EOSC116 Assignment: Some dinosaur fossils from western North America
|
|
|
- Brett Pierce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
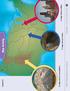
1 EOSC116 Assignment: Some dinosaur fossils from western North America Learning goals 1. Interpret some details about given dinosaur and other fossils. 2. Extend the work done in the previous assignment by considering opportunities and limitations for relating dinosaur populations associated with these specimens with each other. Introduction and purpose The previous assignment introduced you to many real and possible fossils and fossil locations related to western North America in the Late Cretaceous. In this assignment you will work with some of the specific fossil specimens in more detail, interpreting some quantitative characteristics of the organisms, and thinking about the extent to which ages and locations enable (or limit) useful (or not!) comparison between dinosaur populations. Instructions 1. Review the resources you are given about the 5 specimens or specimen locations. While reading, use the following table to gather information needed to answer questions. The table will not be tested but you will need the information while working on questions. 2. Complete a paper copy of this worksheet, answering all questions posed. Maps, fossils and other information are provided in the separate collection of resources. 3. When you are finished this worksheet, proceed to the associated quiz on Connect. This is not a test because you will copy results from your paper worksheet into similar automatically graded questions. This procedure automates the delivery and grading of your work in this fully online course. 4. DO NOT work on the Connect quiz before finishing the paper version. You will run out of time. Location number and place name Specimen (fossil types, organism names) Dates &/or age names
2 Begin here 1. After learning about our five specimens, find location numbers on the map where fossils were found and identify locations in spaces provided in the following table (no zeros, no spaces, just the one or two digit number). Specimen descriptions The Lambeosaurus displayed at the PME. Recently found Theropod thigh bone fossil. Late Cretaceous Carnosaur, Hadrosaurs and Ornithomimus tracks. Early Cretaceous turtle & foot print fossils found by P. Mustard. Late Cretaceous ankylosaur trackways that sparked the discovery of many types of dinosaur and other fossils. Map location 2. Now we will put these fossils into the context of geological time. Your resources include the Jurassic and Cretaceous portion of the Geological time scale published by the Geological Society of America. From which named Age (NOT epoch) do our six fossils come from? Specimen descriptions The Lambeosaurus displayed at the PME. Recently found Theropod thigh bone fossil. Carnosaur, Hadrosaurs and Ornithomimus tracks at Ross River. Youngest turtle & foot print fossils found by P. Mustard. Oldest fossils at Tumbler Ridge. Youngest fossils at Tumbler Ridge. Named age 3. What evidence helped determine the age of the theropod thigh bone recently found in the Gulf Islands of Washington State? a) Dating by association of this fossil with the sediments in which it was buried. b) Radiometric dating of bone material c) Ash layer containing dateable minerals. d) Radiometric dating of surrounding or nearby rock material e) Distinctive characteristics of the bone indicate a type of theropod of well constrained age. 4. What is one reason that this was such an unusual specimen? a) Fossils of such theropods are globally rare. b) Fossilization of this type of specimen is uncommonly difficult c) This area was isolated during the existence of dinosaurs d) It is a land based animal found fossilized in marine rocks e) The region was mostly desert at that time. f) The western edge of North America was too tectonically active to be a suitable dinosaur habitat. 5. Was this fossil part of the thigh of a monster theropod like Daspletosaurus, or a small one like Avimimus Portentosus? (You are not required to know these terms, but it is interesting to look them up.) How can paleontologists estimate the approximate size of this dinosaur with only a fragment of a thigh bone? The answer is by comparing to other theropod fossils that are more complete. Resources contain all the information you need to make your own estimate of the length of the whole thigh bone. What measurement for x do you obtain using the scale (ruler) provided? Enter the number in units of millimetres. You must be correct to within plus or minus 30mm. BE CAREFUL OF UNITS. [ ]
3 6. Now use your value of x and the graph provided to estimate the thigh bone length in units of mm. What estimated length do you obtain? You must be correct to within plus or minus 60mm. [ ] 7. Having read resources about all 5 specimens (Pacific coast theropod, UBC s Lambeosaur, Ross River, Tumbler Ridge, N. of Terrace), at which 3 location was evidence found of Hadrosaurs of any age? 8. In the previous question you identified where evidence of Hadrosaurs was found. However these finds were not all the same age. Which two or more of these age ranges are represented by all these Hadrosaur finds? (You don t have to attach ages to places just identify those ages that are represented by the Hadrosaur finds encountered in this exercise.) a. 120 ± 5Ma b. 90 ±5Ma c. 83 ±5 Ma d. 74 ±5 Ma 9. At which 3 locations did resources you were given indicate that evidence of Theropods or Carnosaurs had been found? 10. In the previous question you identified where evidence of Theropod or Carnosaur fossils was found. However these finds were not all the same age. Which two or more of these age ranges are represented by all these finds? a. 120 ± 5Ma b. 90 ±5Ma c. 83 ±5 Ma d. 74 ±5 Ma 11. At which 3 of the five locations did our resources identify evidence that may be suitable for comparing similarities of dinosaur populations at 83 ±5 Ma? 12. At which of five locations did our resources identify evidence that may be suitable for comparing similarities of dinosaur populations at 73 ±5Ma?
4 13. At which one of these five locations did our resources identify evidence only for dinosaur populations much older than 84Ma? 14. One more fossil worth studying briefly is the PME s fantastic ammonite specimen. The specimen s label on its black base tells us where it was found. Look up this location and identify which of our 13 dot locations this is likely to be closest to. Enter just the dot s number with no words or spaces. [ ]. 15. In this course s previous assignment we claimed that a specimen of type St #3 (a land based organism) was found near the ammonite s location in association with a 65Ma age marker, and another specimen of type St #5 (shallow or coastal waters) was found there in association with an 85Ma age marker. Therefore, which environment was associated with the time closest to the age attributed to the Ammonite? a) Land b) Shallow or coastal c) Deep d) Neither 16. Is this environment consistent with the environment you expect ammonites to have lived in? a) Yes b) No c) Cannot be determined d) I don t know how to answer this. 17. Given that these two different fossils were found in relatively close proximity, which one or more of these explanations might help explain how both of these fossils could be found in this region of Alberta? a) The shape of the shallow sea s coastline could have been variable enough to explain this result even if both fossils were found near this location. b) The time between 65 Ma and the ammonite s age was sufficient for the sea level (i.e. the coast line s position) to have risen and lowered enough so that both fossils could have been found near each other. c) Both fossils could have lived in the same environment. d) One of the fossils could have been transported from elsewhere. e) Either one of these organisms could have moved itself from its normal living environment into the environment normally occupied by the other. f) None of these ideas are reasonable. 18. Let s wrap up this exercise with a summary paragraph. Select correct words for each from these options: increased, decreased, more, less, north, south, east, west. In a previous exercise we learned that before 85 Ma, the ocean plate off the [ ] coast of North America was moving [ ] ward so that elevations in the Rocky Mountains [ ] and elevations in the foreland basin ([ ] of the Rockies) [ ]. Between 85 and 65 Ma ocean plate motion shifted to moving [ ] ward and the inland sea s sea level steadily [ ]. As a result of these tectonic processes, dinosaurs associated with fossils recently found near Vancouver (i.e. [ ] of the Rockies) were [ ] likely to be genetically similar to dinosaurs in Asia and probably [ ] like those living near the inland sea. However, relating geographically separate fossils must be done cautiously. For example, fossils at Terrace are [ ] of the Rockies but are
5 [ ] ancient than all other fossils we encountered. In comparison, fossils at Tumbler ridge are much [ ] varied in age and [ ] varied in terms of organism types. Meanwhile, fossils from different living environments that were found a few kilometers apart in [ ] [ ] ern Alberta, but with a difference in age of 3 5 million years, suggest that the inland sea coast was probably [ ] complicated and [ ] variable over time than might be assumed when finding only single fossils at any one location. That s it for the worksheet. Now proceed to the Connect quiz for data entry. If you have done all work on this worksheet, the Connect quiz should take only 15 minutes or so. It s just a matter of copying answers from this worksheet into multiple choice, matching, fill blank, and drop down choice questions.
MOR SEAWAY TEACHERS. A CHANGING LANDSCAPE Activity Overview BIG IDEA
 MOR SEAWAY 03 Activity Overview BIG IDEA The Earth and its landscapes change over time. Scientists use the fossil record to understand the Earth s environments and climates millions of years ago. OBJECTIVE
MOR SEAWAY 03 Activity Overview BIG IDEA The Earth and its landscapes change over time. Scientists use the fossil record to understand the Earth s environments and climates millions of years ago. OBJECTIVE
Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 7 No School 8 E 9 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Continental Drift Notes
clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 7 No School 8 E 9 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Continental Drift Notes
Geologic Time Scavenger Hunt
 Geologic Time Scavenger Hunt Name: Class Period: For this activity, go to the resource page on our class website. Find the link titled Understanding Geologic Time which can be found under the Plate Tectonics
Geologic Time Scavenger Hunt Name: Class Period: For this activity, go to the resource page on our class website. Find the link titled Understanding Geologic Time which can be found under the Plate Tectonics
1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit?
 Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Earth s Changing Surface Chapter 4
 Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
LINEAGE ACTIVITIES Draft Descriptions December 10, Whale Evolution
 LINEAGE ACTIVITIES Draft Descriptions December 10, 2018 Institutions participating in the Lineage program will receive three fossil-based activities. All participants will receive Whale Evolution, and
LINEAGE ACTIVITIES Draft Descriptions December 10, 2018 Institutions participating in the Lineage program will receive three fossil-based activities. All participants will receive Whale Evolution, and
CRETACEOUS ALBERTA SCIENCE HALL. 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in
 Worksheet Level 3 p. 1 CRETACEOUS ALBERTA 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in 2. What type of dinosaur was found at this site, how many individuals were there, and what was their age range?
Worksheet Level 3 p. 1 CRETACEOUS ALBERTA 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in 2. What type of dinosaur was found at this site, how many individuals were there, and what was their age range?
Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/2 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/2 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 1 No School 2 E 3 O *Vocabulary *Continental Drift Notes and Sea Floor
clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/2 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 1 No School 2 E 3 O *Vocabulary *Continental Drift Notes and Sea Floor
Lab 7: Plate tectonics
 Geology 115/History 150 Name(s): Lab 7: Plate tectonics Plate tectonics is the theory that is used to explain geological phenomena worldwide. For this reason, most of the useful maps that illustrate plate
Geology 115/History 150 Name(s): Lab 7: Plate tectonics Plate tectonics is the theory that is used to explain geological phenomena worldwide. For this reason, most of the useful maps that illustrate plate
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms and bodies of
 Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Refer to the map on page 173 to answer the following questions.
 Chapter 8-1 Plate Tectonics 1. Brainstorm the type of evidence that would indicate a climate change and how this evidence supports the theory of continental drift. Tropical fossils in cold regions Evidence
Chapter 8-1 Plate Tectonics 1. Brainstorm the type of evidence that would indicate a climate change and how this evidence supports the theory of continental drift. Tropical fossils in cold regions Evidence
GEOSCIENCE 105 THE DYNAMIC EARTH FIRST ONE-HOUR EXAMINATION. Tuesday, October 20, 1998 NAME STUDENT #
 GEOSCIENCE 105 THE DYNAMIC EARTH FIRST ONE-HOUR EXAMINATION Tuesday, October 20, 1998 NAME STUDENT # Instructions: 1. Answer all questions legibly. 2. Put your name and student number on this front page.
GEOSCIENCE 105 THE DYNAMIC EARTH FIRST ONE-HOUR EXAMINATION Tuesday, October 20, 1998 NAME STUDENT # Instructions: 1. Answer all questions legibly. 2. Put your name and student number on this front page.
Lab # - Ocean Bottom Topography. Background Information:
 Name Lab Grade /10 Date Period Lab # - Ocean Bottom Topography Background Information: Ocean depth varies markedly from one location to another. Over large areas water depth is less than 200m (650 ft);
Name Lab Grade /10 Date Period Lab # - Ocean Bottom Topography Background Information: Ocean depth varies markedly from one location to another. Over large areas water depth is less than 200m (650 ft);
Geologic Time Composed by: Lee Falkena Adapted By: Braden Conrad-Hiebner & Cherie Haury-Artz
 Topic/Unit - Geologic Time Geologic Time Composed by: Lee Falkena Adapted By: Braden Conrad-Hiebner & Cherie Haury-Artz Grade Level* - 4-8 *(can be adapted for younger grades) Iowa Science Standards 2-
Topic/Unit - Geologic Time Geologic Time Composed by: Lee Falkena Adapted By: Braden Conrad-Hiebner & Cherie Haury-Artz Grade Level* - 4-8 *(can be adapted for younger grades) Iowa Science Standards 2-
TEACHER PAGE Trial Version
 TEACHER PAGE Trial Version * After completion of the lesson, please take a moment to fill out the feedback form on our web site (https://www.cresis.ku.edu/education/k-12/online-data-portal)* Lesson Title:
TEACHER PAGE Trial Version * After completion of the lesson, please take a moment to fill out the feedback form on our web site (https://www.cresis.ku.edu/education/k-12/online-data-portal)* Lesson Title:
Map Activity. A map shows cities. A map shows rivers. A map shows mountains. Lesson 5. Ancient Earth Journey to the Center of the Earth
 Lesson 5 Map Activity A map shows mountains. A map shows rivers. A map shows cities. Lesson 5 1 2 Find the map. Find the mountain. Iceland is an island. There is water all around an island. An island is
Lesson 5 Map Activity A map shows mountains. A map shows rivers. A map shows cities. Lesson 5 1 2 Find the map. Find the mountain. Iceland is an island. There is water all around an island. An island is
Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past
 Table of Contents Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past Section : Section 2: Relative Ages of Rocks Section 3: Absolute Ages of Rocks Traces of the Distant Past Paleontologists, scientists who study fossils,
Table of Contents Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past Section : Section 2: Relative Ages of Rocks Section 3: Absolute Ages of Rocks Traces of the Distant Past Paleontologists, scientists who study fossils,
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced 451/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit P.M. THURSDAY, 10 January 2008 (1 hour) Examiner Question
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 2 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced 451/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit P.M. THURSDAY, 10 January 2008 (1 hour) Examiner Question
Crustal Activity. Plate Tectonics - Plates - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones
 Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
Science 20. Unit C: The Changing Earth. Assignment Booklet C3
 Science 20 Unit C: The Changing Earth Assignment Booklet C3 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 3 Assignment Total Possible Marks 45 Your Mark Science 20 Unit C: The Changing Earth
Science 20 Unit C: The Changing Earth Assignment Booklet C3 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 3 Assignment Total Possible Marks 45 Your Mark Science 20 Unit C: The Changing Earth
MOR TIME TEACHERS. ONCE UPON A TIME Activity Overview BIG IDEA
 MOR TIME 04 Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND The geologic time scale can be challenging for students to understand. This activity explores how scientists divide the Earth s long history
MOR TIME 04 Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND The geologic time scale can be challenging for students to understand. This activity explores how scientists divide the Earth s long history
Geologic History Unit Notes. Relative age - general age statement like older, younger more recent
 Geologic History Unit Notes Relative age - general age statement like older, younger more recent Absolute age - specific age like 4,600 million years old Fundamental Principles of Relative Dating 1. Uniformitarianism
Geologic History Unit Notes Relative age - general age statement like older, younger more recent Absolute age - specific age like 4,600 million years old Fundamental Principles of Relative Dating 1. Uniformitarianism
Lab Activity Mid-Atlantic Ridge
 Lab Activity Mid-Atlantic Ridge Key Features: Constructing Profiles of: Atlantic Ocean floor Age of the Atlantic Ocean bedrock Magnetic Polarity of ocean bedrock By Kaitlin Coder https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/nys-earth-science-and-living-environment-regents
Lab Activity Mid-Atlantic Ridge Key Features: Constructing Profiles of: Atlantic Ocean floor Age of the Atlantic Ocean bedrock Magnetic Polarity of ocean bedrock By Kaitlin Coder https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/nys-earth-science-and-living-environment-regents
Section 1: How Did Life Begin? Chapter 19: History of Life on Earth. Section 2: The Age of Earth
 Chapter 19: History of Life on Earth Section 1: How Did Life Begin? I. The Basic Chemicals of Life A. 1920s B. Earth s early oceans contained large amounts of organic molecules C. Molecules formed spontaneously
Chapter 19: History of Life on Earth Section 1: How Did Life Begin? I. The Basic Chemicals of Life A. 1920s B. Earth s early oceans contained large amounts of organic molecules C. Molecules formed spontaneously
Online Fossil Lab Fossil Formation How Fossils Form 1. Describe the process in which fossils form.
 Name: Online Fossil Lab Fossil Formation How Fossils Form 1. Describe the process in which fossils form. Period: 2. What is a Mold? 3. What is a cast? Getting into the Fossil Record 4. What is the fossil
Name: Online Fossil Lab Fossil Formation How Fossils Form 1. Describe the process in which fossils form. Period: 2. What is a Mold? 3. What is a cast? Getting into the Fossil Record 4. What is the fossil
3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change?
![3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? 3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change?](/thumbs/89/98260180.jpg) Science 8 SCIENCE QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT 2 3. [ES 3] S 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? A. Glaciers melt
Science 8 SCIENCE QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT 2 3. [ES 3] S 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? A. Glaciers melt
24. Ocean Basins p
 24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics. Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events.
 Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) ONE single landmass
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) ONE single landmass
READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 11, Plate Tectonics GEOL 131 Fall pts
 READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 11, Plate Tectonics GEOL 131 Fall 2018 61 pts NAME DUE: Tuesday, November 20 Continental Drift: An Idea Before Its Time (p. 317-321) 1. Fill in the blanks in this sentence from
READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 11, Plate Tectonics GEOL 131 Fall 2018 61 pts NAME DUE: Tuesday, November 20 Continental Drift: An Idea Before Its Time (p. 317-321) 1. Fill in the blanks in this sentence from
Crustal Boundaries. As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries they interact in various ways. Convergent Transform Divergent
 Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Evidence for Continental Drift and The Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Evidence for Continental Drift and The Theory of Plate Tectonics Did you know that the coal that is mined in Pennsylvania was actually formed from tropical plant life near the Equator? How did it travel
Evidence for Continental Drift and The Theory of Plate Tectonics Did you know that the coal that is mined in Pennsylvania was actually formed from tropical plant life near the Equator? How did it travel
Florida s Changing Shape
 Florida s Changing Shape Background: For much of its history, Florida was underwater. At first, Florida consisted solely of the Florida Platform, a limestone base formed from the calcium carbonate remains
Florida s Changing Shape Background: For much of its history, Florida was underwater. At first, Florida consisted solely of the Florida Platform, a limestone base formed from the calcium carbonate remains
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
5. Compare the density of the oceanic crust to continental crust. 6. What kind of plate boundary is this? convergent
 The youngest rock is in the middle (at ridge) and it gets older on either side as you move away in a symmetrical pattern. 1. How does the age of the seafloor compare on either side of the ridge? A = youngest
The youngest rock is in the middle (at ridge) and it gets older on either side as you move away in a symmetrical pattern. 1. How does the age of the seafloor compare on either side of the ridge? A = youngest
Plate Tectonics Tutoiral. Questions. Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman. Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test
 Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman Print Close Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test Plate Tectonics Tutoiral URL: http://www.hartrao.ac.za/geodesy/tectonics.html Questions 1. Fossils of organisms that lived
Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman Print Close Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test Plate Tectonics Tutoiral URL: http://www.hartrao.ac.za/geodesy/tectonics.html Questions 1. Fossils of organisms that lived
Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area
 Excerpt from Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area by Ted Konigsmark ISBN 0-9661316-4-9 GeoPress All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced without written permission in writing,
Excerpt from Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area by Ted Konigsmark ISBN 0-9661316-4-9 GeoPress All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced without written permission in writing,
Slow and Steady By ReadWorks
 By ReadWorks How did all the amazing things on our planet form? How did magnificent mountain ranges rise up in one place and beautiful beaches form elsewhere? Why do some places experience earthquakes
By ReadWorks How did all the amazing things on our planet form? How did magnificent mountain ranges rise up in one place and beautiful beaches form elsewhere? Why do some places experience earthquakes
60% water. Big Bang: 14,000 millions years ago The Earth originated about 4,500 millions years ago its orbit allows water to exist in a liquid state!
 Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Complete by Thursday at 11:00 PM
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Complete by Thursday at 11:00 PM Name Expedition Objectives Learn about the types of plate boundaries and their key characteristics
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Complete by Thursday at 11:00 PM Name Expedition Objectives Learn about the types of plate boundaries and their key characteristics
MiSP Plate Tectonics Worksheet #1 L1
 MiSP Plate Tectonics Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date SEA FLOOR SPREADING (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You have already learned about Continental Drift, divergent, convergent, and transform plate boundaries, mid-ocean
MiSP Plate Tectonics Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date SEA FLOOR SPREADING (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You have already learned about Continental Drift, divergent, convergent, and transform plate boundaries, mid-ocean
FOSSILS IN YOUR BACKYARD
 MOR BACKYARD 12 Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND Millions of years ago, dinosaurs roamed all over our planet Why is it then that we only find dinosaurs in certain geographical locations?
MOR BACKYARD 12 Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND Millions of years ago, dinosaurs roamed all over our planet Why is it then that we only find dinosaurs in certain geographical locations?
test date Name date Review: Geologic Time & Geologic Procesess-: You will record 1-38 answers on the scan sheet! These are worth 1.
 Review: Geologic Time & Geologic Procesess-: You will record 1-38 answers on the scan sheet! These are worth 1.5 points each Use your EARTH HISTORY CHART Part I. Matching All of the statements match to
Review: Geologic Time & Geologic Procesess-: You will record 1-38 answers on the scan sheet! These are worth 1.5 points each Use your EARTH HISTORY CHART Part I. Matching All of the statements match to
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Tales of the Past. Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education
 Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
Activity - Using GPS Data and Geologic Markers to Track Plate Motion
 Name: Date: Hour: Activity - Using GPS Data and Geologic Markers to Track Plate Motion Section Points Received Points Possible Part A Analysis 4.5 Part B Analysis 11.5 Total 16 Introduction: GPS satellites
Name: Date: Hour: Activity - Using GPS Data and Geologic Markers to Track Plate Motion Section Points Received Points Possible Part A Analysis 4.5 Part B Analysis 11.5 Total 16 Introduction: GPS satellites
Geology Project 1 Plate Motions
 Due: 9/9/08 Geology 1002.1 Project 1 Plate Motions Plate Tectonics explains how the earth s lithosphere has evolved over geologic time. This theory explains why the Pacific Northwest has earthquakes and
Due: 9/9/08 Geology 1002.1 Project 1 Plate Motions Plate Tectonics explains how the earth s lithosphere has evolved over geologic time. This theory explains why the Pacific Northwest has earthquakes and
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
Collision and transform Boundaries
 Collision and transform Boundaries I. The collision boundary Sometimes when two plates move together they are both continental rather than one being continental and one being oceanic as at the destructive
Collision and transform Boundaries I. The collision boundary Sometimes when two plates move together they are both continental rather than one being continental and one being oceanic as at the destructive
FOSSIL EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
 Biology FOSSIL EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION You are responsible for knowing all the information contained below. Read the passage before completing the assignment. Scientists have good evidence that the earth
Biology FOSSIL EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION You are responsible for knowing all the information contained below. Read the passage before completing the assignment. Scientists have good evidence that the earth
Chapter 6, Part Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great.
 Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 2 of 40
 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor
 Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Dynamic Crust Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
NAME Lab TA. Introduction to Oceanography, EPSS15 Practice Lecture Exam #1, Fall 2017 Exam#
 NAME Lab TA Introduction to Oceanography, EPSS15 Practice Lecture Eam #1, Fall 2017 Eam# 654321 Instructions 1. PRINT your name and lab TA s name on BOTH the cover sheet of this eam and on the SCANTRON
NAME Lab TA Introduction to Oceanography, EPSS15 Practice Lecture Eam #1, Fall 2017 Eam# 654321 Instructions 1. PRINT your name and lab TA s name on BOTH the cover sheet of this eam and on the SCANTRON
* If occurs, fossils that formed in shallow water may be found in water. Subsidence mean the crust is.
 Name Notes: Topic 5B Topic 5B: The Dynamic Crust A. What evidence exists that proves the Earth s Crust is and has moved? Earth Science 1. Tilted, folded or faulted strata Strata is a term that refers to.
Name Notes: Topic 5B Topic 5B: The Dynamic Crust A. What evidence exists that proves the Earth s Crust is and has moved? Earth Science 1. Tilted, folded or faulted strata Strata is a term that refers to.
Title: Conceptual Learning Outcomes of Google Earth Exploration in Introductory. Learning through Research, Northeastern University, Boston, MA,
 Title: Conceptual Learning Outcomes of Google Earth Exploration in Introductory Geoscience Courses Journal: Research in Science Education Authors: Kelsey S. Bitting, Ph.D. 1, Marsha J. McCartney, Ph.D.
Title: Conceptual Learning Outcomes of Google Earth Exploration in Introductory Geoscience Courses Journal: Research in Science Education Authors: Kelsey S. Bitting, Ph.D. 1, Marsha J. McCartney, Ph.D.
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #16 SUBDUCTION BOUNDARIES*
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #16 SUBDUCTION BOUNDARIES* INTRODUCTION The vast majority of earthquakes occur at plate boundaries. The deepest earthquakes occur at subduction boundaries where lithosphere
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #16 SUBDUCTION BOUNDARIES* INTRODUCTION The vast majority of earthquakes occur at plate boundaries. The deepest earthquakes occur at subduction boundaries where lithosphere
Plate Tectonic Theory
 Have you ever looked at a world map and noticed the shapes of the continents? Have you ever noticed how some continents appear to fit together like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle? Why do you think this
Have you ever looked at a world map and noticed the shapes of the continents? Have you ever noticed how some continents appear to fit together like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle? Why do you think this
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE
 TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
PSc 201 Chapter 3 Homework. Critical Thinking Questions
 PSc 201 Chapter 3 Homework Critical Thinking Questions 1. (adapted from text) Seawater is denser than fresh water. A ship moving from the Atlantic Ocean into the Great Lakes goes from seawater to fresh
PSc 201 Chapter 3 Homework Critical Thinking Questions 1. (adapted from text) Seawater is denser than fresh water. A ship moving from the Atlantic Ocean into the Great Lakes goes from seawater to fresh
A Trip Through Geologic Time
 A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
Module 7, Lesson 1 Water world
 Module 7, Lesson 1 Water world Imagine that the year is 2100. Scientists have determined that the rapidly warming climate of the earth will cause the ice sheets of Antarctica to break apart and melt at
Module 7, Lesson 1 Water world Imagine that the year is 2100. Scientists have determined that the rapidly warming climate of the earth will cause the ice sheets of Antarctica to break apart and melt at
depositional environment = one type of sediment/sedimentary rock = sedimentary structure =
 High School Advanced Geology Exam May 2014 Name: Provide complete short answers to the follow questions. 1. Name one depositional environment for sediment/sedimentary rocks. Name one type of sediment/sedimentary
High School Advanced Geology Exam May 2014 Name: Provide complete short answers to the follow questions. 1. Name one depositional environment for sediment/sedimentary rocks. Name one type of sediment/sedimentary
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics. Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events.
 Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) He noticed that the continents
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) He noticed that the continents
Station 8 Station Station 9 Station Station 10 Station Sample 9 Station
 Fossil Lab Answer sheet It s time to learn Station 1 about Fossils! 1. 2. Station 2 3. 4. Station 8 Station 3 19. 20. 5. 6. 7. Station 9 Station 4 21. 22. 8. 9. 10. Station 10 Station 5 11. 12. Station
Fossil Lab Answer sheet It s time to learn Station 1 about Fossils! 1. 2. Station 2 3. 4. Station 8 Station 3 19. 20. 5. 6. 7. Station 9 Station 4 21. 22. 8. 9. 10. Station 10 Station 5 11. 12. Station
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B
 GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
Movement of the Earth s Crust: Formation of: Mountain s Plateau's and Dome s
 Movement of the Earth s Crust: Formation of: Mountain s Plateau's and Dome s References Information taken from several places including Prentice Hall Earth Science: @ http://www.eram.k12.ny.us/education/components/docmgr/default.php?sectiondetaili
Movement of the Earth s Crust: Formation of: Mountain s Plateau's and Dome s References Information taken from several places including Prentice Hall Earth Science: @ http://www.eram.k12.ny.us/education/components/docmgr/default.php?sectiondetaili
SAMPLE. Guided Instruction
 DIRECTIONS You will learn that scientists have established a fossil record that reveals that evolution can proceed slowly with gradual changes or in spurts with sudden changes. You will also learn that
DIRECTIONS You will learn that scientists have established a fossil record that reveals that evolution can proceed slowly with gradual changes or in spurts with sudden changes. You will also learn that
FOSSIL EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
 FOSSIL EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION You are responsible for knowing all the information contained below. Read the passage before completing the assignment. Scientists have good evidence that the earth is very
FOSSIL EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION You are responsible for knowing all the information contained below. Read the passage before completing the assignment. Scientists have good evidence that the earth is very
Name Geo 4 Practice Match the principle on the left (column A) with the definition (or part of the definition) on the right (column B).
 Name Geo 4 Practice 1 Target 1 2 3 4 Geo 4 I can define the create, alter and/or destroy the rock record. I can interpret a diagram to determine the sequence of events (relative age) in Earth s history
Name Geo 4 Practice 1 Target 1 2 3 4 Geo 4 I can define the create, alter and/or destroy the rock record. I can interpret a diagram to determine the sequence of events (relative age) in Earth s history
Lecture Outline Friday January 12 Friday January 19, 2018
 Lecture Outline Friday January 12 Friday January 19, 2018 Questions?? Key Points for today The structure of the Earth Introduction to Plate Tectonic Theory and Convection Chapter 2 Development of the Plate
Lecture Outline Friday January 12 Friday January 19, 2018 Questions?? Key Points for today The structure of the Earth Introduction to Plate Tectonic Theory and Convection Chapter 2 Development of the Plate
Plate Tectonics. Structure of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
The United States & Canada. A Regional Study of Anglo America
 A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
Exploring geology: The story of the rocks and landscape of the Kettleman Hills
 Exploring geology: The story of the rocks and landscape of the Kettleman Hills Table of contents Lesson Plan Details Overview Overarching question Driving questions for students Module description Length
Exploring geology: The story of the rocks and landscape of the Kettleman Hills Table of contents Lesson Plan Details Overview Overarching question Driving questions for students Module description Length
Unit 5 Possible Test Questions Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras HISTORICAL GEOLOGY
 Revised 8/16 Unit 5 Possible Test Questions Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras HISTORICAL GEOLOGY Mesozoic Era Eons, Eras and Periods 1. List the Mesozoic periods in order (oldest to youngest). End of the Paleozoic
Revised 8/16 Unit 5 Possible Test Questions Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras HISTORICAL GEOLOGY Mesozoic Era Eons, Eras and Periods 1. List the Mesozoic periods in order (oldest to youngest). End of the Paleozoic
Plate Tectonics Practice Test
 Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name:
 Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name: S.W.B.A.T Explain how time can be divided into units Relate changes of Earth s to divisions on the geologic time scale Describe how plate tectonics affects Geologic
Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name: S.W.B.A.T Explain how time can be divided into units Relate changes of Earth s to divisions on the geologic time scale Describe how plate tectonics affects Geologic
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Station Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus
 Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Theory of Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Directed Reading. Section: Continental Drift. years ago? WEGENER S HYPOTHESIS
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Continental Drift 1. Who obtained new information about the continents and their coastlines 400 years ago? 2. What did people notice when they studied new world
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Continental Drift 1. Who obtained new information about the continents and their coastlines 400 years ago? 2. What did people notice when they studied new world
LAB 7. Lab 7. Formation of Geologic Features: How Can We Explain the Growth of the Hawaiian Archipelago Over the Past 100 Million Years?
 LAB 7 Lab Handout Lab 7. Formation of Geologic Features: How Can We Explain the Growth of the Hawaiian Archipelago Over the Past 100 Million Years? Introduction Scientists use the theory of plate tectonics
LAB 7 Lab Handout Lab 7. Formation of Geologic Features: How Can We Explain the Growth of the Hawaiian Archipelago Over the Past 100 Million Years? Introduction Scientists use the theory of plate tectonics
2. Explain why there are these two predominate elevations. (Hint: think about isostasy and the type of materials we used to demonstrate buoyancy).
 IDS 102 Plate Tectonics Questions Part I: Observations- Four maps of world are positioned around the room. Answer the questions associated with each map and record your general observations about the maps.
IDS 102 Plate Tectonics Questions Part I: Observations- Four maps of world are positioned around the room. Answer the questions associated with each map and record your general observations about the maps.
Potential short answer questions: What is Pangea? Describe at least 4 pieces of evidence that led Wegener to suggest the theory of Continental Drift.
 6th Grade Earth Science Fall Semester Mid-Term Study Guide The mid-term may include: 4 short answer questions,1-2 sketches to draw and/or label, 4 partially filled charts which you should complete, 30
6th Grade Earth Science Fall Semester Mid-Term Study Guide The mid-term may include: 4 short answer questions,1-2 sketches to draw and/or label, 4 partially filled charts which you should complete, 30
Geology 101 Study Guide #4
 Geology 101 Study Guide #4 Our last unit is the study of the earthquakes, the Earth s interior and plate tectonics. We live in a region which has been added on to North America through plate tectonics.
Geology 101 Study Guide #4 Our last unit is the study of the earthquakes, the Earth s interior and plate tectonics. We live in a region which has been added on to North America through plate tectonics.
Seafloor Spreading and Paleomagnetism Activity
 Name: PART A: Ocean Bottom Profile Background: Seafloor spreading is the hypothesis that the sea floor moves sideways away from the crest of the mid- ocean ridge. It is estimated that 20 volcanic eruptions
Name: PART A: Ocean Bottom Profile Background: Seafloor spreading is the hypothesis that the sea floor moves sideways away from the crest of the mid- ocean ridge. It is estimated that 20 volcanic eruptions
Visualizing hurricanes
 Visualizing hurricanes NAME: DATE: Scientific visualization is an integral part of the process of simulating natural phenomena. In the computational sciences, the main goal is to understand the workings
Visualizing hurricanes NAME: DATE: Scientific visualization is an integral part of the process of simulating natural phenomena. In the computational sciences, the main goal is to understand the workings
OS 1 The Oceans Fall 2007
 Name: Plate Tectonics (you must turn Activities 1-2 in during Section) Activity 1: Plate Boundaries A plate boundary simply describes where two plates (either oceanic or continental material) meet. There
Name: Plate Tectonics (you must turn Activities 1-2 in during Section) Activity 1: Plate Boundaries A plate boundary simply describes where two plates (either oceanic or continental material) meet. There
What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley
 1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
6. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are
 11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE!
 ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
Internet Interactive Rock Cycle
 Internet Interactive Rock Cycle Directions: Go to the website http://www.uky.edu/as/geology/howell/goodies/elearning/module05swf.swf and answer the questions below. Part I: Igneous Rocks (click on Igneous
Internet Interactive Rock Cycle Directions: Go to the website http://www.uky.edu/as/geology/howell/goodies/elearning/module05swf.swf and answer the questions below. Part I: Igneous Rocks (click on Igneous
Plate Tectonics. Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15
 1 Plate Tectonics Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
1 Plate Tectonics Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
Name: Period: Date: ID: A. Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank.
 Name: Period: _ Date: _ ID: A Unit 7 Practice Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank. 1. What term describes the movement of rock
Name: Period: _ Date: _ ID: A Unit 7 Practice Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank. 1. What term describes the movement of rock
PSI Paleo Sleuth Investigation Grades 4-8
 PSI Paleo Sleuth Investigation Grades 4-8 Paleo Sleuth Investigations, or PSI, includes four activities to be used in succession that focus around fossils in Nebraska and the Ashfall Fossil Beds State
PSI Paleo Sleuth Investigation Grades 4-8 Paleo Sleuth Investigations, or PSI, includes four activities to be used in succession that focus around fossils in Nebraska and the Ashfall Fossil Beds State
