Public Inspection and Maintenance Checklist Sand Filters (Above Ground/Open)
|
|
|
- Silvester Lloyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Public Inspection and Checklist Sand Filters (Above Ground/Open) Sediment Accumulation on top layer* Trash and Debris Sediment/ Debris in Clean-Outs* Sand Filter Media* Prolonged Flows Short Circuiting Erosion Damage to Slopes Rock Pad Missing or Out of Place Flow Spreader* Damaged Pipes Sediment depth exceeds 1/2-inch. Trash and debris accumulated on sand filter bed. When the clean-outs become full or partially plugged with sediment and/or debris. Drawdown of water through the sand filter media takes longer than 24-hours, and/or flow through the overflow pipes occurs frequently. Sand is saturated for prolonged periods of time (several weeks) and does not dry out between storms due to continuous base flow or prolonged flows from detention facilities. When flows become concentrated over one section of the sand filter rather than dispersed. Erosion over 2-inches deep where cause of damage is prevalent or potential for continued erosion is evident. Soil beneath the rock is visible. Flow spreader uneven or clogged so that flows are not uniformly distributed across sand filter. Any part of the piping that is crushed or deformed more than 20% or any other failure to the piping. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day. F:\Sc42\Sc42-24\Bellevue, WA\Inspection Forms\Public AG Sand Filters Inspect Chklst.doc
2 Public Inspection and Checklist Baffle Oil/Water Separators (Api Type) Monitoring Sediment Trash and Debris Oil Damaged Pipes Access Cover Damaged/Not Working Vault Structure Damage Includes Cracks in Walls Bottom, Damage to Frame and/or Top Slab Baffles Access Ladder Damaged Inspection of discharge water for obvious signs of poor water quality. Sediment depth in bottom of vault exceeds 6-inches in depth. Trash and debris accumulation in vault, or pipe inlet/outlet, floatables and non-floatables. Oil accumulations that exceed 1-inch, at the surface of the water. Inlet or outlet piping damaged or broken and in need of repair. Cover cannot be opened, corrosion/deformation of cover. Cracks wider than 1/2-inch or evidence of soil particles entering the structure through the cracks, or maintenance/inspection personnel determine that the vault is not structurally sound. Cracks wider than 1/2-inch at the joint of any inlet/outlet pipe or evidence of soil particles entering through the cracks. Baffles corroding, cracking, warping and/or showing signs of failure as determined by maintenance/inspection person. Ladder is corroded or deteriorated, not functioning properly, not securely attached to structure wall, missing rungs, cracks, and misaligned. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
3 Public Inspection and Checklist Sand Filters (Below Ground/Enclosed) Sediment Accumulation on Sand Media Section* Sediment Accumulation in Pre-Settling Portion of Vault* Trash/Debris Sediment in Drain Pipes/Cleanout s* Short Circuiting Damaged Pipes Access Cover Damaged/Not Working Ventilation Vault Structure Damaged; Includes Cracks in Walls, Bottom, Damage to Frame and/or Top Slab Sediment depth exceeds 1/2-inch. Sediment accumulation in vault bottom exceeds the depth of the sediment zone plus 6-inches. Trash and debris accumulated in vault, or pipe inlet/outlet, floatables and non-floatables. When drain pipes, cleanouts become full with sediment and/or debris. When seepage/flow occurs along the vault walls and corners. Sand eroding near inflow area. Inlet or outlet piping damaged or broken and in need of repair. Cover cannot be opened, corrosion/deformation of cover. person cannot remove cover using normal lifting pressure. Ventilation area blocked or plugged Cracks wider than 1/2-inch or evidence of soil particles entering the structure through the cracks, or maintenance/inspection personnel determine that the vault is not structurally sound. Cracks wider than 1/2-inch at the joint of any inlet/outlet pipe or evidence of soil particles entering through the cracks. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
4 Baffles/Internal walls Access Ladder Damaged Baffles or walls corroding, cracking, warping and/or showing signs of failure as determined by maintenance/inspection person. Ladder is corroded or deteriorated, not functioning properly, not securely attached to structure wall, missing rungs, cracks, and misaligned. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
5 Public Inspection and Checklist Biofiltration Swale Sediment Accumulation on Grass* Standing Water Flow spreader* Constant Baseflow Poor Vegetation Coverage* Vegetation* Excessive Shading Inlet/Outlet* Trash and Debris Erosion/Scouring* Sediment depth exceeds 2 inches. When water stands in the swale between storms and does not drain freely. Flow spreader uneven or clogged so that flows are not uniformly distributed through entire swale width. When small quantities of water continually flow through the swale, even when it has been dry for weeks, and an eroded, muddy channel has formed in the swale bottom. When grass is sparse or bare or eroded patches occur in more than 10% of the swale bottom. When the grass becomes excessively tall (greater than 10- inches); when nuisance weeds and other vegetation starts to take over. Grass growth is poor because sunlight does not reach swale. Inlet/outlet areas clogged with sediment and/or debris. Trash and debris accumulated in the bioswale. Eroded or scoured swale bottom due to flow channelization, or higher flows. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
6 Public Inspection and Checklist Catchbasin Inserts Sediment Trash and Debris Media Insert Not Removing Oil* Media Insert Water Saturated* Media Insert-Oil Saturated* Media Insert Use Beyond Normal Product Life* When sediment forms a cap over the insert media of the insert and/or unit. Trash and debris accumulates on insert unit creating a blockage/restriction. Effluent water from media insert has a visible sheen. Catch basin insert is saturated with water and no longer has the capacity to absorb. Media oil saturated due to petroleum spill that drains into catch basin. Media has been used beyond the typical average life of media insert product. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
7 Public Inspection and Checklist Catch Basins, Manholes, and Inlets Trash & Debris* Sediment* Structure Damage to Frame and/or Top Slab Fractures or Cracks in Basin Walls/ Bottom Trash or debris which is located immediately in front of the catch basin opening or is blocking inletting capacity of the basin by more than 10%. Trash or debris (in the basin) that exceeds 60 percent of the sump depth as measured from the bottom of basin to invert of the lowest pipe into or out of the basin, but in no case less than a minimum of six inches clearance from the debris surface to the invert of the lowest pipe. Trash or debris in any inlet or outlet pipe blocking more than 1/3 of its height. Dead animals or vegetation that could generate odors that could cause complaints or dangerous gases (e.g., methane). Sediment (in the basin) that exceeds 60 percent of the sump depth as measured from the bottom of basin to invert of the lowest pipe into or out of the basin, but in no case less than a minimum of 6 inches clearance from the sediment surface to the invert of the lowest pipe. Top slab has holes larger than 2 square inches or cracks wider than 1/4 inch. Frame not sitting flush on top slab, i.e., separation of more than 3/4 inch of the frame from the top slab. Frame not securely attached person judges that structure is unsound. Grout fillet has separated or cracked wider than 1/2 inch and longer than 1 foot at the joint of any inlet/outlet pipe or any evidence of soil particles entering catch basin through cracks. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
8 Settlement/ Misalignment Vegetation Contamination and Pollution Catch Basin Cover Cover Not in Place Locking Mechanism Not Working Cover Difficult to Remove Ladder Ladder Rungs Unsafe Metal Grates (If Applicable) Grate opening Unsafe Trash and Debris Damaged or Missing. If failure of basin has created a safety, function, or design problem. Vegetation growing across and blocking more than 10% of the basin opening. Vegetation growing in inlet/outlet pipe joints that is more than six inches tall and less than six inches apart. Any evidence of oil, gasoline, contaminants or other pollutants. Cover is missing or only partially in place. Any open catch basin requires maintenance. Mechanism cannot be opened by one maintenance person with proper tools. Bolts into frame have less than 1/2 inch of thread. One maintenance person cannot remove lid after applying normal lifting pressure. (Intent is keep cover from sealing off access to maintenance.) Ladder is unsafe due to missing rungs, not securely attached to basin wall, misalignment, rust, cracks, or sharp edges. Grate with opening wider than 7/8 inch. Trash and debris that is blocking more than 20% of grate surface inletting capacity. Grate missing or broken member(s) of the grate. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
9 Public Inspection and Checklist Control Structure/Flow Restrictor Trash and Debris (Includes Sediment)* Structural Damage Cleanout Gate Damaged or Missing Orifice Plate Damaged or Missing Obstructions* Overflow Pipe Obstructions* Manhole Cover Not in Place Material exceeds 25% of sump depth or 1 foot below orifice plate. Structure is not securely attached to manhole wall. Structure is not in upright position (allow up to 10% from plumb). Connections to outlet pipe are not watertight and show signs of rust. Any holes other than designed holes--in the structure. Cleanout gate is not watertight or is missing. Gate cannot be moved up and down by one maintenance person. Chain/rod leading to gate is missing or damaged. Gate is rusted over 50% of its surface area. Control device is not working properly due to missing, out of place, or bent orifice plate. Any trash, debris, sediment, or vegetation blocking the plate. Any trash or debris blocking (or having the potential of blocking) the overflow pipe. Cover is missing or only partially in place. Any open manhole requires maintenance. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
10 Locking Mechanism Not Working Cover Difficult to Remove Ladder Rungs Unsafe Catch Basin See Catch Basins Mechanism cannot be opened by one maintenance person with proper tools. Bolts into frame have less than 1/2 inch of thread (may not apply to self-locking lids). One maintenance person cannot remove lid after applying normal lifting pressure. Intent is to keep cover from sealing off access to maintenance. Ladder is unsafe due to missing rungs, misalignment, not securely attached to structure wall, rust, or cracks. See Catch Basins : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
11 Public Inspection and Checklist Conveyance Systems (Pipes & Ditches) Pipes Sediment & Debris* Vegetation Damaged Pipe Open Ditches Trash & Debris* Sediment* Vegetation Erosion Damage to Slopes and Channel Bottom* Rock Lining Out of Place or Missing (If Applicable). Accumulated sediment that exceeds 20% of the diameter of the pipe. Vegetation that reduces free movement of water through pipes. Protective coating is damaged; rust is causing more than 50% deterioration to any part of pipe. Any dent that decreases the cross section area of pipe by more than 20% or puncture that impacts performance. Trash and debris > 5 cf/1,000 sf (one standard size garbage can) Visual evidence of dumping Accumulated sediment that exceeds 20% of the design depth. Vegetation that reduces free movement of water through ditches. Eroded damage over 2 inches deep where cause of damage is still present or where there is potential for continued erosion. Any erosion observed on a compacted berm embankment. person can see native soil beneath the rock lining. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
12 Public Inspection and Checklist Coalescing Plate Oil/Water Separators Monitoring Sediment Trash and Debris Oil Damaged Coalescing Plates Damaged Pipes Baffles Vault Structure Damage - Includes Cracks in Walls, Bottom, Damage to Frame and/or Top Slab Access Ladder Damaged Inspection of discharge water for obvious signs of poor water quality. Sediment depth in bottom of vault exceeds 6-inches in depth and/or visible signs of sediment on plates. Trash and debris accumulated in vault, or pipe inlet/outlet, floatables and non-floatables. Oil accumulation that exceeds 1-inch at the water surface. Plate media broken, deformed, cracked and/or showing signs of failure. Inlet or outlet piping damaged or broken and in need of repair. Baffles corroding, cracking, warping and/or showing signs of failure as determined by maintenance/inspection person. Cracks wider than 1/2-inch or evidence of soil particles entering the structure through the cracks, or maintenance/inspection personnel determine that the vault is not structurally sound. Cracks wider than 1/2-inch at the joint of any inlet/outlet pipe or evidence of soil particles entering through the cracks. Ladder is corroded or deteriorated, not functioning properly, not securely attached to structure wall, missing rungs, cracks, and misaligned. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
13 Public Inspection and Checklist Culverts Structural Condition Sediment & debris Vegetation blockage Pipe damage Headwall damage Accumulated sediment & debris exceeds 20% of the pipe diameter. Flow into or through the culvert is impeded. Corrosion affecting more than 50% of wall area. Bent or crushed ends. Large dents that reduce pipe crosssection by more than 20%. Cracks or holes that allow ground water seepage. Cracks >0.5 inches wide, buckled/bulging headwall, erosion behind or around ends of headwall. Fish Passage (culverts on streams) Minimum flow depth Downstream pipe end (culvert outlet) Drop height (downstream end) Upstream pipe end (culvert inlet) <12 inches during low flow conditions Pool depth in stream immediately below culvert less than 1.25 times the culvert drop height. Vertical distance between pipe invert and downstream water surface > 12 inches Channel bottom immediately upstream of culvert less than 1 foot below the culvert inlet. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
14 Public Inspection and Checklist Detention Ponds Trash & Debris* Poisonous Vegetation and noxious weeds Contaminants and Pollution Rodent Holes* Beaver Dams* Insects Tree/Brush Growth and Hazard Trees Side Slopes Erosion* Storage Area Sediment* Liner (If Applicable) Trash and debris >1 cf/1,000 sf (one standard size garbage can) Visual evidence of dumping Poisonous or nuisance vegetation or noxious weeds: morning glory, English ivy, reed canary grass, Japanese knotweed, purple loosestrife, blackberry, Scotch broom, poison oak, stinging nettles, or devil s club Any evidence of oil, gasoline, contaminants or other pollutants Any evidence of rodent holes if facility is acting as a dam or berm, or any evidence of water piping through dam or berm via rodent holes Dam results in change or function of the facility Insects such as wasps and hornets interfere with maintenance activities. Growth does not allow maintenance access or interferes with maintenance activity Dead, diseased, or dying trees Eroded over 2 in. deep where cause of damage is still present or where there is potential for continued erosion. Any erosion on a compacted berm embankment. Accumulated sediment >10% of designed pond depth or affects inletting or outletting condition of the facility. Liner is visible and has more than three 1/4-inch holes in it. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
15 Emergency Overflow/ Spillway and Berms Settlement* Tree Growth Piping* Emergency Overflow/ Spillway Erosion* Berm settlement 4 inches lower than the design elevation. Tree growth on berms or emergency spillway >4 ft in height or covering more than 10% of spillway. Discernable water flow through pond berm. Ongoing erosion with potential for erosion to continue. Only one layer of rock exists above native soil in area five square feet or larger, or any exposure of native soil at the top of out flow path of spillway. (Rip-rap on inside slopes need not be replaced.) See Side Slopes of Pond Debris Barriers (e.g., Trash Racks) Trash and Debris* Damaged/ Missing Bars Inlet/Outlet Pipe Fencing Missing or broken parts Erosion Damaged Parts Deteriorating Paint or Protective Coating Gates Damaged or missing member Trash or debris that is plugging more than 20% of the openings in the barrier. Bars are bent out of shape more than 3 inches. Bars are missing or entire barrier missing. Bars are loose and rust is causing 50% deterioration to any part of barrier. Debris barrier missing or not attached to pipe Any defect in the fence that permits easy entry to a facility. Erosion more than 4 inches high and inches wide permitting an opening under a fence. Damage to gate/fence, posts out of plumb, or rails bent more than 6 inches Part or parts that have a rusting or scaling condition that has affected structural adequacy. Missing gate or locking devices, broken or missing hinges, out of plum more than 6 inches and more than 1 foot out of design alignment, or missing stretcher bar, stretcher bands, and ties. Contact engineering ASAP. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
16 Public Inspection and Checklist Energy Dissipaters External Rock Pad Missing or Moved Rock Erosion Dispersion Trench Pipe Plugged with Sediment* Not Discharging Water Properly Perforations Plugged* Water Flows Out Top of Distributor Catch Basin* Receiving Area Over- Saturated* Internal Manhole/Chamber Worn or Damaged Post, Baffles, Side of Chamber Only one layer of rock exists above native soil in area five square feet or larger, or any exposure of native soil. Soil erosion in or adjacent to rock pad. Accumulated sediment that exceeds 20% of the design depth. Visual evidence of water discharging at concentrated points along trench (normal condition is a sheet flow of water along trench). Intent is to prevent erosion damage. Over 1/2 of perforations in pipe are plugged with debris and sediment. person observes or receives credible report of water flowing out during any storm less than the design storm or its causing or appears likely to cause damage. Water in receiving area is causing or has potential of causing landslide problems. Structure dissipating flow deteriorates to 1/2 of original size or any concentrated worn spot exceeding one square foot which would make structure unsound. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
17 Public Inspection and Checklist Filter Strips Sediment Accumulation on Grass* Vegetation* Trash and Debris Erosion/Scouring* Flow spreader* Sediment depth exceeds 2 inches. When the grass becomes excessively tall (greater than 10- inches); when nuisance weeds and other vegetation starts to take over. Trash and debris accumulated on the filter strip. Eroded or scoured areas due to flow channelization, or higher flows. Flow spreader uneven or clogged so that flows are not uniformly distributed through entire filter width. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
18 Public Inspection and Checklist Infiltration Basins, Trenches, And Swales Trash & Debris* Poisonous Vegetation and noxious weeds Contaminants and Pollution Rodent Holes* Storage Area Sediment* Filter Bags (if applicable) Filled with Sediment and Debris* Rock Filters Sediment and Debris Side Slopes of Pond Erosion* Trash and debris > 5 cf/1,000 sf (one standard size garbage can) Visual evidence of dumping Poisonous or nuisance vegetation or noxious weeds: morning glory, English ivy, reed canary grass, Japanese knotweed, purple loosestrife, blackberry, Scotch broom, poison oak, stinging nettles, or devil s club Any evidence of oil, gasoline, contaminants or other pollutants Any evidence of rodent holes if facility is acting as a dam or berm, or any evidence of water piping through dam or berm via rodent holes Water ponding in infiltration pond after rainfall ceases and appropriate time allowed for infiltration. Sediment and debris fill bag more than 1/2 full. By visual inspection, little or no water flows through filter during heavy rain storms. Eroded over 2 in. deep where cause of damage is still present or where there is potential for continued erosion. Any erosion on a compacted berm embankment. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
19 Emergency Overflow Spillway and Berms over 4 feet in height Tree Growth Piping* Emergency Overflow/ Spillway Erosion* Pre-settling Ponds and Vaults Facility or Sump Filled with Sediment and/or Debris* Tree growth on berms or emergency spillway >4 ft in height or covering more than 10% of spillway. Discernable water flow through pond berm. Ongoing erosion with potential for erosion to continue. Only one layer of rock exists above native soil in area five square feet or larger, or any exposure of native soil at the top of out flow path of spillway. (Rip-rap on inside slopes need not be replaced.) See Side Slopes of Pond 6" or designed sediment trap depth of sediment. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
20 Public Inspection and Checklist STORMFILTER Below Ground Vault Sediment Accumulation on Media* Sediment Accumulation in Vault* Sediment depth exceeds inches. Sediment depth exceeds 6-inches in first chamber. Trash/Debris Sediment in Drain Pipes or Cleanouts* Damaged Pipes Access Cover Damaged/Not Working Vault Structure Includes Cracks in Wall, Bottom, Damage to Frame and/or Top Slab Baffles Access Ladder Damaged Below Ground Cartridge Type Filter Media* Short Circuiting Trash and debris accumulated on compost filter bed. When drain pipes, clean-outs, become full with sediment and/or debris. Any part of the pipes that are crushed or damaged due to corrosion and/or settlement. Cover cannot be opened; one person cannot open the cover using normal lifting pressure, corrosion/deformation of cover. Cracks wider than 1/2-inch or evidence of soil particles entering the structure through the cracks, or maintenance/inspection personnel determine that the vault is not structurally sound. Cracks wider than 1/2-inch at the joint of any inlet/outlet pipe or evidence of soil particles entering through the cracks. Baffles corroding, cracking warping, and/or showing signs of failure as determined by maintenance/inspection person. Ladder is corroded or deteriorated, not functioning properly, not securely attached to structure wall, missing rungs, cracks, and misaligned. Drawdown of water through the media takes longer than 1 hour and/or overflow occurs frequently. Flows do not properly enter filter cartridges. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
21 Public Inspection and Checklist Vaults, Tanks, and Pipes Storage Area Debris and Sediment* Joints Between Tank/Pipe Section Tank Pipe Bent Out of Shape Vault Structure Includes Cracks in Wall, Bottom, Damage to Frame and/or Top Slab Accumulated sediment depth exceeds 10% of the diameter of the storage area for 1/2 length of storage vault or any point depth exceeds 15% of diameter. (Example: 72-inch storage tank would require cleaning when sediment reaches depth of 7 inches for more than 1/2 length of tank.) Any openings or voids allowing material to be transported into facility. (Will require engineering analysis to determine structural stability). Any part of tank/pipe is bent out of shape more than 10% of its design shape. (Review required by engineer to determine structural stability). Cracks wider than 1/2-inch and any evidence of soil particles entering the structure through the cracks, or maintenance/inspection personnel determines that the vault is not structurally sound. Cracks wider than 1/2-inch at the joint of any inlet/outlet pipe or any evidence of soil particles entering the vault through the walls. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
22 Storage Area Cover Not in Place Locking Mechanism Not Working Cover Difficult to Remove Ladder Rungs Unsafe Catch Basins See Catch Basins Cover is missing or only partially in place. Any open manhole requires maintenance. Mechanism cannot be opened by one maintenance person with proper tools. Bolts into frame have less than 1/2 inch of thread (may not apply to self-locking lids). One maintenance person cannot remove lid after applying normal lifting pressure. Intent is to keep cover from sealing off access to maintenance. Ladder is unsafe due to missing rungs, misalignment, not securely attached to structure wall, rust, or cracks. See Catch Basins : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
23 Public Inspection and Checklist Wet Biofiltration Swale Sediment Water Depth Wetland Vegetation* Inlet/Outlet* Trash and Debris Erosion/Scouring* Sediment depth exceeds 2-inches in 10% of the swale treatment area. Water not retained to a depth of about 4 inches during the wet season. Vegetation becomes sparse and does not provide adequate filtration OR vegetation is crowded out by very dense clumps of cattail, which do not allow water to flow through the clumps. Inlet/outlet area clogged with sediment and/or debris. Trash and debris accumulated in the bioswale. Swale has eroded or scoured due to flow channelization, or higher flows. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
24 Public Inspection and Checklist Wetponds Water level First cell is empty, doesn't hold water. Trash and Debris* Inlet/Outlet Pipe* Sediment Accumulation in Pond Bottom* Oil Sheen on Water Erosion* Settlement of Pond Dike/Berm* Internal Berm Overflow Spillway Accumulation that exceeds 1 CF per 1000-SF of pond area. Inlet/Outlet pipe clogged with sediment and/or debris material. Sediment accumulations in pond bottom that exceeds the depth of sediment zone plus 6-inches, usually in the first cell. Prevalent and visible oil sheen. Erosion of the pond s side slopes and/or scouring of the pond bottom, that exceeds 6-inches, or where continued erosion is prevalent. Any part of these components that has settled 4-inches or lower than the design elevation, or inspector determines dike/berm is unsound. Berm dividing cells should be level. Rock is missing and soil is exposed at top of spillway or outside slope. Debris Barriers (e.g., Trash Racks) Trash and Debris* Damaged/ Missing Bars Inlet/Outlet Pipe Trash or debris that is plugging more than 20% of the openings in the barrier. Bars are bent out of shape more than 3 inches. Bars are missing or entire barrier missing. Bars are loose and rust is causing 50% deterioration to any part of barrier. Debris barrier missing or not attached to pipe : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
25 Fencing Missing or broken parts Erosion Damaged Parts Deteriorating Paint or Protective Coating Gates Damaged or missing member Any defect in the fence that permits easy entry to a facility. Erosion more than 4 inches high and inches wide permitting an opening under a fence. Damage to gate/fence, posts out of plumb, or rails bent more than 6 inches Part or parts that have a rusting or scaling condition that has affected structural adequacy. Missing gate or locking devices, broken or missing hinges, out of plum more than 6 inches and more than 1 foot out of design alignment, or missing stretcher bar, stretcher bands, and ties. : Enter 1 if maintenance is need and include WO#. Enter 2 if maintenance was performed same day.
Sediment Trap. A temporary runoff containment area, which promotes sedimentation prior to discharge of the runoff through a stabilized spillway.
 Sediment Trap SC-15 Source: Caltrans Construction Site Best Management Practices Manual, 2003. Description A temporary runoff containment area, which promotes sedimentation prior to discharge of the runoff
Sediment Trap SC-15 Source: Caltrans Construction Site Best Management Practices Manual, 2003. Description A temporary runoff containment area, which promotes sedimentation prior to discharge of the runoff
Materials. Use materials meeting the following.
 208.01 Section 208. SOIL EROSION AND SEDIMENTATION CONTROL 208.01 Description. Install and maintain erosion and sedimentation controls to minimize soil erosion and to control sedimentation from affecting
208.01 Section 208. SOIL EROSION AND SEDIMENTATION CONTROL 208.01 Description. Install and maintain erosion and sedimentation controls to minimize soil erosion and to control sedimentation from affecting
Coarse Sediment Traps
 Coarse Sediment Traps SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils [2] Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Though primarily
Coarse Sediment Traps SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils [2] Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Though primarily
Sediment Control Practices. John Mathews Ohio Dept. of Natural Resources, Division of Soil and Water Resources
 Sediment Control Practices John Mathews Ohio Dept. of Natural Resources, Division of Soil and Water Resources Practices Treat the Largest Soil Particles Sand Sand Silt Clay Treated Untreated Settleable
Sediment Control Practices John Mathews Ohio Dept. of Natural Resources, Division of Soil and Water Resources Practices Treat the Largest Soil Particles Sand Sand Silt Clay Treated Untreated Settleable
Stone Outlet Sediment Trap
 3.12 Sediment Control Description: A stone outlet sediment trap is a small detention area formed by placing a stone embankment with an integral stone filter outlet across a drainage swale for the purpose
3.12 Sediment Control Description: A stone outlet sediment trap is a small detention area formed by placing a stone embankment with an integral stone filter outlet across a drainage swale for the purpose
Sediment Trap. At multiple locations within the project site where sediment control is needed.
 Sediment Trap SE-3 Objectives EC Erosion Control SE Sediment Control TR Tracking Control WE Wind Erosion Control Non-Stormwater NS Management Control Waste Management and WM Materials Pollution Control
Sediment Trap SE-3 Objectives EC Erosion Control SE Sediment Control TR Tracking Control WE Wind Erosion Control Non-Stormwater NS Management Control Waste Management and WM Materials Pollution Control
[1] Performance of the sediment trap depends on the type of outlet structure and the settling pond surface area.
![[1] Performance of the sediment trap depends on the type of outlet structure and the settling pond surface area. [1] Performance of the sediment trap depends on the type of outlet structure and the settling pond surface area.](/thumbs/76/74245181.jpg) Sediment Trench SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System [1] Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Performance of
Sediment Trench SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System [1] Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Performance of
Rock & Aggregate Drop Inlet Protection
 Rock & Aggregate Drop Inlet Protection SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils
Rock & Aggregate Drop Inlet Protection SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils
APPENDIX B WORKSHEETS & EXHIBITS
 APPENDIX B WORKSHEETS & EXHIBITS A worksheet provides the designer a representation of a measure that allows for input of specific design criteria. The plan designer will be required to assess field conditions
APPENDIX B WORKSHEETS & EXHIBITS A worksheet provides the designer a representation of a measure that allows for input of specific design criteria. The plan designer will be required to assess field conditions
TPDES: Soil, Erosion and Sedimentation Methods
 SAWS TPDES: Soil, Erosion and Sedimentation Methods Philip Handley Supervisor-Resource Protection & Compliance August 25, 2014 TPDES: Soil, Erosion and Sedimentation Methods Soil Common term: Dirt Common
SAWS TPDES: Soil, Erosion and Sedimentation Methods Philip Handley Supervisor-Resource Protection & Compliance August 25, 2014 TPDES: Soil, Erosion and Sedimentation Methods Soil Common term: Dirt Common
Suitable Applications Sediment traps should be considered for use:
 Categories EC Erosion Control SE Sediment Control TC Tracking Control WE Wind Erosion Control Non-Stormwater NS Management Control Waste Management and WM Materials Pollution Control Legend: Primary Objective
Categories EC Erosion Control SE Sediment Control TC Tracking Control WE Wind Erosion Control Non-Stormwater NS Management Control Waste Management and WM Materials Pollution Control Legend: Primary Objective
STREUVER FIDELCO CAPPELLI, LLC YONKERS DOWNTOWN DEVELOPMENT PHASE 1. DRAFT ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT For: PALISADES POINT
 STREUVER FIDELCO CAPPELLI, LLC YONKERS DOWNTOWN DEVELOPMENT PHASE 1 DRAFT ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT For: PALISADES POINT Prepared by: PAULUS, SOKOLOWSKI & SARTOR STORMWATER MANAGEMENT 1. Methodology
STREUVER FIDELCO CAPPELLI, LLC YONKERS DOWNTOWN DEVELOPMENT PHASE 1 DRAFT ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT For: PALISADES POINT Prepared by: PAULUS, SOKOLOWSKI & SARTOR STORMWATER MANAGEMENT 1. Methodology
Standards for Soil Erosion and Sediment Control in New Jersey May 2012
 STANDARD FOR SEDIMENT BASIN Definition A barrier, dam, excavated pit, or dugout constructed across a waterway or at other suitable locations to intercept and retain sediment. Basins created by construction
STANDARD FOR SEDIMENT BASIN Definition A barrier, dam, excavated pit, or dugout constructed across a waterway or at other suitable locations to intercept and retain sediment. Basins created by construction
U-Shaped Sediment Traps
 U-Shaped Sediment Traps SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils [1] Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Generally
U-Shaped Sediment Traps SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils [1] Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Generally
B805 TEMPORARY EROSION AND SEDIMENT CONTROL MEASURES - OPSS 805
 B805 MEASURES - OPSS 805 805.1 GENERAL Construction activities frequently remove protective cover and expose soil to accelerated rates of erosion. Sediments generated thereby can be conveyed via runoff
B805 MEASURES - OPSS 805 805.1 GENERAL Construction activities frequently remove protective cover and expose soil to accelerated rates of erosion. Sediments generated thereby can be conveyed via runoff
Flood and Stream Restoration
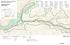 2 3 4 Pedestrian bridge under construction 3 CSPs perched on DS side Large area of sand deposition Bottom layer of gabions has been scoured out large bar of gabion stone Gabions slumping bank slope failure
2 3 4 Pedestrian bridge under construction 3 CSPs perched on DS side Large area of sand deposition Bottom layer of gabions has been scoured out large bar of gabion stone Gabions slumping bank slope failure
Continuing Education Associated with Maintaining CPESC and CESSWI Certification
 Continuing Education Associated with Maintaining CPESC and CESSWI Certification Module 2: Stormwater Management Principles for Earth Disturbing Activities Sponsors: ODOTs Local Technical Assistance Program
Continuing Education Associated with Maintaining CPESC and CESSWI Certification Module 2: Stormwater Management Principles for Earth Disturbing Activities Sponsors: ODOTs Local Technical Assistance Program
Selected Site BMPs: Why s the Water Muddy? John C. Hayes, Ph.D., P. E. Biosystems Engineering Clemson University
 Selected Site BMPs: Why s the Water Muddy? John C. Hayes, Ph.D., P. E. Biosystems Engineering Clemson University The BMP worked fine until last week when it rained! Turbidity Best Management Practices
Selected Site BMPs: Why s the Water Muddy? John C. Hayes, Ph.D., P. E. Biosystems Engineering Clemson University The BMP worked fine until last week when it rained! Turbidity Best Management Practices
APPENDIX G APPENDIX G SEDIMENT CONTAINMENT SYSTEM DESIGN RATIONALE
 APPENDIX G SEDIMENT CONTAINMENT SYSTEM DESIGN RATIONALE March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 G-2 FIGURES Page # Figure G.1 Estimated Runoff from Precipitation Over Different
APPENDIX G SEDIMENT CONTAINMENT SYSTEM DESIGN RATIONALE March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 G-2 FIGURES Page # Figure G.1 Estimated Runoff from Precipitation Over Different
APPENDIX B DESIGN CRITERIA FOR TEMPORARY WATER QUALITY BMPS USED DURING CONSTRUCTION
 APPENDIX B DESIGN CRITERIA FOR TEMPORARY WATER QUALITY BMPS USED DURING CONSTRUCTION This Appendix presents design criteria and example calculations for the following temporary water quality BMPs for use
APPENDIX B DESIGN CRITERIA FOR TEMPORARY WATER QUALITY BMPS USED DURING CONSTRUCTION This Appendix presents design criteria and example calculations for the following temporary water quality BMPs for use
HISTORY OF CONSTRUCTION FOR EXISTING CCR SURFACE IMPOUNDMENT PLANT GASTON ASH POND 40 CFR (c)(1)(i) (xii)
 HISTORY OF CONSTRUCTION FOR EXISTING CCR SURFACE IMPOUNDMENT PLANT GASTON ASH POND 40 CFR 257.73(c)(1)(i) (xii) (i) Site Name and Ownership Information: Site Name: E.C. Gaston Steam Plant Site Location:
HISTORY OF CONSTRUCTION FOR EXISTING CCR SURFACE IMPOUNDMENT PLANT GASTON ASH POND 40 CFR 257.73(c)(1)(i) (xii) (i) Site Name and Ownership Information: Site Name: E.C. Gaston Steam Plant Site Location:
Chutes Part 5: Rock linings
 Chutes Part 5: Rock linings DRAINAGE CONTROL TECHNIQUE Low Gradient Velocity Control Short-Term Steep Gradient Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control [1] Soil Treatment Permanent [2] [1] Chutes
Chutes Part 5: Rock linings DRAINAGE CONTROL TECHNIQUE Low Gradient Velocity Control Short-Term Steep Gradient Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control [1] Soil Treatment Permanent [2] [1] Chutes
Stormwater Guidelines and Case Studies. CAHILL ASSOCIATES Environmental Consultants West Chester, PA (610)
 Stormwater Guidelines and Case Studies CAHILL ASSOCIATES Environmental Consultants West Chester, PA (610) 696-4150 www.thcahill.com Goals and Challenges for Manual State Stormwater Policy More Widespread
Stormwater Guidelines and Case Studies CAHILL ASSOCIATES Environmental Consultants West Chester, PA (610) 696-4150 www.thcahill.com Goals and Challenges for Manual State Stormwater Policy More Widespread
Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System [1] Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils
![Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System [1] Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System [1] Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils](/thumbs/77/76519623.jpg) Sediment Weirs SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System [1] Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Type 3 classification
Sediment Weirs SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System [1] Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Type 3 classification
Construction Exits Rock pads
 Construction Exits Rock pads SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow [1] Clayey Soils Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Minor
Construction Exits Rock pads SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow [1] Clayey Soils Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Minor
APPENDIX A: EROSION & SEDIMENT CONTROL FORMS
 APPENDIX A: EROSION & SEDIMENT CONTROL FORMS Croy Engineering # 1580.08 EROSION & SEDIMENT CONTROL FORMS Appendix-1 This page intentionally left blank. Croy Engineering # 1580.08 EROSION & SEDIMENT CONTROL
APPENDIX A: EROSION & SEDIMENT CONTROL FORMS Croy Engineering # 1580.08 EROSION & SEDIMENT CONTROL FORMS Appendix-1 This page intentionally left blank. Croy Engineering # 1580.08 EROSION & SEDIMENT CONTROL
SILT FENCE EFFECTIVENESS
 SILT FENCE EFFECTIVENESS Michelle G. Holloway, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL 36688. E-mail: MLG@jaguar1.usouthal.edu. Sediment is the number one pollutant in Dog
SILT FENCE EFFECTIVENESS Michelle G. Holloway, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL 36688. E-mail: MLG@jaguar1.usouthal.edu. Sediment is the number one pollutant in Dog
PRELIMINARY ENGINEERING REPORT FOR SANITARY SEWER COLLECTION SYSTEM OSKALOOSA, IOWA 2017
 PRELIMINARY ENGINEERING REPORT FOR SANITARY SEWER COLLECTION SYSTEM OSKALOOSA, IOWA 2017 PRELIMINARY ENGINEERING REPORT FOR SANITARY SEWER COLLECTION SYSTEM OSKALOOSA, IOWA 2017 I hereby certify that this
PRELIMINARY ENGINEERING REPORT FOR SANITARY SEWER COLLECTION SYSTEM OSKALOOSA, IOWA 2017 PRELIMINARY ENGINEERING REPORT FOR SANITARY SEWER COLLECTION SYSTEM OSKALOOSA, IOWA 2017 I hereby certify that this
Sediment Weirs (Instream)
 Sediment Weirs (Instream) INSTREAM PRACTICES Flow Control No Channel Flow Dry Channels Erosion Control Low Channel Flows Shallow Water Sediment Control High Channel Flows [1] Deep Water [1] Sediment weirs
Sediment Weirs (Instream) INSTREAM PRACTICES Flow Control No Channel Flow Dry Channels Erosion Control Low Channel Flows Shallow Water Sediment Control High Channel Flows [1] Deep Water [1] Sediment weirs
Crows Landing Naval Base Easement
 1 of 15 West Stanislaus Resource Conservation District Crows Landing Naval Base Easement Annual Reserve Monitoring Report Jamie McFarlin 11/112012 2 of 15 West Stanislaus Resource Conservation District
1 of 15 West Stanislaus Resource Conservation District Crows Landing Naval Base Easement Annual Reserve Monitoring Report Jamie McFarlin 11/112012 2 of 15 West Stanislaus Resource Conservation District
Rock Sizing for Batter Chutes
 Rock Sizing for Batter Chutes STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined batter chute Photo 2 Rock-lined batter chute 1. Introduction In the stormwater industry a chute is a steep drainage channel,
Rock Sizing for Batter Chutes STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined batter chute Photo 2 Rock-lined batter chute 1. Introduction In the stormwater industry a chute is a steep drainage channel,
Specifications Whitcomb Elementary School Demolition January 15, 2016
 SECTION 31 2500 - EROSION CONTROL PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS: A. The provisions of the Contract Documents apply to the work of this Section. B. The Virginia Erosion and Sediment Control Handbook,
SECTION 31 2500 - EROSION CONTROL PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS: A. The provisions of the Contract Documents apply to the work of this Section. B. The Virginia Erosion and Sediment Control Handbook,
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
1.0 INSPECTION ANNUAL INSPECTION, JUNE 29, 2011 CARMACKS COPPER PROJECT, CARMACKS, YUKON. Dear Mr. West-Sells,
 Doc. No. 162 Rev. 0 Mr. Paul West-Sells President & Chief Operating Officer Western Copper Corporation 2060-1111 West Georgia Street Vancouver, BC V6E 4M3 ANNUAL INSPECTION, JUNE 29, 2011 CARMACKS COPPER
Doc. No. 162 Rev. 0 Mr. Paul West-Sells President & Chief Operating Officer Western Copper Corporation 2060-1111 West Georgia Street Vancouver, BC V6E 4M3 ANNUAL INSPECTION, JUNE 29, 2011 CARMACKS COPPER
CCR Rule Annual Inspection Report (cont.) 2
 The inspection findings consisted of maintenance items and items that were not observed to be signs or potential signs of significant structural weakness. No deficiencies or disrupting conditions that
The inspection findings consisted of maintenance items and items that were not observed to be signs or potential signs of significant structural weakness. No deficiencies or disrupting conditions that
Rock Sizing for Waterway & Gully Chutes
 Rock Sizing for Waterway & Gully Chutes WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined waterway chute Photo 2 Rock-lined gully chute 1. Introduction A waterway chute is a stabilised section of channel
Rock Sizing for Waterway & Gully Chutes WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined waterway chute Photo 2 Rock-lined gully chute 1. Introduction A waterway chute is a stabilised section of channel
WQ Outlet Design Single Orifice Orifice diameter = 24. Perforated riser/orifice Plate Outlet area per perforation row = 4
 These calculations should be used when designing the outlet structures for extended wet and dry detention basins (Sections 4. 7 and 4.8). The water quality outlet size and the trash rack design will vary
These calculations should be used when designing the outlet structures for extended wet and dry detention basins (Sections 4. 7 and 4.8). The water quality outlet size and the trash rack design will vary
Template for Sediment and Erosion Control Plan General Instructions. Section Instructions
 Template for Sediment and Erosion Control Plan General Instructions Introduction: Soil erosion and sediment deposition from farmlands can contribute to degraded surface water quality. Sediment delivery
Template for Sediment and Erosion Control Plan General Instructions Introduction: Soil erosion and sediment deposition from farmlands can contribute to degraded surface water quality. Sediment delivery
Instream Sediment Control Systems
 Instream Sediment Control Systems INSTREAM PRACTICES Photo 1 Photo 2 Modular sediment The information contained within this series of fact sheets deals only with the design of temporary instream sediment
Instream Sediment Control Systems INSTREAM PRACTICES Photo 1 Photo 2 Modular sediment The information contained within this series of fact sheets deals only with the design of temporary instream sediment
Provide sediment tubes for ditch check and Type A inlet structure filter applications that meet the minimum performance requirements of Table 1.
 Supplemental Technical Specification for SEDIMENT TUBES SCDOT Designation: SC-M-815-1 (03/08) 1.0 Sediment Tubes This Supplemental Specification replaces sections 815.1.1.2, 815.2.3, 815.4.5, 815.5, and
Supplemental Technical Specification for SEDIMENT TUBES SCDOT Designation: SC-M-815-1 (03/08) 1.0 Sediment Tubes This Supplemental Specification replaces sections 815.1.1.2, 815.2.3, 815.4.5, 815.5, and
EROSION CONTROL NARRATIVE
 EROSION CONTROL NARRATIVE Erosion and sediment control has been designed for the Willow Bend Phase I Subdivision according to UDFCD and the City of Thornton criteria, in order to minimize erosion and sediment
EROSION CONTROL NARRATIVE Erosion and sediment control has been designed for the Willow Bend Phase I Subdivision according to UDFCD and the City of Thornton criteria, in order to minimize erosion and sediment
Stormwater Outlet Sediment Traps
 Stormwater Outlet Traps SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUES Photo 1 Excavated sediment trap just prior to scheduled clean-out (note energy dissipater at end of pipe) Photo 2 A supplementary straw bale barrier
Stormwater Outlet Traps SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUES Photo 1 Excavated sediment trap just prior to scheduled clean-out (note energy dissipater at end of pipe) Photo 2 A supplementary straw bale barrier
Geosynthetics Applications and Performance Reviews Select Case Histories
 Geosynthetics Applications and Performance Reviews Select Case Histories Debora J. Miller, Ph.D., P.E.; Dean B. Durkee,, Ph.D., P.E.; Michael A. Morrison, P.E., David B. Wilson, P.E., and Kevin Smith,
Geosynthetics Applications and Performance Reviews Select Case Histories Debora J. Miller, Ph.D., P.E.; Dean B. Durkee,, Ph.D., P.E.; Michael A. Morrison, P.E., David B. Wilson, P.E., and Kevin Smith,
Mr. Michael Malone CPS Energy 145 Navarro Street San Antonio, Texas Project No
 January 17, 2018 Mr. Michael Malone 145 Navarro Street San Antonio, Texas 78205 Project No. 0337367 Environmental Resources Management CityCentre Four 840 West Sam Houston Pkwy N. Suite 600 Houston, Texas
January 17, 2018 Mr. Michael Malone 145 Navarro Street San Antonio, Texas 78205 Project No. 0337367 Environmental Resources Management CityCentre Four 840 West Sam Houston Pkwy N. Suite 600 Houston, Texas
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY
 INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART 257.82 PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY EPA s Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals from Electric Utilities Final Rule (40 C.F.R.
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART 257.82 PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY EPA s Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals from Electric Utilities Final Rule (40 C.F.R.
Guide to the use of the Erosion and Sediment Control Evaluation Tool
 Guide to the use of the Erosion and Sediment Control Evaluation Tool December 2017 If you require content in an alternate format please contact us at 905-895-1281 or by email at Accessibility@LSRCA.on.ca
Guide to the use of the Erosion and Sediment Control Evaluation Tool December 2017 If you require content in an alternate format please contact us at 905-895-1281 or by email at Accessibility@LSRCA.on.ca
Agenda. INDOT Office of Environmental Services. Describe Results of FHWA QAR. Landscape and Waterway Permitting Unit. Interviews Site Inspections
 Nathan Saxe Administrator, Ecology and Waterway Permitting Section Back to Basics: Erosion and Sediment Control FHWA INDOT Quality Assurance Review (QAR) Results 1 Agenda INDOT Office of Environmental
Nathan Saxe Administrator, Ecology and Waterway Permitting Section Back to Basics: Erosion and Sediment Control FHWA INDOT Quality Assurance Review (QAR) Results 1 Agenda INDOT Office of Environmental
CONSTRUCTION EXIT SEDIMENT BARRIER
 241428_itizen ield Guide_v3 2/22/06 11:09 M Page 1 (1,1) ONSTRUTION EXIT stone pad located where traffic leaves a construction site to eliminate the transport of soil to public streets. SEDIMENT BRRIER
241428_itizen ield Guide_v3 2/22/06 11:09 M Page 1 (1,1) ONSTRUTION EXIT stone pad located where traffic leaves a construction site to eliminate the transport of soil to public streets. SEDIMENT BRRIER
STRUCTURAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT
 STRUCTURAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT CFR 257.73(d) Bottom Ash Pond Complex Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio October, 2016 Prepared for: Cardinal Operating Company Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio Prepared by: Geotechnical
STRUCTURAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT CFR 257.73(d) Bottom Ash Pond Complex Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio October, 2016 Prepared for: Cardinal Operating Company Cardinal Plant Brilliant, Ohio Prepared by: Geotechnical
FOR PROJECTS INITIATED AFTER NOVEMBER 1, 2008 ITEM 716 EMBANKMENT EARTH OUTLET SEDIMENT TRAP
 AFTER NOVEMBER 1, 2008 ITEM 716 EMBANKMENT EARTH OUTLET SEDIMENT TRAP 716.1 Description. This work shall consist of furnishing, installing, maintaining, and removing temporary erosion protection and sediment
AFTER NOVEMBER 1, 2008 ITEM 716 EMBANKMENT EARTH OUTLET SEDIMENT TRAP 716.1 Description. This work shall consist of furnishing, installing, maintaining, and removing temporary erosion protection and sediment
Stage Discharge Tabulation for Only Orifice Flow
 Stage Discharge Tabulation for Only Orifice Flow DEPTH STAGE DISCHARGE (meters) (feet) (meters) (feet) (m 3 /s) (ft 3 /s) 0 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 1.20 1.40 1.60 1.80 2.00 0.7 1.3 2.0 2.6 3.3 3.9 4.6
Stage Discharge Tabulation for Only Orifice Flow DEPTH STAGE DISCHARGE (meters) (feet) (meters) (feet) (m 3 /s) (ft 3 /s) 0 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 1.20 1.40 1.60 1.80 2.00 0.7 1.3 2.0 2.6 3.3 3.9 4.6
ARMORED DITCH DEGRADATION AND ISSUES WITH EROSION
 ARMORED DITCH DEGRADATION AND ISSUES WITH EROSION Cody Morris, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, Mobile AL, 36688. E- mail: csm805@jagmail.southalabama.edu. When armored ditches
ARMORED DITCH DEGRADATION AND ISSUES WITH EROSION Cody Morris, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, Mobile AL, 36688. E- mail: csm805@jagmail.southalabama.edu. When armored ditches
 Rock Slope Analysis Small and Large Scale Failures Mode of Failure Marklands Test To establish the possibility of wedge failure. Plane failure is a special case of wedge failure. Sliding along
Rock Slope Analysis Small and Large Scale Failures Mode of Failure Marklands Test To establish the possibility of wedge failure. Plane failure is a special case of wedge failure. Sliding along
**Temporary Erosion Control**
 Construction operations And methods **Temporary Erosion Control** The test will more than likely just have a basic word problem dealing with Erosion control, if it has anything on the test. So just review,
Construction operations And methods **Temporary Erosion Control** The test will more than likely just have a basic word problem dealing with Erosion control, if it has anything on the test. So just review,
Fish Passage at Road Crossings
 Fish Passage at Road Crossings 1 Crossing Design Workshop Outline 1:00 to 2:00 Intro, Design Overview, Channel Width 2:00 to 2:15 Break 2:15 to 3:15 No-Slope, Stream Simulation Design 3:15 to 3:30 Break
Fish Passage at Road Crossings 1 Crossing Design Workshop Outline 1:00 to 2:00 Intro, Design Overview, Channel Width 2:00 to 2:15 Break 2:15 to 3:15 No-Slope, Stream Simulation Design 3:15 to 3:30 Break
Limited Visual Dam Safety Inspections OA Oahu Reservoir No Oahu, Hawaii
 Limited Visual Dam Safety Inspections OA00137 Oahu Reservoir No. 155 Oahu, Hawaii Prepared by: U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS HONOLULU DISTRICT STATE OF HAWAII DEPARTMENT OF LAND AND NATURAL RESOURCES May
Limited Visual Dam Safety Inspections OA00137 Oahu Reservoir No. 155 Oahu, Hawaii Prepared by: U.S. ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS HONOLULU DISTRICT STATE OF HAWAII DEPARTMENT OF LAND AND NATURAL RESOURCES May
In-channel coarse sediment trap Best Management Practice
 In-channel coarse sediment trap Best Management Practice By Henry R. Hudson July 2002 Environmental Management Associates Ltd., Christchurch Complexity Environmental Value Cost Low Moderate High Low Moderate
In-channel coarse sediment trap Best Management Practice By Henry R. Hudson July 2002 Environmental Management Associates Ltd., Christchurch Complexity Environmental Value Cost Low Moderate High Low Moderate
Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES. Introduction. The mechanics of gully erosion
 Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES Gully erosion A complex of processes whereby the removal of soil is characterised by incised channels in the landscape. NSW Soil Conservation Service,
Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES Gully erosion A complex of processes whereby the removal of soil is characterised by incised channels in the landscape. NSW Soil Conservation Service,
Construction Exits Vibration grids
 Construction Exits Vibration grids SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils [1] Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1]
Construction Exits Vibration grids SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils [1] Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1]
Stormwater Inlet Sediment Traps
 Stormwater Inlet Sediment Traps SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUES Photo 1 Kerb inlet Photo 2 Field (drop) inlet Table 1 provides the recommended default classification of various sediment control systems suitable
Stormwater Inlet Sediment Traps SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUES Photo 1 Kerb inlet Photo 2 Field (drop) inlet Table 1 provides the recommended default classification of various sediment control systems suitable
Rock Sizing for Small Dam Spillways
 Rock Sizing for Small Dam Spillways STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined spillway on a construction site sediment basin Photo 2 Rock-lined spillway on a small farm dam 1. Introduction A chute
Rock Sizing for Small Dam Spillways STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined spillway on a construction site sediment basin Photo 2 Rock-lined spillway on a small farm dam 1. Introduction A chute
Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget
 Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget Prepared for: Prepared By: - I. Introduction The Black Gore Creek Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) was developed in collaboration
Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget Prepared for: Prepared By: - I. Introduction The Black Gore Creek Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) was developed in collaboration
Rock Sizing for Multi-Pipe & Culvert Outlets
 Rock Sizing for Multi-Pipe & Culvert Outlets STORMWATER AND WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock pad outlet structure at end of a duel stormwater pipe outlet Photo 2 Rock pad outlet structure at
Rock Sizing for Multi-Pipe & Culvert Outlets STORMWATER AND WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock pad outlet structure at end of a duel stormwater pipe outlet Photo 2 Rock pad outlet structure at
Attachment B to Technical Memorandum No.2. Operations Plan of Ross Valley Detention Basins
 Attachment B to Technical Memorandum No.2 Operations Plan of Ross Valley Detention Basins Operations Plan of Ross Valley Detention Basins Stetson Engineers Inc. January 26, 2011 1.0 Introduction Achieving
Attachment B to Technical Memorandum No.2 Operations Plan of Ross Valley Detention Basins Operations Plan of Ross Valley Detention Basins Stetson Engineers Inc. January 26, 2011 1.0 Introduction Achieving
RESERVOIR DRAWDOWN RATES/RESERVOIR DRAWDOWN TEST Iron Gate, Copco (I & II), and JC Boyle Dams
 TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM No. 1 TO: Michael Bowen California Coastal Conservancy Geotechnical & Earthquake Engineering Consultants CC: Eric Ginney Philip Williams & Associates PREPARED BY: Paul Grant SUBJECT:
TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM No. 1 TO: Michael Bowen California Coastal Conservancy Geotechnical & Earthquake Engineering Consultants CC: Eric Ginney Philip Williams & Associates PREPARED BY: Paul Grant SUBJECT:
LOGO Self-Cleansing of Storm Drain through Incipient Motion Design Concept and Flushing Gate
 LOGO Self-Cleansing of Storm Drain through Incipient Motion Design Concept and Flushing Gate River Engineering & Urban Drainage Research Centre (REDAC) Sedimentation Problem Sediment deposits in drainage
LOGO Self-Cleansing of Storm Drain through Incipient Motion Design Concept and Flushing Gate River Engineering & Urban Drainage Research Centre (REDAC) Sedimentation Problem Sediment deposits in drainage
Rucker Pond. Background
 Rucker Pond Background The Rucker Basin consists of two subbasins (East and West) that drain to a single area known as Rucker Pond. Both subbasins have the same hydraulic parameters, but have different
Rucker Pond Background The Rucker Basin consists of two subbasins (East and West) that drain to a single area known as Rucker Pond. Both subbasins have the same hydraulic parameters, but have different
Instream Erosion Control General
 Instream Erosion Control General EROSION CONTROL TECHNIQUES Revegetation Temperate Climates Short-Term Non Vegetation Wet Tropics Long-Term Weed Control [1] Semi-Arid Zones Permanent [1] Weed control attributes
Instream Erosion Control General EROSION CONTROL TECHNIQUES Revegetation Temperate Climates Short-Term Non Vegetation Wet Tropics Long-Term Weed Control [1] Semi-Arid Zones Permanent [1] Weed control attributes
Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent [1]
![Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent [1] Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent [1]](/thumbs/87/96478185.jpg) Rock Linings DRAINAGE CONTROL TECHNIQUE Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent [1] [1] The design of permanent installations
Rock Linings DRAINAGE CONTROL TECHNIQUE Low Gradient Velocity Control Short Term Steep Gradient Channel Lining Medium-Long Term Outlet Control Soil Treatment Permanent [1] [1] The design of permanent installations
Long Valley Meadow Restoration Project
 Long Valley Meadow Restoration Project USDA Forest Service Mogollon Rim Ranger District Coconino National Forest Coconino County, Arizona T13N, R9E, Section 12 and T13N, R10E, Sections 6 and 7 Gila and
Long Valley Meadow Restoration Project USDA Forest Service Mogollon Rim Ranger District Coconino National Forest Coconino County, Arizona T13N, R9E, Section 12 and T13N, R10E, Sections 6 and 7 Gila and
Etobicoke Exfiltration System: Monitoring and Evaluation. Tim Van Seters Ryerson University July 24, 2015
 Etobicoke Exfiltration System: Monitoring and Evaluation Tim Van Seters Ryerson University July 24, 2015 Presentation Outline Summary of 1994 1995 Candaras Associates study Summary of 1996-1998 SWAMP Study
Etobicoke Exfiltration System: Monitoring and Evaluation Tim Van Seters Ryerson University July 24, 2015 Presentation Outline Summary of 1994 1995 Candaras Associates study Summary of 1996-1998 SWAMP Study
Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage
 Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
ATTACHMENT D SNOW REMOVAL AND DE-ICING PROCEDURES
 Interstate Reliability Project 345-kV Transmission Lines Development & Management Plan Volume 2 ATTACHMENT D SNOW REMOVAL AND DE-ICING PROCEDURES INTERSTATE RELIABILITY PROJECT The Interstate Reliability
Interstate Reliability Project 345-kV Transmission Lines Development & Management Plan Volume 2 ATTACHMENT D SNOW REMOVAL AND DE-ICING PROCEDURES INTERSTATE RELIABILITY PROJECT The Interstate Reliability
Stormwater Work Projects 2013
 Stormwater Work Projects 2013 Pound Ln. A customer called in a complaint that every >me it rained, his driveway was flooded from the water coming off the roadway. Driveway Pound Ln. Pound Ln. 16 th Ave.
Stormwater Work Projects 2013 Pound Ln. A customer called in a complaint that every >me it rained, his driveway was flooded from the water coming off the roadway. Driveway Pound Ln. Pound Ln. 16 th Ave.
Little Swan Lake. Dam Inspection & Siltation Study Prepared By: William Klingner, P.E., CFM October 28, 2018
 Little Swan Lake Dam Inspection & Siltation Study Prepared By: William Klingner, P.E., CFM October 28, 2018 Agenda Little Swan Lake Dam Inspection Theoretical Little Swan Lake Siltation Rate Calculations
Little Swan Lake Dam Inspection & Siltation Study Prepared By: William Klingner, P.E., CFM October 28, 2018 Agenda Little Swan Lake Dam Inspection Theoretical Little Swan Lake Siltation Rate Calculations
Observations on Surface Water in the Seminary Fen in Spring, Prepared 6/4/13 by Sam Wetterlin; updated 7/28/13
 Observations on Surface Water in the Seminary Fen in Spring, 2013 Prepared 6/4/13 by Sam Wetterlin; updated 7/28/13 Ordinarily, a calcareous fen is primarily dependent on upwelling mineral-rich, oxygen-poor
Observations on Surface Water in the Seminary Fen in Spring, 2013 Prepared 6/4/13 by Sam Wetterlin; updated 7/28/13 Ordinarily, a calcareous fen is primarily dependent on upwelling mineral-rich, oxygen-poor
ONE ROCK DAM ORD. capture more sediment. The original ORD becomes the splash apron for the new layer. STEP 4: When ORD fills in, add a new layer
 ONE ROCK DAM ORD A low grade control structure built with a single layer of rock on the bed of the channel. ORDs stabilize the bed of the channel by slowing the flow of water, increasing roughness, recruiting
ONE ROCK DAM ORD A low grade control structure built with a single layer of rock on the bed of the channel. ORDs stabilize the bed of the channel by slowing the flow of water, increasing roughness, recruiting
Culvert and Pipe Phasing
 Culvert and Pipe Phasing Barney Blackburn, PE, CPESC, CPSWQ NCDOT Roadside Environmental Unit Soil & Water Engineering Section Supervisor NCDOT Culvert Phasing Process Hydraulics Unit: Culvert Survey Report
Culvert and Pipe Phasing Barney Blackburn, PE, CPESC, CPSWQ NCDOT Roadside Environmental Unit Soil & Water Engineering Section Supervisor NCDOT Culvert Phasing Process Hydraulics Unit: Culvert Survey Report
Table 5-1 Sampling Program Summary for Milltown Ford Avenue Redevelopment Area, NJ.
 Table 5- Sampling Program Summary for Milltown Ford Avenue Redevelopment Area, NJ. Transformer Pads (9 pads: PAD 9) Evaluate if PCBs presently exist in soils adjacent to, and/or beneath the transformer
Table 5- Sampling Program Summary for Milltown Ford Avenue Redevelopment Area, NJ. Transformer Pads (9 pads: PAD 9) Evaluate if PCBs presently exist in soils adjacent to, and/or beneath the transformer
Sediment Control Log (SCL)
 Description A sediment control log is a linear roll made of natural materials such as straw, coconut fiber, or other fibrous material trenched into the ground and held with a wooden stake. Sediment control
Description A sediment control log is a linear roll made of natural materials such as straw, coconut fiber, or other fibrous material trenched into the ground and held with a wooden stake. Sediment control
Background. Valley fills Sites in the Area. Construction over Mine Spoil Fills
 Construction over Mine Spoil Fills Wayne A. Karem, PhD, PE, PG, D.GE 2014 KSPE Annual Conference Background Strip mining; mountaintop and contour mining Creates huge quantities of mine spoil The mine spoil
Construction over Mine Spoil Fills Wayne A. Karem, PhD, PE, PG, D.GE 2014 KSPE Annual Conference Background Strip mining; mountaintop and contour mining Creates huge quantities of mine spoil The mine spoil
Aquifer an underground zone or layer of sand, gravel, or porous rock that is saturated with water.
 Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
Erosion and Sediment Control Measures 2.7 Silt Fences
 Erosion and Sediment Control Measures Silt fences are designed to intercept sheet flow sediment laden stormwater run-off and filter out both the larger and smaller particles of sediment. Silt fences and
Erosion and Sediment Control Measures Silt fences are designed to intercept sheet flow sediment laden stormwater run-off and filter out both the larger and smaller particles of sediment. Silt fences and
Template for Sediment and Erosion Control Plan General Instructions
 Template for Sediment and Erosion Control Plan General Instructions Introduction: Soil erosion and sediment deposition from farmlands can contribute to degraded surface water quality. Sediment delivery
Template for Sediment and Erosion Control Plan General Instructions Introduction: Soil erosion and sediment deposition from farmlands can contribute to degraded surface water quality. Sediment delivery
CR AAO Bridge. Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design. Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District
 CR AAO Bridge Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District Old County Road AAO Bridge Map courtesy of Marquette County Silver Lake Basin McClure Basin
CR AAO Bridge Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District Old County Road AAO Bridge Map courtesy of Marquette County Silver Lake Basin McClure Basin
NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA
 QUAKER RUN Stream and Wetland Restoration As-Built Completion Report and First Year Monitoring Data Coal Township NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA Upstream Before Upstream After Prepared for: COAL TOWNSHIP 805
QUAKER RUN Stream and Wetland Restoration As-Built Completion Report and First Year Monitoring Data Coal Township NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA Upstream Before Upstream After Prepared for: COAL TOWNSHIP 805
Introduction and Organization of Instructions The following is a brief outline for use the skimmer, how to size and shape the basin, how to construct
 A Manual for Designing, Installing, and Maintaining Skimmer Sediment Basins J. W. Faircloth & Son Post Office Box 757 Hillsborough, North Carolina 27278 Telephone/Fax (919) 732-1266 From fairclothskimmer.com,
A Manual for Designing, Installing, and Maintaining Skimmer Sediment Basins J. W. Faircloth & Son Post Office Box 757 Hillsborough, North Carolina 27278 Telephone/Fax (919) 732-1266 From fairclothskimmer.com,
Stream Geomorphology. Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012
 Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Vetiver System for Stream Bank Stabilisation. Paul Truong
 Vetiver System for Stream Bank Stabilisation (With special references to the river and canal bank stabilisation in Australia and Vietnam) Paul Truong Director, The Vetiver Network International, Veticon
Vetiver System for Stream Bank Stabilisation (With special references to the river and canal bank stabilisation in Australia and Vietnam) Paul Truong Director, The Vetiver Network International, Veticon
NRCS - THUNDER ROAD #2, TRIBUTARY TO QUILEUTE RIVER CULVERT REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PLAN CLALLAM COUNTY, WA., WRIA: 20, SITE:
 WDFW CONTROL POINT #1 Re-Bar, Elevation 100.00 Northing 10004.441 Easting 8002.5905 WDFW CONTROL POINT #2 Re-Bar, Elevation 101.36 Northing 10031.6683 Easting 846.0623 WDFW TBM #1 Spike in Tree Elevation
WDFW CONTROL POINT #1 Re-Bar, Elevation 100.00 Northing 10004.441 Easting 8002.5905 WDFW CONTROL POINT #2 Re-Bar, Elevation 101.36 Northing 10031.6683 Easting 846.0623 WDFW TBM #1 Spike in Tree Elevation
WARNING. INJURY HAZARD Failure to observe these instructions could lead to severe injury or death.
 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS ATV Front Plow Mount Kit Part Number: 80031 Applications: 2007+ Honda Rancher 420 2007+ Honda Rancher ES 420 2009+ Honda Rancher AT 420 *Not compatible with 2.5ci or A2000 winches
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS ATV Front Plow Mount Kit Part Number: 80031 Applications: 2007+ Honda Rancher 420 2007+ Honda Rancher ES 420 2009+ Honda Rancher AT 420 *Not compatible with 2.5ci or A2000 winches
CHAPTER FIVE 5.0 STABILITY OF CUT SLOPES IN THE STUDY AREA. them limited by a thick canopy of vegetation and steep slope angles.
 CHAPTER FIVE 5.0 STABILITY OF CUT SLOPES IN THE STUDY AREA 5.1. Introduction Ukay Perdana area is a developing community with continuous building activities and road construction. There are thus only left
CHAPTER FIVE 5.0 STABILITY OF CUT SLOPES IN THE STUDY AREA 5.1. Introduction Ukay Perdana area is a developing community with continuous building activities and road construction. There are thus only left
TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF TABLES. Page
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 11.0 EFFECTS OF THE ENVIRONMENT ON THE PROJECT... 11-1 11.1 Weather Conditions... 11-1 11.2 Flooding... 11-2 11.3 Forest Fires... 11-2 11.4 Permafrost and Subsidence Risk... 11-3
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 11.0 EFFECTS OF THE ENVIRONMENT ON THE PROJECT... 11-1 11.1 Weather Conditions... 11-1 11.2 Flooding... 11-2 11.3 Forest Fires... 11-2 11.4 Permafrost and Subsidence Risk... 11-3
Case Study 14. Rocky Creek Vented Box Culvert Ford
 Case Study. Rocky Creek Vented Box Culvert Ford Location West Central Arkansas. Ouachita National Forest; Oden Ranger District. Rocky Creek crossing on Forest Road 887 (Muddy Gibbs Road). Crossing Description
Case Study. Rocky Creek Vented Box Culvert Ford Location West Central Arkansas. Ouachita National Forest; Oden Ranger District. Rocky Creek crossing on Forest Road 887 (Muddy Gibbs Road). Crossing Description
8. STATIC BARRIER EVALUATION
 8. STATIC BARRIER EVALUATION The construction of the barrier shown in Figure 5.3 permitted the sampling of water and measurement of ph at points along the entire length of each unit. Data on the variation
8. STATIC BARRIER EVALUATION The construction of the barrier shown in Figure 5.3 permitted the sampling of water and measurement of ph at points along the entire length of each unit. Data on the variation
STORMWATER MANAGEMENT REPORT
 STORMWATER MANAGEMENT REPORT THE FAIRWAYS AT EDGEWOOD LOTS 5 & 6, BLOCK 1201 TOWNSHIP OF RIVER VALE BERGEN COUNTY, NEW JERSEY PREPARED BY: DAPHNE A. GALVIN PROFESSIONAL ENGINEER LICENSE NO. 24GE03434900
STORMWATER MANAGEMENT REPORT THE FAIRWAYS AT EDGEWOOD LOTS 5 & 6, BLOCK 1201 TOWNSHIP OF RIVER VALE BERGEN COUNTY, NEW JERSEY PREPARED BY: DAPHNE A. GALVIN PROFESSIONAL ENGINEER LICENSE NO. 24GE03434900
design, construction, operation, and maintenance of the BAP is consistent with recognized and generally accepted good engineering standards.
 design, construction, operation, and maintenance of the BAP is consistent with recognized and generally accepted good engineering standards. In addition to the field inspection, Associated Engineers, Inc.
design, construction, operation, and maintenance of the BAP is consistent with recognized and generally accepted good engineering standards. In addition to the field inspection, Associated Engineers, Inc.
Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report No.2
 MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad. Chapter (7)
 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
A Homeowner s Guide to Landslides for Washington and Oregon
 Protect Your Home and Property 1 A Homeowner s Guide to Landslides for Washington and Oregon Washington Geological Survey and Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries LANDSLIDES ARE ONE OF THE
Protect Your Home and Property 1 A Homeowner s Guide to Landslides for Washington and Oregon Washington Geological Survey and Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries LANDSLIDES ARE ONE OF THE
