MUNISH KAKAR s INSTITUTE OF CHEMISTRY
|
|
|
- Jared Strickland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REACTONS & PREPARATON OF HALOGENATED COMPDS. WS#3 Q1. Reagent for preparing a chloroalkane from an alcohol is (a) SOCl 2 (b) HCl/ZnCl 2 (c) PCl 3 (d) All of these Q2. n the addition of H to propene in the absence of peroxides, the first step involves the addition of (a) H + (b) - (c) H (d) Q3. When propene is heated at 800 o C in the presence of chlorine, it gives the following compound: (a) Polyvinyl chloride (b) No reaction (c) 1,2-Dichloropropane (d) Allyl chloride Q4. Toluene reacts with chlorine in the presence of light to give (a) Benzyl chloride (b) Benzoyl chloride (c) p-chlorotoluene (d) o-chlorotoluene Q5. The compound which reacts with H obeying Markownikov s rule is (a) 2 = 2 (b) cis-2-butene (c) trans-2-butene (d) () 2C = 2 Q6. Alcoholic solution of KOH is a specific reagent for (a) dehydration (b) dehalogenation (c) dehydrohalogenation (d) dehydrogenation Q7. The most reactive among the given compounds is: (a) 2 = Cl (b) 2 = 2Cl (c) 2Cl (d) C 6H 5Cl Q8. Anti-Markownikov addition of H is not observed in (a) Propene (b) 1-Butene (c) 2-Butene (d) 2-Pentene Q9. Alkyl halides can be converted to alkenes by (a) substitution (b) addition (c) elimination (d) rearrangement Q10. When hydrochloric acid gas is treated with propene in presence of benzoyl peroxide, it gives (a) 2-Chloropropane (b) Allyl chloride (c) no reaction (d) n-propyl chloride Q11. S N2 mechanism proceeds through the intervention of (a) carbocation (b) transition state (c) free radical (d) carbanion Q12. Silver benzoate reacts with bromine to (a) C 6H 6 (b) C 6H 5COO (c) m--c 6H 4-COOAg (d) C 6H 5 Q13. n the following groups: -OAc() -OMe() -OSO 2Me() -OSO 2CF 3(V) the order of leaving group ability is (a) > > > V (b) V > > > (c) > > > V (d) > > V > Q14. The intermediate during the addition of HCl to propene in presence of peroxide is
2 (a) C H 2Cl (b) C H (c) 2 C H 3 (d) 2 C H 2 Q15. 2-omopentane is heated with potassium hydroxide in ethanol. The major product obtained is ; (a) 2-Ethoxypentane (c) cis-pent-2-ene (b) Pent-1-ene (d) trans-pent-2-ene Q16. The reaction, COOAg + 2 CCl + CO 2 + Ag is known as 4 a) Finkelsteijn reaction b) Frankland reaction c) Hunsdiecker reaction d) Sandmeyer reaction Q17. Which among the following halogen can be easily displaced as halide by an added nucleophile in 1-omo-4-chloro-2-iodo-3,5-dinitrobenzene? a) odine b)omine c)chlorine d) all of these Q18. The addition of H is easiest with (a) 2 = Cl (b) Cl = Cl (c) -= 2 (d) () 2C= 2 Q19. S N1 reaction of alkyl halides leads to (a) retention of configuration (c) inversion of configuration (b) racemisation (d) none of these Q20. Which of the following has the highest nucleophilicity? (a) F - (b) OH - (c) 3 (d) NH 2 Q21. dentify the set of reagent/reaction conditions X and Y in the following set of transformations: Product X Y (a) X = dilute aqueous NaOH, 20 o C Y = H/acetic acid, 20 o C (b) X = concentrated alcoholic NaOH, 80 o C (c) X = dilute aqueous NaOH, 20 o C (d) X = concentrated alcoholic NaOH, 80 o C Y = H/acetic acid, 20 o C Y = 2/Cl 3, 0 o C Y = 2/Cl 3, 0 o C Q22. The order of reactivity of alkyl halides towards elimination reaction is (a) 3 o > 2 o > 1 o (b) 2 o > 1 o > 3 o (c) 3 o > 1 o > 2 o (d) 1 o > 2 o > 3 o Q23. Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution reaction? (a) 2 = Cl (b) 2Cl (c) 2 = 2Cl (d) () 3C-Cl Q24. Among the following the most reactive towards alcoholic KOH is
3 (a) 2 = (b) CO 2 2 (c) 2 (d) 2 2 Q25. Elimination of bromine from 2-bromobutane results in the formation of (a) predominantly 2-butyne (c) predominantly 2-butene (b) predominantly 1-butene (d) equimolar mixture of 1 and 2-butene Q26. Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by S N1 mechanism? (a) Ethyl chloride (b) sopropyl chloride (c) Chlorobenzene (d) Benzyl chloride Q27. The structure of the major product formed in the following reaction 2 Cl NaCN DMF is 2 CN 2 Cl 2 Cl 2 CN NC (a) CN (b) (c) CN (d) H 3 C 2 + H A Q28. A (predominantly) is ; (a) (b) 2 2 C 2 (c) (d) Q29. The organic chlorocompound, which shows complete stereochemical inversion during of S N 2 reaction, is: (a) Cl (b) (C 2H 5) 2Cl (c) () 3CCl (d) () 2Cl Q30. The major product of the following reaction is
4 Ans : (a) Q31. Which of the following halides would undergo nucleophilic substitution most readily? a) 1-Chloro-1-butene b)2-chloro- 1-butene c) 3-Chloro-1-butene d)4-chloro-1-butene. Q32. When tert-butyl bromide is treated with sodium methoxide in methanol, the major product obtained is ; a) 2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane b) 1-Methoxy-2- methylpropane c) 2-Methylpropene d) Dimethyl ether. Q33. Which is more reactive towards the reactions specified below? a) Chloro cyclohexane or Chlorobenzene ( nucleophilc substitution ) Chloro cyclohexane 1 b) tert. butyl bromide or iso- butyl bromide ( SN mechanism.) tert. butyl bromide 2 c) 2 omobutane or 1 omobutane ( SN mechanism ) 1 omobutane 1 d) 2 omo 2 methylbutane or 2 omobuatne ( E mechanism ) 2 omo 2 methylbutane Q34. Complete the following reactions ; P3 a C OH b) Bu tan 2 ol? conc. HCl ) ( 3) 3? c Methylbu ol SOCl2 ) 3 tan 1? Pyridine Ans : (a) ( 3) 3C Cl (b) 3 ( ) 2 3 (c) 1-Chloro-3-methylbutane Q35. Why an alkyl halide forms different products on reacting with KCN and AgCN separately?
5 CN is an ambident nucelophile. As KCN is ionic hence, CN shows nucelophilic action through carbon. As AgCN is covalent hence CN shows nucleophilic action through nitrogen Q36. Explain the following: (a) Alkyl iodides become darken on standing in presence of light. n Alkyl iodide, C - bond is very weak hence it is easily broken to liberate 2. (b) Vinyl halide is less reactive while allyl halide is more reactive than alkyl halides. n vinyl halide halogen is attached to sp 2 hybridized carbon while in alkyl halide halogen is attached to sp 3 carbon. Due to this reason carbon halogen bond in vinyl halide is stronger than in alkyl halide. (c) 2-Chloro-3-methylbutane on treatment with alcoholic potash gives 2-methylbut-2-ene as the major product. Alc. KOH behaves as base and has chance of rearrangement. Due to this reason2- Methylbut-2-ene is obtained as major product
Indian School Muscat. Chemistry IIT - JEE
 Indian School Muscat Chemistry IIT - JEE HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES 1. Which one of the following is not formed when a mixture of methyl bromide and bromobenzene is heated with sodium metal in the presence
Indian School Muscat Chemistry IIT - JEE HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES 1. Which one of the following is not formed when a mixture of methyl bromide and bromobenzene is heated with sodium metal in the presence
Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes
 alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Elimination. 148 minutes. 145 marks. Page 1 of 22
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
 Unit - 10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES 1. Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds. Br CH = CH C CH (vi) (vii) (ix) (CCl 3 ) 3 CCl 103 XII Chemistry 2. Write the structure of following halogen compounds
Unit - 10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES 1. Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds. Br CH = CH C CH (vi) (vii) (ix) (CCl 3 ) 3 CCl 103 XII Chemistry 2. Write the structure of following halogen compounds
Chapter 10- Halo Alkanes and Halo arenes LEVEL-1 QUESTIONS
 Chapter 10- Halo Alkanes and Halo arenes LEVEL-1 QUESTIONS 1. Out of PCl5 and SOCl2 which one is better reagent for conversion of alcohol to alkylchloride. Why? Answer: SOCl2.Because all the biproducts
Chapter 10- Halo Alkanes and Halo arenes LEVEL-1 QUESTIONS 1. Out of PCl5 and SOCl2 which one is better reagent for conversion of alcohol to alkylchloride. Why? Answer: SOCl2.Because all the biproducts
Alkenes. Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents
 Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES. 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction....
 EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS. Chapterwise Previous year Qs. (a) Na (b) HCl in H2O (c) KOH in C2H5OH (d) Zn in alcohol. Ans: (c)
 122 CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS 1. Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989] Sigma electron density of C Hbond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s- character Acetylene has only open hydrogen
122 CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS 1. Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989] Sigma electron density of C Hbond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s- character Acetylene has only open hydrogen
REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2)
 REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2) 1.) Why do haloalkenes under go nucleophillic substitution whereas haloarenes under go electophillic substitution. Ans. Due to more electro negative
REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2) 1.) Why do haloalkenes under go nucleophillic substitution whereas haloarenes under go electophillic substitution. Ans. Due to more electro negative
UNIT.10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
 UNIT.10 ALOALKANES AND ALOARENES ONE MARKS QUESTIONS 1. What are haloalkanes? aloalkane is a derivative obtained by replacing hydrogen atom of alkane by halogen atom. 2. What is the hybridization of the
UNIT.10 ALOALKANES AND ALOARENES ONE MARKS QUESTIONS 1. What are haloalkanes? aloalkane is a derivative obtained by replacing hydrogen atom of alkane by halogen atom. 2. What is the hybridization of the
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES. Vikasana - CET 2012
 CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Nucleophilic Substitution. 267 minutes. 264 marks. Page 1 of 36
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
8. What is the slow, rate-determining step, in the acidcatalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-2-propanol?
 CHEMISTRY 313-03 MIDTERM # 2 answer key October 25, 2011 Statistics: Average: 68 pts (68%); Highest: 100 pts (100%); Lowest: 30 pts (30%) Number of students performing at or above average: 56 (54%) Number
CHEMISTRY 313-03 MIDTERM # 2 answer key October 25, 2011 Statistics: Average: 68 pts (68%); Highest: 100 pts (100%); Lowest: 30 pts (30%) Number of students performing at or above average: 56 (54%) Number
Elimination Reactions:
 Elimination Reactions: These are just reverse of addition reactions. These involve the removal of atoms or group of atoms from a molecule. Elimination reactions are generally endothermic and take place
Elimination Reactions: These are just reverse of addition reactions. These involve the removal of atoms or group of atoms from a molecule. Elimination reactions are generally endothermic and take place
The C-X bond gets longerand weakergoing down the periodic table.
 Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
1) (100 pts) 5) (20 pts) 3) (35 pts) 4) (25pts. Total (200 pts) More Tutorial at
 Name: Perm number: Question 1) (100 pts) 2) (20 pts) 3) (35 pts) 4) (25pts 5) (20 pts) Total (200 pts) Your score 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Name: Perm number: Question 1) (100 pts) 2) (20 pts) 3) (35 pts) 4) (25pts 5) (20 pts) Total (200 pts) Your score 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions
 Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
2311A and B Practice Problems to help Prepare for Final from Previous Marder Exams.
 2311A and B Practice Problems to help Prepare for Final from Previous Marder Exams. Disclaimer.: Use only to help learn what you need to know and don t expect the final to be in the same form. 1 1. Short
2311A and B Practice Problems to help Prepare for Final from Previous Marder Exams. Disclaimer.: Use only to help learn what you need to know and don t expect the final to be in the same form. 1 1. Short
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI-87
 (iv) benzene 1 Chloromethyl 3 (2, 2 dimethylpropyl) Q1 Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system. (CH 3 ) 3 CCH 2 CH(Br)C 6 H 5 CH 3 C(C 2 H 5 ) 2 CH 2 Br CH 3 CH=CHC(Br)(CH 3 ) 2 (iv) o-br-c
(iv) benzene 1 Chloromethyl 3 (2, 2 dimethylpropyl) Q1 Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system. (CH 3 ) 3 CCH 2 CH(Br)C 6 H 5 CH 3 C(C 2 H 5 ) 2 CH 2 Br CH 3 CH=CHC(Br)(CH 3 ) 2 (iv) o-br-c
FOURTH EXAMINATION. (1)..20 pts... (2)..24 pts... (3)..18 pts... (4)..12 pts... (5)..12 pts... (6).. 6 pts... (7).. 8 pts... Bonus 4 pts...
 Name: CHEM 331 FURTH EXAMINATIN All answers should be written on the exam in the spaces provided. Clearly indicate your answers in the spaces provided; if I have to guess as to what or where your answer
Name: CHEM 331 FURTH EXAMINATIN All answers should be written on the exam in the spaces provided. Clearly indicate your answers in the spaces provided; if I have to guess as to what or where your answer
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide.
 Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
H H C C. Alkenes C n H 2n unsaturated hydrocarbons. C 2 H 4 ethylene. Functional group = carbon-carbon double bond
 Alkenes C n H 2n unsaturated hydrocarbons C 2 H 4 ethylene H H C C H H Functional group = carbon-carbon double bond sp 2 hybridization => flat, 120 o bond angles σ bond & π bond => H 2 C=CH 2 No rotation
Alkenes C n H 2n unsaturated hydrocarbons C 2 H 4 ethylene H H C C H H Functional group = carbon-carbon double bond sp 2 hybridization => flat, 120 o bond angles σ bond & π bond => H 2 C=CH 2 No rotation
Chapter: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
 Characteristics of halo compounds. Chapter: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question 1 Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:(ch 3 ) 3 CCH 2 Br The IUPAC name of the given structure is 2, 2-Dimethylbromopropane.
Characteristics of halo compounds. Chapter: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question 1 Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:(ch 3 ) 3 CCH 2 Br The IUPAC name of the given structure is 2, 2-Dimethylbromopropane.
CHEM 2312 practice final. Version - II
 EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES. Vikasana - CET 2012
 CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
Hydrogen iodide is a strong acid and will drive the reverse reaction, meaning the forward reaction will not occur.
 EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION
 REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
When 2-bromopentane reacts with ethanolic KOH, two structurally isomeric alkenes are formed.
 Q1. Organic reaction mechanisms help chemists to understand how the reactions of organic compounds occur. The following conversions illustrate a number of different types of reaction mechanism. (a) When
Q1. Organic reaction mechanisms help chemists to understand how the reactions of organic compounds occur. The following conversions illustrate a number of different types of reaction mechanism. (a) When
Part I. Multiple choice. (4 points each.) Choose the one best answer and mark your answer on the ScanTron sheet.
 Test 3 Chemistry 2321 April 25, 2003 McMurry, Chapters 9-11 103 Total Points Name Please Print Part I. Multiple choice. (4 points each.) Choose the one best answer and mark your answer on the ScanTron
Test 3 Chemistry 2321 April 25, 2003 McMurry, Chapters 9-11 103 Total Points Name Please Print Part I. Multiple choice. (4 points each.) Choose the one best answer and mark your answer on the ScanTron
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI - 87
 HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Chemistry 2321 Last name, First name (please print) April 22, 2008 McMurry, Chapters 10 and 11 Row # Seat #
 Test 4 Name Chemistry 2321 Last name, First name (please print) April 22, 2008 McMurry, Chapters 10 and 11 Row # Seat # Part 1. Multiple Choice. Choose the one best answer, and clearly mark that answer
Test 4 Name Chemistry 2321 Last name, First name (please print) April 22, 2008 McMurry, Chapters 10 and 11 Row # Seat # Part 1. Multiple Choice. Choose the one best answer, and clearly mark that answer
CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
 CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Nature of C-X bond in alkyl halides: X is more electronegative than carbon. So, the C-X bond is polarized with C having
CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Nature of C-X bond in alkyl halides: X is more electronegative than carbon. So, the C-X bond is polarized with C having
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
MOSTLY ALCOHOLS. Question 2, 2017 The structure of a molecule of an organic compound, threonine, is shown below.
 MOSTLY ALCOHOLS Modified Question 1, 2017 A chemistry class was learning about the chemistry of haloalkanes. They were researching the effect of heat and concentrated potassium hydroxide in ethanol, conc.
MOSTLY ALCOHOLS Modified Question 1, 2017 A chemistry class was learning about the chemistry of haloalkanes. They were researching the effect of heat and concentrated potassium hydroxide in ethanol, conc.
Chemistry 2.5 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence Working to Excellence
 Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Two stereoisomers of but-2-ene are formed when 2-bromobutane reacts with ethanolic potassium hydroxide
 Q1. (a) Name and outline a mechanism for the reaction of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane with ethanolic potassium hydroxide to form the alkene 2-methylpropene, (CH 3) 2C=CH 2 Name of mechanism... Mechanism (4)
Q1. (a) Name and outline a mechanism for the reaction of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane with ethanolic potassium hydroxide to form the alkene 2-methylpropene, (CH 3) 2C=CH 2 Name of mechanism... Mechanism (4)
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
a. (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(Cl)CH 3 b. CH 3 CH 2 CH(CH 3 )CH(C 2 H 5 )Cl c. CH 3 CH 2 C(CH 3 ) 2 CH 2 I d. (CH 3 ) 3 CCH 2 CH(Br)C 6 H 5.
 1. Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides: a. (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(Cl)CH 3 b. CH 3 CH 2 CH(CH 3 )CH(C
1. Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides: a. (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(Cl)CH 3 b. CH 3 CH 2 CH(CH 3 )CH(C
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Physical Properties: Structure:
 Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
 Unit - 11 ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS 1. Write IUPAC names of the following compounds : (ix) C 6 H 5 OC 3 H 7 (x) O Cl 2. Write the structures of the compounds whose names are given below : (i) 3, 5-dimethoxyhexane-1,
Unit - 11 ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS 1. Write IUPAC names of the following compounds : (ix) C 6 H 5 OC 3 H 7 (x) O Cl 2. Write the structures of the compounds whose names are given below : (i) 3, 5-dimethoxyhexane-1,
1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below?
 1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below? 2. Which of the following does not have an octet of electrons surrounding the central atom? A. B 3 B. C
1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below? 2. Which of the following does not have an octet of electrons surrounding the central atom? A. B 3 B. C
Elimination Reactions Heating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a. molecule of HX
 Elimination eactions eating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a molecule of X 1. Potassium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol and the sodium salts of alcohols (such as sodium ethoxide)
Elimination eactions eating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a molecule of X 1. Potassium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol and the sodium salts of alcohols (such as sodium ethoxide)
Test Date: (Sunday) Test Time: 1:00 pm to 2:00 pm Test Venue: Lajpat Bhawan, Madhya Marg, Sector 15-B, Chandigarh
 Test ate: 1.09.015 (Sunday) Test Time: 1:00 pm to :00 pm Test Venue: Lajpat hawan, Madhya Marg, Sector 15-, handigarh r. Sangeeta Khanna Ph. 1 EMISTRY OING IRLE G:\+ Grand test-4 L-1.doc r. Sangeeta Khanna
Test ate: 1.09.015 (Sunday) Test Time: 1:00 pm to :00 pm Test Venue: Lajpat hawan, Madhya Marg, Sector 15-, handigarh r. Sangeeta Khanna Ph. 1 EMISTRY OING IRLE G:\+ Grand test-4 L-1.doc r. Sangeeta Khanna
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade
 Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bankfororganic-chemistry-8th-edition-by-wade/ Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Test Bank Wade
Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bankfororganic-chemistry-8th-edition-by-wade/ Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Test Bank Wade
IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice
 IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice 1. What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene? 1,2-dichlorobutane 2,3-dichlorobutane 1-chlorobutane 2-chlorobutane 2. Which compound can be oxidized
IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice 1. What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene? 1,2-dichlorobutane 2,3-dichlorobutane 1-chlorobutane 2-chlorobutane 2. Which compound can be oxidized
SECTION-I (SINGLE CORRECT CHOICE)
 SECTI-I (SIGLE CRRECT CICE) 1. Which of the following phrases are not correctly associated with an S1 reaction? 1. Rearrangement is possible. 2. Rate is affected by solvent polarity. 3. The strength of
SECTI-I (SIGLE CRRECT CICE) 1. Which of the following phrases are not correctly associated with an S1 reaction? 1. Rearrangement is possible. 2. Rate is affected by solvent polarity. 3. The strength of
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Homework problems Chapters 6 and Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: CH 3 OH + H 2 C CH +
 omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
I C(CH 3 ) 3. (c)2ch 3 OH+(CH 3 ) 3 CCl (CH 3 ) 3 COCH 3 +CH 3 OH + 2 +Cl - (d) CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 Br+NaCN CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CN+NaBr
 6.1 Writer the following as net ionic reactions and designate the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group in each reaction. (a) 3 + 3 2 Na 3 2 3 +Na (b) Na+ 3 2 3 2 +Na (c) 2 3 +( 3 ) 3 ( 3 ) 3 3 + 3
6.1 Writer the following as net ionic reactions and designate the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group in each reaction. (a) 3 + 3 2 Na 3 2 3 +Na (b) Na+ 3 2 3 2 +Na (c) 2 3 +( 3 ) 3 ( 3 ) 3 3 + 3
Organic Halogen Compounds
 8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
17.3 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC ANIONS
 798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
ALKYL HALIDE & ARYL HALIDE
 QUESTION BANK--1 ALKYL ALIDE & ARYL ALIDE LEVEL I 1. SN1reaction of alkyl halides lead to (a) Retention of configuration (c) Inversion of configuration 2. The reaction 3 + O 3O + is (a) SN2 (c) SE1 (b)
QUESTION BANK--1 ALKYL ALIDE & ARYL ALIDE LEVEL I 1. SN1reaction of alkyl halides lead to (a) Retention of configuration (c) Inversion of configuration 2. The reaction 3 + O 3O + is (a) SN2 (c) SE1 (b)
Haloalkanes. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers for C 5 H 11 Br
 Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
(CH 3 ) 3 COH. CH 3 ONa
 1. Rank the following compounds in the trend requested. (15 points each) a. Rank by nucleophilicity. The strongest nucleophile is 1, while the weakest nucleophile is 5. C 3 PNa (C 3 ) 3 C C 3 Na C 3 C
1. Rank the following compounds in the trend requested. (15 points each) a. Rank by nucleophilicity. The strongest nucleophile is 1, while the weakest nucleophile is 5. C 3 PNa (C 3 ) 3 C C 3 Na C 3 C
PRACTICE PROBLEMS UNIT 8
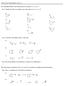 PRACTICE PROBLEMS UNIT 8 8A. Identify halides and carbocations as being 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o 8A.1 assify the following halides and carbocations as 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o. 8A.2 Circle the most stable cation in each
PRACTICE PROBLEMS UNIT 8 8A. Identify halides and carbocations as being 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o 8A.1 assify the following halides and carbocations as 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o. 8A.2 Circle the most stable cation in each
SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. The credit for synthesizing first organic compound in the laboratory went to a) Berzelius b) Wohler c) Kolbe d) Berthelot Ans : b) Wohler [Note : (i) N H 4 Cl+KCNO NH 4 CNO
SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. The credit for synthesizing first organic compound in the laboratory went to a) Berzelius b) Wohler c) Kolbe d) Berthelot Ans : b) Wohler [Note : (i) N H 4 Cl+KCNO NH 4 CNO
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions "
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Chemistry 262 Homework 2 Part II Winter 2018
 Chemistry 262 Homework 2 Part II Winter 2018 The following homework covers Chapter 10 in Loudon & Parise s Organic Chemistry, 6 th ed. and contains 24 questions, valued at 0.3333 point each, as well as
Chemistry 262 Homework 2 Part II Winter 2018 The following homework covers Chapter 10 in Loudon & Parise s Organic Chemistry, 6 th ed. and contains 24 questions, valued at 0.3333 point each, as well as
CHE 275 NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTUION CHAP 8 ASSIGN. 1. Which best depicts the partial charges on methyl bromide and sodium methoxide?
 CHE 275 NUCLEPHILIC SUBSTITUTUIN CHAP 8 ASSIGN 1. Which best depicts the partial charges on methyl bromide and sodium methoxide? 2. Which of the following would be the best (most reactive) nucleophile
CHE 275 NUCLEPHILIC SUBSTITUTUIN CHAP 8 ASSIGN 1. Which best depicts the partial charges on methyl bromide and sodium methoxide? 2. Which of the following would be the best (most reactive) nucleophile
Essential Organic Chemistry. Chapter 9
 Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
Page 2. M1.(a) P 3,3 dimethylbut 1 ene OR accept 3,3 dimethylbutene Ignore absence of commas, hyphens and gaps Require correct spelling Q OR
 M.(a) P 3,3 dimethylbut ene OR accept 3,3 dimethylbutene Ignore absence of commas, hyphens and gaps Require correct spelling Q OR 3 chloro 2,2 dimethylbutane accept 2 chloro 3,3 dimethylbutane In Q, chloro
M.(a) P 3,3 dimethylbut ene OR accept 3,3 dimethylbutene Ignore absence of commas, hyphens and gaps Require correct spelling Q OR 3 chloro 2,2 dimethylbutane accept 2 chloro 3,3 dimethylbutane In Q, chloro
TOPIC 13 ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
Replace one H with a Br for every mole of Br 2
 Substitution A substitution reaction occurs when a hydrogen atom is removed from a hydrocarbon and replaced by a halide substituent. When a bromine molecule absorbs energy, the covalent bond is broken
Substitution A substitution reaction occurs when a hydrogen atom is removed from a hydrocarbon and replaced by a halide substituent. When a bromine molecule absorbs energy, the covalent bond is broken
What is the major product of the following reaction?
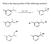 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Class XII Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Chemistry. Question 11.1: Write IUPAC names of the following compounds: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi)
 Question 11.1: Write IUPAC names of the following compounds: (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) Page 1 of 37 (ix) (x) (xi) (xii) 2, 2, 4-Trimethylpentan-3-ol 5-Ethylheptane-2, 4-diol (iii) Butane-2, 3-diol
Question 11.1: Write IUPAC names of the following compounds: (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) Page 1 of 37 (ix) (x) (xi) (xii) 2, 2, 4-Trimethylpentan-3-ol 5-Ethylheptane-2, 4-diol (iii) Butane-2, 3-diol
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Summer Semester 1999 Dr. Somnath Sarkar
 Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Summer Semester 1999 Dr. Somnath Sarkar Examination #3 Elimination Reactions Structure, Synthesis and Reactions of Alkenes and alkynes. Friday, July 23, 1999, 8:40 9:40
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Summer Semester 1999 Dr. Somnath Sarkar Examination #3 Elimination Reactions Structure, Synthesis and Reactions of Alkenes and alkynes. Friday, July 23, 1999, 8:40 9:40
10. Alkyl Halides. What Is an Alkyl Halide. An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen
 10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
trans-cyclooctene 4-fluoro-1-butanol 2-cyclohexenol 4. (5 pts) Provide structural formula for each of the following molecules: Br OH Cl OH
 CEMISTRY 313-01 MIDTERM # 2 answer key March 12, 2009 Statistics: Average: 72 pts (72%); ighest: 98 pts (98%); Lowest: 21 pts (21%) umber of students performing at or above average: 22 (50%) umber of students
CEMISTRY 313-01 MIDTERM # 2 answer key March 12, 2009 Statistics: Average: 72 pts (72%); ighest: 98 pts (98%); Lowest: 21 pts (21%) umber of students performing at or above average: 22 (50%) umber of students
2. An aldehyde can be obtained by the dehydrogenation of an alcohol. The catalyst used in the reaction is
 Class: 12 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry of O compounds No. of Questions: 20 Duration: 60 Min Maximum Marks: 60 1. Rectified spirit is converted to absolute alcohol taking advantage of the
Class: 12 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry of O compounds No. of Questions: 20 Duration: 60 Min Maximum Marks: 60 1. Rectified spirit is converted to absolute alcohol taking advantage of the
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
CHAPTER PRACTICE PROBLEMS CHEMISTRY
 APTER PRACTICE PRBLEMS EMISTRY Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Name : Batch : Date : rientation influence of groups 1. Predict the characteristics of -NH + as a substituent. activating, o/p directing
APTER PRACTICE PRBLEMS EMISTRY Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Name : Batch : Date : rientation influence of groups 1. Predict the characteristics of -NH + as a substituent. activating, o/p directing
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
PAPER No. 5: REACTION MECHANISM MODULE No. 2: Types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Q. No. 4 Chlorination of toluene in the presence of light and heat followed by treatment with aqueous NaOH gives o cresol p cresol 2, 4 dihydroxy tolu
 Q. No. 1 Glycerine has One primary and two secondary OH groups One secondary and two primary OH groups Three primary OH groups Three secondary OH groups Q. No. 2 The structural formula of cyclohexanol
Q. No. 1 Glycerine has One primary and two secondary OH groups One secondary and two primary OH groups Three primary OH groups Three secondary OH groups Q. No. 2 The structural formula of cyclohexanol
2. Which functional groups and structural features are present in the following molecule (strychnine)?
 Chapter 1-2: 1. Which of the following species has a negative charge but NO lone pair of valance shell nonbonding electrons? [all atoms have complete valance shell of electrons, but lone pairs are not
Chapter 1-2: 1. Which of the following species has a negative charge but NO lone pair of valance shell nonbonding electrons? [all atoms have complete valance shell of electrons, but lone pairs are not
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail
 Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail b-elimination Reactions Overview dehydration of alcohols: X = H; Y = OH dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: X = H; Y = Br, etc. X C
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail b-elimination Reactions Overview dehydration of alcohols: X = H; Y = OH dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: X = H; Y = Br, etc. X C
CHAPTER 3 ALKENES, ALKYNES & CONJUGATE DIENES
 CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
CH320/328 M Spring 2014
 CH320/328 M Spring 2014 HW Set #3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your
CH320/328 M Spring 2014 HW Set #3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Class: 12 Subject: chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry of O compounds No. of Questions: 20 Duration: 60 Min Maximum Marks: 60
 Class: 12 Subject: chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry of O compounds No. of Questions: 20 Duration: 60 Min Maximum Marks: 60 1. Ethylene is passed through conc. H 2 SO 4 and the product obtained is diluted
Class: 12 Subject: chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry of O compounds No. of Questions: 20 Duration: 60 Min Maximum Marks: 60 1. Ethylene is passed through conc. H 2 SO 4 and the product obtained is diluted
N_HW1 N_HW1. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this sequence?
 N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
 1 Class XII Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 1. Nature of C-X bond in alkyl halides: X is more electronegative than carbon. So, the C-X bond is polarized with C having a partial positive
1 Class XII Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 1. Nature of C-X bond in alkyl halides: X is more electronegative than carbon. So, the C-X bond is polarized with C having a partial positive
Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions
 Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions Review of Concepts Fill in the blanks below. To verify that your answers are correct, look in your textbook at the end of Chapter 7. Each of the sentences below appears
Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions Review of Concepts Fill in the blanks below. To verify that your answers are correct, look in your textbook at the end of Chapter 7. Each of the sentences below appears
3.2.9 Alkenes. Addition Reactions. 271 minutes. 268 marks. Page 1 of 35
 ..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination
 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides react with a nucleophile in one of two ways. Either they eliminate an X to form an alkene, or they undergo a substitution with the nucleophile, Nu,
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides react with a nucleophile in one of two ways. Either they eliminate an X to form an alkene, or they undergo a substitution with the nucleophile, Nu,
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
 ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
3 free radical is most stable. Q.5. A + Cl 2 hv monochloro product To maximize the yield of monochloro product in the above reaction? Cl 2 must be add
 Q.1. I II III IV IV III II I I III II IV IV II III I I II III IV The decreasing order of the anti knocking value of octane number of the following is: (I) CH 4 (II) C 2 H 6 (III) C 3 H 8 (IV) C 4 H 10
Q.1. I II III IV IV III II I I III II IV IV II III I I II III IV The decreasing order of the anti knocking value of octane number of the following is: (I) CH 4 (II) C 2 H 6 (III) C 3 H 8 (IV) C 4 H 10
Chem 30A Winter Mon March 21st
 Last Name First Name MI Student ID Number: Total Score / 200 Chem 30A Winter 2005 FINAL (180 Min) Mon March 21st Course Grade ***DO NOT OPEN THIS EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO*** ONLY ANSWERS WRITTEN
Last Name First Name MI Student ID Number: Total Score / 200 Chem 30A Winter 2005 FINAL (180 Min) Mon March 21st Course Grade ***DO NOT OPEN THIS EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO*** ONLY ANSWERS WRITTEN
Alcohols. Have seen many reactions to synthesize alcohols: In this chapter we will study reactions of the alcohols
 Alcohols ave seen many reactions to synthesize alcohols: In this chapter we will study reactions of the alcohols Oxidation Need to understand the nomenclature of organic reduction/oxidation In general
Alcohols ave seen many reactions to synthesize alcohols: In this chapter we will study reactions of the alcohols Oxidation Need to understand the nomenclature of organic reduction/oxidation In general
Chapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions
 hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
