Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination
|
|
|
- Susanna West
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides react with a nucleophile in one of two ways. Either they eliminate an X to form an alkene, or they undergo a substitution with the nucleophile, Nu, taking the place of the X. Susbstitution can occur by S N 2 or S N 1 mechanisms depending upon the conditions present. S N 2 (Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution) General Reaction: Nu: δ Nu δ Nu stands for leaving group, which is usually an X. S N 2 reactions take place in one step (concerted). The nucleophile forms a bond to the carbon at the same time that the leaving group leaves. Results in a complete inversion of configuration, which is similar to an umbrella being turned inside out. Kinetics: Since the nucleophile and alkyl halide are both involved in the Rate Determining Step (there is only one step in the reaction), the reaction is said to be bimolecular. The general rate law is: Rate = k [RX] [Nu: - ] where X = l,, I Variables affecting S N 2 Reactions: Substrate: Unhindered substrates work best. indered substrates make the transition state more crowded, contributing steric strain. This makes the energy of activation higher, which means that the number of successful collisions per unit of time is much less than for unhindered substrates. Therefore, a 1 RX would be a better S N 2 substrate than a 2 or 3 RX.
2 Leaving Group: A good leaving group is needed. The leaving group leaves as the nucleophile forms a bond with the substrate. Most leaving groups end up with a negative charge once they are displaced by the incoming nucleophile. The best leaving groups are those that can stablize the negative charge. The weakest bases are usually the best leaving groups. Poor Good Leaving Groups O - F l I TosO Leaving Group Reactivity Nucleophile: A good nucleophile is needed. Remember from chapter 5: 1. Nucleophilicity roughly parallels basicity when comparing nucleophiles that have the same attacking atom. e.g. O - is a stronger base and better nucleophile than O 3-2. Nucleophilicity usually increases going down a column of the periodic table. 3. Negatively charged nucleophiles are usually more reactive than neutral ones. Solvent: Polar aprotic solvents work best. Polar Aprotic Solvents include DMF, DMSO, or MPA. Practice Problems 1) Rank the following compounds in order of their expected reactivity in S N 2 reactions: a) 3 l b) ( 3 ) 2 l c) ( 3 ) 3 l d) 3 2) omplete the following reaction (show stereochemistry): O -? Answer Answer
3 S N 1 (Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution) General Reaction: step 1 In the first step, the leaving group leaves and a carbocation forms. This is the slow step, the rate determining step. step 2 b a a b Nu (retention of stereochem) Nu: Nu (inversion of stereochem) In the second step, the nucleophile attacks the positive charge, forming a bond with the carbon. It can attack from the left side (b) or the right side (a). Attacking from the left side results in a product with inverted configuration (as with S N 2 reactions). Attacking from the right side does not change the configuration. In cases where the leaving group "hangs around" the left side is usually easier for the nucleophile to reach. This results in mixture of products, with the inversion product being slightly favored. Kinetics: Only one molecule is involved in the Rate Determining Step. A reaction can only proceed as fast as the rate of its rate-determining step. The general rate law is therefore: Variables affecting S N 1 Reactions: Rate = k [RX] where X = l,, I Substrate: Substrates that stabilize the positive charge formed in the carbocation, lowering the energy of the transition state, are favored. This is because the more stable the carbocation intermediate, the faster the reaction occurs. Therefore, a 3 RX would be a better S N 1 substrate than a 2 or 1 RX.
4 Stability of arbocations (revisted) R R R R R R methyl primary secondary tertiary Vinylic < < < < note: allylic and benzyl carbocations are particularly stable and reactive. 2 benzyl allylic Leaving Group: Leaving group order for S N 1 follows the same order as S N 2 reactions. Note, however, that neutral molecules, such as water, can act as leaving groups in S N 1 reactions. Nucleophile: Poor nucleophiles, such as water, work just as well good nucleophiles. The nucleophile is not involved in the rate determining step. Thus, it does not affect the rate of the reaction. Solvent: Polar protic solvents work best. Polar protic solvents include water and alcohols. Substitution Summary: The S N 2 reaction is a concerted, one-step reaction. It causes inversion of configuration and is favored with unhindered reactants, such as methyl and primary alkyl halides, good leaving groups, strong nucleophiles, and polar aprotic solvents. The S N 1reaction is a two-step reaction with a carbocation intermediate. It is favored with substrates that can stabilize the carbocation charge, 3 >2 >1, and weak nucleophiles.
5 Practice Problems 3) Rank the following compounds in order of their expected reactivity in S N 1 reactions: a) 3 l b) ( 3 ) 2 l c) ( 3 ) 3 l Answer 4) omplete the following reaction: 2 O 3 3 l? 3 5) omplete the following reaction: Answer 3? O 3 Answer
6 Elimination O - 2 O Elimination can occur by E1 or E2 reactions, depending on the conditions of the reaction. E1 Reaction Mechanism: step The first step for an E1 reaction is identical to the first step in an S N 1 reaction. In the first step, the leaving group leaves and a carbocation forms. This is the slow step, the rate determining step. step ( 3 ) 2 2 Base: In the second step, a base removes an + from a neighboring carbon. The electron pair from the - bond goes to form a pi bond, resulting in an alkene. The conditions that favor E1 and S N 1 are similar. Both are good with weak nucleophiles and polar protic solvents. Both want a good leaving group and tertiary substrates. If S N 1 occurs, then E1 does too. E1 and S N 1 compete with each other.
7 E2 Reaction Occurs when a strong base, such as RO -, reacts with an alkyl halide Mechanism: B: 3 3 Bδ 3 3 ( 3 ) X 3 Xδ The and X involved in the reaction must have anti periplanar geometry. This means that the hydrogen, both carbons and halogen involved in the reaction must all lie in the same plane. (Note: E2 elimination cannot occur in cyclohexanes if either the leaving group or the hydrogen is in an equatorial position). Most common elimination pathway Occurs in 1 step, like the S N 2 reaction Kinetics: Rate = k [RX] [Base] Elimination Summary: The E2 reaction has a concerted, one-step mechanism involving a transition state in which the and X being eliminated have antiperiplanar geometry. The E1 reaction has a two-step mechanism, involving a carbocation intermediate. Deciding Whether Substitution or Elimination Occurs Assume that elimination occurs EXEPT when either of the following conditions is met: 1) Unhindered substrate 2) Weak base ase 1: Unhindered Substrate: In the case of an unhindered substrate, such as 3 l, substitution via S N 2 will be most likely to occur. (Elimination cannot occur with a methyl halide because a double bond cannot form if there is only one carbon present in the molecule). ase 2: Weak Base: Strong bases favor elimination. If the nucleophile is a weak base substitution is more likely to occur.
8 Practice Problems 6) Indicate the products and the most likely mechanisms involved in the following reactions: a. 3 b. 2 3 O 3? Answer O 3 (S) I? Answer
9 Answer 1) Rank the following compounds in order of their expected reactivity in S N 2 reactions: a) 3 l b) ( 3 ) 2 l c) ( 3 ) 3 l d) 3 d>a>b>c Return to Problem
10 Answer 2) omplete the following reaction (show stereochemistry): O -? O - O Return to Problem
11 Answer 3) Rank the following compounds in order of their expected reactivity in S N 1 reactions: a) 3l b) (3)2l c) (3)3l c >b>a Return to Problem
12 Answer 4) omplete the following reaction: 2 O 3 3 l? 2 O l 3 O 2 l O l 3 Return to Problem
13 Answer 5) omplete the following reaction: 3? O 3 O is a poor leaving group. It can be protonated to turn it into water, a better leaving group. Water leaves, forming a carbocation and - adds to the carbon. SN1 O O 3 Return to Problem
14 Answer 6) Indicate the products and the most likely mechanisms involved in the following reactions: a O 3? E2 O major elimination product (more stable alkene) minor product O 3 Return to Problem
15 Answer 6) Indicate the products and the most likely mechanisms involved in the following reactions: b. O 3 (S) I? O 3 (S) I SN2 (R) O 3 I Return to Problem
Chapter 11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Walden Inversion
 hapter 11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Walden Inversion (S)-(-) Malic acid [a] D = -2.3 Ag 2, 2 Pl 5 l Ag 2, 2 ()-2-hlorosuccinic acid l (-)-2-hlorosuccinic acid Pl 5 ()-() Malic acid [a]
hapter 11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Walden Inversion (S)-(-) Malic acid [a] D = -2.3 Ag 2, 2 Pl 5 l Ag 2, 2 ()-2-hlorosuccinic acid l (-)-2-hlorosuccinic acid Pl 5 ()-() Malic acid [a]
Homework problems Chapters 6 and Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: CH 3 OH + H 2 C CH +
 omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides
 Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
BSc. II 3 rd Semester. Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1
 BSc. II 3 rd Semester Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1 Introduction to Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are organic molecules containing a halogen atom bonded to an
BSc. II 3 rd Semester Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1 Introduction to Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are organic molecules containing a halogen atom bonded to an
8.8 Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution S N 1
 8.8 Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution S N 1 A question. Tertiary alkyl halides are very unreactive in substitutions that proceed by the S N 2 mechanism. Do they undergo nucleophilic substitution at
8.8 Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution S N 1 A question. Tertiary alkyl halides are very unreactive in substitutions that proceed by the S N 2 mechanism. Do they undergo nucleophilic substitution at
Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution Reactions Substitution Reactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products
 hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations
 11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Alkyl Halides
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Alkyl Halides
Elimination Reactions Heating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a. molecule of HX
 Elimination eactions eating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a molecule of X 1. Potassium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol and the sodium salts of alcohols (such as sodium ethoxide)
Elimination eactions eating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a molecule of X 1. Potassium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol and the sodium salts of alcohols (such as sodium ethoxide)
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH. 8 - ELIMINATION REACTIONS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE E2 MECHANISM A strong nucleophile reacts with an inaccessible leaving group to produce beta-elimination in one-step. E2 Properties (Circle One) Nucleophile = Strong /
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE E2 MECHANISM A strong nucleophile reacts with an inaccessible leaving group to produce beta-elimination in one-step. E2 Properties (Circle One) Nucleophile = Strong /
Reactions of Alkyl Halides with Nucleophiles and Bases a substitution reaction
 Reactions of Alkyl Halides with Nucleophiles and Bases a substitution reaction Nucleophilic substitution and base induced elimination are among most widely occurring and versatile reaction types in organic
Reactions of Alkyl Halides with Nucleophiles and Bases a substitution reaction Nucleophilic substitution and base induced elimination are among most widely occurring and versatile reaction types in organic
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION
 REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
Walden discovered a series of reactions that could interconvert (-)-malic acid and (+)-malic acid.
 Chapter 11: Reactions of alkyl halides: nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations Alkyl halides are polarized in the C-X bond, making carbon δ+ (electrophilic). A nucleophilecan attack this carbon, displacing
Chapter 11: Reactions of alkyl halides: nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations Alkyl halides are polarized in the C-X bond, making carbon δ+ (electrophilic). A nucleophilecan attack this carbon, displacing
1. The Substrate: CH3, 1 o, 2 o, 3 o, Allyl or Benzyl
 Putting it all together: Substitution and elimination reactions are almost always in competition with each other. In order to predict the products of a reaction, it is necessary to determine which mechanisms
Putting it all together: Substitution and elimination reactions are almost always in competition with each other. In order to predict the products of a reaction, it is necessary to determine which mechanisms
Chapter 5. Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism. by G.DEEPA
 Chapter 5 Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism by G.DEEPA 1 Introduction The polarity of a carbon halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge In alkyl halides this polarity
Chapter 5 Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism by G.DEEPA 1 Introduction The polarity of a carbon halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge In alkyl halides this polarity
Chapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group Transformation By Nucleophilic Substitution
 hapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group Transformation By Nucleophilic Substitution Nu: = l,, I Nu - Nucleophiles are Lewis bases (electron-pair donor) Nucleophiles are often negatively
hapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group Transformation By Nucleophilic Substitution Nu: = l,, I Nu - Nucleophiles are Lewis bases (electron-pair donor) Nucleophiles are often negatively
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Organic Chemistry CHM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl Halides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade)
 rganic Chemistry CM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl alides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade) Chapter utline I. Intro to RX (6-1 - 6-7) II. Substitution Reactions A) S N 2 (6-8,
rganic Chemistry CM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl alides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade) Chapter utline I. Intro to RX (6-1 - 6-7) II. Substitution Reactions A) S N 2 (6-8,
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
7. Haloalkanes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7.1 7. aloalkanes (text 7.1 7.10) A. Structure and Nomenclature Like hydrogen, the halogens have a valence of one. Thus, a halogen atom can
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7.1 7. aloalkanes (text 7.1 7.10) A. Structure and Nomenclature Like hydrogen, the halogens have a valence of one. Thus, a halogen atom can
Elimination reactions
 Chapter 9 Elimination reactions E2 and E1 reactions Competition between S N and E Elimination reactions Ch 9 #2 elimination and/or substitution 2 mechanisms ~ E2 and E1 E2: bimolecular elimination rxn
Chapter 9 Elimination reactions E2 and E1 reactions Competition between S N and E Elimination reactions Ch 9 #2 elimination and/or substitution 2 mechanisms ~ E2 and E1 E2: bimolecular elimination rxn
ORGANIC - EGE 5E CH. 7 - NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION REACTIONS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTITUTION Previously, we discussed the various ways that acids could react with bases: Recall that in these mechanisms, electrons always travel from density
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTITUTION Previously, we discussed the various ways that acids could react with bases: Recall that in these mechanisms, electrons always travel from density
Chapter 9. Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination
 Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
Substitution and Elimination reactions
 PART 3 Substitution and Elimination reactions Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of RX 9. Elimination reactions of RX 10. Substit n/elimin n of other comp ds 11. Organometallic comp ds 12. Radical reactions
PART 3 Substitution and Elimination reactions Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of RX 9. Elimination reactions of RX 10. Substit n/elimin n of other comp ds 11. Organometallic comp ds 12. Radical reactions
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions
 Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides"
 Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides" t Introduction" The polarity of a carbon-halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge"
Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides" t Introduction" The polarity of a carbon-halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge"
S N 1 Displacement Reactions
 S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
PAPER No. 05: TITLE: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-II MODULE No. 12: TITLE: S N 1 Reactions
 Subject hemistry Paper o and Title Module o and Title Module Tag 05, ORGAI EMISTRY-II 12, S 1 Reactions E_P5_M12 EMISTRY PAPER o. 05: TITLE: ORGAI EMISTRY-II TABLE OF OTETS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Subject hemistry Paper o and Title Module o and Title Module Tag 05, ORGAI EMISTRY-II 12, S 1 Reactions E_P5_M12 EMISTRY PAPER o. 05: TITLE: ORGAI EMISTRY-II TABLE OF OTETS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
10. Organohalides. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
1-What is substitution reaction? 2-What are can Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction? 3- SN1 reaction. 4-SN2 reaction 5- mechanisms of SN1&SN2
 1-What is substitution reaction? 2-What are can Nucleophilic Substitution eaction? 3- SN1 reaction. 4-SN2 reaction 5- mechanisms of SN1&SN2 1- SUBSTITUTION EACTIONS 1-Substitution eaction In this type
1-What is substitution reaction? 2-What are can Nucleophilic Substitution eaction? 3- SN1 reaction. 4-SN2 reaction 5- mechanisms of SN1&SN2 1- SUBSTITUTION EACTIONS 1-Substitution eaction In this type
Essential Organic Chemistry. Chapter 9
 Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
PAPER No. : 5; Organic Chemistry-II MODULE No. : 13; Mixed S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 13; Mixed S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions CHE_P5_M13 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Nature
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 13; Mixed S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions CHE_P5_M13 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Nature
Substitution Reactions
 Substitution Reactions Substitution reactions are reactions in which a nucleophile displaces an atom or group of atoms (the leaving group) from a tetrahedral carbon atom. onsider the following general
Substitution Reactions Substitution reactions are reactions in which a nucleophile displaces an atom or group of atoms (the leaving group) from a tetrahedral carbon atom. onsider the following general
Classes of Halides. Chapter 6 Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination. Polarity and Reactivity. Classes of Alkyl Halides
 rganic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 6 Alkyl alides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination lasses of alides Alkyl: alogen, X, is directly bonded to sp 3 carbon. Vinyl: X is bonded to
rganic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 6 Alkyl alides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination lasses of alides Alkyl: alogen, X, is directly bonded to sp 3 carbon. Vinyl: X is bonded to
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Substitution Reactions S N 2 O H H H O H H. Br -
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Substitution Reactions Br Br S N 2 CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of alkyl halides, R X A. Common name:
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Substitution Reactions Br Br S N 2 CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of alkyl halides, R X A. Common name:
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7
 Sevada Chamras, Ph.D. Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7 Description: Examples: 3 Major Types of Organic Halides: 1. Alkyl Halides: Chapter 6 (Part 1/2) : Alkyl
Sevada Chamras, Ph.D. Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7 Description: Examples: 3 Major Types of Organic Halides: 1. Alkyl Halides: Chapter 6 (Part 1/2) : Alkyl
Chapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides
 hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
CONCERTED sp 2 H. HO Et
 Alkyl alides Substitution and Elimination 1 Substitutions (Quick Review) 1.1 SN2 Reactions LB nucleophile "backside attack!" NERTED reaction This is fundamentally just a Lewis acid/base reaction, the Lewis
Alkyl alides Substitution and Elimination 1 Substitutions (Quick Review) 1.1 SN2 Reactions LB nucleophile "backside attack!" NERTED reaction This is fundamentally just a Lewis acid/base reaction, the Lewis
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail
 Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail b-elimination Reactions Overview dehydration of alcohols: X = H; Y = OH dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: X = H; Y = Br, etc. X C
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail b-elimination Reactions Overview dehydration of alcohols: X = H; Y = OH dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: X = H; Y = Br, etc. X C
The Electrophile. S N 2 and E2 least stable most stable least hindered most hindered. S N 1 and E1. > x > >
 The Electrophile 1 Recall that electrophile means electron- loving. When considering substitution and elimination reactions we must consider the carbon attached to the leaving group. Is it a primary, secondary,
The Electrophile 1 Recall that electrophile means electron- loving. When considering substitution and elimination reactions we must consider the carbon attached to the leaving group. Is it a primary, secondary,
Elimination Reactions. Chapter 6 1
 Elimination Reactions Chapter 6 1 E1 Mechanism Step 1: halide ion leaves, forming a carbocation. Step 2: Base abstracts H + from adjacent carbon forming the double bond. Chapter 6 2 E1 Energy Diagram E1:
Elimination Reactions Chapter 6 1 E1 Mechanism Step 1: halide ion leaves, forming a carbocation. Step 2: Base abstracts H + from adjacent carbon forming the double bond. Chapter 6 2 E1 Energy Diagram E1:
How alkyl halides react
 Chapter 10 1 How alkyl halides react δ+ δ- RCH 2 -X X= halogen X = higher EN C = lower EN This polar carbon-halogen bond causes alkyl halide to undergo S N and elimination reaction. 2 The mechanism of
Chapter 10 1 How alkyl halides react δ+ δ- RCH 2 -X X= halogen X = higher EN C = lower EN This polar carbon-halogen bond causes alkyl halide to undergo S N and elimination reaction. 2 The mechanism of
PRACTICE PROBLEMS UNIT 8
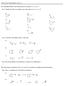 PRACTICE PROBLEMS UNIT 8 8A. Identify halides and carbocations as being 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o 8A.1 assify the following halides and carbocations as 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o. 8A.2 Circle the most stable cation in each
PRACTICE PROBLEMS UNIT 8 8A. Identify halides and carbocations as being 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o 8A.1 assify the following halides and carbocations as 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o. 8A.2 Circle the most stable cation in each
PAPER No. 5: REACTION MECHANISM MODULE No. 2: Types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Dr. Anand Gupta Mr Mahesh Kapil
 Dr. Anand Gupta Mr Mahesh Kapil 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Preparation of Haloalkanes From Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols Carboxylic Acids (Hundsdicker Reaction) Halide
Dr. Anand Gupta Mr Mahesh Kapil 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Preparation of Haloalkanes From Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols Carboxylic Acids (Hundsdicker Reaction) Halide
Alkyl Halides. Alkyl halides are a class of compounds where a halogen atom or atoms are bound to an sp 3 orbital of an alkyl group.
 Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are a class of compounds where a halogen atom or atoms are bound to an sp 3 orbital of an alkyl group. CHCl 3 (Chloroform: organic solvent) CF 2 Cl 2 (Freon-12: refrigerant
Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are a class of compounds where a halogen atom or atoms are bound to an sp 3 orbital of an alkyl group. CHCl 3 (Chloroform: organic solvent) CF 2 Cl 2 (Freon-12: refrigerant
CHAPTER 8 HW SOLUTIONS: ELIMINATIONS REACTIONS
 APTER 8 W SLUTNS: ELMNATNS REATNS S-TRANS SMERSM 1. Use a discussion and drawing of orbitals to help explain why it is generally easy to rotate around single bonds at room temperature, while it is difficult
APTER 8 W SLUTNS: ELMNATNS REATNS S-TRANS SMERSM 1. Use a discussion and drawing of orbitals to help explain why it is generally easy to rotate around single bonds at room temperature, while it is difficult
Hydrogen iodide is a strong acid and will drive the reverse reaction, meaning the forward reaction will not occur.
 EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions
 Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C 3 C C 3 bond length bond strength 2 C C 2 a C=C double bond is stronger than a C C single
Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C 3 C C 3 bond length bond strength 2 C C 2 a C=C double bond is stronger than a C C single
Chapter 8 Alkyl Halides and Elimination Reactions
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 8 Alkyl Halides and Elimination Reactions Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 8 Alkyl Halides and Elimination Reactions Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright
Chapter 9:Nucleophiles & Substitution Reactions
 1. a. Place the following nucleophiles in order of strength (1= strongest; 3 = weakest). i. ii. b. Place the following in order of leaving group ability (1= best; 7 = worst). (A pka table may help you!)
1. a. Place the following nucleophiles in order of strength (1= strongest; 3 = weakest). i. ii. b. Place the following in order of leaving group ability (1= best; 7 = worst). (A pka table may help you!)
Organic Halogen Compounds
 8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
Lab 11 Guide: Nucleophilic Substitution (Nov 10 16)
 Lab 11 Guide: Nucleophilic Substitution (Nov 10 16) Nucleophilic Substitution of Alkyl Halides, Exp. 17A, B, and C, pages 187-192 in Taber This week you will be doing examining real life S N 1 and S N
Lab 11 Guide: Nucleophilic Substitution (Nov 10 16) Nucleophilic Substitution of Alkyl Halides, Exp. 17A, B, and C, pages 187-192 in Taber This week you will be doing examining real life S N 1 and S N
12AL Experiment 11 (3 days): Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
 12AL Experiment 11 (3 days): Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Instructor note: Day 1 (half of the class); Day 2 (other half); Day 3 (everyone to finish up any separation & purification steps etc). Initial
12AL Experiment 11 (3 days): Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Instructor note: Day 1 (half of the class); Day 2 (other half); Day 3 (everyone to finish up any separation & purification steps etc). Initial
+ + CH 11: Substitution and Elimination Substitution reactions
 C 11: Substitution and Elimination Substitution reactions Things to sort out: Nucleophile Electrophile -- > substrate Leaving Group S N 2 S N 1 E 1 E 2 Analysis Scheme Kinetics Reaction profile Substrates
C 11: Substitution and Elimination Substitution reactions Things to sort out: Nucleophile Electrophile -- > substrate Leaving Group S N 2 S N 1 E 1 E 2 Analysis Scheme Kinetics Reaction profile Substrates
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions
 1. Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C bond length bond strength 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C 2 C C 2 3 C a C=C double bond
1. Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C bond length bond strength 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C 2 C C 2 3 C a C=C double bond
Columbia University C99ORG12.DOC S3443D Summer 99 Professor Grace B. Borowitz Exam No. 2 June 14, 1999
 olumbia University 99RG12.D SD Summer 99 Professor Grace B. Borowitz Exam No. 2 June 1, 1999 Name: Sterie hemistry Grade: Please use a non-red pen. Answer questions in the provided space. If you write
olumbia University 99RG12.D SD Summer 99 Professor Grace B. Borowitz Exam No. 2 June 1, 1999 Name: Sterie hemistry Grade: Please use a non-red pen. Answer questions in the provided space. If you write
(b) (CH 3 ) 2 CCH 2 CH 3 D 2 O. (e) A. CH 3 CCl OSO 2 CH 3 C 6 H 5 H 3 C
 278 h a p t e r 7 Further Reactions of aloalkanes 3. arbocations are stabilized by hyperconjugation: Tertiary are the most stable, followed by secondary. Primary and methyl cations are too unstable to
278 h a p t e r 7 Further Reactions of aloalkanes 3. arbocations are stabilized by hyperconjugation: Tertiary are the most stable, followed by secondary. Primary and methyl cations are too unstable to
Alkyl Halides React with Nucleophiles and Bases
 Chapter 11- Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Ashley Piekarski, Ph.D. Alkyl Halides React with Nucleophiles and Bases Alkyl halides are polarized at the carbon- halide
Chapter 11- Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Ashley Piekarski, Ph.D. Alkyl Halides React with Nucleophiles and Bases Alkyl halides are polarized at the carbon- halide
Chapter 08 Nucleophilic Substitution Part 02
 hapter 08 Nucleophilic Substitution Part 02 EM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg ook 2012 Gregory R ook Solvent Effects in Nucleophilic Substitution R X Y R Y X SLVENT Polar reactions - we need polar solvents
hapter 08 Nucleophilic Substitution Part 02 EM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg ook 2012 Gregory R ook Solvent Effects in Nucleophilic Substitution R X Y R Y X SLVENT Polar reactions - we need polar solvents
Sn1 or Sn2 Reactions: A Guide to Deciding Which Reaction is Occurring
 Sn1 or Sn2 Reactions: A Guide to Deciding Which Reaction is Occurring The following is a discussion of the approach you should use in order to determine if a chemical reaction occurs via a Sn1 or Sn2 mechanism.
Sn1 or Sn2 Reactions: A Guide to Deciding Which Reaction is Occurring The following is a discussion of the approach you should use in order to determine if a chemical reaction occurs via a Sn1 or Sn2 mechanism.
UCF - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1 - PROF. DAOUDI UCF PROF. DAOUDI EXAM 3 REVIEW.
 UCF PROF. DAOUDI EXAM 3 REVIEW www.clutchprep.com 1 PRACTICE: Identify the most stable and the least stable alkene PRACTICE: Create the full arrow pushing mechanism which shows all intermediates and all
UCF PROF. DAOUDI EXAM 3 REVIEW www.clutchprep.com 1 PRACTICE: Identify the most stable and the least stable alkene PRACTICE: Create the full arrow pushing mechanism which shows all intermediates and all
Elimination Reactions:
 Elimination Reactions: These are just reverse of addition reactions. These involve the removal of atoms or group of atoms from a molecule. Elimination reactions are generally endothermic and take place
Elimination Reactions: These are just reverse of addition reactions. These involve the removal of atoms or group of atoms from a molecule. Elimination reactions are generally endothermic and take place
Some Arrow-Pushing Guidelines (Section 1.14) 1. Arrows follow electron movement.
 Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 1 Notes 1 Note: The headers and associated chapters don t actually jive with the textbook we are using this summer. But otherwise this highlights a lot of the chemistry from Organic
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 1 Notes 1 Note: The headers and associated chapters don t actually jive with the textbook we are using this summer. But otherwise this highlights a lot of the chemistry from Organic
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Learning Guide for Chapter 10 - Alkyl Halides II
 Learning Guide for Chapter 10 - Alkyl Halides II I. Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides Introduction Mechanisms Beta hydrogens, constitutional isomers, and stereoisomers E2 vs E1 Strong and Weak Bases
Learning Guide for Chapter 10 - Alkyl Halides II I. Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides Introduction Mechanisms Beta hydrogens, constitutional isomers, and stereoisomers E2 vs E1 Strong and Weak Bases
Real life example 1 Let s look at this series of chloroalcohols, and how fast the chloride gets displaced by an external nucleophile.
 Class 2 Carbocations Last time we talked about neighboring group participation in substitution reactions. I want to start today by talking about a few more real life examples. Real life example 1 Let s
Class 2 Carbocations Last time we talked about neighboring group participation in substitution reactions. I want to start today by talking about a few more real life examples. Real life example 1 Let s
c. Cl H Page 1 of 7 major P (E > Z and more substituted over less substituted alkene) LG must be axial are the same Cl -
 CEM 109A 1. Predict the products of the following reactions (a-c E2, d-f E1 KEY focuses only on elimination products, in most cases there will also be substitution products.) a. - LG must be axial - are
CEM 109A 1. Predict the products of the following reactions (a-c E2, d-f E1 KEY focuses only on elimination products, in most cases there will also be substitution products.) a. - LG must be axial - are
Chapter 8 I. Nucleophilic Substitution (in( II. Competion with Elimination. Nucleophilic Substitution
 hapter 8 I. Nucleophilic Substitution (in( depth) II. ompetion with Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Substrate is a sp3 hybridized carbon atom (cannot be an a vinylic halide or an aryl halide except
hapter 8 I. Nucleophilic Substitution (in( depth) II. ompetion with Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Substrate is a sp3 hybridized carbon atom (cannot be an a vinylic halide or an aryl halide except
CHE 275 NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTUION CHAP 8 ASSIGN. 1. Which best depicts the partial charges on methyl bromide and sodium methoxide?
 CHE 275 NUCLEPHILIC SUBSTITUTUIN CHAP 8 ASSIGN 1. Which best depicts the partial charges on methyl bromide and sodium methoxide? 2. Which of the following would be the best (most reactive) nucleophile
CHE 275 NUCLEPHILIC SUBSTITUTUIN CHAP 8 ASSIGN 1. Which best depicts the partial charges on methyl bromide and sodium methoxide? 2. Which of the following would be the best (most reactive) nucleophile
CHEM 302 Organic Chemistry I Problem Set VII Chapter 7 Answers
 CEM 302 rganic Chemistry Problem Set V Chapter 7 Answers 1) The pk a values of acetic acid and trifluroacetic acid are 4.5 and 0.9 respectively. Based on this information, which anion, C 3 C - or CF 3
CEM 302 rganic Chemistry Problem Set V Chapter 7 Answers 1) The pk a values of acetic acid and trifluroacetic acid are 4.5 and 0.9 respectively. Based on this information, which anion, C 3 C - or CF 3
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I
 Andrew Rosen Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I 7.1 - Introduction - The simplest member of the alkenes has the common name of ethylene while the simplest member of the alkyne family has the common name
Andrew Rosen Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I 7.1 - Introduction - The simplest member of the alkenes has the common name of ethylene while the simplest member of the alkyne family has the common name
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2018
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
Reaction mechanism 1/17/19. HCl. HCl. 3 radical can form here. Br 2. hint!
 If the reagents or reaction conditions favor radicals, then it is likely to be a radical reaction. Look for hints like peroxide, AIBN, NBS, hn (UV light). 3 radical can form here Reaction mechanism How
If the reagents or reaction conditions favor radicals, then it is likely to be a radical reaction. Look for hints like peroxide, AIBN, NBS, hn (UV light). 3 radical can form here Reaction mechanism How
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2015
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
Chapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions
 hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW
 REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
Alkyl Halides and Nucleophilic Subs5tu5on Reac5ons. S N 2 and S N 1 Reac,ons
 Alkyl Halides and Nucleophilic Subs5tu5on Reac5ons S N 2 and S N 1 Reac,ons 1 Alkyl Halides The electronega5ve halogen atom in alkyl halides creates a polar C X bond, making the carbon atom electron deficient.
Alkyl Halides and Nucleophilic Subs5tu5on Reac5ons S N 2 and S N 1 Reac,ons 1 Alkyl Halides The electronega5ve halogen atom in alkyl halides creates a polar C X bond, making the carbon atom electron deficient.
Loudon Chapter 9 Review: Reactions of Alkyl Halides Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 5/1/2016
 Chapter 9 covers reactions you can do with alkyl halides. For the most part, these break down into two categories: substitution and elimination. Substitution results in replacing the halogen with some
Chapter 9 covers reactions you can do with alkyl halides. For the most part, these break down into two categories: substitution and elimination. Substitution results in replacing the halogen with some
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions"
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Only five of the molecules below may be prepared as the sole product of allylic halogenation of the respective alkene. Circle those five.
 Chem 232 D. J. Wardrop wardropd@uic.edu Problem Set 6 Answers Question 1. nly five of the molecules below may be prepared as the sole product of allylic halogenation of the respective alkene. Circle those
Chem 232 D. J. Wardrop wardropd@uic.edu Problem Set 6 Answers Question 1. nly five of the molecules below may be prepared as the sole product of allylic halogenation of the respective alkene. Circle those
Elimination Reactions The E2 Mechanism
 Elimination Reactions The E2 Mechanism The E2 Mechanism X X- B: B- δ- B:- δ+ R 1 δ- R 2 δ+ X δ- The E2 Mechanism R 3 R 4 transition state Free energy (G) Eact B:- B R 1 R 2 X R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 4 R 3 X:-
Elimination Reactions The E2 Mechanism The E2 Mechanism X X- B: B- δ- B:- δ+ R 1 δ- R 2 δ+ X δ- The E2 Mechanism R 3 R 4 transition state Free energy (G) Eact B:- B R 1 R 2 X R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 4 R 3 X:-
Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination
 Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination 1. What is β elimination? 2. Alkenes: structure, steroisomerism and stability 3. Elimination Reactions o E2 Mechanism o E1 Mechanism
Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination 1. What is β elimination? 2. Alkenes: structure, steroisomerism and stability 3. Elimination Reactions o E2 Mechanism o E1 Mechanism
Reactions of Haloalkanes
 Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
Methyl > primary > secondary >> tertiary
 Lecture 1 Notes September 6, 2012 Welcome to CHM 427. For some of you, this will be the last organic chemistry class that you will ever take. So I see it as my personal mission to make sure that you know
Lecture 1 Notes September 6, 2012 Welcome to CHM 427. For some of you, this will be the last organic chemistry class that you will ever take. So I see it as my personal mission to make sure that you know
Course Goals for CHEM 202
 Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
11. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
 11. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions A. Introduction It would be beneficial if you review the chapter on substitution reactions in your textbook prior to lab. This is Ch. 11 in the 9 th edition McMurry
11. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions A. Introduction It would be beneficial if you review the chapter on substitution reactions in your textbook prior to lab. This is Ch. 11 in the 9 th edition McMurry
Objective 11. Apply Reactivity Principles to Substitution and Elimination Reactions: compare size and strength of nucleophile to predict major product
 Objective 11 Apply Reactivity Principles to Substitution and Elimination Reactions: compare size and strength of nucleophile to predict major product Given Reactants ----> Predict Products How to figure
Objective 11 Apply Reactivity Principles to Substitution and Elimination Reactions: compare size and strength of nucleophile to predict major product Given Reactants ----> Predict Products How to figure
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/sni
 KNOW MORE Weblinks https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/allyl http://courses.chem.psu.edu/chem210/mol-gallery/allyl/allyl.html https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/nucleophilic_substitution http://polymer.zju.edu.cn/attachments/2012-11/01-1352193505-
KNOW MORE Weblinks https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/allyl http://courses.chem.psu.edu/chem210/mol-gallery/allyl/allyl.html https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/nucleophilic_substitution http://polymer.zju.edu.cn/attachments/2012-11/01-1352193505-
Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers 1
 Andrew Rosen Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers 1 11.1 - Structure and Nomenclature - The common naming calls alcohols as alkyl alcohols (eg: methyl alcohol) - The common names of ethers have the groups
Andrew Rosen Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers 1 11.1 - Structure and Nomenclature - The common naming calls alcohols as alkyl alcohols (eg: methyl alcohol) - The common names of ethers have the groups
CHEM 263 Oct 25, stronger base stronger acid weaker acid weaker base
 CEM 263 ct 25, 2016 Reactions and Synthesis (Preparation) of R- Breaking the - Bond of R- with Metals R + Li 0 or Na 0 or K 0 metal R Li + 1/2 2 alkoxide Breaking the - Bond of R- by Acid-Base Reaction
CEM 263 ct 25, 2016 Reactions and Synthesis (Preparation) of R- Breaking the - Bond of R- with Metals R + Li 0 or Na 0 or K 0 metal R Li + 1/2 2 alkoxide Breaking the - Bond of R- by Acid-Base Reaction
