Be is produced by reactions of cosmic ray protons with N 2 and O 2 in the upper atmosphere
|
|
|
- Roger Baker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10 Be is produced by reactions of cosmic ray protons with N 2 and O 2 in the upper atmosphere 10 Be Be is a particle reactive element becomes concentrated in clayrich oceanic sediments 10 Be then undergoes decay to 10 B with a half-life of about 1.5 Ma (long enough to be subducted, but quickly lost to mantle systems).
2 100 km Ma Time to burial to 100 km 30 Subduction Velocity: 10 cm/a 100 km 2.0 Ma
3 10 Be Incorporation of cosmogenic 10 Be in island arcs? Accreted prism Subducted material underplated Subducted material melted, underplated and intruded as magma? Material returned to mantle
4 10 Be in arc lavas
5 10 Be in arc lavas Smoking gun evidence for sediment subduction Brown et al. (1982) Nature 299 Tera et al. (1986) GCA 50 but no 10 Be in lavas from the Lesser Antilles
6 Direct evidence for subduction 10 Be has been found in lava flows from island arcs e.g. Aleutians and central America! They mark sediment that was subducted, melted and returned at island arcs all within some 5 Ma. Many other subduction zone magmas do not have 10 Be (e.g., Lesser Antilles).
7 Boron isotopes help to define mechanism of mass transfer between slab and overlying mantle wedge 11 B partitions into liquid or vapour phase relative to minerals and silica melt. Boron signals δ 11 B = {[( 11 B/ 10 B) sample /( 11 B/ 10 B) standard ] -1} x 1000 e.g. Izu arc: Ishikawa & Nakamura (1993) Nature 370
8 Boron isotopes 10 B tetrahedrally, 11 B trigonal in aqueous fluids (>50 C) B is trigonal coordinated Boron is transferred from the slab to the arc magma by aqueous fluids and not by silicate melts. Agent of mass transfer is a fluid Keppler (1996) Nature 380 Peacock & Hervig (1999) Chem Geol 160
9 Fluxes How much goes down? No clue Estimates are between km 3 /yr How much comes up in arcs?
10 Boron & Beryllium 10 Be/Be total vs. B/Be for six arcs Each arc forms a linear array, each has a unique slope Homogenization process needed to explain the correlation for different arcs Repeated precipitation and dehydration reactions in the hydrated mantle Morris et al. (1990) Nature 344
11 Who much sediment is recycled to the arc and how much goes down? Mass balance calculations of inputs and outputs will provide an answer to this question
12 Global sediment subduction (GLOSS) GLOSS: 76 wt% terrigenous, 7 wt% calcium carbonate, 10 wt% opal, 7 wt% mineral-bound H 2 O +, similar to upper continental crust Plank & Langmuir: Chem Geol 1998
13 Global sediment subduction (GLOSS) Plank & Langmuir: Nature
14 Global sediment flux into trenches and enrichment in arc basalts P & L considered only the most primitive arc basalts (> 5 wt.% MgO) Avg. composition for each volcano was calculated at a reference value of 6 wt.% MgO e.g., Ba 6.0 = avg. Ba concentration at 6% MgO Plank & Langmuir: Nature
15 Mass balancing the inputs and outputs What goes down must come up Ant: Lesser Antilles Al: Ant: Aleutians Lesser Antilles Al: G: Guatemala Aleutians G: J: Java Guatemala J: Java M: Mexico Mar: Marianas T: Tonga Mex: Mexico Mar: Marianas T: Tonga g yr-1 per cm arc length Ba6.0 = avg. Ba concentration at 6% MgO, normalized to Na6.0 which varies inversely with the extend of melting some keeps going down Plank & Langmuir (1993) Nature 362 Plank & Langmuir (1998) Chem Geol 145
16 Such mass balance calculations show that ~20% of element budget in subducted sediments is recycled to the arc volcanics
17 Are trace elements signature of the continental crust e.g. Ce/Pb, Nb/U, Th/La created at arcs or inherited?
18 Geochemical signatutes of arc magmas: Arc magmas and the continental crust share many chemical features are these newly created by subduction or recycled from subducting sediment? incompatibility during mantle melting: Th > Nb > La GLOSS = global subducting sediment UCC = upper cont. crust BCC = bulk cont. crust T.Plank (2005) J Petrol 46:
19 Geochemical signatutes of arc magmas: Sedimentary endmember corresponds to the same as local trench sediment Mantle end-member varies for different arcs between depleted and enriched T.Plank (2005) J Petrol 46:
20 Crust has lost 25-60% of its (low Th/La) mafic residues to founderinig Intracrustal differentiation (partial melting, crystal fractionation, granulite facies metamorphism) is needed to create high Th/La upper crust and low-th/la lower crust
21 238 U- 230 Thdisequilibrium in volcanic rocks
22 U-Th-Ra isotopes in arc magmas 238 U 234 U 230 Th 226 Ra 206 Pb (excluding some shorties ) T 1/2 = 75 ka T 1/2 = 1.6 ka A Equilibrium: λ 1 N 1 = λ 2 N 2 A 1 = A 2 ( 230 Th/ 238 U) = 1 A Allègre & Condomines (1976) EPSL 28, (1982) Nature 299
23 Relation between activity ratio and isotope ratio für A A λ N = = 1 gilt : λ N 2 2 A A = λ λ N N Th U = a a 1 1 =
24 U-Th-Ra isotopes in arc magmas 238 U 234 U 230 Th 226 Ra 206 Pb (excluding some shorties ) T 1/2 = 75 ka T 1/2 = 1.6 ka A Equilibrium: λ 1 N 1 = λ 2 N 2 A 1 = A 2 ( 230 Th/ 238 U) = 1 A Allègre & Condomines (1976) EPSL 28, (1982) Nature 299
25 U-Th isotopes in arc magmas 238 U 234 U 230 Th 206 Pb (excluding some shorties ) T 1/2 = 75 ka For equilibrium: λ 1 N 1 = λ 2 N 2 A 1 = A 2 ( 230 Th/ 238 U) = 1
26 U-Th isotopes in arc magmas A A (1 e λ 230t 238 λ 230t 232 = Bateman s equation: A A 232 e A + A 232 ) unsupported Allègre & Condomines (1976) EPSL 28,
27 U-Th isotopes in arc magmas A 230 A 230 = A238 = A232 A A = N N λ λ A A N N = A A λ λ Thorium-Uran Verhältnis: Condomines et al. (1981) EPSL 55, N N = =
28 U-Th isotopes in arc magmas Th U = λ λ U Th = 2.57 Newman et al. (1983) EPSL 65, 17-33
29 U Th isotopes
30 U Th isotopes Hawkesworth et al. (1997) Science 276
31 Melting of a subducting oceanic slab? Sigmarsson et al. (1998) Nature 394
32 Melting of a subducting oceanic slab? Sigmarsson et al. (1998) Nature 394
33 Timescales of melt transport 238 U 234 U 230 Th 226 Ra 206 Pb (excluding some shorties ) T 1/2 = 75 ka T 1/2 = 1.6 ka Lesser Antilles Southern Chile Chabaux et al. (1999) Chem Geol 153 Sigmarsson et al. (2002) EPSL 196 Ultrafast source to surface movement: m/year
34 Adakites (High Mg-andesites) Geochemical characteristics intermediate to acidic calc-alkaline volcanic rock Anomalously steep rare-earth-element pattern, low HREE High Al 2 O 3 and Sr contents High Sr/Y ratios Enriched in compatible elements such as Mg, Cr and Ni Defant and Drummond (1990) defined it as having Yb < 1.8 ppm, Y < ppm, Sr/Y >40 and it may be of low-, medium- or high-k 2 O type Petrogenesis, Tectonic setting derives from high pressure partial melting of subducted oceanic crust,.subducted oceanic ridges or underplated mafic material A fractional crystallization origin of calc-alkaline basaltic magma is precluded.by its trace element characteristics Slab melting process also proposed for formation of Archean crust ( TTGs)
35 Boninites (High-Mg andesites & dacites) Geochemical characteristics high SiO 2 (>55%), high-mgo (~9%), low Al 2 O 3, low TiO 2 lavas Enriched in compatible elements such as Cr and Ni V -shaped REE pattern (as in metasomatized harzburgite xenoliths) Petrogenesis, Tectonic setting derivation from strongly depleted mantle sources under hydrous conditions near-primary partial melts (not fractionated) occur often during start of subduction
36 Adakites - references Defant MJ, Drummond MS (1990) Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 347, Castillo PR (2006) An overview of adakite petrogenesis. Chinese Science Bulletin 51, Boninites - references Crawford AJ, Beccaluva L, Serri G (1981) Tectono-magmatic evolution of the West Philippine-Mariana region and the origin of boninites. Earth Planet Sci Lett 54, Hickey RL, Frey FA (1982) Geochemical characteristics of boninite series volcanics: implications for their source. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46,
37 Arc magmatic tempos Looking at the temporal behavior of arc magmatism central portion of the Sierra Nevada Batholith (Late Cretaceous) showing its voluminous nature (Photo: Scott Paterson) Ducea et al (2015) Elements
38 Arc magmatic tempos U Pb crystallization ages for over 100,000 detrital zircon grains (Voice et al. 2011). The zircon peaks and occurrences of ultra-high temperature metamorphism correlate to the ages of supercontinent assembly (Cawood et al. 2013). John Valley (2015) Elements
39 Arc magmatic tempos Exposed bedrock U Pb zircon ages & detrital zircon U Pb LA-ICP MS ages from the Sierra Nevada Batholith (California) Both data sets temporally define the beginning (~250 Ma) and cessation (~85 Ma) of Mesozoic magmatism plus timing of three magmatic flare-ups and four lulls Paterson & Ducea (2015) Elements
40 Arc magmatic tempos Depth comparison of bedrock Sierran U Pb igneous ages, with ages separated into surface volcanic, shallow plutons (emplaced above 6 kbar), and deep plutons (>6 kbar emplacement). Timing of flare-ups and lulls appears depth independent, although volcanism may peak slightly earlier than plutonism in the Jurassic and Cretaceous flareups. Paterson & Ducea (2015) Elements
41 Arc magmatic tempos Calculated magma addition rates, measured in km 3 for 10 My age bins for both plutonic and volcanic materials in a 110 km wide corridor, central Sierra Nevada curves show huge (100 to 1000) increases of magma added during flare-ups versus lulls resulting in plutonic/volcanic ratios of ~30/1 Paterson & Ducea (2015) Elements flare-ups and lulls display apparent wave-like patterns of waxing and waning magmatism
42
43 Arc magmatic tempos in oceanic arcs Paterson & Ducea (2015) Elements ages normalized to when arc magmatism started
44 Arc magmatic tempos intrusive rates versus age for various segments of the Mesozoic to early Cenozoic magmatic arcs in the western North American Cordillera Ducea et al. (2015) Elements
45 Vertical wall of rocks that show the same age range from the surface to the dept is a characteristic of most arcs. This attests to the verticality of magma transport, petrogenetic processes, and the emplacement in arc rocks. Schematic crustal column though the Ordovician Famatinian arc (Argentina) arc compositions become more mafic and richer in cumulate/restite assemblages (residues) with depth. magmatic arc products dominate everywhere in the crust. intrusive and/or volcanic ages and their relative distribution typical of the upper crust are identical with those in the lower crust. Ducea et al. (2015) Elements
46 Magma and crust production rates Jicha & Jagoutz (2015) Elements
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas
 Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Crustal thickness control on Sr/Y signatures of recent arc magmas: an Earth scale perspective Massimo Chiaradia Section of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Geneva,
Supplementary Information Crustal thickness control on Sr/Y signatures of recent arc magmas: an Earth scale perspective Massimo Chiaradia Section of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Geneva,
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Evidences for geochemically distinct mantle components
 Evidences for geochemically distinct mantle components 1 Mantle Array Oceanic basalts, including seamounts, oceanic islands and middle ocean ridge basalts, were used. 2 Binary All analyses fall between
Evidences for geochemically distinct mantle components 1 Mantle Array Oceanic basalts, including seamounts, oceanic islands and middle ocean ridge basalts, were used. 2 Binary All analyses fall between
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism
 Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
GSA Data Repository
 GSA Data Repository 218145 Parolari et al., 218, A balancing act of crust creation and destruction along the western Mexican convergent margin: Geology, https://doi.org/1.113/g39972.1. 218145_Tables DR1-DR4.xls
GSA Data Repository 218145 Parolari et al., 218, A balancing act of crust creation and destruction along the western Mexican convergent margin: Geology, https://doi.org/1.113/g39972.1. 218145_Tables DR1-DR4.xls
Igneous Rocks of the Convergent Margins
 Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Trace Elements. Today s lecture
 Trace Elements 300 Ni 200 ppm 100 0 300 Zr 200 100 0 40 50 60 70 80 SiO 2 wt. % Updates: M&M due date: Tuesday Today s lecture Topics: Trace element compositions Trace element behavior Partitioning Spider(
Trace Elements 300 Ni 200 ppm 100 0 300 Zr 200 100 0 40 50 60 70 80 SiO 2 wt. % Updates: M&M due date: Tuesday Today s lecture Topics: Trace element compositions Trace element behavior Partitioning Spider(
The Lead 206/207 Dating Method
 The Lead 206/207 Dating Method 1 U Pb Zircon Ages, Chemical Geology, Volume 211 (2004) Pages 87 109 2 Lead Isotope Planetary Profiling, Chemical Geology, Volume 233 (2006) Pages 1 45 3 U Pb Step-Leaching
The Lead 206/207 Dating Method 1 U Pb Zircon Ages, Chemical Geology, Volume 211 (2004) Pages 87 109 2 Lead Isotope Planetary Profiling, Chemical Geology, Volume 233 (2006) Pages 1 45 3 U Pb Step-Leaching
Lecture 38. Igneous geochemistry. Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already
 Lecture 38 Igneous geochemistry Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already Today. Magma mixing/afc 2. Spot light on using the Rare Earth Elements (REE) to constrain mantle sources and conditions of petrogenesis
Lecture 38 Igneous geochemistry Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already Today. Magma mixing/afc 2. Spot light on using the Rare Earth Elements (REE) to constrain mantle sources and conditions of petrogenesis
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli
 GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism
 5. 3 Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism Where can we observe magmatic/volcanic activities along subduction zones? Characteristics of arc magmatism (vs. mid-ocean ridge/intraplate magmatism) Structure of
5. 3 Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism Where can we observe magmatic/volcanic activities along subduction zones? Characteristics of arc magmatism (vs. mid-ocean ridge/intraplate magmatism) Structure of
Assigned Topic: How does the composition of island arc crust evolve as the convergent plate boundary matures?
 Assigned Topic: How does the composition of island arc crust evolve as the convergent plate boundary matures? Jim Gill Earth and Planetary Sciences UC Santa Cruz A perspective from 50 years work in Fiji-Tonga
Assigned Topic: How does the composition of island arc crust evolve as the convergent plate boundary matures? Jim Gill Earth and Planetary Sciences UC Santa Cruz A perspective from 50 years work in Fiji-Tonga
Chang Wenbo.
 The spatial and temporal distributions of the late Mesozoic volcanic successions in the Changling fa ult depression of the Songliao Basin, NE China, and their controlling effects Chang Wenbo susanna0703@163.com
The spatial and temporal distributions of the late Mesozoic volcanic successions in the Changling fa ult depression of the Songliao Basin, NE China, and their controlling effects Chang Wenbo susanna0703@163.com
Secular Archaean. Pronounced secular trends from. However, also. Cr, intermediate to felsic magmas, and
 Secular Archaean Pronounced secular trends from 1. early sodic granites (TTGs) 2. later potassic granites However, also 1. LILE- & LREE-enriched, high MgO, Mg#, Ni, Cr, intermediate to felsic magmas, and
Secular Archaean Pronounced secular trends from 1. early sodic granites (TTGs) 2. later potassic granites However, also 1. LILE- & LREE-enriched, high MgO, Mg#, Ni, Cr, intermediate to felsic magmas, and
The ~ Ma magmatism along the Mesozoic arc is far more voluminous than would be expected for a typical arc.
 The ~120-80 Ma magmatism along the Mesozoic arc is far more voluminous than would be expected for a typical arc. Is Hildebrand s model substantially different from the under-thrusting of continental sediments
The ~120-80 Ma magmatism along the Mesozoic arc is far more voluminous than would be expected for a typical arc. Is Hildebrand s model substantially different from the under-thrusting of continental sediments
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Supplementary Figure 1 Map of the study area Sample locations and main physiographic features of the study area. Contour interval is 200m (a) and 40m
 Supplementary Figure 1 Map of the study area Sample locations and main physiographic features of the study area. Contour interval is 200m (a) and 40m (b). Dashed lines represent the two successive ridge
Supplementary Figure 1 Map of the study area Sample locations and main physiographic features of the study area. Contour interval is 200m (a) and 40m (b). Dashed lines represent the two successive ridge
Overview of the KAHT system. Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland
 Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr
 Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Igneous activity is related to convergent plate situations that result in the subduction of one plate beneath another Ocean-ocean Island Arc
 Igneous activity related to subduction (Chapters 16, 17) Subduction-related activity Igneous activity is related to convergent plate situations that result in the subduction of one plate beneath another
Igneous activity related to subduction (Chapters 16, 17) Subduction-related activity Igneous activity is related to convergent plate situations that result in the subduction of one plate beneath another
Lower arc crust A review of some important exhumed crustal sections and xenolith localities from the Americas
 Lower arc crust A review of some important exhumed crustal sections and xenolith localities from the Americas Mihai Ducea University of Arizona For the ExTerra group workshop August, 24, 2013, Florence,
Lower arc crust A review of some important exhumed crustal sections and xenolith localities from the Americas Mihai Ducea University of Arizona For the ExTerra group workshop August, 24, 2013, Florence,
1 Potassic adakite magmas and where they come from: a mystery solved?
 1 Potassic adakite magmas and where they come from: a mystery solved? 2 3 John Clemens Kingston University (London) Long Xiao China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) 4 Adakites are volcanic and intrusive
1 Potassic adakite magmas and where they come from: a mystery solved? 2 3 John Clemens Kingston University (London) Long Xiao China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) 4 Adakites are volcanic and intrusive
predictive iscovery Why is the gold where it is? redictive mineral ineral discovery pmd CRC
 The Y2 project (2001-2004) Time-space evolution of the Yilgarn Craton: implications for geodynamics Kevin Cassidy and the Y2 team Reduced D Risk through Improved Targeting ineral d Why is the gold where
The Y2 project (2001-2004) Time-space evolution of the Yilgarn Craton: implications for geodynamics Kevin Cassidy and the Y2 team Reduced D Risk through Improved Targeting ineral d Why is the gold where
An Introduction of Aleutian Subduction Zone. Chuanmao Yang, Hong Yang, Meng Zhang, Wenzhong Wang 2016/04/29
 An Introduction of Aleutian Subduction Zone Chuanmao Yang, Hong Yang, Meng Zhang, Wenzhong Wang 2016/04/29 Outline General Introduction Formation history Structure from seismic study geochemical features
An Introduction of Aleutian Subduction Zone Chuanmao Yang, Hong Yang, Meng Zhang, Wenzhong Wang 2016/04/29 Outline General Introduction Formation history Structure from seismic study geochemical features
At the beginning. Matter + antimatter. Matter has the advantage. baryons quarks, leptons, electrons, photons (no protons or neutrons)
 At the beginning Matter + antimatter Matter has the advantage baryons quarks, leptons, electrons, photons (no protons or neutrons) Hadrons protons, neutrons Hydrogen, helium (:0 H:He) Origin of the Universe
At the beginning Matter + antimatter Matter has the advantage baryons quarks, leptons, electrons, photons (no protons or neutrons) Hadrons protons, neutrons Hydrogen, helium (:0 H:He) Origin of the Universe
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Structure of the Earth
 And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
Introduction. Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth
 Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE
 Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts
 Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
Lecture 36. Igneous geochemistry
 Lecture 36 Igneous geochemistry Reading - White Chapter 7 Today 1. Overview 2. solid-melt distribution coefficients Igneous geochemistry The chemistry of igneous systems provides clues to a number of important
Lecture 36 Igneous geochemistry Reading - White Chapter 7 Today 1. Overview 2. solid-melt distribution coefficients Igneous geochemistry The chemistry of igneous systems provides clues to a number of important
12. Data from Ito et al. (1987) Chemical Geology, 62, ; Figure ; and LeRoex et al. (1983) J. Petrol., 24,
 Announcements Reading for Wed: p.363-399!!! p.362-366; p.373-378; p.383-386; p.392-394; p.395-399 Last lecture on Wednesday Bring food for pizza party Bring class notes, labs, book N-MORBs: 87 Sr/ 86 Sr
Announcements Reading for Wed: p.363-399!!! p.362-366; p.373-378; p.383-386; p.392-394; p.395-399 Last lecture on Wednesday Bring food for pizza party Bring class notes, labs, book N-MORBs: 87 Sr/ 86 Sr
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington
 Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us?
 The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
The High Lava Plains Project: Understanding the Causes of Continental Intraplate Tectonomagmatism
 The High Lava Plains Project: Understanding the Causes of Continental Intraplate Tectonomagmatism The High Lava Plains (HLP) of the northwestern USA is one of the most accessible yet least understood examples
The High Lava Plains Project: Understanding the Causes of Continental Intraplate Tectonomagmatism The High Lava Plains (HLP) of the northwestern USA is one of the most accessible yet least understood examples
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Differentiation of the Continental Crust by Relamination. Bradley Hacker
 Differentiation of the Continental Crust by Relamination Bradley Hacker Three Common Paradigms lower continental cr ust is basaltic/mafic continents ar e made in volcanoplutonic ar cs continents ar e r
Differentiation of the Continental Crust by Relamination Bradley Hacker Three Common Paradigms lower continental cr ust is basaltic/mafic continents ar e made in volcanoplutonic ar cs continents ar e r
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System. The Structure of the Earth. Temperature 3000º ºC. Mantle
 The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System Objectives: Understand the structure of the planet Earth Review the geologic timescale as a point of reference for the history of the Earth Examine the major relief
The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System Objectives: Understand the structure of the planet Earth Review the geologic timescale as a point of reference for the history of the Earth Examine the major relief
 Kelemen et al. Fig 1. 60 N 55 N 50 N 190 W 180 W 170 W Komandorsky Komandorsky Islands dredge 70-B29 Attu Island Buldir Island BERING SEA Distal Aleutians Adak area Adak Island Atka Island block Amak Island
Kelemen et al. Fig 1. 60 N 55 N 50 N 190 W 180 W 170 W Komandorsky Komandorsky Islands dredge 70-B29 Attu Island Buldir Island BERING SEA Distal Aleutians Adak area Adak Island Atka Island block Amak Island
Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data)
 Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data) Peter Kibarov, Peter Marchev, Maria Ovtcharova, Raya Raycheva,
Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data) Peter Kibarov, Peter Marchev, Maria Ovtcharova, Raya Raycheva,
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology. Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments
 GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
Overview of the IBM Arc System: The Igneous Rocks
 Overview of the IBM Arc System: The Igneous Rocks Robert J. Stern, Geosciences Department, University of Texas at Dallas, Box 830688, Richardson TX 75083-0688, U.S.A. rjstern@utdallas.edu The Izu-Bonin-Mariana
Overview of the IBM Arc System: The Igneous Rocks Robert J. Stern, Geosciences Department, University of Texas at Dallas, Box 830688, Richardson TX 75083-0688, U.S.A. rjstern@utdallas.edu The Izu-Bonin-Mariana
Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0
 N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Constitution of Magmas. Magmas. Gas Law. Composition. Atomic Structure of Magma. Structural Model. PV = nrt H 2 O + O -2 = 2(OH) -
 Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Petrology and tectonics of Phanerozoic continent formation: From island arcs to accretion and continental arc magmatism
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Earth and Planetary Science Letters 263 (2007) 370 387 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Petrology and tectonics of Phanerozoic continent formation: From island arcs
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Earth and Planetary Science Letters 263 (2007) 370 387 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Petrology and tectonics of Phanerozoic continent formation: From island arcs
EARTH S ENERGY SOURCES
 EARTH S ENERGY SOURCES The geological processes that shape the Earth s surface are powered by two major sources of energy; geothermal heat from the Earth s interior and external energy from the sun. The
EARTH S ENERGY SOURCES The geological processes that shape the Earth s surface are powered by two major sources of energy; geothermal heat from the Earth s interior and external energy from the sun. The
Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms.
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Regional and local variations in geochemistry and tectonics along and across Central America
 Regional and local variations in geochemistry and tectonics along and across Central America Michael J. Carr, Department of Geological Sciences, Wright Lab Rutgers University, 610 Taylor Rd., Piscataway
Regional and local variations in geochemistry and tectonics along and across Central America Michael J. Carr, Department of Geological Sciences, Wright Lab Rutgers University, 610 Taylor Rd., Piscataway
Questions and Topics
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
APPLICATIONS OF ISOTOPES TO IGNEOUS PETROGENESIS
 APPLICATIONS OF ISOTOPES TO IGNEOUS PETROGENESIS Elisabeth Widom Miami University, Oxford, Ohio, USA Keywords: cosmogenic nuclides, crustal recycling, decay series, fractionation, igneous petrology, isochron,
APPLICATIONS OF ISOTOPES TO IGNEOUS PETROGENESIS Elisabeth Widom Miami University, Oxford, Ohio, USA Keywords: cosmogenic nuclides, crustal recycling, decay series, fractionation, igneous petrology, isochron,
Lecture 12 COMPLEX MELTING MODELS. (see books by Shaw, Trace Elements in Magmas (2006) and Zou, Quantitative Geochemistry (2007))
 Lecture 12 COMPLEX MELTING MODELS (see books by Shaw, Trace Elements in Magmas (2006) and Zou, Quantitative Geochemistry (2007)) Thus far we have considered two end-member melting models, batch melting
Lecture 12 COMPLEX MELTING MODELS (see books by Shaw, Trace Elements in Magmas (2006) and Zou, Quantitative Geochemistry (2007)) Thus far we have considered two end-member melting models, batch melting
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10326 Supplementary Discussion All known modern terrestrial mantle reservoirs evolved from a primitive precursor with superchondritic 143 Nd/ 144 Nd. What is this reservoir? The terms
doi:10.1038/nature10326 Supplementary Discussion All known modern terrestrial mantle reservoirs evolved from a primitive precursor with superchondritic 143 Nd/ 144 Nd. What is this reservoir? The terms
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay. Harvard University
 What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
6. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
Evolution of the Slave Province and Abitibi Subprovince Based on U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopic Composition of Zircon
 Evolution of the Slave Province and Abitibi Subprovince Based on U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopic Composition of Zircon John W.F. Ketchum 1, Wouter Bleeker 2, William L. Griffin 1, Suzanne Y. O Reilly 1, Norman
Evolution of the Slave Province and Abitibi Subprovince Based on U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopic Composition of Zircon John W.F. Ketchum 1, Wouter Bleeker 2, William L. Griffin 1, Suzanne Y. O Reilly 1, Norman
The subduction factory: Its role in the evolution of the Earth s mantle
 The subduction factory: Its role in the evolution of the Earth s mantle Yoshiyuki Tatsumi and Tetsu Kogiso Research Program for Geochemical Evolution, Institute for Frontier Research on Earth Evolution
The subduction factory: Its role in the evolution of the Earth s mantle Yoshiyuki Tatsumi and Tetsu Kogiso Research Program for Geochemical Evolution, Institute for Frontier Research on Earth Evolution
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
Plate Tectonics. Structure of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Ocean islands and seamounts Commonly associated with hot spots. After Crough (1983) Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 11,
 MORB Petrogenesis Ocean islands and seamounts Commonly associated with hot spots After Crough (1983) Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 11, 165-193. Types of OIB Magmas Two principal magma series Tholeii:c
MORB Petrogenesis Ocean islands and seamounts Commonly associated with hot spots After Crough (1983) Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 11, 165-193. Types of OIB Magmas Two principal magma series Tholeii:c
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information
 Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Fluids, melts, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones
 cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
Figure 2. Location map of Himalayan Mountains and the Tibetan Plateau (from Searle et al., 1997).
 Nazca Plate Figure 1. Location map of Central Andes arc. This map also shows the extent of the high Altiplano-Puna plateau (from Allmendinger et al., 1997). 33 Figure 2. Location map of Himalayan Mountains
Nazca Plate Figure 1. Location map of Central Andes arc. This map also shows the extent of the high Altiplano-Puna plateau (from Allmendinger et al., 1997). 33 Figure 2. Location map of Himalayan Mountains
Layer Composition Thickness State of Matter
 Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # Main Idea:
 Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones
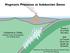 Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms
 Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
HP and UHP garnet peridotites and pyroxenites
 HP and UHP garnet peridotites and pyroxenites Mantle wedge The least known piece of the subduction factory Mantle-wedge peridotites emplace within subducting continental crust (Brueckner, 998; van Roermund
HP and UHP garnet peridotites and pyroxenites Mantle wedge The least known piece of the subduction factory Mantle-wedge peridotites emplace within subducting continental crust (Brueckner, 998; van Roermund
1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers
 1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers 2. When did the Earth form? A. About 540 million years ago B. About 2.5 billion years ago
1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers 2. When did the Earth form? A. About 540 million years ago B. About 2.5 billion years ago
The continental lithosphere
 Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution. (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins)
 Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Michele Lustrino a,b,* Rome Italy. Studi di Roma La Sapienza, P.le A. Moro, 5, Rome Italy. * address:
 Pyroxenites everywhere. Comment on High-pressure melting experiments on garnet clinopyroxenite and the alkalic to tholeiitic transition in ocean-island basalts by Keshav et al. [Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.
Pyroxenites everywhere. Comment on High-pressure melting experiments on garnet clinopyroxenite and the alkalic to tholeiitic transition in ocean-island basalts by Keshav et al. [Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Continental ice sheets increase the weight of the Earth
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Continental ice sheets increase the weight of the Earth
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
Today we will discuss places mobility Natural disasters lead to California s beauty Aesthenosphere
 Agenda 2. Geologic History Today we will discuss What Physical Geography is Brief geologic history of California Geography 106 California Geography M. Pesses Antelope Valley College Physical Geographers
Agenda 2. Geologic History Today we will discuss What Physical Geography is Brief geologic history of California Geography 106 California Geography M. Pesses Antelope Valley College Physical Geographers
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
PUBLICATIONS. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems
 PUBLICATIONS Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Source and magma mixing processes are evident in continental subduction factory The heterogeneous mantle source is generated
PUBLICATIONS Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Source and magma mixing processes are evident in continental subduction factory The heterogeneous mantle source is generated
Geol. 655 Isotope Geochemistry
 ISOTOPIC GEOCHEMISTRY OF THE CONTINENTAL CRUST Isotope systems have particular value in studies of mantle geochemistry because of the difficulty of obtaining direct, representative samples of mantle. Because
ISOTOPIC GEOCHEMISTRY OF THE CONTINENTAL CRUST Isotope systems have particular value in studies of mantle geochemistry because of the difficulty of obtaining direct, representative samples of mantle. Because
Geochemical and mineralogical technics to investigate the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. 07/11/2017 GEO-DEEP 9300 Claire Aupart
 Geochemical and mineralogical technics to investigate the lithosphere and the asthenosphere 07/11/2017 GEO-DEEP 9300 Claire Aupart Introduction Introduction Getting samples Cores: Maximum depth reach in
Geochemical and mineralogical technics to investigate the lithosphere and the asthenosphere 07/11/2017 GEO-DEEP 9300 Claire Aupart Introduction Introduction Getting samples Cores: Maximum depth reach in
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity. Aka Volcano Under the City
 Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Happy Tuesday. Pull out a ½ sheet of paper
 Happy Tuesday Pull out a ½ sheet of paper 1. Physical properties of a mineral are predominantly related to 1. the external conditions of temperature, pressure, and amount of space available for growth.
Happy Tuesday Pull out a ½ sheet of paper 1. Physical properties of a mineral are predominantly related to 1. the external conditions of temperature, pressure, and amount of space available for growth.
Classification and Origin of Granites. A Multi-faceted Question
 Classification and Origin of Granites A Multi-faceted Question What is a granite? IUGS classification Based on Modal Mineralogy Plutonic rock with less than 90% mafic minerals Alkali Granite Granite Quartz
Classification and Origin of Granites A Multi-faceted Question What is a granite? IUGS classification Based on Modal Mineralogy Plutonic rock with less than 90% mafic minerals Alkali Granite Granite Quartz
