Application of SWAT Model to Estimate the Runoff and Sediment Load from the Right Bank Valleys of Mosul Dam Reservoir
|
|
|
- Kerry Randell Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ICSE6 Paris - August 7-, ICSE6- Application of SWAT Model to Estimate the and Sediment Load from the Right Bank Valleys of Mosul Dam Reservoir Mohammad EZZ-ALDEEN MOHAMMAD, Nadhir AL-ANSARI, Sven KNUTSSON Ass. Professor/Mosul University Postal address: Mosul University, College of Engineering, Mosul, Iraq mohammad_ezzaldeen@yahoo.com & Professor/Lulea University of Technology Postal address Dept. Civil, Environment and Natural Resources Eng.,SE LULEÅ Sweden- e- mail :nadhir.alansari@ltu.se,sven.knutsson@ltu.se ABSTRACT Mosul Dam is the biggest hydraulic structure on the River Tigris in Iraq with. billion m storage capacity. The dam is a multipurpose project. It is used to store the water for irrigation, hydropower generation, and flood control. As in other dams in the world, this dam also have sedimentation problem. Sediment accumulation in its reservoir can effect the dam operation (pumping station, hydropower plants, and bottom outlets) and it will definitely shorten the life span of the dam. In this study, the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) under Geographical Information System (GIS) was applied to simulate the yearly surface runoff and sediment load for the main three valleys on the right bank of Mosul Dam Reservoir. The simulation considered for the twenty one years begin from the dam operation in to 8. The resultant values of the average annual sediment load are 5.6*, 4.9*, and.* ton, while the average values of sediment concentration are.7,.65, and.7 kg/m for the considered valleys one, two and three respectively. This implies that significant sediment load enters the reservoir from these valleys. To minimize the sediment load entering the reservoir, a check dams is to be constructed in suitable sites especially for valley one. The check dam can store the runoff water and trap the sediment load, and then the flow can be released to the reservoir. Key words Mosul Dam,, Sediment load, SWAT model, GIS I INTRODUCTION Deposition of sediment in reservoirs can cause serious problems. They reduce the storage capacity of the reservoir and they can cause serious problems concerning the operation and stability of the dam (Yang, ). One of the important factors in reservoirs design and operation is the sedimentation problem. Sediment delivered to the reservoir comes from two main sources. The first source is the main river entering the reservoir and the second source is the side valleys on both sides of the reservoir. Due to the importance of the problem several empirical methods were developed and later modeling techniques was adopted (US Department of Interior, Bureau of Reclamation, 6). Several types of models are used to predict sediment load. Among these Srinivasan et al.,; Fernandez, et al., ; Kim H.,6; Yüksel et al.,8; Baigorria and Romero,7; Engda,9;Gitas et al., 9; Nangia et al., ; Jain et al.,. In 8, Kim, J. et al. developed the SWAT ArcView GIS Patch II for steep slope watersheds. Dos Santos, I. et al. () applied these model and got good results on Apucaraninha River watershed in southern of Brazil. Douglas-Mankin, K, et. al. (), reviewed and introduced a number of selected papers which present and applied the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT). Corresponding author 8
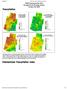
2 ICSE6 Paris - August 7-, Mosul dam is one of the biggest dams in Iraq; the dam is multipurpose project, for flood control, irrigation, power generation, and water supply. In the last years, sediment accumulation near the pump station that supply the irrigation water for Al-Jazera irrigation project appeared, which is one of the important projects in North of Iraq. This problem is becoming more severe with time and it is affecting the pumping rate and irrigation schedule of the project. The source sediment is from the main river and others runoff flow of valleys around the reservoir. The objective of this study is to estimate the runoff volume and sediment loads entering Mosul Dam Reservoir from the main valleys on the right bank side. The accumulated yearly runoff and sediment loads were estimated for the period from -8. This period represent the first years of the life operation of the dam. II STUDY AREA The studied area is located north of Iraq on the right bank of Mosul Dam reservoir (Figure ). The dam is about 6 Km north of Mosul City. There are three main valleys that pour the runoff and the sediment load in the reservoir directly. High percent of studied area is a planted with seasonal crops (wheat and barley), vegetables and pastures, while the soil classification is mostly of silty loam, silty clay loam, and clay, (Mohammad, 6 and Al-Daghastani, 8). Table () shows the topographic properties of the three studied valleys,, and (Figure ). For valley one shown in Figure (a), the maximum elevation is 77. m.a.s.l, and the minimum elevation near the outlets is.5 m.a.s.l. About 96% of the valley area is covered with a winter wheat crop, while the remaining 4% is a pasture land. The soil classification distribution is 6% of silty loam, 7% is silty clay loam, and the remaining % is clay soil. For valley two shown in Figure (b), the maximum elevation is 449. m.a.s.l, and the minimum elevation is 6.5 m.a.s.l. The crop cover area is 67.% with winter wheat and vegetables, and.7% is pasture lands. The soil classification is 64% is silty loam, 5.6% clay, and the remaining.4% is silty clay loam. For valley three shown in Figure (c), the maximum elevation is 54.5 m.a.s.l., and the minimum elevation near the outlet is.9 m.a.s.l. About 46.% of the total area in valley three is covered with wheat crop, 45.% agricultural lands, and remaining 8.6% is pasture lands. The soil classification is 68.4% silty loam,.9% silty clay loam, and.7% is clay soil. Fig. : Location of Mosul dam with the main valleys in the right bank. 8
3 ICSE6 Paris - August 7-, Valley No. Area (km ) Slope % Length (km) Shape factor Average level (m.a.s.l) Table (): The topographic properties of the main valleys in the right bank of Mosul Dam. (a) (b) (c) Figure (a, b and c): Watershed boundary, sub-basins elevation, and flow net (a) for valley-, (b) for valley-, and (c) for valley-. 8
4 ICSE6 Paris - August 7-, III APPLICATION OF THE MODEL Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) is a physically based model was developed to simulate and predict the runoff, sediment load, and agricultural chemical yields for large and complex watersheds having different soil type, land use (Arnold et al.,, ; Neitsch et al. ) as quoted by Asharge (9). The model is a continuous simulation tool which can be applied for long period of time. In SWAT model, the surface runoff is estimated by two methods (Winchell, 7): curve number procedure, and Green-Ampt infiltration method. In curve number method the values of the curve number (CN ) which is the tabulated curve number considered for average conditions. These values corrected for dry condition (CN ) and for moisture conditions (CN ). The Green-Ampt infiltration method (Chow, ), on which the effective hydraulic conductivity is estimated based on saturated hydraulic conductivity and curve number as given by (Nearing et al. ). In SWAT model the estimation of erosion and sediment load yields based on Modified Universal Soil Loss Equation (MUSLE) (Williams as quoted by Chaplot. 5). In order to verify and evaluate the model s results in the studied area, similar watershed was used. This watershed referred to as al-khoser Seasonal River near the study area (Figure ). The selected watershed is similar to the studied area in geology, surface soil and climate (Jassim and Goff, 6). The studied area covers about 695 km. The main part of the area is a silty clay loam, silty clay, silty loam, which covers 7%, 6%, and 4% respectively. The remaining 8.% is composed of dolomite, limestone, marl and marly limestone, which is very tough and highly jointed and fractured, and can not be used for agricultural practices (Al-Naqib, 98, and Mohammad 5). Three single storms were measured in this area (Mohammad 5), including the rainfall depth, runoff and sediment hydrographs. These storms were simulated in SWAT Model to evaluate and calibrate the model to be verification for the studied area. The observed and simulated runoff depth and sediment load for the three considered storm are shown in Table (). Stor m No Date Rain (mm) Observed Volume (MCM) Simulated Volume (MCM) Observed Average (* ton) Simulated Average (* ton) I 9// II 5// III // Table (): Observed and simulated runoff volume and sediment load for the considered storm of model verification. The results showed a good agreement between the observed and simulated values for both runoff volume and sediment load, for the runoff volume, the determination coefficient between observed and simulated values is.94 and the Nash-Sutcliffe, model efficiency value (E) is.8. IV RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The daily rainfall data, maximum and minimum temperature, sunshine, humidity, and wind speed of Mosul Dam and Mosul stations for the period to 8 were considered in this study. The data were used to estimate the annual runoff volume and sediment load that delivered from the main valleys of right bank on Mosul Dam Reservoir. The Soil and Water Assessment Tool SWAT was considered for yearly simulation for both runoff and sediment of the three considered valleys. The results of total annual runoff volume indicate that the average values are.6* 6,.* 6, and.8* 6 m for valleys one, two, and three respectively (Figure a,b,c). The contribution of these valleys for the reservoir inflow rate is limited. The maximum annual runoff volume for the considered valleys was in (6.* 6, 9.7* 6 and.8 * 6 m for the three valleys respectively) which are due the maximum annual rainfall depth in that year (656 mm). The minimum runoff volume were.8* 6, 84
5 ICSE6 Paris - August 7-,.* 6, and.* 6 m for the three valleys respectively for the year 8 which had a minimum average annual rainfall depth of 78 mm. The results of sediment load indicate that the average annual load carried by the runoff flow is 5.6*, 4.9*, and.* ton for the three valleys respectively (Figure 4a, b, and c). From these figures, we can see that the sediment concentration is highly fluctuating with time. This is due to the effect of rainfall intensity variation and other factors effecting sediment load concentration. The maximum sediment concentrations are.,.7, and 4.5 kg/m for the selected valleys respectively for the year. The maximum rainfall intensity in that year was 6mm/day. The number of rainy days in that year was little while the intensity was high (5, and mm/day) and this was reflected on sediment concentration. During the year () also relatively high sediment concentration can be recognized. In this year the rainfalldepth and runoff volume was the maximum, while the sediment load was not at its maximum value. This is due to the fact that the rainy days having effective rainfall depth are distributed along the rainy season with maximum intensity of 55 mm. The maximum annual sediment loads took place in (4.56*, 9.8*, and.5* ton) for the selected valleys respectively (Figure 4a, b, and c). This year had the maximum annual rainfall depth of 656 mm and maximum runoff volume for all the valleys. 7 6 Rainfall Rainfall Rainfall (mm) (MCM) Rainfall (mm) (MCM) (a) (b) 7 6 Rainfall.5 Rainfall (mm) (MCM) (c) Figure (a, b and d): Yearly rainfall depth and runoff volume, (a) for valley-, (b) for valley-, and (c) for valley- for the considered period. SedimentConcentration (Kg/m) Sediment Concentration *^ (ton) Sediment Concentration (Kg/m^) Sediment Concentration *^ (ton)
6 ICSE6 Paris - August 7-, (a) Sedimet Concentration (Kg/m^) Sediment Consentration *^ (ton) (b) 99 (c) Figure 4 (a, b and c ) : Yearly sediment load and sediment concentration, (a) for valley-, (b) for valley- and (c) for valley- for the considered period. V CONCLUSIONS The Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT-9) working under Geographical Information System (GIS) was applied to estimate the yearly runoff and sediment load carrying from the main valleys at the right bank of Mosul Dam Reservoir. The simulation of the runoff and sediment load extended for twenty one years starting. The objective is to estimate the total load that was carried with the runoff flow and delivered directly in to the reservoir. The results indicates that total annual sediment load entering the reservoir from the right bank valleys have a significant amount. This has negative effect on reservoir storage capacity and different hydraulic structures. The total sediment load of the considered period reaches to 747.5* ton for valley one, 4.* ton for valley two, and 45.9* ton for valley three. This makes the total volume of sediment deposited within the reservoir 8.8* 76.6* m. From these values, the average annual rate of erosion in the studied valleys are 78.9, 6.4, and 4.9 ton/km respectively. These values of sediment load must be considered especially for valley one, a check dam in a suitable site may be constructed to store the temporary runoff water for a short period to settle the sediment load and then release the runoff to the main reservoir with minimum load. VI REFERENCES: Al-Daghastani H., S., (8), Land use and Land Cover map of Nineah Governorate Using Remote Sensing Data, Remote Sensing Center, Mosul University, Iraq. Al-Naqib, S. Q. (98).- Geology of Atrush area. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Mosul, Mosul, Iraq.!!!pp Ashagre, B. (9), SWAT to identify watershed management option: (Anjeni Watershed, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia). M.Sc. Thesis, Cornell Univrsity, New York, USA. pp. Baigorria, G. and Romero, C. (7) Assessment of erosion hotspots in a watershed: integrating the WEPP model and GIS in a case study in the Peruvian Andes. Environmental Modelling and Software,,75-8. Chaplot,V. (5), Impact of DEM mesh size and soil map scale on SWAT runoff, sediment, and NO N, loads predictions, Journal of Hydrology ( 7 ). Chow, Ven Te; Maidment, David R.; Mays, Larry W. ()- Applied Hydrology, McGraw Hill, NY. 77, 57 pp. Dos Santos, I., Andriolo, M. Gibertoni, R. and Kobiyama, M. (), Use of the SWAT model to evaluate the impact of different land use scenarios on discharge and sediment transport in the Apucaraninha River watershed, southern Brazil. International association of hydrological science, 7,
7 ICSE6 Paris - August 7-, Doughlas-Mankin, K. R., Srinivasan, R., and Arnold, J. G., ()-Soil and water Assessment tool (SWAT) model: Current development and application, Transaction of ASABE, 5,5, (4-4). Engda, T, (9)- Modeling rainfall, runoff and soil loss relationships in the northeastern highlands of Ethiopia, andit tid watershed. M.Sc. thesis, Cornell University, USA. 84 pp. Fernandez, C., Wu, J., McCool, D., and Stockle, C. () - Estimation water erosion and sediment yield with GIS, RUSLE, and SEDD. J. of Soil and Water Conservation. 58 (), 8-6. Gitas, I, Douros, K,, Minakou, C, Silleos, G. and Karydas, C, (9)- Multi-temporal soil erosion risk assessment in n. chalkidiki using a modified usle raster model. EARSeL e-proceedings 8, (4-5). Jain, M., Mishra, S and Shah, R. ()- Estimation of sediment yield and areas vulnerable to soil erosion and deposition in a Himalayan watershed using GIS. CURRENT SCIENCE, 98,, ( -). Jassim, S.Z. and Goff J.C. (6) - Geology of Iraq, Dolin, Prague and Moravian Museum, Brno, 4p. Kim, H. (6)-Soil erosion modeling using RUSLE and GIS on the imha watershed, south Korea. M.Sc. Thesis, Colorado State University, Colorado, USA,. pp. Kim, J.-G, Park, Y., Yoo, D., Kim, N., Engel, B., Kim, S., Kim, K., Lim, K. (8) - Development of a SWAT ArcView GIS patch for accurate analysis of soil erosion and sediment yield at steep sloping watershed. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers Annual International Meeting,. 9, Mohammad, A., (6)- Using remote sensing data to evaluate land use for some soil properties south west Mosul Dam Reservoir, M.Sc. thesis, University of Mosul, Mosul, Iraq, 5 pp. Mohammad, E. M., (5)- A Conceptual Model for Flow and Sediment Routing for a Watershed Northern Iraq, PhD, thesis, University of Mosul, Mosul, Iraq, 7 pp.. Nangia, V., Wymar, P., and Klang, J. ()- Evaluation of a GIS-based watershed modeling approach for sediment transport. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering,, (-). Nearing, M., Liu, B., Risse, L., and Zhang, X., ()- Curve number and Green-Ampt effective hydraulic conductivity. WRB, American Water Resources Association, (), 5-6. Srinivasan, R, Ramanarayanan, T, Arnold, G, and Bednarz, S. ()- Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment Part-II model application. J. of the American water Resources Association 4(), 9-. US Department of Interior, Bureau of Reclamation (6)- Erosion and Sedimentation Manual, US Department of Interior, Bureau of Reclamation, Technical Service Center, Sedimentation and River Hydraulic Group, Denver, Colorado, 58 pp. Winchell, M., Srinivasan, R., Di Luzio, M. and Arnold J. (7) ARCSWAT interface for SWAT 5, User guide. Blackland Research Center, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, and Grassland, Soil and Water Research Laboratory, USDA Agricultural Research Services, Texas, USA. 4 pp. Yang, C.T. ()- Sediment Transport: Theory and Practice, McGraw Hill, NY, 95pp. Yüksel, A., Akay, A., Gundogan, R., Reis, M., and Cetiner, M. (8)- Application of GeoWEPP for determining sediment yield and runoff in the Orcan Creek Watershed Kahramanmaras, Turkey. Sensors, 8,
Application of SWAT Model to Estimate the Runoff and Sediment Load from the Right Bank Valleys of Mosul Dam Reservoir
 Application of SWAT Model to Estimate the Runoff and Sediment Load from the Right Bank Valleys of Mosul Dam Reservoir Dr Mohammad Ezeel Deen Prof. Nadhir Al-Ansari Prof Sven Knutsson Figure 1.Map of Iraq
Application of SWAT Model to Estimate the Runoff and Sediment Load from the Right Bank Valleys of Mosul Dam Reservoir Dr Mohammad Ezeel Deen Prof. Nadhir Al-Ansari Prof Sven Knutsson Figure 1.Map of Iraq
Application of SWAT model to estimate the annual runoff and sediment of Duhok reservoir watershed
 Scour and Erosion Harris, Whitehouse & Moxon (Eds) 2016 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02979-8 Application of SWAT model to estimate the annual runoff and sediment of Duhok reservoir watershed
Scour and Erosion Harris, Whitehouse & Moxon (Eds) 2016 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02979-8 Application of SWAT model to estimate the annual runoff and sediment of Duhok reservoir watershed
MODULE 8 LECTURE NOTES 2 REMOTE SENSING APPLICATIONS IN RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODELLING
 MODULE 8 LECTURE NOTES 2 REMOTE SENSING APPLICATIONS IN RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODELLING 1. Introduction The most common application of the remote sensing techniques in the rainfall-runoff studies is the estimation
MODULE 8 LECTURE NOTES 2 REMOTE SENSING APPLICATIONS IN RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODELLING 1. Introduction The most common application of the remote sensing techniques in the rainfall-runoff studies is the estimation
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT
 Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
Conservation Planning evaluate land management alternatives to reduce soil erosion to acceptable levels. Resource Inventories estimate current and
 Conservation Planning evaluate land management alternatives to reduce soil erosion to acceptable levels. Resource Inventories estimate current and projected erosion levels and their impact on natural resource
Conservation Planning evaluate land management alternatives to reduce soil erosion to acceptable levels. Resource Inventories estimate current and projected erosion levels and their impact on natural resource
Sediment in Mosul Dam reservoir using the HEC-RAS model
 Lakes and Reservoirs: Research and Management 2016 21: 235 244 Sediment in Mosul Dam reservoir using the HEC-RAS model Mohammad E. Mohammad, 1 Nadhir Al-Ansari, 2 * Issa E. Issa 1,2 and Sven Knutsson 2
Lakes and Reservoirs: Research and Management 2016 21: 235 244 Sediment in Mosul Dam reservoir using the HEC-RAS model Mohammad E. Mohammad, 1 Nadhir Al-Ansari, 2 * Issa E. Issa 1,2 and Sven Knutsson 2
A Near Real-time Flood Prediction using Hourly NEXRAD Rainfall for the State of Texas Bakkiyalakshmi Palanisamy
 A Near Real-time Flood Prediction using Hourly NEXRAD for the State of Texas Bakkiyalakshmi Palanisamy Introduction Radar derived precipitation data is becoming the driving force for hydrological modeling.
A Near Real-time Flood Prediction using Hourly NEXRAD for the State of Texas Bakkiyalakshmi Palanisamy Introduction Radar derived precipitation data is becoming the driving force for hydrological modeling.
Watershed Processes and Modeling
 Watershed Processes and Modeling Pierre Y. Julien Hyeonsik Kim Department of Civil Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado Kuala Lumpur - May Objectives Brief overview of Watershed
Watershed Processes and Modeling Pierre Y. Julien Hyeonsik Kim Department of Civil Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado Kuala Lumpur - May Objectives Brief overview of Watershed
Hydrological Modeling of Semi-Arid Region in Ungauged Watershed using AGWA Model
 Hydrological Modeling of Semi-Arid Region in Ungauged Watershed using AGWA Model 1,* Adnan Ismael, 2 Saleh Suleiman and 3 Abdulnaser Ahmed 1 Lecturer, Technical Institute/ Northern Technical University,
Hydrological Modeling of Semi-Arid Region in Ungauged Watershed using AGWA Model 1,* Adnan Ismael, 2 Saleh Suleiman and 3 Abdulnaser Ahmed 1 Lecturer, Technical Institute/ Northern Technical University,
Use of SWAT to Scale Sediment Delivery from Field to Watershed in an Agricultural Landscape with Depressions
 Use of SWAT to Scale Sediment Delivery from Field to Watershed in an Agricultural Landscape with Depressions James E. Almendinger St. Croix Watershed Research Station, Science Museum of Minnesota Marylee
Use of SWAT to Scale Sediment Delivery from Field to Watershed in an Agricultural Landscape with Depressions James E. Almendinger St. Croix Watershed Research Station, Science Museum of Minnesota Marylee
Modeling Sediment Accumulation at Kenyir Reservoir Using GSTARS3
 ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Vol, 04 Issue, 10 October 2014 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Modeling Sediment Accumulation at Kenyir Reservoir Using GSTARS3 Manal M.A. Albayati
ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Vol, 04 Issue, 10 October 2014 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Modeling Sediment Accumulation at Kenyir Reservoir Using GSTARS3 Manal M.A. Albayati
Floodplain modeling. Ovidius University of Constanta (P4) Romania & Technological Educational Institute of Serres, Greece
 Floodplain modeling Ovidius University of Constanta (P4) Romania & Technological Educational Institute of Serres, Greece Scientific Staff: Dr Carmen Maftei, Professor, Civil Engineering Dept. Dr Konstantinos
Floodplain modeling Ovidius University of Constanta (P4) Romania & Technological Educational Institute of Serres, Greece Scientific Staff: Dr Carmen Maftei, Professor, Civil Engineering Dept. Dr Konstantinos
Assessment of solid load and siltation potential of dams reservoirs in the High Atlas of Marrakech (Moorcco) using SWAT Model
 Assessment of solid load and siltation potential of dams reservoirs in the High Atlas of Marrakech (Moorcco) using SWAT Model Amal Markhi: Phd Student Supervisor: Pr :N.Laftrouhi Contextualization Facing
Assessment of solid load and siltation potential of dams reservoirs in the High Atlas of Marrakech (Moorcco) using SWAT Model Amal Markhi: Phd Student Supervisor: Pr :N.Laftrouhi Contextualization Facing
12 SWAT USER S MANUAL, VERSION 98.1
 12 SWAT USER S MANUAL, VERSION 98.1 CANOPY STORAGE. Canopy storage is the water intercepted by vegetative surfaces (the canopy) where it is held and made available for evaporation. When using the curve
12 SWAT USER S MANUAL, VERSION 98.1 CANOPY STORAGE. Canopy storage is the water intercepted by vegetative surfaces (the canopy) where it is held and made available for evaporation. When using the curve
KINEROS2/AGWA. Fig. 1. Schematic view (Woolhiser et al., 1990).
 KINEROS2/AGWA Introduction Kineros2 (KINematic runoff and EROSion) (K2) model was originated at the USDA-ARS in late 1960s and released until 1990 (Smith et al., 1995; Woolhiser et al., 1990). The spatial
KINEROS2/AGWA Introduction Kineros2 (KINematic runoff and EROSion) (K2) model was originated at the USDA-ARS in late 1960s and released until 1990 (Smith et al., 1995; Woolhiser et al., 1990). The spatial
Which map shows the stream drainage pattern that most likely formed on the surface of this volcano? A) B)
 1. When snow cover on the land melts, the water will most likely become surface runoff if the land surface is A) frozen B) porous C) grass covered D) unconsolidated gravel Base your answers to questions
1. When snow cover on the land melts, the water will most likely become surface runoff if the land surface is A) frozen B) porous C) grass covered D) unconsolidated gravel Base your answers to questions
CASE STUDY NATHPA JHAKRI, INDIA
 SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY NATHPA JHAKRI, INDIA Key project features Name: Nathpa Jhakri Country: India Category: reduce sediment production (watershed management); upstream sediment trapping; bypass
SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY NATHPA JHAKRI, INDIA Key project features Name: Nathpa Jhakri Country: India Category: reduce sediment production (watershed management); upstream sediment trapping; bypass
CASE STUDY NATHPA JHAKRI, INDIA
 SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY NATHPA JHAKRI, INDIA Key project features Name: Nathpa Jhakri Country: India Category: reforestation/revegetation; upstream sediment trapping; bypass channel/tunnel; reservoir
SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY NATHPA JHAKRI, INDIA Key project features Name: Nathpa Jhakri Country: India Category: reforestation/revegetation; upstream sediment trapping; bypass channel/tunnel; reservoir
Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. Case study of reservoir sedimentation
 Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. HR Wallingford, Wallingford, UK Published in the proceedings of River Flow 2012, 5-7 September 2012 Abstract Reservoir sedimentation is a main concern in the Tarbela reservoir
Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. HR Wallingford, Wallingford, UK Published in the proceedings of River Flow 2012, 5-7 September 2012 Abstract Reservoir sedimentation is a main concern in the Tarbela reservoir
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "SUSTAINABLE TECHNOLOGIES IN CIVIL
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "SUSTAINABLE TECHNOLOGIES IN CIVIL
Subject Name: SOIL AND WATER CONSERVATION ENGINEERING 3(2+1) COURSE OUTLINE
 Subject Name: SOIL AND WATER CONSERVATION ENGINEERING 3(2+1) COURSE OUTLINE (Name of Course Developer: Prof. Ashok Mishra, AgFE Department, IIT Kharagpur, Kharagpur 721 302) Module 1: Introduction and
Subject Name: SOIL AND WATER CONSERVATION ENGINEERING 3(2+1) COURSE OUTLINE (Name of Course Developer: Prof. Ashok Mishra, AgFE Department, IIT Kharagpur, Kharagpur 721 302) Module 1: Introduction and
CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS
 80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
Sediment yield estimation from a hydrographic survey: A case study for the Kremasta reservoir, Western Greece
 Sediment yield estimation from a hydrographic survey: A case study for the Kremasta reservoir, Western Greece 5 th International Conference Water Resources Management in the Era of Transition,, Athens,
Sediment yield estimation from a hydrographic survey: A case study for the Kremasta reservoir, Western Greece 5 th International Conference Water Resources Management in the Era of Transition,, Athens,
How to integrate wetland processes in river basin modeling? A West African case study
 How to integrate wetland processes in river basin modeling? A West African case study stefan.liersch@pik-potsdam.de fred.hattermann@pik-potsdam.de June 2011 Outline Why is an inundation module required?
How to integrate wetland processes in river basin modeling? A West African case study stefan.liersch@pik-potsdam.de fred.hattermann@pik-potsdam.de June 2011 Outline Why is an inundation module required?
A distributed runoff model for flood prediction in ungauged basins
 Predictions in Ungauged Basins: PUB Kick-off (Proceedings of the PUB Kick-off meeting held in Brasilia, 2 22 November 22). IAHS Publ. 39, 27. 267 A distributed runoff model for flood prediction in ungauged
Predictions in Ungauged Basins: PUB Kick-off (Proceedings of the PUB Kick-off meeting held in Brasilia, 2 22 November 22). IAHS Publ. 39, 27. 267 A distributed runoff model for flood prediction in ungauged
Vulnerability assessment of Sta.Rosa-Silang subwatershed using SWAT
 Vulnerability assessment of Sta.Rosa-Silang subwatershed using SWAT Damasa B. Magcale-Macandog, Charles Gunay and Milben A. Bragais Institute of Biological Sciences, University of the Philippines Los Baños,
Vulnerability assessment of Sta.Rosa-Silang subwatershed using SWAT Damasa B. Magcale-Macandog, Charles Gunay and Milben A. Bragais Institute of Biological Sciences, University of the Philippines Los Baños,
ISSN Vol.03,Issue.10 May-2014, Pages:
 www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.10 May-2014, Pages:2187-2191 YIN YIN HTWE 1, AYE AYE THANT 2 1 Dept of Civil Engineering, Mandalay Technological University, Mandalay, Myanmar,
www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.10 May-2014, Pages:2187-2191 YIN YIN HTWE 1, AYE AYE THANT 2 1 Dept of Civil Engineering, Mandalay Technological University, Mandalay, Myanmar,
Dr. S.SURIYA. Assistant professor. Department of Civil Engineering. B. S. Abdur Rahman University. Chennai
 Hydrograph simulation for a rural watershed using SCS curve number and Geographic Information System Dr. S.SURIYA Assistant professor Department of Civil Engineering B. S. Abdur Rahman University Chennai
Hydrograph simulation for a rural watershed using SCS curve number and Geographic Information System Dr. S.SURIYA Assistant professor Department of Civil Engineering B. S. Abdur Rahman University Chennai
The Geometric and Hydraulic Simulation of Detention Dams by Integrating HEC-HMS and GIS (Case Study: Neka River Drainage Basin)
 Current World Environment Vol. 10(Special Issue 1), 842-851 (2015) The Geometric and Hydraulic Simulation of Detention Dams by Integrating HEC-HMS and GIS (Case Study: Neka River Drainage Basin) Arman
Current World Environment Vol. 10(Special Issue 1), 842-851 (2015) The Geometric and Hydraulic Simulation of Detention Dams by Integrating HEC-HMS and GIS (Case Study: Neka River Drainage Basin) Arman
Simulation of Runoff and Sediment Load for Reservior Sedimentation of River Ole Dam using Swat and Wepp Models
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research Agriculture and Veterinary Volume 13 Issue 13 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research Agriculture and Veterinary Volume 13 Issue 13 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Erosion modelling in the upper Blue Nile basin: The case of Mizewa watershed in Ethiopia
 Erosion modelling in the upper Blue Nile basin: The case of Mizewa watershed in Ethiopia Citation: Assegahegn, M.A. and Zemadim, B. Erosion modelling in the upper Blue Nile basin: The case of Mizewa watershed
Erosion modelling in the upper Blue Nile basin: The case of Mizewa watershed in Ethiopia Citation: Assegahegn, M.A. and Zemadim, B. Erosion modelling in the upper Blue Nile basin: The case of Mizewa watershed
Evaluation of the SWAT Model Setup Process Through A Case Study in Roxo Catchment, Portugal
 Evaluation of the SWAT Model Setup Process Through A Case Study in Roxo Catchment, Portugal Mustafa Gökmen Master Degree in on Geo-information and Earth Observation for Integrated Catchment and Water Resources
Evaluation of the SWAT Model Setup Process Through A Case Study in Roxo Catchment, Portugal Mustafa Gökmen Master Degree in on Geo-information and Earth Observation for Integrated Catchment and Water Resources
SEDIMENT INFLOW ESTIMATION AND MAPPING ITS SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION AT SUB-BASIN SCALE: THE CASE OF TENDAHO DAM, AFAR REGIONAL STATE, ETHIOPIA
 Ethiopian Journal of Environmental Studies & Management 10(3): 315 339, 2017. ISSN:1998-0507 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4314/ejesm.v10i3.4 Submitted: December 10, 2016 Accepted: April 08, 2017 SEDIMENT
Ethiopian Journal of Environmental Studies & Management 10(3): 315 339, 2017. ISSN:1998-0507 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4314/ejesm.v10i3.4 Submitted: December 10, 2016 Accepted: April 08, 2017 SEDIMENT
ESTIMATION OF DISCHARGE FOR UNGAUGED CATCHMENTS USING RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL IN DIDESSA SUB-BASIN: THE CASE OF BLUE NILE RIVER BASIN, ETHIOPIA.
 ESTIMATION OF DISCHARGE FOR UNGAUGED CATCHMENTS USING RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL IN DIDESSA SUB-BASIN: THE CASE OF BLUE NILE RIVER BASIN, ETHIOPIA. CHEKOLE TAMALEW Department of water resources and irrigation
ESTIMATION OF DISCHARGE FOR UNGAUGED CATCHMENTS USING RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL IN DIDESSA SUB-BASIN: THE CASE OF BLUE NILE RIVER BASIN, ETHIOPIA. CHEKOLE TAMALEW Department of water resources and irrigation
EFFICIENCY OF THE INTEGRATED RESERVOIR OPERATION FOR FLOOD CONTROL IN THE UPPER TONE RIVER OF JAPAN CONSIDERING SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF RAINFALL
 EFFICIENCY OF THE INTEGRATED RESERVOIR OPERATION FOR FLOOD CONTROL IN THE UPPER TONE RIVER OF JAPAN CONSIDERING SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF RAINFALL Dawen YANG, Eik Chay LOW and Toshio KOIKE Department of
EFFICIENCY OF THE INTEGRATED RESERVOIR OPERATION FOR FLOOD CONTROL IN THE UPPER TONE RIVER OF JAPAN CONSIDERING SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF RAINFALL Dawen YANG, Eik Chay LOW and Toshio KOIKE Department of
Assessment of Lake Forest Lake Sediment Trapping Efficiency and Capacity. Marlon R. Cook Groundwater Assessment Program Geological Survey of Alabama
 Assessment of Lake Forest Lake Sediment Trapping Efficiency and Capacity Marlon R. Cook Groundwater Assessment Program Geological Survey of Alabama Impacts of the Lake at Lake Forest on the connectivity
Assessment of Lake Forest Lake Sediment Trapping Efficiency and Capacity Marlon R. Cook Groundwater Assessment Program Geological Survey of Alabama Impacts of the Lake at Lake Forest on the connectivity
Extension of the WASA model: Water and sediment routing in the river network
 Extension of the WASA model: Water and sediment routing in the river network Working Report SESAM-Project, University of Potsdam, July 2005 Eva Nora Müller enmue@uni-potsdam.de 1 Introduction to model
Extension of the WASA model: Water and sediment routing in the river network Working Report SESAM-Project, University of Potsdam, July 2005 Eva Nora Müller enmue@uni-potsdam.de 1 Introduction to model
Application of SWAT Model for Mountainous Catchment
 LARS 2007 Catchment and Lake Research Application of SWAT Model for Mountainous Catchment Birhanu, B.Z, Ndomba, P.M and Mtalo, F.W. University of Dar es Salaam, Water Resources Engineering Abstract A GIS
LARS 2007 Catchment and Lake Research Application of SWAT Model for Mountainous Catchment Birhanu, B.Z, Ndomba, P.M and Mtalo, F.W. University of Dar es Salaam, Water Resources Engineering Abstract A GIS
Watershed Application of WEPP and Geospatial Interfaces. Dennis C. Flanagan
 Watershed Application of WEPP and Geospatial Interfaces Dennis C. Flanagan Research Agricultural Engineer USDA-Agricultural Research Service Adjunct Professor Purdue Univ., Dept. of Agric. & Biol. Eng.
Watershed Application of WEPP and Geospatial Interfaces Dennis C. Flanagan Research Agricultural Engineer USDA-Agricultural Research Service Adjunct Professor Purdue Univ., Dept. of Agric. & Biol. Eng.
Roger Andy Gaines, Research Civil Engineer, PhD, P.E.
 Roger Andy Gaines, Research Civil Engineer, PhD, P.E. Research Civil Engineer/Regional Technical Specialist Memphis District August 24, 2010 Objectives Where we have been (recap of situation and what s
Roger Andy Gaines, Research Civil Engineer, PhD, P.E. Research Civil Engineer/Regional Technical Specialist Memphis District August 24, 2010 Objectives Where we have been (recap of situation and what s
Calibration of Manning s Friction Factor for Rivers in Iraq Using Hydraulic Model (Al-Kufa River as Case study)
 Calibration of Manning s Friction Factor for Rivers in Iraq Using Hydraulic Model (Al-Kufa River as Case study) Luay Kadhim Hameed, Civil Engineering Dept./ University of Kufa Hayder Sami Mohammed, Structure
Calibration of Manning s Friction Factor for Rivers in Iraq Using Hydraulic Model (Al-Kufa River as Case study) Luay Kadhim Hameed, Civil Engineering Dept./ University of Kufa Hayder Sami Mohammed, Structure
Analyzing spatial and temporal variation of water balance components in La Vi catchment, Binh Dinh province, Vietnam
 Analyzing spatial and temporal variation of water balance components in La Vi catchment, Binh Dinh province, Vietnam Nguyen Duy Liem, Vo Ngoc Quynh Tram, Nguyen Le Tan Dat, Nguyen Kim Loi Nong Lam University-
Analyzing spatial and temporal variation of water balance components in La Vi catchment, Binh Dinh province, Vietnam Nguyen Duy Liem, Vo Ngoc Quynh Tram, Nguyen Le Tan Dat, Nguyen Kim Loi Nong Lam University-
Influence of the timing of flood events on sediment yield in the north-western Algeria
 Calabria, 5-7 Septembre 2 4th International Workshop on Hydrological Extremes Session A : Modelling and forecast of hydrological extreme event Influence of the timing of flood events on sediment yield
Calabria, 5-7 Septembre 2 4th International Workshop on Hydrological Extremes Session A : Modelling and forecast of hydrological extreme event Influence of the timing of flood events on sediment yield
Soil Erosion Calculation using Remote Sensing and GIS in Río Grande de Arecibo Watershed, Puerto Rico
 Soil Erosion Calculation using Remote Sensing and GIS in Río Grande de Arecibo Watershed, Puerto Rico Alejandra M. Rojas González Department of Civil Engineering University of Puerto Rico at Mayaguez.
Soil Erosion Calculation using Remote Sensing and GIS in Río Grande de Arecibo Watershed, Puerto Rico Alejandra M. Rojas González Department of Civil Engineering University of Puerto Rico at Mayaguez.
SPECIFIC DEGRADATION AND RESERVOIR SEDIMENTATION. By Renee Vandermause & Chun-Yao Yang
 SPECIFIC DEGRADATION AND RESERVOIR SEDIMENTATION By Renee Vandermause & Chun-Yao Yang Outline Sediment Degradation - Erosion vs Sediment Yield - Sediment Yield - Methods for estimation - Defining Sediment
SPECIFIC DEGRADATION AND RESERVOIR SEDIMENTATION By Renee Vandermause & Chun-Yao Yang Outline Sediment Degradation - Erosion vs Sediment Yield - Sediment Yield - Methods for estimation - Defining Sediment
Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Soil Erosion Vulnerability Across the Conterminous U.S.
 Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Soil Erosion Vulnerability Across the Conterminous U.S. Catalina Segura 1, Ge Sun 2, Steve McNulty 2, and Yang Zhang 1 1 2 1 Soil Erosion Natural process by which
Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Soil Erosion Vulnerability Across the Conterminous U.S. Catalina Segura 1, Ge Sun 2, Steve McNulty 2, and Yang Zhang 1 1 2 1 Soil Erosion Natural process by which
Sediment- yield estimation, by M-PSIAC method in a GIS environment, case study:jonaghn river sub basin(karun basin)
 Sediment- yield estimation, by M-PSIAC method in a GIS environment, case study:jonaghn river sub basin(karun basin) Yavari-shahla *,Khdabakhsh-Saeed,Mohseni-Hasan, Rezai- Khalil Corresponding author: a
Sediment- yield estimation, by M-PSIAC method in a GIS environment, case study:jonaghn river sub basin(karun basin) Yavari-shahla *,Khdabakhsh-Saeed,Mohseni-Hasan, Rezai- Khalil Corresponding author: a
Challenges in Calibrating a Large Watershed Model with Varying Hydrogeologic Conditions
 Challenges in Calibrating a Large Watershed Model with Varying Hydrogeologic Conditions Presented by Johnathan R. Bumgarner, P.G., Celine A.L. Louwers, & Monica P. Suarez, P.E. In cooperation with the
Challenges in Calibrating a Large Watershed Model with Varying Hydrogeologic Conditions Presented by Johnathan R. Bumgarner, P.G., Celine A.L. Louwers, & Monica P. Suarez, P.E. In cooperation with the
Determination of Urban Runoff Using ILLUDAS and GIS
 Texas A&M University Department of Civil Engineering Instructor: Dr. Francisco Olivera CVEN689 Applications of GIS to Civil Engineering Determination of Urban Runoff Using ILLUDAS and GIS Tae Jin Kim 03.
Texas A&M University Department of Civil Engineering Instructor: Dr. Francisco Olivera CVEN689 Applications of GIS to Civil Engineering Determination of Urban Runoff Using ILLUDAS and GIS Tae Jin Kim 03.
AN ASSESSMENT OF THE IMPACT OF RETENTION PONDS
 AN ASSESSMENT OF THE IMPACT OF RETENTION PONDS FOR SEDIMENT TRAPPING IN THE ADA CREEK AND LONGWOOD COVE USING REMOTELY SENSED DATA AND GIS ANALYSIS Sudhanshu Sekhar Panda Associate Professor, GIS/Env.
AN ASSESSMENT OF THE IMPACT OF RETENTION PONDS FOR SEDIMENT TRAPPING IN THE ADA CREEK AND LONGWOOD COVE USING REMOTELY SENSED DATA AND GIS ANALYSIS Sudhanshu Sekhar Panda Associate Professor, GIS/Env.
The relationship between drainage density and soil erosion rate: a study of five watersheds in Ardebil Province, Iran
 River Basin Management VIII 129 The relationship between drainage density and soil erosion rate: a study of five watersheds in Ardebil Province, Iran A. Moeini 1, N. K. Zarandi 1, E. Pazira 1 & Y. Badiollahi
River Basin Management VIII 129 The relationship between drainage density and soil erosion rate: a study of five watersheds in Ardebil Province, Iran A. Moeini 1, N. K. Zarandi 1, E. Pazira 1 & Y. Badiollahi
DETERMINATION OF DETENTION POND SEDIMENT LOADS USING MONTE CARLO SIMULATION, MALAYSIA
 JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 19 2011 DETERMINATION OF DETENTION
JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 19 2011 DETERMINATION OF DETENTION
Sedimentation in the Nile River
 Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Sedimentation in the Nile River Prof. Dr. Abdalla Abdelsalam Ahmed 10-16 Oct. 2007, IRTCES, Beijing, China CWR,Sudan 1 Water is essential for mankind
Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Sedimentation in the Nile River Prof. Dr. Abdalla Abdelsalam Ahmed 10-16 Oct. 2007, IRTCES, Beijing, China CWR,Sudan 1 Water is essential for mankind
Modeling Vegetative Buffer Performance Considering Topographic Data Accuracy
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln USDA Forest Service / UNL Faculty Publications U.S. Department of Agriculture: Forest Service -- National Agroforestry Center
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln USDA Forest Service / UNL Faculty Publications U.S. Department of Agriculture: Forest Service -- National Agroforestry Center
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF FLUVIAL SEDIMENT DELIVERY, NEKA RIVER, IRAN. S.E. Kermani H. Golmaee M.Z. Ahmadi
 JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 16 2008 MATHEMATICAL MODELING
JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 16 2008 MATHEMATICAL MODELING
The Importance of Snowmelt Runoff Modeling for Sustainable Development and Disaster Prevention
 The Importance of Snowmelt Runoff Modeling for Sustainable Development and Disaster Prevention Muzafar Malikov Space Research Centre Academy of Sciences Republic of Uzbekistan Water H 2 O Gas - Water Vapor
The Importance of Snowmelt Runoff Modeling for Sustainable Development and Disaster Prevention Muzafar Malikov Space Research Centre Academy of Sciences Republic of Uzbekistan Water H 2 O Gas - Water Vapor
Modeling soil erosion by water on agricultural land in Cenei, Timiş County, Romania
 Modeling soil erosion by water on agricultural land in Cenei, Timiş County, Romania GEORGE NARCIS PELEA, IOANA ALINA COSTESCU, ERIKA BEILICCI, TEODOR EUGEN MAN, ROBERT BEILICCI Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Modeling soil erosion by water on agricultural land in Cenei, Timiş County, Romania GEORGE NARCIS PELEA, IOANA ALINA COSTESCU, ERIKA BEILICCI, TEODOR EUGEN MAN, ROBERT BEILICCI Faculty of Civil Engineering,
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System October 30, 2018
 10/30/2018 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System October 30, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS,
10/30/2018 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System October 30, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS,
Review Using the Geographical Information System and Remote Sensing Techniques for Soil Erosion Assessment
 Polish J. of Environ. Stud. Vol. 19, No. 5 (2010), 881-886 Review Using the Geographical Information System and Remote Sensing Techniques for Soil Erosion Assessment Nuket Benzer* Landscape Architecture
Polish J. of Environ. Stud. Vol. 19, No. 5 (2010), 881-886 Review Using the Geographical Information System and Remote Sensing Techniques for Soil Erosion Assessment Nuket Benzer* Landscape Architecture
STREAM FLOW MODELING IN THE NACUNDAY RIVER BASIN (PARAGUAY, SOUTH AMERICA) USING SWAT MODEL. Sandra Mongelos and Manoj K. Jain
 STREAM FLOW MODELING IN THE NACUNDAY RIVER BASIN (PARAGUAY, SOUTH AMERICA) USING SWAT MODEL Sandra Mongelos and Manoj K. Jain DEPARTMENT OF HYDROLOGY INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE ROORKEE 247
STREAM FLOW MODELING IN THE NACUNDAY RIVER BASIN (PARAGUAY, SOUTH AMERICA) USING SWAT MODEL Sandra Mongelos and Manoj K. Jain DEPARTMENT OF HYDROLOGY INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE ROORKEE 247
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
Watershed Conservation Management Planning Using the Integrated Field & Channel Technology of AnnAGNPS & CONCEPTS
 Watershed Conservation Management Planning Using the Integrated Field & Channel Technology of AnnAGNPS & CONCEPTS Eddy Langendoen Ron Bingner USDA-ARS National Sedimentation Laboratory, Oxford, Mississippi
Watershed Conservation Management Planning Using the Integrated Field & Channel Technology of AnnAGNPS & CONCEPTS Eddy Langendoen Ron Bingner USDA-ARS National Sedimentation Laboratory, Oxford, Mississippi
WATER ON AND UNDER GROUND. Objectives. The Hydrologic Cycle
 WATER ON AND UNDER GROUND Objectives Define and describe the hydrologic cycle. Identify the basic characteristics of streams. Define drainage basin. Describe how floods occur and what factors may make
WATER ON AND UNDER GROUND Objectives Define and describe the hydrologic cycle. Identify the basic characteristics of streams. Define drainage basin. Describe how floods occur and what factors may make
STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Surface Water Movement
 Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
MODELING OF WATERSHED EROSION AND SEDIMENT RETENTION IN MINING ACTIVITY
 I2SM Montreal 2016 MODELING OF WATERSHED EROSION AND SEDIMENT RETENTION IN MINING ACTIVITY Esmeralda Atarama Ticerán and Mishel Meléndez Bernardo Anddes Asociados SAC, Peru ABSTRACT In Peru, mining has
I2SM Montreal 2016 MODELING OF WATERSHED EROSION AND SEDIMENT RETENTION IN MINING ACTIVITY Esmeralda Atarama Ticerán and Mishel Meléndez Bernardo Anddes Asociados SAC, Peru ABSTRACT In Peru, mining has
Hydrology and Hydraulics Design Report. Background Summary
 To: National Park Services Montezuma Castle National Monument Richard Goepfrich, Facility Manager From: Multicultural Technical Engineers Date: Tuesday - February 13, 2018 Subject: 30% Hydrology and Hydraulics
To: National Park Services Montezuma Castle National Monument Richard Goepfrich, Facility Manager From: Multicultural Technical Engineers Date: Tuesday - February 13, 2018 Subject: 30% Hydrology and Hydraulics
Development of the Hydrologic Model
 Kick-off meeting on enhancing hydrological data management and exchange procedures Water and Climate Adaptation Plan (WATCAP) for Sava River Basin Development of the Hydrologic Model David Heywood Team
Kick-off meeting on enhancing hydrological data management and exchange procedures Water and Climate Adaptation Plan (WATCAP) for Sava River Basin Development of the Hydrologic Model David Heywood Team
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY
 ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
ISSUES AND APPROACHES TO COUPLING GIS TO AN IRRIGATION DISTRIBUTION NETWORK AND SEEPAGE LOSS MODELS ABSTRACT
 ISSUES AND APPROACHES TO COUPLING GIS TO AN IRRIGATION DISTRIBUTION NETWORK AND SEEPAGE LOSS MODELS Yanbo Huang 1, Milton Henry 2, David Flahive 3, Guy Fipps 4 ABSTRACT Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
ISSUES AND APPROACHES TO COUPLING GIS TO AN IRRIGATION DISTRIBUTION NETWORK AND SEEPAGE LOSS MODELS Yanbo Huang 1, Milton Henry 2, David Flahive 3, Guy Fipps 4 ABSTRACT Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Solution: The ratio of normal rainfall at station A to normal rainfall at station i or NR A /NR i has been calculated and is given in table below.
 3.6 ESTIMATION OF MISSING DATA Data for the period of missing rainfall data could be filled using estimation technique. The length of period up to which the data could be filled is dependent on individual
3.6 ESTIMATION OF MISSING DATA Data for the period of missing rainfall data could be filled using estimation technique. The length of period up to which the data could be filled is dependent on individual
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin?
 How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Assessing Vulnerability to Soil Erosion of a Watershed of Tons River Basin in Madhya Pradesh using Remote Sensing and GIS
 International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments
 GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
Modeling Surface Runoff Path and Soil Erosion in Catchment Area of Hanp River of District Kabeerdham, CG, INDIA, Using GIS
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 5, May 2016 645 Modeling Surface Runoff Path and Soil Erosion in Catchment Area of Hanp River of District Kabeerdham, CG,
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 5, May 2016 645 Modeling Surface Runoff Path and Soil Erosion in Catchment Area of Hanp River of District Kabeerdham, CG,
EROSION AND SEDIMENT TRANSPORT IN A PROPOSED REGIONAL SANITARY LANDFILL. Jorge Rivera Santos 1 * Godofredo Canino 2
 EROSION AND SEDIMENT TRANSPORT IN A PROPOSED REGIONAL SANITARY LANDFILL Jorge Rivera Santos 1 * Godofredo Canino 2 1 Puerto Rico Water Resources Research Institute School of Engineering P.O.Box 5000 Mayagüez,
EROSION AND SEDIMENT TRANSPORT IN A PROPOSED REGIONAL SANITARY LANDFILL Jorge Rivera Santos 1 * Godofredo Canino 2 1 Puerto Rico Water Resources Research Institute School of Engineering P.O.Box 5000 Mayagüez,
The Effect of Land Use Change to Land Erosion and Sediment Transported on The Cacthment Area of Mrica Reservoir
 The Effect of Land Use Change to Land Erosion and Sediment Transported on The Cacthment Area of Mrica Reservoir Lukman Hidayat 1, Putu Sudira 2, Sahid Susanto 2, and Rachmad Jayadi 3 1 Agricultural Technology
The Effect of Land Use Change to Land Erosion and Sediment Transported on The Cacthment Area of Mrica Reservoir Lukman Hidayat 1, Putu Sudira 2, Sahid Susanto 2, and Rachmad Jayadi 3 1 Agricultural Technology
Flood Forecasting Tools for Ungauged Streams in Alberta: Status and Lessons from the Flood of 2013
 Flood Forecasting Tools for Ungauged Streams in Alberta: Status and Lessons from the Flood of 2013 John Pomeroy, Xing Fang, Kevin Shook, Tom Brown Centre for Hydrology, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon
Flood Forecasting Tools for Ungauged Streams in Alberta: Status and Lessons from the Flood of 2013 John Pomeroy, Xing Fang, Kevin Shook, Tom Brown Centre for Hydrology, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon
Coupling a basin erosion and river sediment transport model into a large scale hydrological model
 Hydrology and Geodynamics of the basins of South America 4 th scientific meeting of ORE HYBAM www.ore-hybam.org Lima, 6-9 September 2011 Coupling a basin erosion and river sediment transport model into
Hydrology and Geodynamics of the basins of South America 4 th scientific meeting of ORE HYBAM www.ore-hybam.org Lima, 6-9 September 2011 Coupling a basin erosion and river sediment transport model into
REPRESENTATIVE HILLSLOPE METHODS FOR APPLYING
 REPRESENTATIVE HILLSLOPE METHODS FOR APPLYING THE WEPP MODEL WITH DEMS AND GIS T. A. Cochrane, D. C. Flanagan ABSTRACT. In watershed modeling with WEPP, the process of manually identifying hillslopes and
REPRESENTATIVE HILLSLOPE METHODS FOR APPLYING THE WEPP MODEL WITH DEMS AND GIS T. A. Cochrane, D. C. Flanagan ABSTRACT. In watershed modeling with WEPP, the process of manually identifying hillslopes and
Technical Memorandum No
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
HYDRAULIC MODELING OF SOIL ERORION
 18-21 August 28, Daejeon, Korea HYDRAULIC MODELING OF SOIL ERORION Liu Qing-quan Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 18, China. Email: qqliu@imech.ac.cn ABSTRACT: The prediction
18-21 August 28, Daejeon, Korea HYDRAULIC MODELING OF SOIL ERORION Liu Qing-quan Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 18, China. Email: qqliu@imech.ac.cn ABSTRACT: The prediction
13 Watershed Delineation & Modeling
 Module 4 (L12 - L18): Watershed Modeling Standard modeling approaches and classifications, system concept for watershed modeling, overall description of different hydrologic processes, modeling of rainfall,
Module 4 (L12 - L18): Watershed Modeling Standard modeling approaches and classifications, system concept for watershed modeling, overall description of different hydrologic processes, modeling of rainfall,
Near Real-Time Runoff Estimation Using Spatially Distributed Radar Rainfall Data. Jennifer Hadley 22 April 2003
 Near Real-Time Runoff Estimation Using Spatially Distributed Radar Rainfall Data Jennifer Hadley 22 April 2003 Introduction Water availability has become a major issue in Texas in the last several years,
Near Real-Time Runoff Estimation Using Spatially Distributed Radar Rainfall Data Jennifer Hadley 22 April 2003 Introduction Water availability has become a major issue in Texas in the last several years,
Nutrient Delivery from the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico and Effects of Cropland Conservation
 Nutrient Delivery from the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico and Effects of Cropland Conservation Mike White, Jeff Arnold, Lee Norfleet, Santhi Chinnasamy, and Mauro DiLuzio USDA-ARS Grassland, Soil
Nutrient Delivery from the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico and Effects of Cropland Conservation Mike White, Jeff Arnold, Lee Norfleet, Santhi Chinnasamy, and Mauro DiLuzio USDA-ARS Grassland, Soil
Effect of GIS data quality on small watershed stream flow and sediment simulations
 HYDROLOGICAL PROCESSES Hydrol. Process. 19, 629 650 (2005) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/hyp.5612 Effect of GIS data quality on small watershed stream
HYDROLOGICAL PROCESSES Hydrol. Process. 19, 629 650 (2005) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/hyp.5612 Effect of GIS data quality on small watershed stream
Climatic Change Implications for Hydrologic Systems in the Sierra Nevada
 Climatic Change Implications for Hydrologic Systems in the Sierra Nevada Part Two: The HSPF Model: Basis For Watershed Yield Calculator Part two presents an an overview of why the hydrologic yield calculator
Climatic Change Implications for Hydrologic Systems in the Sierra Nevada Part Two: The HSPF Model: Basis For Watershed Yield Calculator Part two presents an an overview of why the hydrologic yield calculator
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-HMS
 INTRODUCTION TO HEC-HMS Hydrologic Engineering Center- Hydrologic Modeling System US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center HEC-HMS Uses Schematics Enter properties: watershed, rivers (reaches),
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-HMS Hydrologic Engineering Center- Hydrologic Modeling System US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center HEC-HMS Uses Schematics Enter properties: watershed, rivers (reaches),
Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI
 Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI Deciding Alternative Land Use Options in a Watershed Using GIS Source: Anita Prakash
Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI Deciding Alternative Land Use Options in a Watershed Using GIS Source: Anita Prakash
DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION OF A HYDROCLIMATOLOGICAL STREAM TEMPERATURE MODEL WITHIN SWAT
 DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION OF A HYDROCLIMATOLOGICAL STREAM TEMPERATURE MODEL WITHIN SWAT Darren L. Ficklin 1, Yuzhou Luo 2, Iris T. Stewart 1, Edwin P. Maurer 3 1 Environmental Studies Institute, Santa
DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION OF A HYDROCLIMATOLOGICAL STREAM TEMPERATURE MODEL WITHIN SWAT Darren L. Ficklin 1, Yuzhou Luo 2, Iris T. Stewart 1, Edwin P. Maurer 3 1 Environmental Studies Institute, Santa
5. Off-Site effect of soil erosion: A case study of the Mae Thang reservoir in northern Thailand.
 5. Off-Site effect of soil erosion: A case study of the Mae Thang reservoir in northern Thailand. Jean Louis Janeau 1, Amado R. Maglinao 1, Céline Lorent 2, Jean Pierre Bricquet 1 and Arthorn Boonsaner
5. Off-Site effect of soil erosion: A case study of the Mae Thang reservoir in northern Thailand. Jean Louis Janeau 1, Amado R. Maglinao 1, Céline Lorent 2, Jean Pierre Bricquet 1 and Arthorn Boonsaner
Estimating of Manning s Roughness Coefficient for Hilla River through Calibration Using HEC-RAS Model
 Estimating of Manning s Roughness Coefficient for Hilla River through Calibration Using HEC-RAS Model Luay Kadhim Hameed 1) and Salah Tawfeek Ali 2) 1) University of Kufa, Kufa, Iraq 2) University of Babylon,
Estimating of Manning s Roughness Coefficient for Hilla River through Calibration Using HEC-RAS Model Luay Kadhim Hameed 1) and Salah Tawfeek Ali 2) 1) University of Kufa, Kufa, Iraq 2) University of Babylon,
Basin characteristics
 Basin characteristics From hydrological processes at the point scale to hydrological processes throughout the space continuum: point scale à river basin The watershed characteristics (shape, length, topography,
Basin characteristics From hydrological processes at the point scale to hydrological processes throughout the space continuum: point scale à river basin The watershed characteristics (shape, length, topography,
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY
 INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART 257.82 PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY EPA s Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals from Electric Utilities Final Rule (40 C.F.R.
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART 257.82 PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY EPA s Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals from Electric Utilities Final Rule (40 C.F.R.
Each basin is surrounded & defined by a drainage divide (high point from which water flows away) Channel initiation
 DRAINAGE BASINS A drainage basin or watershed is defined from a downstream point, working upstream, to include all of the hillslope & channel areas which drain to that point Each basin is surrounded &
DRAINAGE BASINS A drainage basin or watershed is defined from a downstream point, working upstream, to include all of the hillslope & channel areas which drain to that point Each basin is surrounded &
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10)
 Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
What Is Water Erosion? Aren t they the same thing? What Is Sediment? What Is Sedimentation? How can Sediment Yields be Minimized?
 Jerald S. Fifield, Ph.D. CISEC HydroDynamics Incorporated Parker, CO 303-841-0377 Aren t they the same thing? What Is Sediment? Soil particles deposited or suspended in water or air The process of depositing
Jerald S. Fifield, Ph.D. CISEC HydroDynamics Incorporated Parker, CO 303-841-0377 Aren t they the same thing? What Is Sediment? Soil particles deposited or suspended in water or air The process of depositing
Influence of land surface topography on flood hydrograph. Mohsen Masoudian 1, Stephan Theobald 2. Resources, Sari, Iran
 Influence of land surface topography on flood hydrograph Mohsen Masoudian 1, Stephan Theobald 2 1. Assistant professor, Department of Water Engineering, Sari University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural
Influence of land surface topography on flood hydrograph Mohsen Masoudian 1, Stephan Theobald 2 1. Assistant professor, Department of Water Engineering, Sari University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural
Morphological Changes of Reach Two of the Nile River
 ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Morphological Changes of Reach Two of the Nile River E. Said Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency,
ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Morphological Changes of Reach Two of the Nile River E. Said Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 3, March ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 3, March-2015 1338 Modeling of Sediment Transport Upstream of Al- Shamia Barrage Prof. Dr. Saleh I. Khassaf, Mohammed jaber Abbas
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 3, March-2015 1338 Modeling of Sediment Transport Upstream of Al- Shamia Barrage Prof. Dr. Saleh I. Khassaf, Mohammed jaber Abbas
Study of Hydrometeorology in a Hard Rock Terrain, Kadirischist Belt Area, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh
 Open Journal of Geology, 2012, 2, 294-300 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2012.24028 Published Online October 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg) Study of Hydrometeorology in a Hard Rock Terrain, Kadirischist
Open Journal of Geology, 2012, 2, 294-300 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2012.24028 Published Online October 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg) Study of Hydrometeorology in a Hard Rock Terrain, Kadirischist
