Supplementary Information for. Mechanochemical route to the synthesis of nanostructured Aluminium nitride
|
|
|
- Alannah Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information for Mechanochemical route to the synthesis of nanostructured Aluminium nitride S. A. Rounaghi 1,*, H. Eshghi 2, S. Scudino 3, **, A. Vyalikh 4, D. E. P. Vanpoucke 5, W. Gruner 3, S. Oswald 3, A.-R. Kiani-Rashid 6, M. Samadi-Khoshkhoo 3, U. Scheler 7, J. Eckert 8,9 1) Department of Materials Engineering, Birjand University of Technology, Birjand, Iran. 2) Department of Chemistry, School of Sciences, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran. 3) Institut für Komplexe Materialien, IFW Dresden, Helmholtzstraße 20, Dresden, Germany. 4) Institut für Experimentelle Physik, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Leipziger Str. 23, Freiberg, Germany. 5) Center for Molecular Modeling, Ghent University, Technologiepark 903, 9052 Zwijnaarde, Belgium. 6) Department of Materials Engineering, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, , Mashhad, Iran. 7) Leibniz-Institut für Polymerforschung Dresden e.v., Hohe Str. 6, Dresden, Germany. 8) Erich Schmid Institute of Materials Science, Austrian Academy of Sciences, Jahnstraße 12, A-8700 Leoben, Austria 9) Department Materials Physics, Montanuniversität Leoben, Jahnstraße 12, A-8700 Leoben, Austria *, **) Corresponding authors. 1- DFT simulation of N-incorporated Al structure The system consisting of the Al slab and N atoms situated at different sites has been geometrically optimized. N atoms were opted to occupy the most probable positions, i.e. substitutional and interstitial sites, for which the latter includes tetrahedral and octahedral ones (Figure S1). Moreover, two bulk systems were optimized with two distinct complexes comprising of 4 and 6 N atoms respectively placed in the tetrahedral and octahedral positions around a single Al site in FCC Al. S1
2 The energy of formation has been calculated according to the following equation: E E / E E (1) where E f is the energy of formation, E N/Al is the energy of the system when atomic N occupies an individual site in the aluminium structure (Al slab) and E N and E Al are the energies of the isolated atomic N and Al slab, respectively. Table S1 gives the energy values calculated for the mentioned situations. The negative values of the energy indicate that the diffusion of N into Al is favourable from the thermodynamic point of view. The formation energy of the substituted N is much higher than any of the interstitial cases, indicating this site to be the least favourable of those studied. Due to the small size of the N atom, the lattice shows a minute contraction (note that we have a N concentration of 1/108, i.e. <1%). The surrounding Al atoms also move slightly toward the N atom with Al-N bond lengths of 2.77 Å compared to 2.85 for Al-Al. In contrast, N at the interstitial sites is very favourable from the energetics point of view, indicating that the N atoms are likely to diffuse from the surface into the Al bulk via the interstitial sites. In such cases, the N atom positioned in tetrahedral and octahedral sites of Al crystal clearly forms bonds with the surrounding Al atoms (bond lengths of Å and Å for tetrahedral and octahedral sites, respectively). In addition, the calculated Hirshfeld-I charges [1, 2] show that there is a clear charge transfer from the N atom to the surrounding Al, which is a typical behaviour for dopant elements [3]. The octahedral site, however, is slightly less stable than the tetrahedral one (~19 kcal/mol). Furthermore, the formation of interstitial complexes comprised of multiple N atoms appears to be very favourable, since the defect formation energy of the complexes is lower than that of a single N interstitial. Furthermore, the defect formation energy per N atom of a single complex is also more favourable than that of a single N interstitial, indicating the preference for clustering of the N interstitials. This beneficial energetics picture of the complexes allows us to consider them as seeds for the FCC-Al to h-aln phase transition. Although the energetics of the complexes shows a preference for S2
3 clustering, the atomic structure shows that no N 2 is formed but an AlN phase is retained. This is due to the internal N-distances, which in this case are about Å, therefore much longer than the N 2 bond length (~1.11 Å). Similar to the interstitially diffused single N, the defect formation energy for a single N atom in the tetrahedral complex (an Al surrounded by 4 N) is lower than in the octahedral one. The results show that the complex containing 4 N in tetrahedral sites around a single Al, is less stable than the complex containing 6 N atoms in octahedral sites around a single Al. Furthermore, constructing a complex with 8 N atoms in the tetrahedral sites around a single Al atom leads, following the structure optimization, to a structure with only 4 N in the tetrahedral sites surrounding the central Al, while the other 4 N atoms have moved to the next available tetrahedral sites which do not neighbour upon the central Al. Figure S1. A schematic representation of the possible sites occupied by N atom(s) after diffusion into an Al slab. S3
4 Table S1. The lattice parameter and energies of the optimized N incorporated Al slab with doped N atoms placed at different situations. System a = b = c (Å) E f (ev/cell) Pure Al Substitutional N Tetrahedral N Octahedral N Tetrahedral N complex (4x) Octahedral N complex (6x) S4
5 2- Analysis of gaseous by-products Figure S2. The vial equipped with gas analysis apparatus. Figure S3. QMS spectra of the gaseous by-products formed after milling for 6 h and (inset) sketch of the experimental setup. S5
6 3- References [1] D.E.P. Vanpoucke, I. Van Driessche, P. Bultinck. Reply to comment on extending Hirshfeld-I to bulk and periodic materials, Journal of Computational Chemistry 34 (2013) [2] D.E.P. Vanpoucke, P. Bultinck, I. Van Driessche. Extending Hirshfeld-I to bulk and periodic materials, Journal of Computational Chemistry 34 (2013) [3] D.E.P. Vanpoucke, S. Cottenier, V. Van Speybroeck, I. Van Driessche, P. Bultinck. Tetravalent Doping of CeO2: The Impact of Valence Electron Character on Group IV Dopant Influence, Journal of the American Ceramic Society 97 (2014) S6
High Area Capacity Lithium-Sulfur Full-cell Battery with Prelitiathed Silicon Nanowire-Carbon Anodes for Long Cycling Stability
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION High Area Capacity Lithium-Sulfur Full-cell Battery with Prelitiathed Silicon Nanowire-Carbon Anodes for Long Cycling Stability Andreas Krause 1,2*, Susanne Dörfler 3,4, Markus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION High Area Capacity Lithium-Sulfur Full-cell Battery with Prelitiathed Silicon Nanowire-Carbon Anodes for Long Cycling Stability Andreas Krause 1,2*, Susanne Dörfler 3,4, Markus
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2015 Supporting Information SEI-Component Formation on Sub 5 nm Sized Silicon Nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2015 Supporting Information SEI-Component Formation on Sub 5 nm Sized Silicon Nanoparticles
Curriculum Vitae Dr. Dr. Danny E. P. Vanpoucke
 Curriculum Vitae Dr. Dr. Current Affiliation: Universiteit Hasselt - Hasselt University Wide Bandgap Materials (WBGM) Campus Diepenbeek, Wetenschapspark 1, 3590 Diepenbeek Belgium room: IMO-1.39 e-mail:
Curriculum Vitae Dr. Dr. Current Affiliation: Universiteit Hasselt - Hasselt University Wide Bandgap Materials (WBGM) Campus Diepenbeek, Wetenschapspark 1, 3590 Diepenbeek Belgium room: IMO-1.39 e-mail:
Ab initio Berechungen für Datenbanken
 J Ab initio Berechungen für Datenbanken Jörg Neugebauer University of Paderborn Lehrstuhl Computational Materials Science Computational Materials Science Group CMS Group Scaling Problem in Modeling length
J Ab initio Berechungen für Datenbanken Jörg Neugebauer University of Paderborn Lehrstuhl Computational Materials Science Computational Materials Science Group CMS Group Scaling Problem in Modeling length
Lecture 04 Structure of Ceramics 1 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000.
 MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 04 Structure of Ceramics 1 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000. Prof. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka
MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 04 Structure of Ceramics 1 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000. Prof. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka
Defects. Defects. Kap. 3 States of aggregation. Perfect Crystal
 Kap. 3 States of aggregation Defects Perfect Crystal A A perfect crystal with every atom in the correct position does not exist. Only a hypothetical situation at 0 K Crystals are like people: it is the
Kap. 3 States of aggregation Defects Perfect Crystal A A perfect crystal with every atom in the correct position does not exist. Only a hypothetical situation at 0 K Crystals are like people: it is the
Stoichiometric defects, viz. no ateration in composition. Interstitial ( between lattice points) Vacancies (empty possitions) Wrong type atoms
 Perfect Crystal A A perfect crystal with every atom in the correct position does not eist. Only a hypothetical situation at 0 Crystals are like people: it is the defects in them which tend to make them
Perfect Crystal A A perfect crystal with every atom in the correct position does not eist. Only a hypothetical situation at 0 Crystals are like people: it is the defects in them which tend to make them
A novel p type half-heusler from high-throughput transport and defect calculations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 06 A novel p type half-heusler from high-throughput transport and defect calculations
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 06 A novel p type half-heusler from high-throughput transport and defect calculations
Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level
 Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level Contents 1 Dopant materials 1 2 E F in extrinsic semiconductors 5 3 Temperature dependence of carrier concentration 6 3.1 Low temperature regime (T < T
Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level Contents 1 Dopant materials 1 2 E F in extrinsic semiconductors 5 3 Temperature dependence of carrier concentration 6 3.1 Low temperature regime (T < T
An interatomic potential study of the properties of gallium nitride
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9 (1997) 9517 9525. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(97)82806-8 An interatomic potential study of the properties of gallium nitride Peter Zapol, Ravindra Pandey and Julian D
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9 (1997) 9517 9525. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(97)82806-8 An interatomic potential study of the properties of gallium nitride Peter Zapol, Ravindra Pandey and Julian D
Supplementary Information: Supplementary Figure 1. Resistance dependence on pressure in the semiconducting region.
 Supplementary Information: Supplementary Figure 1. Resistance dependence on pressure in the semiconducting region. The pressure activated carrier transport model shows good agreement with the experimental
Supplementary Information: Supplementary Figure 1. Resistance dependence on pressure in the semiconducting region. The pressure activated carrier transport model shows good agreement with the experimental
Electronic Properties of Hydrogenated Quasi-Free-Standing Graphene
 GCOE Symposium Tohoku University 2011 Electronic Properties of Hydrogenated Quasi-Free-Standing Graphene Danny Haberer Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden Co-workers Supervising
GCOE Symposium Tohoku University 2011 Electronic Properties of Hydrogenated Quasi-Free-Standing Graphene Danny Haberer Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden Co-workers Supervising
Ion Implantation ECE723
 Ion Implantation Topic covered: Process and Advantages of Ion Implantation Ion Distribution and Removal of Lattice Damage Simulation of Ion Implantation Range of Implanted Ions Ion Implantation is the
Ion Implantation Topic covered: Process and Advantages of Ion Implantation Ion Distribution and Removal of Lattice Damage Simulation of Ion Implantation Range of Implanted Ions Ion Implantation is the
First-principles studies of beryllium doping of GaN
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 63, 24525 First-principles studies of beryllium doping of GaN Chris G. Van de Walle * and Sukit Limpijumnong Xerox Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road, Palo Alto,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 63, 24525 First-principles studies of beryllium doping of GaN Chris G. Van de Walle * and Sukit Limpijumnong Xerox Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road, Palo Alto,
Investigation of Free Volume in Polymers by Positron Annihilation Lifetime Spectroscopy (PALS)
 Investigation of Free Volume in Polymers by Positron Annihilation Lifetime Spectroscopy (PALS) Master Thesis by M. Qasim Shaikh Under supervision of Prof. Reinhard Krause-Rehberg Martin-Luther-Universität
Investigation of Free Volume in Polymers by Positron Annihilation Lifetime Spectroscopy (PALS) Master Thesis by M. Qasim Shaikh Under supervision of Prof. Reinhard Krause-Rehberg Martin-Luther-Universität
The effect of light impurities on the binding energy of hydrogen in magnesium metal and magnesium hydride
 The effect of light impurities on the binding energy of hydrogen in magnesium metal and magnesium hydride Finnbogi Óskarsson Science Institute, University of Iceland, Dunhaga 3, IS-107 Reykjavík, Iceland
The effect of light impurities on the binding energy of hydrogen in magnesium metal and magnesium hydride Finnbogi Óskarsson Science Institute, University of Iceland, Dunhaga 3, IS-107 Reykjavík, Iceland
Understanding the growth mechanism of graphene on Ge/Si(001) surfaces
 Supplementary material for the manuscript: Understanding the growth mechanism of graphene on Ge/Si(001) surfaces J. Dabrowski, 1 G. Lippert, 1 J. Avila, 2 J. Baringhaus, 3 I. Colambo, 4 Yu. S. Dedkov,
Supplementary material for the manuscript: Understanding the growth mechanism of graphene on Ge/Si(001) surfaces J. Dabrowski, 1 G. Lippert, 1 J. Avila, 2 J. Baringhaus, 3 I. Colambo, 4 Yu. S. Dedkov,
Southeast University, Nanjing, China 2 Department of Applied Physics, Aalto University,
 Supplementary Information to Solubility of Boron, Carbon and Nitrogen in Transition Metals: Getting Insight into Trends from First-Principles Calculations Xiaohui Hu, 1,2 Torbjörn Björkman 2,3, Harri Lipsanen
Supplementary Information to Solubility of Boron, Carbon and Nitrogen in Transition Metals: Getting Insight into Trends from First-Principles Calculations Xiaohui Hu, 1,2 Torbjörn Björkman 2,3, Harri Lipsanen
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 19 Dec 2006](/thumbs/91/104898931.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/678v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Dec 6 Abstract Electronic structure of the Au/benzene-,-dithiol/Au transport interface: Effects of chemical bonding U. Schwingenschlögl, C. Schuster Institut für
arxiv:cond-mat/678v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Dec 6 Abstract Electronic structure of the Au/benzene-,-dithiol/Au transport interface: Effects of chemical bonding U. Schwingenschlögl, C. Schuster Institut für
Topics to discuss...
 MME 467: Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 18 Defects in Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch6, McGraw-Hill, 2000 Prof. A. K. M. B. Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka Topics
MME 467: Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 18 Defects in Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch6, McGraw-Hill, 2000 Prof. A. K. M. B. Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka Topics
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Density functional theory calculations of atomic, electronic and thermodynamic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Density functional theory calculations of atomic, electronic and thermodynamic
Ceramic Bonding. CaF 2 : large SiC: small
 Recall ceramic bonding: - Mixed ionic and covalent. - % ionic character ( f ) increases with difference in electronegativity Large vs small ionic bond character: Ceramic Bonding CaF : large SiC: small
Recall ceramic bonding: - Mixed ionic and covalent. - % ionic character ( f ) increases with difference in electronegativity Large vs small ionic bond character: Ceramic Bonding CaF : large SiC: small
INTRODUCTION TO THE DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS DEFECTS, DEFECTS, DEFECTS CAN T LIVE WITH THEM!!! CAN T LIVE WITHOUT THEM!!! INTRODUCTION TO DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS DEFECTS, DEFECTS, DEFECTS Perfect crystals
INTRODUCTION TO THE DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS DEFECTS, DEFECTS, DEFECTS CAN T LIVE WITH THEM!!! CAN T LIVE WITHOUT THEM!!! INTRODUCTION TO DEFECT STATE IN MATERIALS DEFECTS, DEFECTS, DEFECTS Perfect crystals
Charles A. Weatherford, + Kalayu G. Belay + and Gennady L. Gutsev *
 Charles A. Weatherford, + Kalayu G. Belay + and Gennady L. Gutsev * Department of Physics and Center for Plasma Science and Technology Florida A&M University Tallahassee, Florida 32307 SPONSORS: + NSF
Charles A. Weatherford, + Kalayu G. Belay + and Gennady L. Gutsev * Department of Physics and Center for Plasma Science and Technology Florida A&M University Tallahassee, Florida 32307 SPONSORS: + NSF
Hussein Ayedh. PhD Studet Department of Physics
 Hussein Ayedh PhD Studet Department of Physics OUTLINE Introduction Semiconductors Basics DLTS Theory DLTS Requirements Example Summary Introduction Energetically "deep trapping levels in semiconductor
Hussein Ayedh PhD Studet Department of Physics OUTLINE Introduction Semiconductors Basics DLTS Theory DLTS Requirements Example Summary Introduction Energetically "deep trapping levels in semiconductor
Semiconductor physics I. The Crystal Structure of Solids
 Lecture 3 Semiconductor physics I The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 Semiconductor materials Types of solids Space lattices Atomic Bonding Imperfection and doping in SOLIDS 2 Semiconductor Semiconductors
Lecture 3 Semiconductor physics I The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 Semiconductor materials Types of solids Space lattices Atomic Bonding Imperfection and doping in SOLIDS 2 Semiconductor Semiconductors
Quantum Monte Carlo Calculations of Point Defects in Alumina
 Quantum Monte Carlo Calculations of Nicholas Hine Condensed Matter Theory Group Imperial College London Sunday 22nd July 2007 Dramatis Personae Collaborators Matthew Foulkes Mike Finnis Kilian Frensch
Quantum Monte Carlo Calculations of Nicholas Hine Condensed Matter Theory Group Imperial College London Sunday 22nd July 2007 Dramatis Personae Collaborators Matthew Foulkes Mike Finnis Kilian Frensch
Numerical modeling of hydrogen/deuterium absorption in transition-metal alloys
 Numerical modeling of hydrogen/deuterium absorption in transition-metal alloys Olga Dmitriyeva, Rick Cantwell, Matt McConnell Coolescence LLC Boulder, Colorado, U.S.A. 1 QuantumEspresso Electronic structure
Numerical modeling of hydrogen/deuterium absorption in transition-metal alloys Olga Dmitriyeva, Rick Cantwell, Matt McConnell Coolescence LLC Boulder, Colorado, U.S.A. 1 QuantumEspresso Electronic structure
Supporting Information
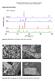 Supporting Information Figure S1. XRD patterns of ZnGa 2 O 4, GaN, ZnO, and Ga 2 O 3. Figure S2. SEM micrographs for ZnO (A), Ga 2 O 3 (B), GaN (C), ZnGa 2 O 4 (D). Figure S3A. Raman shifts associated
Supporting Information Figure S1. XRD patterns of ZnGa 2 O 4, GaN, ZnO, and Ga 2 O 3. Figure S2. SEM micrographs for ZnO (A), Ga 2 O 3 (B), GaN (C), ZnGa 2 O 4 (D). Figure S3A. Raman shifts associated
Crystalline Solids have atoms arranged in an orderly repeating pattern. Amorphous Solids lack the order found in crystalline solids
 Ch 12: Solids and Modern Materials Learning goals and key skills: Classify solids base on bonding/intermolecular forces and understand how difference in bonding relates to physical properties Know the
Ch 12: Solids and Modern Materials Learning goals and key skills: Classify solids base on bonding/intermolecular forces and understand how difference in bonding relates to physical properties Know the
Supporting Information for. Graphene Nucleation on a Surface-MoltenCopperCatalyst: Quantum Chemical Molecular Dynamics Simulations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. his journal is he Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information for Graphene Nucleation on a Surface-MoltenCopperCatalyst: Quantum
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. his journal is he Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information for Graphene Nucleation on a Surface-MoltenCopperCatalyst: Quantum
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Controlled Growth of Ceria Nanoarrays on Anatase Titania Powder: A Bottom-up Physical Picture Hyun You Kim 1, Mark S. Hybertsen 2*, and Ping Liu 2* 1 Department of Materials Science
Supporting Information Controlled Growth of Ceria Nanoarrays on Anatase Titania Powder: A Bottom-up Physical Picture Hyun You Kim 1, Mark S. Hybertsen 2*, and Ping Liu 2* 1 Department of Materials Science
Semiconductor Devices and Circuits Fall Midterm Exam. Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp, Professor of Electrical Engineering. Name: Mat. -Nr.
 Semiconductor Devices and Circuits Fall 2003 Midterm Exam Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp, Professor of Electrical Engineering Name: Mat. -Nr.: Guidelines: Duration of the Midterm: 1 hour The exam is a closed
Semiconductor Devices and Circuits Fall 2003 Midterm Exam Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp, Professor of Electrical Engineering Name: Mat. -Nr.: Guidelines: Duration of the Midterm: 1 hour The exam is a closed
EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRY ON POINT DEFECTS AND IMPURITIES IN GALLIUM NITRIDE
 EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRY ON POINT DEFECTS AND IMPURITIES IN GALLIUM NITRIDE C. G. VAN DE WALLE AND J. E. NORTHRUP Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road, Palo Alto, CA 930, USA E-mail: vandewalle@parc.com
EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRY ON POINT DEFECTS AND IMPURITIES IN GALLIUM NITRIDE C. G. VAN DE WALLE AND J. E. NORTHRUP Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road, Palo Alto, CA 930, USA E-mail: vandewalle@parc.com
Rh 3d. Co 2p. Binding Energy (ev) Binding Energy (ev) (b) (a)
 Co 2p Co(0) 778.3 Rh 3d Rh (0) 307.2 810 800 790 780 770 Binding Energy (ev) (a) 320 315 310 305 Binding Energy (ev) (b) Supplementary Figure 1 Photoemission features of a catalyst precursor which was
Co 2p Co(0) 778.3 Rh 3d Rh (0) 307.2 810 800 790 780 770 Binding Energy (ev) (a) 320 315 310 305 Binding Energy (ev) (b) Supplementary Figure 1 Photoemission features of a catalyst precursor which was
Atomistic simulations on the mobility of di- and tri-interstitials in Si
 Atomistic simulations on the mobility of di- and tri-interstitials in Si related publications (since 2001): Posselt, M., Gao, F., Zwicker, D., Atomistic study of the migration of di- and tri-interstitials
Atomistic simulations on the mobility of di- and tri-interstitials in Si related publications (since 2001): Posselt, M., Gao, F., Zwicker, D., Atomistic study of the migration of di- and tri-interstitials
Research Highlights. Salient results from our group. Mixed phosphides in Sn-P and Sn-Mn-P systems
 Research Highlights Dilute magnetic semiconductors and Spintronics Spintronics is a branch of electronics emerged from the dilute magnetic semiconductor in an aspect of utilization of the spin in addition
Research Highlights Dilute magnetic semiconductors and Spintronics Spintronics is a branch of electronics emerged from the dilute magnetic semiconductor in an aspect of utilization of the spin in addition
5.03 In-Class Exam 2
 5.03 In-Class Exam 2 Christopher C. Cummins March 12, 2010 Instructions Clearly write your name at the top of this front page, but otherwise do not write on this front page as it will be used for scoring.
5.03 In-Class Exam 2 Christopher C. Cummins March 12, 2010 Instructions Clearly write your name at the top of this front page, but otherwise do not write on this front page as it will be used for scoring.
Self-compensating incorporation of Mn in Ga 1 x Mn x As
 Self-compensating incorporation of Mn in Ga 1 x Mn x As arxiv:cond-mat/0201131v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Jan 2002 J. Mašek and F. Máca Institute of Physics, Academy of Sciences of the CR CZ-182 21 Praha
Self-compensating incorporation of Mn in Ga 1 x Mn x As arxiv:cond-mat/0201131v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Jan 2002 J. Mašek and F. Máca Institute of Physics, Academy of Sciences of the CR CZ-182 21 Praha
Structure and dynamics of the diarsenic complex in crystalline silicon
 Structure and dynamics of the diarsenic complex in crystalline silicon Scott A. Harrison, Thomas F. Edgar, and Gyeong S. Hwang* Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Texas, Austin, Texas 78713,
Structure and dynamics of the diarsenic complex in crystalline silicon Scott A. Harrison, Thomas F. Edgar, and Gyeong S. Hwang* Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Texas, Austin, Texas 78713,
J name Supplementary information Direct synthesis of graphene from adsorbed organic solvent molecules over copper
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2015 not adjust margins J name PAPER Received 00th January 20xx, Accepted 00th January
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2015 not adjust margins J name PAPER Received 00th January 20xx, Accepted 00th January
Energy-Level Alignment at the Interface of Graphene Fluoride and Boron Nitride Monolayers: An Investigation by Many-Body Perturbation Theory
 Supporting Information Energy-Level Alignment at the Interface of Graphene Fluoride and Boron Nitride Monolayers: An Investigation by Many-Body Perturbation Theory Qiang Fu, Dmitrii Nabok, and Claudia
Supporting Information Energy-Level Alignment at the Interface of Graphene Fluoride and Boron Nitride Monolayers: An Investigation by Many-Body Perturbation Theory Qiang Fu, Dmitrii Nabok, and Claudia
Atomic Arrangement. Primer Materials For Science Teaching Spring
 Atomic Arrangement Primer Materials For Science Teaching Spring 2016 31.3.2015 Levels of atomic arrangements No order In gases, for example the atoms have no order, they are randomly distributed filling
Atomic Arrangement Primer Materials For Science Teaching Spring 2016 31.3.2015 Levels of atomic arrangements No order In gases, for example the atoms have no order, they are randomly distributed filling
Supporting Information: From Permeation to Cluster Arrays: Graphene on. Ir(111) Exposed to Carbon Vapor
 Supporting Information: From Permeation to Cluster Arrays: Graphene on Ir(111) Exposed to Carbon Vapor Charlotte Herbig,, Timo Knispel, Sabina Simon,, Ulrike A. Schröder, Antonio J. Martínez-Galera, Mohammad
Supporting Information: From Permeation to Cluster Arrays: Graphene on Ir(111) Exposed to Carbon Vapor Charlotte Herbig,, Timo Knispel, Sabina Simon,, Ulrike A. Schröder, Antonio J. Martínez-Galera, Mohammad
A semiconductor is an almost insulating material, in which by contamination (doping) positive or negative charge carriers can be introduced.
 Semiconductor A semiconductor is an almost insulating material, in which by contamination (doping) positive or negative charge carriers can be introduced. Page 2 Semiconductor materials Page 3 Energy levels
Semiconductor A semiconductor is an almost insulating material, in which by contamination (doping) positive or negative charge carriers can be introduced. Page 2 Semiconductor materials Page 3 Energy levels
Ga and P Atoms to Covalent Solid GaP
 Ga and P Atoms to Covalent Solid GaP Band Gaps in Binary Group III-V Semiconductors Mixed Semiconductors Affect of replacing some of the As with P in GaAs Band Gap (ev) (nm) GaAs 1.35 919 (IR) GaP 2.24
Ga and P Atoms to Covalent Solid GaP Band Gaps in Binary Group III-V Semiconductors Mixed Semiconductors Affect of replacing some of the As with P in GaAs Band Gap (ev) (nm) GaAs 1.35 919 (IR) GaP 2.24
Plasmonic nanomeshes: their ambivalent role as transparent electrodes in organic solar cells
 Supplementary Information Plasmonic nanomeshes: their ambivalent role as transparent electrodes in organic solar cells Christian Stelling 1, Chetan R. Singh 2, Matthias Karg 3, Tobias König 4 *, Mukundan
Supplementary Information Plasmonic nanomeshes: their ambivalent role as transparent electrodes in organic solar cells Christian Stelling 1, Chetan R. Singh 2, Matthias Karg 3, Tobias König 4 *, Mukundan
Electronic and Magnetic properties of pure and doped manganese clusters
 Electronic and Magnetic properties of pure and doped manganese clusters relevance to the IIIV semiconductor ferromagnetism Mukul Kabir Theoretical Condensed Matter Group S. N. Bose National Centre for
Electronic and Magnetic properties of pure and doped manganese clusters relevance to the IIIV semiconductor ferromagnetism Mukul Kabir Theoretical Condensed Matter Group S. N. Bose National Centre for
Help me understanding the effect of organic acceptor molecules on coinage metals.
 Help me understanding the effect of organic acceptor molecules on coinage metals. Gerold M. Rangger, 1 Oliver T. Hofmann, 1 Anna M. Track, 1 Ferdinand Rissner, 1 Lorenz Romaner, 1,2 Georg Heimel, 2 Benjamin
Help me understanding the effect of organic acceptor molecules on coinage metals. Gerold M. Rangger, 1 Oliver T. Hofmann, 1 Anna M. Track, 1 Ferdinand Rissner, 1 Lorenz Romaner, 1,2 Georg Heimel, 2 Benjamin
Chapter 1 Semiconductor basics
 Chapter 1 Semiconductor basics ELEC-H402/CH1: Semiconductor basics 1 Basic semiconductor concepts Semiconductor basics Semiconductors, silicon and hole-electron pair Intrinsic silicon properties Doped
Chapter 1 Semiconductor basics ELEC-H402/CH1: Semiconductor basics 1 Basic semiconductor concepts Semiconductor basics Semiconductors, silicon and hole-electron pair Intrinsic silicon properties Doped
CHAPTER 6. ELECTRONIC AND MAGNETIC STRUCTURE OF ZINC-BLENDE TYPE CaX (X = P, As and Sb) COMPOUNDS
 143 CHAPTER 6 ELECTRONIC AND MAGNETIC STRUCTURE OF ZINC-BLENDE TYPE CaX (X = P, As and Sb) COMPOUNDS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Almost the complete search for possible magnetic materials has been performed utilizing
143 CHAPTER 6 ELECTRONIC AND MAGNETIC STRUCTURE OF ZINC-BLENDE TYPE CaX (X = P, As and Sb) COMPOUNDS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Almost the complete search for possible magnetic materials has been performed utilizing
Mat E 272 Lecture 25: Electrical properties of materials
 Mat E 272 Lecture 25: Electrical properties of materials December 6, 2001 Introduction: Calcium and copper are both metals; Ca has a valence of +2 (2 electrons per atom) while Cu has a valence of +1 (1
Mat E 272 Lecture 25: Electrical properties of materials December 6, 2001 Introduction: Calcium and copper are both metals; Ca has a valence of +2 (2 electrons per atom) while Cu has a valence of +1 (1
Solid State Spectroscopy Problem Set 7
 Solid State Spectroscopy Problem Set 7 Due date: June 29th, 2015 Problem 5.1 EXAFS Study of Mn/Fe substitution in Y(Mn 1-x Fe x ) 2 O 5 From article «EXAFS, XANES, and DFT study of the mixed-valence compound
Solid State Spectroscopy Problem Set 7 Due date: June 29th, 2015 Problem 5.1 EXAFS Study of Mn/Fe substitution in Y(Mn 1-x Fe x ) 2 O 5 From article «EXAFS, XANES, and DFT study of the mixed-valence compound
Basic Semiconductor Physics
 6 Basic Semiconductor Physics 6.1 Introduction With this chapter we start with the discussion of some important concepts from semiconductor physics, which are required to understand the operation of solar
6 Basic Semiconductor Physics 6.1 Introduction With this chapter we start with the discussion of some important concepts from semiconductor physics, which are required to understand the operation of solar
ECE 335: Electronic Engineering Lecture 2: Semiconductors
 Faculty of Engineering ECE 335: Electronic Engineering Lecture 2: Semiconductors Agenda Intrinsic Semiconductors Extrinsic Semiconductors N-type P-type Carrier Transport Drift Diffusion Semiconductors
Faculty of Engineering ECE 335: Electronic Engineering Lecture 2: Semiconductors Agenda Intrinsic Semiconductors Extrinsic Semiconductors N-type P-type Carrier Transport Drift Diffusion Semiconductors
The Structural Disorder and Lattice Stability of (Ba,Sr)(Co,Fe)O 3 Complex Perovskites
 The Structural Disorder and Lattice Stability of (Ba,Sr)(Co,Fe)O 3 Complex Perovskites M.M. Kuklja a, Yu. A. Mastrikov a,b, S.N. Rashkeev c, and E.A. Kotomin b,d a Materials Science and Engineering Department,
The Structural Disorder and Lattice Stability of (Ba,Sr)(Co,Fe)O 3 Complex Perovskites M.M. Kuklja a, Yu. A. Mastrikov a,b, S.N. Rashkeev c, and E.A. Kotomin b,d a Materials Science and Engineering Department,
Electronic Structure Theory for Periodic Systems: The Concepts. Christian Ratsch
 Electronic Structure Theory for Periodic Systems: The Concepts Christian Ratsch Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics and Department of Mathematics, UCLA Motivation There are 10 20 atoms in 1 mm 3
Electronic Structure Theory for Periodic Systems: The Concepts Christian Ratsch Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics and Department of Mathematics, UCLA Motivation There are 10 20 atoms in 1 mm 3
Doping properties of C, Si, and Ge impurities in GaN and AlN
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 56, NUMBER 15 15 OCTOBER 1997-I Doping properties of C, Si, and Ge impurities in GaN and AlN P. Bogusławski Department of Physics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 56, NUMBER 15 15 OCTOBER 1997-I Doping properties of C, Si, and Ge impurities in GaN and AlN P. Bogusławski Department of Physics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North
Electronic Supporting Information for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supporting Information for Probing the Energy Levels in Hole-doped Molecular
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supporting Information for Probing the Energy Levels in Hole-doped Molecular
Propensity of Different AgBr Surfaces for Photoinduced Silver Cluster Formation: A Molecular Orbital Analysis
 8184 J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 8184-8190 Propensity of Different AgBr Surfaces for Photoinduced Silver Cluster Formation: A Molecular Orbital Analysis Pradeep Gutta and Roald Hoffmann* Department of
8184 J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 8184-8190 Propensity of Different AgBr Surfaces for Photoinduced Silver Cluster Formation: A Molecular Orbital Analysis Pradeep Gutta and Roald Hoffmann* Department of
Defect structure and oxygen diffusion in PZT ceramics
 Defect structure and oxygen diffusion in PZT ceramics Adam Georg Balogh Institute of Materials Science Technische Universität Darmstadt A. G. Balogh Folie 1 Introduction Ferroelectrics are of great technical
Defect structure and oxygen diffusion in PZT ceramics Adam Georg Balogh Institute of Materials Science Technische Universität Darmstadt A. G. Balogh Folie 1 Introduction Ferroelectrics are of great technical
CO Adsorption Site Preference on Platinum: Charge Is the Essence
 Supporting Information CO Adsorption Site Preference on Platinum: Charge Is the Essence G.T. Kasun Kalhara Gunasooriya, and Mark Saeys *, Laboratory for Chemical Technology, Ghent University, Technologiepark
Supporting Information CO Adsorption Site Preference on Platinum: Charge Is the Essence G.T. Kasun Kalhara Gunasooriya, and Mark Saeys *, Laboratory for Chemical Technology, Ghent University, Technologiepark
Quiz #1 Practice Problem Set
 Name: Student Number: ELEC 3908 Physical Electronics Quiz #1 Practice Problem Set? Minutes January 22, 2016 - No aids except a non-programmable calculator - All questions must be answered - All questions
Name: Student Number: ELEC 3908 Physical Electronics Quiz #1 Practice Problem Set? Minutes January 22, 2016 - No aids except a non-programmable calculator - All questions must be answered - All questions
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Methods Materials Synthesis The In 4 Se 3-δ crystal ingots were grown by the Bridgeman method. The In and Se elements were placed in an evacuated quartz ampoule with an excess of In (5-10
Supplementary Methods Materials Synthesis The In 4 Se 3-δ crystal ingots were grown by the Bridgeman method. The In and Se elements were placed in an evacuated quartz ampoule with an excess of In (5-10
Chapter 11 Answers. Practice Examples
 hapter Answers Practice Examples a. There are three half-filled p orbitals on, and one half-filled 5p orbital on I. Each halffilled p orbital from will overlap with one half-filled 5p orbital of an I.
hapter Answers Practice Examples a. There are three half-filled p orbitals on, and one half-filled 5p orbital on I. Each halffilled p orbital from will overlap with one half-filled 5p orbital of an I.
Lecture 6: Individual nanoparticles, nanocrystals and quantum dots
 Lecture 6: Individual nanoparticles, nanocrystals and quantum dots Definition of nanoparticle: Size definition arbitrary More interesting: definition based on change in physical properties. Size smaller
Lecture 6: Individual nanoparticles, nanocrystals and quantum dots Definition of nanoparticle: Size definition arbitrary More interesting: definition based on change in physical properties. Size smaller
Ionic Bonding. Chem
 Whereas the term covalent implies sharing of electrons between atoms, the term ionic indicates that electrons are taken from one atom by another. The nature of ionic bonding is very different than that
Whereas the term covalent implies sharing of electrons between atoms, the term ionic indicates that electrons are taken from one atom by another. The nature of ionic bonding is very different than that
First-principles calculations of the formation and structures of point defects on GaN (0001) surface
 American Journal of Physical Chemistry 2014; 3(4): 47-53 Published online September 30, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajpc) doi: 10.11648/j.ajpc.20140304.12 ISS: 2327-2430 (Print); ISS:
American Journal of Physical Chemistry 2014; 3(4): 47-53 Published online September 30, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajpc) doi: 10.11648/j.ajpc.20140304.12 ISS: 2327-2430 (Print); ISS:
Electronic Supplementary Information for MS:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for MS: Solid State Structural Transformation of Bromide
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for MS: Solid State Structural Transformation of Bromide
Structure of Crystalline Solids
 Structure of Crystalline Solids Solids- Effect of IMF s on Phase Kinetic energy overcome by intermolecular forces C 60 molecule llotropes of Carbon Network-Covalent solid Molecular solid Does not flow
Structure of Crystalline Solids Solids- Effect of IMF s on Phase Kinetic energy overcome by intermolecular forces C 60 molecule llotropes of Carbon Network-Covalent solid Molecular solid Does not flow
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Co-doping of MOF-5 framework and its effect on gas adsorption behaviour J.A. Botas a,*, G. Calleja a, M. Sánchez-Sánchez,b, M.G. Orcajo a a Department of Chemical and Energy Technology,
Supplementary Information Co-doping of MOF-5 framework and its effect on gas adsorption behaviour J.A. Botas a,*, G. Calleja a, M. Sánchez-Sánchez,b, M.G. Orcajo a a Department of Chemical and Energy Technology,
Atomic Arrangement. Primer in Materials Spring
 Atomic Arrangement Primer in Materials Spring 2017 30.4.2017 1 Levels of atomic arrangements No order In gases, for example the atoms have no order, they are randomly distributed filling the volume to
Atomic Arrangement Primer in Materials Spring 2017 30.4.2017 1 Levels of atomic arrangements No order In gases, for example the atoms have no order, they are randomly distributed filling the volume to
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 22 Oct 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 22 Oct 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 22 Oct 2007](/thumbs/78/78401876.jpg) Conformational Transitions of Heteropolymers arxiv:0710.4095v1 [cond-mat.soft] 22 Oct 2007 Michael Bachmann and Wolfhard Janke Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Leipzig, Augustusplatz 10/11,
Conformational Transitions of Heteropolymers arxiv:0710.4095v1 [cond-mat.soft] 22 Oct 2007 Michael Bachmann and Wolfhard Janke Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Leipzig, Augustusplatz 10/11,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 10 May 1996
 Cohesive energies of cubic III-V semiconductors Beate Paulus, Peter Fulde Max-Planck-Institut für Physik komplexer Systeme, Bayreuther Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany arxiv:cond-mat/9605064v1 10 May 1996
Cohesive energies of cubic III-V semiconductors Beate Paulus, Peter Fulde Max-Planck-Institut für Physik komplexer Systeme, Bayreuther Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany arxiv:cond-mat/9605064v1 10 May 1996
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (1 Mark)
 UNIT I 10 Chemistry-XII THE SOLID STATE VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (1 Mark) Q. 1. What do you mean by paramagnetic substance? Ans. Weakly attracted by magnetic eld and these substances are made of
UNIT I 10 Chemistry-XII THE SOLID STATE VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (1 Mark) Q. 1. What do you mean by paramagnetic substance? Ans. Weakly attracted by magnetic eld and these substances are made of
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics
 Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Bonding and structure of ceramic materials as compared with metals Chapter 12-1 Atomic Bonding in Ceramics Bonding: -- Can be ionic
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Bonding and structure of ceramic materials as compared with metals Chapter 12-1 Atomic Bonding in Ceramics Bonding: -- Can be ionic
Multi-Scale Modeling from First Principles
 m mm Multi-Scale Modeling from First Principles μm nm m mm μm nm space space Predictive modeling and simulations must address all time and Continuum Equations, densityfunctional space scales Rate Equations
m mm Multi-Scale Modeling from First Principles μm nm m mm μm nm space space Predictive modeling and simulations must address all time and Continuum Equations, densityfunctional space scales Rate Equations
Adsorption of Atomic H and O on the (111) Surface of Pt 3 Ni Alloys
 J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 8311-8323 8311 Adsorption of Atomic H and O on the (111) Surface of Pt 3 Ni Alloys Timo Jacob and William A. Goddard, III* Materials and Process Simulation Center, Beckman Institute
J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 8311-8323 8311 Adsorption of Atomic H and O on the (111) Surface of Pt 3 Ni Alloys Timo Jacob and William A. Goddard, III* Materials and Process Simulation Center, Beckman Institute
CHEM1902/ N-2 November 2014
 CHEM1902/4 2014-N-2 November 2014 The cubic form of boron nitride (borazon) is the second-hardest material after diamond and it crystallizes with the structure shown below. The large spheres represent
CHEM1902/4 2014-N-2 November 2014 The cubic form of boron nitride (borazon) is the second-hardest material after diamond and it crystallizes with the structure shown below. The large spheres represent
Supplementary material: The origin of the measured chemical shift of 129 Xe in UiO-66 and UiO-67 revealed by DFT investigations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Supplementary material: The origin of the measured chemical shift of 129 Xe in
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Supplementary material: The origin of the measured chemical shift of 129 Xe in
SaifulIslam. Chemistry, Surrey April, Protons & Dopants. in Oxide Materials
 Protons & Dopants Chemistry, Surrey in Oxide Materials Outline Background & Methods Proton conductors: AZrO 3 ; ACeO 3 perovskite-type Proton transport Dopant sites Proton-dopant interactions Non-stoichiometry
Protons & Dopants Chemistry, Surrey in Oxide Materials Outline Background & Methods Proton conductors: AZrO 3 ; ACeO 3 perovskite-type Proton transport Dopant sites Proton-dopant interactions Non-stoichiometry
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers CHAPTER 2. Nature of Materials
 Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers CHAPTER 2 Nature of Materials Bonds 1. Primary Bond: forms when atoms interchange or share electrons in order to fill the outer (valence) shells like noble
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers CHAPTER 2 Nature of Materials Bonds 1. Primary Bond: forms when atoms interchange or share electrons in order to fill the outer (valence) shells like noble
Electrons, Holes, and Defect ionization
 Electrons, Holes, and Defect ionization The process of forming intrinsic electron-hole pairs is excitation a cross the band gap ( formation energy ). intrinsic electronic reaction : null e + h When electrons
Electrons, Holes, and Defect ionization The process of forming intrinsic electron-hole pairs is excitation a cross the band gap ( formation energy ). intrinsic electronic reaction : null e + h When electrons
Supplementary information: Topological Properties Determined by Atomic Buckling in Self-Assembled Ultrathin Bi (110)
 Supplementary information: Topological Properties Determined by Atomic Buckling in Self-Assembled Ultrathin Bi (110) Yunhao Lu, *,, Wentao Xu, Mingang Zeng, Guanggeng Yao, Lei Shen, Ming Yang, Ziyu Luo,
Supplementary information: Topological Properties Determined by Atomic Buckling in Self-Assembled Ultrathin Bi (110) Yunhao Lu, *,, Wentao Xu, Mingang Zeng, Guanggeng Yao, Lei Shen, Ming Yang, Ziyu Luo,
Properties of Individual Nanoparticles
 TIGP Introduction technology (I) October 15, 2007 Properties of Individual Nanoparticles Clusters 1. Very small -- difficult to image individual nanoparticles. 2. New physical and/or chemical properties
TIGP Introduction technology (I) October 15, 2007 Properties of Individual Nanoparticles Clusters 1. Very small -- difficult to image individual nanoparticles. 2. New physical and/or chemical properties
Lecture 30: Kinetics of Epitaxial Growth: Surface Diffusion and
 Lecture 30: Kinetics of Epitaxial Growth: Surface Diffusion and Nucleation Today s topics Understanding the basics of epitaxial techniques used for surface growth of crystalline structures (films, or layers).
Lecture 30: Kinetics of Epitaxial Growth: Surface Diffusion and Nucleation Today s topics Understanding the basics of epitaxial techniques used for surface growth of crystalline structures (films, or layers).
2 Fundamentals of Flash Lamp Annealing of Shallow Boron-Doped Silicon
 2 Fundamentals of Flash Lamp Annealing of Shallow Boron-Doped Silicon MSA of semiconductors is usually performed using flash lamps. It has been shown that FLA holds the balance between effective dopant
2 Fundamentals of Flash Lamp Annealing of Shallow Boron-Doped Silicon MSA of semiconductors is usually performed using flash lamps. It has been shown that FLA holds the balance between effective dopant
ECE 442. Spring, Lecture -2
 ECE 442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated circuits Spring, 2006 University of Illinois at Chicago Lecture -2 Semiconductor physics band structures and charge carriers 1. What are the types of
ECE 442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated circuits Spring, 2006 University of Illinois at Chicago Lecture -2 Semiconductor physics band structures and charge carriers 1. What are the types of
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Region mapping. a Pristine and b Mn-doped Bi 2 Te 3. Arrows point at characteristic defects present on the pristine surface which have been used as markers
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Region mapping. a Pristine and b Mn-doped Bi 2 Te 3. Arrows point at characteristic defects present on the pristine surface which have been used as markers
Final Exam, MENA3000 / MENA4000 Functional Materials, 6 th June 2016
 Final Exam, MENA3000 / MENA4000 Functional Materials, 6 th June 2016 Task 1 Crystal structure, chemical bonding and non-stoichiometry (25 %) For one of the modifications of molybdenum disulphide, MoS 2,
Final Exam, MENA3000 / MENA4000 Functional Materials, 6 th June 2016 Task 1 Crystal structure, chemical bonding and non-stoichiometry (25 %) For one of the modifications of molybdenum disulphide, MoS 2,
Facet Effect of Single-Crystalline Ag 3 PO 4 Sub-microcrystals on Photocatalytic Properties. Experimental Section
 Supporting Information for Facet Effect of Single-Crystalline Ag 3 PO 4 Sub-microcrystals on Photocatalytic Properties Yingpu Bi, Shuxin Ouyang, Naoto Umezawa, Junyu Cao, and Jinhua Ye* International Center
Supporting Information for Facet Effect of Single-Crystalline Ag 3 PO 4 Sub-microcrystals on Photocatalytic Properties Yingpu Bi, Shuxin Ouyang, Naoto Umezawa, Junyu Cao, and Jinhua Ye* International Center
Supplementary information for: Making graphene. nanoribbons photoluminescent
 Supplementary information for: Making graphene nanoribbons photoluminescent B.V. Senkovskiy,,,@ M. Pfeiffer,,@ S.K. Alavi,,,@ A. Bliesener, J. Zhu, S. Michel, A.V. Fedorov,,, R. German, D. Hertel, D. Haberer,
Supplementary information for: Making graphene nanoribbons photoluminescent B.V. Senkovskiy,,,@ M. Pfeiffer,,@ S.K. Alavi,,,@ A. Bliesener, J. Zhu, S. Michel, A.V. Fedorov,,, R. German, D. Hertel, D. Haberer,
1-amino-9-octadecene, HAuCl 4, hexane, ethanol 55 o C, 16h AuSSs on GO
 Supplementary Figures GO Supplementary Figure S1 1-amino-9-octadecene, HAuCl 4, hexane, ethanol 55 o C, 16h AuSSs on GO Schematic illustration of synthesis of Au square sheets on graphene oxide sheets.
Supplementary Figures GO Supplementary Figure S1 1-amino-9-octadecene, HAuCl 4, hexane, ethanol 55 o C, 16h AuSSs on GO Schematic illustration of synthesis of Au square sheets on graphene oxide sheets.
NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION REVIEW COPY. Na 2 IrO 3 as a molecular orbital crystal
 Na 2 IrO 3 as a molecular orbital crystal I. I. Mazin, 1 Harald O. Jeschke, 2 Kateryna Foyevtsova, 2 Roser Valentí, 2 and D. I. Khomskii 3 1 Code 6393, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC 237, USA
Na 2 IrO 3 as a molecular orbital crystal I. I. Mazin, 1 Harald O. Jeschke, 2 Kateryna Foyevtsova, 2 Roser Valentí, 2 and D. I. Khomskii 3 1 Code 6393, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC 237, USA
Effects of substitutions of C atoms by Al and N in the w-aln compound
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of substitutions of C atoms by Al and N in the w-aln compound To cite this article: J F Murillo et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 687 012114
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of substitutions of C atoms by Al and N in the w-aln compound To cite this article: J F Murillo et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 687 012114
EPSC501 Crystal Chemistry WEEK 5
 EPSC501 Crystal Chemistry WEEK 5 Oxidation states of transition elements (many more in aqueous solutions than in the common rock-forming minerals) Notice that almost every transition metal has a +2 oxidation
EPSC501 Crystal Chemistry WEEK 5 Oxidation states of transition elements (many more in aqueous solutions than in the common rock-forming minerals) Notice that almost every transition metal has a +2 oxidation
Atomic structure and stability of AlN 0001 and 0001 surfaces
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 20 15 MAY 1997-II Atomic structure and stability of AlN 0001 and 0001 surfaces John E. Northrup and R. Di Felice Xerox Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 20 15 MAY 1997-II Atomic structure and stability of AlN 0001 and 0001 surfaces John E. Northrup and R. Di Felice Xerox Palo Alto Research Center, 3333 Coyote Hill Road,
per unit cell Motif: Re at (0, 0, 0); 3O at ( 1 / 2, 0), (0, 0, 1 / 2 ) Re: 6 (octahedral coordination) O: 2 (linear coordination) ReO 6
 Lattice: Primitive Cubic 1ReO 3 per unit cell Motif: Re at (0, 0, 0); 3O at ( 1 / 2, 0, 0), (0, 1 / 2, 0), (0, 0, 1 / 2 ) Re: 6 (octahedral coordination) O: 2 (linear coordination) ReO 6 octahedra share
Lattice: Primitive Cubic 1ReO 3 per unit cell Motif: Re at (0, 0, 0); 3O at ( 1 / 2, 0, 0), (0, 1 / 2, 0), (0, 0, 1 / 2 ) Re: 6 (octahedral coordination) O: 2 (linear coordination) ReO 6 octahedra share
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Microstructure, morphology and chemical composition of the carbon microspheres: (a) A SEM image of the CM-NFs; and EDS spectra of CM-NFs (b), CM-Ns (d) and
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Microstructure, morphology and chemical composition of the carbon microspheres: (a) A SEM image of the CM-NFs; and EDS spectra of CM-NFs (b), CM-Ns (d) and
Defects in TiO 2 Crystals
 , March 13-15, 2013, Hong Kong Defects in TiO 2 Crystals Richard Rivera, Arvids Stashans 1 Abstract-TiO 2 crystals, anatase and rutile, have been studied using Density Functional Theory (DFT) and the Generalized
, March 13-15, 2013, Hong Kong Defects in TiO 2 Crystals Richard Rivera, Arvids Stashans 1 Abstract-TiO 2 crystals, anatase and rutile, have been studied using Density Functional Theory (DFT) and the Generalized
