The effect of water on strain localization in calcite fault gouge sheared at seismic slip rates. By Tyler Lagasse
|
|
|
- Bruno Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The effect of water on strain localization in calcite fault gouge sheared at seismic slip rates By Tyler Lagasse
2 Co-seismic slip depth limited within sub-cm-thick gouge & cataclastic-bearing principal slip zones Localization to sub-mm scale during single co-seismic slip events Introduction High-velocity (V max = 1 m/s) rotary-shear normal stress (σ n ) of 3-20 Mpa done under room-dry & wet conditions Natural fault zones in limestone more susceptible to rapid dynamic weakening if water is in granular slipping zones
3 Material & methods There were 2 different rotary-shear apparatus utilized I. Slow to High Velocity Apparatus (SHIVA) II. Pressurized High-Velocity (Phv)
4 18 experiments using strain markers Max. slip rate: 1 m/s Accel. & Decel.: 6 m/s 2 σ n : 3-20 Mpa Total displacements: m under room-dry & waterdampened condiditons Gouge layer inner/outer diameters: 35 & 55 mm Setup of SHIVA
5 24 experiments under room-dry & controlled pore-pressure conditions Max. slip rate:1 m/s Acceleration: 0.5 m/s 2 Gouge layer inner/outer diameters: 30 & 60 mm σ n : 3-12 Mpa Pore-fluid pressure: Mpa Perfomed w/room-dry & water-saturated conditions, no strain markers Data 1 khz rate Setup of Phv
6 Calcite group from crushed Carrara marble Both gouges sieved to <250μm Sample prep & analysis techniques 5 g of calcite gouge used to get 3 mm thickness for SHIVA tests 15 g of calcite gouge used to get 3mm thickness for Phv tests Dark grey dolomite marker is sheared in slip & finite strain different positions within gouge layer τ = tan ϕ = dx/x = horizontal displacement/layer thickness
7 Mechanical behavior of room-dry & waterdampened calcite gouge In SHIVA, peak stress (σ peak ) is MPa normal stress (σ n ) correlating to peak friction coefficient (μ = τ/σ n ) of ~0.6 to 0.7 Absolute shear stress values higher in Phv than in SHIVA Results Compaction rate change higher for room-dry samples Strengthening phases shorten with increased σ n in roomdry experiments Higher acceleration, longer strengthening phases for SHIVA tests in wet conditions than for Phv 2 water-dampened SHIVA tests suggest rising length of strengthening values Dynamic weakening initiates after strengthening phase
8 Results
9
10 Results
11 Progressive microstructure development Microstructure of sheared calcite gouge changes w/displacement growth In both wet & dry gouges, zone of comminution grows Results Both samples show rapid change from high to low strain Little change in preserved samples in microstructure of both dry & wet gouges Both gouges show high strain zone go from general zone of slightly compacted pulverized powder to highly comminuted and compressed gouge sliced by a discrete principal slip surface
12
13 Results Quantitative strain analysis 14 of 18 SHIVA experiments kept a strain marker used to add up strain distribution in gouge layer Marker boundaries appear straight and are traceable Angle of distortion (0-60 O ) leads to low strains (0-2 Mpa) Finite strain solved by subtracting finite strain from low to intermediate strain zones from bulk strain Finite strain show little to no total displacement dependence, & is similar in dry & wet samples At short total displacements, high strain zone s strain is bigger in water-dampened tests than non-dry tests
14 Results
15 PURPOSE: to investigate water s effect on strain localization process in calcite groups Discussion Progressive strain localization No microstructural differences Most slip is hosted in principal slip zone after localization is met regardless of conditions suggesting the presence of substantial strain & velocity gradient Calcite gouge high velocity shows quicker dynamic weakening w/water present Gouges w/20% H 2 O (SHIVA) behaved in same way as completely saturated gouges deformed w/stable pore pressure (Phv) Rapid weakening in wet conditions not caused by faster localization Emergence of dynamic weakening in calcite-bearing fault zone relies on normal stress.
16 Discussion Potential dynamic weakening mechanisms More efficient or different active weakening mechanism for rapid weakening in wet conditions Phv pore pressure is not elevated, has little effect on mechanical behavior, based on results from SHIVA & Phv High efficiency stress corrosion in wet conditions due to 3x less fracture surface energy for calcite in water Lower steady-state shear stress & higher levels of weakening under dry conditions
17 Implications for natural faults Discussion If critical shear stress due to tectonic loading is met, frictional sliding will occur & potential for dynamic weakening of a fault increases Gouge-bearing faults in carbonates become vulnerable to rapid dynamic weakening in water at shallow depths Results say dynamic weakening will come sooner in slip zone water
18 Conclusion Difference in mechanical behavior for wet & dry 1 m/s Dry gouges show extended strengthening phase prior to dynamic weakening Wet gouges dynamically weaken instantaneously to a slightly larger steady-state shear stress High strain slipping zone & slip surface set up most of displacement Amount of strain & velocity gradient found in gouge s thin layer
19 Ben-Zion, Y., Sammis, C.G., Characterization of Fault Zones. Pure Appl. Geophys. 160 (3-4), Boullier, A.M., Yeh, E.C., et al., Microscale anatomy of the 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake fault zone. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 10. Bullock, R.J., De Paola, N., et al., An experimental investigation into the role of phyllosilicate content on earthquake propogation during seismic slip in carbonate faults. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 120 (5), Chester, F.M., Chester, J.S., Ultracataclasite structure and friction processes of the Punchbowl fault, San Andreas system, California. Tectonophysics 295 (1), References Chester, F.M., Evans, J.P., et al., Internal structure and weakening mechanisms of the Sanandreas fault. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 98 (B1), De Paola, N., Hirose, T., et al., Fault lubrication and earthquake propogation in thermally unstable rocks. Geology 39 (1), Di Toro, G., Niemeijer, A., et al., From field geology to earthquake simulation: a new state-ofthe-art tool to investigate rock friction during the seismic cycle (SHIVA). Rendiconti lincei 21 (1), Faulkner, D., Mitchell, T., et al., Stuck in the mud? Earthquake nucleation and propagation through accretionary forearcs. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38 (18). Fondreist, M., Smith S.A., et al., Fault zone structure and seismic slip localization in dolostones, an example from the Southern Alps, Italy. J. Struct. Geol. 45, Fondreist, M., Smith, S.A.F., et al., Mirror-like faults and power dissipation during earthquakes. Geology 41 (11)
20 Han, R., Hirose, T., Clay-clast aggregates in fault gouge: an unequivocal indicatorof seismic faulting at shallow depths? J. Struct. Geol. 43, Han, R., Hirose, T., et al., Strong velocity weakening and powder lubrication of simulated carbonate faults at seismic slip rates. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 115 (B3). Heermance, R., Shipton, Z.K., et al., Fault structure control on fault slip and ground motion during the 1999 rupture of the Chelungpu fault, Taiwan. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 93 (3) Herwegh, M., Handy, M The origin of shape preferred orientations in mylonite: inferences from in-situ experiments on polycrystalline norcamphor. J. Struct. Geol. 20 (6), Morrow, C., Moore, D.E., et al., The effect of mineral bond strength and adsorbed water on fault gouge frictional strength. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27 (6), Proctor, B., Mitchell, T., et al., Dynamic weakening of serpentinite gouges and bare surfaces at seismic slip rates. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 119 (11), Rockwell, T.K., Ben-Zion, Y., High localization of primary slip zones in large earthquakes from paleoseismic trenches: observations and implications for earthquake physics. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 112 (B10). Sibson, R.H., Thickness of the seismic slip zone. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 93 (3), Siman-Tov, S., Aharonov, E., et al., Nanograins form carbonate fault mirrors. Geology 41 (6), Smith, S., Nielsen, S., et al., Strain localization and the onset of dynamic weakening in calcite fault gouge. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 413, Smith, S.A.F., Di Toro, G., et al., Coseismic recrystallization during shallow earthquake slip. Geology 41 (1), Snoke, A.W., Tullis, J., et al., 1998., Fault-related rocks: A Photographic Atlas. Princeton University Press. Tadai, O., Tanikawa, W., et al., Design of new frictional testing machine for shallow fault materials. In: AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts. Tanikawa, W., Mukoyoshi, H., et al., Experimental investigation of the influence of slip velocity and temperature on permeability during and after high-velocity fault slip. J. Struct. Geol. 38, Ujiie, K., Tsutsumi, A., High-velocity frictional properties of clay-rich fault gouge in a megasplay fault zone, Nankai subduction zone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37. Verbene, B.A., Plumper, O., et al., 2014b. Superplastic nanofibrous slip zones control seismogenic fault friction. Science 346 (6215),
Shear localization due to thermal pressurization of pore fluids in rapidly sheared granular media
 BIOT-5 Conference, Vienna, 10-12 July 2013, Symposium MS02, Mechanics of fluid-infiltrated earth materials - in memory of Terzaghi and Biot Session MS02-2, Localization and failure, presentation MS02-2.1,
BIOT-5 Conference, Vienna, 10-12 July 2013, Symposium MS02, Mechanics of fluid-infiltrated earth materials - in memory of Terzaghi and Biot Session MS02-2, Localization and failure, presentation MS02-2.1,
Shear localization due to thermal pressurization of pore fluids in rapidly sheared granular media
 Symposium on the Application of Mechanics to Geophysics Scripps Institute of Oceanography, University of California at San Diego 17 and 18 January 2015 Shear localization due to thermal pressurization
Symposium on the Application of Mechanics to Geophysics Scripps Institute of Oceanography, University of California at San Diego 17 and 18 January 2015 Shear localization due to thermal pressurization
1/22/2015. High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics
 High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip
 Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
The Missing Sinks: Slip Localization in Faults, Damage Zones, and the Seismic Energy Budget
 The Missing Sinks: Slip Localization in Faults, Damage Zones, and the Seismic Energy Budget Zoe K. Shipton 1, James P. Evans 2, Rachel E. Abercrombie 3, and Emily E. Brodsky 4 The majority of work done
The Missing Sinks: Slip Localization in Faults, Damage Zones, and the Seismic Energy Budget Zoe K. Shipton 1, James P. Evans 2, Rachel E. Abercrombie 3, and Emily E. Brodsky 4 The majority of work done
THE SEISMIC CYCLE IN CARBONATE-BEARING FAULTS
 THE SEISMIC CYCLE IN CARBONATE-BEARING FAULTS PhD candidate: MICHELE FONDRIEST, II course Tutor: Prof. GIULIO DI TORO Co-Tutors: PhD STEVEN SMITH, Prof. DARIO ZAMPIERI Cycle: XXVI Abstract The study of
THE SEISMIC CYCLE IN CARBONATE-BEARING FAULTS PhD candidate: MICHELE FONDRIEST, II course Tutor: Prof. GIULIO DI TORO Co-Tutors: PhD STEVEN SMITH, Prof. DARIO ZAMPIERI Cycle: XXVI Abstract The study of
Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture Propagation: Evidence from Geological and Seismological Observations
 Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
3D modeling of the cycle of a great Tohoku oki earthquake, considering frictional behavior at low to high slip velocities
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049308, 2011 3D modeling of the cycle of a great Tohoku oki earthquake, considering frictional behavior at low to high slip velocities B. Shibazaki,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049308, 2011 3D modeling of the cycle of a great Tohoku oki earthquake, considering frictional behavior at low to high slip velocities B. Shibazaki,
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Abstract
 Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area. Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC
 Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Supplementary Information
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2016015 Yao et al. (E-mail: yaolu_cug@163.com) Supplementary Information This file provides supporting information for article The crucial role of temperature in high-velocity weakening
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2016015 Yao et al. (E-mail: yaolu_cug@163.com) Supplementary Information This file provides supporting information for article The crucial role of temperature in high-velocity weakening
Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle. Read KK&V chapter 2.10
 Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE. Kyle Withers Qian Yao
 FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
Fault gouge graphitization as evidence of past seismic slip. Li-Wei Kuo*, Fabio Di Felice, Elena Spagnuolo, Giulio Di Toro, Sheng-Rong Song, Stefano
 GSA Data Repository 2017329 Fault gouge graphitization as evidence of past seismic slip Li-Wei Kuo*, Fabio Di Felice, Elena Spagnuolo, Giulio Di Toro, Sheng-Rong Song, Stefano Aretusini, Haibing Li, John
GSA Data Repository 2017329 Fault gouge graphitization as evidence of past seismic slip Li-Wei Kuo*, Fabio Di Felice, Elena Spagnuolo, Giulio Di Toro, Sheng-Rong Song, Stefano Aretusini, Haibing Li, John
Fabric induced weakness of tectonic faults
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041689, 2010 Fabric induced weakness of tectonic faults André Niemeijer, 1,2,3,4 Chris Marone, 2,3 and Derek Elsworth
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041689, 2010 Fabric induced weakness of tectonic faults André Niemeijer, 1,2,3,4 Chris Marone, 2,3 and Derek Elsworth
Megathrust Earthquakes
 Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta. California Institute of Technology
 Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 16, 9 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Energy Balance of dynamic rupture Crack tip stress field Frictional Rupture Fronts Meet in the lab (522
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 16, 9 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Energy Balance of dynamic rupture Crack tip stress field Frictional Rupture Fronts Meet in the lab (522
Friction in Rocks Assigned Reading: {Marone, 1998 #3905; Chapter 8 in \Paterson, 2005 #5865} Resource reading: {Scholz, 1990 #4288; Ruina, 1985 #1586}
 12.524, 2005 09 28 LE04: Friction and Constitutive Laws 1 Friction in Rocks Assigned Reading: {Marone, 1998 #3905; Chapter 8 in \Paterson, 2005 #5865} Resource reading: {Scholz, 1990 #4288; Ruina, 1985
12.524, 2005 09 28 LE04: Friction and Constitutive Laws 1 Friction in Rocks Assigned Reading: {Marone, 1998 #3905; Chapter 8 in \Paterson, 2005 #5865} Resource reading: {Scholz, 1990 #4288; Ruina, 1985
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA
 3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
Fault gouge porosity from 2D simulations of fractal particle size distribution
 Fault gouge porosity from 2D simulations of fractal particle size distribution Reza Sehhati (1), Sujana Ganta (2), and Jafar Hadizadeh (3) Civil and Environmental Engineering Department, University of
Fault gouge porosity from 2D simulations of fractal particle size distribution Reza Sehhati (1), Sujana Ganta (2), and Jafar Hadizadeh (3) Civil and Environmental Engineering Department, University of
Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation
 Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation Zac Meadows UC Davis - Department of Physics Summer 2012 REU September 3, 2012 Abstract To better understand the spatial and temporal complexity
Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation Zac Meadows UC Davis - Department of Physics Summer 2012 REU September 3, 2012 Abstract To better understand the spatial and temporal complexity
Influence of dilatancy on the frictional constitutive behavior of a saturated fault zone under a variety of drainage conditions
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008556, 2011 Influence of dilatancy on the frictional constitutive behavior of a saturated fault zone under a variety of drainage conditions
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008556, 2011 Influence of dilatancy on the frictional constitutive behavior of a saturated fault zone under a variety of drainage conditions
Fault-Zone Properties arid Earthquake Rupture Dynamics
 Fault-Zone Properties arid Earthquake Rupture Dynamics Eiichi Fukuyama National Research Institute for Earth Science,and Disaster Prevention Tsukuba, Japan i ':-> i' ' -':'.." \,' " '' L VH ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM
Fault-Zone Properties arid Earthquake Rupture Dynamics Eiichi Fukuyama National Research Institute for Earth Science,and Disaster Prevention Tsukuba, Japan i ':-> i' ' -':'.." \,' " '' L VH ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM
Clay mineral anomalies in the fault zone of the Chelungpu Fault, Taiwan, and their implications
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18306, doi:10.1029/2009gl039269, 2009 Clay mineral anomalies in the fault zone of the Chelungpu Fault, Taiwan, and their implications
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L18306, doi:10.1029/2009gl039269, 2009 Clay mineral anomalies in the fault zone of the Chelungpu Fault, Taiwan, and their implications
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09838 (A) N330 (Instron 8500) V = 0.075 m/s σ n = 5 MPa HVR381c (Kyoto Univ.) V = 0.048 m/s σ n = 5 MPa Fig. A. Experiments performed with nov aculite (99.9% quartz) in the Instron 8500
doi:10.1038/nature09838 (A) N330 (Instron 8500) V = 0.075 m/s σ n = 5 MPa HVR381c (Kyoto Univ.) V = 0.048 m/s σ n = 5 MPa Fig. A. Experiments performed with nov aculite (99.9% quartz) in the Instron 8500
Elastic Rebound Theory
 Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Crustal Deformation. Earth Systems 3209
 Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Geology for Engineers Rock Mechanics and Deformation of Earth Materials
 89.325 Geology for Engineers Rock Mechanics and Deformation of Earth Materials Why do rocks break? Rock mechanics experiments a first order understanding. Faults and Fractures Triaxial load machine. a)
89.325 Geology for Engineers Rock Mechanics and Deformation of Earth Materials Why do rocks break? Rock mechanics experiments a first order understanding. Faults and Fractures Triaxial load machine. a)
Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes
 Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2+,**0 pp.,/3,00 Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes Paul Somerville* and Arben Pitarka
Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2+,**0 pp.,/3,00 Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes Paul Somerville* and Arben Pitarka
Mechanics of faulting
 Mechanics of faulting http://www.sanandre asfault.org Jyr-Ching Hu, Dept. Geosciences National Taiwan University Strengths of active thrust-belt wedges & their basal detachments: directly determined from
Mechanics of faulting http://www.sanandre asfault.org Jyr-Ching Hu, Dept. Geosciences National Taiwan University Strengths of active thrust-belt wedges & their basal detachments: directly determined from
The role of fault zone fabric and lithification state on frictional strength, constitutive behavior, and deformation microstructure
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008264, 2011 The role of fault zone fabric and lithification state on frictional strength, constitutive behavior, and deformation microstructure
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008264, 2011 The role of fault zone fabric and lithification state on frictional strength, constitutive behavior, and deformation microstructure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Going beyond failure in mechanics From bifurcation theory to strain localization and earthquake control
 Séminaire de Calcul Scientifique du CERMICS Going beyond failure in mechanics From bifurcation theory to strain localization and earthquake control Ioannis Stefanou (Navier, ENPC) 19 avril 2018 Going beyond
Séminaire de Calcul Scientifique du CERMICS Going beyond failure in mechanics From bifurcation theory to strain localization and earthquake control Ioannis Stefanou (Navier, ENPC) 19 avril 2018 Going beyond
The Influence of Brines and Temperature on the Frictional Properties of Laboratory Fault Gouge. Cody W. Bomberger ABSTRACT
 The Influence of Brines and Temperature on the Frictional Properties of Laboratory Fault Gouge Cody W. Bomberger ABSTRACT The frictional properties of gouge material within tectonic faults zones dictate
The Influence of Brines and Temperature on the Frictional Properties of Laboratory Fault Gouge Cody W. Bomberger ABSTRACT The frictional properties of gouge material within tectonic faults zones dictate
The Frictional Regime
 The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
Frictional behavior of materials in the 3D SAFOD volume
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L05302, doi:10.1029/2008gl036660, 2009 Frictional behavior of materials in the 3D SAFOD volume B. M. Carpenter, 1 C. Marone, 1 and D.
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L05302, doi:10.1029/2008gl036660, 2009 Frictional behavior of materials in the 3D SAFOD volume B. M. Carpenter, 1 C. Marone, 1 and D.
Reservoir Geomechanics and Faults
 Reservoir Geomechanics and Faults Dr David McNamara National University of Ireland, Galway david.d.mcnamara@nuigalway.ie @mcnamadd What is a Geological Structure? Geological structures include fractures
Reservoir Geomechanics and Faults Dr David McNamara National University of Ireland, Galway david.d.mcnamara@nuigalway.ie @mcnamadd What is a Geological Structure? Geological structures include fractures
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law
 Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ).
 Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Dynamic weakening and the depth dependence of earthquake fauling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, 1 2 Dynamic weakening and the depth dependence of earthquake fauling Nicolas Brantut 1, John D. Platt 2 N. Brantut, Rock and Ice Physics Laboratory,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, 1 2 Dynamic weakening and the depth dependence of earthquake fauling Nicolas Brantut 1, John D. Platt 2 N. Brantut, Rock and Ice Physics Laboratory,
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f
 Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
The depth-dependence of dynamic weakening
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.19/, The depth-dependence of dynamic weakening Nicolas Brantut 1, John D. Platt Abstract. Earthquake propagation along faults is controlled by both
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.19/, The depth-dependence of dynamic weakening Nicolas Brantut 1, John D. Platt Abstract. Earthquake propagation along faults is controlled by both
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
28th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies PREPARING FOR THE 2006 ALASKA PERMAFROST EXPERIMENT
 PREPARING FOR THE 2006 ALASKA PERMAFROST EXPERIMENT Charles G. Sammis and Ronald L. Biegel University of Southern California Sponsored by Air Force Research Laboratory Contract No. FA8718-04-C-0012 ABSTRACT
PREPARING FOR THE 2006 ALASKA PERMAFROST EXPERIMENT Charles G. Sammis and Ronald L. Biegel University of Southern California Sponsored by Air Force Research Laboratory Contract No. FA8718-04-C-0012 ABSTRACT
Fault Rheology and Earthquake Mechanisms:
 Workshop: Frontiers in Studies of Earthquakes and Faults SUSTech, Shenzhen, China (Nov. 27-Dec. 1, 2017) Fault Rheology and Earthquake Mechanisms: The Current Status and Future Perspectives Toshihiko Shimamoto
Workshop: Frontiers in Studies of Earthquakes and Faults SUSTech, Shenzhen, China (Nov. 27-Dec. 1, 2017) Fault Rheology and Earthquake Mechanisms: The Current Status and Future Perspectives Toshihiko Shimamoto
Source parameters II. Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop
 Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Effect of hydration state on the frictional properties of montmorillonite-based fault gouge
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004748, 2007 Effect of hydration state on the frictional properties of montmorillonite-based fault gouge Matt J.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004748, 2007 Effect of hydration state on the frictional properties of montmorillonite-based fault gouge Matt J.
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics
 Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Seismic Stability of Tailings Dams, an Overview
 Seismic Stability of Tailings Dams, an Overview BY Gonzalo Castro, Ph.D., P.E. Principal International Workshop on Seismic Stability of Tailings Dams Case Western Reserve University, November 2003 Small
Seismic Stability of Tailings Dams, an Overview BY Gonzalo Castro, Ph.D., P.E. Principal International Workshop on Seismic Stability of Tailings Dams Case Western Reserve University, November 2003 Small
Hitoshi Hirose (1), and Kazuro Hirahara (2) Abstract. Introduction
 Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Inferring fault strength from earthquake rupture properties and the tectonic implications of high pore pressure faulting
 Earth Planets Space, 54, 1173 1179, 22 Inferring fault strength from earthquake rupture properties and the tectonic implications of high pore pressure faulting Stephen A. Miller Geophysics Institute, ETH-Zurich
Earth Planets Space, 54, 1173 1179, 22 Inferring fault strength from earthquake rupture properties and the tectonic implications of high pore pressure faulting Stephen A. Miller Geophysics Institute, ETH-Zurich
Faults. Strike-slip fault. Normal fault. Thrust fault
 Faults Strike-slip fault Normal fault Thrust fault Fault any surface or narrow zone with visible shear displacement along the zone Normal fault Strike-slip fault Reverse fault Thrust fault
Faults Strike-slip fault Normal fault Thrust fault Fault any surface or narrow zone with visible shear displacement along the zone Normal fault Strike-slip fault Reverse fault Thrust fault
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II
 Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
Author's personal copy
 Tectonophysics 612 613 (2014) 56 62 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Tectonophysics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tecto Inelastic response of compliant fault zones to nearby earthquakes
Tectonophysics 612 613 (2014) 56 62 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Tectonophysics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tecto Inelastic response of compliant fault zones to nearby earthquakes
An Examination of Accretionary Prisms at the Nobeoka Thrust
 Evan Tam, University of Connecticut UTRIP 2012 Participant, Kimura Labs An Examination of Accretionary Prisms at the Nobeoka Thrust Introduction Accretionary prisms form at convergent plate boundaries,
Evan Tam, University of Connecticut UTRIP 2012 Participant, Kimura Labs An Examination of Accretionary Prisms at the Nobeoka Thrust Introduction Accretionary prisms form at convergent plate boundaries,
INSIGHTS INTO EARTHQUAKE RUPTURE AND RECOVERY FROM STUDIES OF PALEOSEISMIC FAULTS CHRISTIE ROWE, MCGILL UNIVERSITY
 INSIGHTS INTO EARTHQUAKE RUPTURE AND RECOVERY FROM STUDIES OF PALEOSEISMIC FAULTS CHRISTIE ROWE, MCGILL UNIVERSITY DEFINITION OF AN EARTHQUAKE 1.Fast fault slip (~1 m/s) generates heat 2.Slip propagates
INSIGHTS INTO EARTHQUAKE RUPTURE AND RECOVERY FROM STUDIES OF PALEOSEISMIC FAULTS CHRISTIE ROWE, MCGILL UNIVERSITY DEFINITION OF AN EARTHQUAKE 1.Fast fault slip (~1 m/s) generates heat 2.Slip propagates
PUBLICATIONS. Geophysical Research Letters. Fault mirrors in seismically active fault zones: A fossil of small earthquakes at shallow depths
 PUBLICATIONS Geophysical Research Letters RESEARCH LETTER Key Points: Fault mirrors in the studied fault zones are composed of silica gel and melt patches Melt patches were generated in small fast slip
PUBLICATIONS Geophysical Research Letters RESEARCH LETTER Key Points: Fault mirrors in the studied fault zones are composed of silica gel and melt patches Melt patches were generated in small fast slip
Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes
 Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes M. Acosta, F. Passelègue, A. Schubnel et M. Violay (mateo.acosta@epfl.ch) Context Induced Seismicity in Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes M. Acosta, F. Passelègue, A. Schubnel et M. Violay (mateo.acosta@epfl.ch) Context Induced Seismicity in Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Accelerating energy release prior to large events in simulated earthquake cycles: implications for earthquake forecasting
 Accelerating energy release prior to large events in simulated earthquake cycles: implications for earthquake forecasting Peter Mora and David Place QUAKES, Department of Earth Sciences, The University
Accelerating energy release prior to large events in simulated earthquake cycles: implications for earthquake forecasting Peter Mora and David Place QUAKES, Department of Earth Sciences, The University
Research Themes in Stimulation Geomechanics. How do we optimize slickwater frac ing?
 Research Themes in Stimulation Geomechanics How do stress, fractures and rock properties affect the success of stimulation? How do pressure and stress (and formation properties) evolve during stimulation?
Research Themes in Stimulation Geomechanics How do stress, fractures and rock properties affect the success of stimulation? How do pressure and stress (and formation properties) evolve during stimulation?
EFFECTS OF NON-LINEAR WEAKENING ON EARTHQUAKE SOURCE SCALINGS
 Extended abstract for the 11th International Conference on Fracture 2005 1 EFFECTS OF NON-LINEAR WEAKENING ON EARTHQUAKE SOURCE SCALINGS J.-P. Ampuero Geosciences Department, Princeton University, USA
Extended abstract for the 11th International Conference on Fracture 2005 1 EFFECTS OF NON-LINEAR WEAKENING ON EARTHQUAKE SOURCE SCALINGS J.-P. Ampuero Geosciences Department, Princeton University, USA
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 199, 956 967 GJI Mineral physics, rheology, heat flow and volcanology doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu306 In situ frictional properties of San Andreas Fault
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 199, 956 967 GJI Mineral physics, rheology, heat flow and volcanology doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu306 In situ frictional properties of San Andreas Fault
Influence of fault slip rate on shear induced permeability
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb007013, 2010 Influence of fault slip rate on shear induced permeability Wataru Tanikawa, 1 Masumi Sakaguchi, 2
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb007013, 2010 Influence of fault slip rate on shear induced permeability Wataru Tanikawa, 1 Masumi Sakaguchi, 2
A PRESSURE VESSEL FOR TRUE-TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION & FLUID FLOW DURING FRICTIONAL SHEAR
 A PRESSURE VESSEL FOR TRUE-TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION & FLUID FLOW DURING FRICTIONAL SHEAR Chris Marone, Brett Carperter, Derek Elsworth, Igor Faoro, Matt Ikari, Matt Knuth, André Niemeijer, Demian Saffer, and
A PRESSURE VESSEL FOR TRUE-TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION & FLUID FLOW DURING FRICTIONAL SHEAR Chris Marone, Brett Carperter, Derek Elsworth, Igor Faoro, Matt Ikari, Matt Knuth, André Niemeijer, Demian Saffer, and
Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes
 1 Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada, kelin.wang@canada.ca Introduction Once upon a time, there was a belief that
1 Study megathrust creep to understand megathrust earthquakes Kelin Wang Pacific Geoscience Centre, Geological Survey of Canada, kelin.wang@canada.ca Introduction Once upon a time, there was a belief that
Tectonics. Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting GNH7/GG09/GEOL4002 EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE HAZARD
 Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
friction friction a-b slow fast increases during sliding
 µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
Strain localization driven by thermal decomposition during seismic shear
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 12, DOI:1.12/214JB11493, 215 Strain localization driven by thermal decomposition during seismic shear John D. Platt 1,2, Nicolas Brantut 3, and James R. Rice 1,4 Abstract.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 12, DOI:1.12/214JB11493, 215 Strain localization driven by thermal decomposition during seismic shear John D. Platt 1,2, Nicolas Brantut 3, and James R. Rice 1,4 Abstract.
Frictional rheologies have a wide range of applications in engineering
 A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
Fault Rocks. EARS5136 slide 1
 Fault Rocks EARS5136 slide 1 Fault rocks Fault rock types Examples of deformation features in cores Microstructures Porosity and permeability Lithological and lithification control EARS5136 slide 2 Deformation
Fault Rocks EARS5136 slide 1 Fault rocks Fault rock types Examples of deformation features in cores Microstructures Porosity and permeability Lithological and lithification control EARS5136 slide 2 Deformation
Nonplanar Faults: Mechanics of Slip and Off-fault Damage
 Pure appl. geophys. 166 (2009) 1799 1815 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2009 0033 4553/09/101799 17 DOI 10.1007/s00024-009-0517-y Pure and Applied Geophysics Nonplanar Faults: Mechanics of Slip and Off-fault
Pure appl. geophys. 166 (2009) 1799 1815 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2009 0033 4553/09/101799 17 DOI 10.1007/s00024-009-0517-y Pure and Applied Geophysics Nonplanar Faults: Mechanics of Slip and Off-fault
Effects of Off-fault Damage on Earthquake Rupture Propagation: Experimental Studies
 Pure appl. geophys. 166 (2009) 1629 1648 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2009 0033 4553/09/101629 20 DOI 10.1007/s00024-009-0512-3 Pure and Applied Geophysics Effects of Off-fault Damage on Earthquake Rupture
Pure appl. geophys. 166 (2009) 1629 1648 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2009 0033 4553/09/101629 20 DOI 10.1007/s00024-009-0512-3 Pure and Applied Geophysics Effects of Off-fault Damage on Earthquake Rupture
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities
 Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge, 1. Linearized stability analysis
 JOURNAL OF GOPHYSICAL RSARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:0.029/, Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge,. Linearized stability analysis James R. Rice,,2, John W. Rudnicki 3,4,
JOURNAL OF GOPHYSICAL RSARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:0.029/, Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge,. Linearized stability analysis James R. Rice,,2, John W. Rudnicki 3,4,
I point out two possible paradoxical difficulties in the important target of the IODP in subduction zones, i.e.,
 Drilling the Seismogenic Zone: Some Paradoxes Tetsuzo Seno Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo (Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst., subumitted on January 16, 2003; accepted on July 22, 2003) Abstract
Drilling the Seismogenic Zone: Some Paradoxes Tetsuzo Seno Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo (Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst., subumitted on January 16, 2003; accepted on July 22, 2003) Abstract
High magnetic susceptibility produced in high velocity frictional tests on core
 1 2 High magnetic susceptibility produced in high velocity frictional tests on core samples from the Chelungpu fault in Taiwan 3 Wataru Tanikawa 1 * 4 Toshiaki Mishima 2 5 Tetsuro Hirono 3 6 Weiren Lin
1 2 High magnetic susceptibility produced in high velocity frictional tests on core samples from the Chelungpu fault in Taiwan 3 Wataru Tanikawa 1 * 4 Toshiaki Mishima 2 5 Tetsuro Hirono 3 6 Weiren Lin
Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge: 1. Linearized Stability Analysis
 Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge:. Linearized Stability Analysis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge:. Linearized Stability Analysis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
282 INDEX Computer models for brittle damage, 15f, 17f for damage zone thickness, 245f 247f, 249f for displacement, 86f for dynamic rupture, 43f, 248,
 INDEX Acoustic emissions (AEs) in faults, 235f in fault strength, 231 32, 231t, 232f, 234 35, 235f friction and, 233f Acoustic energy, 238f 239f Active faults, 4f AEs. See Acoustic emissions Alaska. See
INDEX Acoustic emissions (AEs) in faults, 235f in fault strength, 231 32, 231t, 232f, 234 35, 235f friction and, 233f Acoustic energy, 238f 239f Active faults, 4f AEs. See Acoustic emissions Alaska. See
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Faults and Faulting. Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics. Ben van der Pluijm. WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/2/ :47
 Faults and Faulting Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/2/2017 14:47 We Discuss Faults Types and Geometries Systems Fault bends Dimensions
Faults and Faulting Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/2/2017 14:47 We Discuss Faults Types and Geometries Systems Fault bends Dimensions
Rotation of the Principal Stress Directions Due to Earthquake Faulting and Its Seismological Implications
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 85, No. 5, pp. 1513-1517, October 1995 Rotation of the Principal Stress Directions Due to Earthquake Faulting and Its Seismological Implications by
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 85, No. 5, pp. 1513-1517, October 1995 Rotation of the Principal Stress Directions Due to Earthquake Faulting and Its Seismological Implications by
A constitutive model for fault gouge deformation in dynamic rupture simulations
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, A constitutive model for fault gouge deformation in dynamic rupture simulations Eric G. Daub and Jean M. Carlson Department of Physics, University
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, A constitutive model for fault gouge deformation in dynamic rupture simulations Eric G. Daub and Jean M. Carlson Department of Physics, University
Textures in experimentally deformed olivine aggregates: the effects of added water and melt.
 Textures in experimentally deformed olivine aggregates: the effects of added water and melt. F. Heidelbach 1, a, B. Holtzman 2, b, S. Hier-Majumder 2, c and D. Kohlstedt 2, d 1 Bayerisches Geoinstitut,
Textures in experimentally deformed olivine aggregates: the effects of added water and melt. F. Heidelbach 1, a, B. Holtzman 2, b, S. Hier-Majumder 2, c and D. Kohlstedt 2, d 1 Bayerisches Geoinstitut,
Influence of material contrast on fault branching behavior
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047849, 2011 Influence of material contrast on fault branching behavior Nora DeDontney, 1 James R. Rice, 1,2 and Renata Dmowska 2 Received 20 April
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047849, 2011 Influence of material contrast on fault branching behavior Nora DeDontney, 1 James R. Rice, 1,2 and Renata Dmowska 2 Received 20 April
Multiscale Seismic Signature of a Small Fault Zone in a Carbonate Reservoir: Relationships Between V P Imaging, Fault Zone Architecture and Cohesion*
 Multiscale Seismic Signature of a Small Fault Zone in a Carbonate Reservoir: Relationships Between V P Imaging, Fault Zone Architecture and Cohesion* Pierre Jeanne 1,2, Yves Guglielmi 2, and Frédéric Cappa
Multiscale Seismic Signature of a Small Fault Zone in a Carbonate Reservoir: Relationships Between V P Imaging, Fault Zone Architecture and Cohesion* Pierre Jeanne 1,2, Yves Guglielmi 2, and Frédéric Cappa
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
Module 5: Failure Criteria of Rock and Rock masses. Contents Hydrostatic compression Deviatoric compression
 FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
Data report: frictional healing and compressibility of sheared sediment from fault zones, Sites C0004 and C0007 1
 Kinoshita, M., Tobin, H., Ashi, J., Kimura, G., Lallemant, S., Screaton, E.J., Curewitz, D., Masago, H., Moe, K.T., and the Expedition 31/315/31 Scientists Proceedings of the Integrated Ocean Drilling
Kinoshita, M., Tobin, H., Ashi, J., Kimura, G., Lallemant, S., Screaton, E.J., Curewitz, D., Masago, H., Moe, K.T., and the Expedition 31/315/31 Scientists Proceedings of the Integrated Ocean Drilling
Challenges in earthquake physics and source imaging
 Challenges in earthquake physics and source imaging Jean-Paul Ampuero and Nadia Lapusta (Caltech Seismolab) Main goals and current issues in earthquake dynamics The source imaging inverse problem Parallels
Challenges in earthquake physics and source imaging Jean-Paul Ampuero and Nadia Lapusta (Caltech Seismolab) Main goals and current issues in earthquake dynamics The source imaging inverse problem Parallels
3D Finite Element Modeling of fault-slip triggering caused by porepressure
 3D Finite Element Modeling of fault-slip triggering caused by porepressure changes Arsalan Sattari and David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Suary We present a 3D model using a
3D Finite Element Modeling of fault-slip triggering caused by porepressure changes Arsalan Sattari and David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Suary We present a 3D model using a
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
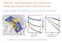 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Characterization of Fault Zones
 Pure appl. geophys. 160 (2003) 677 715 0033 4553/03/040677 39 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2003 Pure and Applied Geophysics Characterization of Fault Zones YEHUDA BEN-ZION 1 and CHARLES G. SAMMIS 1 Abstract
Pure appl. geophys. 160 (2003) 677 715 0033 4553/03/040677 39 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2003 Pure and Applied Geophysics Characterization of Fault Zones YEHUDA BEN-ZION 1 and CHARLES G. SAMMIS 1 Abstract
This paper was prepared for presentation at the Americas Unconventional Resources Conference held in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA, 5 7 June 2012.
 SPE 155476 The Importance of Slow Slip on Faults During Hydraulic Fracturing Stimulation of Shale Gas Reservoirs Mark D. Zoback, SPE, Arjun Kohli, Indrajit Das and Mark McClure, SPE Stanford University
SPE 155476 The Importance of Slow Slip on Faults During Hydraulic Fracturing Stimulation of Shale Gas Reservoirs Mark D. Zoback, SPE, Arjun Kohli, Indrajit Das and Mark McClure, SPE Stanford University
How pore fluid pressurization influences crack tip processes during dynamic rupture
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, How pore fluid pressurization influences crack tip processes during dynamic rupture Nicolas Brantut,,2,3 and James R. Rice 3 We calculate temperature
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, How pore fluid pressurization influences crack tip processes during dynamic rupture Nicolas Brantut,,2,3 and James R. Rice 3 We calculate temperature
