IDENTIFICATION AND MAPPING OF TECTONICALLY ACTIVE POTENTIAL ZONES IN NORTHEASTERN PART OF ARAVALLI MOUNTAIN RANGE
|
|
|
- Audra Banks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IDENTIFICATION AND MAPPING OF TECTONICALLY ACTIVE POTENTIAL ZONES IN NORTHEASTERN PART OF ARAVALLI MOUNTAIN RANGE Nitin Gupta, Jayanta K. Jena, Swati Jain, P. K. Verma School of Studies in Geology, Vikram University, Ujjain (M. P.) Tel Fax E mail: drpkverma@rediffmail.com Commission VI WG VIII/2 ABSTRACT: KEY WORDS: Active Tectonics, Aravalli Mountain Range, India, GIS The Great Boundary Fault (GBF) forms the eastern margin of the Aravalli Mountain Range (AMR) and, is exposed as boundary between highly deformed rocks of the AMR and relatively undeformed Vindhyan rocks. The GBF acts as important active dislocation zone between Himalayan regime in the north and, Son-Narmada regime in the south. Nevertheless, the intensity of active tectonics along GBF is relatively mild and hence, it requires special technique to identify and map active tectonics zone along this thrust. The thematic maps of geology, geomorphology, slope, and vegetation index of study area have been prepared using Landsat 7 ETM + digital data. These themes are integrated in GIS environment to assess the active tectonic potential in the area. The observed four high potential zones in the area are located at the intersection of NE-SW lineaments. The study brings out methodology for assessing active tectonic potential of the area. 1. INTRODUCTION Area is well connected by roads and the conveniences are easily available. The state of Rajasthan is regarded as geologist s paradise. The tectonic features ranging from magnificent regional scale folds and thrusts to local scale crenulations and faults are beautifully portrayed in the outcrops of the Aravalli Mountain Range (AMR) (Heron, 1953, Sinha Roy et al., 1998). The Great Boundary Fault (GBF) forms the eastern margin of the AMR and, is exposed as boundary between highly deformed rocks of the AMR and relatively unreformed Vindhyans rocks (Verma and Greiling, 1995, Verma, 1996). The GBF acts as important active dislocation zone between compressional Himalayan regime in the north and, extensional Son-Narmada regime in the south. Nevertheless, the intensity of active tectonics along GBF is relatively mild and hence, it requires special technique to identify and map active tectonics zone along this thrust. The present work attempt to evolve effective GIS for identification and mapping of mild active tectonics zones with focused example from part of the GBF terrain N E E N 2. LOCATION AND APPROACH The present study area (Figure 1) is a part of eastern Rajasthan, which is situated under Three district of Rajasthan, these districts are Sawai Madhopur, Karauli and Dausa.The study area covers sq. Km. area and it is located between longitude E and latitude N on map. The area falls on Survey of India Toposheets no.54b/5,6,7,9,10,11,13,14,15 and 54F/1,2,3 Gangapur city, Karauli, Hindaun and Lalsot are the major cities of this area. Delhi-Mumbai train route passes through the Gangapur city. Figure 1 Location map of Karauli-Lalsot area of NE Rajasthan 3. METHODOLOGY The basic data used in present study includes digital products of Landsat-7 ETM, IRS ID (LISS III & WiFS), IRS-P4 (OCM), Digital Elevation Model (DEM) 30 m data of Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission (SRTM) and, SOI topographical sheets at 1:1M, 1:250,000 and 1:50,000 scales. The general image interpretation elements (tone, texture, pattern etc.) are
2 used in rock type and geomorphic features discrimination. The visual image interpretation techniques (tone, texture, pattern etc.) were followed in delineating geology, geomorphology and lineaments features. The digital image analysis and visual interpretation were carried out on IBM platform using ERDAS Imagine software. The UTM coordinate system was used for data input in the present study. A drainage map of the area is prepared to illustrate the major characteristic of topography morphology and also to emphasis the impact of the faulting on the final geometry of the area. Morphometric analysis is carried out and different parameters are calculated viz. Bifurcation ratio, Drainage density, Length of over land flow, Stream Frequency, Form factor etc. (Strahler, 1964). A polygon map is prepared by assigning a code for each category. The important geomorphic parameters, which help in identification of active tectonics in the area (viz. sinuosity of river, mountain front sinuosity, valley floor width and height ratio, concavity index etc.) are quantified. The important morphotectonic parameters, which help in identification of active tectonics in the area (viz. sinuosity of river and mountain front sinuosity) and the indices of sinuosity (Muller, 1968) are calculated as follows. shales and limestones. These rocks are nearly horizontal to sub horizontal, however, near the GBF, this sequence is steeply dipping and intricately folded. The Delhi Supergroup contains metamorphic succession with limestones and quartzites of the Raialo Group (Figure 2). Geomorphologically, the area represents a fairly rugged topography with presence of structural hill ranges, linear and curvilinear ridges, and plateaus with intermontane valleys. The pediments as well as pediplains are frequently observed (Figure 3). Channel Index (CI)=CL/AL (CL is channel length and AL is air length) Valley Index (VI)=VL/AL (VL is valley length) Standard Sinuosity Index (SSI)=CI/VI Hydraulic Sinuosity Index (HSI)=(CI-VI/CI-1)*100. Topographic Sinuosity Index (TSI)= (VI-1/CI-1)*100. Mountain front sinuosity (S) is defined as the ratio of observed length along the margin of the topographic mountain piedmont junction (Lmf) to the overall length of the mountain front (Ls). Smf=Lmf/Ls Sinousity Fractal dimension (SFD) values have been computed for each of the river considering the whole drainage basin as a spatial unit. The calculation has been done by using Box Flex method (Barton, 1995). Figure 2 Geological map of the study area Following digitization, rastorisation of all maps are carried out in the ERDAS imagine. The UTM coordinate system is used for data input in the present study. The four characteristic indicators of active tectonics in this area are identified as geology geomorphology, slope, and vegetation index. Each of these characteristic indicators is assigned weight value of 0 and 25 at minimum and maximum, respectively to obtain a 100 point scale for active tectonics intensity. Accordingly, the integrated weight of prepared active tectonics intensity zone map ranges between 0 and 100. The area has been contoured based on integrated weight to demarcate zones of active tectonics intensity. 4. GEOLOGY AND GEOMORPHOLOGY The area is occupied mainly by the rocks belonging to the Vindhyan, Delhi Supergroups and Aravalli rock covering part of the area (Sinha Roy, 1984; Sinha Roy et al., 1995; Banerjee and Singh, 1981; Gupta et al., 1997; Roy and Jhakar, 2002). The Great Boundary Fault separates the Vindhyan rocks from the older rocks of Aravalli Mountain Range (Hacket, 1881; Roy, 1988). The Vindhyan supergroup, in general, contains undeformed and unmetamorphosed conglomerate, sandstones, Figure 3 Geomorphological map of the study area 5. MORPHOMETRIC AND MORPHOTECTONIC CHARACTERISTICS
3 The river systems often adjust themselves against changes in ground slope conditions arising due to tectonic processes. These changes are often reflected in river lateral and longitudinal profiles (Hack, 1957; Bull & Knuepfer, 1987; Sinha Roy, 2001a). The area is mainly drained by Kareli River, which is left branch of the Morel River. The general flow direction of the river is NW- SE. The total catchment of the river covers an area of 720 sq km and basin perimeter of about 153 km. Morphometric study of the area reveals the predominance of dendritic, subparallel and trellis drainage patterns. A systematic drainage analysis indicates the presence of the 5 th order stream. Most of these streams are rain fed and dry up during the summer. The computed values of Bifurcation ratio is 3.9, Infiltration number (If) is 1.47, Stream Frequency (Sf) is 1.3, Ruggedness (Hd) is 0.29 and Texture Ratio (Tu) is drainage density of the area suggests that the area has higher density of joints and fractures. Further, high infiltration and low runoff suggests highly fractured underlying rocks. Table 1 Values of sinuosity parameters calculated for the different sections of Kareli River S.No. CL (Km) VL (Km) AL (K m) HSI TSI SSI Table 2 Fractal value of Kareli River S. No. Slope value Fractal value The river sinuosity is important parameter that undergoes rapid modification during episodic and/or continuous tectonic processes and, thus, the sinuosity parameter of rivers becomes an important indicator of tectonic history of drainage basins (Schumm, 1963; Muller, 1968; Burnett and Schumm, 1983). The present work is an attempt to assess various sinuosity indices as indicator of active tectonics in the area. These parameters are computed for different segment of Karli river basin. Sinuosity value of fractal dimension of Kareli River basin ranges from to (Table 1). The SSI values of all 12 sections range between 1.02 and 1.33 indicating nonsinuous course for all the sections (Table 2). The study area indicates higher topographic factor with the values of TSI Kareli River 53.9%. The difference between TSI and HSI in the study area, however, is not very contrasting indicating very slow rate of tectonic activity with TSI being at slightly higher side due to ongoing tectonics and corresponding topographic modifications. The values for all sections are indicative of late youth to early maturity stage of basin development. The low value of HSI and correspondingly higher values of TSI Index in section suggest that the streams do not belong to the initial denudation cycle but the area has been rejuvenated. Mountain front sinuosity assesses the influence of tectonic uplift, assuming that tectonically inactive mountain fronts will be more embayed than those of similar lithology undergoing recent tectonic uplift. Mountain front sinuosity (Smf) is defined as the ratio of observed length along the margin of the topographic mountain piedmont junction (Lmf) to the overall length of the mountain front (Ls) front (Smf = Lmf/Ls; Bull & McFadden 1977, Keller& Pinter 2001). The Smf values lower than 1.4 indicate tectonically active fronts (Rockwell et al. 1984, Keller, 1986) while higher Smf values (>3) are normally associated with inactive fronts in which the initial range front fault may be more than 1 Km away from the present erosional front. 6. LINEAMENT FABRIC Lineament is defined as mappable, simple or composite linear features of a surface, whose parts are aligned in a rectilinear or slightly curvilinear relationship and which differs distinctly from the patterns of adjacent features and presumably reflects a subsurface phenomenon (O Leary et al., 1976). The lineament analysis reveals a distinct variation in the frequency and distribution of lineaments in the area (Figure 4). The rose diagrams plotted with respect to Frequency azimuth and Length azimuth indicate three significant trends that are well correlated with the observed tectonic trends in the field. Lineament Intersection map, number of lineament map and lineament total length map have been prepared using unit grid size of 25 sq km. The lineament intersection contour map shows that the northwestern part of area has higher values of intersections. The lineament length contour map illustrates that the northwestern and some part of southeast of the area have larger length of lineaments. Lineament number contour map depicts that the greater number of lineaments are concentrated in the NW part of the study area.
4 many classes, is simplified by classifying the values into three classes, namely, high active zone, moderate active zone and low active zone. The following four thematic layers have been used in generation of active tectonic potential map. 7.1 Geomorphological Map Geomorphological units are reclassified by giving more importance to structural hills (weight value 9). This unit covers major part of the study area and is characterized mostly by hard and compact sandstone with steep slope. The valley fills are less important from tectonic point of view (Table 3, Figure 3) 7.2 Geological map Figure 4 Lineament map of the study area 7. ACTIVE TECTONICS ZONES Based on the result obtained during the present investigation, an active tectonics potential map has been generated. This map show different zones with the estimated potential for present day tectonic activity. The four important parameters identified for assessing degree and potential of active tectonics in the area are Geomorphology, Geology, Slope and index for which thematic maps have been generated. The four thematic maps are classified with value ranging between 0 and 10. The weight value that have been assigned to the individual classes are mainly on the basis of literature, result obtained during the present investigation and knowledge about the present terrain. This exercise consists of following four steps for identification and grading of active zones. Step-1: Assigning weight value to the classes of the parameter maps. The weight values are assigned in tables connected to the raster map. First a table is created for each map and then a column weight is created, in which weight values for different classes are added. In present case weight value ranging 0 10 is given to different components. Four important parameters characterizing the tectonic zones are identified. Each of these parameters (Geomorphology, Geology, Slope and index) is assigned weight value of 0 and 10 at minimum and maximum respectively. Thus the integrated weight of final map ranges between 0 and 100. Geological units are reclassified on the basis of their relative hardness, higher the hardness higher the value and vice-versa. In this study Ajabgarh Group has higher weight value (9) and recent alluviums having lesser weight value (0). The groups having higher value are most important from tectonic point of view then others. The weight values are represent in following table (Table 3) and the weighted geological map is shown (Figure 2). 7.3 Slope map The interpolated raster image of contour lines is used for preparing the slope. The gradient filters DF DX and DF DY are used respectively in X and Y direction. The application of gradient filters yields pixel values as attribute difference per unit cell in X or Y direction. The maps are created by applying the equation: Slope map = {[HYP (DX, DY)/12]*100} The slope map is classified into five classes based on slope percentage (Table 3 Figure 5). The very low slopes (<10%) are mainly associated with valley fills. The low slopes (10-15%) observed in undulating pediplain areas. The moderately sloping areas (20-25%) are in association with pediment, residual/ denudational hills and intermountain valley zone. Steep slopes (25-30%) and very steep slope (>30%) are associated with neck of dissected ridges, structural hills, ravenous land and escarpments. This map is reclassified by giving more importance to areas having steeper slope. Step-2: Renumbering the parameter map to weight maps. The combination of each parameter map with the weight values derived from the table created in the previous step is called renumbering. Step-3: Combining the weight maps in to one single active tectonics map. The weight map is combined in this exercise by simply summing them up. In the present case, the sum of all four components comes to be maximum 100 and minimum 0. Step-4: Classifying the combined weight map into active tectonics zone map. The combined weight map, which has
5 Table 3: Geomorphic, Slope and index units with assigned weight values Geological Sst, Qtz, Ajabgarh, Phyllite, Slate Shale Shale Alluvium Sst, Qtz, Shale, Alluvium Recent Alluvium Geomorphic Structural hill Dissected Pateau Pediment Intermountain valley Ravenous land Residual/ denudational hill Pediplain Valley Fills/River valley Slope Very high ate ate High ate to high ate Very low Very low to medium vegetation ate High Water (moisture zone) Assigne d Weight Figure 6 NDVI Map of study area with Weightage value Final result is obtained in form of Neotectonic Potential Zone Map ((Figure 7). This map shows that the less part of the study area is affected with neotectonic activity and North-western part of the study area is showing prominently Neotectnic zone. Figure 5 Slope Map of study area with Weightage value 7.4 index maps (NDVI) The following formula is used to calculate NDVI in map Calc function: NDVI = (Infrared Band- Red Band)/ (Infrared Band + Red band) This map is classified into five subclasses based on the vegetation index values. The vegetation index values are divided in very low or barren land ( ), low ( ), to moderate ( ), moderate ( ) and high vegetation (>0.35) classes. The very low vegetation is found in very steep slopes and structural hills areas Higher vegetation index points to lower weathering potential (Table 3 Figure 6) Figure 7 Neotectonic Potential Map CONCLUSION There are several direct and indirect evidences for active tectonics. The evidences are more pronounced where the rate of tectonism is higher. The quantification of these evidences to formulate a yard stick for measuring present and potential tectonic zone is possible using GIS technique. The GIS developed in the present study distinctly assesses the active tectonics in Karauli-Bayana area and classifies the area into active tectonic zones based on present and potential tectonic activities. Interestingly, the high tectonic potential zones identified through this technique are also characterized by the presence of areas of high heat flow. The methodology may be well suited for studies pertaining to land stability, seismic zonation and related programs.
6 REFERENCES. Banerjee, A.K. and Singh Maharaja, H. J., 1981: Palaeogeography and sedimentation of Vindhyans in eastern Rajasthan. Geol. Surv. Ind., Misc. Publ. No. 50, pp Barton, C.C. (1995) Fractal analysis of scaling and spatial clustering of fractures. In: C.C., Barton, and P.R., La Pointe (eds.), Fractals in the Earth Sciences. New York: Plenum Press, pp Bull W., and McFadden L. (1977) Tectonic geomorphology north and south of the Garlock Fault, California, Geomorphology in Arid regions, D. O. Doehring, ed., Publications in Geomorphology, State University of New York at Bingamton, pp Bull, W.L. & Knuepfer, P.L.K. (1987). Adjustments by the Charwell River, New Zealand, to uplift and climatic changes. Geomorphology, vol. 1, (L). Burnett, A.W., Schumm, S.A., (1983). Alluvial-river response to neotectonic deformation in Louisiana and Mississippi, Science, 222: Hack, J.T., (1957). Studies of longitudinal stream profiles in Virginia and Maryland, U.S. Geol. Survey Prof. paper 294-B. Hacket, C.A., 1881: On the Geology of the Aravalli region, eastern Rajputana, Rec. Geol. Surv. of India, V. 14(4), pp Heron A. M. (1953) The geology of Central Rajputana. Mem. Geol. Surv. India, 79(1) : 389 p. Keller E. (1986) Investigation of active tectonics: use of surficial earth processes. In: Wallace, R. E. (eds), Active Tectonics studies in Geophysics. Nat. Acad. Press, Washington, Dc, pp Keller E., and Pinter, N., 2001: Active Tectonics, Earthquakes, Uplift and Landscape, Earth Sciences Series, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ. Muller, J. E. (1968). An introduction to the hydraulic and topographic sinuosity indexes. Annals Asso. Am. Geogr. 58: pp O Leary, D.W., Driedman, J.D. and Pohn, H.A. (1976) Lineaments, linear, lineation: some proposed new standards for old terms. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 87:pp Rockwell T., Keller E., Johnson D. (1984) Tectonic geomorphology of alluvial fans and mountain fronts near Ventura, California. In: Morisawa, M., Hack T. J. (eds), Tectonic Geomorphology. Publ. In Geomorphology, State University of New York, Binghamton, pp Roy A.B. and Jakhar S.R. (2002) Geology of Rajasthan (NW India)- Precambrian to Recent. Scientific Publisher, Jodhpur, 421 p. Schumm, S.A., 1963: Sinuosity of alluvial rivers on the great plain., Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., v. 74, pp Sinha Roy S., Malhotra G. and Mohanty M. (1998) Geology of Rajasthan. Geological Society of India, Bangalore, 278 p. Sinha Roy, S a: Neotectonic significance of longitudinal river profiles: An example from the Banas drainage basin, Rajasthan. Journal of Geological Society of India, V. 58, pp Sinha Roy, S., 1984: Precambrian crustal interaction in Rajasthan, NW India. In: Seminar Vol. Crustal evolution of Indian shield and its bearing on metallogeny. Ind. Jour. Earth Sci., pp Sinha Roy, S., Malhotra, G. and Guha, D.B., 1995: A transect across Rajasthan Precambrian in relation to geology, tectonics and crustal evolution of south-central Rajasthan. In: S. Sinha- Roy and K.R. Gupta (eds.) Continental crust of northwest and central India, Mem. Geol. Soc. India, V. 31, pp Strahler (1964) Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basins and channel networks, Handbook of Applied Hydrology: Ed. By Ven Te Chow, McGraw Hill Book Company. New York, pp Verma P. K. (1996) Evolution and age of the Great Boundary Fault. In: A. Bhattacharyya (Ed.), Recent Advances in Vindhyan Geology. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, No. 36, pp Verma P. K. and Greiling R. O. (1995) Tectonic evolution of the Aravalli Orogen (NW India): an inverted Proterozoic rift basin. Geol. Rundsch.. V. 84. pp
Drainage Characteristics of Tectonically Active Areas: An Example from Rajasthan, India
 Int. J. Econ. & Environ. Geol. Vol:1(1) 11-16 Drainage Characteristics of Tectonically Active Areas: An Example from Rajasthan, India SWATI JAIN AND P. K. VERMA School of Studies in Geology, Vikram University,
Int. J. Econ. & Environ. Geol. Vol:1(1) 11-16 Drainage Characteristics of Tectonically Active Areas: An Example from Rajasthan, India SWATI JAIN AND P. K. VERMA School of Studies in Geology, Vikram University,
Figure 2.1: Constituent Area
 2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Morphotectonic Analysis in the Ghezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran
 Morphotectonic Analysis in the Ghezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran Vahid Hosseini Toudeshki (Corresponding author) Department of Civil Engineering Zanjan Branch Islamic Azad University Zanjan Iran. Tel: 091-266-129-89
Morphotectonic Analysis in the Ghezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran Vahid Hosseini Toudeshki (Corresponding author) Department of Civil Engineering Zanjan Branch Islamic Azad University Zanjan Iran. Tel: 091-266-129-89
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS
 LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Hypsometric Analysis of Varattaru
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Hypsometric Analysis of Varattaru
Sub-watershed prioritization based on potential zones of Kuttiadi river basin, A Geo-Morphometric approach using GIS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 8, No 1, 2018 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Sub-watershed prioritization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 8, No 1, 2018 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Sub-watershed prioritization
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF ADYAR WATERSHED
 MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF ADYAR WATERSHED A.K.Bharadwaj 1,Pradeep.C 2,D.Thirumalaivasan 3,C.P.Shankar 4, N.Madhavan 5 1,2,3,4,5 Institute of Remote Sensing, Anna University, Guindy, Chennai, India- 600025.
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF ADYAR WATERSHED A.K.Bharadwaj 1,Pradeep.C 2,D.Thirumalaivasan 3,C.P.Shankar 4, N.Madhavan 5 1,2,3,4,5 Institute of Remote Sensing, Anna University, Guindy, Chennai, India- 600025.
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH
 GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
About the Author: E mail ID: Contact: proceedings. Page 1 of 8
 Catchment Delineation and Morphometric Analysis Using Geographical Information System of Naina Gorma Basin of Rewa District, M.P., India Vimala Singh 1, L.K. Sinha 2 Research Associate 1, DTRL, DRDO Scientist
Catchment Delineation and Morphometric Analysis Using Geographical Information System of Naina Gorma Basin of Rewa District, M.P., India Vimala Singh 1, L.K. Sinha 2 Research Associate 1, DTRL, DRDO Scientist
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY
 MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1170 COLLEGE : SIDDAGANGA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1170 COLLEGE : SIDDAGANGA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
International Journal of Research (IJR) Vol-1, Issue-10 November 2014 ISSN
 Morphological Parameter Estimation Derived From ASTER-DEM Using GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques A Study on Hosakote Watershed of Dakshina Pinakini River Basin, Karnataka, India K. Satish 1* and H.C.
Morphological Parameter Estimation Derived From ASTER-DEM Using GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques A Study on Hosakote Watershed of Dakshina Pinakini River Basin, Karnataka, India K. Satish 1* and H.C.
Morphotectonic and Lineament analysis from Bhatia and Jaigarh Creek, Ratnagiri, MS, India: Neotectonic Implication
 International Research Journal of Earth Sciences ISSN 2321 2527 Int. Res.J. Earth Sci. Morphotectonic and Lineament analysis from Bhatia and Jaigarh Creek, Ratnagiri, MS, India: Neotectonic Implication
International Research Journal of Earth Sciences ISSN 2321 2527 Int. Res.J. Earth Sci. Morphotectonic and Lineament analysis from Bhatia and Jaigarh Creek, Ratnagiri, MS, India: Neotectonic Implication
Morphometric Analysis of Chamundi Hills, Mysuru, India Using Geographical Information System
 Volume-7, Issue-1, January-February 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 279-283 Morphometric Analysis of s, Mysuru, India Using Geographical Information System
Volume-7, Issue-1, January-February 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 279-283 Morphometric Analysis of s, Mysuru, India Using Geographical Information System
Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin
 Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin Luna Moin Das North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong Abstract: Basin morphometry is an important means of understanding a drainage basin using mathematically
Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin Luna Moin Das North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong Abstract: Basin morphometry is an important means of understanding a drainage basin using mathematically
General Overview and Facts about the Irobland
 Using Geoinformation Science to Reveal the Impact of the Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission s Decision on Irobland and People By Alema Tesfaye, Washington DC, USA Part I General Overview and Facts about
Using Geoinformation Science to Reveal the Impact of the Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission s Decision on Irobland and People By Alema Tesfaye, Washington DC, USA Part I General Overview and Facts about
Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands
 Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF LAKSHMANTIRTHA RIVER BASIN AROUND HUNSUR TALUK, MYSORE, KARNATAKA, (INDIA)
 MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF LAKSHMANTIRTHA RIVER BASIN AROUND HUNSUR TALUK, MYSORE, KARNATAKA, (INDIA) Nilufer Arshad* and G.S. Gopalakrishna DOS in Geology University of Mysore, Mysore, (INDIA) Received
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF LAKSHMANTIRTHA RIVER BASIN AROUND HUNSUR TALUK, MYSORE, KARNATAKA, (INDIA) Nilufer Arshad* and G.S. Gopalakrishna DOS in Geology University of Mysore, Mysore, (INDIA) Received
Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal
 Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal Martina Böhme Institute of Geology, University of Mining and Technology, Freiberg, Germany Abstract.
Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal Martina Böhme Institute of Geology, University of Mining and Technology, Freiberg, Germany Abstract.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 1, No 4, 2011
 Morphometric analysis of Nanjangud taluk, Mysore District, Karnataka, India, using GIS Techniques Mahadevaswamy.G 1, Nagaraju.D 1, Siddalingamurthy.S 1, Lakshmamma 1, Mohammad Subhan lone, Nagesh.P.C 2,
Morphometric analysis of Nanjangud taluk, Mysore District, Karnataka, India, using GIS Techniques Mahadevaswamy.G 1, Nagaraju.D 1, Siddalingamurthy.S 1, Lakshmamma 1, Mohammad Subhan lone, Nagesh.P.C 2,
Geospatial Data Integration For Groundwater Recharge Estimation In Hard Rock Terrain. Authors,
 Geospatial Data Integration For Groundwater Recharge Estimation In Hard Rock Terrain Authors, Dr. Y. B. Katpatal Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Visvesvaraya National Institute of
Geospatial Data Integration For Groundwater Recharge Estimation In Hard Rock Terrain Authors, Dr. Y. B. Katpatal Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Visvesvaraya National Institute of
PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE.
 PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE. Spyridoula Vassilopoulou * Institute of Cartography
PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE. Spyridoula Vassilopoulou * Institute of Cartography
About the Author: Abstract:
 Identification of groundwater prospecting zones using Remote Sensing and GIS techniques in upper Vena river watersheds Nagpur district, Maharashtra, India B.S. Manjare Department of Geology RTM Nagpur
Identification of groundwater prospecting zones using Remote Sensing and GIS techniques in upper Vena river watersheds Nagpur district, Maharashtra, India B.S. Manjare Department of Geology RTM Nagpur
Active Tectonics. Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape. Edward A. Keller University of California, Santa Barbara
 Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 OBJECTIVE
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
Correspondence should be addressed to B.S. Manjare,
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2013, Volume 2, Issue 1, pp. 333-340, Article ID Tech-158 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Mapping of Lineaments in
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2013, Volume 2, Issue 1, pp. 333-340, Article ID Tech-158 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Mapping of Lineaments in
Structural Analysis and Tectonic Investigation of Chamshir Dam Site, South West Zagros
 Open Journal of Geology, 2015, 5, 136-143 Published Online March 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2015.53013 Structural Analysis and Tectonic Investigation
Open Journal of Geology, 2015, 5, 136-143 Published Online March 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2015.53013 Structural Analysis and Tectonic Investigation
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: April, 2016
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 1, No 3, 2010
 Integrated approach using RS and GIS techniques for mapping of ground water prospects in Lower Sanjai Watershed, Jharkhand Binay Kumar 1, Uday Kumar 2 1 Geomatics Solutions Development Group, Centre for
Integrated approach using RS and GIS techniques for mapping of ground water prospects in Lower Sanjai Watershed, Jharkhand Binay Kumar 1, Uday Kumar 2 1 Geomatics Solutions Development Group, Centre for
Landforms and Rock Structure
 Landforms and Rock Structure Rock Structure as a Landform Control Landforms of Horizontal Strata and Coastal Plains Landforms of Warped Rock Layers Landforms Developed on Other Land-Mass Types Landforms
Landforms and Rock Structure Rock Structure as a Landform Control Landforms of Horizontal Strata and Coastal Plains Landforms of Warped Rock Layers Landforms Developed on Other Land-Mass Types Landforms
[Penumaka, 7(1): January-March 2017] ISSN Impact Factor
![[Penumaka, 7(1): January-March 2017] ISSN Impact Factor [Penumaka, 7(1): January-March 2017] ISSN Impact Factor](/thumbs/95/124653515.jpg) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES &MANAGEMENT HYDROGEOMORPHOLOGY OF CHEVELLA BASIN, RANGA REDDY DISTRICT, TELANGANA STATE Penumaka Ramesh* 1 & Podila Sankara Pitchaiah 2 * 1&2 Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES &MANAGEMENT HYDROGEOMORPHOLOGY OF CHEVELLA BASIN, RANGA REDDY DISTRICT, TELANGANA STATE Penumaka Ramesh* 1 & Podila Sankara Pitchaiah 2 * 1&2 Department of
ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh District, Jharkhand, India
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 2, February-2012 1 ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 2, February-2012 1 ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Remote Sensing and GIS Based Tectonic
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Remote Sensing and GIS Based Tectonic
Integration of Thematic Maps Through GIS for Identification of Groundwater Potential zones. Amaresh Kr. Singh & S. Ravi Prakash
 Integration of Thematic Maps Through GIS for Identification of Groundwater Potential zones Amaresh Kr. Singh & S. Ravi Prakash Remote Sensing Applications Centre, U.P., Sector -G, Jankipuram, Lucknow rsacup@sancharnet.in,
Integration of Thematic Maps Through GIS for Identification of Groundwater Potential zones Amaresh Kr. Singh & S. Ravi Prakash Remote Sensing Applications Centre, U.P., Sector -G, Jankipuram, Lucknow rsacup@sancharnet.in,
Landforms. Why does the land look like it does? 1. Controlled by water 2. Controlled by the rocks
 Landforms Why does the land look like it does? 1. Controlled by water 2. Controlled by the rocks Landforms Made by Running Water Stream erosion The evolution of a river system Entrenched meanders Fluvial
Landforms Why does the land look like it does? 1. Controlled by water 2. Controlled by the rocks Landforms Made by Running Water Stream erosion The evolution of a river system Entrenched meanders Fluvial
SPECTRAL DISCRIMINATION OF ROCK TYPES IN THE ARAVALLI MOUNTAIN RANGES OF RAJASTHAN (INDIA) USING LANDSAT THEMATIC MAPPER DATA
 SPECTRAL DISCRIMINATION OF ROCK TYPES IN THE ARAVALLI MOUNTAIN RANGES OF RAJASTHAN (INDIA) USING LANDSAT THEMATIC MAPPER DATA Dr. Nilanchal Patel Reader, Department of Remote Sensing Birla Institute of
SPECTRAL DISCRIMINATION OF ROCK TYPES IN THE ARAVALLI MOUNTAIN RANGES OF RAJASTHAN (INDIA) USING LANDSAT THEMATIC MAPPER DATA Dr. Nilanchal Patel Reader, Department of Remote Sensing Birla Institute of
ABSTRACT. Watershed management has emerged as a new paradigm for planning,
 JLSstract ABSTRACT Watershed management has emerged as a new paradigm for planning, development and management of land, water and biomass resources with a focus on social and environmental aspects following
JLSstract ABSTRACT Watershed management has emerged as a new paradigm for planning, development and management of land, water and biomass resources with a focus on social and environmental aspects following
Geomorphic Evidence of Active Tectonics in the Dhundsir Gad Watershed of Alaknada Basin, Uttarakhand, India
 Geomorphic Evidence of Active Tectonics in the Dhundsir Gad Watershed of Alaknada Basin, Uttarakhand, India Hari Ballabh 1, Devi Datt Chauniyal 1 & Mahendra Singh Lodhi 2, * 1. Department of Geography,
Geomorphic Evidence of Active Tectonics in the Dhundsir Gad Watershed of Alaknada Basin, Uttarakhand, India Hari Ballabh 1, Devi Datt Chauniyal 1 & Mahendra Singh Lodhi 2, * 1. Department of Geography,
MAPPING POTENTIAL LAND DEGRADATION IN BHUTAN
 MAPPING POTENTIAL LAND DEGRADATION IN BHUTAN Moe Myint, Geoinformatics Consultant Rue du Midi-8, CH-1196, Gland, Switzerland moemyint@bluewin.ch Pema Thinley, GIS Analyst Renewable Natural Resources Research
MAPPING POTENTIAL LAND DEGRADATION IN BHUTAN Moe Myint, Geoinformatics Consultant Rue du Midi-8, CH-1196, Gland, Switzerland moemyint@bluewin.ch Pema Thinley, GIS Analyst Renewable Natural Resources Research
Satellite Based Seismic Technology
 Satellite Based Seismic Technology Dr. V.K. Srivastava, R. Ghosh*, B.B Chhualsingh Department of Applied Geophysics, Indian School of mines, Dhanbad. E- mail: ismkvinay@hotmail.com, ghosh.ramesh@rediffmail.com,
Satellite Based Seismic Technology Dr. V.K. Srivastava, R. Ghosh*, B.B Chhualsingh Department of Applied Geophysics, Indian School of mines, Dhanbad. E- mail: ismkvinay@hotmail.com, ghosh.ramesh@rediffmail.com,
ESTIMATION OF MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETERS AND RUNOFF USING RS & GIS TECHNIQUES
 ESTIMATION OF MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETERS AND RUNOFF USING RS & GIS TECHNIQUES Shrudha. V. K¹, Hafeezunnisa² 1 Assistant Professor, Rajarajeshwari College of Engineering Bangalore 2 Assistant Engineer, WRDO
ESTIMATION OF MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETERS AND RUNOFF USING RS & GIS TECHNIQUES Shrudha. V. K¹, Hafeezunnisa² 1 Assistant Professor, Rajarajeshwari College of Engineering Bangalore 2 Assistant Engineer, WRDO
Prashant P. Magar 1 and Nirupama P. Magar 2 1
 Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 4, 2016 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Application of Hack s Stream Gradient Index (SL Index) to Longitudinal Profiles of the Rivers Flowing
Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 4, 2016 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Application of Hack s Stream Gradient Index (SL Index) to Longitudinal Profiles of the Rivers Flowing
Assessing Vulnerability to Soil Erosion of a Watershed of Tons River Basin in Madhya Pradesh using Remote Sensing and GIS
 International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
Environmental Impact Assessment Land Use and Land Cover CISMHE 7.1 INTRODUCTION
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
QUANTITATIVE GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE DRAINAGE BASIN IN SEMI-ARID ENVIRONMENT
 I" QUANTITATIVE GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE DRAINAGE BASIN IN SEMI-ARID ENVIRONMENT BIMAL GROSE, S. PANDEY AND S SINGH Gentral Arid Zone Research Institute, Jodhpur INTRODUCTION In India Ghose et al (963, 967)
I" QUANTITATIVE GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE DRAINAGE BASIN IN SEMI-ARID ENVIRONMENT BIMAL GROSE, S. PANDEY AND S SINGH Gentral Arid Zone Research Institute, Jodhpur INTRODUCTION In India Ghose et al (963, 967)
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF ALUVIAL FANS FROM ASTER L1 SATELLITE DATA AND A DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL USING OBJECT-ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS
 AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF ALUVIAL FANS FROM ASTER L1 SATELLITE DATA AND A DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL USING OBJECT-ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS Demetre P. Argialas, Angelos Tzotsos Laboratory of Remote Sensing, Department
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF ALUVIAL FANS FROM ASTER L1 SATELLITE DATA AND A DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL USING OBJECT-ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS Demetre P. Argialas, Angelos Tzotsos Laboratory of Remote Sensing, Department
International Journal of Remote Sensing & Geoscience (IJRSG) ASTER DEM BASED GEOLOGICAL AND GEOMOR-
 ASTER DEM BASED GEOLOGICAL AND GEOMOR- PHOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION USING GIS TECHNOLOGY IN KOLLI HILL, SOUTH INDIA Gurugnanam.B, Centre for Applied Geology, Gandhigram Rural Institute-Deemed University, Tamilnadu,
ASTER DEM BASED GEOLOGICAL AND GEOMOR- PHOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION USING GIS TECHNOLOGY IN KOLLI HILL, SOUTH INDIA Gurugnanam.B, Centre for Applied Geology, Gandhigram Rural Institute-Deemed University, Tamilnadu,
Geomorphological Analysis of Aralamallige Watershed, Bangalore Using Remote Sensing and GIS Approach
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 2, Issue 1, February 2014, PP 6-10 www.arcjournals.org Geomorphological Analysis of Aralamallige Watershed, Bangalore Using Remote
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 2, Issue 1, February 2014, PP 6-10 www.arcjournals.org Geomorphological Analysis of Aralamallige Watershed, Bangalore Using Remote
USE OF SATELLITE DATA FOR TECTONIC INTERPRETATION, NW HIMALAYA
 COVER ARTCLE Photonirvachak Journal of the ndian Society of Remote Sensing, Vol. 32, No. 3, 2004 USE OF SATELLTE DATA FOR TECTONC NTERPRETATON, NW HMALAYA CHRASHREE MOHANTY, DBYA J. BARAL* AND JAVED N.
COVER ARTCLE Photonirvachak Journal of the ndian Society of Remote Sensing, Vol. 32, No. 3, 2004 USE OF SATELLTE DATA FOR TECTONC NTERPRETATON, NW HMALAYA CHRASHREE MOHANTY, DBYA J. BARAL* AND JAVED N.
A STUDY ON MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETER OF A WATERSHED FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER CONSERVATION
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 9, September 2017, pp. 271 278, Article ID: IJCIET_08_09_031 Available online at http://http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=9
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 9, September 2017, pp. 271 278, Article ID: IJCIET_08_09_031 Available online at http://http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=9
Implication of drainage basin parameters for the Bunbuni River Basin in Chotanagpur Plateau region, India
 IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 21, Issue12, Ver. 4 (December. 2016) PP 01-08 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. www.iosrjournals.org Implication of drainage basin parameters
IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 21, Issue12, Ver. 4 (December. 2016) PP 01-08 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. www.iosrjournals.org Implication of drainage basin parameters
Geospatial Approach for Delineation of Landslide Susceptible Areas in Karnaprayag, Chamoli district, Uttrakhand, India
 Geospatial Approach for Delineation of Landslide Susceptible Areas in Karnaprayag, Chamoli district, Uttrakhand, India Ajay Kumar Sharma & Anand Mohan Singh Overview Landslide - movement of a mass of rock,
Geospatial Approach for Delineation of Landslide Susceptible Areas in Karnaprayag, Chamoli district, Uttrakhand, India Ajay Kumar Sharma & Anand Mohan Singh Overview Landslide - movement of a mass of rock,
Earth Science. STREAM DRAINAGE PATTERNS (start by reading the first page of these notes!)
 Name _ Earth Science STREAM DRAINAGE PATTERNS (start by reading the first page of these notes!) WHAT IS A DRAINAGE PATTERN? Streams seek the lowest path as they move downhill, and they tend to erode their
Name _ Earth Science STREAM DRAINAGE PATTERNS (start by reading the first page of these notes!) WHAT IS A DRAINAGE PATTERN? Streams seek the lowest path as they move downhill, and they tend to erode their
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 1, No 1, 2010
 An Integrated Approach with GIS and Remote Sensing Technique for Landslide Hazard Zonation S.Evany Nithya 1 P. Rajesh Prasanna 2 1. Lecturer, 2. Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Anna
An Integrated Approach with GIS and Remote Sensing Technique for Landslide Hazard Zonation S.Evany Nithya 1 P. Rajesh Prasanna 2 1. Lecturer, 2. Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Anna
Watershed Development Prioritization by Applying WERM Model and GIS Techniques in Takoli Watershed of District Tehri (Uttarakhand)
 Watershed Development Prioritization by Applying WERM Model and GIS Techniques in Takoli Watershed of District Tehri (Uttarakhand) Anju Panwar Uttarakhand Space Application Centre Dehradun, Uttarkhand
Watershed Development Prioritization by Applying WERM Model and GIS Techniques in Takoli Watershed of District Tehri (Uttarakhand) Anju Panwar Uttarakhand Space Application Centre Dehradun, Uttarkhand
MAPPING OF HGM ENVIRONMENT USING SATELITE DATA A case study of Block Datia, Madhya Pradesh (INDIA)
 MAPPING OF HGM ENVIRONMENT USING SATELITE DATA A case study of Block Datia, Madhya Pradesh (INDIA) Satish K. Chakravarty* and D.R. Tiwari Department of Geology, Govt. M.V.M Bhopal (INDIA) Received June
MAPPING OF HGM ENVIRONMENT USING SATELITE DATA A case study of Block Datia, Madhya Pradesh (INDIA) Satish K. Chakravarty* and D.R. Tiwari Department of Geology, Govt. M.V.M Bhopal (INDIA) Received June
GIS Based Delineation of Micro-watershed and its Applications: Mahendergarh District, Haryana
 Kamla-Raj 2012 J Hum Ecol, 38(2): 155-164 (2012) GIS Based Delineation of Micro-watershed and its Applications: Mahendergarh District, Haryana Gulshan Mehra and Rajeshwari * Department of Geography, Kurukshetra
Kamla-Raj 2012 J Hum Ecol, 38(2): 155-164 (2012) GIS Based Delineation of Micro-watershed and its Applications: Mahendergarh District, Haryana Gulshan Mehra and Rajeshwari * Department of Geography, Kurukshetra
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Geo-Hydrological study
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Geo-Hydrological study
DECIPNERING DIFFERENTIAL UPLIFT IN SHLLONG PLATEAU USING REMOTE SENSING
 SHORT COMMUNICATlON DECIPNERING DIFFERENTIAL UPLIFT IN SHLLONG PLATEAU USING REMOTE SENSING Geological Survey of India, Tripura-Mizoram Division, B.K. Road, Banamalipur, Agartala - 790 001 Email: v+srinivasan_geo
SHORT COMMUNICATlON DECIPNERING DIFFERENTIAL UPLIFT IN SHLLONG PLATEAU USING REMOTE SENSING Geological Survey of India, Tripura-Mizoram Division, B.K. Road, Banamalipur, Agartala - 790 001 Email: v+srinivasan_geo
Ground Water Potential Mapping in Chinnar Watershed (Koneri Sub Watershed) Using Remote Sensing & GIS
 Ground Water Potential Mapping in Chinnar Watershed (Koneri Sub Watershed) Using Remote Sensing & GIS T.Velmurugan 1 Dr.D.Srinivasan 2 1 Assistant professor/civil, Roever Engineering College, Perambalur.
Ground Water Potential Mapping in Chinnar Watershed (Koneri Sub Watershed) Using Remote Sensing & GIS T.Velmurugan 1 Dr.D.Srinivasan 2 1 Assistant professor/civil, Roever Engineering College, Perambalur.
Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan
 Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan Abstract Longitudinal Valley was the suture zone between the Philippine Sea plate and the Eurasia plate. Peinanshan was the southest segment of the
Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan Abstract Longitudinal Valley was the suture zone between the Philippine Sea plate and the Eurasia plate. Peinanshan was the southest segment of the
Morphometric Analysis for Evaluating Groundwater Potential Zones, In Kusangai Jor Watershed Area, Dist. Bolangir, Orissa.
 Morphometric Analysis for Evaluating Groundwater Potential Zones, In Kusangai Jor Watershed Area, Dist. Bolangir, Orissa. Alokesh Chatterjee 1, Asish Tantubay 1 1 Department of Geology, Presidency College,
Morphometric Analysis for Evaluating Groundwater Potential Zones, In Kusangai Jor Watershed Area, Dist. Bolangir, Orissa. Alokesh Chatterjee 1, Asish Tantubay 1 1 Department of Geology, Presidency College,
Chapter 1 Quantitative Analysis of Geomorphometric Parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS
 Chapter 1 Quantitative Analysis of Geomorphometric Parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Yahya Farhan, Ali Anbar, Omar Enaba, Nisrin Al-Shaikh Geomorphometric analysis was carried
Chapter 1 Quantitative Analysis of Geomorphometric Parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Yahya Farhan, Ali Anbar, Omar Enaba, Nisrin Al-Shaikh Geomorphometric analysis was carried
GIS based quantitative morphometric analysis and its consequences: a case study from Shanur River Basin, Maharashtra India
 Appl Water Sci (2017) 7:861 871 DOI 10.1007/s13201-015-0298-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE GIS based quantitative morphometric analysis and its consequences: a case study from Shanur River Basin, Maharashtra India
Appl Water Sci (2017) 7:861 871 DOI 10.1007/s13201-015-0298-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE GIS based quantitative morphometric analysis and its consequences: a case study from Shanur River Basin, Maharashtra India
GIS AS A TOOL FOR MINERAL EXPLORATION
 GIS AS A TOOL FOR MINERAL EXPLORATION By Njagi Dennis Muriithi I13/3169/2008 SGL 413: PROJECT IN GEOLOGY Course coordinators: Dr. C. M. Gichaba Dr. E. Dindi Supervisor: Dr. C. M. Gichaba OUTLINE Introduction
GIS AS A TOOL FOR MINERAL EXPLORATION By Njagi Dennis Muriithi I13/3169/2008 SGL 413: PROJECT IN GEOLOGY Course coordinators: Dr. C. M. Gichaba Dr. E. Dindi Supervisor: Dr. C. M. Gichaba OUTLINE Introduction
CHAPTER 9 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 CHAPTER 9 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The following are the important conclusions and salient features of the present study. 1. The evaluation of groundwater potential is a prerequisite for any kind of planning
CHAPTER 9 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The following are the important conclusions and salient features of the present study. 1. The evaluation of groundwater potential is a prerequisite for any kind of planning
Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study
 Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Chapter 5. Morphometric Control on Food
 Chapter 5 Morphometric Control on Food Key Words: Morphometry, Linear Morphometry, Areal Morphometry, Relief Morphometry, Morphometric Control and Flood 5.1 Morphometric Aspects Drainage basin or basins
Chapter 5 Morphometric Control on Food Key Words: Morphometry, Linear Morphometry, Areal Morphometry, Relief Morphometry, Morphometric Control and Flood 5.1 Morphometric Aspects Drainage basin or basins
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Portion of the Grand Canyon
 Landscapes Packet 9 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 2 Performance Indicator 2.1 Use the concepts of density and heat energy to explain observations of weather patterns, seasonal
Landscapes Packet 9 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 2 Performance Indicator 2.1 Use the concepts of density and heat energy to explain observations of weather patterns, seasonal
Study on Saravan Fault Activities on the Basis of Earthquake and Morphotectonics Evidences
 Open Journal of Geology, 2016, 6, 79-86 Published Online February 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2016.62008 Study on Saravan Fault Activities on the Basis
Open Journal of Geology, 2016, 6, 79-86 Published Online February 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2016.62008 Study on Saravan Fault Activities on the Basis
Active Tectonics of Qezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran
 2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4215 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Active Tectonics of Qezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran Mehran Arian *, Ph.D.; Vahid Hosseini
2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4215 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Active Tectonics of Qezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran Mehran Arian *, Ph.D.; Vahid Hosseini
LANDSAT-TM IMAGES IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SURNAYA GAD AREA, DADELDHURA DISTRICT WEST NEPAL
 LANDSAT-TM IMAGES IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SURNAYA GAD AREA, DADELDHURA DISTRICT WEST NEPAL L. N. Rimal* A. K. Duvadi* S. P. Manandhar* *Department of Mines and Geology Lainchaur, Kathmandu, Nepal E-mail:
LANDSAT-TM IMAGES IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SURNAYA GAD AREA, DADELDHURA DISTRICT WEST NEPAL L. N. Rimal* A. K. Duvadi* S. P. Manandhar* *Department of Mines and Geology Lainchaur, Kathmandu, Nepal E-mail:
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
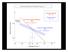 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Morphometric Analysis for Hard Rock Terrain of Upper Ponnaiyar Watershed, Tamilnadu A GIS Approach
 International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 1, Issue 9, December 2014, PP 205-209 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Morphometric Analysis for
International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 1, Issue 9, December 2014, PP 205-209 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Morphometric Analysis for
The Neotectonic Activity Along the Lower Khazir River by Using SRTM Image and Geomorphic Indices
 Earth Sciences 2015; 4(1): 50-58 Published online February 13, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/earth) doi: 10.11648/j.earth.20150401.15 ISSN: 2328-5974 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5982 (Online) The
Earth Sciences 2015; 4(1): 50-58 Published online February 13, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/earth) doi: 10.11648/j.earth.20150401.15 ISSN: 2328-5974 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5982 (Online) The
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 5, May -2017 Watershed Delineation of Purna River using Geographical
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 5, May -2017 Watershed Delineation of Purna River using Geographical
Potential Groundwater Accumulations Assessment in Drought Prone Area using Remote Sensing and GIS Technology
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 3, pp. 2080-2087 ISSN 2320-0243 doi: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.70 Research Article Open Access Potential Groundwater
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 3, pp. 2080-2087 ISSN 2320-0243 doi: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.70 Research Article Open Access Potential Groundwater
Morphometric Estimation of Parameters of Uttar Mand River Basin, Satara District, Maharashtra, India.
 Morphometric Estimation of Parameters of Uttar Mand River Basin, Satara District, Maharashtra, India. Mr.S.S.Chokakkar 1, Mr.G.N.ChavanPatil, Dr.D.N.Mudgal 3, Dr..Shreenivasa 4 1M.Sc., B.Ed, NET, PhD(Pur.)
Morphometric Estimation of Parameters of Uttar Mand River Basin, Satara District, Maharashtra, India. Mr.S.S.Chokakkar 1, Mr.G.N.ChavanPatil, Dr.D.N.Mudgal 3, Dr..Shreenivasa 4 1M.Sc., B.Ed, NET, PhD(Pur.)
Prioritization of sub-watersheds in semi arid region, Western Maharashtra, India using Geographical Information System
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-10, pp-128-135 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Prioritization of sub-watersheds in semi arid
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-10, pp-128-135 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Prioritization of sub-watersheds in semi arid
Evaluation of Morphometric parameters of drainage networks derived from Topographic Map and Digital Elevation Model using Remote Sensing and GIS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 4, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Evaluation of Morphometric
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 4, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Evaluation of Morphometric
Morphometric Analysis of Sonbhadra Sub- Watershed of Tawa Reservoir Catchment Area of Hoshangabad District, Madhya Pradesh using GIS Techniques
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 2 Issue 07 December 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Morphometric Analysis of Sonbhadra Sub- Watershed of Tawa Reservoir
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 2 Issue 07 December 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Morphometric Analysis of Sonbhadra Sub- Watershed of Tawa Reservoir
MOUNTAIN ORDERING: A METHOD FOR CLASSIFYING MOUNTAINS BASED ON THEIR MORPHOMETRY
 Earth Surface Processes and Landforms Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 24, 653±660 (1999) MOUNTAIN ORDERING: A METHOD FOR CLASSIFYING MOUNTAINS BASED ON THEIR MORPHOMETRY SHUJI YAMADA Department of Geography,
Earth Surface Processes and Landforms Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 24, 653±660 (1999) MOUNTAIN ORDERING: A METHOD FOR CLASSIFYING MOUNTAINS BASED ON THEIR MORPHOMETRY SHUJI YAMADA Department of Geography,
MORPHOMETRY OF BUGGAVANKA WATERSHED IN KADAPA, ANDHRA PRADESH, INDIA USING SPATIAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
 BEST: International Journal of Humanities, Arts, Medicine and Sciences (BEST: IJHAMS) ISSN 2348-0521 Vol. 3, Issue 2, Feb 2015, 1-8 BEST Journals MORPHOMETRY OF BUGGAVANKA WATERSHED IN KADAPA, ANDHRA PRADESH,
BEST: International Journal of Humanities, Arts, Medicine and Sciences (BEST: IJHAMS) ISSN 2348-0521 Vol. 3, Issue 2, Feb 2015, 1-8 BEST Journals MORPHOMETRY OF BUGGAVANKA WATERSHED IN KADAPA, ANDHRA PRADESH,
Landslide Disasters in Uttarakhand: A Case of Landslide Susceptibility Zonation of Alaknanda Valley in Garhwal Himalaya
 Global Journal of Current Research Vol. 2 No. 1. 2013. Pp. 19-26 Copyright by CRDEEP. All Rights Reserved. Full Length Research Paper Landslide Disasters in Uttarakhand: A Case of Landslide Susceptibility
Global Journal of Current Research Vol. 2 No. 1. 2013. Pp. 19-26 Copyright by CRDEEP. All Rights Reserved. Full Length Research Paper Landslide Disasters in Uttarakhand: A Case of Landslide Susceptibility
Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems
 Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 5, 2017 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems Leszek Starkel Department of Geoenvironmental
Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 5, 2017 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems Leszek Starkel Department of Geoenvironmental
MORPHOTECTONIC ANALYSIS IN THE ELIKI FAULT ZONE (GULF OF CORINTH, GREECE)
 ελτίο της Ελληνικής Γεωλογικής Εταιρίας τοµ. XXXVI, 2004 Πρακτικά 10 ου ιεθνούς Συνεδρίου, Θεσ/νίκη Απρίλιος 2004 Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece vol. XXXVI, 2004 Proceedings of the 10 th
ελτίο της Ελληνικής Γεωλογικής Εταιρίας τοµ. XXXVI, 2004 Πρακτικά 10 ου ιεθνούς Συνεδρίου, Θεσ/νίκη Απρίλιος 2004 Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece vol. XXXVI, 2004 Proceedings of the 10 th
Morphometric Analysis of Shaliganga Sub Catchment, Kashmir Valley, India Using Geographical Information System
 Morphometric Analysis of Shaliganga Sub Catchment, Kashmir Valley, India Using Geographical Information System Mohd Iqbal 1, Haroon Sajjad 1, F.A. Bhat 2 1 Department of Geography, Faculty of Natural Sciences,
Morphometric Analysis of Shaliganga Sub Catchment, Kashmir Valley, India Using Geographical Information System Mohd Iqbal 1, Haroon Sajjad 1, F.A. Bhat 2 1 Department of Geography, Faculty of Natural Sciences,
Gis Based On Morphometric Analysis of Part of Manair River Basin in Karimnagar District, Telangana State.
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 0990, p-issn: 098.Volume, Issue Ver. II (Sep. Oct. 07), PP 0-07 www.iosrjournals.org Gis Based On Morphometric Analysis of Part of Manair
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 0990, p-issn: 098.Volume, Issue Ver. II (Sep. Oct. 07), PP 0-07 www.iosrjournals.org Gis Based On Morphometric Analysis of Part of Manair
HW #2 Landscape Travel from A to B 12,
 HW #2 Landscape 2016 Section: Name: ate: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the map below, which represents two bridges that cross the Green River. Letters,, and represent locations
HW #2 Landscape 2016 Section: Name: ate: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the map below, which represents two bridges that cross the Green River. Letters,, and represent locations
DRAINAGE BASIN MORPHOLOGY. Morphometric analysis is defined as the numerical
 C H A P T E R 3 DRAINAGE BASIN MORPHOLOGY 3.1 Introduction Morphometric analysis is defined as the numerical systematization of landform elements measured from topographic maps and provides real basis
C H A P T E R 3 DRAINAGE BASIN MORPHOLOGY 3.1 Introduction Morphometric analysis is defined as the numerical systematization of landform elements measured from topographic maps and provides real basis
Journal of Environment and Earth Science ISSN (Paper) ISSN (Online) Vol. 4, No.5, 2014
 Preparation of Geomorphological Map and Their Characterisation with the help of Remote Sensing and GIS: a case study of Sankha Nadi Drainage Basin Sadhan Malik Guest Lecturer, Memari College, University
Preparation of Geomorphological Map and Their Characterisation with the help of Remote Sensing and GIS: a case study of Sankha Nadi Drainage Basin Sadhan Malik Guest Lecturer, Memari College, University
Springshed Springshed Management Training Curriculum
 Springshed Springshed Management Training Curriculum Management Training Curriculum Draft Version 2 January 2016 The Springs Initiative 2016 The Springs Initiative SESSION TITLE: Section Mapping SECTION:
Springshed Springshed Management Training Curriculum Management Training Curriculum Draft Version 2 January 2016 The Springs Initiative 2016 The Springs Initiative SESSION TITLE: Section Mapping SECTION:
Paper presented in the Annual Meeting of Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, USA, March 2009 ABSTRACT
 Paper presented in the Annual Meeting of Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, USA, March 2009 ABSTRACT CHANGING GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE KOSI RIVER SYSTEM IN THE INDIAN SUBCONTINENT Nupur Bose,
Paper presented in the Annual Meeting of Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, USA, March 2009 ABSTRACT CHANGING GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE KOSI RIVER SYSTEM IN THE INDIAN SUBCONTINENT Nupur Bose,
THE GLOBE DEM PARAMETERIZATION OF THE MOUNTAIN FEATURES OF MINOR ASIA INTRODUCTION AND AIM
 THE GLOBE DEM PARAMETERIZATION OF THE MOUNTAIN FEATURES OF MINOR ASIA George Ch. Miliaresis Department of Topography Technological Educational Institute of Athens 38 Tripoleos Str. Athens, 104-42, Greece
THE GLOBE DEM PARAMETERIZATION OF THE MOUNTAIN FEATURES OF MINOR ASIA George Ch. Miliaresis Department of Topography Technological Educational Institute of Athens 38 Tripoleos Str. Athens, 104-42, Greece
Neoproterozoic Malani Magmatism, northwestern Indian shield: Not a plume product. Kamal K. Sharma
 Neoproterozoic Malani Magmatism, northwestern Indian shield: Not a plume product Kamal K. Sharma Department of Geology, Government Postgraduate College, Sirohi (Rajasthan) 307001 India sharmasirohi@yahoo.com
Neoproterozoic Malani Magmatism, northwestern Indian shield: Not a plume product Kamal K. Sharma Department of Geology, Government Postgraduate College, Sirohi (Rajasthan) 307001 India sharmasirohi@yahoo.com
INTRODUCTION. Climate
 INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
Morphometric analysis of Kharlikani watershed in Odisha, India using spatial information technology Kishor Choudhari 1, Panigrahi B 2, Paul J.
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 4, 2014 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Morphometric analysis of Kharlikani
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 4, 2014 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Morphometric analysis of Kharlikani
CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS
 80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
