Dynamics connect substrate recognition to catalysis in protein kinase A
|
|
|
- Amber Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information for Dynamics connect substrate recognition to catalysis in protein kinase A Larry R. Masterson 1,2, Cecilia Cheng 3, Tao Yu 2, Lei Shi 2, Marco Tonelli 3, Yi Wang 2, Susan S. Taylor 4*, and Gianluigi Veglia 1,2 Departments of 1 Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, and Biophysics and 2 Chemistry, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota , and the 3 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of San Diego, San Diego CA , and 4 National Magnetic Resonance Facility at Madison, Department of Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin
2 Supplementary Results Table 1. Data collection and refinement statistics for Protein Data Bank accession number 3O7L. Phospholamban1-19 : C-subunit complex Data collection Space group P6 1 Cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) 92.2, 92.2, α, β, γ ( ) 90.0, 90.0, Resolution (Å) 2.8 R sym or R merge (0.456) * I / σi 38.8 (5.1) Completeness (%) 99.5 (100) Redundancy 10.5 (10.1) No. reflections No. molecules per 2 asymmetrical unit Refinement Resolution (Å) R work / R free / Number of protein atoms 5210 Number of water molecules 21 Wilson B-factors (Å 2 ) 51.6 R.m.s. deviations Bond lengths (Å) Bond angles ( ) Ramachandran angles (%) most favored 85.8 disallowed none *Highest-resolution shell ( Å) is shown in parentheses. 2
3 Table 2. Mean and trimmed mean of backbone amide 15 N R 1, R 2, and H-X NOE for PKA-C. Parameter Apo AMP-PNP Bound AMP-PNP/PLN 1-20 Bound R 1 (s -1 ) ± ± ± Trimmed R 1 (s -1 ) ± ± ± R 2 (s -1 ) 27.8 ± ± ± 2.9 Trimmed R 2 (s -1 ) 51.9 ± ± ± 3.2 Trimmed R 2 /R ± ± ± 4.2 H-X NOE 0.71 ± ± ± 0.32 Trimmed H-X NOE 0.76 ± ± ± 0.16 H-X NOE (Glycine-loop) 0.76 ± ± ± 0.05 H-X NOE (DFG/Activation/Peptide-loop) 0.65 ± ± ± 0.10 % of Residues with R ex >8 Hz 4.9% 15.7% 12.6% 3
4 Fig. 1: Steady-state phosphorylation kinetics of (a) PLN 1-20 and (b) full-length PLN (AFA mutant which is monomeric) in DMPC/DHPC isotropic bicelles. Michaelis-Menten pararmeters provided in the plots indicate no major differences in catalytic efficiency between the two substrates. Therefore, the use of the peptide corresponding to the cytoplasmic portion of PLN was used as a model for the full-length protein. 4
5 Fig. 2: Details of stabilizing interactions between PKA-C and PLN Hydrophobic packing (a) between the apo enzyme of PKA-C and the N-terminal region of the PLN 1-19 peptide was observed in the crystal structure. However, the conserved recognition sequence of the substrate (residues 12-17) makes key electrostatic interactions in the ternary complex (b). The positioning of the γ-po4 of AMP-PNP toward the hydroxyl of Ser16, and the interaction of Gly200 with Thr17 of PLN 1-19 are also shown in a. The interactions of the essential P-2 (Arg14) and P-3 (Arg13) of PLN 1-19 are depicted in b. 5
6 Fig. 3: Mapping of B-factors for the (a) PKA-C apo state, (b) PKA-C ternary complex, and (c) PLN 1-19 bound to PKA-C. 6
7 Fig. 4: Nuclear spin dynamics of 2 H, 15 N-labeled PLN 1-20 in the free state (black) and in the ternary complex with PKA-C (red). (a) H-X NOE, (b) R 2, (c) R 1, and (d) R 2 /R 1 values are plotted for both of these states. 7
8 Fig. 5: Nuclear spin dynamics of 2H, 15N-labeled PKA-C along its pathway to the ternary complex: (a) Apo-enzyme, (b) nucleotide bound, and (c) bound to both nucleotide and PLN
9 Fig. 6: Amide resonance inverse peak heights mapped for PKA-C in the (a) Apo, (b) AMP-PNP bound, and (c) AMP-PNP/PLN 1-20 bound states. Large values of inverse peak heights are indicative of conformational exchange on the µs-ms timescale (R ex ) and qualitative agreement between the residues displaying R ex and large inverse peak heights are expected to occur. 9
10 Fig. 7: Conformational interconversion of the highly conserved C-helix and Mg 2+ -loop in the AMP-PNP (shown in blue) bound state of PKA-C. Residues highlighted in red spheres are those which experienced significant R ex contributions. Both regions depicted here exhibited dynamics on a similar timescale of ~25 s
11 Fig. 8: Details of residues which were synchronous with opening and closing (black) and those which were not (red). Dynamics of the AMP-PNP bound (a) and AMP-PNP/PLN 1-20 bound (b) states are shown. 11
12 Supplementary Methods Peptide synthesis. Peptides were synthesized using standard Fmoc chemistry starting with Fmoc- Glu(OtBu)-PEG-PS resin (0.4 g, 0.5 mmol/g). Side chain protecting groups were 2,2,5,78- pentamethylchroman-6-sulfonyl (Pmc) for arginine, N ω -triphenylmethyl (Trt) for asparagine and glutamine, tert-butyl etster (OtBu) for glutamic acid, and tert-butyl ethers (tbu) for serine, threonine, and tyrosine. Deprotection of the resin-bound peptide was done using Reagent K (82.5% TFA, 5% phenol, 5% thioanisole, 2.5% 1,2-ethandiol, and 5% water) for 3 hours at 298 K. The resin mixture was washed three times (2 ml each) using the same cocktail and filtrate was collected. The peptide was precipitated overnight at 273 K in 80 ml of diethyl ether, then collected by centrifugation and washing the pellet 3 times with 30 ml of diethyl ether. The crude peptide was then purified by preparative HPLC using a Waters C18 reversed-phase cartridge (2.5 x 10 cm, 15 µm, 300 Ǻ) with 0.1% TFA and CH 3 CN as eluents and detection at 220 nm. A linear gradient of 100:0 to 70:30 over 30 minutes at 5 ml/min was used. Purities of pooled fractions were >90% as determined by analytical HPLC using a Vydac C18 column (0.46 x 25 cm) and confirmed by ESI-TOF (PLN 1-19, calculated m/z, found m/z). Aliquots of peptide were prepared in water from the same purified stock, lyophilized, and concentrations of these solutions were verified by amino acid analysis. Kinetic Assays. The steady-state enzymatic rate of PLN 1-20 phosphorylation was measured spectrophotometrically at 299 K following the procedure by Cook, et al 1. The values of V max, k cat, and K M were determined from non-linear fitting of initial velocities versus substrate concentration according to: 12
13 v = V K [ S] [ S] max (1) M + Where v is the initial velocity, [S] is the concentration of substrate, V max is the maximum velocity for the reaction, and K M is the Michaelis-Menten constant. Determination of k cat values was made by dividing V max by the total enzyme concentration. Reactions for full-length PLN were conducted using isotropic bicelles (q=0.5, 5% C L ) composed of DMPC/DHPC (Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc.). X-ray Crystallography. Optimization of crystallization conditions The mixture containing PKA-C/PLN 1-19 /AMP-PNP was incubated on ice then filtered with 0.2 μm centrifugal devices (Life Sciences). Crystallization trials were setup on CrystalClear Duo sitting drop plates (Douglas Instruments) using the Oryx8 Protein Crystallization Robot (Douglas Instruments, UK). Commercial HT crystal screens were used to determine initial crystallization conditions (PACT, JCSG, Proplex, Structure Screen I&II, Clear Strategy I, and Clear Strategy II, Molecular Dimensions). Screens were done with 0.5 μl drops, testing both 50% and 70% protein concentrations and 4 C and 22.5 C temperatures. Initial crystal hits were optimized using the Oryx8 robot. The final condition was 4.3 mg/ml PKA-C, 0.09 M sodium malonate (ph 7.0), 15.5% PEG 3350, which produced μm sized tetragonal crystals at 22.5 C. Data refinement All ambiguous main chains and side chains were removed and manually rebuilt using Coot 2, followed by iterative cycles of structure refinement using REFMAC in the CCP4 suite 3. Upon inspection of the F o -F c maps, electron density in the N-terminal lobe for one of the two molecules did not match with the model so residues were removed. Both peptide and 13
14 nucleotide appeared to be absent in this molecule, so an apo form was assumed. Alignment of the large lobes of the apo structure (PDB code 1J3H) 4 and our second molecule to obtain a rough estimate of the small lobe position. Coot was utilized in subsequent model building and REFMAC for refinement. The phospholamban peptide was not manually built until all atoms in PKA-C were satisfactorily refined. TLS refinement 5 was implemented for each lobe. Simulated annealing via the program Phenix 6,7 was used in the final stages of refinement because geometric restraints were too loose with REFMAC. Water molecules were manually incorporated. 14
15 References 1. Cook, P. F., Neville,M.E., Vrana,K.E., Hartl,F.T. and Roskoshi,R. Adenosine cyclic 3'5'- monophosphate dependent protein kinase: Kinetic mechanism for the bovine skeletal muscle catalytic subunit. Biochemistry. 21, (1982). 2. Emsley, P. and Cowtan,K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, (2004). 3. Murshudov, G. N., Vagin,A.A. and Dodson,E.J. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 53, (1997). 4. Akamine, P., Madhusudan, Wu,J., Xuong,N.H., Ten Eyck,L.F. and Taylor,S.S. Dynamic features of camp-dependent protein kinase revealed by apoenzyme crystal structure. J. Mol. Biol. 327, (2003). 5. Winn, M. D., Isupov,M.N. and Murshudov,G.N. Use of TLS parameters to model anisotropic displacements in macromolecular refinement. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 57, (2001). 6. Adams, P. D., et al. PHENIX: Building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 58, (2002). 7. Adams, P. D., et al. Recent developments in the PHENIX software for automated crystallographic structure determination. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 11, (2004). 15
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Masterson et al. 10.1073/pnas.1102701108 SI Materials and Methods Production of Synthetic Peptides. Peptides were synthesized using standard Fmoc chemistry on a microwave synthesizer
Supporting Information Masterson et al. 10.1073/pnas.1102701108 SI Materials and Methods Production of Synthetic Peptides. Peptides were synthesized using standard Fmoc chemistry on a microwave synthesizer
Supporting Information. Synthesis of Aspartame by Thermolysin : An X-ray Structural Study
 Supporting Information Synthesis of Aspartame by Thermolysin : An X-ray Structural Study Gabriel Birrane, Balaji Bhyravbhatla, and Manuel A. Navia METHODS Crystallization. Thermolysin (TLN) from Calbiochem
Supporting Information Synthesis of Aspartame by Thermolysin : An X-ray Structural Study Gabriel Birrane, Balaji Bhyravbhatla, and Manuel A. Navia METHODS Crystallization. Thermolysin (TLN) from Calbiochem
Computational Modeling of Protein Kinase A and Comparison with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data
 Computational Modeling of Protein Kinase A and Comparison with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data ABSTRACT Keyword Lei Shi 1 Advisor: Gianluigi Veglia 1,2 Department of Chemistry 1, & Biochemistry, Molecular
Computational Modeling of Protein Kinase A and Comparison with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data ABSTRACT Keyword Lei Shi 1 Advisor: Gianluigi Veglia 1,2 Department of Chemistry 1, & Biochemistry, Molecular
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Tuning the Thermosensitive Properties of Hybrid Collagen Peptide-Polymer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Tuning the Thermosensitive Properties of Hybrid Collagen Peptide-Polymer
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/4/e1600663/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A dynamic hydrophobic core orchestrates allostery in protein kinases Jonggul Kim, Lalima G. Ahuja, Fa-An Chao, Youlin
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/4/e1600663/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A dynamic hydrophobic core orchestrates allostery in protein kinases Jonggul Kim, Lalima G. Ahuja, Fa-An Chao, Youlin
Cks1 CDK1 CDK1 CDK1 CKS1. are ice- lobe. conserved. conserved
 Cks1 d CKS1 Supplementary Figure 1 The -Cks1 crystal lattice. (a) Schematic of the - Cks1 crystal lattice. -Cks1 crystallizes in a lattice that contains c 4 copies of the t - Cks1 dimer in the crystallographic
Cks1 d CKS1 Supplementary Figure 1 The -Cks1 crystal lattice. (a) Schematic of the - Cks1 crystal lattice. -Cks1 crystallizes in a lattice that contains c 4 copies of the t - Cks1 dimer in the crystallographic
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Horne et al. 10.1073/pnas.0902663106 SI Materials and Methods Peptide Synthesis. Protected 3 -amino acids were purchased from PepTech. Cyclically constrained -residues, Fmoc-ACPC
Supporting Information Horne et al. 10.1073/pnas.0902663106 SI Materials and Methods Peptide Synthesis. Protected 3 -amino acids were purchased from PepTech. Cyclically constrained -residues, Fmoc-ACPC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
type GroEL-GroES complex. Crystals were grown in buffer D (100 mm HEPES, ph 7.5,
 Supplementary Material Supplementary Materials and Methods Structure Determination of SR1-GroES-ADP AlF x SR1-GroES-ADP AlF x was purified as described in Materials and Methods for the wild type GroEL-GroES
Supplementary Material Supplementary Materials and Methods Structure Determination of SR1-GroES-ADP AlF x SR1-GroES-ADP AlF x was purified as described in Materials and Methods for the wild type GroEL-GroES
Acta Crystallographica Section D
 Supporting information Acta Crystallographica Section D Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structural characterization of the virulence factor Nuclease A from Streptococcus agalactiae
Supporting information Acta Crystallographica Section D Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structural characterization of the virulence factor Nuclease A from Streptococcus agalactiae
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chem. Commun. Unveiling the three- dimensional structure of the green pigment of nitrite- cured meat
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chem. Commun. Unveiling the three- dimensional structure of the green pigment of nitrite- cured meat Jun Yi* and George B. Richter- Addo* Department of Chemistry
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chem. Commun. Unveiling the three- dimensional structure of the green pigment of nitrite- cured meat Jun Yi* and George B. Richter- Addo* Department of Chemistry
BSc and MSc Degree Examinations
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BSc and MSc Degree Examinations 2018-9 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Part I Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BSc and MSc Degree Examinations 2018-9 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Part I Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking
Folding Thermodynamics of Protein-Like Oligomers with Heterogeneous Backbones
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Folding Thermodynamics of Protein-Like Oligomers with Heterogeneous Backbones Zachary E.
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Folding Thermodynamics of Protein-Like Oligomers with Heterogeneous Backbones Zachary E.
(d, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.80 (m, 2H), 1.65 (m, 2H), 1.49 (m, 2H), 1.46 (s, 9H) ppm; 13 C NMR
 Site-Specific Protein Immobilization by Staudinger Ligation Matthew B. Soellner, Kimberly A. Dickson, Bradley L. ilsson, and Ronald T. Raines Departments of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin,
Site-Specific Protein Immobilization by Staudinger Ligation Matthew B. Soellner, Kimberly A. Dickson, Bradley L. ilsson, and Ronald T. Raines Departments of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin,
Backbone modification of a parathyroid hormone receptor-1 antagonist/inverse agonist
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Backbone modification of a parathyroid hormone receptor-1 antagonist/inverse agonist Ross W. Cheloha, Tomoyuki Watanabe, Thomas Dean, Samuel H. Gellman*, Thomas J. Gardella* *Corresponding
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Backbone modification of a parathyroid hormone receptor-1 antagonist/inverse agonist Ross W. Cheloha, Tomoyuki Watanabe, Thomas Dean, Samuel H. Gellman*, Thomas J. Gardella* *Corresponding
Structurale, Université Grenoble Alpes, CNRS, CEA, Grenoble, France
 Supplementary Information to Lysine relay mechanism coordinates intermediate transfer in vitamin B6 biosynthesis Matthew J. Rodrigues 1,2, Volker Windeisen 1,3, Yang Zhang 4, Gabriela Guédez 3, Stefan
Supplementary Information to Lysine relay mechanism coordinates intermediate transfer in vitamin B6 biosynthesis Matthew J. Rodrigues 1,2, Volker Windeisen 1,3, Yang Zhang 4, Gabriela Guédez 3, Stefan
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Structural Basis of the Antiproliferative Activity of Largazole, a Depsipeptide Inhibitor of the Histone Deacetylases Kathryn E. Cole 1, Daniel P. Dowling 1,2, Matthew A. Boone 3,
Supporting Information Structural Basis of the Antiproliferative Activity of Largazole, a Depsipeptide Inhibitor of the Histone Deacetylases Kathryn E. Cole 1, Daniel P. Dowling 1,2, Matthew A. Boone 3,
Supplementary Information. Structural basis for precursor protein-directed ribosomal peptide macrocyclization
 Supplementary Information Structural basis for precursor protein-directed ribosomal peptide macrocyclization Kunhua Li 1,3, Heather L. Condurso 1,3, Gengnan Li 1, Yousong Ding 2 and Steven D. Bruner 1*
Supplementary Information Structural basis for precursor protein-directed ribosomal peptide macrocyclization Kunhua Li 1,3, Heather L. Condurso 1,3, Gengnan Li 1, Yousong Ding 2 and Steven D. Bruner 1*
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Structural Analysis of the Binding of Type I, I 1/2, and II Inhibitors to Eph Tyrosine Kinases Jing Dong, *1 Hongtao Zhao, 1 Ting Zhou, 1 Dimitrios Spiliotopoulos, 1 Chitra Rajendran,
Supporting Information Structural Analysis of the Binding of Type I, I 1/2, and II Inhibitors to Eph Tyrosine Kinases Jing Dong, *1 Hongtao Zhao, 1 Ting Zhou, 1 Dimitrios Spiliotopoulos, 1 Chitra Rajendran,
A Review of camp-dependent Protein Kinase A Catalytic Subunit Structure, Function and Regulation
 A Review of camp-dependent Protein Kinase A Catalytic Subunit Structure, Function and Regulation Kaitlyn McLeod* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA Abstract
A Review of camp-dependent Protein Kinase A Catalytic Subunit Structure, Function and Regulation Kaitlyn McLeod* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA Abstract
Development and Validation of a Fluorescence Method to. Follow the Build-up of Short Peptide Sequences on Solid. 2D Surfaces
 Supporting Information for Development and Validation of a Fluorescence Method to Follow the Build-up of Short Peptide Sequences on Solid 2D Surfaces Mischa Zelzer a* David J. Scurr, Morgan R. Alexander,
Supporting Information for Development and Validation of a Fluorescence Method to Follow the Build-up of Short Peptide Sequences on Solid 2D Surfaces Mischa Zelzer a* David J. Scurr, Morgan R. Alexander,
Supporting Information for. PNA FRET Pair Miniprobes for Quantitative. Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization to Telomeric DNA in Cells and Tissue
 Supporting Information for PNA FRET Pair Miniprobes for Quantitative Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization to Telomeric DNA in Cells and Tissue Orenstein, et al Page S2... PNA synthesis procedure Page S3...
Supporting Information for PNA FRET Pair Miniprobes for Quantitative Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization to Telomeric DNA in Cells and Tissue Orenstein, et al Page S2... PNA synthesis procedure Page S3...
High-resolution crystal structure of ERAP1 with bound phosphinic transition-state analogue inhibitor
 High-resolution crystal structure of ERAP1 with bound phosphinic transition-state analogue inhibitor Petros Giastas 1, Margarete Neu 2, Paul Rowland 2, and Efstratios Stratikos 1 1 National Center for
High-resolution crystal structure of ERAP1 with bound phosphinic transition-state analogue inhibitor Petros Giastas 1, Margarete Neu 2, Paul Rowland 2, and Efstratios Stratikos 1 1 National Center for
Supporting Information For:
 Supporting Information For: Peptidic α-ketocarboxylic Acids and Sulfonamides as Inhibitors of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases Yen Ting Chen, Jian Xie, and Christopher T. Seto* Department of Chemistry, Brown
Supporting Information For: Peptidic α-ketocarboxylic Acids and Sulfonamides as Inhibitors of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases Yen Ting Chen, Jian Xie, and Christopher T. Seto* Department of Chemistry, Brown
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
I690/B680 Structural Bioinformatics Spring Protein Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy
 I690/B680 Structural Bioinformatics Spring 2006 Protein Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy Suggested Reading (1) Van Holde, Johnson, Ho. Principles of Physical Biochemistry, 2 nd Ed., Prentice
I690/B680 Structural Bioinformatics Spring 2006 Protein Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy Suggested Reading (1) Van Holde, Johnson, Ho. Principles of Physical Biochemistry, 2 nd Ed., Prentice
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
Pathogenic C9ORF72 Antisense Repeat RNA Forms a Double Helix with Tandem C:C Mismatches
 Supporting Information Pathogenic C9ORF72 Antisense Repeat RNA Forms a Double Helix with Tandem C:C Mismatches David W. Dodd, Diana R. Tomchick, David R. Corey, and Keith T. Gagnon METHODS S1 RNA synthesis.
Supporting Information Pathogenic C9ORF72 Antisense Repeat RNA Forms a Double Helix with Tandem C:C Mismatches David W. Dodd, Diana R. Tomchick, David R. Corey, and Keith T. Gagnon METHODS S1 RNA synthesis.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Syntheses and characterizations: Compound 1 was synthesized according to Scheme S-1. Scheme S-1 2 N N 5 i N 4 P Et Et iii N 6 ii P Et Et iv v, vi N N i) Fmoc-Su, DIPEA, Acetone;
Supporting Information Syntheses and characterizations: Compound 1 was synthesized according to Scheme S-1. Scheme S-1 2 N N 5 i N 4 P Et Et iii N 6 ii P Et Et iv v, vi N N i) Fmoc-Su, DIPEA, Acetone;
One-pot synthesis of dual functional peptides by Sortase A-mediated on-resin cleavage and ligation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic Chemistry Frontiers. This journal is the Partner Organisations 2017 One-pot synthesis of dual functional peptides by Sortase A-mediated on-resin cleavage
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic Chemistry Frontiers. This journal is the Partner Organisations 2017 One-pot synthesis of dual functional peptides by Sortase A-mediated on-resin cleavage
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Structural analysis of leader peptide binding enables leaderfree cyanobactin processing Jesko Koehnke 1,2, Greg Mann 1,2, Andrew F Bent 1,2, Hannes Ludewig 1, Sally Shirran 1,
Supplementary Information Structural analysis of leader peptide binding enables leaderfree cyanobactin processing Jesko Koehnke 1,2, Greg Mann 1,2, Andrew F Bent 1,2, Hannes Ludewig 1, Sally Shirran 1,
Supplementary Material Novel phosphopeptides as surface-active agents in iron nanoparticle synthesis
 10.1071/CH12168_AC CSIRO 2012 Australian Journal of Chemistry 2012, 65(6), 680 685 Supplementary Material Novel phosphopeptides as surface-active agents in iron nanoparticle synthesis Raoul Peltier, A,D
10.1071/CH12168_AC CSIRO 2012 Australian Journal of Chemistry 2012, 65(6), 680 685 Supplementary Material Novel phosphopeptides as surface-active agents in iron nanoparticle synthesis Raoul Peltier, A,D
Serine-7 but not serine-5 phosphorylation primes RNA polymerase II CTD for P-TEFb recognition
 Supplementary Information to Serine-7 but not serine-5 phosphorylation primes RNA polymerase II CTD for P-TEFb recognition Nadine Czudnochowski 1,2, *, Christian A. Bösken 1, * & Matthias Geyer 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut
Supplementary Information to Serine-7 but not serine-5 phosphorylation primes RNA polymerase II CTD for P-TEFb recognition Nadine Czudnochowski 1,2, *, Christian A. Bösken 1, * & Matthias Geyer 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut
Postsynthetic modification of unprotected peptides via S-tritylation reaction
 Supporting Information Postsynthetic modification of unprotected peptides via S-tritylation reaction Masayoshi Mochizuki, Hajime Hibino and Yuji Nishiuchi *,, SAITO Research Center, Peptide Institute,
Supporting Information Postsynthetic modification of unprotected peptides via S-tritylation reaction Masayoshi Mochizuki, Hajime Hibino and Yuji Nishiuchi *,, SAITO Research Center, Peptide Institute,
A prevalent intraresidue hydrogen bond stabilizes proteins
 Supplementary Information A prevalent intraresidue hydrogen bond stabilizes proteins Robert W. Newberry 1 & Ronald T. Raines 1,2 * 1 Department of Chemistry and 2 Department of Biochemistry, University
Supplementary Information A prevalent intraresidue hydrogen bond stabilizes proteins Robert W. Newberry 1 & Ronald T. Raines 1,2 * 1 Department of Chemistry and 2 Department of Biochemistry, University
Rational design of a hexapeptide hydrogelator for controlled-release drug delivery
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information for Rational design of a hexapeptide hydrogelator
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information for Rational design of a hexapeptide hydrogelator
4 Examples of enzymes
 Catalysis 1 4 Examples of enzymes Adding water to a substrate: Serine proteases. Carbonic anhydrase. Restrictions Endonuclease. Transfer of a Phosphoryl group from ATP to a nucleotide. Nucleoside monophosphate
Catalysis 1 4 Examples of enzymes Adding water to a substrate: Serine proteases. Carbonic anhydrase. Restrictions Endonuclease. Transfer of a Phosphoryl group from ATP to a nucleotide. Nucleoside monophosphate
CRYSTALLOGRAPHY AND STORYTELLING WITH DATA. President, Association of Women in Science, Bethesda Chapter STEM Consultant
 CRYSTALLOGRAPHY AND STORYTELLING WITH DATA President, Association of Women in Science, Bethesda Chapter STEM Consultant MY STORY Passion for Science BS Biology Major MS Biotechnology & Project in Bioinformatics
CRYSTALLOGRAPHY AND STORYTELLING WITH DATA President, Association of Women in Science, Bethesda Chapter STEM Consultant MY STORY Passion for Science BS Biology Major MS Biotechnology & Project in Bioinformatics
Linear Dependence of Water Proton Transverse Relaxation Rate on Shear Modulus in Hydrogels
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 ESI (Electronic Support Information) Linear Dependence of Water Proton Transverse Relaxation Rate
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 ESI (Electronic Support Information) Linear Dependence of Water Proton Transverse Relaxation Rate
Module No. 31: Peptide Synthesis: Definition, Methodology & applications
 PAPER 9: TECHNIQUES USED IN MOLECULAR BIOPHYSICS I Module No. 31: Peptide Synthesis: Definition, Methodology & applications Objectives: 1. Introduction 2. Synthesis of peptide 2.1. N-terminal protected
PAPER 9: TECHNIQUES USED IN MOLECULAR BIOPHYSICS I Module No. 31: Peptide Synthesis: Definition, Methodology & applications Objectives: 1. Introduction 2. Synthesis of peptide 2.1. N-terminal protected
Read more about Pauling and more scientists at: Profiles in Science, The National Library of Medicine, profiles.nlm.nih.gov
 2018 Biochemistry 110 California Institute of Technology Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure Linus Pauling (1901-1994) began his studies at Caltech in 1922 and was directed by Arthur Amos oyes to
2018 Biochemistry 110 California Institute of Technology Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure Linus Pauling (1901-1994) began his studies at Caltech in 1922 and was directed by Arthur Amos oyes to
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary materials Figure S1 Fusion protein of Sulfolobus solfataricus SRP54 and a signal peptide. a, Expression vector for the fusion protein. The signal peptide of yeast dipeptidyl aminopeptidase
Supplementary materials Figure S1 Fusion protein of Sulfolobus solfataricus SRP54 and a signal peptide. a, Expression vector for the fusion protein. The signal peptide of yeast dipeptidyl aminopeptidase
Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a. [Co 24 ] cluster
![Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a. [Co 24 ] cluster Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a. [Co 24 ] cluster](/thumbs/76/73822148.jpg) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a [Co 24 ] cluster Guang-Ming Liang, Qing-Ling
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Rare double spin canting antiferromagnetic behaviours in a [Co 24 ] cluster Guang-Ming Liang, Qing-Ling
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Self-Assembly of Single Amino acid-pyrene Conjugates with Unique Structure-Morphology Relationship
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Self-Assembly of Single Amino acid-pyrene Conjugates with Unique Structure-Morphology Relationship
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Self-Assembly of Single Amino acid-pyrene Conjugates with Unique Structure-Morphology Relationship
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPRTIG IFRMATI Salicylaldehyde Ester-Induced Chemoselective Peptide Ligations Enabling Generation of atural Peptidic Linkages at the Serine/Threonine Sites Xuechen Li,* iu Yung Lam, Yinfeng Zhang, Chun
SUPPRTIG IFRMATI Salicylaldehyde Ester-Induced Chemoselective Peptide Ligations Enabling Generation of atural Peptidic Linkages at the Serine/Threonine Sites Xuechen Li,* iu Yung Lam, Yinfeng Zhang, Chun
FRAGMENT SCREENING IN LEAD DISCOVERY BY WEAK AFFINITY CHROMATOGRAPHY (WAC )
 FRAGMENT SCREENING IN LEAD DISCOVERY BY WEAK AFFINITY CHROMATOGRAPHY (WAC ) SARomics Biostructures AB & Red Glead Discovery AB Medicon Village, Lund, Sweden Fragment-based lead discovery The basic idea:
FRAGMENT SCREENING IN LEAD DISCOVERY BY WEAK AFFINITY CHROMATOGRAPHY (WAC ) SARomics Biostructures AB & Red Glead Discovery AB Medicon Village, Lund, Sweden Fragment-based lead discovery The basic idea:
Synthesis of Peptide-Grafted Comb Polypeptides via Polymerisation of NCA-Peptides
 Supporting Information to Synthesis of Peptide-Grafted Comb Polypeptides via Polymerisation of NCA-Peptides Hiroshi Enomoto, Benjamin Nottelet, Soultan Al Halifa, Christine Enjalbal, Mathieu Dupré, Julien
Supporting Information to Synthesis of Peptide-Grafted Comb Polypeptides via Polymerisation of NCA-Peptides Hiroshi Enomoto, Benjamin Nottelet, Soultan Al Halifa, Christine Enjalbal, Mathieu Dupré, Julien
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/243/ra68/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Superbinder SH2 Domains Act as Antagonists of Cell Signaling Tomonori Kaneko, Haiming Huang, Xuan Cao, Xing Li, Chengjun
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/243/ra68/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Superbinder SH2 Domains Act as Antagonists of Cell Signaling Tomonori Kaneko, Haiming Huang, Xuan Cao, Xing Li, Chengjun
SOCS3 binds specific receptor JAK complexes to control cytokine signaling by direct kinase inhibition SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SOCS3 binds specific receptor JAK complexes to control cytokine signaling by direct kinase inhibition Nadia J. Kershaw 1,2, James M. Murphy 1,2, Nicholas P.D. Liau 1,2, Leila N. Varghese 1,2, Artem Laktyushin
SOCS3 binds specific receptor JAK complexes to control cytokine signaling by direct kinase inhibition Nadia J. Kershaw 1,2, James M. Murphy 1,2, Nicholas P.D. Liau 1,2, Leila N. Varghese 1,2, Artem Laktyushin
Magnetic Metal-Organic Framework Exhibiting Quick and. Selective Solvatochromic Behavior Along With The Reversible
 Magnetic Metal-Organic Framework Exhibiting Quick and Selective Solvatochromic Behavior Along With The Reversible Crystal-to-Amorphous-to-Crystal Transformation Peng Hu,, Lei Yin,, Angelo Kirchon,, Jiangli
Magnetic Metal-Organic Framework Exhibiting Quick and Selective Solvatochromic Behavior Along With The Reversible Crystal-to-Amorphous-to-Crystal Transformation Peng Hu,, Lei Yin,, Angelo Kirchon,, Jiangli
New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase: Structural Insights into β- Lactam Recognition and Inhibition
 Supporting Information New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase: Structural Insights into β- Lactam Recognition and Inhibition Dustin T. King, Liam J. Worrall, Robert Gruninger, Natalie C.J. Strynadka* AUTHOR ADDRESS:
Supporting Information New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase: Structural Insights into β- Lactam Recognition and Inhibition Dustin T. King, Liam J. Worrall, Robert Gruninger, Natalie C.J. Strynadka* AUTHOR ADDRESS:
Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2
 2 Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2 Overview Viewing the accessible surface Analyzing the properties of proteins containing thousands of atoms is best accomplished by representing
2 Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2 Overview Viewing the accessible surface Analyzing the properties of proteins containing thousands of atoms is best accomplished by representing
Electronic Supplementary Information for
 Electronic Supplementary Information for Sequence Selective Dual-Emission Detection of (i, i+1) Bis-Phosphorylated Peptide Using Diazastilbene-Type Zn(II)-Dpa Chemosensor Yoshiyuki Ishida, Masa-aki Inoue,
Electronic Supplementary Information for Sequence Selective Dual-Emission Detection of (i, i+1) Bis-Phosphorylated Peptide Using Diazastilbene-Type Zn(II)-Dpa Chemosensor Yoshiyuki Ishida, Masa-aki Inoue,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
Under strongly acidic conditions at ph = 1 every functional group in phosphoserine that can pick up a proton, does.
 1. (48 pts) a. L-Phosphoserine is a modified amino acid that is generated in proteins by phosphorylation of serine residues. The amino acid side chain has two acidic protons, which exhibit different pk
1. (48 pts) a. L-Phosphoserine is a modified amino acid that is generated in proteins by phosphorylation of serine residues. The amino acid side chain has two acidic protons, which exhibit different pk
Biomolecules: lecture 9
 Biomolecules: lecture 9 - understanding further why amino acids are the building block for proteins - understanding the chemical properties amino acids bring to proteins - realizing that many proteins
Biomolecules: lecture 9 - understanding further why amino acids are the building block for proteins - understanding the chemical properties amino acids bring to proteins - realizing that many proteins
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
PROTEIN STRUCTURE AMINO ACIDS H R. Zwitterion (dipolar ion) CO 2 H. PEPTIDES Formal reactions showing formation of peptide bond by dehydration:
 PTEI STUTUE ydrolysis of proteins with aqueous acid or base yields a mixture of free amino acids. Each type of protein yields a characteristic mixture of the ~ 20 amino acids. AMI AIDS Zwitterion (dipolar
PTEI STUTUE ydrolysis of proteins with aqueous acid or base yields a mixture of free amino acids. Each type of protein yields a characteristic mixture of the ~ 20 amino acids. AMI AIDS Zwitterion (dipolar
The Depsipeptide Methodology for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis: Circumventing Side Reactions and Development of an Automated Technique via
 Supporting Information The Depsipeptide Methodology for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis: Circumventing Side Reactions and Development of an Automated Technique via Depsidipeptide Units. Irene Coin, Rudolf
Supporting Information The Depsipeptide Methodology for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis: Circumventing Side Reactions and Development of an Automated Technique via Depsidipeptide Units. Irene Coin, Rudolf
IgE binds asymmetrically to its B cell receptor CD23
 Supplementary Information IgE binds asymmetrically to its B cell receptor CD23 Balvinder Dhaliwal 1*, Marie O. Y. Pang 2, Anthony H. Keeble 2,3, Louisa K. James 2,4, Hannah J. Gould 2, James M. McDonnell
Supplementary Information IgE binds asymmetrically to its B cell receptor CD23 Balvinder Dhaliwal 1*, Marie O. Y. Pang 2, Anthony H. Keeble 2,3, Louisa K. James 2,4, Hannah J. Gould 2, James M. McDonnell
Catalytic Mechanism of the Glycyl Radical Enzyme 4-Hydroxyphenylacetate Decarboxylase from Continuum Electrostatic and QC/MM Calculations
 Catalytic Mechanism of the Glycyl Radical Enzyme 4-Hydroxyphenylacetate Decarboxylase from Continuum Electrostatic and QC/MM Calculations Supplementary Materials Mikolaj Feliks, 1 Berta M. Martins, 2 G.
Catalytic Mechanism of the Glycyl Radical Enzyme 4-Hydroxyphenylacetate Decarboxylase from Continuum Electrostatic and QC/MM Calculations Supplementary Materials Mikolaj Feliks, 1 Berta M. Martins, 2 G.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.108/nature0608 a c pmol L-[ H]Leu / mg LeuT pmol L-[ H]Leu / min / mg LeuT 900 50 600 450 00 150 200 150 100 0 0.0 2.5 5.0.5 10.0.5 50 N Cl CMI IMI DMI H C CH N N H C CH N Time (min) 0 0 100 200
doi: 10.108/nature0608 a c pmol L-[ H]Leu / mg LeuT pmol L-[ H]Leu / min / mg LeuT 900 50 600 450 00 150 200 150 100 0 0.0 2.5 5.0.5 10.0.5 50 N Cl CMI IMI DMI H C CH N N H C CH N Time (min) 0 0 100 200
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I. 1. Of the 20 standard amino acids, only is not optically active. The reason is that its side chain.
 Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wan et al. 10.1073/pnas.1415856111 SI Materials and Methods Proposals for Keto-Enol Tautomerization of Substrate and the DHFR Catalytic Mechanism. As noted in the main text, competing
Supporting Information Wan et al. 10.1073/pnas.1415856111 SI Materials and Methods Proposals for Keto-Enol Tautomerization of Substrate and the DHFR Catalytic Mechanism. As noted in the main text, competing
Supporting Information
 Electronic upplementary Material (EI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal ociety of Chemistry 2014 upporting Information Materials and methods: Chemicals: Fmoc-amino acids were obtained from GL Biochem
Electronic upplementary Material (EI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal ociety of Chemistry 2014 upporting Information Materials and methods: Chemicals: Fmoc-amino acids were obtained from GL Biochem
1 Supporting Information. 2 3 Materials and methods: 4 Chemicals: Fmoc-amino acids were obtained from GL Biochem (Shanghai).
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 1 Supporting Information 2 3 Materials and methods: 4 Chemicals: Fmoc-amino acids were obtained
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 1 Supporting Information 2 3 Materials and methods: 4 Chemicals: Fmoc-amino acids were obtained
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Combinatorial Readout of Unmodified H3R2 and Acetylated H3K14 by the Tandem PHD Finger of MOZ Reveals a Regulatory Mechanism for HOXA9 Transcription Yu Qiu 1, Lei Liu 1, Chen Zhao
Supplemental Information Combinatorial Readout of Unmodified H3R2 and Acetylated H3K14 by the Tandem PHD Finger of MOZ Reveals a Regulatory Mechanism for HOXA9 Transcription Yu Qiu 1, Lei Liu 1, Chen Zhao
Supporting Information. Time-Resolved Botulinum Neurotoxin A Activity Monitored using. Peptide-Functionalized Au Nanoparticle Energy Transfer Sensors
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Time-Resolved Botulinum Neurotoxin A Activity Monitored using Peptide-Functionalized
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Time-Resolved Botulinum Neurotoxin A Activity Monitored using Peptide-Functionalized
Introduction to" Protein Structure
 Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Figure 1. Molecules geometries of 5021 and Each neutral group in CHARMM topology was grouped in dash circle.
 Project I Chemistry 8021, Spring 2005/2/23 This document was turned in by a student as a homework paper. 1. Methods First, the cartesian coordinates of 5021 and 8021 molecules (Fig. 1) are generated, in
Project I Chemistry 8021, Spring 2005/2/23 This document was turned in by a student as a homework paper. 1. Methods First, the cartesian coordinates of 5021 and 8021 molecules (Fig. 1) are generated, in
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Novel diphenylmethyl-derived amide protecting group for efficient liquid-phase peptide synthesis; AJIPHASE Daisuke Takahashi*, Tatsuya Yano and Tatsuya Fukui Research Institute For
Supporting Information Novel diphenylmethyl-derived amide protecting group for efficient liquid-phase peptide synthesis; AJIPHASE Daisuke Takahashi*, Tatsuya Yano and Tatsuya Fukui Research Institute For
Near UV-Visible Electronic Absorption Originating from Charged
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Near UV-Visible Electronic Absorption Originating from Charged Amino
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Near UV-Visible Electronic Absorption Originating from Charged Amino
LS1a Fall 2014 Problem Set #2 Due Monday 10/6 at 6 pm in the drop boxes on the Science Center 2 nd Floor
 LS1a Fall 2014 Problem Set #2 Due Monday 10/6 at 6 pm in the drop boxes on the Science Center 2 nd Floor Note: Adequate space is given for each answer. Questions that require a brief explanation should
LS1a Fall 2014 Problem Set #2 Due Monday 10/6 at 6 pm in the drop boxes on the Science Center 2 nd Floor Note: Adequate space is given for each answer. Questions that require a brief explanation should
4. What is the general expression Keq (the equilibrium constant) in terms of product and reactant concentration? tell us about the enzyme.
 Section 8 Enzyme Kinetics Pre-Activity Assignment 1. Produce a reading log for the sections in your text that discuss the Michaelis-Menten equation and including kcat. 2. Focus on the derivation of the
Section 8 Enzyme Kinetics Pre-Activity Assignment 1. Produce a reading log for the sections in your text that discuss the Michaelis-Menten equation and including kcat. 2. Focus on the derivation of the
Interpreting and evaluating biological NMR in the literature. Worksheet 1
 Interpreting and evaluating biological NMR in the literature Worksheet 1 1D NMR spectra Application of RF pulses of specified lengths and frequencies can make certain nuclei detectable We can selectively
Interpreting and evaluating biological NMR in the literature Worksheet 1 1D NMR spectra Application of RF pulses of specified lengths and frequencies can make certain nuclei detectable We can selectively
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2007
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Supporting Information for Head-to-Tail Cyclized
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2007 Supporting Information for Head-to-Tail Cyclized
Protein Structure Bioinformatics Introduction
 1 Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Protein Structure Bioinformatics Introduction Basel, 27. September 2004 Torsten Schwede Biozentrum - Universität Basel Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Klingelbergstr
1 Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Protein Structure Bioinformatics Introduction Basel, 27. September 2004 Torsten Schwede Biozentrum - Universität Basel Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Klingelbergstr
4. The Michaelis-Menten combined rate constant Km, is defined for the following kinetic mechanism as k 1 k 2 E + S ES E + P k -1
 Fall 2000 CH 595C Exam 1 Answer Key Multiple Choice 1. One of the reasons that enzymes are such efficient catalysts is that a) the energy level of the enzyme-transition state complex is much higher than
Fall 2000 CH 595C Exam 1 Answer Key Multiple Choice 1. One of the reasons that enzymes are such efficient catalysts is that a) the energy level of the enzyme-transition state complex is much higher than
Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e Chapter 04
 01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
Supplementary Figure S1 a, wireframe view of the crystal structure of compound 11. b, view of the pyridinium sites. c, crystal packing of compound
 a b c Supplementary Figure S1 a, wireframe view of the crystal structure of compound 11. b, view of the pyridinium sites. c, crystal packing of compound 11. 1 a b c Supplementary Figure S2 a, wireframe
a b c Supplementary Figure S1 a, wireframe view of the crystal structure of compound 11. b, view of the pyridinium sites. c, crystal packing of compound 11. 1 a b c Supplementary Figure S2 a, wireframe
Supporting Information. A fluorogenic assay for screening Sirt6 modulators
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 213 Supporting Information A fluorogenic assay for screening Sirt6 modulators Jing Hu, Bin He, Shiva Bhargava, Hening Lin* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 213 Supporting Information A fluorogenic assay for screening Sirt6 modulators Jing Hu, Bin He, Shiva Bhargava, Hening Lin* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Acta Cryst. (2017). D73, doi: /s
 Acta Cryst. (2017). D73, doi:10.1107/s2059798317010932 Supporting information Volume 73 (2017) Supporting information for article: Designing better diffracting crystals of biotin carboxyl carrier protein
Acta Cryst. (2017). D73, doi:10.1107/s2059798317010932 Supporting information Volume 73 (2017) Supporting information for article: Designing better diffracting crystals of biotin carboxyl carrier protein
Hydroxyproline Ring Pucker Causes Frustration of Helix Parameters in the Collagen Triple Helix
 Supporting Information for Hydroxyproline Ring Pucker Causes Frustration of Helix Parameters in the Collagen Triple Helix W. Ying Chow,1, Dominique Bihan,2, Chris J. Forman,1 David A. Slatter,3 David G.
Supporting Information for Hydroxyproline Ring Pucker Causes Frustration of Helix Parameters in the Collagen Triple Helix W. Ying Chow,1, Dominique Bihan,2, Chris J. Forman,1 David A. Slatter,3 David G.
(Supplementary Information)
 (Supplementary Information) Peptidomimetic-based Multi-Domain Targeting Offers Critical Evaluation of Aβ Structure and Toxic Function Sunil Kumar 1*, Anja Henning-Knechtel 2, Mazin Magzoub 2, and Andrew
(Supplementary Information) Peptidomimetic-based Multi-Domain Targeting Offers Critical Evaluation of Aβ Structure and Toxic Function Sunil Kumar 1*, Anja Henning-Knechtel 2, Mazin Magzoub 2, and Andrew
The copper active site in CBM33 polysaccharide oxygenases
 Supporting Information for: The copper active site in CBM33 polysaccharide oxygenases Glyn R. Hemsworth, Edward J. Taylor, Robbert Q. Kim, Rebecca C. Gregory, Sally J. Lewis, Johan P. Turkenburg, Alison
Supporting Information for: The copper active site in CBM33 polysaccharide oxygenases Glyn R. Hemsworth, Edward J. Taylor, Robbert Q. Kim, Rebecca C. Gregory, Sally J. Lewis, Johan P. Turkenburg, Alison
Timescales of Protein Dynamics
 Timescales of Protein Dynamics From Henzler-Wildman and Kern, Nature 2007 Dynamics from NMR Show spies Amide Nitrogen Spies Report On Conformational Dynamics Amide Hydrogen Transverse Relaxation Ensemble
Timescales of Protein Dynamics From Henzler-Wildman and Kern, Nature 2007 Dynamics from NMR Show spies Amide Nitrogen Spies Report On Conformational Dynamics Amide Hydrogen Transverse Relaxation Ensemble
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Carbene Activation of P 4 and Subsequent Derivatization Jason D. Masuda, Wolfgang W. Schoeller, Bruno Donnadieu, and Guy Bertrand * [*] Dr.
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Carbene Activation of P 4 and Subsequent Derivatization Jason D. Masuda, Wolfgang W. Schoeller, Bruno Donnadieu, and Guy Bertrand * [*] Dr.
Convenient Synthesis of Nucleoside 5 -Triphosphates for RNA Transcription. Supplemental Materials
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2010 Convenient Synthesis of ucleoside 5 -Triphosphates for RA Transcription Julianne Caton-Williams,
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2010 Convenient Synthesis of ucleoside 5 -Triphosphates for RA Transcription Julianne Caton-Williams,
CHAPTER 29 HW: AMINO ACIDS + PROTEINS
 CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
Supplementary Figure 1. Structures of substrates tested with 1. Only one enantiomer is shown.
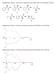 Supplementary Figure 1. Structures of substrates tested with 1. Only one enantiomer is shown. Supplementary Figure 2. CD spectra obtained using 1 and (R)-3 (blue) and (S)-3 (red) Supplementary Figure 3.
Supplementary Figure 1. Structures of substrates tested with 1. Only one enantiomer is shown. Supplementary Figure 2. CD spectra obtained using 1 and (R)-3 (blue) and (S)-3 (red) Supplementary Figure 3.
A Plausible Model Correlates Prebiotic Peptide Synthesis with. Primordial Genetic Code
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 A Plausible Model Correlates Prebiotic Peptide Synthesis with Primordial Genetic Code Jianxi Ying,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 A Plausible Model Correlates Prebiotic Peptide Synthesis with Primordial Genetic Code Jianxi Ying,
BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Part I Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Part I Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes
1,4-Dihydropyridyl Complexes of Magnesium: Synthesis by Pyridine. Insertion into the Magnesium-Silicon Bond of Triphenylsilyls and
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information 1,4-Dihydropyridyl Complexes of Magnesium: Synthesis
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supporting Information 1,4-Dihydropyridyl Complexes of Magnesium: Synthesis
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Anion clamp allows flexible protein to impose coordination geometry on
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Anion clamp allows flexible protein to impose coordination geometry on
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
Introduction solution NMR
 2 NMR journey Introduction solution NMR Alexandre Bonvin Bijvoet Center for Biomolecular Research with thanks to Dr. Klaartje Houben EMBO Global Exchange course, IHEP, Beijing April 28 - May 5, 20 3 Topics
2 NMR journey Introduction solution NMR Alexandre Bonvin Bijvoet Center for Biomolecular Research with thanks to Dr. Klaartje Houben EMBO Global Exchange course, IHEP, Beijing April 28 - May 5, 20 3 Topics
BIOCHEMISTRY Course Outline (Fall, 2011)
 BIOCHEMISTRY 402 - Course Outline (Fall, 2011) Number OVERVIEW OF LECTURE TOPICS: of Lectures INSTRUCTOR 1. Structural Components of Proteins G. Brayer (a) Amino Acids and the Polypeptide Chain Backbone...2
BIOCHEMISTRY 402 - Course Outline (Fall, 2011) Number OVERVIEW OF LECTURE TOPICS: of Lectures INSTRUCTOR 1. Structural Components of Proteins G. Brayer (a) Amino Acids and the Polypeptide Chain Backbone...2
BCH 4053 Exam I Review Spring 2017
 BCH 4053 SI - Spring 2017 Reed BCH 4053 Exam I Review Spring 2017 Chapter 1 1. Calculate G for the reaction A + A P + Q. Assume the following equilibrium concentrations: [A] = 20mM, [Q] = [P] = 40fM. Assume
BCH 4053 SI - Spring 2017 Reed BCH 4053 Exam I Review Spring 2017 Chapter 1 1. Calculate G for the reaction A + A P + Q. Assume the following equilibrium concentrations: [A] = 20mM, [Q] = [P] = 40fM. Assume
