Animal Population Dynamics
|
|
|
- Silvester King
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Animal Population Dynamics Jennifer Gervais Weniger Syllabus Course webpage There is something fascinating about science. One gets such a wholesale return of conjecture out of a trifling investment of fact. - Mark Twain Population Dynamics: A Brief History Population dynamics is the study of how and why population numbers change in time and space -Peter Turchin, Complex Population Dynamics, Princeton Univ. Press Objectives: 1. Review development of field 2. Introduce some of the key people and ideas 3. Summarize current state of affairs For more on the topic, see S.E. Kingsland s book, Modeling Nature Univ. Chicago Press. In The Beginning Population fluctuations of animals have been recognized for millenia However, scientific study relatively recent Both mathematical exploration and empirical approaches; human demography and applied pest management Thomas Malthus Early Roots An essay on the principle of population published 1798 went through 6 editions Discussed issue of limited food supply for humanity early population regulation! Human population limited by pestilence and famine perfectability of society limited 1
2 Early Roots Pierre François Verhulst Published the logistic equation in 1838 Key idea: forces that prevent population growth increase proportionally as a function of the excess population Decided it wasn t a law because not clear how exactly to mathematically describe obstacles to growth. Back on the Farm Hatch Act Agriculture experiment stations Emphasis on understanding and controlling pest outbreaks in ag Development of a more scientific basis for the study of natural history Alfred Lotka Physical chemist by training and vocation! Later, a professional demographer Author of Elements of Physical Biology application of physical principles to biological systems. Later republished as Elements of Mathematical Ecology Predator-prey oscillations, and Vito Volterra Alfred Lotka, Mathematical models as powerful aids to understanding Raymond Pearl Human demographer and biometrician Discovered Lotka, collaborated extensively Major proponent of quantitative demography e.g., The Biology of Population Growth Sought law of population growth- and latched onto the logistic equation Raymond Pearl, Work with Lowell J. Reed on logistic equation quite controversial! 2
3 The empirical approach William Thompson, Charles S. Elton, Elton s Contributions 1924: Fluctuations in the numbers of animals, their causes and effects (Br. J. Expl. Biol). 1927: Animal Ecology (later, Animal Ecology and Evolution- 1930) 1931: Study of epidemic diseases among wild animals 1942: Voles, Mice and Lemmings: Problems in Population Dynamics 1958: The Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants Elton s Contributions 1932: Began the Bureau of Animal Populations 1932: founded Journal of Animal Ecology See Do Lemmings Commit Suicide? Beautiful Hypotheses and Ugly Facts by D. Chitty for an insider view of Elton and his legacy From the Laboratory Experimental studies of populations with Drosophila, Tribolium, and others Questions of genetics, evolution, life history, population dynamics Applying demographic techniques first developed for humans (Pearl) A new idea Were population fluctuations actually the result of internal dynamics rather than external forces? This arose from modeling and the lab, whereas field studies by Elton and others had concentrated on external environmental drivers 3
4 Population Regulation The Great Density Dependence Debate What stops populations from growing? internal versus external factors David Lack, Natural Regulation of Animal Numbers (1954) H. G. Andrewartha and L. C. Birch, The Distribution and Abundance of Animals (1954) Through the 50 s and 60 s The ecological niche Georgii Gause G. Evelyn Hutchinson David Lack Implications for Population Ecology Robert MacArthur Models for Dummies Robert MacArthur and Richard Levins Levins view: Generality Precision Realism You can only have two out of three! The tension over place and history See Levins American Scientist 54: Understanding Growth of Populations Approaches to Developing and Evaluating Hypotheses and Theory A posteriori Elton Pearl The Role of Theoretical Models In Population Ecology Seeking simple, unifying laws of nature Verhulst, Pearl Lotka A priori Thompson Bailey Lotka Nicholson MacArthur Empirical Theoretical Thompson, Gause, Hutchinson, MacArthur Seeking general patterns for further experimental exploration 4
5 Graeme Caughley The Next Generation Robert May Peter Kareiva Peter Turchin Caughley s Two Threads of Conservation Biology Ex a ct l y a s pr ed ict ed. Small-Population Paradigm Pr (Extinction ) Year Decreasing Population Declining-Species Paradigm The Enlightened Applied Ecologists Great, that gives us S = ± 0.02, just what I needed for my Individual-Based Model! H mm 1, 2, 5, bu t. An d w el l Yes, a burrowing owl Red XL indeed! and many others Drawings by John Megahan A Modern Convergence? Theoretical approaches + Applied problem solving Conservation Mathematical and management modeling Experimental populations And Currently Ever-greater sophistication in quantitative tools Enduring tension between theory and observation, pure and applied science Biological knowledge crucial! Conclusions Population ecology and dynamics rooted in economics, physical sciences, and human demography Early tensions over role of theory and mathematical modeling versus detailed natural history studies still resonate Continuing controversy over role of regulation, existence of laws, and influence of history 5
LECTURE 1: Introduction and Brief History of Population Ecology
 WMAN 512 SPRING 2010 ADV WILDL POP ECOL LECTURE 1: Introduction and Brief History of Population Ecology Cappuccino, N. 1995. Novel approaches to the study of population dynamics. pp 2-16 in Population
WMAN 512 SPRING 2010 ADV WILDL POP ECOL LECTURE 1: Introduction and Brief History of Population Ecology Cappuccino, N. 1995. Novel approaches to the study of population dynamics. pp 2-16 in Population
What is essential difference between snake behind glass versus a wild animal?
 What is essential difference between snake behind glass versus a wild animal? intact cells physiological properties genetics some extent behavior Caged animal is out of context Removed from natural surroundings
What is essential difference between snake behind glass versus a wild animal? intact cells physiological properties genetics some extent behavior Caged animal is out of context Removed from natural surroundings
BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences D. POPULATION & COMMUNITY DYNAMICS Week 10. Population models 1: Lecture summary: Distribution and abundance
BIOS 5970: Plant-Herbivore Interactions Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences D. POPULATION & COMMUNITY DYNAMICS Week 10. Population models 1: Lecture summary: Distribution and abundance
BIOS 5445: Human Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 5445: Human Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Lecture 4. Population ecology: Lecture summary: Population growth: Growth curves. Rates of increase. Mortality & survivorship.
BIOS 5445: Human Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Lecture 4. Population ecology: Lecture summary: Population growth: Growth curves. Rates of increase. Mortality & survivorship.
The struggle for existence
 Module BIO- M1- S06 Evolu3onary ecology The struggle for existence David Claessen! Institut de Biologie de l ENS! Equipe Eco-Evolution Mathématique Thomas Robert Malthus The increase of popula0on is necessarily
Module BIO- M1- S06 Evolu3onary ecology The struggle for existence David Claessen! Institut de Biologie de l ENS! Equipe Eco-Evolution Mathématique Thomas Robert Malthus The increase of popula0on is necessarily
Gary G. Mittelbach Michigan State University
 Community Ecology Gary G. Mittelbach Michigan State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Brief Table of Contents 1 Community Ecology s Roots 1 PART I The Big
Community Ecology Gary G. Mittelbach Michigan State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A. Brief Table of Contents 1 Community Ecology s Roots 1 PART I The Big
Ecology Regulation, Fluctuations and Metapopulations
 Ecology Regulation, Fluctuations and Metapopulations The Influence of Density on Population Growth and Consideration of Geographic Structure in Populations Predictions of Logistic Growth The reality of
Ecology Regulation, Fluctuations and Metapopulations The Influence of Density on Population Growth and Consideration of Geographic Structure in Populations Predictions of Logistic Growth The reality of
1 This book is a translation of an amended and enlarged version of Part 1 of the following monograph
 Introduction to Social Macrodynamics. Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth by Andrey Korotayev, Artemy Malkov, and Daria Khaltourina. Moscow: Editorial URSS, 2006. Pp. 5 9. Introduction 1 Human
Introduction to Social Macrodynamics. Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth by Andrey Korotayev, Artemy Malkov, and Daria Khaltourina. Moscow: Editorial URSS, 2006. Pp. 5 9. Introduction 1 Human
Selection 10: Theory of Natural Selection
 Selection 10: Theory of Natural Selection Darwin began his voyage thinking that species could not change His experience during the five-year journey altered his thinking Variation of similar species among
Selection 10: Theory of Natural Selection Darwin began his voyage thinking that species could not change His experience during the five-year journey altered his thinking Variation of similar species among
Computational Ecology Introduction to Ecological Science. Sonny Bleicher Ph.D.
 Computational Ecology Introduction to Ecological Science Sonny Bleicher Ph.D. Ecos Logos Defining Ecology Interactions: Organisms: Plants Animals: Bacteria Fungi Invertebrates Vertebrates The physical
Computational Ecology Introduction to Ecological Science Sonny Bleicher Ph.D. Ecos Logos Defining Ecology Interactions: Organisms: Plants Animals: Bacteria Fungi Invertebrates Vertebrates The physical
Name Student ID. Good luck and impress us with your toolkit of ecological knowledge and concepts!
 Page 1 BIOLOGY 150 Final Exam Winter Quarter 2000 Before starting be sure to put your name and student number on the top of each page. MINUS 3 POINTS IF YOU DO NOT WRITE YOUR NAME ON EACH PAGE! You have
Page 1 BIOLOGY 150 Final Exam Winter Quarter 2000 Before starting be sure to put your name and student number on the top of each page. MINUS 3 POINTS IF YOU DO NOT WRITE YOUR NAME ON EACH PAGE! You have
Interspecific Competition
 Interspecific Competition Intraspecific competition Classic logistic model Interspecific extension of densitydependence Individuals of other species may also have an effect on per capita birth & death
Interspecific Competition Intraspecific competition Classic logistic model Interspecific extension of densitydependence Individuals of other species may also have an effect on per capita birth & death
14 Ideas That Shaped Darwin's Thinking Slide 1 of 27
 14 Ideas That Shaped 1 of 27 An Ancient, Changing Earth An Ancient, Changing Earth How did Hutton and Lyell describe geological change? 2 of 27 An Ancient, Changing Earth Hutton and Lyell helped scientists
14 Ideas That Shaped 1 of 27 An Ancient, Changing Earth An Ancient, Changing Earth How did Hutton and Lyell describe geological change? 2 of 27 An Ancient, Changing Earth Hutton and Lyell helped scientists
Evidence for Competition
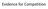 Evidence for Competition Population growth in laboratory experiments carried out by the Russian scientist Gause on growth rates in two different yeast species Each of the species has the same food e.g.,
Evidence for Competition Population growth in laboratory experiments carried out by the Russian scientist Gause on growth rates in two different yeast species Each of the species has the same food e.g.,
Concepts and Principles of Population Dynamics
 Reprinted from Vkislas on Nemtology Concepts and Principles of Population Dynamics H. FERRIS AND L. T. WILSON Professor, Division of Nematology, University of California, Davis, CA 956 16. Associate Professor,
Reprinted from Vkislas on Nemtology Concepts and Principles of Population Dynamics H. FERRIS AND L. T. WILSON Professor, Division of Nematology, University of California, Davis, CA 956 16. Associate Professor,
MA 138: Calculus II for the Life Sciences
 MA 138: Calculus II for the Life Sciences David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky. Spring 2016 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 138: Section 11.4.2 Spring 2016 1
MA 138: Calculus II for the Life Sciences David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky. Spring 2016 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 138: Section 11.4.2 Spring 2016 1
Population Ecology Density dependence, regulation and the Allee effect
 2/22/15 Population Ecology Density dependence, regulation and the Allee effect ESRM 450 Wildlife Ecology and Conservation Wildlife Populations Groups of animals, all of the same species, that live together
2/22/15 Population Ecology Density dependence, regulation and the Allee effect ESRM 450 Wildlife Ecology and Conservation Wildlife Populations Groups of animals, all of the same species, that live together
15-1 The Puzzle of Life's Diversity Slide 1 of 20
 1 of 20 Evolution is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. * Known as biological change over time A scientific theory is a well-supported testable explanation of
1 of 20 Evolution is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. * Known as biological change over time A scientific theory is a well-supported testable explanation of
The Moose on Isle. An island in Lake Superior. Original migration. Another case study of the environment and environmentalists
 The Moose on Isle Royale Another case study of the environment and environmentalists 1 An island in Lake Superior Isle Royale is a large forested island, in Lake Superior, named by French explorers 200
The Moose on Isle Royale Another case study of the environment and environmentalists 1 An island in Lake Superior Isle Royale is a large forested island, in Lake Superior, named by French explorers 200
A NUMERICAL STUDY ON PREDATOR PREY MODEL
 International Conference Mathematical and Computational Biology 2011 International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 9 (2012) 347 353 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512005417
International Conference Mathematical and Computational Biology 2011 International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 9 (2012) 347 353 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512005417
Evolution Notes Darwin and His Ideas
 Evolution Notes Darwin and His Ideas Charles Darwin Charles Darwin was born in 1809 (on the same day as Abraham Lincoln) In Darwin s day, scientists were just starting to come around to the idea the Earth
Evolution Notes Darwin and His Ideas Charles Darwin Charles Darwin was born in 1809 (on the same day as Abraham Lincoln) In Darwin s day, scientists were just starting to come around to the idea the Earth
15 2 Ideas That Shaped Darwin's Thinking
 1 of 27 Belief of his time 1. Earth was young (~4,000 years old) 2. Plants/ animals never changed 2 of 27 An Ancient, Changing Earth Fossils challenged both of these Beliefs 3 of 27 Geologist gave evidence
1 of 27 Belief of his time 1. Earth was young (~4,000 years old) 2. Plants/ animals never changed 2 of 27 An Ancient, Changing Earth Fossils challenged both of these Beliefs 3 of 27 Geologist gave evidence
Stability and complexity in model ecosystems
 Stability and complexity in model ecosystems Level 2 module in Modelling course in population and evolutionary biology (701-1418-00) Module author: Sebastian Bonhoeffer Course director: Sebastian Bonhoeffer
Stability and complexity in model ecosystems Level 2 module in Modelling course in population and evolutionary biology (701-1418-00) Module author: Sebastian Bonhoeffer Course director: Sebastian Bonhoeffer
The Living World Continued: Populations and Communities
 The Living World Continued: Populations and Communities Ecosystem Communities Populations Review: Parts of an Ecosystem 1) An individual in a species: One organism of a species. a species must be genetically
The Living World Continued: Populations and Communities Ecosystem Communities Populations Review: Parts of an Ecosystem 1) An individual in a species: One organism of a species. a species must be genetically
5/23/2017. XAVIER RECYCLES! Please place recyclable material in the common area recycling containers
 YES: paper, cardboard, and empty plastic containers NO: cans, glass, liquid, garbage, food waste XAVIER RECYCLES! Please place recyclable material in the common area recycling containers Topics Biodiversity
YES: paper, cardboard, and empty plastic containers NO: cans, glass, liquid, garbage, food waste XAVIER RECYCLES! Please place recyclable material in the common area recycling containers Topics Biodiversity
Biology 3201 Unit 4 Evolution Ch Introducing Evolution (part 1) What is Evolution?
 Biology 3201 Unit 4 Evolution Ch. 19 - Introducing Evolution (part 1) What is Evolution? Evolution: the relative change in the characteristics of a population over successive generations A population is
Biology 3201 Unit 4 Evolution Ch. 19 - Introducing Evolution (part 1) What is Evolution? Evolution: the relative change in the characteristics of a population over successive generations A population is
Dynamical Systems and Chaos Part II: Biology Applications. Lecture 6: Population dynamics. Ilya Potapov Mathematics Department, TUT Room TD325
 Dynamical Systems and Chaos Part II: Biology Applications Lecture 6: Population dynamics Ilya Potapov Mathematics Department, TUT Room TD325 Living things are dynamical systems Dynamical systems theory
Dynamical Systems and Chaos Part II: Biology Applications Lecture 6: Population dynamics Ilya Potapov Mathematics Department, TUT Room TD325 Living things are dynamical systems Dynamical systems theory
This week. Topics 1. The ecological niche 2. Physiological ecology 3. Spatial distributions. Readings 1. CBH: ch. 4,5
 This week Topics 1. The ecological niche 2. Physiological ecology 3. Spatial distributions Readings 1. CBH: ch. 4,5 Ecology Evolution (micro) Life history Evolution (macro) Spatial distributions Physiological
This week Topics 1. The ecological niche 2. Physiological ecology 3. Spatial distributions Readings 1. CBH: ch. 4,5 Ecology Evolution (micro) Life history Evolution (macro) Spatial distributions Physiological
CHAPTER 2--THE DEVELOPMENT OF EVOLUTIONARY THEORY
 CHAPTER 2--THE DEVELOPMENT OF EVOLUTIONARY THEORY Student: 1. In Europe during the Middle Ages, it was believed that. A. all species had evolved from a common ancestor B. evolution was the result of natural
CHAPTER 2--THE DEVELOPMENT OF EVOLUTIONARY THEORY Student: 1. In Europe during the Middle Ages, it was believed that. A. all species had evolved from a common ancestor B. evolution was the result of natural
Learning objectives. Evolution in Action. Chapter 8: Evolution and Natural Selection. By the end of today s topic students should be able to:
 ANNOUNCEMENTS Thursday February 13, 2014 Chapter 8: Evolution and Natural Selection Dr. Traver returns next week. Movie on Tuesday afternoon What Darwin Never Knew. Midterm 2 is next week 2/20/2014 Use
ANNOUNCEMENTS Thursday February 13, 2014 Chapter 8: Evolution and Natural Selection Dr. Traver returns next week. Movie on Tuesday afternoon What Darwin Never Knew. Midterm 2 is next week 2/20/2014 Use
Intermediate Differential Equations. John A. Burns
 Intermediate Differential Equations Delay Differential Equations John A. Burns jaburns@vt.edu Interdisciplinary Center for Applied Mathematics Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg,
Intermediate Differential Equations Delay Differential Equations John A. Burns jaburns@vt.edu Interdisciplinary Center for Applied Mathematics Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg,
The Balance of Nature and Human Impact, ed. Klaus Rohde. Published by Cambridge University Press. Cambridge University Press 2013.
 Introduction Klaus Rohde It is obvious that nature is undergoing rapid changes as a result of human activities such as industry, agriculture, travel, fisheries, urbanization, etc. What effects do these
Introduction Klaus Rohde It is obvious that nature is undergoing rapid changes as a result of human activities such as industry, agriculture, travel, fisheries, urbanization, etc. What effects do these
Darwin s Theory of Natural Selection
 Darwin s Theory of Natural Selection Question: Has Life Ever Changed? In 1700 s, scientists examined fossils that showed how extinct species look very different than they do today. Scientists began to
Darwin s Theory of Natural Selection Question: Has Life Ever Changed? In 1700 s, scientists examined fossils that showed how extinct species look very different than they do today. Scientists began to
Darwin s Theory of Evolution. Geological Change. Lyell's Principles of Geology Ideas That Shaped Darwin s Thinking
 Darwin s Theory of Evolution 15.2 Ideas That Shaped Darwin s Thinking Geological Change In 1795, James Hutton published a hypothesis about the geological forces that shaped Earth. Most of these geological
Darwin s Theory of Evolution 15.2 Ideas That Shaped Darwin s Thinking Geological Change In 1795, James Hutton published a hypothesis about the geological forces that shaped Earth. Most of these geological
3.5 Competition Models: Principle of Competitive Exclusion
 94 3. Models for Interacting Populations different dimensional parameter changes. For example, doubling the carrying capacity K is exactly equivalent to halving the predator response parameter D. The dimensionless
94 3. Models for Interacting Populations different dimensional parameter changes. For example, doubling the carrying capacity K is exactly equivalent to halving the predator response parameter D. The dimensionless
9/19/2016 CHAPTER 1: THE STUDY OF LIFE SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION TO THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 1: THE STUDY OF LIFE SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY Ms. Diana THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology is the study of living things. In biology, you study the origins and history of life and once-living
CHAPTER 1: THE STUDY OF LIFE SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY Ms. Diana THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology is the study of living things. In biology, you study the origins and history of life and once-living
Lesson 1 Syllabus Reference
 Lesson 1 Syllabus Reference Outcomes A student Explains how biological understanding has advanced through scientific discoveries, technological developments and the needs of society. Content The theory
Lesson 1 Syllabus Reference Outcomes A student Explains how biological understanding has advanced through scientific discoveries, technological developments and the needs of society. Content The theory
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology
 Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board,
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board,
Analysis of bacterial population growth using extended logistic Growth model with distributed delay. Abstract INTRODUCTION
 Analysis of bacterial population growth using extended logistic Growth model with distributed delay Tahani Ali Omer Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Missouri-ansas City ansas City,
Analysis of bacterial population growth using extended logistic Growth model with distributed delay Tahani Ali Omer Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Missouri-ansas City ansas City,
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology. Thursday, October 19, 17
 Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Module 18 The Abundance and Distribution of After reading this module you should be able to explain how nature exists at several levels of complexity. discuss
Chapter 6 Population and Community Ecology Module 18 The Abundance and Distribution of After reading this module you should be able to explain how nature exists at several levels of complexity. discuss
Math 266: Autonomous equation and population dynamics
 Math 266: Autonomous equation and population namics Long Jin Purdue, Spring 2018 Autonomous equation An autonomous equation is a differential equation which only involves the unknown function y and its
Math 266: Autonomous equation and population namics Long Jin Purdue, Spring 2018 Autonomous equation An autonomous equation is a differential equation which only involves the unknown function y and its
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences
 BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 7: Dynamics of Predation. Lecture summary: Categories of predation. Linked prey-predator cycles. Lotka-Volterra model. Density-dependence.
BIOS 6150: Ecology Dr. Stephen Malcolm, Department of Biological Sciences Week 7: Dynamics of Predation. Lecture summary: Categories of predation. Linked prey-predator cycles. Lotka-Volterra model. Density-dependence.
second order Runge-Kutta time scheme is a good compromise for solving ODEs unstable for oscillators
 ODE Examples We have seen so far that the second order Runge-Kutta time scheme is a good compromise for solving ODEs with a good precision, without making the calculations too heavy! It is unstable for
ODE Examples We have seen so far that the second order Runge-Kutta time scheme is a good compromise for solving ODEs with a good precision, without making the calculations too heavy! It is unstable for
The word ecology comes from the Greek
 Mathematical Challenges in Spatial Ecology Claudia Neuhauser The word ecology comes from the Greek oikos, which means house, and was coined by the German zoologist Ernst Haeckel in 1870. It is, according
Mathematical Challenges in Spatial Ecology Claudia Neuhauser The word ecology comes from the Greek oikos, which means house, and was coined by the German zoologist Ernst Haeckel in 1870. It is, according
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 4.2: Biodiversity Notes Biodiversity is the variety of living organisms, over time the variety of life on Earth has become more extensive but now it is being threatened by
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 4.2: Biodiversity Notes Biodiversity is the variety of living organisms, over time the variety of life on Earth has become more extensive but now it is being threatened by
Introduction. Chapter What is this book about?
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is this book about? This book is about how to construct and use computational models of specific parts of the nervous system, such as a neuron, a part of a neuron or a network
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is this book about? This book is about how to construct and use computational models of specific parts of the nervous system, such as a neuron, a part of a neuron or a network
Ch.5 Evolution and Community Ecology How do organisms become so well suited to their environment? Evolution and Natural Selection
 Ch.5 Evolution and Community Ecology How do organisms become so well suited to their environment? Evolution and Natural Selection Gene: A sequence of DNA that codes for a particular trait Gene pool: All
Ch.5 Evolution and Community Ecology How do organisms become so well suited to their environment? Evolution and Natural Selection Gene: A sequence of DNA that codes for a particular trait Gene pool: All
Biology 182: Study Guide PART IV. ECOLOGY, BEHAVIOR & CONSERVATION: Ch
 Biology 182: Study Guide PART IV. ECOLOGY, BEHAVIOR & CONSERVATION: Ch. 51-56 The field of ecology has expanded dramatically over the last few decades, with an ever greater focus on the effects of humans
Biology 182: Study Guide PART IV. ECOLOGY, BEHAVIOR & CONSERVATION: Ch. 51-56 The field of ecology has expanded dramatically over the last few decades, with an ever greater focus on the effects of humans
Chapter 54: Community Ecology
 AP Biology Guided Reading Name Chapter 54: Community Ecology Overview 1. What does community ecology explore? Concept 54.1 Community interactions are classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect
AP Biology Guided Reading Name Chapter 54: Community Ecology Overview 1. What does community ecology explore? Concept 54.1 Community interactions are classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect
Principles of Evolution. Ch Early Ideas About Evolution Early Ideas About Evolution Early Ideas About Evolution 3/21/2016
 Principles of Evolution Ch. 10 "Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution." 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution The Puzzle of Life s Diversity o Evolution - modern organisms have descended
Principles of Evolution Ch. 10 "Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution." 10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution The Puzzle of Life s Diversity o Evolution - modern organisms have descended
Natural Selection. Charles Darwin & Alfred Russell Wallace
 Natural Selection Charles Darwin & Alfred Russell Wallace Darwin s Influences Darwin observed such variations in species on his voyage as a naturalist on the HMS Beagle Darwin s Influences Kept vast diaries
Natural Selection Charles Darwin & Alfred Russell Wallace Darwin s Influences Darwin observed such variations in species on his voyage as a naturalist on the HMS Beagle Darwin s Influences Kept vast diaries
SIMPLE MATHEMATICAL MODELS WITH EXCEL
 SIMPLE MATHEMATICAL MODELS WITH EXCEL Traugott H. Schelker Abstract Maybe twenty or thirty years ago only physicists and engineers had any use for mathematical models. Today the situation has totally changed.
SIMPLE MATHEMATICAL MODELS WITH EXCEL Traugott H. Schelker Abstract Maybe twenty or thirty years ago only physicists and engineers had any use for mathematical models. Today the situation has totally changed.
5 Alfred Lotka, Vito Volterra, and Population Cycles
 5 Alfred Lotka, Vito Volterra, and opulation Cycles Dr. Umberto D Ancona entertained me several times with statistics that he was compiling about fishing during the period of the war and in periods previous
5 Alfred Lotka, Vito Volterra, and opulation Cycles Dr. Umberto D Ancona entertained me several times with statistics that he was compiling about fishing during the period of the war and in periods previous
Reading: Most of the material in today s lecture comes from pages 1 6 of Chapter 1in
 Lecture 1 First Steps Reading: Most of the material in today s lecture comes from pages 1 6 of Chapter 1in James D. Murray (2002), Mathematical Biology I: An Introduction, 3rd edition. If you are at the
Lecture 1 First Steps Reading: Most of the material in today s lecture comes from pages 1 6 of Chapter 1in James D. Murray (2002), Mathematical Biology I: An Introduction, 3rd edition. If you are at the
Physics: spring-mass system, planet motion, pendulum. Biology: ecology problem, neural conduction, epidemics
 Applications of nonlinear ODE systems: Physics: spring-mass system, planet motion, pendulum Chemistry: mixing problems, chemical reactions Biology: ecology problem, neural conduction, epidemics Economy:
Applications of nonlinear ODE systems: Physics: spring-mass system, planet motion, pendulum Chemistry: mixing problems, chemical reactions Biology: ecology problem, neural conduction, epidemics Economy:
Ecology Test Biology Honors
 Do Not Write On Test Ecology Test Biology Honors Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The study of the interaction of living organisms with
Do Not Write On Test Ecology Test Biology Honors Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The study of the interaction of living organisms with
MA 138 Calculus 2 with Life Science Applications Handout
 .. MA 138 Calculus 2 with Life Science Applications Handout Alberto Corso alberto.corso@uky.edu Department of Mathematics University of Kentucky February 17, 2017 . Example 4 (Lotka-Volterra Predator-Prey
.. MA 138 Calculus 2 with Life Science Applications Handout Alberto Corso alberto.corso@uky.edu Department of Mathematics University of Kentucky February 17, 2017 . Example 4 (Lotka-Volterra Predator-Prey
The Logistic Model of Growth
 AU J.T. 11(2: 99-14 (Oct. 27 The Logistic Model of Growth Graham Kenneth Winley Faculty of Science and Technology Assumption University Bangkok Thailand Abstract This article
AU J.T. 11(2: 99-14 (Oct. 27 The Logistic Model of Growth Graham Kenneth Winley Faculty of Science and Technology Assumption University Bangkok Thailand Abstract This article
Thursday, March 21, 13. Evolution
 Evolution What is Evolution? Evolution involves inheritable changes in a population of organisms through time Fundamental to biology and paleontology Paleontology is the study of life history as revealed
Evolution What is Evolution? Evolution involves inheritable changes in a population of organisms through time Fundamental to biology and paleontology Paleontology is the study of life history as revealed
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) One important feature of the world's population with the most significant future implications
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) One important feature of the world's population with the most significant future implications
Direction fields of differential equations...with SAGE
 Direction fields of differential equations...with SAGE Many differential equations cannot be solved conveniently by analytical methods, so it is important to consider what qualitative information can be
Direction fields of differential equations...with SAGE Many differential equations cannot be solved conveniently by analytical methods, so it is important to consider what qualitative information can be
The Evolution of Evolutionary Thought
 The Evolution of Evolutionary Thought Evolution simply means change over time So, what has evolved? With new information and discoveries, our thoughts on how living things have evolved have evolved as
The Evolution of Evolutionary Thought Evolution simply means change over time So, what has evolved? With new information and discoveries, our thoughts on how living things have evolved have evolved as
Multiple choice 2 pts each): x 2 = 18) Essay (pre-prepared) / 15 points. 19) Short Answer: / 2 points. 20) Short Answer / 5 points
 P 1 Biology 217: Ecology Second Exam Fall 2004 There should be 7 ps in this exam - take a moment and count them now. Put your name on the first p of the exam, and on each of the ps with short answer questions.
P 1 Biology 217: Ecology Second Exam Fall 2004 There should be 7 ps in this exam - take a moment and count them now. Put your name on the first p of the exam, and on each of the ps with short answer questions.
The Dynamic Behaviour of the Competing Species with Linear and Holling Type II Functional Responses by the Second Competitor
 , pp. 35-46 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijbsbt.2017.9.3.04 The Dynamic Behaviour of the Competing Species with Linear and Holling Type II Functional Responses by the Second Competitor Alemu Geleta Wedajo
, pp. 35-46 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijbsbt.2017.9.3.04 The Dynamic Behaviour of the Competing Species with Linear and Holling Type II Functional Responses by the Second Competitor Alemu Geleta Wedajo
Course ID May 2017 COURSE OUTLINE. Biology 102 (C-ID Number: BIOL 140) General Biology (C-ID Title: Organismal Biology)
 Degree Applicable Glendale Community College Course ID 005073 May 2017 COURSE OUTLINE Biology 102 (C-ID Number: BIOL 140) General Biology (C-ID Title: Organismal Biology) Catalog Statement BIOL 102 provides
Degree Applicable Glendale Community College Course ID 005073 May 2017 COURSE OUTLINE Biology 102 (C-ID Number: BIOL 140) General Biology (C-ID Title: Organismal Biology) Catalog Statement BIOL 102 provides
Community ecology. Abdulhafez A Selim, MD, PhD
 Community ecology Abdulhafez A Selim, MD, PhD Community ecology is very complex Niches The term 'Niche' was coined by the naturalist Joseph Grinnell in 1917, in his paper "The niche relationships of the
Community ecology Abdulhafez A Selim, MD, PhD Community ecology is very complex Niches The term 'Niche' was coined by the naturalist Joseph Grinnell in 1917, in his paper "The niche relationships of the
Chapter 2 Evolution: Constructing a Fundamental Scientific Theory
 Chapter 2 Evolution: Constructing a Fundamental Scientific Theory TRUE/FALSE 1. Organisms classified in two different biological orders can still belong to the same genus. 2. Before 1700, most Western
Chapter 2 Evolution: Constructing a Fundamental Scientific Theory TRUE/FALSE 1. Organisms classified in two different biological orders can still belong to the same genus. 2. Before 1700, most Western
Stability Of Specialists Feeding On A Generalist
 Stability Of Specialists Feeding On A Generalist Tomoyuki Sakata, Kei-ichi Tainaka, Yu Ito and Jin Yoshimura Department of Systems Engineering, Shizuoka University Abstract The investigation of ecosystem
Stability Of Specialists Feeding On A Generalist Tomoyuki Sakata, Kei-ichi Tainaka, Yu Ito and Jin Yoshimura Department of Systems Engineering, Shizuoka University Abstract The investigation of ecosystem
Adaptation and Change
 Adaptation and Change An adaptation is any structure or behavioral trait that improves an organism's success at reproducing and surviving. Most adaptations serve one of three purposes: 1. help an organism
Adaptation and Change An adaptation is any structure or behavioral trait that improves an organism's success at reproducing and surviving. Most adaptations serve one of three purposes: 1. help an organism
BIOS 3010: ECOLOGY. Dr Stephen Malcolm. Laboratory 6: Lotka-Volterra, the logistic. equation & Isle Royale
 BIOS 3010: ECOLOGY Dr Stephen Malcolm Laboratory 6: Lotka-Volterra, the logistic equation & Isle Royale This is a computer-based activity using Populus software (P), followed by EcoBeaker analyses of moose
BIOS 3010: ECOLOGY Dr Stephen Malcolm Laboratory 6: Lotka-Volterra, the logistic equation & Isle Royale This is a computer-based activity using Populus software (P), followed by EcoBeaker analyses of moose
Stochastic logistic model with environmental noise. Brian Dennis Dept Fish and Wildlife Resources and Dept Statistical Science University of Idaho
 Stochastic logistic model with environmental noise Brian Dennis Dept Fish and Wildlife Resources and Dept Statistical Science University of Idaho Questions I. What plausible biological mechanisms, if any,
Stochastic logistic model with environmental noise Brian Dennis Dept Fish and Wildlife Resources and Dept Statistical Science University of Idaho Questions I. What plausible biological mechanisms, if any,
ADAPTATIONS. Characteristics that give an organism a better chance of survival.
 ADAPTATIONS Characteristics that give an organism a better chance of survival. Special traits that help living organisms survive in a particular environment. Ex: Polar bear s thick white fur keeps him
ADAPTATIONS Characteristics that give an organism a better chance of survival. Special traits that help living organisms survive in a particular environment. Ex: Polar bear s thick white fur keeps him
Charles Darwin & Natural Selection
 Charles Darwin & Natural Selection Darwin Born in Shrewsbury, England, in 1809 Studied medicine at Edinburgh University (1825-1827) where the sight of blood and surgery without anesthetics repulsed him
Charles Darwin & Natural Selection Darwin Born in Shrewsbury, England, in 1809 Studied medicine at Edinburgh University (1825-1827) where the sight of blood and surgery without anesthetics repulsed him
Ecology is studied at several levels
 Ecology is studied at several levels Ecology and evolution are tightly intertwined Biosphere = the total living things on Earth and the areas they inhabit Ecosystem = communities and the nonliving material
Ecology is studied at several levels Ecology and evolution are tightly intertwined Biosphere = the total living things on Earth and the areas they inhabit Ecosystem = communities and the nonliving material
Chapter 9 Population Dynamics, Carrying Capacity, and Conservation Biology
 Chapter 9 Population Dynamics, Carrying Capacity, and Conservation Biology 9-1 Population Dynamics & Carrying Capacity Populations change in response to enviromental stress or changes in evironmental conditions
Chapter 9 Population Dynamics, Carrying Capacity, and Conservation Biology 9-1 Population Dynamics & Carrying Capacity Populations change in response to enviromental stress or changes in evironmental conditions
Charles Darwin became a naturalist, a scientist who studies nature, during a voyage on the British ship HMS Beagle.
 Theory of Evolution Darwin s Voyage What did Darwin observe? Charles Darwin became a naturalist, a scientist who studies nature, during a voyage on the British ship HMS Beagle. On his journey, Darwin observed
Theory of Evolution Darwin s Voyage What did Darwin observe? Charles Darwin became a naturalist, a scientist who studies nature, during a voyage on the British ship HMS Beagle. On his journey, Darwin observed
Biology Slide 1 of 41
 Biology 1 of 41 15-3 Darwin Presents His Case 2 of 41 15-3 Darwin Presents His Case Publication of On the Origin of Species Publication of On the Origin of Species Darwin filled notebooks with his ideas
Biology 1 of 41 15-3 Darwin Presents His Case 2 of 41 15-3 Darwin Presents His Case Publication of On the Origin of Species Publication of On the Origin of Species Darwin filled notebooks with his ideas
III. Evolutionary thinking before Darwin. Influences on Darwin. I. Evolution and its core principles. II. The importance of evolution as a concept
 I. Evolution and its core principles Evolution: cumulative changes in traits of a species or population over time. Common descent with modification: The modification of species in successive generations,
I. Evolution and its core principles Evolution: cumulative changes in traits of a species or population over time. Common descent with modification: The modification of species in successive generations,
Biology. Slide 1 of 41. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 41 15-3 Darwin Presents His Case 2 of 41 Publication of On the Origin of Species Publication of On the Origin of Species Darwin filled notebooks with his ideas about species diversity and
Biology 1 of 41 15-3 Darwin Presents His Case 2 of 41 Publication of On the Origin of Species Publication of On the Origin of Species Darwin filled notebooks with his ideas about species diversity and
The Cultural Landscape: Introduction to Human Geography Chapter 1 Thinking Geographically Chapter 2 Population
 The Cultural Landscape: Introduction to Human Geography Chapter 1 Thinking Geographically Chapter 2 Population 1) Scale is A) the system used by geographers to transfer locations from a globe to a map.
The Cultural Landscape: Introduction to Human Geography Chapter 1 Thinking Geographically Chapter 2 Population 1) Scale is A) the system used by geographers to transfer locations from a globe to a map.
Publication of On the Origin of Species Darwin Presents His Case
 Publication of On the Origin of Species Publication of On the Origin of Species Darwin filled notebooks with his ideas about species diversity and the evolution process. Darwin was stunned and disturbed
Publication of On the Origin of Species Publication of On the Origin of Species Darwin filled notebooks with his ideas about species diversity and the evolution process. Darwin was stunned and disturbed
Behaviour of simple population models under ecological processes
 J. Biosci., Vol. 19, Number 2, June 1994, pp 247 254. Printed in India. Behaviour of simple population models under ecological processes SOMDATTA SINHA* and S PARTHASARATHY Centre for Cellular and Molecular
J. Biosci., Vol. 19, Number 2, June 1994, pp 247 254. Printed in India. Behaviour of simple population models under ecological processes SOMDATTA SINHA* and S PARTHASARATHY Centre for Cellular and Molecular
A change in an inherited characteristic of a population over time. Individuals DO NOT evolve!
 Evolution Unit 1 A change in an inherited characteristic of a population over time. Individuals DO NOT evolve! Evolution Unit evolution the process of biological change by which descendants come to differ
Evolution Unit 1 A change in an inherited characteristic of a population over time. Individuals DO NOT evolve! Evolution Unit evolution the process of biological change by which descendants come to differ
Phenomenon: Canadian lynx and snowshoe hares
 Outline Outline of Topics Shan He School for Computational Science University of Birmingham Module 06-23836: Computational Modelling with MATLAB Phenomenon: Canadian lynx and snowshoe hares All began with
Outline Outline of Topics Shan He School for Computational Science University of Birmingham Module 06-23836: Computational Modelling with MATLAB Phenomenon: Canadian lynx and snowshoe hares All began with
Marine Ecology BIOL 529, 529L, 529I. Course Objectives. Text and other Reading Textbook: No textbook. Format of Course. Grading. What is Ecology?
 Marine Ecology BIOL 529, 529L, 529I Course Objectives Dr. Mark Steele Magnolia 4100 Office Hours: Tue & Thur 11-12, or by appt. Mike Schram Magnolia 4103 Office Hours: Wed 10-11, or by appt. 1. Gain a
Marine Ecology BIOL 529, 529L, 529I Course Objectives Dr. Mark Steele Magnolia 4100 Office Hours: Tue & Thur 11-12, or by appt. Mike Schram Magnolia 4103 Office Hours: Wed 10-11, or by appt. 1. Gain a
The perfect mixing paradox and the logistic equation: Verhulst vs. Lotka
 The perfect mixing paradox and the logistic equation: Verhulst vs. Lotka ROGER ARDITI, LOUIS-F ELIX BERSIER, AND RUDOLF P. ROHR Ecology and Evolution Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, Chemin
The perfect mixing paradox and the logistic equation: Verhulst vs. Lotka ROGER ARDITI, LOUIS-F ELIX BERSIER, AND RUDOLF P. ROHR Ecology and Evolution Department of Biology, University of Fribourg, Chemin
Continuities in Sociological Human Ecology
 Continuities in Sociological Human Ecology Edited by Michael Micklin National Institutes of Health Bethesda, Maryland and Dudley L Poston, Jr. Texas A&M University College Station, Texas Plenum Press New
Continuities in Sociological Human Ecology Edited by Michael Micklin National Institutes of Health Bethesda, Maryland and Dudley L Poston, Jr. Texas A&M University College Station, Texas Plenum Press New
Predator-Prey Population Models
 21 Predator-Prey Population Models Tools Used in Lab 21 Hudson Bay Data (Hare- Lynx) Lotka-Volterra Lotka-Volterra with Harvest How can we model the interaction between a species of predators and their
21 Predator-Prey Population Models Tools Used in Lab 21 Hudson Bay Data (Hare- Lynx) Lotka-Volterra Lotka-Volterra with Harvest How can we model the interaction between a species of predators and their
THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION. Darwin, the people who contributed to his ideas, and what it all really means.
 THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Darwin, the people who contributed to his ideas, and what it all really means. DARWIN S JOURNEY Charles Darwin was born in England on February 12, 1809. Geologists were suggesting
THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Darwin, the people who contributed to his ideas, and what it all really means. DARWIN S JOURNEY Charles Darwin was born in England on February 12, 1809. Geologists were suggesting
Introduction to population dynamics & adaptation
 Introduction to population dynamics & adaptation David Claessen Ecole Normale Supérieure CERES-ERTI, 24 rue Lhomond, Paris & Laboratory «Ecology and Evolution» UMR 7625 CNRS-ENS-UPMC 13/06/12 1 Plan Introduction
Introduction to population dynamics & adaptation David Claessen Ecole Normale Supérieure CERES-ERTI, 24 rue Lhomond, Paris & Laboratory «Ecology and Evolution» UMR 7625 CNRS-ENS-UPMC 13/06/12 1 Plan Introduction
History and meaning of the word Ecology A. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live
 History and meaning of the word Ecology A. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live B. Etymology study of the origin and development of a word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869)
History and meaning of the word Ecology A. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live B. Etymology study of the origin and development of a word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869)
W/F = 10:00 AM - 1:00 PM Other times available by appointment only
 Course BY 101-05 Principles of Biology Fall 2015 BY 103-01 Honors Biology Course Meeting Time BY 101-05 T/Th 9:30 10:45 PM BG 109 BY 103-01 Lab 01 M 8:00 AM - 9:50 AM Lab 02 M 10:10 12:00 PM Lab 03 M 1:25
Course BY 101-05 Principles of Biology Fall 2015 BY 103-01 Honors Biology Course Meeting Time BY 101-05 T/Th 9:30 10:45 PM BG 109 BY 103-01 Lab 01 M 8:00 AM - 9:50 AM Lab 02 M 10:10 12:00 PM Lab 03 M 1:25
Part I History and ecological basis of species distribution modeling
 Part I History and ecological basis of species distribution modeling Recent decades have seen an explosion of interest in species distribution modeling. This has resulted from a confluence of the growing
Part I History and ecological basis of species distribution modeling Recent decades have seen an explosion of interest in species distribution modeling. This has resulted from a confluence of the growing
Biologists Study the Interactions of Life
 What is Biology? Biologists Study the Interactions of Life Living things do not live in isolation. They interact with their environment and depend on other living/non-living things for survival. Biologists
What is Biology? Biologists Study the Interactions of Life Living things do not live in isolation. They interact with their environment and depend on other living/non-living things for survival. Biologists
Key words and phrases. Bifurcation, Difference Equations, Fixed Points, Predator - Prey System, Stability.
 ISO 9001:008 Certified Volume, Issue, March 013 Dynamical Behavior in a Discrete Prey- Predator Interactions M.ReniSagaya Raj 1, A.George Maria Selvam, R.Janagaraj 3.and D.Pushparajan 4 1,,3 Sacred Heart
ISO 9001:008 Certified Volume, Issue, March 013 Dynamical Behavior in a Discrete Prey- Predator Interactions M.ReniSagaya Raj 1, A.George Maria Selvam, R.Janagaraj 3.and D.Pushparajan 4 1,,3 Sacred Heart
Unit 8: Ecology: Ecosystems and Communities
 Unit 8: Ecology: Ecosystems and Communities An ecosystem consists of all the plants and animals that interact with the nonliving things in an area. Biosphere = area on Earth where living things are found
Unit 8: Ecology: Ecosystems and Communities An ecosystem consists of all the plants and animals that interact with the nonliving things in an area. Biosphere = area on Earth where living things are found
Community Interactions
 Name Class Date 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Lesson Objectives Define niche. Describe the role competition plays in shaping communities. Describe the role predation and herbivory play in shaping
Name Class Date 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Lesson Objectives Define niche. Describe the role competition plays in shaping communities. Describe the role predation and herbivory play in shaping
Madhya Pradesh Bhoj Open University. Bhopal M.sc Zoology Final Year
 Subject : Comparative Anatomy of Vertebrates Q.1 Describe the inter-relationship of Uro chords and cephalochordates and their relationship with other deuterostomes. Q.2 Describe origin, evolution and general
Subject : Comparative Anatomy of Vertebrates Q.1 Describe the inter-relationship of Uro chords and cephalochordates and their relationship with other deuterostomes. Q.2 Describe origin, evolution and general
Summary - Mon and Wed
 Unit 1: Evolution 1 Summary - Mon and Wed 1. Wrap up red tape 2. Short answers - the tautology 3. Recap scientific method/inference to the best explanation 4. The natural sciences before Darwin 5. Influences
Unit 1: Evolution 1 Summary - Mon and Wed 1. Wrap up red tape 2. Short answers - the tautology 3. Recap scientific method/inference to the best explanation 4. The natural sciences before Darwin 5. Influences
8 Ecosystem stability
 8 Ecosystem stability References: May [47], Strogatz [48]. In these lectures we consider models of populations, with an emphasis on the conditions for stability and instability. 8.1 Dynamics of a single
8 Ecosystem stability References: May [47], Strogatz [48]. In these lectures we consider models of populations, with an emphasis on the conditions for stability and instability. 8.1 Dynamics of a single
