Enhancement of mechanical properties for reinforced Iraqi bentonite clay polyvinyl chloride composite using ultrasonic technique
|
|
|
- Blake Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Enhancement of mechanical properties for reinforced Iraqi bentonite clay polyvinyl chloride composite using ultrasonic technique Foaad Sh. Hashim Physics Department, College of Education for pure science, Babylon University, Iraq PO box 4, Babylon, Iraq of corresponding author: Abstract This research is depended an accurate style in preparing homogenous solution of PVC- Iraqi Bentonite clay composite adoption of careful balance mechanism in the selection of the ratio of solvent and mixing time according to the speed of mixing 40 rpm. Particle sizes selected for Bentonite clay is <7 & <0µm and the calcination process was performed at 300, 700, and 900oC for hr. The Bentonite particles were mixed with known concentration of PVA solution at 80oC for half an hour, then dried, milled, and sieved for particle sizes as mention above. Mixture of PVC solution with reinforced Bentonite clay is used to prepare the composite under study. Effect of mentioned parameters on mechanical properties of PVC were performed by ultrasonic technique using frequency of 30 KHz. Addition of reinforced Bentonite generally enhanced the mechanical properties of PVC. Evidently the composite prepared from reinforced powder <7µm is a good medium for transfer ultrasound waves particularly at calcination temperature 300oC, that is mean it has a good stability against mechanical waves, so they can be used as a coated material for objects that we don t want them to be detected by sonar, while in the case of particles <0μm is not. Failure to obtain the same result at temperatures higher than 300oC and the granular size <0µm due to the presence strong intermolecular interaction that is responsible for reducing the elasticity of composite, in other words, leave it semibrittle, i.e. not have good stability. Highest enhancement in the absorption coefficient appears at 900oC with preference to the specimen of particles <0μm,and the composite becomes good absorber for ultrasound. Moreover the addition causing a reduction in compressibility, thus there is a small strain in the composite as a result of ultrasonic stress. Keywords: PVC composite, Bentonite clay, Ultrasonic technique. Introduction A composite is a structural material that consist of two or more constituents that are combined at a macroscopic level and are not soluble in each other. One constituent is called the reinforcing phase, which is mixing with materials that has coupling agents properties to prevent the collapse of the mechanical properties of a composite material,and the other in which it is embedded is called the matrix. Inefficient industrial fillers (clays, black carbon and silica) used to reduce the cost of composite materials []. PVC in the form of powders, slurries, liquids and tablets. It has a wide range properties such as a wide range of colors, solid, rigid and stiff materials (with high viscosity) at room temperature, light weight with a good resistance to bases & acids, alcohol, oils, compound hydrocarbon aliphatic. PVC's relatively low cost, biological and chemical resistance and workability and can form easily have resulted in it being used for a wide variety of applications, such as insulation on electrical cables,solid pipe manufacturing,window frames and doors, bottles, containers, furniture industry []. Bentonite is the rock composed essentially of clay minerals of the smectic, usually montmorillonite. Other smectic group minerals include hectorite, saponite, beidelite and nontronite. The theoretical formula for the structure mentioned above are (OH) 4 Si 8 AL 4 O 0 n (interlayer) H O,and the chemical formula for the montmorillonite group is (Al,Mg) (OH) (Al,Si) 4 O 0 [3]. Bentonite has a high content of montmorillonite and a less amount of other clay minerals. Nowadays many different industrial branches such as ceramics, paper, rubber, wine, soaps and cleaning and polishing of compounds, and drug industries are using these materials, waste water purification and even into different 4
2 aspects of nano-technology because of nano sizes of its particles [4]. Bentonite group minerals show a colloidal structure in water, due to their internal structure and small particle size. They have a large adsorption capacity for polymer compounds due to their unique crystal structure []. The polymer concentration, molecular weight, hydrolysis degree of polymer, clay particle's size, shape, and surface charge, clay concentration in dispersion, clay's PH, and temperature are effective factors when clay particles interact with the polymers [6]. The aim of present work is to enhancement of mechanical properties including ultrasound velocity, density, absorption coefficient, shear viscosity, relaxation amplitude, relaxation time, compressibility, acoustic impedance, and bulk modulus of PVC by adding reinforced Iraqi bentonite clay.. Experimental and theoretical calculations The work have been into six specimens depending on the certain selected of particles size (<7 & <0) µm and calcinations process (300,700, and 900) o C for Iraqi Bentonite clay..preparation and testing reinforced Bentonite clay The Bentonite particles were dispersed in distilled water to dispose from the salts and some of impurities that dissolved in water, and shaken extensively for 4hr at room temperature, after filtration, the specimen was dried at 00 o C for 4hr by using the dryer type F. G. BODE&CO- Laboratory - Equipment - Hamburg-90. The chemical composition of Iraqi bentonite, which were supplied by state company of geological survey and minority in Iraq are listed in Table (). The mineralogical analysis of the final powder of Iraqi Bentonite is listed in Table (). The addition of PVA solution (PH~3) association as a coated layer covered the bentonite before applied it as filler. The mixture was mixed with heat treatment continued to get slurry form and to insure homogeneity with high viscosity (the mixing process was adopted according to the method of green land) [7], then dried, milled and sieved to particle sizes < 7, and <0µm.. Preparation PVC - reinforced Bentonite composite A solution of g of PVC were prepared by using Sikloheksanon solvent in temperature of 80 o C using a heater plate and mechanical mixer with feather glass type (Heidolph RZR 00 electronic) and speed of mixing 40 rpm. By continuously mix we obtained a homogenous emulsion milky color. Incremental amount of reinforced Bentonite was added to prepared PVC solution after an investigation the case of emulsion and homogenized through a process of heating and mixing half an hour, as shown in Table (3),then we added the calcium stearate as stabilizer heat for certain quantity as defined in Table (3), and continued to mix that we have a brown emulsion. Then the material is poured into a glass template parallelogram. The specimen is kept in an incubator at 30 o C for three days, and then moved to a container drying (we follow the same way to prepare the other specimens). After that the piece was prepared in the form of models of disks with a diameter 40mm for the purpose of examination. Mechanical properties were measured using ultrasonic technique at frequency of 30 KHz..3. Theoretical calculations The absorption coefficient (α) was calculated from Beer Lambert law [8]: A/A 0 = e (- α x) () Where (A 0 ) is the initially amplitude of the ultrasonic waves, (A) is the wave amplitude after absorption, and (x) is the thickness of the specimen. The relaxation amplitude of ultrasonic wave was calculated from the equation [9] : D = α/ f () Where (f) is the frequency. The method of measuring the speed of ultrasound wave was by calculating the thickness of the sample (x) and the time it takes inside the specimen (t) [0]: v = x / t (3) The acoustic impedance of a medium (Z) is a material property was calculated by equation [] : Z = ρ v.. (4)
3 Where (ρ) is the density. The bulk modulus (B) of a substance measures and the substance's resistance to uniform compression, it is defined as the pressure increase needed to decrease the volume; its base unit is the Pascal (Pa.) was calculated by equation []: B = ρ v. () Compressibility (β) is a measure of the relative volume change of a fluid or solid as a response to a pressure (or mean stress) change, it was calculated by equation [3]: β = (ρ v ) - (6) On the basis that all solids flow to a small extent in response to small shear stress, some researchers have contended that substances known as amorphous solids, such as glass and many polymers may be considered to have viscosity. This has led some to the view that solids are simply "liquids" with a very high viscosity; the viscosity of the samples was measured by using the equation [4, ]: η s = 3 α ρ v 3 / 8 π f. (7) The relaxation time (τ) was calculated from the equation[6] : 3. Results and discussion τ =4 η s /3ρ v... (8) Ultrasonic velocity for all prepared specimens is higher compared with PVC as shown in Fig., specified by specimen from reinforced powder <7μm at 300 o C. This attributed to the interaction causing association between the three types of molecules; polymer, solvent and bentonite molecules, so their will be entanglement action of high molecular weight of PVC to reinforced bentonite powder that can fills the spaces between polymer chains, and these entanglements enhanced the prepared composite to be a good medium for transferring ultrasonic waves. The velocity of ultrasound in the specimens prepared from reinforced powder <0μm is nearly constant and remain less than it is in the case of <7μm at all calcinations temperatures since the new lattice has not been good stability against ultrasonic waves as a result of not completely that specimens of 0μm can fills the whole spaces leaving somewhere that attenuated ultrasonic waves for improve relaxation times [7] as we will see later in Fig. 6. This behavior similar to that obtained by Boro Djardjevic for other materials [8]. The above result supported by the behavior of density as shown in Fig., where we find the specimens prepared from reinforced powder <7 μm have the highest density than that of 0μm particularly at 300 o C. The absorption coefficient for all prepared specimens is higher compared with PVC as shown in Fig. 3. This attributed that the attenuation of ultrasonic energy depends on shear viscosity, thermal conductivity, scattering, and intermolecular interaction. Thermal conductivity and scattering effects are known to be negligible [9], so the shear viscosity is the main cause of increasing absorption coefficient and as we look to the Fig. 4, especially obvious at 300 o C. High values at all calcinations temperatures attributed to the mechanism of hydrogen bonding attached to oxygen sites, which lead to increase the entanglement between filler molecules of size <7μm and polymer chains that randomly coiled so increasing shear viscosity [0], while in the case of 0μm the shear viscosity are nearly constant with temperature, because of an tied large grains within the lattice that leaving the specimen semi-brittle or not have good stability particularly in calcinations temperature higher than 300 o C [3,0]. This result supported by the behavior of variable bulk modulus verses calcinations temperature as we come to that later. The high relaxation amplitude for both specimens prepared from reinforced powder <7μm and <0 μm as shown in Fig. associated with high absorption coefficient as shown previously, so that the absorbed molecules take time to relax to their equilibrium positions. Effect of the calcinations process over the values of relaxation time after additives as shown in Fig. 6, because of the ultrasonic waves are propagated in the form of compression and rarefaction when interact with polymer molecules, so as a pure specimens its molecules take a time to relax to their original position against sound waves,while the additives restrict these molecules that increase the relax time particularly in specimens prepared from reinforced powder <7μm at 300 o C because it has stability higher than that of <0μm. 6
4 The general decreasing in compressibility after additives reinforced Bentonite of different sizes compared with PVC and improve it with calcinations temperature as shown in Fig. 7, is attributed to the inversely relation between velocity and compressibility, since the polymer molecules be closer to each other and there will be interactions of strongly bonds obtained as a result of increasing calcinations temperature. Effect of addition reinforced Bentonite of different sizes on the values of specific acoustic impedance as shown in Fig. 8 interpreted on the basis that the increase in velocity caused an increase in specific acoustic impedance largest in specimens prepared from reinforced powder <7μm particularly at 300 o C, because of high stability against sound waves [,]. Bulk modulus also increasing after additives as shown in Fig. 9. This attributed to the fact that compressibility is inversely related to the Bulk modulus by means of Eq. and Eq.6, when compressibility decrease bulk modulus must be increasing particularly for specimens prepared from reinforced powder <7μm at 300 o C. 4. Conclusions From the experimental results we can show that the mechanical properties of composites can be changed using the reinforced Bentonite. - The addition of reinforced bentonite generally enhanced the mechanical properties of PVC. -The composite prepared from reinforced powder <7µm is a good medium for transfer ultrasound waves particularly at calcinations temperature of 300 o C, that is mean it has a good stability against mechanical waves, so they can be used as a coated material for objects that we don t want them to be detected by sonar, while in the case of particles <0μm is not. 3- Failure to obtain the same result at temperatures higher than 300 o C and the granular size <0µm due to the presence strong intermolecular interaction that is responsible for reducing the elasticity of composite, in other words, leave it semi-brittle, i.e. not have good stability. 4- Highest enhancement in the absorption coefficient appears at 900 o C with preference to the spacemen of particles <0μm, then the composite becomes good absorber for ultrasound. -The addition of reinforced Bentonite causing a reduction in compressibility and thus there is a small strain in the composite as a result of ultrasonic stress. References Al- jeebory, A.A, Al-Mosawi, A.I.,(009), "Effect of percentage of fibers reinforcement on thermal and mechanical properties for polymeric composite material", the Iraqi journal of mechanical and materials engineering, st conference of engineering college. Al-Bermany K.J.,(0)" Study the rheological and mechanical properties of PVA/ NH 4 Cl by ultrasonic" Journal of chemistry and material research,,, Al-Bermany, k. J., (009),"Enhancement mechanical and rheological properties and some its different industrial applications", journal of college of education no. vol., no.. Al-Bermany, k. J., (00), "Visco-relaxation study of effect on polyethylene oxide by ultrasonic " Journal of Babylon, 3,. Boro Djordjevic, B.,(009),"Ultrasonic characterization of advanced composite materials", the 0 th International Conference of the Slovenian Society for Non- Destructive Testing (Application of Contemporary Non-Destructive Testing in Engineering), Ljubljana, Slovenia, Boutouyrie, P., Briet, M., Collin,C., Vermeersch, S. and Pannier, B. (009), "Assessment of pulse wave velocity ", Artery Research 3,, 3 8 Callen, Herbert B. (98). Thermodynamics and an Introduction to Thermostatistics (nd Ed. ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons. Cohen, Marvin (98). "Calculation of bulk moduli of diamond and zinc-blende solids". Phys. Rev. B 3,
5 Curi, E, Companha S. (006) "Marco mol. Sci." A43, 4. Green Land, D.J., (963),"Adsorption of polyvinyl Alcohols by Montmorillonite ",J. of colloid science,8, Grim, R.E., (970), "Bentonite ", Elsevier scientific publishing company New York. Hassun, S.k., (990)" Visco relaxation study of polystyrene solutions in different solutions by ultrasonic", act a polymeric Journal, 4, 8. Hunter, R.J., (986), "Foundation of colloid science" (New York: Clarendon press). Ingle, J. D., and Crouch, S. R., (988), "Spectrochemical Analysis", Prentice Hall, New Jersey. Isci, S., Unlu,C.H., Atici, O. and Gungor, N. (006) "Rheology and structure of aqueous bentonite-polyvinyl alcohol dispersions", Indian Academy of Sciences, 9,, Jarlath Mc Hugh,(008), "Ultrasound Technique for the Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers", Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM) Berlin Krautkramer, Josef and Herbert,(990) "Ultrasonic testing of materials" 4th edition. Kumagai, Naoichi; Sadao Sasajima, Hidebumi Ito, (008). Journal of the Society of Materials Science (Japan) (Japan Energy Society) 7, 93, 7 6 Raghad, S.A., (009), "study the effect of Iraqi bentonite clay addition on the properties of porcelain body prepared from local material clays ",ph. D., thesis, university of Baghdad. Shah Rahman(007),"PVC pipe &fittings: Underground solution for water and sewer systems in north America", nd Brazilian PVC congress, sao Paulo, Brazil. Tomasz hornowski, (00), Effect of polyethylene Glycol coating on the acoustic properties of biocompatible fluid", international journal,thermophysics, 3, Zong Faug wul and bung C. Lin, (0) "Method of improved scaterer size estimation without attenuation known a prior IEEE, Table. Chemical composition of used Bentonite. Oxide Wt% OxideWt% Oxide SiO 6.77 MgO 3.4 SO3 AlO3 6. NaO. Cl FeO3. KO 0.6 L.O.I CaO 4.48 PO 0.6 ( loss of ignition) Wt%
6 Table. Mineralogical analysis of used Bentonite. Minerals Percentage % Montmorillonite [OH] Al SiO 0 79 Attapulgate 7 Mg Si 8 O 0 [OH] 8H O Apatite Ca [Fe, Cl] P 3 O 3 Calcite CaCO 3 Gypsum CaSO 4 H O Halite NaCl Quartz SiO Table 3. The ratios and type of components, calcinations temperature and particle size of filler powder. Sample NO. Particle size (µm) Calcinations temperature o C Filler preparation condition (reinforced) Calcinations time (hr) Filler(Bentonite)wt% PVA wt% PVC wt% PVC preparation condition (matrix) Ratio Solvent (gm :ml) Stabilizer % Mixing temperature o C Mixing time (hr) A A B B C C <7 <0 <7 <0 <7 < : :. : 3 :. : :
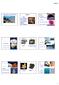
7 Figure. Plot of ultrasonic velocity versus calcination temperature. Figure. Plot of density versus calcinations temperature. Figure 3. Plot of absorption coefficient of ultrasonic waves versus calcinations temperature. 30
8 Figure 4. Plot of Shear viscosity versus of calcination temperature. Figure. Plot of relaxation amplitude versus calcination temperature. Figure 6. Plot of relaxation time versus calcination temperature. 3
9 Figure 7. Plot of compressibility versus calcination temperature. Figure 8. Plot of specific acoustic impedance versus calcinations Temperature. Figure 9. Plot of bulk modulus versus calcinations temperature. 3
Study the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of PVA/CuCl 2. by Ultrasonic
 Study the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of PVA/CuCl 2 by Ultrasonic 1 Abdul-Kareem Jawad Rashid 2 Burak Yahya Kadem 3 Lamis F.Naser 1. University of Babylon, College of Science, Physics Department,
Study the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of PVA/CuCl 2 by Ultrasonic 1 Abdul-Kareem Jawad Rashid 2 Burak Yahya Kadem 3 Lamis F.Naser 1. University of Babylon, College of Science, Physics Department,
Cronicon CHEMISTRY. Research Article. Rheological Properties of NBR-PVC Blend
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS CHEMISTRY Research Article Rheological Properties of NBR-PVC Blend Mohammed H Al-Maamori 1, Ali I Al-Mosawi 2 *, Shaymaa Abbas Abdulsada 3 and Haider A Yasser 1 1 College of Engineering
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS CHEMISTRY Research Article Rheological Properties of NBR-PVC Blend Mohammed H Al-Maamori 1, Ali I Al-Mosawi 2 *, Shaymaa Abbas Abdulsada 3 and Haider A Yasser 1 1 College of Engineering
Modification of Nano clay systems: An approach to stabilizing drilling fluids
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-11-15 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 829, pp 818-824 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.829.818 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Modification of Nano clay systems:
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-11-15 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 829, pp 818-824 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.829.818 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Modification of Nano clay systems:
Experimental Study on the Rheological Properties of Polymer Solutions and Solid Suspensions
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Experimental
Chapter Outline: Ceramics. Chapter 13: Structure and Properties of Ceramics
 Chapter Outline: Ceramics Chapter 13: Structure and Properties of Ceramics Crystal Structures Silicate Ceramics Carbon Imperfections in Ceramics Optional reading: 13.6 13.10 University of Virginia, Dept.
Chapter Outline: Ceramics Chapter 13: Structure and Properties of Ceramics Crystal Structures Silicate Ceramics Carbon Imperfections in Ceramics Optional reading: 13.6 13.10 University of Virginia, Dept.
ENVI.2030L - Minerals
 ENVI.2030L - Minerals Name I. Minerals Minerals are crystalline solids - the particles (atoms) that make-up the solid have a regular arrangement. In glasses, on the other hand, the atoms are not arranged
ENVI.2030L - Minerals Name I. Minerals Minerals are crystalline solids - the particles (atoms) that make-up the solid have a regular arrangement. In glasses, on the other hand, the atoms are not arranged
THE STUDY OF MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS IN STABILIZERS AND PLASTICIZER THROUGH ULTRASONIC MEASUREMENTS
 27 THE STUDY OF MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS IN STABILIZERS AND PLASTICIZER THROUGH ULTRASONIC MEASUREMENTS 1 R. KAVITHA, 2 S. JAYAKUMAR, 3 R. UMA 1 Department of Chemistry, Easwari Engineering College, Chennai
27 THE STUDY OF MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS IN STABILIZERS AND PLASTICIZER THROUGH ULTRASONIC MEASUREMENTS 1 R. KAVITHA, 2 S. JAYAKUMAR, 3 R. UMA 1 Department of Chemistry, Easwari Engineering College, Chennai
Properties of Compounds
 Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics
 Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Structures of ceramic materials: How do they differ from those of metals? Point defects: How are they different from those in metals?
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Structures of ceramic materials: How do they differ from those of metals? Point defects: How are they different from those in metals?
Online Publication Date: 20 December, 2011 Publisher: Asian Economic and Social Society
 Online Publication Date: 20 December, 2011 Publisher: Asian Economic and Social Society Preparation organic-metallic compounds from Schiff bases and study some mechanical properties Abdul-Aziz O. Musa
Online Publication Date: 20 December, 2011 Publisher: Asian Economic and Social Society Preparation organic-metallic compounds from Schiff bases and study some mechanical properties Abdul-Aziz O. Musa
Molecular Association Studies on Polyvinyl Alochol At 303k
 ISSN (Online) : 239-8753 Molecular Association Studies on Polyvinyl Alochol At 303k Jayakumar.S, Preetha Mary George 2, Shubhashree.N.S 2, Divya.P 2, M. Anees Ahmed 3 Department of Physics, RKM Vivekananda
ISSN (Online) : 239-8753 Molecular Association Studies on Polyvinyl Alochol At 303k Jayakumar.S, Preetha Mary George 2, Shubhashree.N.S 2, Divya.P 2, M. Anees Ahmed 3 Department of Physics, RKM Vivekananda
Online Publication Date: 20 December, 2011 Publisher: Asian Economic and Social Society
 Online Publication Date: 20 December, 2011 Publisher: Asian Economic and Social Society Preparation organic-metallic compounds from Schiff bases and study some mechanical properties Abdul Kareem J. AL-Bermany
Online Publication Date: 20 December, 2011 Publisher: Asian Economic and Social Society Preparation organic-metallic compounds from Schiff bases and study some mechanical properties Abdul Kareem J. AL-Bermany
EXPERIMENT #4 Separation of a Three-Component Mixture
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #4 Separation of a Three-Component Mixture Define chemical and physical properties, mixture, solubility, filtration, sublimation, and percent Separate a mixture of sodium chloride
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #4 Separation of a Three-Component Mixture Define chemical and physical properties, mixture, solubility, filtration, sublimation, and percent Separate a mixture of sodium chloride
Minerals. Atoms, Elements, and Chemical Bonding. Definition of a Mineral 2-1
 Minerals In order to define a what we mean by a mineral we must first make some definitions: 2-1 Most of the Earth s surface is composed of rocky material. An element is a substance which cannot be broken
Minerals In order to define a what we mean by a mineral we must first make some definitions: 2-1 Most of the Earth s surface is composed of rocky material. An element is a substance which cannot be broken
Periodic table with the elements associated with commercial polymers in color.
 Polymers 1. What are polymers 2. Polymerization 3. Structure features of polymers 4. Thermoplastic polymers and thermosetting polymers 5. Additives 6. Polymer crystals 7. Mechanical properties of polymers
Polymers 1. What are polymers 2. Polymerization 3. Structure features of polymers 4. Thermoplastic polymers and thermosetting polymers 5. Additives 6. Polymer crystals 7. Mechanical properties of polymers
Investigation of Acoustical Parameters of Polyvinyl Acetate
 Investigation of Acoustical Parameters of Polyvinyl Acetate Pankaj K.Singh (Corresponding author) Department of Physics, H.N.B.Garhwal University Srinagar (Garhwal) 246174 Uttarakhand, India Tel: 91-989-710-3871
Investigation of Acoustical Parameters of Polyvinyl Acetate Pankaj K.Singh (Corresponding author) Department of Physics, H.N.B.Garhwal University Srinagar (Garhwal) 246174 Uttarakhand, India Tel: 91-989-710-3871
Chemistry and Materials Research ISSN (Print) ISSN (Online) Vol 1, No.1, 2011
 Preparation PVA/TiO 2 composite and study some acoustic properties by ultrasound. Dr. Prof.Abed Al-Kareem J.Rashid University of Babylon /college of science/physics department/babylon/iraq * E-mail of
Preparation PVA/TiO 2 composite and study some acoustic properties by ultrasound. Dr. Prof.Abed Al-Kareem J.Rashid University of Babylon /college of science/physics department/babylon/iraq * E-mail of
Chapter 3. Atoms and Minerals. Earth Materials
 Chapter 3 Atoms and Minerals Earth Materials Atoms and Elements: Isotopes and Ions A Review of Chemistry Atoms Atoms are composed of Protons, Neutrons and Electrons A proton has an electric charge of +1
Chapter 3 Atoms and Minerals Earth Materials Atoms and Elements: Isotopes and Ions A Review of Chemistry Atoms Atoms are composed of Protons, Neutrons and Electrons A proton has an electric charge of +1
Interactions Between Surface Treated Ultrafine Mineral Filler and Silicone Rubber Matrix
 Interactions Between Surface Treated Ultrafine Filler and Silicone Rubber Matrix Interactions Between Surface Treated Ultrafine Filler and Silicone Rubber Matrix Jihuai Wu*, Zhen Shen, Congrong Wei, Yike
Interactions Between Surface Treated Ultrafine Filler and Silicone Rubber Matrix Interactions Between Surface Treated Ultrafine Filler and Silicone Rubber Matrix Jihuai Wu*, Zhen Shen, Congrong Wei, Yike
Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview. Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore
 Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore UGC-NRCM Summer School on Mechanical Property Characterization- June 2012 Overview of polymer
Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore UGC-NRCM Summer School on Mechanical Property Characterization- June 2012 Overview of polymer
Rheologyical Properties
 / / / : % g ml ( μm) o c o c ( khz) study some rheologyical and electrical properties for polymer-kaolin by Ultrasonic Waves Abstract : In the present work, the study of some rheologyical and electrical
/ / / : % g ml ( μm) o c o c ( khz) study some rheologyical and electrical properties for polymer-kaolin by Ultrasonic Waves Abstract : In the present work, the study of some rheologyical and electrical
Pharmaceutical compounding I Colloidal and Surface-Chemical Aspects of Dosage Forms Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz H. Ali
 University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Compounding Pharmaceutical compounding I Colloidal and Surface-Chemical Aspects of Dosage Forms Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz H. Ali
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Compounding Pharmaceutical compounding I Colloidal and Surface-Chemical Aspects of Dosage Forms Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz H. Ali
Analysis of Clays and Soils by XRD
 Analysis of Clays and Soils by XRD I. Introduction Proper sample preparation is one of the most important requirements in the analysis of powder samples by X-ray diffraction (XRD). This statement is especially
Analysis of Clays and Soils by XRD I. Introduction Proper sample preparation is one of the most important requirements in the analysis of powder samples by X-ray diffraction (XRD). This statement is especially
Chemistry I 2nd Semester Exam Study Guide
 Chemistry I 2nd Semester Exam Study Guide Study the following topics and be able to apply these concepts to answer related questions to best prepare for the Chemistry exam. You should be able to: 1. Identify
Chemistry I 2nd Semester Exam Study Guide Study the following topics and be able to apply these concepts to answer related questions to best prepare for the Chemistry exam. You should be able to: 1. Identify
A Study the Effect of ZrO 3 on the Electrical and Mechanical Properties of ( PMMA - Cr 2 O 3 )
 A Study the Effect of ZrO 3 on the Electrical and Mechanical Properties of ( PMMA - Cr 2 O 3 ) Ali Razzaq Abdul Ridha Babylon University, College of Education for Pure Sciences, Department of Physics E-mail:
A Study the Effect of ZrO 3 on the Electrical and Mechanical Properties of ( PMMA - Cr 2 O 3 ) Ali Razzaq Abdul Ridha Babylon University, College of Education for Pure Sciences, Department of Physics E-mail:
Concentrations. 3. A total of 60 g of sodium chloride (NaCl) are dissolved in 240 g water. Give the NaCl concentration in mass percent.
 Concentrations Most chemical reactions take place in solutions. We therefore have no pure substances but certain amounts of them in a certain amount of a solvent. Thus, the important thing is the ratio
Concentrations Most chemical reactions take place in solutions. We therefore have no pure substances but certain amounts of them in a certain amount of a solvent. Thus, the important thing is the ratio
Adsorption Processes. Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
Density. Physical Properties of Materials. Which Ones? THEORETICAL DENSITY, ρ. What would make a material dense? Concept Question. Physical Properties
 Physical Properties of Materials Let s get physical!! density Physical Properties electrical thermal expansion shock Density Which Ones? melting point What is density? = THEORETICAL DENSITY, ρ Concept
Physical Properties of Materials Let s get physical!! density Physical Properties electrical thermal expansion shock Density Which Ones? melting point What is density? = THEORETICAL DENSITY, ρ Concept
9.1 Water. Chapter 9 Solutions. Water. Water in Foods
 Chapter 9 s 9.1 Water 9.1 Properties of Water 9.2 s 9.3 Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes 9.6 Percent Concentration 9.7 Molarity Water is the most common solvent. The water molecule is polar. Hydrogen bonds
Chapter 9 s 9.1 Water 9.1 Properties of Water 9.2 s 9.3 Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes 9.6 Percent Concentration 9.7 Molarity Water is the most common solvent. The water molecule is polar. Hydrogen bonds
Chap 10 Part 3a.notebook December 12, 2017
 Metallic Bonding and Semiconductors Chapter 10 Sect 4 Metallic Bonding positive metal ions surrounded by a "sea of electrons" Bonding is strong and nondirectional Iron, Silver, alloys, Brass, Bronze Forces
Metallic Bonding and Semiconductors Chapter 10 Sect 4 Metallic Bonding positive metal ions surrounded by a "sea of electrons" Bonding is strong and nondirectional Iron, Silver, alloys, Brass, Bronze Forces
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Second Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Second Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 (10021002) 11 March (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used.
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Second Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 (10021002) 11 March (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used.
Liquids and Solids Chapter 10
 Liquids and Solids Chapter 10 Nov 15 9:56 AM Types of Solids Crystalline solids: Solids with highly regular arrangement of their components Amorphous solids: Solids with considerable disorder in their
Liquids and Solids Chapter 10 Nov 15 9:56 AM Types of Solids Crystalline solids: Solids with highly regular arrangement of their components Amorphous solids: Solids with considerable disorder in their
3) Accounts for strands of DNA being held together into a double helix. 7) Accounts for the cohesive nature of water and its high surface tension
 AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 11) Multiple Choice (50%) Please use the following choices to answer questions 1-7. A) London dispersion forces B) Ion-ion attractions C) Dipole-dipole attractions D) Dipole-ion
AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 11) Multiple Choice (50%) Please use the following choices to answer questions 1-7. A) London dispersion forces B) Ion-ion attractions C) Dipole-dipole attractions D) Dipole-ion
Material History. Is American culture currently being defined
 Introduction ti to Materials What Are Materials? Substances out of which all things are made Currently MatWeb Material Property Data website lists over 76,000 individually unique materials What materials
Introduction ti to Materials What Are Materials? Substances out of which all things are made Currently MatWeb Material Property Data website lists over 76,000 individually unique materials What materials
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(5):348-358 Ultrasonic study of molecular dynamics in some
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(5):348-358 Ultrasonic study of molecular dynamics in some
1. Demonstrate that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number of 8 is
 1. Demonstrate that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number of 8 is 0.732. This problem asks us to show that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number
1. Demonstrate that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number of 8 is 0.732. This problem asks us to show that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number
ACTIVATED BLEACHING CLAY FOR THE FUTURE. AndrevJ Torok ThomaE D Thomp~on Georgia Kaolin Company Elizabeth, New JerEey
 PREPRINT NUMBER 71-H-22 ACTIVATED BLEACHING CLAY FOR THE FUTURE AndrevJ Torok ThomaE D Thomp~on Georgia Kaolin Company Elizabeth, New JerEey ThiE paper is to be preeented at the AIME CENTENNIAL ANNUAL
PREPRINT NUMBER 71-H-22 ACTIVATED BLEACHING CLAY FOR THE FUTURE AndrevJ Torok ThomaE D Thomp~on Georgia Kaolin Company Elizabeth, New JerEey ThiE paper is to be preeented at the AIME CENTENNIAL ANNUAL
CH5716 Processing of Materials
 CH5716 Processing of Materials Ceramic Thick Film Processing Lecture MC5 Slurry Characterisation Specific Surface Area Powder size & specific surface area (area per unit wt) closely related As particle
CH5716 Processing of Materials Ceramic Thick Film Processing Lecture MC5 Slurry Characterisation Specific Surface Area Powder size & specific surface area (area per unit wt) closely related As particle
Supplemental Materials. Sorption of Tetracycline to Varying-Sized Montmorillonite Fractions
 Supplemental Materials Sorption of Tetracycline to Varying-Sized Montmorillonite Fractions 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 Huaizhou Xu, 1, Xiaolei Qu, 1 Hui Li, Cheng Gu 1, and Dongqiang Zhu 1* 1 State Key Laboratory
Supplemental Materials Sorption of Tetracycline to Varying-Sized Montmorillonite Fractions 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 Huaizhou Xu, 1, Xiaolei Qu, 1 Hui Li, Cheng Gu 1, and Dongqiang Zhu 1* 1 State Key Laboratory
Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering. Lecture 14: Amorphous State February 14, 2001
 Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering Lecture 14: Amorphous State February 14, 2001 Objectives! To provide guidance toward understanding why an amorphous polymer glass may be considered
Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering Lecture 14: Amorphous State February 14, 2001 Objectives! To provide guidance toward understanding why an amorphous polymer glass may be considered
Ultrasonic studies of N, N-Dimethylacetamide and N-Methylacetamide with Alkoxyethanols in Carbon tetrachloride at different temperatures
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 2011, 3 (2):568-576 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 2011, 3 (2):568-576 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X
Classification of Mystery Substances
 Classification of Mystery Substances This document supports the safety activity Mystery Substance Identification: The Identification of Unlabeled Chemicals Found on School Premises from Flinn Scientific.
Classification of Mystery Substances This document supports the safety activity Mystery Substance Identification: The Identification of Unlabeled Chemicals Found on School Premises from Flinn Scientific.
MATERIALS SCIENCE POLYMERS
 POLYMERS 1) Types of Polymer (a) Plastic Possibly the largest number of different polymeric materials come under the plastic classification. Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene,
POLYMERS 1) Types of Polymer (a) Plastic Possibly the largest number of different polymeric materials come under the plastic classification. Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene,
Chemical Reactions and Equations
 Chemical Reactions and Equations 1991 B The molecular formula of a hydrocarbon is to be determined by analyzing its combustion products and investigating its colligative properties. (a) The hydrocarbon
Chemical Reactions and Equations 1991 B The molecular formula of a hydrocarbon is to be determined by analyzing its combustion products and investigating its colligative properties. (a) The hydrocarbon
Experiment Nine Acids and Bases
 Name: Lab Section: Experiment Nine Acids and Bases Objective Identifying and understanding the nature of acids and bases is an important part of the laboratory toolbox, the purpose of this lab is to help
Name: Lab Section: Experiment Nine Acids and Bases Objective Identifying and understanding the nature of acids and bases is an important part of the laboratory toolbox, the purpose of this lab is to help
INVESTIGATION ON GEOTHERMAL DRILLING MUDS WITH HIGH TEMPERATURE STABILITY
 INVESTIGATION ON GEOTHERMAL DRILLING MUDS WITH HIGH TEMPERATURE STABILITY Umran Serpen ITÜ, Petroleum and Natural Gas Eng. Dept., Maslak, 80626, Istanbul, Turkey Key Words: Drilling-mud, geothermal, sepiolite,
INVESTIGATION ON GEOTHERMAL DRILLING MUDS WITH HIGH TEMPERATURE STABILITY Umran Serpen ITÜ, Petroleum and Natural Gas Eng. Dept., Maslak, 80626, Istanbul, Turkey Key Words: Drilling-mud, geothermal, sepiolite,
Effect of Type and Concentration of Different Water Soluble Polymer Solutions on Rheological Properties
 Nahrain University, College of Engineering Journal (NUCEJ) Vol. No., 9 pp.6-37 Dr. Muhanned A.R. Mohammed Assist. Prof. in Chemical Engineering Nahrain Unversity Areej Jasim Mohammed Former Post graduat
Nahrain University, College of Engineering Journal (NUCEJ) Vol. No., 9 pp.6-37 Dr. Muhanned A.R. Mohammed Assist. Prof. in Chemical Engineering Nahrain Unversity Areej Jasim Mohammed Former Post graduat
Industrial In-line and Multi Component Monitor Using Absorption Spectroscopy and Its Application
 FFeature Article Article Industrial In-line and Multi Component Monitor Using Absorption Spectroscopy and Its Application Yoko NAKAI HORIBA s CS-Series chemical concentration monitors that use ultraviolet
FFeature Article Article Industrial In-line and Multi Component Monitor Using Absorption Spectroscopy and Its Application Yoko NAKAI HORIBA s CS-Series chemical concentration monitors that use ultraviolet
Name: Regents Review Quiz #1 2016
 Name: Regents Review Quiz #1 2016 1. Which two particle diagrams represent mixtures of diatomic elements? A) A and B B) A and C C) B and C D) B and D 2. At STP, which physical property of aluminum always
Name: Regents Review Quiz #1 2016 1. Which two particle diagrams represent mixtures of diatomic elements? A) A and B B) A and C C) B and C D) B and D 2. At STP, which physical property of aluminum always
Weathering and mineral equilibria. Seminar at NGU 23 May 2016 Håkon Rueslåtten
 Weathering and mineral equilibria Seminar at NGU 23 May 2016 Håkon Rueslåtten Weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals that are exposed to surface processes (climatically controlled). Water is
Weathering and mineral equilibria Seminar at NGU 23 May 2016 Håkon Rueslåtten Weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals that are exposed to surface processes (climatically controlled). Water is
INFLUENCE OF CLAY ON MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF POLYVINYL(ALCOHOL)/ MONTMORILLONITE MEMBRANES
 INFLUENCE OF CLAY ON MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF POLYVINYL(ALCOHOL)/ MONTMORILLONITE MEMBRANES Maria C. Carrera 1*, Eleonora Erdmann 1, Hugo A. Destéfanis 1 Marcos L. Dias 2, Victor J. R. R. Pita 2 1 Instituto
INFLUENCE OF CLAY ON MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF POLYVINYL(ALCOHOL)/ MONTMORILLONITE MEMBRANES Maria C. Carrera 1*, Eleonora Erdmann 1, Hugo A. Destéfanis 1 Marcos L. Dias 2, Victor J. R. R. Pita 2 1 Instituto
Physical pharmacy. The Gaseous State. dr basam al zayady. States of matter
 Physical pharmacy Lec 5 dr basam al zayady States of matter The Gaseous State Gas molecules have vigorous and rapid motion that result in collisions not only with one another but also with the walls of
Physical pharmacy Lec 5 dr basam al zayady States of matter The Gaseous State Gas molecules have vigorous and rapid motion that result in collisions not only with one another but also with the walls of
Covalent Compounds 1 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 Covalent Compounds 1 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Covalent Compounds 2 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are covalent bonds? 3 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2016 When atoms share pairs of electrons, they form covalent
Covalent Compounds 1 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Covalent Compounds 2 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are covalent bonds? 3 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2016 When atoms share pairs of electrons, they form covalent
MICROMECHANICAL DEFORMATIONS IN PARTICULATE FILLED POLYMERS: THE EFFECT OF ADHESION
 MICROMECHANICAL DEFORMATIONS IN PARTICULATE FILLED POLYMERS: THE EFFECT OF ADHESION K. Renner, J. Móczó, B. Pukánszky Laboratory of Plastics and Rubber Technology, Department of Physical Chemistry and
MICROMECHANICAL DEFORMATIONS IN PARTICULATE FILLED POLYMERS: THE EFFECT OF ADHESION K. Renner, J. Móczó, B. Pukánszky Laboratory of Plastics and Rubber Technology, Department of Physical Chemistry and
Water and Aqueous Systems
 Water and Aqueous Systems The Water Molecule: a Review Water is a simple tri-atomic molecule, H 2 O Each O-H bond is highly polar, because of the high electronegativity of the oxygen (N, O, F, and Cl have
Water and Aqueous Systems The Water Molecule: a Review Water is a simple tri-atomic molecule, H 2 O Each O-H bond is highly polar, because of the high electronegativity of the oxygen (N, O, F, and Cl have
Chem 1100 Pre-Test 3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chem 1100 Pre-Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the oxidation number of the underlined element in K 2CO 3. a. 1 b. 2 c.
Chem 1100 Pre-Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the oxidation number of the underlined element in K 2CO 3. a. 1 b. 2 c.
Particles in aqueous environments
 Lecture 11 Particle-Aqueous Solute Interactions Today 1. Particle types and sizes 2. Particle charges 3. Particle-solute Interactions Next time Please continue to read Manahan Chapter 4. 1. Fresh-salt
Lecture 11 Particle-Aqueous Solute Interactions Today 1. Particle types and sizes 2. Particle charges 3. Particle-solute Interactions Next time Please continue to read Manahan Chapter 4. 1. Fresh-salt
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions
 Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids 3.1. Crystal structures
 Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids 3.1. Crystal structures 3.1.1. Fundamental concepts 3.1.2. Unit cells 3.1.3. Metallic crystal structures 3.1.4. Ceramic crystal structures 3.1.5. Silicate
Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids 3.1. Crystal structures 3.1.1. Fundamental concepts 3.1.2. Unit cells 3.1.3. Metallic crystal structures 3.1.4. Ceramic crystal structures 3.1.5. Silicate
Surface Chemistry & States of Matter
 Surface Chemistry & States of Matter S. Sunil Kumar Lecturer in Chemistry 1. Adsorption is a. Colligative property b. Oxidation process c. Reduction process d. Surface phenomenon Ans. d 2. When adsorption
Surface Chemistry & States of Matter S. Sunil Kumar Lecturer in Chemistry 1. Adsorption is a. Colligative property b. Oxidation process c. Reduction process d. Surface phenomenon Ans. d 2. When adsorption
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 12: Structures and Properties of Ceramics. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 12: Structures and Properties of Ceramics Dr. Coates 12.1 Introduction Ceramics Compounds between metallic & non-metallic elements Predominantly ionic
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 12: Structures and Properties of Ceramics Dr. Coates 12.1 Introduction Ceramics Compounds between metallic & non-metallic elements Predominantly ionic
CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL
 *P15* Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2012 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2012 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions
*P15* Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2012 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2012 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions
Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics. Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi
 Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
CHEM-102 EXAM I Name Fall 2004 Section
 CHEM-102 EXAM I Name Fall 2004 Section 10 11 12 Version A (Circle one) Instructions: 1. Put your name and section number on both page 1 and the answer key. Do not detach the answer key from the back of
CHEM-102 EXAM I Name Fall 2004 Section 10 11 12 Version A (Circle one) Instructions: 1. Put your name and section number on both page 1 and the answer key. Do not detach the answer key from the back of
CATION EXCHANGE BETWEEN MIXTURES OF CLAY MINERALS AND BETWEEN A ZEOLITE AND A CLAY MINERAL*
 CATION EXCHANGE BETWEEN MIXTURES OF CLAY MINERALS AND BETWEEN A ZEOLITE AND A CLAY MINERAL* by PATRICK J. DENNY and RUSTUM ROY Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pa. ABSTRACT The electron
CATION EXCHANGE BETWEEN MIXTURES OF CLAY MINERALS AND BETWEEN A ZEOLITE AND A CLAY MINERAL* by PATRICK J. DENNY and RUSTUM ROY Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pa. ABSTRACT The electron
Chemistry Matter Unit. What is matter? What is chemistry? What is the organization of matter? What is the nature of matter?
 Chemistry Matter Unit What is matter? What is chemistry? What is the organization of matter? What is the nature of matter? What is NOT Matter? Energy! Types of Energies Mechanical Chemical Heat Atomic
Chemistry Matter Unit What is matter? What is chemistry? What is the organization of matter? What is the nature of matter? What is NOT Matter? Energy! Types of Energies Mechanical Chemical Heat Atomic
STUDY OF THERMOACOUSTICAL PARAMETERS OF BINARY LIQUID MIXTURES OF METHYL BENZOATE WITH 1-NONANOL AT DIFFERENT TEMPERATURES
 STUDY OF THERMOACOUSTICAL PARAMETERS OF BINARY LIQUID MIXTURES OF METHYL BENZOATE WITH 1-NONANOL AT DIFFERENT TEMPERATURES Gutta Sridevi Associate Professor, Department of Physics, V.R. Siddhartha Engineering
STUDY OF THERMOACOUSTICAL PARAMETERS OF BINARY LIQUID MIXTURES OF METHYL BENZOATE WITH 1-NONANOL AT DIFFERENT TEMPERATURES Gutta Sridevi Associate Professor, Department of Physics, V.R. Siddhartha Engineering
DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF EPOXIDISED NATURAL RUBBER
 DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF EPOXIDISED NATURAL RUBBER Mahmud Iskandar Seth A Rahim, Kirill Horoshenkov and Jem Rongong Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Sheffield, Velocity House, Sheffield,
DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF EPOXIDISED NATURAL RUBBER Mahmud Iskandar Seth A Rahim, Kirill Horoshenkov and Jem Rongong Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Sheffield, Velocity House, Sheffield,
Copyright SOIL STRUCTURE and CLAY MINERALS
 SOIL STRUCTURE and CLAY MINERALS Soil Structure Structure of a soil may be defined as the mode of arrangement of soil grains relative to each other and the forces acting between them to hold them in their
SOIL STRUCTURE and CLAY MINERALS Soil Structure Structure of a soil may be defined as the mode of arrangement of soil grains relative to each other and the forces acting between them to hold them in their
Particle size effect on XRF measurements of Copper and Zinc particles suspended in hydrocarbon materials
 Particle size effect on XRF measurements of Copper and Zinc particles suspended in hydrocarbon materials Abdulhadi K.Jedran* Harith I.Jaffar** Zareh A.Serkes*** Date of acceptance 14/6/2007 Abstract: Copper
Particle size effect on XRF measurements of Copper and Zinc particles suspended in hydrocarbon materials Abdulhadi K.Jedran* Harith I.Jaffar** Zareh A.Serkes*** Date of acceptance 14/6/2007 Abstract: Copper
CHAPTER 1: Chemistry, An Introduction
 CHAPTER 1: Chemistry, An Introduction science: the study of nature to explain what one observes 1.4 THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD: How Chemists Think Applying the Scientific Method 1. Make an observation, and
CHAPTER 1: Chemistry, An Introduction science: the study of nature to explain what one observes 1.4 THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD: How Chemists Think Applying the Scientific Method 1. Make an observation, and
CALCIUM CHLORIDE (HT Fines 94-97%)
 CALCIUM CHLORIDE (HT Fines 94-97%) Calcium Chlorides HT Fines(CaCl 2 2H 2 O) a palletized manufactured salt, which is hygroscopic and highly soluble in water. PROPERTIES Physical Chemical Appearance: White
CALCIUM CHLORIDE (HT Fines 94-97%) Calcium Chlorides HT Fines(CaCl 2 2H 2 O) a palletized manufactured salt, which is hygroscopic and highly soluble in water. PROPERTIES Physical Chemical Appearance: White
Chapter 10. Dipole Moments. Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules. Polar or Nonpolar Molecules?
 Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules Chapter 10 Liquids, Solids, and Phase Changes Draw Lewis Structures for CCl 4 and CH 3 Cl. What s the same? What s different? 1 Polar Covalent Bonds and Dipole Moments Bonds
Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules Chapter 10 Liquids, Solids, and Phase Changes Draw Lewis Structures for CCl 4 and CH 3 Cl. What s the same? What s different? 1 Polar Covalent Bonds and Dipole Moments Bonds
Experiment Eight Acids and Bases
 Name: Lab Section: Experiment Eight Acids and Bases Objective Identifying and understanding the nature of acids and bases is an important part of the laboratory toolbox, the purpose of this lab is to help
Name: Lab Section: Experiment Eight Acids and Bases Objective Identifying and understanding the nature of acids and bases is an important part of the laboratory toolbox, the purpose of this lab is to help
Microorganisms. Dissolved inorganics. Native vs. Introduced; Oligotrophic vs. Eutrophic Millions to billions per ml or g Complex consortia
 1 Microorganisms Native vs. Introduced; Oligotrophic vs. Eutrophic Millions to billions per ml or g Complex consortia Species makeup: f(t, O 2, ph, nutrients, etc.) Indicators & pathogens Dissolved inorganics
1 Microorganisms Native vs. Introduced; Oligotrophic vs. Eutrophic Millions to billions per ml or g Complex consortia Species makeup: f(t, O 2, ph, nutrients, etc.) Indicators & pathogens Dissolved inorganics
Structure and Properties of Chitosan/Chitin-Nanofibrils Based Materials
 Structure and Properties of Chitosan/Chitin-Nanofibrils Based Materials Jindřich Hašek, IBT AV ČR Praha Chitosan random co-polymer GlcN/GlcNac with content of GlcNac (i.e. DA - Degree of Acetylation) lower
Structure and Properties of Chitosan/Chitin-Nanofibrils Based Materials Jindřich Hašek, IBT AV ČR Praha Chitosan random co-polymer GlcN/GlcNac with content of GlcNac (i.e. DA - Degree of Acetylation) lower
Dispersion-Flocculation Behavior of Fine Lead Particles in an Organic Solvent
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 49, No. 9 (2) pp. 2119 to 2123 #2 The Mining and Materials Processing Institute of Japan Dispersion-Flocculation Behavior of Fine Lead Particles in an Organic Solvent Masami
Materials Transactions, Vol. 49, No. 9 (2) pp. 2119 to 2123 #2 The Mining and Materials Processing Institute of Japan Dispersion-Flocculation Behavior of Fine Lead Particles in an Organic Solvent Masami
Polymeric Materials. Sunan Tiptipakorn, D.Eng.
 Polymeric Materials Sunan Tiptipakorn, D.Eng. Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Liberal Arts and Science, Kasetsart University, Kamphaen Saen Campus, Nakorn Phathom, 73140 Thailand. Introduction Material
Polymeric Materials Sunan Tiptipakorn, D.Eng. Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Liberal Arts and Science, Kasetsart University, Kamphaen Saen Campus, Nakorn Phathom, 73140 Thailand. Introduction Material
Solid Type of solid Type of particle Al(s) aluminium MgCl2 Magnesium chloride S8(s) sulfur
 QUESTION (2017:1) (iii) Sodium chloride, NaCl, is another compound that is excreted from the body in sweat. Use your knowledge of structure and bonding to explain the dissolving process of sodium chloride,
QUESTION (2017:1) (iii) Sodium chloride, NaCl, is another compound that is excreted from the body in sweat. Use your knowledge of structure and bonding to explain the dissolving process of sodium chloride,
Supramolecular Structure of Hydrocarbon Gels of the Solvates of Lithium Tetraalkyl Borates
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research & Developments in Chemistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/chem/chem.html Vol. 2016 (2016), Article ID 313916, 8 pages DOI: 10.5171/2016.313916 Research Article
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research & Developments in Chemistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/chem/chem.html Vol. 2016 (2016), Article ID 313916, 8 pages DOI: 10.5171/2016.313916 Research Article
Chem 1100 Pre-Test 3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chem 1100 Pre-Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An open-tube manometer is used to measure the pressure in a flask. The atmospheric
Chem 1100 Pre-Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An open-tube manometer is used to measure the pressure in a flask. The atmospheric
Aqueous Colloidal Processing and green sheet properties of. Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) ceramics made by Tape. Casting.
 Aqueous Colloidal Processing and green sheet properties of Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) ceramics made by Tape Casting. A. Navarro, J.R.Alcock and R.W.Whatmore Nanotechnology Dept, SIMS, Cranfield University,
Aqueous Colloidal Processing and green sheet properties of Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) ceramics made by Tape Casting. A. Navarro, J.R.Alcock and R.W.Whatmore Nanotechnology Dept, SIMS, Cranfield University,
Chapter 11. Liquids and Intermolecular Forces
 Chapter 11 Liquids and Intermolecular Forces States of Matter The three states of matter are 1) Solid Definite shape Definite volume 2) Liquid Indefinite shape Definite volume 3) Gas Indefinite shape Indefinite
Chapter 11 Liquids and Intermolecular Forces States of Matter The three states of matter are 1) Solid Definite shape Definite volume 2) Liquid Indefinite shape Definite volume 3) Gas Indefinite shape Indefinite
Mechanical Properties of Polymers. Scope. MSE 383, Unit 3-1. Joshua U. Otaigbe Iowa State University Materials Science & Engineering Dept.
 Mechanical Properties of Polymers Scope MSE 383, Unit 3-1 Joshua U. Otaigbe Iowa State University Materials Science & Engineering Dept. Structure - mechanical properties relations Time-dependent mechanical
Mechanical Properties of Polymers Scope MSE 383, Unit 3-1 Joshua U. Otaigbe Iowa State University Materials Science & Engineering Dept. Structure - mechanical properties relations Time-dependent mechanical
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHAPTER 4 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A substance is a brittle crystal that conducts electricity in molten liquid state
CHAPTER 4 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A substance is a brittle crystal that conducts electricity in molten liquid state
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes
 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Introduction to Work in Laboratory
 INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY AND LABORATORY MEDICINE Introduction to Work in Measuring volumes, filtration, centrifugation, solubility, separation Practical in Medical Biochemistry General Medicine
INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY AND LABORATORY MEDICINE Introduction to Work in Measuring volumes, filtration, centrifugation, solubility, separation Practical in Medical Biochemistry General Medicine
6. Place the following elements in order of increasing atomic radii: Mg, Na, Rb, Cl.
 CH141 Practice Problems/Practice Final Exam Page 1 of 12 Name: 1. What is the SO 4 2- concentration of a solution prepared by dissolving 3.00 g of Na 2 SO 4 in 1.00 L of water? 2. What is the hybridization
CH141 Practice Problems/Practice Final Exam Page 1 of 12 Name: 1. What is the SO 4 2- concentration of a solution prepared by dissolving 3.00 g of Na 2 SO 4 in 1.00 L of water? 2. What is the hybridization
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry
 NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 2 Cleaning Products 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 2 ::: Cleaning Products 9.2.2 A wide range of cleaning products are made
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 2 Cleaning Products 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 2 ::: Cleaning Products 9.2.2 A wide range of cleaning products are made
CERAMIC MATERIALS I. Asst. Prof. Dr. Ayşe KALEMTAŞ
 CERAMIC MATERIALS I akalemtas@mu.edu.tr, akalemtas@gmail.com, Phone: 211 19 17 Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department Traditional Ceramics Clay products Main Components Clay Feldspar Silica
CERAMIC MATERIALS I akalemtas@mu.edu.tr, akalemtas@gmail.com, Phone: 211 19 17 Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department Traditional Ceramics Clay products Main Components Clay Feldspar Silica
ULTRASONIC STUDIES AND MOLECULAR INTERACTION STUDIES ON SARDINE FISH OIL AND ANILINE BINARY MIXTURE
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 6, Issue 10, Oct 2015, pp. 86-96, Article ID: IJARET_06_10_013 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=6&itype=10
International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 6, Issue 10, Oct 2015, pp. 86-96, Article ID: IJARET_06_10_013 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=6&itype=10
Tuesday, September 15, Ionic Compounds
 Ionic Compounds Compounds Compound: Two or more elements chemically combined. Ionic Compounds Called an ionic compound because it is made up of negative and positive ions that have resulted from the transfer
Ionic Compounds Compounds Compound: Two or more elements chemically combined. Ionic Compounds Called an ionic compound because it is made up of negative and positive ions that have resulted from the transfer
10/8/15. Earth Materials Minerals and Rocks. I) Minerals. Minerals. (A) Definition: Topics: -- naturally occurring What are minerals?
 minerals Earth Materials Minerals and Rocks I) Minerals Minerals Topics: What are minerals? Basic Chemistry Amethysts in geode: minerals Characteristics of Minerals Types of Minerals -- orderly arrangement
minerals Earth Materials Minerals and Rocks I) Minerals Minerals Topics: What are minerals? Basic Chemistry Amethysts in geode: minerals Characteristics of Minerals Types of Minerals -- orderly arrangement
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2. Enthalpy changes. N Goalby chemrevise.org
 2. Enthalpy changes In an exothermic change energy is transferred from the system (chemicals) to the surroundings. The have less energy than the If an enthalpy change occurs then energy is transferred
2. Enthalpy changes In an exothermic change energy is transferred from the system (chemicals) to the surroundings. The have less energy than the If an enthalpy change occurs then energy is transferred
2. Amorphous or Crystalline Structurally, polymers in the solid state may be amorphous or crystalline. When polymers are cooled from the molten state
 2. Amorphous or Crystalline Structurally, polymers in the solid state may be amorphous or crystalline. When polymers are cooled from the molten state or concentrated from the solution, molecules are often
2. Amorphous or Crystalline Structurally, polymers in the solid state may be amorphous or crystalline. When polymers are cooled from the molten state or concentrated from the solution, molecules are often
Non contact measurement of viscoelastic properties of biopolymers
 Non contact measurement of viscoelastic properties of biopolymers Christelle Tisserand, Anton Kotzev, Mathias Fleury, Laurent Brunel, Pascal Bru, Gérard Meunier Formulaction, 10 impasse Borde Basse, 31240
Non contact measurement of viscoelastic properties of biopolymers Christelle Tisserand, Anton Kotzev, Mathias Fleury, Laurent Brunel, Pascal Bru, Gérard Meunier Formulaction, 10 impasse Borde Basse, 31240
Rheology and structure of aqueous bentonite polyvinyl alcohol dispersions
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 29, No. 5, October 2006, pp. 449 456. Indian Academy of Sciences. Rheology and structure of aqueous bentonite polyvinyl alcohol dispersions S øùdø, C H ÜNLÜ, O ATICI* and N GÜNGÖR
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 29, No. 5, October 2006, pp. 449 456. Indian Academy of Sciences. Rheology and structure of aqueous bentonite polyvinyl alcohol dispersions S øùdø, C H ÜNLÜ, O ATICI* and N GÜNGÖR
PROPERTIES OF IONIC COMPOUNDS Excerpt from chemistry.about.com
 PROPERTIES OF IONIC COMPOUNDS Excerpt from chemistry.about.com Here are the properties shared by the ionic compounds. Notice that the properties of ionic compounds relate to how strongly the positive and
PROPERTIES OF IONIC COMPOUNDS Excerpt from chemistry.about.com Here are the properties shared by the ionic compounds. Notice that the properties of ionic compounds relate to how strongly the positive and
