Using Phylogeny to Infer Vicariance. Reading: Lars Brundin
|
|
|
- Opal Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using Phylogeny to Infer Vicariance Reading: Lars Brundin
2 Lecture 5 Recap Alfred Wegener
3 Alfred Wegener In his book, Wegener described how the con(nents of SA and Africa fit together (not the first to describe this) First to compare the conjnents with fossil evidence as evidence for being joined Also looked at rock strata at the margins of con(nents which suggested that these conjnents were formed in the same manner
4 Alfred Wegener However, there was no mechanism described and so the idea had to wait for advances in technology and other discoveries Sea floor spreading and magne(sm Differences in rock density between con(nents and seafloor Seismic concentra(ons, or hotspots
5 Alfred Wegener Subduc(on Zones Takes place at convergent boundaries of tectonic plates Process where heavy, dense oceanic plate is moved underneath a lighter, less dense plate (usually a conjnental plate) Without this process plate tectonics could not occur as new seafloor at spreading sites needs older crust to be returned to the mantle
6 Joseph Dalton Hooker the botanical rela.onship [of the three great areas of land in the southern la.tudes] is as strong as that which prevails throughout the lands within the Arc.c and Northern Temperature zones, and which is not to be accounted for by any theory of transport or varia.on, but which is agreeable to the hypothesis of all being members of a once more extensive flora, which has been broken up by geological and clima.c causes.
7 Sven Ekman Time, which in reality nothing more than a succession of events, that is historical happenings, is a factor of profound importance for all manifesta.ons of life. biogeography cannot confine itself simply to describing the occurrence of living forms, arranging them regionally, inves.ga.ng the ecological causes of distribu.on. It must also proceed historically.
8 Sven Ekman We cannot understand the present day biogeographical distribujons of animals and plants without an understanding of the history of the planet Historical biogeography arempts to reconstruct the origin of taxa; sequences of their dispersal, isolajon, and exjncjon; and to explain how geological events have shaped present day parerns of distribujon Addresses the how, when, and why of species distribujons
9 Carl Linnaeus Two schools of thought: 1. Dispersal biogeography follows from the premise that species spread outward from a center of origin so that present day biota results from the accumulated dispersal of the various descendant lineages 2. Vicariance biogeography follows that an unstable earth is involved in the spliyng of biota into isolated populajons by emerging barriers (TECO events)
10 Alfred Wegener TECO events Tectonic plate movements and orogeny EustaJc changing sea levels ClimaJc shi\ing climate belts, ice ages Oceanographic oceanographic circulajon changes
11 Alfred Wegener Carl Linnaeus In reality, large- scale disjunct distribujon parerns can result from dispersal or vicariance or both, and distribujonal parerns are clearly modified over Jme by evolujonary and ecological processes
12 Lars Brundin Now that there was knowledge that conjnents are not fixed through Jme, it facilitated the development of analyjcal techniques The field was no longer based on narrajve approaches A classic study was one by Lars Brundin that employed phylogene.c models to demonstrate concordance between animal distribujons and plate tectonics
13 Willi Hennig We first have to understand the phylogenejc approach Cladis.c biogeography German scienjst who is considered the father of phylogenejc systemajcs Sent to Italy during WWII to fight malaria, captured by the BriJsh forces and during his Jme as a POW dra\ed Basic Outline of a Theory of Phylogene.c Systema.cs (1950) We will revisit Hennig in Week 4
14 Willi Hennig Nodes represent most recent common ancestor Further back on the tree the farther back in relajve Jme ExJnct clades are usually represented by abrupt, short branches, or one that fades away
15 Lars Brundin Transantarc.c Rela.onships and Their Significance, as Evidenced by Chironomid Midges One must understand vicariant parerns in biogeography before arempjng to decipher chance dispersal parerns
16 Lars Brundin What about the general suitability of chironomid midges as indicators in biogeography? In the possession of a developmental cycle comprising larva, pupa, and imago these orders offer three quite different types of organiza4on and adapta4on within the limits of a species. We thus have the great advantage of being able to cross- check the phylogene4c conclusions drawn from one stage with the others, thus asaining a high degree of reliability by the establishment of monophyle.c sister groups.
17 Lars Brundin Advantages to using midges as a model organism Accessibility to samples many and easy to collect Extremely cold- resistant less affected by glaciajon Very small easier to maintain a populajon during stress Feed on diatoms almost always abundant Habitat unchangeable always will be mountain streams Old enough traced back to the Jurassic at least (200mya) PaRerns results of processes beyond the acjon of man
18 Lars Brundin
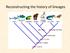
19 Earth History, Vicariance, and Dispersal Lars Brundin NZ S. America S. Af Aus
20 Lars Brundin Major observa(ons from phylogeny The sister group of a NZ group lives always in S. America, or in S. America and Tasmania- Aus. There are no direct connecjons between a group of Tasmania- Aus. and group of NZ A group of Tasmania- Aus. Is always an apomorph (morphological advance) offshoot of the S. American fauna.
21 Lars Brundin
22 Lars Brundin
23 Lars Brundin The cases of 25 transantarc.c phyle.c connec.ons and their amphitropical ramifica.ons analyzed in the present paper tell a story of orderly dispersal which goes back to the middle Mesozoic. There is not the slightest evidence of chance dispersal over wide stretches of ocean or of any sort of hopping of ancestral forms from island to islands between the southern con.nents.
24 Joseph Dalton Hooker the botanical rela.onship [of the three great areas of land in the southern la.tudes] is as strong as that which prevails throughout the lands within the Arc.c and Northern Temperature zones, and which is not to be accounted for by any theory of transport or varia.on, but which is agreeable to the hypothesis of all being members of a once more extensive flora, which has been broken up by geological and clima.c causes.
25 Lars Brundin Main Points The advent of plate tectonics led to the field of biogeography becoming analyjcal rather than narrajve Brundin used Hennig s phylogenejcs and a model order to demonstrate vicariant parerns of speciajon Brundin showed that by finding general rules in phylogenejc trees, one can trace back vicariant events to hundreds of millions of years ago This work verified observajons by Hooker and others about the relatedness of the southern flora and fauna
26 QuesJons on the reading?
27 Discussion Point 1 Lars Brundin What belongs to main pasern, what is barely excep.onal? What did Brundin mean by this statement in the relajon to the midges? How do we separate regular parern from excepjonal occurrences? How do we judge what is important?
28 Discussion Point 2 Lars Brundin all scien.sts studying phylogenies are poten.al biogeographers in a truly progressive sense. How is this statement meaningful in relajon to Hennig and Ekman?
The Importance of Systema2cs and Rassenkreis. Reading: Willi Hennig
 The Importance of Systema2cs and Rassenkreis Reading: Throughout the class so far we seen that the distribu2on of an organism is the result of its biological history as well as geologic and clima4c history
The Importance of Systema2cs and Rassenkreis Reading: Throughout the class so far we seen that the distribu2on of an organism is the result of its biological history as well as geologic and clima4c history
Panama and the Great American Interchange. Reading: Marshall et al. 1982
 Panama and the Great American Interchange Reading: Marshall et al. 1982 Lecture 6 Recap Lars Brundin Lars Brundin What about the general suitability of chironomid midges as indicators in biogeography?
Panama and the Great American Interchange Reading: Marshall et al. 1982 Lecture 6 Recap Lars Brundin Lars Brundin What about the general suitability of chironomid midges as indicators in biogeography?
Plate Tectonics: An Unstable Earth. Reading: Alfred Wegener
 Plate Tectonics: An Unstable Earth Reading: Classical Biogeography: Early Perspec=ves Lecture 4 Recap Wallace Sven Ekman Classical Biogeography: Early Perspec=ves Wallace Richard Lydekker Lydekker s line
Plate Tectonics: An Unstable Earth Reading: Classical Biogeography: Early Perspec=ves Lecture 4 Recap Wallace Sven Ekman Classical Biogeography: Early Perspec=ves Wallace Richard Lydekker Lydekker s line
Early theories: Joseph Hooker (1853) vs. Charles Darwin (1859)
 Gondwanan Plants of the Sydney Region Presentation Dr Peter Weston 25/11/2017 Honorary Research Associate, Science and Conservation Branch, Royal Botanic Gardens and Domain Trust Summary: Dr Marilyn Cross,
Gondwanan Plants of the Sydney Region Presentation Dr Peter Weston 25/11/2017 Honorary Research Associate, Science and Conservation Branch, Royal Botanic Gardens and Domain Trust Summary: Dr Marilyn Cross,
Evidence for Continental Drift and The Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Evidence for Continental Drift and The Theory of Plate Tectonics Did you know that the coal that is mined in Pennsylvania was actually formed from tropical plant life near the Equator? How did it travel
Evidence for Continental Drift and The Theory of Plate Tectonics Did you know that the coal that is mined in Pennsylvania was actually formed from tropical plant life near the Equator? How did it travel
Reconstructing the history of lineages
 Reconstructing the history of lineages Class outline Systematics Phylogenetic systematics Phylogenetic trees and maps Class outline Definitions Systematics Phylogenetic systematics/cladistics Systematics
Reconstructing the history of lineages Class outline Systematics Phylogenetic systematics Phylogenetic trees and maps Class outline Definitions Systematics Phylogenetic systematics/cladistics Systematics
Ch 17 Plate Tectonics Big Idea: Most geologic activity occurs at the boundaries between plates.
 Ch 17 Plate Tectonics Big Idea: Most geologic activity occurs at the boundaries between plates. 17.1 Drifting Continents 17.2 Seafloor Spreading 17.3 Plate Boundaries 17.4 Causes of Plate Motions Learning
Ch 17 Plate Tectonics Big Idea: Most geologic activity occurs at the boundaries between plates. 17.1 Drifting Continents 17.2 Seafloor Spreading 17.3 Plate Boundaries 17.4 Causes of Plate Motions Learning
The Moving Story of Plate Tectonics
 08 January 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com The Moving Story of Plate Tectonics AP Smoke and ash from Italy's Mount Etna volcano last week FAITH LAPIDUS: This is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS in VOA Special English.
08 January 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com The Moving Story of Plate Tectonics AP Smoke and ash from Italy's Mount Etna volcano last week FAITH LAPIDUS: This is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS in VOA Special English.
Continental Drift. The idea that the world s land masses are slowly moving over time
 Alfred Wegener Continental Drift The idea that the world s land masses are slowly moving over time Pangaea The supercontinent made of all continents that existed millions of years ago. Present Cretaceous
Alfred Wegener Continental Drift The idea that the world s land masses are slowly moving over time Pangaea The supercontinent made of all continents that existed millions of years ago. Present Cretaceous
Unit 4 Lesson 2 Plate Tectonics. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Puzzling Evidence What evidence suggests that continents move? In the late 1800s, Alfred Wegener proposed his hypothesis of continental drift. According to this hypothesis, the continents once formed a
Puzzling Evidence What evidence suggests that continents move? In the late 1800s, Alfred Wegener proposed his hypothesis of continental drift. According to this hypothesis, the continents once formed a
What is PLATE TECTONICS?
 What is PLATE TECTONICS? It s the theory that states: The surface of the Earth is not fixed and eternal, but it is in constant everchanging motion. If you look at a map of the world, you may notice that
What is PLATE TECTONICS? It s the theory that states: The surface of the Earth is not fixed and eternal, but it is in constant everchanging motion. If you look at a map of the world, you may notice that
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17
 Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
The ACTIVE EARTH!!!!!
 The ACTIVE EARTH!!!!! Continental Drift Theory Alfred Wegener meterologist and geophysicist who, in 1912, proposed this theory. He stated that earth s crust might be moving and changing & that the continents
The ACTIVE EARTH!!!!! Continental Drift Theory Alfred Wegener meterologist and geophysicist who, in 1912, proposed this theory. He stated that earth s crust might be moving and changing & that the continents
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution. (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins)
 Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics
 SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics From VOA Learning English, this is Science in the News. I m Anna Matteo. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean
SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics From VOA Learning English, this is Science in the News. I m Anna Matteo. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean
Chapter Nineteen: Changing Earth
 Chapter Nineteen: Changing Earth 19.1 Inside Earth 19.2 Plate Tectonics 19.3 Plate Boundaries 19.4 Metamorphic Rocks 19.2 Learning Goals Discuss hypotheses which ultimately led to plate tectonics theory.
Chapter Nineteen: Changing Earth 19.1 Inside Earth 19.2 Plate Tectonics 19.3 Plate Boundaries 19.4 Metamorphic Rocks 19.2 Learning Goals Discuss hypotheses which ultimately led to plate tectonics theory.
Name Date Class. continents looked as if they might fit like puzzle pieces into and.
 Chapter Outline Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 4 Lesson 1: Continental Drift A. Drifting Continents 1. People looking at early maps noticed that the edges of the American continents looked as if they might fit
Chapter Outline Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 4 Lesson 1: Continental Drift A. Drifting Continents 1. People looking at early maps noticed that the edges of the American continents looked as if they might fit
From VOA Learning English, this is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in Special English. I m Kelly Jean Kelly.
 From VOA Learning English, this is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in Special English. I m Kelly Jean Kelly. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are
From VOA Learning English, this is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in Special English. I m Kelly Jean Kelly. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are
Ch 9.1 Notes. Objective: Be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to explain evidence that supports it.
 Ch 9.1 Notes Objective: Be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to explain evidence that supports it. Pangaea Alfred Wegener proposed that land on Earth formed a single, huge landmass.
Ch 9.1 Notes Objective: Be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to explain evidence that supports it. Pangaea Alfred Wegener proposed that land on Earth formed a single, huge landmass.
Science in the News - Plate Tectonics 1. Story
 Science in the News - Plate Tectonics 1. Story Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are always moving. This movement sometimes can be violent, causing death and destruction.
Science in the News - Plate Tectonics 1. Story Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are always moving. This movement sometimes can be violent, causing death and destruction.
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY
 CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY Proof or crazy idea? CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY What is Continental Drift Theory? Continental drift theory (CDT): Alfred Wegener found all the continents were once together called
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY Proof or crazy idea? CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY What is Continental Drift Theory? Continental drift theory (CDT): Alfred Wegener found all the continents were once together called
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure. Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Nineteen: Changing Earth 19.1 Inside Earth 19.2 Plate Tectonics
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Nineteen: Changing Earth 19.1 Inside Earth 19.2 Plate Tectonics
Copyright 2016 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2016 Edmentum - All rights reserved. SI: Quiz 13 Question #1 The Earth's crust is made up of plates that can move. Which of the following topographic features could be directly formed by the
Copyright 2016 Edmentum - All rights reserved. SI: Quiz 13 Question #1 The Earth's crust is made up of plates that can move. Which of the following topographic features could be directly formed by the
Plate Tectonics. Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries
 Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics. Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events.
 Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) ONE single landmass
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) ONE single landmass
Do Now: Vocabulary: Objectives. Vocabulary: 1/5/2016. Wegener? (Can they move?) the idea that continents have moved over time?
 Do Now: 1. Who was Alfred Wegener? 2. What was Pangaea? 3. Are continents fixed? (Can they move?) 4. What evidence supports the idea that continents have moved over time? Objectives What evidence suggests
Do Now: 1. Who was Alfred Wegener? 2. What was Pangaea? 3. Are continents fixed? (Can they move?) 4. What evidence supports the idea that continents have moved over time? Objectives What evidence suggests
22.4 Plate Tectonics. Africa
 The Red Sea between Africa and the Arabian peninsula in Asia marks a region where two pieces of the lithosphere are slowly moving apart. Over the next 100 million years, the Red Sea could become an ocean.
The Red Sea between Africa and the Arabian peninsula in Asia marks a region where two pieces of the lithosphere are slowly moving apart. Over the next 100 million years, the Red Sea could become an ocean.
1. I can describe evidence for continental drift theory (e.g., fossil evidence, mountain belts, paleoglaciation)
 Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Name Date Class. Plate Tectonics
 Chapter Review Plate Tectonics Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Write the term that matches each description below in the spaces provided. Then unscramble the letters in the boxes to reveal the mystery
Chapter Review Plate Tectonics Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Write the term that matches each description below in the spaces provided. Then unscramble the letters in the boxes to reveal the mystery
Question. Question. Question. Question. What are the topics of our last class? is the tendency of some minerals to break along flat surfaces?
 Question What are the topics of our last class? Question is the tendency of some minerals to break along flat surfaces? A. Crystal habit; B. Cleavage; C. Fracture; D. Hardness Question Calcite is a mineral.
Question What are the topics of our last class? Question is the tendency of some minerals to break along flat surfaces? A. Crystal habit; B. Cleavage; C. Fracture; D. Hardness Question Calcite is a mineral.
Name Date Class. How have geologists learned about Earth s inner structure? What are the characteristics of Earth s crust, mantle, and core?
 Chapter 4 Plate Tectonics Section 1 Summary Earth s Interior How have geologists learned about Earth s inner structure? What are the characteristics of Earth s crust, mantle, and core? Earth s surface
Chapter 4 Plate Tectonics Section 1 Summary Earth s Interior How have geologists learned about Earth s inner structure? What are the characteristics of Earth s crust, mantle, and core? Earth s surface
PLATE TECTONICS THEORY
 PLATE TECTONICS THEORY Continental drift Sea floor spreading CONTINENTAL DRIFT CONTINENTAL DRIFT 1. The fitness of continents and Continental Reconstruction Earth ~200 million years ago 1.1 Geometrical
PLATE TECTONICS THEORY Continental drift Sea floor spreading CONTINENTAL DRIFT CONTINENTAL DRIFT 1. The fitness of continents and Continental Reconstruction Earth ~200 million years ago 1.1 Geometrical
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics
 Unit 4 Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics Indiana Standards 7.2.1 Describe how the earth is a layered structure composed of lithospheric plates, a mantle and a dense core. 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics Indiana Standards 7.2.1 Describe how the earth is a layered structure composed of lithospheric plates, a mantle and a dense core. 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics. Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events.
 Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) He noticed that the continents
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) He noticed that the continents
Plate Tectonics. These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page.
 Plate Tectonics These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are
Plate Tectonics These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds
 Chapter 2 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Tarbuck and Lutgens From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the
Chapter 2 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Tarbuck and Lutgens From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the
Plate Tectonics. And Plate Boundaries HORRAH!!!
 Plate Tectonics And Plate Boundaries HORRAH!!! History of Plate Tectonics and Alfred Wegener In the 1500 s, a Dutch mapmaker, Abraham Ortelius noticed the continents across the Atlantic Ocean fit like
Plate Tectonics And Plate Boundaries HORRAH!!! History of Plate Tectonics and Alfred Wegener In the 1500 s, a Dutch mapmaker, Abraham Ortelius noticed the continents across the Atlantic Ocean fit like
READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 11, Plate Tectonics GEOL 131 Fall pts
 READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 11, Plate Tectonics GEOL 131 Fall 2018 61 pts NAME DUE: Tuesday, November 20 Continental Drift: An Idea Before Its Time (p. 317-321) 1. Fill in the blanks in this sentence from
READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 11, Plate Tectonics GEOL 131 Fall 2018 61 pts NAME DUE: Tuesday, November 20 Continental Drift: An Idea Before Its Time (p. 317-321) 1. Fill in the blanks in this sentence from
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
UNIT 11 PLATE TECTONICS
 UNIT 11 PLATE TECTONICS A. ALFRED WEGENER 1. Continental drift hypothesis Single supercontinent called Pangaea 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their present
UNIT 11 PLATE TECTONICS A. ALFRED WEGENER 1. Continental drift hypothesis Single supercontinent called Pangaea 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their present
THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
 UNIT 1 THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH 1.1.Earth s interior layers The interior of the Earth can be divided into layers according to: -Composition layers ( organized in order of increasing density
UNIT 1 THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH 1.1.Earth s interior layers The interior of the Earth can be divided into layers according to: -Composition layers ( organized in order of increasing density
Plate Tectonics Practice Test
 Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
Plate Tectonics. Chapter 17. Great Idea: The entire Earth is still changing, due to the slow convection of soft, hot rocks deep within the planet.
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 17 Great Idea: The entire Earth is still changing, due to the slow convection of soft, hot rocks deep within the planet. 1 Chapter Outline The Dynamic Earth Plate Tectonics: A Unifying
Plate Tectonics Chapter 17 Great Idea: The entire Earth is still changing, due to the slow convection of soft, hot rocks deep within the planet. 1 Chapter Outline The Dynamic Earth Plate Tectonics: A Unifying
Changing Earth: Plate Tectonics
 Changing Earth: Plate Tectonics Static Earth Theory People used to believe that the Earth and its continents could not change since it was created They thought that earthquakes and volcanoes were caused
Changing Earth: Plate Tectonics Static Earth Theory People used to believe that the Earth and its continents could not change since it was created They thought that earthquakes and volcanoes were caused
Building a con,nent; plate tectonics. GEOL115 Alexander Lusk
 Building a con,nent; plate tectonics GEOL115 Alexander Lusk Lecture goals: 1. Earth structure (con,nued) 2. Plate boundaries Divergent plate boundaries Convergent plate boundaries Transform boundaries
Building a con,nent; plate tectonics GEOL115 Alexander Lusk Lecture goals: 1. Earth structure (con,nued) 2. Plate boundaries Divergent plate boundaries Convergent plate boundaries Transform boundaries
Species diversification in space: biogeographic patterns
 Species diversification in space: biogeographic patterns Outline Endemism and cosmopolitanism Disjunctions Biogeographic regions Barriers and interchanges Divergence and convergence Biogeographic patterns
Species diversification in space: biogeographic patterns Outline Endemism and cosmopolitanism Disjunctions Biogeographic regions Barriers and interchanges Divergence and convergence Biogeographic patterns
Unit 11: Plate Tectonics
 Unit 11: Plate Tectonics A. Alfred Wegner 1. Continental drift hypothesis a. single supercontinent called Pangaea b. 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their
Unit 11: Plate Tectonics A. Alfred Wegner 1. Continental drift hypothesis a. single supercontinent called Pangaea b. 200 million years ago Pangaea (all land) began to break up and started drifting to their
10/27/2014. Before We Begin, You Need to Understand These Terms: Earth s Structural Key Elements & the Hazards of Plate Movement
 Earth s Structural Key Elements & the Hazards of Plate Movement Before We Begin, You Need to Understand These Terms: Density Convection Currents AICE EM: Lithosphere Key Content 1 & 2 Density: heat rises,
Earth s Structural Key Elements & the Hazards of Plate Movement Before We Begin, You Need to Understand These Terms: Density Convection Currents AICE EM: Lithosphere Key Content 1 & 2 Density: heat rises,
PLATE TECTONICS REVIEW GAME!!!!
 PLATE TECTONICS REVIEW GAME!!!! Name the four layers of the earth - crust - mantle - outer core - inner core Which part of Earth s structure contains tectonic plates? LITHOSPHERE Name one reason why the
PLATE TECTONICS REVIEW GAME!!!! Name the four layers of the earth - crust - mantle - outer core - inner core Which part of Earth s structure contains tectonic plates? LITHOSPHERE Name one reason why the
PLATE TECTONICS. SECTION 17.1 Drifting Continents
 Date Period Name PLATE TECTONICS SECTION.1 Drifting Continents In your textbook, read about continental drift. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes each statement. 1. Early mapmakers thought
Date Period Name PLATE TECTONICS SECTION.1 Drifting Continents In your textbook, read about continental drift. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes each statement. 1. Early mapmakers thought
Plate Tectonics. 8 th grade
 Plate Tectonics 8 th grade Not in notes- look at picture If you look at a map of Earth s surface, you can see that the edges of some continents look as though they could fit together like a puzzle Wegener
Plate Tectonics 8 th grade Not in notes- look at picture If you look at a map of Earth s surface, you can see that the edges of some continents look as though they could fit together like a puzzle Wegener
What is the theory of plate tectonics? Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3
 Name Plate Tectonics What is the theory of plate tectonics? Date Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about plate tectonics Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Name Plate Tectonics What is the theory of plate tectonics? Date Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about plate tectonics Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
 Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. Wegener proposed that the
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. Wegener proposed that the
Continental Drift. & Plate Tectonics
 Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics Alfred Wegener, a German scientist, proposed the hypothesis of CONTINENTAL DRIFT, in 1912. Hypothesis stated: All Earth s continents were once a single landmass (Pangaea)
Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics Alfred Wegener, a German scientist, proposed the hypothesis of CONTINENTAL DRIFT, in 1912. Hypothesis stated: All Earth s continents were once a single landmass (Pangaea)
Name. Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 2245/2245W Exam 2 1 March 2014
 Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 2245/2245W Exam 2 1 March 2014 1. Use the following matrix of nucleotide sequence data and the corresponding tree to answer questions a. through h. below. (16 points)
Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 2245/2245W Exam 2 1 March 2014 1. Use the following matrix of nucleotide sequence data and the corresponding tree to answer questions a. through h. below. (16 points)
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide
 Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
1. In your own words, what is the Earth s crust?
 The Structure of Earth Classwork Classwork #1 Name: 1. In your own words, what is the Earth s crust? 2. The Earth s surface became the way it is: A. only very recently. B. because of one event in history.
The Structure of Earth Classwork Classwork #1 Name: 1. In your own words, what is the Earth s crust? 2. The Earth s surface became the way it is: A. only very recently. B. because of one event in history.
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life
 Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
EARTH S INTERIOR, EVIDENCE FOR PLATE TECTONICS AND PLATE BOUNDARIES
 EARTH S INTERIOR, EVIDENCE FOR PLATE TECTONICS AND PLATE BOUNDARIES LAYERS OF THE EARTH Crust Inner Core Most Dense Solid Iron & Nickel Mantle Thickest layer Outer Core Liquid Iron & Nickel ANOTHER LOOK
EARTH S INTERIOR, EVIDENCE FOR PLATE TECTONICS AND PLATE BOUNDARIES LAYERS OF THE EARTH Crust Inner Core Most Dense Solid Iron & Nickel Mantle Thickest layer Outer Core Liquid Iron & Nickel ANOTHER LOOK
8 th Grade Campus Assessment- NSMS Plate Tectonics
 1. A group of students were discussing plate tectonics in their science class. All of the following statements about the tectonic plates are incorrect EXCEPT: A. The Eurasian Plate consists of the Asian
1. A group of students were discussing plate tectonics in their science class. All of the following statements about the tectonic plates are incorrect EXCEPT: A. The Eurasian Plate consists of the Asian
TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE. Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor of Geoscience Winona State University
 TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor of Geoscience Winona State University 1 TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor
TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor of Geoscience Winona State University 1 TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor
sonar seismic wave basalt granite
 geologist sonar crust geology seismic wave mantle constructive force basalt inner core destructive force granite outer core The solid, rocky, surface layer of the earth. an instrument that can find objects
geologist sonar crust geology seismic wave mantle constructive force basalt inner core destructive force granite outer core The solid, rocky, surface layer of the earth. an instrument that can find objects
Science 10 PROVINCIAL EXAM STUDY BOOKLET. Unit 4. Earth Science
 Science 10 PROVNCAL EXAM STUDY BOOKLET Unit 4 Earth Science Student nstructions 1. Ensure that you have blank paper and a Data Booklet. 2. Record all answers on a separate piece of paper. 3. Answer keys
Science 10 PROVNCAL EXAM STUDY BOOKLET Unit 4 Earth Science Student nstructions 1. Ensure that you have blank paper and a Data Booklet. 2. Record all answers on a separate piece of paper. 3. Answer keys
Bell Ringer 5 Minutes. Click Picture to Start Timing
 Plate Tectonics SC.7.E.6.5: Explore the scien6fic theory of plate tectonics by describing how the movement of Earth s crustal plates causes both slow and rapid changes in Earth s surface, including volcanic
Plate Tectonics SC.7.E.6.5: Explore the scien6fic theory of plate tectonics by describing how the movement of Earth s crustal plates causes both slow and rapid changes in Earth s surface, including volcanic
Questions and Topics
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
3. Evidence for Continental Drift
 YEAR 111 BIOLOGY EVOLUTION OF AUSTRALIAN BIOTA LESSON 1: GONDWANALAND SAMPLE RESOURCES 1300 008 008 www.matrix.edu.auu 3. Evidence for Continental Drift Students learn to: Identify and describe evidence
YEAR 111 BIOLOGY EVOLUTION OF AUSTRALIAN BIOTA LESSON 1: GONDWANALAND SAMPLE RESOURCES 1300 008 008 www.matrix.edu.auu 3. Evidence for Continental Drift Students learn to: Identify and describe evidence
2 Earth s Changing Continents
 CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 2 Earth s Changing Continents California Science Standards 7.4.a, 7.4.e, 7.4.f BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 2 Earth s Changing Continents California Science Standards 7.4.a, 7.4.e, 7.4.f BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
Section 1: How Did Life Begin? Chapter 19: History of Life on Earth. Section 2: The Age of Earth
 Chapter 19: History of Life on Earth Section 1: How Did Life Begin? I. The Basic Chemicals of Life A. 1920s B. Earth s early oceans contained large amounts of organic molecules C. Molecules formed spontaneously
Chapter 19: History of Life on Earth Section 1: How Did Life Begin? I. The Basic Chemicals of Life A. 1920s B. Earth s early oceans contained large amounts of organic molecules C. Molecules formed spontaneously
Procedure: 1) Cut out each continent- cut along the dashed line. Cut out the key to paste onto your sheet later.
 Name: Pangea and Continental Drift Lab Science: Introduction: Alfred Wegener (a German Geologist), considered the Father of Plate Tectonics, was the first to coin the term Continental Drift. After collecting
Name: Pangea and Continental Drift Lab Science: Introduction: Alfred Wegener (a German Geologist), considered the Father of Plate Tectonics, was the first to coin the term Continental Drift. After collecting
* If occurs, fossils that formed in shallow water may be found in water. Subsidence mean the crust is.
 Name Notes: Topic 5B Topic 5B: The Dynamic Crust A. What evidence exists that proves the Earth s Crust is and has moved? Earth Science 1. Tilted, folded or faulted strata Strata is a term that refers to.
Name Notes: Topic 5B Topic 5B: The Dynamic Crust A. What evidence exists that proves the Earth s Crust is and has moved? Earth Science 1. Tilted, folded or faulted strata Strata is a term that refers to.
8.9A the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory
 8.9A the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory Theory of Plate Tectonics the theory that pieces of Earth s lithosphere are in constant motion on the asthenosphere. The
8.9A the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory Theory of Plate Tectonics the theory that pieces of Earth s lithosphere are in constant motion on the asthenosphere. The
The Theory of Continental Drift. Continental Drift Discovery
 The Theory of Continental Drift Continental Drift Discovery The World ALFRED WEGENER THEORY OF CONTINENTAL DRIFT Found evidence for PANGAEA and proposed the theory of continental drift. Continental Drift
The Theory of Continental Drift Continental Drift Discovery The World ALFRED WEGENER THEORY OF CONTINENTAL DRIFT Found evidence for PANGAEA and proposed the theory of continental drift. Continental Drift
Theory of Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Earth s Interior. Use Target Reading Skills. Exploring Inside Earth
 Plate Tectonics Name Date Class Earth s Interior This section explains how scientists learn about Earth s interior. The section also describes the layers that make up Earth and explains why Earth acts
Plate Tectonics Name Date Class Earth s Interior This section explains how scientists learn about Earth s interior. The section also describes the layers that make up Earth and explains why Earth acts
Plate Tectonics I: Discovery. Paradigms and Scien.fic Revolu.ons Wegener and Con.nental Dri9 Sea Floor Spreading Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics I: Discovery Paradigms and Scien.fic Revolu.ons Wegener and Con.nental Dri9 Sea Floor Spreading Plate Tectonics Thomas Kuhn. 1962. The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, University of
Plate Tectonics I: Discovery Paradigms and Scien.fic Revolu.ons Wegener and Con.nental Dri9 Sea Floor Spreading Plate Tectonics Thomas Kuhn. 1962. The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, University of
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT (2 ND CANADIAN EDITION)
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Plate Tectonics. How do the plates move?
 Plate Tectonics How do the plates move? Continental Drift Hypothesis In 1915, Alfred Wegener s hypothesis about Continental Drift couldn t explain the forces that could move continents. Wegener wasn t
Plate Tectonics How do the plates move? Continental Drift Hypothesis In 1915, Alfred Wegener s hypothesis about Continental Drift couldn t explain the forces that could move continents. Wegener wasn t
PLATE TECTONICS Chapter 4 Notes
 PLATE TECTONICS Chapter 4 Notes Review Earth s Interior Ch 1. Geologists have used two main types of evidence to learn about Earth s interior: Direct evidence from rocks drilled from deep inside Earth
PLATE TECTONICS Chapter 4 Notes Review Earth s Interior Ch 1. Geologists have used two main types of evidence to learn about Earth s interior: Direct evidence from rocks drilled from deep inside Earth
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p ) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by:
 Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
Latitude and Longitude
 Seafloor Magnetism, Seafloor Spreading: Developing the Theory of Plate Tectonics Graphics: (top) Earth topography, (bottom) Garrison, Fig. 3.14. Earthquakes and the Dynamic Earth The Earth is not entirely
Seafloor Magnetism, Seafloor Spreading: Developing the Theory of Plate Tectonics Graphics: (top) Earth topography, (bottom) Garrison, Fig. 3.14. Earthquakes and the Dynamic Earth The Earth is not entirely
Slow and Steady By ReadWorks
 By ReadWorks How did all the amazing things on our planet form? How did magnificent mountain ranges rise up in one place and beautiful beaches form elsewhere? Why do some places experience earthquakes
By ReadWorks How did all the amazing things on our planet form? How did magnificent mountain ranges rise up in one place and beautiful beaches form elsewhere? Why do some places experience earthquakes
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
 The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth is made up of 4 main layers: Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core The Crust This is where
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth is made up of 4 main layers: Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core The Crust This is where
STAG1032: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY (Geologi Fizik) Continental Drift Concept
 STAG1032: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY (Geologi Fizik) Continental Drift Concept (Konsep Hanyutan Benua) Hypothesis die Verschieburg der Kontinente Dr. Wan Zuhairi Wan Yaacob Program Geologi, UKM Konsep Hanyutan Benua
STAG1032: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY (Geologi Fizik) Continental Drift Concept (Konsep Hanyutan Benua) Hypothesis die Verschieburg der Kontinente Dr. Wan Zuhairi Wan Yaacob Program Geologi, UKM Konsep Hanyutan Benua
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE
 TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
Exploring Geography. Chapter 1
 Exploring Geography Chapter 1 The Study of Geography Geography is the study of where people, places, and things are located and how they relate to each other. Greek meaning writing about or describing
Exploring Geography Chapter 1 The Study of Geography Geography is the study of where people, places, and things are located and how they relate to each other. Greek meaning writing about or describing
Origin of an idea about origins
 Origin of an idea about origins Biological evolution is the process of change during the course of time because of the alteration of the genotype and the transfer of these altered genes to the next generation.
Origin of an idea about origins Biological evolution is the process of change during the course of time because of the alteration of the genotype and the transfer of these altered genes to the next generation.
5/24/2018. Plate Tectonics. A Scientific Revolution Unfolds
 1 Plate Tectonics A Scientific Revolution Unfolds 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the late 1960s, most geologists believed that the
1 Plate Tectonics A Scientific Revolution Unfolds 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the late 1960s, most geologists believed that the
Plate Tectonics. I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics II. A Mosaic of Plates III. Types of Plate Boundaries IV. How Plates Move
 Plate Tectonics I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics II. A Mosaic of Plates III. Types of Plate Boundaries IV. How Plates Move I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift (Alfred Wegener) Proposed
Plate Tectonics I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics II. A Mosaic of Plates III. Types of Plate Boundaries IV. How Plates Move I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift (Alfred Wegener) Proposed
Directed Reading. Section: Continental Drift. years ago? WEGENER S HYPOTHESIS
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Continental Drift 1. Who obtained new information about the continents and their coastlines 400 years ago? 2. What did people notice when they studied new world
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Continental Drift 1. Who obtained new information about the continents and their coastlines 400 years ago? 2. What did people notice when they studied new world
Section 1: Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics Section 1 Section 1: Continental Drift Preview Key Ideas Wegener s Hypothesis Sea-Floor Spreading Paleomagnetism Wegener Redeemed Continental Drift (Pangaea) Plate Tectonics Section 1 Key
Plate Tectonics Section 1 Section 1: Continental Drift Preview Key Ideas Wegener s Hypothesis Sea-Floor Spreading Paleomagnetism Wegener Redeemed Continental Drift (Pangaea) Plate Tectonics Section 1 Key
The Earth. February 26, 2013
 The Earth February 26, 2013 The Planets 2 How long ago did the solar system form? Definition: Cosmic Rays High-energy particles that constantly bombard objects in space Mostly they are hydrogen nuclei
The Earth February 26, 2013 The Planets 2 How long ago did the solar system form? Definition: Cosmic Rays High-energy particles that constantly bombard objects in space Mostly they are hydrogen nuclei
Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics. Physical Science Section 17.1
 Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Physical Science Section 17.1 This is how the continents formed. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tzzgpf Vx32M&list=PLABDC7B24FAFE33FD The Earth is like a parfait, it
Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Physical Science Section 17.1 This is how the continents formed. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tzzgpf Vx32M&list=PLABDC7B24FAFE33FD The Earth is like a parfait, it
Geography of Evolution
 Geography of Evolution Biogeography - the study of the geographic distribution of organisms. The current distribution of organisms can be explained by historical events and current climatic patterns. Darwin
Geography of Evolution Biogeography - the study of the geographic distribution of organisms. The current distribution of organisms can be explained by historical events and current climatic patterns. Darwin
Mr. Petersen EARTH SCIENCE LESSON th Grade
 Teacher Prep Materials and stuff needed: Cutout Glue Sticks or Rice Glue PowerPoint Plate Tectonics Set up the students for taking notes. Model for the students using the camera projector. Use the Prentice
Teacher Prep Materials and stuff needed: Cutout Glue Sticks or Rice Glue PowerPoint Plate Tectonics Set up the students for taking notes. Model for the students using the camera projector. Use the Prentice
Processes that Shape the Earth
 Grade 8 Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Processes that Shape the Earth Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Explain the role of differential heating and convection
Grade 8 Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Processes that Shape the Earth Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Explain the role of differential heating and convection
Unit 3 Target 1. I can explain the evidence for continental drift.
 Unit 3 Target 1 I can explain the evidence for continental drift. Question? Look at the map below, do you see any puzzle pieces, if so where would they fit? Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Possible Answers!
Unit 3 Target 1 I can explain the evidence for continental drift. Question? Look at the map below, do you see any puzzle pieces, if so where would they fit? Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Possible Answers!
Continental Drift. Wegener theory that the crustal plates are moving and once were a super continent called Pangaea.
 PLATE TECTONICS WHAT IS TECTONICS? Tectonism is the faulting or folding or other deformation of the outer layer of a planet. It happens very slowly, on the scale of millions of years. Tectonic activity
PLATE TECTONICS WHAT IS TECTONICS? Tectonism is the faulting or folding or other deformation of the outer layer of a planet. It happens very slowly, on the scale of millions of years. Tectonic activity
plate tectonics and continental drift.notebook March 27, 2014
 Theories: CONTINENTAL DRIFT This theory stated that all the continents in the world were joined together a long time ago. The great big super continent (which he called Pangaea) cracked apart into several
Theories: CONTINENTAL DRIFT This theory stated that all the continents in the world were joined together a long time ago. The great big super continent (which he called Pangaea) cracked apart into several
