Faults and Faulting. Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics. Ben van der Pluijm. WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/2/ :47
|
|
|
- Rolf Welch
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Faults and Faulting Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/2/ :47
2 We Discuss Faults Types and Geometries Systems Fault bends Dimensions Fault Surfaces Fault Rocks Cataclasites Mylonites Pseudotachylytes Character with Depth More on Mechanics of (Reverse) Faulting Thrust Paradox Thrust Wedges Structure and Society Earthquakes Resources Faults PSG&T 2
3 Faults, Fault Zones and Shear Zones a) Fault. b) Fault zone, with cataclastic deformation. c) Principal fault and fault splays. d) Anastomosing faults. e) Shear zone. Faults PSG&T 3
4 Fault Types: Dip-slip and Strike-slip Faults Faults PSG&T 4
5 Fault Types: Oblique-slip Faults Faults PSG&T 5
6 Field Example: Normal Fault Faults PSG&T 6
7 Modern Fault Scarp: Norcia (Italy) Earthquake ( ) A Notaro, m P Galli, 2016 Faults PSG&T 7
8 Field Example: Reverse (Thrust) Fault Hoback Canyon (U-M s Camp Davis area) Faults PSG&T 8
9 Field Example: Lateral-slip (or Strike-slip) Fault Alpine Fault New Zealand (S Island) Faults PSG&T 9
10 Extensional and Contractional Faults a) Starting condition b) Extension c) Contraction B-B B -B Note horizontal length changes. Shortening is: Faults PSG&T 11
11 Fault Systems Normal Fault ( detachment ) systems Faults PSG&T 12
12 Example: Low-angle Normal Fault ( detachment ) Whipple Mtns Faults PSG&T 13
13 Fault Systems Normal Fault ( detachment ) systems Reverse Fault ( thrust ) Systems Lateral-slip Fault System Faults PSG&T 14
14 Field Example: Reverse or Thrust Faults Swiss Alps Faults PSG&T 15
15 Fault Bends: Thrust Ramps and Flats (a) Cross section with future ramps and flats along a thrust fault. (b) Cross section illustrating hangingwall and footwall flats and ramps, and ramp anticline. Ramp anticline (Segment AB is hangingwall flat on footwall flat. Segment BC is hanging-wall flat on footwall ramp. Segment CD is hangingwall ramp on footwall flat, and segment DE is hanging-wall flat on footwall flat.) Faults PSG&T 16
16 (Erosional) Klippe and Window Klippe, window, allochthon and autochthon in thrust-faulted region. Chief Mtn, MT Minimum fault displacement defined by farthest distance between thrust outcrops in klippe and window (blue line). Faults PSG&T 17
17 Restraining and Releasing Fault Bends Map-views of: (a) restraining bend along a right-lateral (dextral) slip fault. (b) releasing bend along a right-lateral (dextral) slip fault. Faults PSG&T 18
18 Subsidiary Faults R-, R -, and P-shears (a) Clay deforms when underlying blocks of wood slide past one another. (b) Top surface of clay layer, with orientation of Riedel (R), conjugate Riedel (R ), and P-shears. Note that acute bisector of R- and R - shears is parallel to σ 1 and faults at 30 o, following Andersonian theory. Faults PSG&T 19
19 Fault Terminations (a) Fault terminates at ground surface at A; at B, fault is cut by a pluton; at C and D, one fault cuts another; at E, fault was eroded at unconformity. (b) Termination of fault by merging with another fault (at A), by horsetailing (at B) and dying out into zone of distributed deformation (at C). (c) Series of thrust ramps merging at depth with single fault (floor thrust or decollement ). Faults PSG&T 20
20 Fault Scaling and Self-similarity Displacement on fault increases as fault grows (i.e., fault length increases) Measures of maximum displacement and fault length gives empirical relationship: D(isplacement) is ~3% of L(ength) Faults PSG&T 21
21 Fault Surfaces: Striations and Polish SAFOD samples Faults PSG&T 22
22 Fault surfaces: Slickensides (polish) and Slickenlines (fibers) Faults PSG&T 23
23 Fault Rock Classification Cataclasite Mylonite Descriptions of fault rock classes by hand-specimen appearance and degree of cohesion: Argille scagliose Cataclasite Fault breccia Vein-filled breccia Fault gouge Pseudotachylyte Mylonite Also used: Foliated vs. Non-foliated. Faults PSG&T 24
24 Fault Rocks: Cataclasite, (Tectonic) Breccia and Gouge Gouge Breccia Faults PSG&T 25
25 Fault Rocks: Mylonites (Shear Zones) Faults PSG&T 26
26 Types of Mylonites 2/2/2017 Shear Zones EarthStructure 27
27 Fault Rocks: Pseudotachylyte (Friction Melts) Alpine Fault (~500Ka) and Grenville Front (~1.1Ga) Faults PSG&T 28
28 Synoptic Fault Zone and Character with Depth Changing fault character with depth (steeply dipping fault). Also, change in fault zone width and types of fault rock with depth. Faults PSG&T 29
29 Return to Fault Mechanics Canadian Rockies Faults PSG&T 30
30 Mechanics: Thrust Paradox Sliding block: 100(w) x 10(l) x 5(h) km block; r = 2600 kg/m 3 σ n is stress from loading, σ f is frictional resistance (=σ s ), σ l is boundary load at end of thrust sheet, P H2O is pore pressure s n = F/area = (a.m)/area = 9.8 x (2600x1E5x1E4x5E3) /1E5x1E4 = 127 x 10E6 Pa = 127 MPa s f = m x s n, m = 0.7 so σ l ~90 MPa Compressive strength of natural rock on same order, so fracturing at front instead of sliding Faults PSG&T 31
31 Effective Friction: Fluid Pressure Scenario s f = C + m (s n P f ); fracture or s f = m (s n P f ); friction So, m effective = m (1 P f /s n ) m effective m ; Note: P f < s 3 (a) Pushed from rear (b) High fluid pressure at basal detachment σ n is stress from loading, σ f is frictional resistance (=σ s ), σ l is boundary load at end of thrust sheet, P H2O is fluid pressure (P f ) Faults PSG&T 32
32 Low Friction: Lubricant Scenario Sliding block: 100 x 10 x 5 km r = 2600 kg/m 3 s n = F/area = 127 MPa s f = m x s n (a) Pushed from rear (b) Low friction material at basal detachment σ n is stress from loading, σ f is frictional resistance, σ l is boundary load at end of thrust sheet m = 0.2, so σ f ~25 MPa Strength of natural rock greater, so sliding Faults PSG&T 33
33 Extra: Role of Gravity (a) Gravity Sliding down a foreland-tilted slope. (b) Gravity sliding partly downslope and partly upslope. (c) Gravity mechanics creates wedge shape (gravity spreading; think, warm brie). Role of fluid pressure: Dry sliding: dip is o (angle of repose) Wet sliding: l = P f /P l l = 1 (P f =P lith ), dip is ~0 o l = 0.8, dip ~10 o Faults PSG&T 34
34 Mechanics: Thrust Wedges Plow analogy: Wedge of snow or sand extends with continued shortening; thrusts initiate from hinterland to foreland. As thrusts add material at toe of wedge, hinterland portions develop penetrative strain, normal faults and slumps. Faults PSG&T 35
35 Wedge Mechanics: Critical Taper Theory Critical taper (angle φ c ) is sum of surface slope angle (α 1 ) and basal slope angle (β). a) Stress acting on wedge, partly horizontal boundary load caused by backstop (σ bs ) and partly caused by gravity (σ g ). b) If backstop moves, wedge thickens, so surface slope increases, and taper (φ) eventually exceeds φ c. c) Wedge slides toward foreland and new material is added to toe, and extension of wedge occurs so that surface slope decreases. φ c Faults PSG&T 36
36 Structure and Society: Earthquake Impact Date Location Deaths Magnitude January 23, 1556 China, Shansi 830,000 ~8 October 11, 1737 India, Calcutta** 300,000 January 12, 2010 Haiti, Port au Prince 300, July 27, 1976 China, Tangshan 255, August 9, 1138 Syria, Aleppo 230,000 December 26, 2004 Sumatra, Indonesia 225, May 22, 1927 China, near Xining 200, December 22, 856+ Iran,Damghan 200,000 December 16, 1920 China,Gansu 200, September 1, 1923 Japan, Kwanto/Tokyo 143, October 8, 2005 Pakistan 75, May 12, 2008 China, Sichuan 70, December 28, 1908 Italy, Messina 70, November 1, 1755 Portugal, Lisbon 70, May 31, 1970 Peru 66, June 20, 1990 Iran 50, August 17, 1999 Turkey, Izmit 45, March 11, 2011 Japan, Sendai 20, Frictional Regime PSG&T
37 Earthquakes and (Stick-)Slip EQ spectrum: form seismic slip (earthquake), tremor (slow earthquakes to aseismic slip (creep) EQ EQ EQ EQ Stick-slip behavior: elastic stress built-up and (partial) stress release ( stress drop ). Note: EQ stress drop is 1-10MPa, which is 1/10 th of differential stress! Frictional Regime PSG&T 38
38 Structure and Society: Faults Resources: Fossil Fuels Resources: Mineralization Faults PSG&T 39
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
The Frictional Regime
 The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
GEOL372: Week 5 Thrust fault systems. Contractional regimes
 4/3/15 GEOL372: Week 5 Thrust fault systems Contractional regimes Thrust faulting accommodates shortening σ3 σ1 1 Thrust geometry Thrust geometry RAMP segment of fault with different strike and/or dip
4/3/15 GEOL372: Week 5 Thrust fault systems Contractional regimes Thrust faulting accommodates shortening σ3 σ1 1 Thrust geometry Thrust geometry RAMP segment of fault with different strike and/or dip
Lecture 15. Fold-Thrust Belts, and the NJ Ridge and Valley Thrust System
 Lecture 15 Fold-Thrust Belts, and the NJ Ridge and Valley Thrust System Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton; unless noted otherwise
Lecture 15 Fold-Thrust Belts, and the NJ Ridge and Valley Thrust System Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton; unless noted otherwise
GEOL 321 Structural Geology and Tectonics
 GEOL 321 Structural Geology and Tectonics Geology 321 Structure and Tectonics will be given in Spring 2017. The course provides a general coverage of the structures produced by brittle and ductile rock
GEOL 321 Structural Geology and Tectonics Geology 321 Structure and Tectonics will be given in Spring 2017. The course provides a general coverage of the structures produced by brittle and ductile rock
What Causes Rock to Deform?
 Crustal Deformation Earth, Chapter 10 Chapter 10 Crustal Deformation What Causes Rock to Deform? Deformation is a general term that refers to all changes in the shape or position of a rock body in response
Crustal Deformation Earth, Chapter 10 Chapter 10 Crustal Deformation What Causes Rock to Deform? Deformation is a general term that refers to all changes in the shape or position of a rock body in response
Tectonics. Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting GNH7/GG09/GEOL4002 EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE HAZARD
 Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
Contractional Tectonics: Convergence and Collision
 Contractional Tectonics: Convergence and Collision Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/12/2017 5:21 PM We Discuss Contractional Tectonics
Contractional Tectonics: Convergence and Collision Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/12/2017 5:21 PM We Discuss Contractional Tectonics
Crustal Deformation. Earth Systems 3209
 Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Chapter 15 Structures
 Chapter 15 Structures Plummer/McGeary/Carlson (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. TECTONIC FORCES AT WORK Stress & Strain Stress Strain Compressive stress Shortening strain Tensional stress stretching
Chapter 15 Structures Plummer/McGeary/Carlson (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. TECTONIC FORCES AT WORK Stress & Strain Stress Strain Compressive stress Shortening strain Tensional stress stretching
Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting
 Crustal Deformation AKA Structural geology (adapted from Brunkel, 2012) Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting How Rocks Deform: 4 Controls
Crustal Deformation AKA Structural geology (adapted from Brunkel, 2012) Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting How Rocks Deform: 4 Controls
Exam Deformatie en Metamorfose van de Korst Educatorium zaal ALFA
 Naam Studentnummer... Exam Deformatie en Metamorfose van de Korst Educatorium zaal ALFA Do not forget to put your name and student number on each of the question and answer sheets and to return both of
Naam Studentnummer... Exam Deformatie en Metamorfose van de Korst Educatorium zaal ALFA Do not forget to put your name and student number on each of the question and answer sheets and to return both of
Folds and Folding. Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics. Ben van der Pluijm. WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/4/ :15
 Folds and Folding Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/4/2017 17:15 We Discuss Folds and Folding Fold Description Fold Classification
Folds and Folding Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/4/2017 17:15 We Discuss Folds and Folding Fold Description Fold Classification
Unit 4 Lesson 7 Mountain Building
 Indiana Standards 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in the mantle cause lithospheric plates to move causing fast changes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and slow changes like creation of mountains
Indiana Standards 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in the mantle cause lithospheric plates to move causing fast changes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and slow changes like creation of mountains
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM
 Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
Geology for Engineers Rock Mechanics and Deformation of Earth Materials
 89.325 Geology for Engineers Rock Mechanics and Deformation of Earth Materials Why do rocks break? Rock mechanics experiments a first order understanding. Faults and Fractures Triaxial load machine. a)
89.325 Geology for Engineers Rock Mechanics and Deformation of Earth Materials Why do rocks break? Rock mechanics experiments a first order understanding. Faults and Fractures Triaxial load machine. a)
Force and Stress. Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics. Ben van der Pluijm. WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/9/ :35 PM
 Force and Stress Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/9/2017 12:35 PM We Discuss Force and Stress Force and Units (Trigonometry) Newtonian
Force and Stress Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/9/2017 12:35 PM We Discuss Force and Stress Force and Units (Trigonometry) Newtonian
Structural Geology and Geology Maps Lab
 Structural Geology and Geology Maps Lab Mesa College Geology 101 Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Structural Geology Lab Pre-Lab Resources Pre-Lab Internet Links 1) Fundamentals of Structural Geology 2) Visualizing
Structural Geology and Geology Maps Lab Mesa College Geology 101 Lab Ray Rector: Instructor Structural Geology Lab Pre-Lab Resources Pre-Lab Internet Links 1) Fundamentals of Structural Geology 2) Visualizing
Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building
 Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared
Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared
Fault Architecture, Associated Structures and Uranium Mineralization, Eastern Athabasca Basin: A Provisional Empirical Classification
 December 2014 Fault Architecture, Associated Structures and Uranium Mineralization, Eastern Athabasca Basin: A Provisional Empirical Classification David Thomas, Alex Aubin, Dan Brisbin, Joshua Mukwakwami,
December 2014 Fault Architecture, Associated Structures and Uranium Mineralization, Eastern Athabasca Basin: A Provisional Empirical Classification David Thomas, Alex Aubin, Dan Brisbin, Joshua Mukwakwami,
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen?
 San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
Geology 3120: Fault Rocks. Brittle shear zone, CO Natl Mon
 Geology 3120: Fault Rocks Brittle shear zone, CO Natl Mon Outline Fault rocks and strength Fault zone processes Fault rocks Example from Death Valley Fault Rocks and Strength Brittle Fault Zone Processes
Geology 3120: Fault Rocks Brittle shear zone, CO Natl Mon Outline Fault rocks and strength Fault zone processes Fault rocks Example from Death Valley Fault Rocks and Strength Brittle Fault Zone Processes
GEOL5690: Fold and Thrust Belts and Orogenic Wedges ! = S 0
 GEOL569: Fold and Thrust Belts and Orogenic Wedges One of the earlier mysteries in geology was the discovery in the 19 th century of large scale overthrusts in the Alps. Sheets of rock were found to have
GEOL569: Fold and Thrust Belts and Orogenic Wedges One of the earlier mysteries in geology was the discovery in the 19 th century of large scale overthrusts in the Alps. Sheets of rock were found to have
Learning goals - January 16, Describe the geometry of a fault (1) orientation of the plane (strike and dip) (2) slip vector
 Learning goals - January 16, 2012 You will understand how to: Describe the geometry of a fault (1) orientation of the plane (strike and dip) (2) slip vector Understand concept of slip rate and how it is
Learning goals - January 16, 2012 You will understand how to: Describe the geometry of a fault (1) orientation of the plane (strike and dip) (2) slip vector Understand concept of slip rate and how it is
Lecture 6 Folds, Faults and Deformation Dr. Shwan Omar
 Fold: A fold is a bend or wrinkle of rock layers or foliation; folds form as a sequence of ductile deformation. Folding is the processes by which crustal forces deform an area of crust so that layers of
Fold: A fold is a bend or wrinkle of rock layers or foliation; folds form as a sequence of ductile deformation. Folding is the processes by which crustal forces deform an area of crust so that layers of
Introduction Faults blind attitude strike dip
 Chapter 5 Faults by G.H. Girty, Department of Geological Sciences, San Diego State University Page 1 Introduction Faults are surfaces across which Earth material has lost cohesion and across which there
Chapter 5 Faults by G.H. Girty, Department of Geological Sciences, San Diego State University Page 1 Introduction Faults are surfaces across which Earth material has lost cohesion and across which there
Lecture 9 faults, folds and mountain building
 Lecture 9 faults, folds and mountain building Rock deformation Deformation = all changes in size, shape, orientation, or position of a rock mass Structural geology is the study of rock deformation Deformation
Lecture 9 faults, folds and mountain building Rock deformation Deformation = all changes in size, shape, orientation, or position of a rock mass Structural geology is the study of rock deformation Deformation
Dynamic analysis. 1. Force and stress
 Dynamic analysis 1. Force and stress Dynamics is the part of structural geology that involves energy, force, stress, and strength. It's very important to distinguish dynamic concepts from kinematic ones.
Dynamic analysis 1. Force and stress Dynamics is the part of structural geology that involves energy, force, stress, and strength. It's very important to distinguish dynamic concepts from kinematic ones.
swisstopo, Swiss Geological Survey, Wabern, Switzerland, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Earth & Environmental Sciences Area, Berkeley, USA
 Aseismic fault slip and leakage preceding an earthquake induced during an in-situ fault reactivation experiment in the Opalinus Clay, Mont Terri rock laboratory, Switzerland Christophe Nussbaum 1, Yves
Aseismic fault slip and leakage preceding an earthquake induced during an in-situ fault reactivation experiment in the Opalinus Clay, Mont Terri rock laboratory, Switzerland Christophe Nussbaum 1, Yves
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11
 Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
Stress and Strain. Stress is a force per unit area. Strain is a change in size or shape in response to stress
 Geologic Structures Geologic structures are dynamically-produced patterns or arrangements of rock or sediment that result from, and give information about, forces within the Earth Produced as rocks change
Geologic Structures Geologic structures are dynamically-produced patterns or arrangements of rock or sediment that result from, and give information about, forces within the Earth Produced as rocks change
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 31: Mountain Building 1: Isostasy and Thrusting Last Time Earthquakes A) Earthquake intensity and magnitude B) Seismographs C) Case Studies
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 31: Mountain Building 1: Isostasy and Thrusting Last Time Earthquakes A) Earthquake intensity and magnitude B) Seismographs C) Case Studies
Faults, folds and mountain building
 Faults, folds and mountain building Mountain belts Deformation Orogens (Oro = Greek all changes for mountain, in size, shape, genesis orientation, = Greek for or formation) position of a rock mass Structural
Faults, folds and mountain building Mountain belts Deformation Orogens (Oro = Greek all changes for mountain, in size, shape, genesis orientation, = Greek for or formation) position of a rock mass Structural
Deformation of Rocks. Orientation of Deformed Rocks
 Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Elastic rebound theory
 Elastic rebound theory Focus epicenter - wave propagation Dip-Slip Fault - Normal Normal Fault vertical motion due to tensional stress Hanging wall moves down, relative to the footwall Opal Mountain, Mojave
Elastic rebound theory Focus epicenter - wave propagation Dip-Slip Fault - Normal Normal Fault vertical motion due to tensional stress Hanging wall moves down, relative to the footwall Opal Mountain, Mojave
Learning Objectives (LO) What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
on the earthquake's strength. The Richter scale is a rating of an earthquake s magnitude based on the size of the
 Earthquakes and Seismic Waves An earthquake is the shaking and trembling that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface. The point beneath Earth s surface where rock under stress breaks
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves An earthquake is the shaking and trembling that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface. The point beneath Earth s surface where rock under stress breaks
AN APPROACH TO THE CLASSIFICATION OF SLOPE MOVEMENTS
 Training/workshop on Earthquake Vulnerability and Multi-Hazard Risk Assessment: Geospatial Tools for Rehabilitation and Reconstruction Effort 13 31 March 2006, Islamabad, Pakistan AN APPROACH TO THE CLASSIFICATION
Training/workshop on Earthquake Vulnerability and Multi-Hazard Risk Assessment: Geospatial Tools for Rehabilitation and Reconstruction Effort 13 31 March 2006, Islamabad, Pakistan AN APPROACH TO THE CLASSIFICATION
UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS
 UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS ROCK DEFORMATION Tectonic forces exert different types of stress on rocks in different geologic environments. STRESS The first, called confining stress
UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS ROCK DEFORMATION Tectonic forces exert different types of stress on rocks in different geologic environments. STRESS The first, called confining stress
Preface and Overview. Folded strata in the mountains of Italy (ca AD), Leonardo da Vinci
 Preface and Overview Folded strata in the mountains of Italy (ca. 1500 AD), Leonardo da Vinci Models of Mountain Building and Associated Deformation as represented by G.P. Scrope Deformation Feature: Scales
Preface and Overview Folded strata in the mountains of Italy (ca. 1500 AD), Leonardo da Vinci Models of Mountain Building and Associated Deformation as represented by G.P. Scrope Deformation Feature: Scales
Unit 4 Lesson 3 Mountain Building. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Stressed Out How can tectonic plate motion cause deformation? The movement of tectonic plates causes stress on rock structures. Stress is the amount of force per unit area that is placed on an object.
Stressed Out How can tectonic plate motion cause deformation? The movement of tectonic plates causes stress on rock structures. Stress is the amount of force per unit area that is placed on an object.
Joints and Veins. Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics. Ben van der Pluijm. WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/26/ :28
 Joints and Veins Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/26/2017 18:28 We Discuss Joints and Veins Crack Modes Surface Features Formation
Joints and Veins Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/26/2017 18:28 We Discuss Joints and Veins Crack Modes Surface Features Formation
Description of faults
 GLG310 Structural Geology Description of faults Horizontal stretch Crustal thickness Regional elevation Regional character Issues Normal Thrust/reverse Strike-slip >1 1 in one direction and < 1 in
GLG310 Structural Geology Description of faults Horizontal stretch Crustal thickness Regional elevation Regional character Issues Normal Thrust/reverse Strike-slip >1 1 in one direction and < 1 in
Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter Pearson Education, Inc.
 Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter 10 Structural Geology Structural geologists study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. A working knowledge of rock structures
Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter 10 Structural Geology Structural geologists study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. A working knowledge of rock structures
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5
 Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Faults. Strike-slip fault. Normal fault. Thrust fault
 Faults Strike-slip fault Normal fault Thrust fault Fault any surface or narrow zone with visible shear displacement along the zone Normal fault Strike-slip fault Reverse fault Thrust fault
Faults Strike-slip fault Normal fault Thrust fault Fault any surface or narrow zone with visible shear displacement along the zone Normal fault Strike-slip fault Reverse fault Thrust fault
SEISMIC SOURCES 1: FAULTING
 SEISMOLOGY Master Degree Programme in Physics - UNITS Physics of the Earth and of the Environment SEISMIC SOURCES 1: FAULTING FABIO ROMANELLI Department of Mathematics & Geosciences University of Trieste
SEISMOLOGY Master Degree Programme in Physics - UNITS Physics of the Earth and of the Environment SEISMIC SOURCES 1: FAULTING FABIO ROMANELLI Department of Mathematics & Geosciences University of Trieste
Chapter. Mountain Building
 Chapter Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock type, and
Chapter Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock type, and
Rheology and the Lithosphere
 Rheology and the Lithosphere Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/8/2017 16:51 We Discuss Rheology and the Lithosphere What is rheology?
Rheology and the Lithosphere Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/8/2017 16:51 We Discuss Rheology and the Lithosphere What is rheology?
The Sandbox Experiment
 Geological Sciences 101 Lab #7 - Introduction to Deformation Some of the most dramatic evidence that great forces have shaped the Earth are the rocks that one finds deformed in mountain belts. Rocks can
Geological Sciences 101 Lab #7 - Introduction to Deformation Some of the most dramatic evidence that great forces have shaped the Earth are the rocks that one finds deformed in mountain belts. Rocks can
Lecture Outline Friday March 2 thru Wednesday March 7, 2018
 Lecture Outline Friday March 2 thru Wednesday March 7, 2018 Questions? Lecture Exam Friday March 9, 2018 Same time, Same room Bring Pencils and WSU ID 50 question Multiple Choice, Computer Graded Interlude
Lecture Outline Friday March 2 thru Wednesday March 7, 2018 Questions? Lecture Exam Friday March 9, 2018 Same time, Same room Bring Pencils and WSU ID 50 question Multiple Choice, Computer Graded Interlude
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Lecture 5. Rheology. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 5 Rheology Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton; unless noted otherwise Rheology is... the study of deformation and flow of
Lecture 5 Rheology Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton; unless noted otherwise Rheology is... the study of deformation and flow of
Strike-Slip Faults. ! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.
 Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B
 GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
Blocks Module Content Guide
 Blocks Module Content Guide This guide covers the basics of the content within the Interactive 3D Geologic Blocks Module. The content guide is intended to assist you, the teacher, in creating effective
Blocks Module Content Guide This guide covers the basics of the content within the Interactive 3D Geologic Blocks Module. The content guide is intended to assist you, the teacher, in creating effective
Course Title: Discipline: Geology Level: Basic-Intermediate Duration: 5 Days Instructor: Prof. Charles Kluth. About the course: Audience: Agenda:
 Course Title: Structural Geology Discipline: Geology Level: Basic-Intermediate Duration: 5 Days Instructor: Prof. Charles Kluth About the course: This course covers the basic ideas of structural geometry
Course Title: Structural Geology Discipline: Geology Level: Basic-Intermediate Duration: 5 Days Instructor: Prof. Charles Kluth About the course: This course covers the basic ideas of structural geometry
Earthquakes. Forces Within Eartth. Faults form when the forces acting on rock exceed the rock s strength.
 Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Lab 7: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY FOLDS AND FAULTS
 Lab 7: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY FOLDS AND FAULTS This set of labs will focus on the structures that result from deformation in earth s crust, namely folds and faults. By the end of these labs you should be able
Lab 7: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY FOLDS AND FAULTS This set of labs will focus on the structures that result from deformation in earth s crust, namely folds and faults. By the end of these labs you should be able
Mass Wasting. Revisit: Erosion, Transportation, and Deposition
 Mass Wasting Revisit: Erosion, Transportation, and Deposition While landslides are a normal part of erosion and surface processes, they can be very destructive to life and property! - Mass wasting: downslope
Mass Wasting Revisit: Erosion, Transportation, and Deposition While landslides are a normal part of erosion and surface processes, they can be very destructive to life and property! - Mass wasting: downslope
Deepwater Niger Delta fold-and-thrust belt modeled as a critical-taper wedge: The influence of a weak detachment on styles of fault-related folds
 Deepwater Niger Delta fold-and-thrust belt modeled as a critical-taper wedge: The influence of a weak detachment on styles of fault-related folds Frank Bilotti 1, Chris Guzofski 1, John H. Shaw 2 1 Chevron
Deepwater Niger Delta fold-and-thrust belt modeled as a critical-taper wedge: The influence of a weak detachment on styles of fault-related folds Frank Bilotti 1, Chris Guzofski 1, John H. Shaw 2 1 Chevron
Section 3 Deforming Earth s Crust
 Section 3 Deforming Earth s Crust Key Concept Tectonic plate motions deform Earth s crust. Deformation causes rock layers to bend and break and causes mountains to form. What You Will Learn Stress is placed
Section 3 Deforming Earth s Crust Key Concept Tectonic plate motions deform Earth s crust. Deformation causes rock layers to bend and break and causes mountains to form. What You Will Learn Stress is placed
Part I. PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts:
 Student Name: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory #13 Structural Geology II Drawing and Analyzing Folds and Faults Grade: Introduction & Purpose: Structural geology is the study of how geologic rock units
Student Name: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory #13 Structural Geology II Drawing and Analyzing Folds and Faults Grade: Introduction & Purpose: Structural geology is the study of how geologic rock units
STRIKE-SLIP AND OBLIQUE-SLIP TECTONICS
 STRIKE-SLIP AND OBLIQUE-SLIP TECTONICS 173 Strike slip faulting is a common mode of deformation in both continental and oceanic crust and occurs at a wide range of scales. Strike slip systems are relatively
STRIKE-SLIP AND OBLIQUE-SLIP TECTONICS 173 Strike slip faulting is a common mode of deformation in both continental and oceanic crust and occurs at a wide range of scales. Strike slip systems are relatively
Forces in Earth s Crust
 Forces in Earth s Crust This section explains how stresses in Earth s crust cause breaks, or faults, in the crust. The section also explains how faults and folds in Earth s crust form mountains. Use Target
Forces in Earth s Crust This section explains how stresses in Earth s crust cause breaks, or faults, in the crust. The section also explains how faults and folds in Earth s crust form mountains. Use Target
Constrained Fault Construction
 Constrained Fault Construction Providing realistic interpretations of faults is critical in hydrocarbon and mineral exploration. Faults can act as conduits or barriers to subsurface fluid migration and
Constrained Fault Construction Providing realistic interpretations of faults is critical in hydrocarbon and mineral exploration. Faults can act as conduits or barriers to subsurface fluid migration and
Forces in Earth s Crust
 Forces in Earth s Crust (pages 180 186) Types of Stress (page 181) Key Concept: Tension, compression, and shearing work over millions of years to change the shape and volume of rock. When Earth s plates
Forces in Earth s Crust (pages 180 186) Types of Stress (page 181) Key Concept: Tension, compression, and shearing work over millions of years to change the shape and volume of rock. When Earth s plates
Lecture # 6. Geological Structures
 1 Lecture # 6 Geological Structures ( Folds, Faults and Joints) Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 The wavy undulations
1 Lecture # 6 Geological Structures ( Folds, Faults and Joints) Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 The wavy undulations
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building. Fig. 10.1
 Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
Mountains are then built by deforming crust: Deformation & Mountain Building. Mountains form where stresses are high!
 Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
CRUSTAL DEFORMATION. Chapter 10
 CRUSTAL DEFORMATION and dgeologic Structures t Chapter 10 Deformation Df Deformation involves: Stress the amount of force applied to a given area. Types of Stress: Confining Stress stress applied equally
CRUSTAL DEFORMATION and dgeologic Structures t Chapter 10 Deformation Df Deformation involves: Stress the amount of force applied to a given area. Types of Stress: Confining Stress stress applied equally
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building
 Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
c) Plot stability diagrams (Figure 11, p 10 of notes) for cases i) - iv), all on the same graph.
 12.520 Problem Set 4 1) (100%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ; ii) φ = 30,
12.520 Problem Set 4 1) (100%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ; ii) φ = 30,
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle. Read KK&V chapter 2.10
 Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
Geologic Structures. Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress
 Geologic Structures Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress Figure 15.19 Can be as big as a breadbox Or much bigger than a breadbox Three basic types Fractures >>>
Geologic Structures Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress Figure 15.19 Can be as big as a breadbox Or much bigger than a breadbox Three basic types Fractures >>>
Deformation: Modification of Rocks by Folding and Fracturing
 CHAPTER 7 Deformation: Modification of Rocks by Folding and Fracturing Chapter Summary A geologic map is a scientific model of rock formations that are exposed on the Earth s surface showing outcrops,
CHAPTER 7 Deformation: Modification of Rocks by Folding and Fracturing Chapter Summary A geologic map is a scientific model of rock formations that are exposed on the Earth s surface showing outcrops,
Earthquakes. Pt Reyes Station 1906
 Earthquakes Pt Reyes Station 1906 Earthquakes Ground shaking caused by the sudden release of accumulated strain by an abrupt shift of rock along a fracture in the earth. You Live in Earthquake Country
Earthquakes Pt Reyes Station 1906 Earthquakes Ground shaking caused by the sudden release of accumulated strain by an abrupt shift of rock along a fracture in the earth. You Live in Earthquake Country
Lecture 7. Joints and Veins. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 7 Joints and Veins Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton; unless noted otherwise Joints Three sets of systematic joints controlling
Lecture 7 Joints and Veins Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton; unless noted otherwise Joints Three sets of systematic joints controlling
An earthquake can cause:
 Earthquakes An earthquake is a sudden rapid shaking of the earth. They are caused by the breaking and shifting of the rock beneath the earth s surface. Often found in conjunction with Plate tectonic boundaries.
Earthquakes An earthquake is a sudden rapid shaking of the earth. They are caused by the breaking and shifting of the rock beneath the earth s surface. Often found in conjunction with Plate tectonic boundaries.
Azimuth with RH rule. Quadrant. S 180 Quadrant Azimuth. Azimuth with RH rule N 45 W. Quadrant Azimuth
 30 45 30 45 Strike and dip notation (a) N30 E, 45 SE ("Quadrant"): the bearing of the strike direction is 30 degrees east of north and the dip is 45 degrees in a southeast (SE) direction. For a given strike,
30 45 30 45 Strike and dip notation (a) N30 E, 45 SE ("Quadrant"): the bearing of the strike direction is 30 degrees east of north and the dip is 45 degrees in a southeast (SE) direction. For a given strike,
GG 454 March 19, EFFECTIVE STRESS AND MOHR-COULOMB FAILURE (26)
 GG 454 March 19, 2002 1 EFFECTIVE STRESS AND MOHR-COULOMB FAILURE (26) I Main Topics A Driving and resisting stresses at the base of an inclined block B Factor of safety C Effective stress D Mohr-Coulomb
GG 454 March 19, 2002 1 EFFECTIVE STRESS AND MOHR-COULOMB FAILURE (26) I Main Topics A Driving and resisting stresses at the base of an inclined block B Factor of safety C Effective stress D Mohr-Coulomb
Brittle Deformation. FAULT is a structural plane along which considerable amount of movement is visible. Prof.Dr.Kadir Dirik Lecture Notes
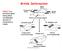 Brittle Deformation FAULT is a structural plane along which considerable amount of movement is visible. 1 2 3 4 5 Fault Fault zone Shear zone 6 Three basic criteria: Criteria for the Recognition of Faults
Brittle Deformation FAULT is a structural plane along which considerable amount of movement is visible. 1 2 3 4 5 Fault Fault zone Shear zone 6 Three basic criteria: Criteria for the Recognition of Faults
Crustal Deformation. (Building Earth s Surface, Part 1) Science 330 Summer Mapping geologic structures
 Crustal Deformation (Building Earth s Surface, Part 1) Science 330 Summer 2005 Mapping geologic structures When conducting a study of a region, a geologist identifies and describes the dominant rock structures
Crustal Deformation (Building Earth s Surface, Part 1) Science 330 Summer 2005 Mapping geologic structures When conducting a study of a region, a geologist identifies and describes the dominant rock structures
Mass Wasting. Requirements for Mass Wasting. Slope Stability. Geol 104: mass wasting
 Mass Wasting Movement of earth materials downslope, driven by Gravitational Forces. Landslides - general term for rock or soil movement. In U.S., on average, mass wasting causes 1 to 2 billion dollars
Mass Wasting Movement of earth materials downslope, driven by Gravitational Forces. Landslides - general term for rock or soil movement. In U.S., on average, mass wasting causes 1 to 2 billion dollars
Theme 7. Metamorphic rocks. Distinguishing rock types
 Theme 7. Metamorphic rocks. Distinguishing rock types 7.1. Metamorphic rocks formation 7.2. Classification of metamorphic rocks 7.3. Distinguishing rock types 7.1. Metamorphic rocks formation 7.1. Metamorphic
Theme 7. Metamorphic rocks. Distinguishing rock types 7.1. Metamorphic rocks formation 7.2. Classification of metamorphic rocks 7.3. Distinguishing rock types 7.1. Metamorphic rocks formation 7.1. Metamorphic
Chapter 16. Mountain Building. Mountain Building. Mountains and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection?
 Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 11 10/30/2013. Mass Wasting. Introduction. Factors That Influence Mass Wasting. Introduction. Factors That Influence Mass Wasting
 Introduction Chapter 11 Mass wasting - The downslope movement of material resulting from the force of gravity. Mass Wasting Mass wasting results when the force of gravity acting on a slope exceeds the
Introduction Chapter 11 Mass wasting - The downslope movement of material resulting from the force of gravity. Mass Wasting Mass wasting results when the force of gravity acting on a slope exceeds the
Deformation and Strain
 Deformation and Strain Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/13/2017 15:13 We Discuss Deformation and Strain Deformation Components
Deformation and Strain Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/13/2017 15:13 We Discuss Deformation and Strain Deformation Components
Mass Wasting: The Work of Gravity
 Chapter 15 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Mass Wasting: The Work of Gravity Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 15 Mass Wasting The Importance of Mass Wasting Slopes are the
Chapter 15 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Mass Wasting: The Work of Gravity Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 15 Mass Wasting The Importance of Mass Wasting Slopes are the
Lab 6: Plate tectonics, structural geology and geologic maps
 Geology 103 Name(s): Lab 6: Plate tectonics, structural geology and geologic maps Objective: To show the effects of plate tectonics on a large-scale set of rocks and to reconstruct the geological history
Geology 103 Name(s): Lab 6: Plate tectonics, structural geology and geologic maps Objective: To show the effects of plate tectonics on a large-scale set of rocks and to reconstruct the geological history
GE 11a, 2014, Lecture 4 Seismic wave types and velocities
 GE 11a, 2014, Lecture 4 Seismic wave types and velocities Seismic activity on earth is widespread, frequent, localized and powerful The earth may be unique in the solar system in this respect Weak, diffuse
GE 11a, 2014, Lecture 4 Seismic wave types and velocities Seismic activity on earth is widespread, frequent, localized and powerful The earth may be unique in the solar system in this respect Weak, diffuse
PROCEEDINGS, INDONESIAN PETROLEUM ASSOCIATION Thirty-Ninth Annual Convention and Exhibition, May 2015
 IPA15-SG-089 PROCEEDINGS, INDONESIAN PETROLEUM ASSOCIATION Thirty-Ninth Annual Convention and Exhibition, May 2015 STRUCTURAL INTERPRETATION OF TECTONICALLY ASSOCIATED NORMAL AND REVERSE FAULTS OF BUKIT
IPA15-SG-089 PROCEEDINGS, INDONESIAN PETROLEUM ASSOCIATION Thirty-Ninth Annual Convention and Exhibition, May 2015 STRUCTURAL INTERPRETATION OF TECTONICALLY ASSOCIATED NORMAL AND REVERSE FAULTS OF BUKIT
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Fault Rocks. EARS5136 slide 1
 Fault Rocks EARS5136 slide 1 Fault rocks Fault rock types Examples of deformation features in cores Microstructures Porosity and permeability Lithological and lithification control EARS5136 slide 2 Deformation
Fault Rocks EARS5136 slide 1 Fault rocks Fault rock types Examples of deformation features in cores Microstructures Porosity and permeability Lithological and lithification control EARS5136 slide 2 Deformation
c) Plot stability diagrams (Figure 11, p 10 of notes) for cases i) - iv), all on the same graph.
 12.520 Problem Set 4 Due 10/25/06 1) (90%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ;
12.520 Problem Set 4 Due 10/25/06 1) (90%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ;
PROBLEM SET #X. 2) Draw a cross section from A-A using the topographic profile provided on page 3.
 PROBLEM SET #X PART A: The geologic map on page 3 is from an area consisting of faulted Miocene sedimentary rocks. There are two major faults exposed here: the Rattlesnake fault and the Jackrabbit fault.
PROBLEM SET #X PART A: The geologic map on page 3 is from an area consisting of faulted Miocene sedimentary rocks. There are two major faults exposed here: the Rattlesnake fault and the Jackrabbit fault.
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Unsafe Ground: Landslides and Other Mass Movements
 Unsafe Ground: Landslides and Other Mass Movements Mass Movements Downslope motion of earth materials by gravity. Mass movements are a type of natural hazard. Natural feature of the environment. Can cause
Unsafe Ground: Landslides and Other Mass Movements Mass Movements Downslope motion of earth materials by gravity. Mass movements are a type of natural hazard. Natural feature of the environment. Can cause
FOLDS ABOVE ANGULAR FAULT BENDS: MECHANICAL CONSTRAINTS FOR BACKLIMB TRISHEAR KINEMATIC MODELS. A Thesis LI ZHANG
 FOLDS ABOVE ANGULAR FAULT BENDS: MECHANICAL CONSTRAINTS FOR BACKLIMB TRISHEAR KINEMATIC MODELS A Thesis by LI ZHANG Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
FOLDS ABOVE ANGULAR FAULT BENDS: MECHANICAL CONSTRAINTS FOR BACKLIMB TRISHEAR KINEMATIC MODELS A Thesis by LI ZHANG Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
