Secondary project proposal Personal prospective MOTIVATION My interests for earthquake
Slow Slip and Tremor Along San Andreas fault system
 Slow Slip and Tremor Along San Andreas fault system Slow slip in Upper Crust Aseismic creep, afterslip and spontaneous slow slip events on some faults in upper 15 km Mostly aseismic but accompanied by
Slow Slip and Tremor Along San Andreas fault system Slow slip in Upper Crust Aseismic creep, afterslip and spontaneous slow slip events on some faults in upper 15 km Mostly aseismic but accompanied by
Generic Earthquake Simulator
 Generic Earthquake Simulator by Terry E. Tullis, Keith Richards-Dinger, Michael Barall, James H. Dieterich, Edward H. Field, Eric Heien, Louise H. Kellogg, Fred Pollitz, John Rundle, Michael Sachs, Donald
Generic Earthquake Simulator by Terry E. Tullis, Keith Richards-Dinger, Michael Barall, James H. Dieterich, Edward H. Field, Eric Heien, Louise H. Kellogg, Fred Pollitz, John Rundle, Michael Sachs, Donald
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise
 GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 20, 30 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Aki, Scaling law
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 20, 30 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Aki, Scaling law
San Francisco Bay Area Earthquake Simulations: A step toward a Standard Physical Earthquake Model
 San Francisco Bay Area Earthquake Simulations: A step toward a Standard Physical Earthquake Model Steven N. Ward Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA,
San Francisco Bay Area Earthquake Simulations: A step toward a Standard Physical Earthquake Model Steven N. Ward Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA,
Spectral element modeling of spontaneous earthquake rupture on rate and state faults: Effect of velocity-strengthening friction at shallow depths
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005553, 2008 Spectral element modeling of spontaneous earthquake rupture on rate and state faults: Effect of velocity-strengthening friction
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005553, 2008 Spectral element modeling of spontaneous earthquake rupture on rate and state faults: Effect of velocity-strengthening friction
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors
 Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law
 Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Megathrust Earthquakes
 Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Author's personal copy
 Tectonophysics 612 613 (2014) 56 62 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Tectonophysics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tecto Inelastic response of compliant fault zones to nearby earthquakes
Tectonophysics 612 613 (2014) 56 62 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Tectonophysics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tecto Inelastic response of compliant fault zones to nearby earthquakes
Frictional Properties on the San Andreas Fault near Parkfield, California, Inferred from Models of Afterslip following the 2004 Earthquake
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 96, No. 4B, pp. S321 S338, September 2006, doi: 10.1785/0120050808 Frictional Properties on the San Andreas Fault near Parkfield, California, Inferred
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 96, No. 4B, pp. S321 S338, September 2006, doi: 10.1785/0120050808 Frictional Properties on the San Andreas Fault near Parkfield, California, Inferred
Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation
 Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation Zac Meadows UC Davis - Department of Physics Summer 2012 REU September 3, 2012 Abstract To better understand the spatial and temporal complexity
Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation Zac Meadows UC Davis - Department of Physics Summer 2012 REU September 3, 2012 Abstract To better understand the spatial and temporal complexity
Earthquake stress drop estimates: What are they telling us?
 Earthquake stress drop estimates: What are they telling us? Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego October 27, 2014 SCEC Community Stress Model Workshop Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions,
Earthquake stress drop estimates: What are they telling us? Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego October 27, 2014 SCEC Community Stress Model Workshop Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions,
The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a
 The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a A German seismogram of the 1906 SF EQ Image courtesy of San Francisco Public Library Stages of the Earthquake Cycle The Earthquake cycle is split into several distinct
The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a A German seismogram of the 1906 SF EQ Image courtesy of San Francisco Public Library Stages of the Earthquake Cycle The Earthquake cycle is split into several distinct
Defmod, an earthquake simulator that adaptively switches between quasi-static and dynamic states
 Defmod, an earthquake simulator that adaptively switches between quasi-static and dynamic states C. Meng (cmeng@mit.edu) B. Hager ERL, MIT May 16, 2016 Reservoir production/injection induced seismicity
Defmod, an earthquake simulator that adaptively switches between quasi-static and dynamic states C. Meng (cmeng@mit.edu) B. Hager ERL, MIT May 16, 2016 Reservoir production/injection induced seismicity
Heterogeneous Coulomb stress perturbation during earthquake cycles in a 3D rate-and-state fault model
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L21306, doi:10.1029/2008gl035614, 2008 Heterogeneous Coulomb stress perturbation during earthquake cycles in a 3D rate-and-state fault
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L21306, doi:10.1029/2008gl035614, 2008 Heterogeneous Coulomb stress perturbation during earthquake cycles in a 3D rate-and-state fault
Toward a SCEC Community Rheology Model: TAG Kickoff and Workshop SCEC Workshop Proposal Final Report
 Toward a SCEC Community Rheology Model: TAG Kickoff and Workshop SCEC Workshop Proposal 17206 Final Report A one-day Community Rheology Model workshop was held at the Palm Springs Hilton on the Saturday
Toward a SCEC Community Rheology Model: TAG Kickoff and Workshop SCEC Workshop Proposal 17206 Final Report A one-day Community Rheology Model workshop was held at the Palm Springs Hilton on the Saturday
The Deep Fault Drilling Project, Alpine Fault Getting Inside the Earthquake Machine
 The Deep Fault Drilling Project, Alpine Fault Getting Inside the Earthquake Machine John Townend Director, EQC Programme in Seismology and Fault Mechanics Head, School of Geography, Environment and Earth
The Deep Fault Drilling Project, Alpine Fault Getting Inside the Earthquake Machine John Townend Director, EQC Programme in Seismology and Fault Mechanics Head, School of Geography, Environment and Earth
Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes
 1 Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada, kelin.wang@canada.ca Introduction Once upon a time, there was a belief that
1 Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada, kelin.wang@canada.ca Introduction Once upon a time, there was a belief that
to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San
 Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
Spectral Element simulation of rupture dynamics
 Spectral Element simulation of rupture dynamics J.-P. Vilotte & G. Festa Department of Seismology, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, 75252 France ABSTRACT Numerical modeling is an important tool,
Spectral Element simulation of rupture dynamics J.-P. Vilotte & G. Festa Department of Seismology, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, 75252 France ABSTRACT Numerical modeling is an important tool,
STRIKE SLIP SPLAY USING DYNAMIC RUPTURE MODELS
 STRIKE SLIP SPLAY USING DYNAMIC RUPTURE MODELS Julian Lozos (PEER, UC Berkeley) SWUS GMC Workshop #2, Berkeley, CA, 24 October 2013 Outline Issues in the dynamics of fault branches. Advantages and disadvantages
STRIKE SLIP SPLAY USING DYNAMIC RUPTURE MODELS Julian Lozos (PEER, UC Berkeley) SWUS GMC Workshop #2, Berkeley, CA, 24 October 2013 Outline Issues in the dynamics of fault branches. Advantages and disadvantages
Southern California Earthquake Center. SCEC Annual Meeting. Palm Springs, California September 2016
 SCEC Annual Meeting Palm Springs, California 11-14 September 2016 Welcome to Palm Springs! Southern California SCEC Annual Meetings 707 pre-registrants 347 poster abstracts 211 first-time attendees (145
SCEC Annual Meeting Palm Springs, California 11-14 September 2016 Welcome to Palm Springs! Southern California SCEC Annual Meetings 707 pre-registrants 347 poster abstracts 211 first-time attendees (145
High-Harmonic Geoid Signatures due to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Subduction and Seismic Deformation
 High-Harmonic Geoid Signatures due to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Subduction and Seismic Deformation L.L.A. Vermeersen (1), H. Schotman (1), M.-W. Jansen (1), R. Riva (1) and R. Sabadini (2) (1) DEOS,
High-Harmonic Geoid Signatures due to Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Subduction and Seismic Deformation L.L.A. Vermeersen (1), H. Schotman (1), M.-W. Jansen (1), R. Riva (1) and R. Sabadini (2) (1) DEOS,
Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Synthetic Seismicity Models of Multiple Interacting Faults
 Synthetic Seismicity Models of Multiple Interacting Faults Russell Robinson and Rafael Benites Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Box 30368, Lower Hutt, New Zealand (email: r.robinson@gns.cri.nz).
Synthetic Seismicity Models of Multiple Interacting Faults Russell Robinson and Rafael Benites Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences, Box 30368, Lower Hutt, New Zealand (email: r.robinson@gns.cri.nz).
Creep or Stick? Spatial variations of fault friction, implications for earthquake hazard. Jean-Philippe Avouac. Collaborators
 Creep or Stick? Spatial variations of fault friction, implications for earthquake hazard Jean-Philippe Avouac Collaborators Vicky Stevens Marion Thomas Thomas Ader Ozgun Konca Laurent Bollinger Francois
Creep or Stick? Spatial variations of fault friction, implications for earthquake hazard Jean-Philippe Avouac Collaborators Vicky Stevens Marion Thomas Thomas Ader Ozgun Konca Laurent Bollinger Francois
Can geodetic strain rate be useful in seismic hazard studies?
 Can geodetic strain rate be useful in seismic hazard studies? F. Riguzzi 1, R. Devoti 1, G. Pietrantonio 1, M. Crespi 2, C. Doglioni 2, A.R. Pisani 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia 2 Università
Can geodetic strain rate be useful in seismic hazard studies? F. Riguzzi 1, R. Devoti 1, G. Pietrantonio 1, M. Crespi 2, C. Doglioni 2, A.R. Pisani 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia 2 Università
Limitations of Earthquake Triggering Models*
 Limitations of Earthquake Triggering Models* Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 16, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute * in Southern California Why do earthquakes cluster in time and space?
Limitations of Earthquake Triggering Models* Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 16, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute * in Southern California Why do earthquakes cluster in time and space?
Slip-weakening models of the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake and. constraints on stress drop and fracture energy
 Slip-weakening models of the 211 Tohoku-Oki earthquake and constraints on stress drop and fracture energy Yihe Huang 1, Jean-Paul Ampuero 1, Hiroo Kanamori 1 1 Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences,
Slip-weakening models of the 211 Tohoku-Oki earthquake and constraints on stress drop and fracture energy Yihe Huang 1, Jean-Paul Ampuero 1, Hiroo Kanamori 1 1 Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences,
Frictional rheologies have a wide range of applications in engineering
 A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
To Editor of Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America Kinematic inversion of physically plausible earthquake source models obtained from dynamic rupture simulations --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Article
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America Kinematic inversion of physically plausible earthquake source models obtained from dynamic rupture simulations --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Article
Geometrical effects of a subducted seamount on stopping megathrust ruptures
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1 6, doi:10.1002/grl.50509, 2013 Geometrical effects of a subducted seamount on stopping megathrust ruptures Hongfeng Yang, 1,2 Yajing Liu, 1,3 and Jian Lin 1 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1 6, doi:10.1002/grl.50509, 2013 Geometrical effects of a subducted seamount on stopping megathrust ruptures Hongfeng Yang, 1,2 Yajing Liu, 1,3 and Jian Lin 1 Received
Separating Tectonic, Magmatic, Hydrological, and Landslide Signals in GPS Measurements near Lake Tahoe, Nevada-California
 Separating Tectonic, Magmatic, Hydrological, and Landslide Signals in GPS Measurements near Lake Tahoe, Nevada-California Geoffrey Blewitt, Corné Kreemer, William C. Hammond, & Hans-Peter Plag NV Geodetic
Separating Tectonic, Magmatic, Hydrological, and Landslide Signals in GPS Measurements near Lake Tahoe, Nevada-California Geoffrey Blewitt, Corné Kreemer, William C. Hammond, & Hans-Peter Plag NV Geodetic
Predicted reversal and recovery of surface creep on the Hayward fault following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L19305, doi:10.1029/2008gl035270, 2008 Predicted reversal and recovery of surface creep on the Hayward fault following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake D. A. Schmidt
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L19305, doi:10.1029/2008gl035270, 2008 Predicted reversal and recovery of surface creep on the Hayward fault following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake D. A. Schmidt
Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault
 Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault Introduction Duncan Agnew, Andy Michael We propose the PBO instrument, with GPS and borehole strainmeters, the creeping section of
Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault Introduction Duncan Agnew, Andy Michael We propose the PBO instrument, with GPS and borehole strainmeters, the creeping section of
Deterministic Generation of Broadband Ground Motions! with Simulations of Dynamic Ruptures on Rough Faults! for Physics-Based Seismic Hazard Analysis
 Deterministic Generation of Broadband Ground Motions! with Simulations of Dynamic Ruptures on Rough Faults! for Physics-Based Seismic Hazard Analysis Zheqiang Shi and Steven M. Day! Department of Geological
Deterministic Generation of Broadband Ground Motions! with Simulations of Dynamic Ruptures on Rough Faults! for Physics-Based Seismic Hazard Analysis Zheqiang Shi and Steven M. Day! Department of Geological
Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes
 Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes Brad Aagaard May 21, 2009 Surface Rupture from Kinematic Rupture Models Objective Holistic approach to calculating surface
Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes Brad Aagaard May 21, 2009 Surface Rupture from Kinematic Rupture Models Objective Holistic approach to calculating surface
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Nonuniform prestress from prior earthquakes and the effect on dynamics of branched fault systems
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004443, 2007 Nonuniform prestress from prior earthquakes and the effect on dynamics of branched fault systems Benchun
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004443, 2007 Nonuniform prestress from prior earthquakes and the effect on dynamics of branched fault systems Benchun
Earthquake modelling with complex geometries by curved grid finite-difference method
 FSEF2017, Shenzhen, China Nov 27 Dec. 1, 2017 Earthquake modelling with complex geometries by curved grid finite-difference method Zhenguo Zhang Department of Earth and Space Sciences, Southern University
FSEF2017, Shenzhen, China Nov 27 Dec. 1, 2017 Earthquake modelling with complex geometries by curved grid finite-difference method Zhenguo Zhang Department of Earth and Space Sciences, Southern University
Elizabeth H. Hearn modified from W. Behr
 Reconciling postseismic and interseismic surface deformation around strike-slip faults: Earthquake-cycle models with finite ruptures and viscous shear zones Elizabeth H. Hearn hearn.liz@gmail.com modified
Reconciling postseismic and interseismic surface deformation around strike-slip faults: Earthquake-cycle models with finite ruptures and viscous shear zones Elizabeth H. Hearn hearn.liz@gmail.com modified
Numerical approximation of rate-and-state friction problems
 Preprint No. 1 Numerical approximation of rate-and-state friction problems Elias Pipping Ralf Kornhuber Matthias Rosenau Onno Oncken April, 2015 Project B01 This research has been funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Preprint No. 1 Numerical approximation of rate-and-state friction problems Elias Pipping Ralf Kornhuber Matthias Rosenau Onno Oncken April, 2015 Project B01 This research has been funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
 RESEARCH ARTICLE This article is a companion to Godano et al. [2015], doi:10.1002/2015jb012217. Key Points: Mechanical modeling of a persistent multiplet Coseismic slip on complex multiplets could be used
RESEARCH ARTICLE This article is a companion to Godano et al. [2015], doi:10.1002/2015jb012217. Key Points: Mechanical modeling of a persistent multiplet Coseismic slip on complex multiplets could be used
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (212) 189, 1797 186 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.212.5464.x A new paradigm for simulating pulse-like ruptures: the pulse energy equation Ahmed E. Elbanna 1
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (212) 189, 1797 186 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.212.5464.x A new paradigm for simulating pulse-like ruptures: the pulse energy equation Ahmed E. Elbanna 1
Homogeneous vs. realistic heterogeneous material-properties in subduction zone models: Coseismic and postseismic deformation
 Homogeneous vs. realistic heterogeneous material-properties in subduction zone models: Coseismic and postseismic deformation T. Masterlark 1, C. DeMets 2, H.F. Wang 2, O. S nchez 3, and J. Stock 4 1 US
Homogeneous vs. realistic heterogeneous material-properties in subduction zone models: Coseismic and postseismic deformation T. Masterlark 1, C. DeMets 2, H.F. Wang 2, O. S nchez 3, and J. Stock 4 1 US
New Challenges In Earthquake Dynamics: Observing And Modelling A Multi-Scale System
 RESEARCH CONFERENCES ESF-FWF Conference in Partnership with LFUI New Challenges In Earthquake Dynamics: Observing And Modelling A Multi-Scale System Universitätszentrum Obergurgl (Ötz Valley, near Innsbruck)
RESEARCH CONFERENCES ESF-FWF Conference in Partnership with LFUI New Challenges In Earthquake Dynamics: Observing And Modelling A Multi-Scale System Universitätszentrum Obergurgl (Ötz Valley, near Innsbruck)
Interactions and triggering in a 3-D rate-and-state asperity model
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 118, 5 45, doi:1.1/jgrb.5187, 13 Interactions and triggering in a 3-D rate-and-state asperity model P. Dublanchet, 1 P. Bernard, 1 and P. Favreau 1 Received
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 118, 5 45, doi:1.1/jgrb.5187, 13 Interactions and triggering in a 3-D rate-and-state asperity model P. Dublanchet, 1 P. Bernard, 1 and P. Favreau 1 Received
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update
 The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
The Earthquake of Padang, Sumatra of 30 September 2009 scientific information and update 01-October-2009 Christophe Vigny Directeur de recherches at CNRS Laboratoire de Géologie Geoscience Dept. Of ENS,
Journal of Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for
 Journal of Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for InSAR observations of strain accumulation and fault creep along the Chaman Fault system, Pakistan and Afghanistan H. Fattahi 1, F. Amelung
Journal of Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for InSAR observations of strain accumulation and fault creep along the Chaman Fault system, Pakistan and Afghanistan H. Fattahi 1, F. Amelung
Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
Rotation of the Principal Stress Directions Due to Earthquake Faulting and Its Seismological Implications
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 85, No. 5, pp. 1513-1517, October 1995 Rotation of the Principal Stress Directions Due to Earthquake Faulting and Its Seismological Implications by
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 85, No. 5, pp. 1513-1517, October 1995 Rotation of the Principal Stress Directions Due to Earthquake Faulting and Its Seismological Implications by
Scaling Laws. σ 1. σ = mean stress, which is needed to compute σ 0. η = percent strain energy released in eq. Introduction.
 Scaling Laws Introduction Scaling Laws or Relationships are the result of empirical observation. They describe how one physical parameter varies as a function of another physical parameter within a system.
Scaling Laws Introduction Scaling Laws or Relationships are the result of empirical observation. They describe how one physical parameter varies as a function of another physical parameter within a system.
Improvement in the Fault Boundary Conditions for a Staggered Grid Finite-difference Method
 Pure appl. geophys. 63 (6) 977 99 33 553/6/9977 DOI.7/s-6-8- Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 6 Pure and Applied Geophysics Improvement in the Fault Boundary Conditions for a Staggered Grid Finite-difference
Pure appl. geophys. 63 (6) 977 99 33 553/6/9977 DOI.7/s-6-8- Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 6 Pure and Applied Geophysics Improvement in the Fault Boundary Conditions for a Staggered Grid Finite-difference
Validation of Earthquake Simulations and Their Effects on Tall Buildings Considering Spectral Shape and Duration
 Validation of Earthquake Simulations and Their Effects on Tall Buildings Considering Spectral Shape and Duration SCEC Annual Meeting 2013 Ting Lin Marquette University Greg Deierlein Nenad Bijelic Stanford
Validation of Earthquake Simulations and Their Effects on Tall Buildings Considering Spectral Shape and Duration SCEC Annual Meeting 2013 Ting Lin Marquette University Greg Deierlein Nenad Bijelic Stanford
Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes
 Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes Mathew Pritchard Teh-Ru A. Song Yuri Fialko Luis Rivera Mark Simons UJNR Earthquake Research Panel, Morioka, Japan - Nov 6, 2002 Goals Accurate and high
Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes Mathew Pritchard Teh-Ru A. Song Yuri Fialko Luis Rivera Mark Simons UJNR Earthquake Research Panel, Morioka, Japan - Nov 6, 2002 Goals Accurate and high
Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion
 4 th IASPEI / IAEE International Symposium: Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion August 23 26, 2011 University of California Santa Barbara NEAR-SOURCE GROUND MOTION VARIABILITY FROM M~6.5 DYNAMIC
4 th IASPEI / IAEE International Symposium: Effects of Surface Geology on Seismic Motion August 23 26, 2011 University of California Santa Barbara NEAR-SOURCE GROUND MOTION VARIABILITY FROM M~6.5 DYNAMIC
Southern California Earthquake Center 2018 Science Plan
 Southern California Earthquake Center 2018 Science Plan Proposals Due: November 15, 2017 Table of Contents 1. New This Year...2 2. Overview... 3 2.1. The SCEC5 Research Vision...3 2.2. The SCEC5 Science
Southern California Earthquake Center 2018 Science Plan Proposals Due: November 15, 2017 Table of Contents 1. New This Year...2 2. Overview... 3 2.1. The SCEC5 Research Vision...3 2.2. The SCEC5 Science
The Three-Dimensional Dynamics of a Nonplanar Thrust Fault
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 93, No., pp. 2222 223, October 23 The Three-Dimensional Dynamics of a Nonplanar Thrust Fault by David D. Oglesby and Ralph J. Archuleta Abstract Advances
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 93, No., pp. 2222 223, October 23 The Three-Dimensional Dynamics of a Nonplanar Thrust Fault by David D. Oglesby and Ralph J. Archuleta Abstract Advances
S e i s m i c W a v e s
 Project Report S e i s m i c W a v e s PORTLAND STATE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS 213 SPRING TERM 2005 Instructor: Dr. Andres La Rosa Student Name: Prisciliano Peralta-Ramirez Table Of Contents 1. Cover Sheet 2.
Project Report S e i s m i c W a v e s PORTLAND STATE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS 213 SPRING TERM 2005 Instructor: Dr. Andres La Rosa Student Name: Prisciliano Peralta-Ramirez Table Of Contents 1. Cover Sheet 2.
