Dirty Snow and Arctic Climate
|
|
|
- Robert Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dirty Snow and Arctic Climate Charlie Zender and Mark Flanner Department of Earth System Science, University of California, Irvine Laboratoire de Glaciologie Géophysique de l Environnement, (LGGE), Grenoble, France National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), Boulder, Colorado Collaborators: M. Andreae (MPI), T. Bond (UIUC), F. Dominé (LGGE), N. Mahowald (NCAR), D. Muhs (USGS), T. Painter (NSIDC/UU), P. Rasch (NCAR), T. Roush (NASA) Presented to: Short-lived Pollutants and Arctic Climate (SPAC) Workshop Kjeller, Norway, November 5 8, 2007 (Web: snw spac pdf)
2 Abstract 1. Motivations to understand snow-albedo feedback (SAF) 2. SAF enhancement by snowpack vertical heating profile 3. Linking snowpack microphysics and aging to albedo 4. Snowpack forcing by and response to aerosol impurities 5. Related problems and projects
3 Monitoring to Quantify BC Cryosphere Interactions Make Continual or Regular-interval surface measurements at snow observatories to characterize 1. Reflectance dependence on specific surface area, impurity content 2. Surface-atmosphere exchange/deposition velocity 3. Reflectance diurnal cycle, variability 4. Closure of broadband surface reflectance Useful measurements include: 1. Snow and air temperatures, humidity, wind, precipitation, liquid 2. Aerosol Optical Depth (e.g., AERONET) 3. Multi-channel spectral and broadband solar reflectance Use spectral reflectances to estimate: 1. Snow specific surface area (SSA) 2. Impurity concentration (using SSA and visible channels) Replicates in perennial and seasonal snowpacks, e.g., Summit and Barrow.
4 Episodic Measurements of BC Cryosphere Interactions Make Opportunitistic and Episodic (e.g., pre/post aerosol plume) field measurements at observatories to 1. Calibrate optical BC estimates against mass-based measurements 2. Understand BC optical property aging since emission 3. Quantify BC scavenging above/within snowpack 4. Force and falsify snow evolution models used in GCMs Useful measurements include: 1. Snow BC optical properties and mixing state 2. Near-surface air BC concentration and optical properties 3. Snowpack density, BC concentration, temperature profiles Use chemical transport models to link field measurements to complementary laboratory studies and to regional and synoptic observations and campaigns involving aircraft/satellites. Use GCMs to extend across space and time scales.
5 Laboratory Measurements of BC Cryosphere Interactions Make controlled, complementary Laboratory measurements to: 1. Verify snow/ice reflectance perturbation by impurities with known microphysical optical properties 2. Devise/assess optical methods to estimate/segregate BC, OC, dust 3. Characterize metamorphism and hysteresis near melt-point 4. Melt-scavenging of impurities with known size/hygroscopic properties Useful Measurements include: 1. Spectral reflectance and SSA for snow with/out known impurities 2. Spectral reflectance and SSA evolution for different temperatures, temperature gradients, densities, and near-melt conditions 3. Impurity mass before/after melt events Laboratory data help to formulate, calibrate, and extend (beyond field conditions) the predictive relationships that models use to simulate aerosol cryosphere interactions.
6 FIGURE SPM-2. Global-average radiative forcing (RF) estimates and ranges in 2005 for anthropogenic carbon Figure dioxide 1: (CO Global-mean 2 ), methane radiative (CH 4 ), nitrous forcing oxide estimates, (N 2 O) and scale, other and important certainty agents in and mechanisms, (IPCC, 2007) together with the typical geographical extent (spatial scale) of the forcing and the assessed level of scientific understanding (LOSU). The net anthropogenic radiative forcing and its range are also shown.
7 Table 1: Arctic Response to Short-Lived Pollutants a Forcing Mechanism Temperature Response T [ C] Winter Spring Summer Fall Aerosol Direct Effect Aerosol Indirect Effect Thin Cloud Emissivity Black Carbon Snow Albedo BC/Snow Our Estimate Tropospheric Ozone Methane Total Total Our Estimate a Sources: Quinn et al. (2007, Submitted to Eos), Hansen et al. (2007, Clim. Dyn.), and Flanner et al. (2007, JGR)
8 H land for the y is for F. The ] were e same found period s from e (solid b) The er NH iments, iments r T s )is a s (T s ) eighted hough climate lues of Figure 3. Scatterplot of simulated springtime Da s /DT s values in climate change (ordinate) vs. simulated springtime Figure 2: Simulated springtime A s / T s north of 30 N under IPCC AR4 720 ppm scenario (ordinate) and present springtime seasonal cycle A s / T s (abscissa). (Hall and Qu, 2006, GRL)
9 1. References References Flanner, M. G., C. S. Zender, J. T. Randerson and P. J. Rasch, 2007: Presentday climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow. J. Geophys. Res., 112, D11202, doi: /2006jd Hall, A. and X. Qu, 2006: Using the current seasonal cycle to constrain snow albedo feedback in future climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33(L03502), doi: /2005gl Hansen, J., M. Sato, R. Ruedy, P. Kharecha, A. Lacis, R. Miller, L. Nazarenko, K. Lo, G. A. Schmidt, G. Russell, I. Aleinov, S. Bauer, E. Baum, B. Cairns, V. Canuto, M. Chandler, Y. Cheng, A. Cohen, A. D. Genio, G. Faluvegi, E. Fleming, A. Friend, T. Hall, C. Jackman, J. Jonas, M. Kelley, N. Y. Kiang, D. Koch, G. Labow, J. Lerner, S. Menon, T. Novakov, V. Oinas, J. Perlwitz, J. Perlwitz, D. Rind, A. Romanou, R. Schmunk, D. Shindell, P. Stone, S. Sun, D. Streets, N. Tausnev, D. Thresher, N. Unger, M. Yao and S. Zhang, 2007: Climate simulations
10 for with GISS modele. Clim. Dyn., pp. doi: /s IPCC, 2007: Climate change 2007: The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. p Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, NY, USA. Painter, T. H., J. Dozier, D. A. Roberts, R. E. Davis and R. O. Green, 2003: Retrieval of subpixel snow-covered area and grain size from imaging spectrometer data. Rem. Sens. Environ., 85, 64 77, doi: /s (02) Quinn, P. K., T. S. Bates, E. Baum, N. Doubleday, A. Fiore, M. Flanner, A. Fridlind, T. Garrett, D. Koch, S. Menon, D. Shindell, A. Stohl and s. G. Warren, 2007: Short-lived pollutants in the Arctic: Their climate impact and possible mitigation strategies. Submitted to Eos.
11 2. Problem: Can Dirty Snow be Remotely Sensed Snow grain-size has been remotely sensed with radiance-ratio techniques (e.g., Painter et al., 2003). Can snow impurities be monitored from space? Steve Warren is dubious because: Cloud contamination! Pristine sky NIR radiance ratios can yield information on snow grain size, which, combined with visible radiance, estimates surface soot concentration. Iterative procedure required because anisotropic reflectance factor (ARF) depends on wavelength, snow grain-size, and soot concentration. ARF sensitive to surface roughness, e.g., ripples, sastrugi, suncups Soot mimicked by thin snow, vegetation, sea-ice leads Atmospheric soot has similar spectral signature to surface soot
Present, Past, and Future Climate Effects and Efficacy of Dirty Snow
 Present, Past, and Future Climate Effects and Efficacy of Dirty Snow Charlie Zender, Mark Flanner, and Jim Randerson Department of Earth System Science, University of California, Irvine Natalie Mahowald,
Present, Past, and Future Climate Effects and Efficacy of Dirty Snow Charlie Zender, Mark Flanner, and Jim Randerson Department of Earth System Science, University of California, Irvine Natalie Mahowald,
Solar Influence on climate: Particle precipitation effects on the southern hemisphere tropical/subtropical lower stratosphere temperature
 Solar Influence on climate: Particle precipitation effects on the southern hemisphere tropical/subtropical lower stratosphere temperature Luis Eduardo Vieira and Ligia Alves da Silva SOHO observations
Solar Influence on climate: Particle precipitation effects on the southern hemisphere tropical/subtropical lower stratosphere temperature Luis Eduardo Vieira and Ligia Alves da Silva SOHO observations
Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols
 Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols Mark Flanner November 2, 2011 Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change 1 / 18 Arctic: Unique vulnerability to positive
Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols Mark Flanner November 2, 2011 Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change 1 / 18 Arctic: Unique vulnerability to positive
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle
 Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
Darkening of soot-doped natural snow: Measurements and model
 Darkening of soot-doped natural snow: Measurements and model C. S. Zender 1,2, F. Dominé 1, J.-C. Gallet 1, G. Picard 1 1 Laboratoire de Glaciologie et Géophysique de l Environnement, Grenoble, France
Darkening of soot-doped natural snow: Measurements and model C. S. Zender 1,2, F. Dominé 1, J.-C. Gallet 1, G. Picard 1 1 Laboratoire de Glaciologie et Géophysique de l Environnement, Grenoble, France
Black carbon in snow and its radiative forcing over the Arctic and Northern China: uncertainty associated with deposition and in-snow processes
 1 2 3 Black carbon in snow and its radiative forcing over the Arctic and Northern China: uncertainty associated with deposition and in-snow processes 4 5 Yun Qian 1*, Hailong Wang 1, Rudong Zhang 2,1,
1 2 3 Black carbon in snow and its radiative forcing over the Arctic and Northern China: uncertainty associated with deposition and in-snow processes 4 5 Yun Qian 1*, Hailong Wang 1, Rudong Zhang 2,1,
Light Absorbing Carbonaceous Aerosols (BC and BrnC) and their Climate Impacts
 Light Absorbing Carbonaceous Aerosols (BC and BrnC) and their Climate Impacts J I U M E N G L I U E A S 8 8 0 2 : C L O U D S, A E R O S O L S A N D C L I M AT E M A R. 2 5, 2 0 1 3 Terminology Light absorbing
Light Absorbing Carbonaceous Aerosols (BC and BrnC) and their Climate Impacts J I U M E N G L I U E A S 8 8 0 2 : C L O U D S, A E R O S O L S A N D C L I M AT E M A R. 2 5, 2 0 1 3 Terminology Light absorbing
INVESTIGATION ON THE RELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL AND RADIOMETRICAL PROPERTIES OF SNOW COVERS
 EARSeL eproceedings 7, 1/2008 68 INVESTIGATION ON THE RELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL AND RADIOMETRICAL PROPERTIES OF SNOW COVERS Roberto Salzano 1, Rosamaria Salvatori 1 and Florent Dominé 2 1. CNR, Institute
EARSeL eproceedings 7, 1/2008 68 INVESTIGATION ON THE RELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL AND RADIOMETRICAL PROPERTIES OF SNOW COVERS Roberto Salzano 1, Rosamaria Salvatori 1 and Florent Dominé 2 1. CNR, Institute
Consequences for Climate Feedback Interpretations
 CO 2 Forcing Induces Semi-direct Effects with Consequences for Climate Feedback Interpretations Timothy Andrews and Piers M. Forster School of Earth and Environment, University of Leeds, Leeds, LS2 9JT,
CO 2 Forcing Induces Semi-direct Effects with Consequences for Climate Feedback Interpretations Timothy Andrews and Piers M. Forster School of Earth and Environment, University of Leeds, Leeds, LS2 9JT,
Andreas Stohl Norwegian Institute for Air Research (NILU) and
 Andreas Stohl Norwegian Institute for Air Research (NILU) and E. Andrews, T. Berg, J. F. Burkhart, A. M. Fjæraa, C. Forster, A. Herber, S. Hoch, Ø. Hov, D. Kowal, C. Lunder, T. Mefford, W. W. McMillan,
Andreas Stohl Norwegian Institute for Air Research (NILU) and E. Andrews, T. Berg, J. F. Burkhart, A. M. Fjæraa, C. Forster, A. Herber, S. Hoch, Ø. Hov, D. Kowal, C. Lunder, T. Mefford, W. W. McMillan,
The role of snow-darkening effect in the Asian monsoon region
 The third ACAM Workshop in 1 Guangzhou, China (June 5-9, 2017) Theme 2.1 Aerosols and Clouds The role of snow-darkening effect in the Asian monsoon region Faculty of Engineering & Arctic Research Center
The third ACAM Workshop in 1 Guangzhou, China (June 5-9, 2017) Theme 2.1 Aerosols and Clouds The role of snow-darkening effect in the Asian monsoon region Faculty of Engineering & Arctic Research Center
MIZMAS: Modeling the Evolution of Ice Thickness and Floe Size Distributions in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. MIZMAS: Modeling the Evolution of Ice Thickness and Floe Size Distributions in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Chukchi and
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. MIZMAS: Modeling the Evolution of Ice Thickness and Floe Size Distributions in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Chukchi and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Radiative forcing and albedo feedback from the northern hemisphere cryosphere between 1979 and 2008 M. G. Flanner 1 *, K. M. Shell 2, M. Barlage 3, D. K. Perovich 4, & M. A. Tschudi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Radiative forcing and albedo feedback from the northern hemisphere cryosphere between 1979 and 2008 M. G. Flanner 1 *, K. M. Shell 2, M. Barlage 3, D. K. Perovich 4, & M. A. Tschudi
HUMAN FINGERPRINTS (1): OBSERVATIONS
 HUMAN FINGERPRINTS (1): OBSERVATIONS 1. Introduction: the story so far. 2. Global warming: the last 150 years 3. Is it really warming? 4. Fingerprints: the stratosphere, the hockey sticks Radiance (mw.m
HUMAN FINGERPRINTS (1): OBSERVATIONS 1. Introduction: the story so far. 2. Global warming: the last 150 years 3. Is it really warming? 4. Fingerprints: the stratosphere, the hockey sticks Radiance (mw.m
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science. Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
Wrap-up of Lecture 2. Aerosol Forcing and a Critique of the Global Warming Consensus
 Wrap-up of Lecture 2 Massive research efforts over the past two decades have allowed aerosol scientists to put boundaries on the "direct" and "cloud-albedo" forcings. [IPCC 2007, Fig SPM.2] When climate
Wrap-up of Lecture 2 Massive research efforts over the past two decades have allowed aerosol scientists to put boundaries on the "direct" and "cloud-albedo" forcings. [IPCC 2007, Fig SPM.2] When climate
CHAPTER 8. AEROSOLS 8.1 SOURCES AND SINKS OF AEROSOLS
 1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
!"#$%&'()*+,-./ I!"#$%&
 www.climatechange.cn Q = O OMMU P ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol.4, No.2 March, 2 8!"673-79 (28) 2--6 &'()*+,-./ I & NIO == N N=&' =NMMMUN O= &'()*+, =RNMSRR = NCAR! GCM CAM3. &'()*+,-&'()*+,
www.climatechange.cn Q = O OMMU P ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol.4, No.2 March, 2 8!"673-79 (28) 2--6 &'()*+,-./ I & NIO == N N=&' =NMMMUN O= &'()*+, =RNMSRR = NCAR! GCM CAM3. &'()*+,-&'()*+,
Modeled response of Greenland snowmelt to the presence of biomass burning based absorbing aerosols
 Modeled response of Greenland snowmelt to the presence of biomass burning based absorbing aerosols Jamie Ward University of Michigan Climate and Space Science 1 Introduction Black carbon (BC): aerosol
Modeled response of Greenland snowmelt to the presence of biomass burning based absorbing aerosols Jamie Ward University of Michigan Climate and Space Science 1 Introduction Black carbon (BC): aerosol
Arctic Chemistry And Climate
 21 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Chemistry And Climate Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
21 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Chemistry And Climate Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
Variability in Global Top-of-Atmosphere Shortwave Radiation Between 2000 And 2005
 Variability in Global Top-of-Atmosphere Shortwave Radiation Between 2000 And 2005 Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Collaborators: B.A. Wielicki, F.G. Rose, D.R. Doelling February
Variability in Global Top-of-Atmosphere Shortwave Radiation Between 2000 And 2005 Norman G. Loeb NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA Collaborators: B.A. Wielicki, F.G. Rose, D.R. Doelling February
MIZMAS: Modeling the Evolution of Ice Thickness and Floe Size Distributions in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. MIZMAS: Modeling the Evolution of Ice Thickness and Floe Size Distributions in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Chukchi and
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. MIZMAS: Modeling the Evolution of Ice Thickness and Floe Size Distributions in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Chukchi and
Métamorphisme de la neige et climat
 Neige 5 ème partie Métamorphisme de la neige et climat * Impact des conditions du métamorphisme sur la surface spécifique et l albédo * Impact des conditions du métamorphisme sur la conductivité thermique
Neige 5 ème partie Métamorphisme de la neige et climat * Impact des conditions du métamorphisme sur la surface spécifique et l albédo * Impact des conditions du métamorphisme sur la conductivité thermique
Radiative Climatology of the North Slope of Alaska and the Adjacent Arctic Ocean
 Radiative Climatology of the North Slope of Alaska and the Adjacent Arctic Ocean C. Marty, R. Storvold, and X. Xiong Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, Alaska K. H. Stamnes Stevens Institute
Radiative Climatology of the North Slope of Alaska and the Adjacent Arctic Ocean C. Marty, R. Storvold, and X. Xiong Geophysical Institute University of Alaska Fairbanks, Alaska K. H. Stamnes Stevens Institute
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback
 Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Arctic surface temperature change to emissions of black carbon within Arctic or midlatitudes
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 7788 7798, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50613, 2013 Arctic surface temperature change to emissions of black carbon within Arctic or midlatitudes Maria Sand,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 7788 7798, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50613, 2013 Arctic surface temperature change to emissions of black carbon within Arctic or midlatitudes Maria Sand,
Relation of atmospheric humidity and cloud properties to surface-near temperatures derived from GOME satellite observations
 Relation of atmospheric humidity and cloud properties to surface-near temperatures derived from GOME satellite observations Thomas Wagner 1, Steffen Beirle 1, Tim Deutschmann 2, Michael Grzegorski 2, Ulrich
Relation of atmospheric humidity and cloud properties to surface-near temperatures derived from GOME satellite observations Thomas Wagner 1, Steffen Beirle 1, Tim Deutschmann 2, Michael Grzegorski 2, Ulrich
HTAP-2 analysis for the Arctic
 Institute for Climate and Atmospheric Science SCHOOL OF EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT Photo: Chuck Brock, NOAA. HTAP-2 analysis for the Arctic Steve R. Arnold 1, Louisa K. Emmons 2, Kathy S. Law 3, Sarah A. Monks
Institute for Climate and Atmospheric Science SCHOOL OF EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT Photo: Chuck Brock, NOAA. HTAP-2 analysis for the Arctic Steve R. Arnold 1, Louisa K. Emmons 2, Kathy S. Law 3, Sarah A. Monks
Arctic Climate Response to Forcing from Light-Absorbing Particles in Snow and Sea Ice in CESM
 Manuscript prepared for Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: 30 December 11 Arctic Climate Response to Forcing from Light-Absorbing Particles
Manuscript prepared for Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: 30 December 11 Arctic Climate Response to Forcing from Light-Absorbing Particles
Temperature responses to spectral solar variability on decadal time scales
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041898, 2010 Temperature responses to spectral solar variability on decadal time scales Robert F. Cahalan, 1 Guoyong
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041898, 2010 Temperature responses to spectral solar variability on decadal time scales Robert F. Cahalan, 1 Guoyong
Climatic attribution at the regional scale: a case study on the role of circulation patterns and external forcings
 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 14: 301 305 (2013) Published online 19 September 2013 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/asl2.463 Climatic attribution at the regional
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 14: 301 305 (2013) Published online 19 September 2013 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/asl2.463 Climatic attribution at the regional
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms
 Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
Characterization and Direct Radiative Impact of Arctic Aerosols: observed and modeled
 Third Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change Santa Fe, New Mexico, October 31 November 2, 2011 Characterization and Direct Radiative Impact of Arctic Aerosols: observed and modeled R.
Third Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change Santa Fe, New Mexico, October 31 November 2, 2011 Characterization and Direct Radiative Impact of Arctic Aerosols: observed and modeled R.
Global warming and Extremes of Weather. Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Global warming and Extremes of Weather Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate change Can we
Global warming and Extremes of Weather Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate change Can we
Stefan-Boltzmann law for the Earth as a black body (or perfect radiator) gives:
 2. Derivation of IPCC expression ΔF = 5.35 ln (C/C 0 ) 2.1 Derivation One The assumptions we will make allow us to represent the real atmosphere. This remarkably reasonable representation of the real atmosphere
2. Derivation of IPCC expression ΔF = 5.35 ln (C/C 0 ) 2.1 Derivation One The assumptions we will make allow us to represent the real atmosphere. This remarkably reasonable representation of the real atmosphere
Effect of Solar Activity on Earth's Climate during Solar Cycles 23 and 24
 Effect of Solar Activity on Earth's Climate during Solar Cycles 3 and 4 Abstract 1 1 Bharti Nigam, Prithvi Raj Singh, Pramod Kumar Chamadia, Ajay Kumar Saxena, Chandra Mani Tiwari 1 Govt. Autonomous P.
Effect of Solar Activity on Earth's Climate during Solar Cycles 3 and 4 Abstract 1 1 Bharti Nigam, Prithvi Raj Singh, Pramod Kumar Chamadia, Ajay Kumar Saxena, Chandra Mani Tiwari 1 Govt. Autonomous P.
Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
Major climate change triggers
 Major climate change triggers Variations in solar output Milankovitch cycles Elevation & distribution of continents Ocean interactions Atmospheric composition change (CO 2 and other volcanic gasses) Biological
Major climate change triggers Variations in solar output Milankovitch cycles Elevation & distribution of continents Ocean interactions Atmospheric composition change (CO 2 and other volcanic gasses) Biological
Global Temperature. James Hansen, Makiko Sato, Reto Ruedy, Ken Lo
 Global Temperature James Hansen, Makiko Sato, Reto Ruedy, Ken Lo November 3, 2005 This note responds to recent inquiries about 2005 global temperature, the inquiries stimulated by a 13 October Washington
Global Temperature James Hansen, Makiko Sato, Reto Ruedy, Ken Lo November 3, 2005 This note responds to recent inquiries about 2005 global temperature, the inquiries stimulated by a 13 October Washington
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics
 An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
An Annual Cycle of Arctic Cloud Microphysics M. D. Shupe Science and Technology Corporation National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory Boulder, Colorado T. Uttal
New Insights into Aerosol Asymmetry Parameter
 New Insights into Aerosol Asymmetry Parameter J.A. Ogren, E. Andrews, A. McComiskey, P. Sheridan, A. Jefferson, and M. Fiebig National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/ Earth System Research Laboratory
New Insights into Aerosol Asymmetry Parameter J.A. Ogren, E. Andrews, A. McComiskey, P. Sheridan, A. Jefferson, and M. Fiebig National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/ Earth System Research Laboratory
Assessing Snow Albedo Feedback in. Simulated Climate Change
 Assessing Snow Albedo Feedback in Simulated Climate Change Xin Qu and Alex Hall Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California corresponding
Assessing Snow Albedo Feedback in Simulated Climate Change Xin Qu and Alex Hall Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California corresponding
Changes in Earth s Albedo Measured by satellite
 Changes in Earth s Albedo Measured by satellite Bruce A. Wielicki, Takmeng Wong, Norman Loeb, Patrick Minnis, Kory Priestley, Robert Kandel Presented by Yunsoo Choi Earth s albedo Earth s albedo The climate
Changes in Earth s Albedo Measured by satellite Bruce A. Wielicki, Takmeng Wong, Norman Loeb, Patrick Minnis, Kory Priestley, Robert Kandel Presented by Yunsoo Choi Earth s albedo Earth s albedo The climate
How good are our models?
 direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
The Spectral Radiative Effects of Inhomogeneous Clouds and Aerosols
 The Spectral Radiative Effects of Inhomogeneous Clouds and Aerosols S. Schmidt, B. Kindel, & P. Pilewskie Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics University of Colorado SORCE Science Meeting, 13-16
The Spectral Radiative Effects of Inhomogeneous Clouds and Aerosols S. Schmidt, B. Kindel, & P. Pilewskie Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics University of Colorado SORCE Science Meeting, 13-16
Remote sensing with FAAM to evaluate model performance
 Remote sensing with FAAM to evaluate model performance YOPP-UK Workshop Chawn Harlow, Exeter 10 November 2015 Contents This presentation covers the following areas Introduce myself Focus of radiation research
Remote sensing with FAAM to evaluate model performance YOPP-UK Workshop Chawn Harlow, Exeter 10 November 2015 Contents This presentation covers the following areas Introduce myself Focus of radiation research
Radiative forcing due to stratospheric water vapour from CH 4 oxidation
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L01807, doi:10.1029/2006gl027472, 2007 Radiative forcing due to stratospheric water vapour from CH 4 oxidation Gunnar Myhre, 1,2 Jørgen
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L01807, doi:10.1029/2006gl027472, 2007 Radiative forcing due to stratospheric water vapour from CH 4 oxidation Gunnar Myhre, 1,2 Jørgen
Exploration of California High Resolution Snowpack Modeling with Realistic Surface-Atmospheric Radiation Physics
 Exploration of California High Resolution Snowpack Modeling with Realistic Surface-Atmospheric Radiation Physics Chaincy Kuo, Alan Rhoades, Daniel Feldman Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory AMS 15th
Exploration of California High Resolution Snowpack Modeling with Realistic Surface-Atmospheric Radiation Physics Chaincy Kuo, Alan Rhoades, Daniel Feldman Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory AMS 15th
Direct radiative effect of mineral dust and volcanic aerosols in a simple aerosol climate model
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007197, 2007 Direct radiative effect of mineral dust and volcanic aerosols in a simple aerosol climate model Karen
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007197, 2007 Direct radiative effect of mineral dust and volcanic aerosols in a simple aerosol climate model Karen
GEOL 437 Global Climate Change 2/1/18: Solar radiation and the annual cycle
 GEOL 437 Global Climate Change 2/1/18: Solar radiation and the annual cycle Why are there seasons? How does the climate respond to the radiative annual cycle? How does the climate respond to changes in
GEOL 437 Global Climate Change 2/1/18: Solar radiation and the annual cycle Why are there seasons? How does the climate respond to the radiative annual cycle? How does the climate respond to changes in
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions
 UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
Observed State of the Global Climate
 WMO Observed State of the Global Climate Jerry Lengoasa WMO June 2013 WMO Observations of Changes of the physical state of the climate ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLES OCEANIC ATMOSPHERIC TERRESTRIAL Surface
WMO Observed State of the Global Climate Jerry Lengoasa WMO June 2013 WMO Observations of Changes of the physical state of the climate ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLES OCEANIC ATMOSPHERIC TERRESTRIAL Surface
Can black carbon in snow be detected by remote sensing?
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 779 786, doi:10.1029/2012jd018476, 2013 Can black carbon in snow be detected by remote sensing? Stephen G. Warren 1 Received 11 July 2012; revised
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 118, 779 786, doi:10.1029/2012jd018476, 2013 Can black carbon in snow be detected by remote sensing? Stephen G. Warren 1 Received 11 July 2012; revised
MIZMAS: Modeling the Evolution of Ice Thickness and Floe Size Distributions in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. MIZMAS: Modeling the Evolution of Ice Thickness and Floe Size Distributions in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Chukchi and
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. MIZMAS: Modeling the Evolution of Ice Thickness and Floe Size Distributions in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Chukchi and
Equation for Global Warming
 Equation for Global Warming Derivation and Application Contents 1. Amazing carbon dioxide How can a small change in carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) content make a critical difference to the actual global surface
Equation for Global Warming Derivation and Application Contents 1. Amazing carbon dioxide How can a small change in carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) content make a critical difference to the actual global surface
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales. John Houghton. C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth
 Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Why build a climate model
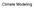 Climate Modeling Why build a climate model Atmosphere H2O vapor and Clouds Absorbing gases CO2 Aerosol Land/Biota Surface vegetation Ice Sea ice Ice sheets (glaciers) Ocean Box Model (0 D) E IN = E OUT
Climate Modeling Why build a climate model Atmosphere H2O vapor and Clouds Absorbing gases CO2 Aerosol Land/Biota Surface vegetation Ice Sea ice Ice sheets (glaciers) Ocean Box Model (0 D) E IN = E OUT
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Lecture 27 Dec
 Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Three examples where the specific surface area of snow increased over time
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln US Army Research U.S. Department of Defense 2009 Three examples where the specific surface area of snow increased over time
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln US Army Research U.S. Department of Defense 2009 Three examples where the specific surface area of snow increased over time
Using GOME and SCIAMACHY NO 2 measurements to constrain emission inventories potential and limitations
 Institute of Environmental Physics and Remote Sensing IUP/IFE-UB Department 1 Physics/Electrical Engineering TP-HTAP WMO Geneva, 25 January 2007 Using GOME and SCIAMACHY NO 2 measurements to constrain
Institute of Environmental Physics and Remote Sensing IUP/IFE-UB Department 1 Physics/Electrical Engineering TP-HTAP WMO Geneva, 25 January 2007 Using GOME and SCIAMACHY NO 2 measurements to constrain
Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
 Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Sea of Okhotsk, MODIS image Feb. 6, 2007, NASA Earth Observatory Arctic Aerosol Remote Sensing Overview
Satellite Constraints on Arctic-region Airborne Particles Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Sea of Okhotsk, MODIS image Feb. 6, 2007, NASA Earth Observatory Arctic Aerosol Remote Sensing Overview
Arctic bias improvements with longwave spectral surface emissivity modeling in CESM
 Arctic bias improvements with longwave spectral surface emissivity modeling in CESM Chaincy Kuo1, Daniel Feldman1, Xianglei Huang2, Mark Flanner2, Ping Yang3, Xiuhong Chen2 1Lawrence Berkeley National
Arctic bias improvements with longwave spectral surface emissivity modeling in CESM Chaincy Kuo1, Daniel Feldman1, Xianglei Huang2, Mark Flanner2, Ping Yang3, Xiuhong Chen2 1Lawrence Berkeley National
The Assessment of Aviation Cloudiness in IPCC Climate Change The Physical Science Basis
 The Assessment of Aviation Cloudiness in IPCC Climate Change 2007 - The Physical Science Basis I. Introduction II. IPCC Science Assessment III. Aviation cloudiness - linear contrails - contrail (induced)
The Assessment of Aviation Cloudiness in IPCC Climate Change 2007 - The Physical Science Basis I. Introduction II. IPCC Science Assessment III. Aviation cloudiness - linear contrails - contrail (induced)
Constraining Model Predictions of Arctic Sea Ice With Observations. Chris Ander 27 April 2010 Atmos 6030
 Constraining Model Predictions of Arctic Sea Ice With Observations Chris Ander 27 April 2010 Atmos 6030 Main Sources Boe et al., 2009: September sea-ice cover in the Arctic Ocean projected to vanish by
Constraining Model Predictions of Arctic Sea Ice With Observations Chris Ander 27 April 2010 Atmos 6030 Main Sources Boe et al., 2009: September sea-ice cover in the Arctic Ocean projected to vanish by
9/5/16. Section 3-4: Radiation, Energy, Climate. Common Forms of Energy Transfer in Climate. Electromagnetic radiation.
 Section 3-4: Radiation, Energy, Climate Learning outcomes types of energy important to the climate system Earth energy balance (top of atm., surface) greenhouse effect natural and anthropogenic forcings
Section 3-4: Radiation, Energy, Climate Learning outcomes types of energy important to the climate system Earth energy balance (top of atm., surface) greenhouse effect natural and anthropogenic forcings
Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
 1/23 Remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol, clouds and aerosol-cloud interactions. Bremen, 16-19 December 2013 Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
1/23 Remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol, clouds and aerosol-cloud interactions. Bremen, 16-19 December 2013 Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
Origin and radiative forcing of black carbon transported. to the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau
 Origin and radiative forcing of black carbon transported to the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau Kopacz, M. 1, Mauzerall, D.L. 1,2, Wang, J. 3, Leibensperger, E.M. 4, Henze, D.K. 5, Singh, K. 6 1. Woodrow
Origin and radiative forcing of black carbon transported to the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau Kopacz, M. 1, Mauzerall, D.L. 1,2, Wang, J. 3, Leibensperger, E.M. 4, Henze, D.K. 5, Singh, K. 6 1. Woodrow
Global Change and Air Pollution (EPA-STAR GCAP) Daniel J. Jacob
 Global Change and Air Pollution (EPA-STAR GCAP) and some more recent work on climate-aq interactions Daniel J. Jacob (djacob@fas.harvard.edu) with Eric M. Leibensperger, Shiliang Wu, Amos Tai, and Loretta
Global Change and Air Pollution (EPA-STAR GCAP) and some more recent work on climate-aq interactions Daniel J. Jacob (djacob@fas.harvard.edu) with Eric M. Leibensperger, Shiliang Wu, Amos Tai, and Loretta
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks. Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC
 Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Aerosol Impacts on Earth s Energy Budget: What We Can Say, and What We Can t. Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
 Aerosol Impacts on Earth s Energy Budget: What We Can Say, and What We Can t Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Trenberth, Fasullo, Kiehl, BAMS 2009 Even DARF and Anthropogenic DARF are NOT Solved
Aerosol Impacts on Earth s Energy Budget: What We Can Say, and What We Can t Ralph Kahn NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Trenberth, Fasullo, Kiehl, BAMS 2009 Even DARF and Anthropogenic DARF are NOT Solved
Aerosols AP sizes AP types Sources Sinks Amount and lifetime Aerosol radiative effects. Aerosols. Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21
 Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Monitoring Climate Change from Space
 Monitoring Climate Change from Space Richard Allan (email: r.p.allan@reading.ac.uk twitter: @rpallanuk) Department of Meteorology, University of Reading Why Monitor Earth s Climate from Space? Global Spectrum
Monitoring Climate Change from Space Richard Allan (email: r.p.allan@reading.ac.uk twitter: @rpallanuk) Department of Meteorology, University of Reading Why Monitor Earth s Climate from Space? Global Spectrum
13.10 RECENT ARCTIC CLIMATE TRENDS OBSERVED FROM SPACE AND THE CLOUD-RADIATION FEEDBACK
 13.10 RECENT ARCTIC CLIMATE TRENDS OBSERVED FROM SPACE AND THE CLOUD-RADIATION FEEDBACK Xuanji Wang 1 * and Jeffrey R. Key 2 1 Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies University of Wisconsin-Madison
13.10 RECENT ARCTIC CLIMATE TRENDS OBSERVED FROM SPACE AND THE CLOUD-RADIATION FEEDBACK Xuanji Wang 1 * and Jeffrey R. Key 2 1 Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies University of Wisconsin-Madison
What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
 IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements
 Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements Norman G. Loeb Hampton University/NASA Langley Research Center Bruce
Influence of Clouds and Aerosols on the Earth s Radiation Budget Using Clouds and the Earth s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Measurements Norman G. Loeb Hampton University/NASA Langley Research Center Bruce
Climate Roles of Land Surface
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Figure 1.1. Schematic overview of the primary blackcarbon emission sources and the processes that control the distribution of black carbon in the
 Figure 1.1. Schematic overview of the primary blackcarbon emission sources and the processes that control the distribution of black carbon in the atmosphere and determine its role in the climate system.
Figure 1.1. Schematic overview of the primary blackcarbon emission sources and the processes that control the distribution of black carbon in the atmosphere and determine its role in the climate system.
What controls the strength of snow albedo feedback?
 What controls the strength of snow albedo feedback? Xin Qu and Alex Hall Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California corresponding author
What controls the strength of snow albedo feedback? Xin Qu and Alex Hall Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California corresponding author
Arctic Oxidation Chemistry
 19 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Oxidation Chemistry Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
19 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Oxidation Chemistry Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
Aerosol Air Mass Distinctions over Jalisco using Multi-Angle Imaging Spectroradiometer
 Instituto Tecnológico y de Estudios Superiores de Occidente Repositorio Institucional del ITESO rei.iteso.mx Departamento de Electrónica, Sistemas e Informática DESI - Artículos y ponencias con arbitraje
Instituto Tecnológico y de Estudios Superiores de Occidente Repositorio Institucional del ITESO rei.iteso.mx Departamento de Electrónica, Sistemas e Informática DESI - Artículos y ponencias con arbitraje
Microphysical Properties of Single and Mixed-Phase Arctic Clouds Derived From Ground-Based AERI Observations
 Microphysical Properties of Single and Mixed-Phase Arctic Clouds Derived From Ground-Based AERI Observations Dave Turner University of Wisconsin-Madison Pacific Northwest National Laboratory 8 May 2003
Microphysical Properties of Single and Mixed-Phase Arctic Clouds Derived From Ground-Based AERI Observations Dave Turner University of Wisconsin-Madison Pacific Northwest National Laboratory 8 May 2003
Remote sensing of ice clouds
 Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives
 Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
B C, a byproduct of combustion, has a unique role as a climate forcing agent. It absorbs the most solar light per
 Black carbon aerosol size in snow J. P. Schwarz 1,2, R. S. Gao 1, A. E. Perring 1,2, J. R. Spackman 3,4 & D. W. Fahey 1,2 SUBJECT AREAS: ATMOSPHERIC DYNAMICS CRYOSPHERIC SCIENCE 1 Chemical Sciences Division,
Black carbon aerosol size in snow J. P. Schwarz 1,2, R. S. Gao 1, A. E. Perring 1,2, J. R. Spackman 3,4 & D. W. Fahey 1,2 SUBJECT AREAS: ATMOSPHERIC DYNAMICS CRYOSPHERIC SCIENCE 1 Chemical Sciences Division,
Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd008003, 2007 Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow Mark G. Flanner, 1 Charles S. Zender,
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd008003, 2007 Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow Mark G. Flanner, 1 Charles S. Zender,
Measurements of aerosol optical depths and black carbon over Bay of Bengal during post-monsoon season
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L16115, doi:10.1029/2004gl020681, 2004 Measurements of aerosol optical depths and black carbon over Bay of Bengal during post-monsoon season E. Sumanth, 1 K. Mallikarjuna,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L16115, doi:10.1029/2004gl020681, 2004 Measurements of aerosol optical depths and black carbon over Bay of Bengal during post-monsoon season E. Sumanth, 1 K. Mallikarjuna,
Comparison of aerosol radiative forcing over the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal
 Advances in Space Research 33 (2004) 1104 1108 www.elsevier.com/locate/asr Comparison of aerosol radiative forcing over the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal S. Dey a, S. Sarkar b, R.P. Singh a, * a Department
Advances in Space Research 33 (2004) 1104 1108 www.elsevier.com/locate/asr Comparison of aerosol radiative forcing over the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal S. Dey a, S. Sarkar b, R.P. Singh a, * a Department
O. Boucher, J. Haywood and A. Jones, Met Office Hadley Centre, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, EX1
 1 2 3 4 Geoengineering by stratospheric SO 2 injection: results from the Met Office HadGEM2 climate model and comparison with the Goddard Institute for Space Studies ModelE Andy Jones 1, Jim Haywood 1,
1 2 3 4 Geoengineering by stratospheric SO 2 injection: results from the Met Office HadGEM2 climate model and comparison with the Goddard Institute for Space Studies ModelE Andy Jones 1, Jim Haywood 1,
This presentation was assembled as part of the outreach initiative for the Canadian Network for the Detection of Atmospheric Change.
 This will be a lesson for students in grades 9-12. The subject matter is climate change - the greenhouse effect, greenhouse gases, how greenhouse gases are measured and studied, and the impacts of climate
This will be a lesson for students in grades 9-12. The subject matter is climate change - the greenhouse effect, greenhouse gases, how greenhouse gases are measured and studied, and the impacts of climate
Comparing different MODIS snow products with distributed simulation of the snowpack in the French Alps
 Comparing different MODIS snow products with distributed simulation of the snowpack in the French Alps Luc Charrois 1, Marie Dumont 1,*, Pascal Sirguey 2, Samuel Morin 1, Matthieu Lafaysse 1 and Fatima
Comparing different MODIS snow products with distributed simulation of the snowpack in the French Alps Luc Charrois 1, Marie Dumont 1,*, Pascal Sirguey 2, Samuel Morin 1, Matthieu Lafaysse 1 and Fatima
THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
 ASTRONOMY READER THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT 35.1 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT Overview Planets are heated by light from the Sun. Planets cool off by giving off an invisible kind of light, longwave infrared light.
ASTRONOMY READER THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT 35.1 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT Overview Planets are heated by light from the Sun. Planets cool off by giving off an invisible kind of light, longwave infrared light.
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling. requirements of energy and water cycle. Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki
 A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
A perturbed physics ensemble climate modeling study for defining satellite measurement requirements of energy and water cycle Yong Hu and Bruce Wielicki Motivation 1. Uncertainty of climate sensitivity
ATM S 111 Global Warming Exam Review. Jennifer Fletcher Day 31, August 3, 2010
 ATM S 111 Global Warming Exam Review Jennifer Fletcher Day 31, August 3, 2010 Earth gets most of its energy from the sun. Solar Radiation Solar radiation is mostly in visible, near infrared, and near UV
ATM S 111 Global Warming Exam Review Jennifer Fletcher Day 31, August 3, 2010 Earth gets most of its energy from the sun. Solar Radiation Solar radiation is mostly in visible, near infrared, and near UV
A study of regional and long-term variation of radiation budget using general circulation. model. Makiko Mukai* University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Japan
 A study of regional and long-term variation of radiation budget using general circulation model P3.7 Makiko Mukai* University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Japan Abstract The analysis of solar radiation at the surface
A study of regional and long-term variation of radiation budget using general circulation model P3.7 Makiko Mukai* University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Japan Abstract The analysis of solar radiation at the surface
Aspects of a climate observing system: energy and water. Kevin E Trenberth NCAR
 Aspects of a climate observing system: energy and water Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Tracking Earth s Global Energy Where has global warming from increased GHGs gone? Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Where did the heat
Aspects of a climate observing system: energy and water Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Tracking Earth s Global Energy Where has global warming from increased GHGs gone? Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Where did the heat
The aerosol- and water vapor-related variability of precipitation in the West Africa Monsoon
 The aerosol- and water vapor-related variability of precipitation in the West Africa Monsoon Jingfeng Huang *, C. Zhang and J. M. Prospero Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, University
The aerosol- and water vapor-related variability of precipitation in the West Africa Monsoon Jingfeng Huang *, C. Zhang and J. M. Prospero Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, University
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future. Basic Concepts
 Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Projections of future climate change
 Projections of future climate change Matthew Collins 1,2 and Catherine A. Senior 2 1 Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading 2 Met Office Hadley Centre,
Projections of future climate change Matthew Collins 1,2 and Catherine A. Senior 2 1 Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading 2 Met Office Hadley Centre,
The Cryosphere Radiative Effect in CESM. Justin Perket Mark Flanner CESM Polar Climate Working Group Meeting Wednesday June 19, 2013
 The Cryosphere Radiative Effect in CESM Justin Perket Mark Flanner CESM Polar Climate Working Group Meeting Wednesday June 19, 2013 Cryosphere Radiative Effect (CrRE) A new diagnostic feature is available
The Cryosphere Radiative Effect in CESM Justin Perket Mark Flanner CESM Polar Climate Working Group Meeting Wednesday June 19, 2013 Cryosphere Radiative Effect (CrRE) A new diagnostic feature is available
