Core Biology Checklist
|
|
|
- Sylvia Annice Wells
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Core Biology Checklist KEEPING HEALTHY Describe the components of a balanced diet and say why each is needed. Describe the effects of an unbalanced diet eating too much or too little. Describe how exercise affects health. Explain metabolic rate and the affect of exercise on metabolic rate. State how inherited factors may affect metabolic rate or cholesterol. Define pathogen. Describe how viruses and bacteria make us ill. State some ways the body protects against pathogens. Describe the 3 ways white blood cells work. Describe how an individual may become immune to a pathogen. Describe how vaccinations can protect individuals and populations. Describe the work of Semmelweiss and explain its importance. State how some different types of medicines work. Explain why antibiotics don t work on viral infections, and why treatment is difficult. Explain antibiotic resistance. HIGHER Give some of the problems with resistance strains of bacteria or viruses. HIGHER Write a method for culturing microorganisms in sterile conditions. Explain differences in school & industrial conditions for growing microbes. NERVES AND HORMONES State the role of the nervous system in responding to the environment. Link some examples of stimuli and receptor cells. State some of the features of light receptor cells. Describe the pathway of a simple reflex action. Explain how water, ions, temperature & blood sugar levels are controlled. Describe the general role of hormones in the body. Describe the role of hormones in controlling the menstrual cycle. Explain the use of hormones in controlling fertility Describe how plants are sensitive to light, moisture and gravity. Explain how hormones can control growth in plants. Give some agricultural uses of hormones. USE AND ABUSE OF DRUGS. Describe the stages in developing and testing new medical drugs. State the use of statins. Describe the problems, and current use of, thalidomide. Describe what a drug is and the problems with dependence and addiction. State some of the effects of misuse of legal and illegal recreational drugs. Describe some examples of performance enhancing drugs in sport.
2 Core Biology Checklist INTERDEPENDENCE AND ADAPTATION Describe what animals compete Describe what plants compete for Explain how particular adaptations help animals to survive in their habitats Explain what extremophiles are Describe how distribution of organisms can change when the environment changes State some examples of changes in the environment Explain how lichens and invertebrates can be used as indicator species Describe how we can use equipment to measure oxygen levels, temperature and rainfall ENERGY AND BIOMASS IN FOOD CHAINS State that the sun is the source of energy for living organisms Describe the energy transfer that takes place during photosynthesis Draw a pyramid of biomass for a food chain Explain why the energy and biomass decrease further up the pyramid WASTE MATERIALS FROM PLANTS AND ANIMALS State that living things remove materials from the environment State that when organisms die and decay, materials are returned to the environment Define the term decay & describe the conditions that microorganisms grow fastest in Explain why decay is important for plant growth Describe a stable community in terms of the materials being cycled within it State how carbon dioxide is removed from, and released into the atmosphere Describe the role of plants, animals and microorganisms in the carbon cycle Explain how combustion affects carbon dioxide levels GENETIC VARIATION AND ITS CONTROL Define the term gene & describe how genes are passed on from parents to offspring State that genes control characteristics Give reasons to describe why there may be differences in characteristics in organisms Describe what sexual reproduction is Describe what asexual reproduction is Explain if offspring will be identical or different to their parents based the type of reproduction Describe the process of taking cuttings & state some advantages of taking cuttings Describe the stages involved in tissue culture, embryo transplants and adult cell cloning Describe what genetic engineering is Define what GM (genetically modified) is Give examples of ways in which we could modify crops and evaluate GM crops EVOLUTION Describe Darwin s theory of evolution Give three reasons why the theory of natural selection was not accepted at first Describe the main stages of natural selection State that variation can occur due to mutation State the groups that living are classified into Interpret evolutionary trees Describe Lamarck s theory of evolution
3 ADDITIONAL Biology Checklist Cells and Simple Transport Label an animal cell and a plant cell. Give the functions of each of the parts of a cell. Label a bacteria cell and a yeast cell. Give examples of specialised cells and explain how they are adapted to their function. Define diffusion. Give a factor that affects the rate of diffusion. Explain why diffusion is important for respiration. Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems Describe what organisms are made up of in terms of cells, tissues, organs & systems. Give the functions of muscular, glandular, and epithelial tissue in the stomach. Label the digestive system. Describe the role of the main organs in the digestive system. Give examples of plant organs. Describe the role of plant tissues (mesophyll, xylem, phloem, epidermis). Label the internal structure of a leaf. Photosynthesis Describe the process of photosynthesis. Explain how the rate of photosynthesis can be limited by different factors. Evaluate the pros and cons of artificially manipulating conditions within a greenhouse. State what plants use glucose and nitrate ions for. Organisms and their environment Be able to calculate the mean, median and mode. Describe how to collect valid data on distribution of organisms and check reproducibility. State some physical factors that can affect the distribution of organisms. Evaluate the methods used to collect environmental data.
4 ADDITIONAL Biology Checklist 1=confident, 2=needs improvement, 3=revision priority Proteins and Enzymes Describe what proteins are made of. State some types of proteins in the body. Describe the role of a catalyst. Describe factors that affect the shape of an enzyme. Name enzymes involved in digestion & name the substrate & product breakdown. Explain how hydrochloric acid & bile help enzymes in digestion. Describe the role of enzymes in home & industry. Evaluate the role of enzymes in home & industry. Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration State where respiration takes place. Give the word equation for aerobic respiration. Describe what the energy released is used for in plants and animals. Explain changes that take place to the heart & breathing rate during respiration. Describe what anaerobic respiration is and why it happens. Compare anaerobic & aerobic respiration in terms of energy released. Explain what oxygen debt means. Explain why muscles become fatigued after long periods of exercise. Cell Division and Inheritance Describe where, why & how mitosis takes place. Describe where & why meiosis takes place. Describe the process of meiosis. Describe what happens during fertilisation. Describe what stem cells are. Evaluate the use of stem cells in research & medicine. Explain how sexual reproduction leads to genetic variation. Define the terms gene, allele, chromosomes & DNA. State the sex chromosomes in males & females. Explain the link between genes, amino acids & proteins. Describe what genetic fingerprinting could be used for. Describe what polydactyl is. Draw and interpret genetic diagrams for the inheritance of polydactyl. Describe what cystic fibrosis is/ Draw and interpret genetic diagrams for the inheritance of cystic fibrosis. Construct genetic diagrams using heterozygous, homozygous, genotype, phenotype. Evaluate embryo screening. Speciation Describe how fossils are formed. Explain why some organisms did not leave fossils behind. Explain how fossils can be used to help us find out about changes to organisms. State factors that can cause extinction. Describe the process of speciation.
5 Core Chemistry Checklist Fundamental Ideas in Chemistry Annotate a diagram of an atom with names and features of each part. State the numbers of protons and electrons in an atom and use this to explain the overall charge. Define element, mass number, and atomic number. Draw diagrams to show electronic structure of the first 20 elements. State and explain the relationship between elements in the same group. State what noble gases are and explain why they are so unreactive. Define compound and molecule. Explain how ionic compounds are formed from metals and non-metals. Explain how molecular compounds are formed from non-metals. Limestone and Building Materials Give the chemical name and formula for limestone. Describe how limestone is quarried. Describe thermal decomposition of carbonates calcium, magnesium, zinc and sodium. Describe the reaction of calcium oxide with water and of limestone. Describe how limestone is used to make cement and how cement is used. Metals and their uses Link how metals are found in the earth s crust to their reactivity. Describe how metals can be extracted by reduction or electrolysis. Choose which method of extraction would be used, depending on the reactivity of a metal. Describe how copper, aluminium, and titanium are extracted and purified. Evaluate the benefits of recycling. Explain the properties of different iron and steels. Link some properties of everyday alloys to their uses. Define transition metals. Link some properties of transition metals to their uses. Link the properties of copper to its uses in electrical wiring and plumbing. Crude oil and fuels Define mixture and describe what crude oil is and what it is made up of. Recognise & define alkanes, name & draw the first 4 hydrocarbons in formulae/diagrams. Describe how fractional distillation is used. Link the size of the molecule to its boiling point, viscosity and flammability. State products of combustion of fuels, e.g. sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide. Give the environmental problems with some of these products. Describe how levels of sulphur dioxide can be reduced. Evaluate the advantages of biofuels.
6 Core Chemistry Checklist Other Uses of Crude Oil State why hydrocarbons are cracked. Describe the process of cracking and state the products of cracking. Give the general formula for alkenes. Recognise alkenes from their names & formula and draw out the structure. Describe the bromine test. State that some products of cracking can be used as fuels. State what monomers and polymers are. Match monomers to the polymers they would make. Explain why waste disposal is a problem of using polymers. Explain why plastic bags are being made from corn-starch. Give the advantages and disadvantages to using and disposing of polymers. Describe how ethanol can be produced from ethane or from fermentation. Plant oils and their uses Describe the stages involved in extracting vegetable oils. Describe why vegetable oils are important in foods. State how the boiling points of vegetable oils compare to water. Explain how fried foods are different to boiled foods. Describe what an emulsion is. State some uses of emulsions based on their special properties. Describe how emulsifiers work. Describe how we can identify unsaturated vegetable oil. Describe how vegetable oils can be hardened. Explain the properties of hydrogenated vegetable oils and link these to their uses. Changes in the Earth and its atmosphere State the layers of the Earth. Describe the layers of the Earth in terms of size and properties. Describe why tectonic plates move. Explain how earthquakes and volcanoes happen. State what the Earth s atmosphere is made up of and how the atmosphere changed over time. Explain one theory of how life was formed and the Miller-Urey experiment. Describe how oxygen became part of the atmosphere. Describe two reasons why the levels of carbon dioxide have decreased. Explain why increased levels of carbon dioxide in the oceans can be a problem. Explain why burning fossil fuels is a problem. Explain how the gases in the air can be separated. Describe some industrial processes that the gases in the air can be used for.
7 Additional Chemistry Checklist Structure and Bonding Write the formula for ionic compounds from given symbols & charges Represent the electronic structure of ions (e.g. NaCl, MgO) Represent covalent bonds as dot & cross diagrams Represent covalent bonds as single lines Draw a diagram to represent bonding in metals Define compound Describe the process of making ions to allow ionic bonding to occur Draw the ions made from Group 1 & Group 7 Explain why ionic compounds can form giant ionic structures Explain why covalent compounds are often simple molecules Describe & explain the properties of giant covalent structures Explain how delocalised electrons occur in metals Structure and Properties Explain why simple molecules are gases, liquids or solids with low melting & boiling points Understand that the intermolecular forces are overcome when a simple substance melts or boils NOT covalent bonds Explain why simple molecules do not conduct electricity Explain why ionic compounds have high melting/boiling points Explain how ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water Explain why the boning in diamond allows it to be hard Explain why the bonding in graphite allows it to be soft & slippery Explain how delocalised electron allow graphite to conduct heat & electricity Describe the use of fullerenes Explain why the structure of metals allow them to conduct heat & electricity Explain why metals can be bent and shaped State what an alloy is & explain how they are different to pure metals State what is unique about shape memory alloys Describe how the properties of polymers depend on what they are made of & the conditions they were made under Explain why thermosetting polymers don t melt but thermosoftening to Describe the sizes of nanoparticles & list their uses Analysis & quantitative Chemistry Recall the masses & charges of protons, neutrons & electrons Remember that proton + neutron = mass number Define the word isotope Recall what relative atomic mass and relative formula mass are State that the (Mr) of a substance in grams, is equal to one mole Describe the benefits of using instrumental methods to detect chemicals Describe how to use paper chromatography, gas chromatography & mass spectroscopy & the advantage/disadvantages of each Calculate the percentage of an element within a compound Calculate the empirical formula of a compound from its mass/percentage Calculate the masses of reactant or products from a balanced equation Calculate the percentage yield from a chemical reaction
8 Additional Chemistry Checklist Rates of Reactions Look at a graph and work out the rate of reaction from the products forming Describe the changing ROR by looking at a graph State what a catalysts is and what it does Evaluate the advantages/disadvantages of using catalysts in industry Calculate the ROR using the correct equation Name the factors that would affect the ROR Describe collision theory in terms of particles and energy Recall the name of the energy need to be overcome to start a reaction Explain how each factor would affect the ROR using collision theory Recall the unit of concentrations of solutions Recall that equal volumes of gases at the same temperature/pressure have the same number of molecules Exothermic/Endothermic Reactions State that when a chemical reaction occurs, energy is transferred to/from the surroundings Define an exothermic & exothermic reaction is in terms of energy & give examples Recall that id a reversible reaction is exothermic in on direction, it will be endothermic in the opposite direction Write equations to represent reversible reactions Acids, bases & salts Use state symbols correctly in an equation Describe how soluble salts can be made by reaction acids with metals, bases, or alkalis Describe how salt solutions can be made mixing certain salts in solutions (precipitate) Describe how precipitation can be used to remove unwanted ions from solutions Describe the difference between a base and alkali Name the different salts produced by HCl, HNO3, H2SO4 Describe how ammonium salts form and that they are important to fertilisers Recall that the ph scale is a measure of the acidity/alkalinity of a solution Identify the ions present in acids and alkalis Represent a neutralisation reaction using ion equation Electrolysis Describe what electrolysis is and does Describe the properties of an electrolyte Describe which ions move to which electrode & what happens there Describe how electrolysis is used to electroplate objects Remember OIL RIG & what it means in terms of electrons Recall that if there s a mix of ions, the products depend on reactivity Represent reactions at electrodes using half equations Describe how aluminium is manufactured using electrolysis Explain why cryolite & carbon electrodes are needed Describe the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution (brine) Explain why the products of brine electrolysis are useful
9 Core Physics Checklist Transfer of energy in heating State what infrared radiation is and that objects emit and absorb it. Describe how the amount of infrared radiation can vary. Describe how different surfaces vary in their absorption and reflection of infrared radiation. Describe the particle arrangement and different levels of energy in the states of matter. Explain the different energy states using kinetic theory. Describe the bonds between particles in the different states of matter. Describe what is meant by conduction, in terms of particles, including the role of electrons. Describe what is meant by convection, in terms of particles, including explaining density. Describe how energy is transferred in evaporation and condensation and factor affecting each. Describe the factors that affect the rate of heat transfer from an object. State the use of U-Values. Describe how solar panels work. Describe what is meant by specific heat capacity and use the equation. Energy and efficiency Describe how energy is wasted and what happens to it. Construct and read information from a Sankey diagram. Calculate the efficiency of a device using the equation. Describe payback time and calculate it. Usefulness of electrical appliances Describe energy transfers in everyday electrical appliances. Link the amount of energy transferred to the power and the amount of time switched on. Calculate the energy transferred when you know the time and power. Calculate the cost of electricity given the cost per kilowatt-hour. Revision tools for all Science Subjects The King John School VLE has a variety of resources available online: The KJS VLE has Bobbie s posh words for ISA revision. The KJS VLE also has well over 30 past papers. A/A* banks of questions on VLE.
10 Core Physics Checklist Generating electricity Using Waves State some energy sources that are used to generate electricity (heat water). Describe the processes that occur in different power stations. Describe alternative methods of generating electricity. Evaluate alternative methods of generating electricity. Explain what a pumped storage system does. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of small scale energy production. State what the National grid is. Label the different essential parts of the National Grid. Explain the use of transformers. Describe the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves, using sound and electromagnetic waves. Define and calculate the speed, frequency or wavelength of a wave. State the speed of an electromagnetic wave and describe what is meant by the electromagnetic spectrum. State which electromagnetic waves are used for communication. Describe the hazards associated with electromagnetic waves. Describe what happens when a wave is reflected including law of reflection and images in a plane mirror. Explain how waves can be refracted. Explain how waves can be diffracted. Describe what is meant by frequency and how this relates to pitch. Describe what an echo is. Explain the Doppler effect and relate this to frequency and wavelength of waves. Explain how the evidence from red-shift supports the Big Bang Theory. Describe what Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) is. Useful Revision links A list of other useful websites and links for pupils to uses as additional support materials. gcsescience.com/ A log in is required but can be created for free. Core videos are free, additional videos require subscription. Search Youtube for My GCSE Science videos Revision videos with comprehensive coverage of key topics.
11 Additional Physics Checklist Forces and their effects To understand that forces work in pairs To know what resultant force is and how to calculate it To describe how a change in resultant causes changes to motion To draw and interpret distance-time graphs and velocity-time graphs To know the difference between speed and velocity To calculate the speed and acceleration of an object from the gradient of a graph To calculate the acceleration of an object To calculate the distance an object travels from a velocity-time graph To explain reaction time To explain the difference between thinking, braking & stopping distance Recall the factors that affect a drivers ability to react & braking distance To know which forces act on an object moving in fluid To describe and explain how velocity changes as an object moves through a fluid To understand how a parachute reduces terminal velocity To explain the difference between weight and mass To understand that when elastic objects are stretched they store elastic potential energy To explain the relationship between force and extension in elastic objects and use the relevant equation The Kinetic Energy of objects speeding up and slowing down To calculate work done and power To understand that a raised object is doing work and gains GPE To calculate the change in GPE To understand the transfer of KE when an object falls To calculate kinetic energy To calculate momentum and change in momentum To know that momentum is conserved in a collision and explosion Currents in electrical circuits To know that opposite charges attract and like charges repel To explain the role of electron movement in charging insulators To know the uses and dangers of static electricity To recall what current is and calculate it using the correct equation To know the symbols for circuit components and draw circuit diagrams To explain what potential difference is and calculate it To know Ohms Law and to be able to calculate resistance To explain what resistance is and how it can be measured To know the difference between series and parallel circuits To be able to recognise/interpret current-potential difference graphs for resistors, filament bulbs and diodes To describe the use of LED s To describe the uses of an LDR explain how the resistance of an LDR changes with light intensity To know what a thermistor is and explain how the resistance changes with temperature
12 Additional Physics Checklist Using Mains electricity safely and the power of electrical appliances Know the difference between AC and DC current Compare and calculate the frequency of potential difference of AC & DC from an oscilloscope trace Know how we can use an oscilloscope to measure the frequency of an alternating current To know the frequency of a mains supply To know the structure of a 2 core and 3 core cable and how a plug should be wired Recall the colour coding of the wires in a plug and explain the need for a fuse and earth wire Explain that RCCB s detect a difference in current between the live a neutral wires and compare them to fuses Know how to choose the right fuse by calculation Understand that heat is wasted in filament bulbs compared to CFL s Use the equations P=E/t and P=IV Calculate charge flow Know that potential difference, charge and energy transferred are related by the equation E=VQ Radioactive substances Know the structure of an atom, its mass and charge Know that the atom is mostly empty space Explain that atoms have no overall charge Explain how the results of Rutherford s scattering let to a change in the accepted model of the atom Explain atomic number and mass number Describe how an ion is formed Know that radioactive decay is a random process Know what causes background radiation Recall the properties of alpha, beta and gamma radiation and explain why they are suitable for their uses Explain why alpha & beta particles are deflected in magnetic fields due to their relative charge/mass Know & balance nuclear equations to show alpha and beta decay Recall the definition of half life Understand the shape of a radioactive decay graph & calculate half-life from the graph Choose a radioactive source for a particular job based on its half life Nuclear Fission and Fusion Describe nuclear fission and explain a chain reaction Sketch & label a chain reaction diagram Describe what happens in nuclear fusion Explain the life cycle of a star Know that elements up to iron are formed during the stable phase Know that elements heavier than iron are formed during a Supernova Explain why the early universe contained only hydrogen & now contains other elements Evaluate the uses of nuclear fusion and fission in generating electricity.
13 GCSE Science Examination Command Words Calculate Candidates should use numbers given in the question to work out the answer. They should always show their working, as it may be possible for the examiner to award some marks for the method even if the final answer is wrong. Candidates should always give the units sometimes a mark may be awarded for the correct units, even if the calculation is wrong. Compare This requires the candidate to describe the similarities and/or differences between things, not just write about one. If candidates are asked to compare x with y, they need to write down something about x and something about y, and should give a comparison. Complete Answers should be written in the space provided, e.g. on a diagram, in spaces in a sentence or in a table. Describe Candidates should recall some facts, events or process in an accurate way - for example an experiment they have done. They may need to give an account of what something looked like, or what happened, e.g. a trend in some data. Evaluate Candidates should use information supplied or their own knowledge and understanding to consider the evidence for and against and draw conclusions. This goes further than compare. For example, they may be given a passage to read and told to Evaluate the benefits of using system x and system y. This means they will need to write down some of the pros and cons for both systems, AND then state which one is better and why. The candidate should complete their answer with a conclusion. Explain Candidates should make something clear, or state the reasons for something happening. The points in the answer must be linked coherently and logically. The answer should not be a simple list of reasons. State, give, name, write down Only a short answer is required, not an explanation or a description. Often it can be answered with a single word, phrase or sentence. If the question asks the candidate to state, give, or write down one (or two etc) examples, they should write down only the specified number of answers, or they may lose marks for any wrong examples given. Suggest This term is used in questions where candidates need to apply their knowledge and understanding to a new situation. Often there may be more than one correct answer as candidates are expected to base their answers on scientific knowledge and/or principles.
Science Years 9 to 10
 Boardworks Contents Guide Boardworks Presentations: Acids and metal oxides 10 slides Reactions of metal oxides with acids. Adapting to changes 9 slides Ways that animals adapt to their habitats. Air pollution
Boardworks Contents Guide Boardworks Presentations: Acids and metal oxides 10 slides Reactions of metal oxides with acids. Adapting to changes 9 slides Ways that animals adapt to their habitats. Air pollution
Additional Science. Important exam information and revision booklet
 Additional Science Important exam information and revision booklet CONTENTS PAGE Page Introduction 3 Section One When are my exams? What will they test 4 Useful places to help you to revise Additional
Additional Science Important exam information and revision booklet CONTENTS PAGE Page Introduction 3 Section One When are my exams? What will they test 4 Useful places to help you to revise Additional
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks
 Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks Cell Biology (Yr9) Cell Organisation (Yr9) Infection and Response (Yr10) Bioenergetics (Yr10) Cells Cell Organisation Competition Photosynthesis Microscopy Enzymes Abiotic
Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks Cell Biology (Yr9) Cell Organisation (Yr9) Infection and Response (Yr10) Bioenergetics (Yr10) Cells Cell Organisation Competition Photosynthesis Microscopy Enzymes Abiotic
Science. synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis Using physics to make things work 3 Magnetic fields to keep things moving Energy calculations 4 Energy
 Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
Subject: GCSE Physics
 Subject: GCSE Physics Density States of matter SHC Atoms and radiation Discovery of the nucleus Changes in the nucleus Alpha, beta and gamma Activity and half life Nuclear radiation and medicine Nuclear
Subject: GCSE Physics Density States of matter SHC Atoms and radiation Discovery of the nucleus Changes in the nucleus Alpha, beta and gamma Activity and half life Nuclear radiation and medicine Nuclear
for sodium ion (Na + )
 3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
Science 9-1 Grades Guidance
 U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
H Li. Mass Number. Number of Electrons Hydrogen He Draw diagrams to show the electronic structure of the elements above.
 AQA Knowledge test Unit 1 Chemistry C1 C1.1 The fundamental Ideas in Chemistry C1.1.1 Atoms 1. What is an atom? 2. What is an element? 3. Match the name of the element with the symbol Element Oxygen Sodium
AQA Knowledge test Unit 1 Chemistry C1 C1.1 The fundamental Ideas in Chemistry C1.1.1 Atoms 1. What is an atom? 2. What is an element? 3. Match the name of the element with the symbol Element Oxygen Sodium
Science. Biology Year 7. Chemistry Year 7. Physics Year 7
 Science Biology Year 7 Chemistry Year 7 Physics Year 7 Using a microscope Slide Preparation o Prepare specimens of plant cells and animal cells o Describe the role of stain in specimen preparation o Draw
Science Biology Year 7 Chemistry Year 7 Physics Year 7 Using a microscope Slide Preparation o Prepare specimens of plant cells and animal cells o Describe the role of stain in specimen preparation o Draw
YEAR 7. St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map New AQA Course Started November 2016
 YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists. Name: Teacher:
 AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists Name: Teacher: Paper 1-4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists Name: Teacher: Paper 1-4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
Time (s) Velocity (m/s)
 29.01.18 22.01.18 15.01.18 w/c Weekly Combined Science revision countdown plan (revision guide / workbook page numbers) *content across both paper 1 and paper 2 15 14 13 Revise *Key concepts in biology
29.01.18 22.01.18 15.01.18 w/c Weekly Combined Science revision countdown plan (revision guide / workbook page numbers) *content across both paper 1 and paper 2 15 14 13 Revise *Key concepts in biology
This unit will help you define health, learn about some pathogens and the diseases they cause, medicines and about the immune system.
 YEAR 10 Biology Units 1-5 Biology Unit CB1 Key biological concepts [Paper 1 & CB2 Cells and Control CB3 Genetics CB4 Natural Selection and Genetic Modification CB5 Health, Disease and the Development of
YEAR 10 Biology Units 1-5 Biology Unit CB1 Key biological concepts [Paper 1 & CB2 Cells and Control CB3 Genetics CB4 Natural Selection and Genetic Modification CB5 Health, Disease and the Development of
Lymm High School- KS3 Life after levels - Science Y9
 Biology BRONZE SILVER GOLD PLATINUM D and below= GCSE 1,2,3 C= GCSE 4 C/B= GCSE 5,6 A/A*= GCSE 7,8,9 Explain that cells are very Demonstrate an small and a microscope is understanding of the scale needed
Biology BRONZE SILVER GOLD PLATINUM D and below= GCSE 1,2,3 C= GCSE 4 C/B= GCSE 5,6 A/A*= GCSE 7,8,9 Explain that cells are very Demonstrate an small and a microscope is understanding of the scale needed
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview
 Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Review Chemistry Paper 1
 Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
Paper Atomic structure and the periodic table
 Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes. Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3. C2.1.1a Structure and bonding
 Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our previous GCSE Chemistry (4402) to the new specification (8462). Our new specifications
Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our previous GCSE Chemistry (4402) to the new specification (8462). Our new specifications
Globe Academy Science Department C2 and P2 GCSE Additional Science Homework Booklet Spring 1 Contents: Date Set. Feedback/ Marking.
 Globe Academy Science Department C2 and P2 GCSE Additional Science Homework Booklet Spring 1 Contents: Topic 1 Revision Questions on Chemistry 2 Oxides, Hydroxides and Ammonia 3 Electrolysis and Electroplating
Globe Academy Science Department C2 and P2 GCSE Additional Science Homework Booklet Spring 1 Contents: Topic 1 Revision Questions on Chemistry 2 Oxides, Hydroxides and Ammonia 3 Electrolysis and Electroplating
GCSE Biology B2 Revision Questions. 1. Draw and label the parts of these different types of cell, explaining what the role of each part is -
 B2.1 Cells and Simple Cell Transport GCSE Biology B2 Revision Questions 1. Draw and label the parts of these different types of cell, explaining what the role of each part is - a) Animal cell b) Plant
B2.1 Cells and Simple Cell Transport GCSE Biology B2 Revision Questions 1. Draw and label the parts of these different types of cell, explaining what the role of each part is - a) Animal cell b) Plant
Same theme covered in Combined but extra content Extra parts atomic symbols (first 20, Group 1 and Group 7)
 Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
Cell Structure. Cell Structure. Investigating Cells. Investigating Cells. Cell Division. Cell Division. Transport In and Out of Cells
 Cell Structure What are the two main types of cell? Cell Structure The two main types of cell are prokaryotic and eukaryotic. 1 1 Investigating Cells How is magnification calculated? 2 Investigating Cells
Cell Structure What are the two main types of cell? Cell Structure The two main types of cell are prokaryotic and eukaryotic. 1 1 Investigating Cells How is magnification calculated? 2 Investigating Cells
What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of the cell wall. membrane?
 Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) To pic. Student Checklist
 Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Year 8 Tracking Document. Year 8 Science National Curriculum. Health and Lifestyle
 Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
Level 789 Pathway: Combined Science Double Award
 Level 789 Pathway: Combined Science Double Award Yr Combined Science Targets: Pathway 8 11 Biology a) Explain in detail the role of the hormone ADH on the nephron b) Explain in detail the process by which
Level 789 Pathway: Combined Science Double Award Yr Combined Science Targets: Pathway 8 11 Biology a) Explain in detail the role of the hormone ADH on the nephron b) Explain in detail the process by which
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Unit C1: Chemistry in our world Page 1 of 5
 Unit C1: Chemistry in our world Page 1 of 5 Lesson Specification learning outcomes Edexcel 360 Science Specification match Edexcel 360 Science GCSE Science Students Book page reference Additional information
Unit C1: Chemistry in our world Page 1 of 5 Lesson Specification learning outcomes Edexcel 360 Science Specification match Edexcel 360 Science GCSE Science Students Book page reference Additional information
Departmental Curriculum Planning
 Department: Btec Subject: Biology Key Stage: 4 Year Group: 10 Learning aim A: Investigate the relationships that different organisms have with each other and with their environment Learning aim B: Demonstrate
Department: Btec Subject: Biology Key Stage: 4 Year Group: 10 Learning aim A: Investigate the relationships that different organisms have with each other and with their environment Learning aim B: Demonstrate
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST
 GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
LONGMAN STUDY GUIDES. Science. Di Barton. SUB Q6ttlngen B1842 LONGMAN
 LONGMAN STUDY GUIDES Science Di Barton SUB Q6ttlngen 206 451 652 97B1842 LONGMAN CONTENTS Editors' Preface vii Acknowledgements vii Information about this book viii 1 Revision, examinations and coursework
LONGMAN STUDY GUIDES Science Di Barton SUB Q6ttlngen 206 451 652 97B1842 LONGMAN CONTENTS Editors' Preface vii Acknowledgements vii Information about this book viii 1 Revision, examinations and coursework
Science curriculum overview Yr7 (Draft arrangement as the school may need flexibility as the need arises)
 Science curriculum overview Yr7 (Draft arrangement as the school may need flexibility as the need arises) Term Topic and key questions Assessment structure Autumn 1 CHEMISTRY Test 1: The particle 1.The
Science curriculum overview Yr7 (Draft arrangement as the school may need flexibility as the need arises) Term Topic and key questions Assessment structure Autumn 1 CHEMISTRY Test 1: The particle 1.The
Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions)
 Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions) Metallic (electrostatic attraction between + metal ions and delocalised electrons) Group 1 ions 1+
Covalent (sharing of electron pairs) Ionic ( electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions) Metallic (electrostatic attraction between + metal ions and delocalised electrons) Group 1 ions 1+
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
1.2. How our bodies defend themselves against infectious diseases
 HIGHER LEVEL SCIENCE BIOLOGY SYLLABUS 1. Keeping Healthy A combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise is needed to help keep the body healthy. 1.1. Diet and exercise a) A healthy diet contains
HIGHER LEVEL SCIENCE BIOLOGY SYLLABUS 1. Keeping Healthy A combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise is needed to help keep the body healthy. 1.1. Diet and exercise a) A healthy diet contains
Queen s Park High School Key Stage 3 Assessment Science - Earth IA6 target.
 Year 7 Enquiry Skills Queen s Park High School Key Stage 3 Assessment Science - Earth IA6 target. EARTH STRUCTURE AND UNIVERSE Draw simple graphs outlining information about planets Construct models of
Year 7 Enquiry Skills Queen s Park High School Key Stage 3 Assessment Science - Earth IA6 target. EARTH STRUCTURE AND UNIVERSE Draw simple graphs outlining information about planets Construct models of
C2 Chemistry. Key Recall Questions
 C Chemistry Additional Science Key Recall Questions *Cover up the answers, ask yourself a question (or get your partner to ask you), if you get it right then tick the chart, wrong put a cross. Keep practising
C Chemistry Additional Science Key Recall Questions *Cover up the answers, ask yourself a question (or get your partner to ask you), if you get it right then tick the chart, wrong put a cross. Keep practising
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Lesson title Lesson objectives AQA specification reference 1.1 Elements and compounds
 1.1 Elements and compounds 1.2 Atoms, formulae and equations Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and compounds. Identify the elements in a compound
1.1 Elements and compounds 1.2 Atoms, formulae and equations Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and compounds. Identify the elements in a compound
KS4 CURRICULUM. Science - BTEC
 KS4 CURRICULUM Science - BTEC Students have four lessons per fortnight completing a BTEC in the Principles of Applied Science. This is the equivalent to one GCSE. Unit One Principles of Science; externally
KS4 CURRICULUM Science - BTEC Students have four lessons per fortnight completing a BTEC in the Principles of Applied Science. This is the equivalent to one GCSE. Unit One Principles of Science; externally
Reproduction Chemical Reactions. 8J Light 8G Metals & Their Uses 8C Breathing & Respiration 8D Unicellular Organisms
 Science: Key Stage 3 Based on the Exploring Science Scheme of Learning Term 1 & 2 Term 3 & 4 Term 5 & 6 Year 7 Cells, Tissues & Organs Particles Forces & Motion Reproduction Chemical Reactions Chemical
Science: Key Stage 3 Based on the Exploring Science Scheme of Learning Term 1 & 2 Term 3 & 4 Term 5 & 6 Year 7 Cells, Tissues & Organs Particles Forces & Motion Reproduction Chemical Reactions Chemical
Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined. Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours
 Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours Half Term.7.. Communities Competition Ecosystems Interdependence ASSESSED HOMEWORK (Communities).7.. Abiotic
Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours Half Term.7.. Communities Competition Ecosystems Interdependence ASSESSED HOMEWORK (Communities).7.. Abiotic
KS3 Science Levelness Posters
 KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
Science Scheme of Work
 Cherry Tree Hill Primary School Science Scheme of Work Essential characteristics: High-quality science education provides the foundations for understanding the world through the specific disciplines of
Cherry Tree Hill Primary School Science Scheme of Work Essential characteristics: High-quality science education provides the foundations for understanding the world through the specific disciplines of
Q1. Fresh milk is a mixture of compounds including lipid, protein and about 5% lactose sugar.
 Q1. Fresh milk is a mixture of compounds including lipid, protein and about 5% lactose sugar. Lactose must be digested by the enzyme lactase, before the products can be absorbed. Lactase can be added to
Q1. Fresh milk is a mixture of compounds including lipid, protein and about 5% lactose sugar. Lactose must be digested by the enzyme lactase, before the products can be absorbed. Lactase can be added to
STANDARD GRADE CHEMISTRY : GENERAL LEVEL
 STANDARD GRADE CHEMISTRY : GENERAL LEVEL NEED TO KNOW SHEETS (BASED ON 1998 2006 EXAMS) TOPIC NO 1 -ide means two elements only ate/-ite means two elements + oxygen a solution contains a solid (solute)
STANDARD GRADE CHEMISTRY : GENERAL LEVEL NEED TO KNOW SHEETS (BASED ON 1998 2006 EXAMS) TOPIC NO 1 -ide means two elements only ate/-ite means two elements + oxygen a solution contains a solid (solute)
Globe Academy Science Department GCSE Core Science Year 9 Homework Booklet Summer 2 Contents: Date Set. Feedback/ Marking. Due
 Globe Academy Science Department GCSE Core Science Year 9 Homework Booklet Summer 2 Contents: Topic 1 Vaccines and Antibiotics Revision 2 Alkali Metals and Noble Gases Revision Mid-Term Assessment Revision
Globe Academy Science Department GCSE Core Science Year 9 Homework Booklet Summer 2 Contents: Topic 1 Vaccines and Antibiotics Revision 2 Alkali Metals and Noble Gases Revision Mid-Term Assessment Revision
Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and recall names used for these inter-conversions
 Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY
 B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY What are the 7 components of a healthy diet? 1.. 2.. 3.. 4.. 5.. 6.. 7.. What are the different methods of infection? Describe the issues with being overweight Describe
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY What are the 7 components of a healthy diet? 1.. 2.. 3.. 4.. 5.. 6.. 7.. What are the different methods of infection? Describe the issues with being overweight Describe
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Trilogy Chemistry Paper 1
 AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State
AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Chemistry Paper 1
 AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State that elements
AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State that elements
Noadswood Science. Revision Cards. Science A (Core) Chemistry Basics.
 Noadswood Science Revision Cards Science A (Core) Chemistry Basics www.noadswoodscience.com How to use the revision cards It is suggested you cut the pack of cards out, so that there is a question on one
Noadswood Science Revision Cards Science A (Core) Chemistry Basics www.noadswoodscience.com How to use the revision cards It is suggested you cut the pack of cards out, so that there is a question on one
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview
 Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Chemistry (separate) for November PPE
 1.1 Elements and 1.2 Atoms, formulae and Chapter 1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and. Identify the elements
1.1 Elements and 1.2 Atoms, formulae and Chapter 1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and. Identify the elements
GCSE in SCIENCE (Double Award) (Wales)
 GCSE SCIENCE (Double Award) 1 Y9&Y10 GCSE in SCIENCE (Double Award) (Wales) Summary of Assessment There are two tiers of entry for this qualification: Higher Tier Grades A* - D Foundation Tier Grades C
GCSE SCIENCE (Double Award) 1 Y9&Y10 GCSE in SCIENCE (Double Award) (Wales) Summary of Assessment There are two tiers of entry for this qualification: Higher Tier Grades A* - D Foundation Tier Grades C
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Chemistry Paper 2
 AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.6 The rate and extent of chemical change Calculate the rate of a chemical reaction over time, using either the quantity of reactant used or the quantity of product
AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.6 The rate and extent of chemical change Calculate the rate of a chemical reaction over time, using either the quantity of reactant used or the quantity of product
New Specification 2018 Recurring Exam Questions. How Science Works. C1 - Particles. Atom with the same atomic number and different mass number
 How Science Works Why is it important that scientist publish their results? Results can be checked Further evidence can be collected How do scientists publish their work? Scientific conference Scientific
How Science Works Why is it important that scientist publish their results? Results can be checked Further evidence can be collected How do scientists publish their work? Scientific conference Scientific
Part 6- Chemistry Paper 1 Bonding Application Questions Triple Science
 Part 6- Chemistry Paper 1 Bonding Application Questions Triple Science How bonding and structure are related to the properties of substances A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
Part 6- Chemistry Paper 1 Bonding Application Questions Triple Science How bonding and structure are related to the properties of substances A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8. atom.
 Student checklist C1 Atomic structure Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8 C1.1 Atoms I can define the word element. I can classify familiar substances as elements or compounds. I can use the periodic table
Student checklist C1 Atomic structure Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8 C1.1 Atoms I can define the word element. I can classify familiar substances as elements or compounds. I can use the periodic table
Atoms, Elements, Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures. Compounds and Mixtures. Atoms and the Periodic Table. Atoms and the.
 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
C2.1 Structure and bonding
 C2.1 Structure and bonding C2 1.1 Chemical bonding Key words: A compound contains two or more elements which are chemically combined Covalent bonding sharing electrons Ionic bonding transferring electrons
C2.1 Structure and bonding C2 1.1 Chemical bonding Key words: A compound contains two or more elements which are chemically combined Covalent bonding sharing electrons Ionic bonding transferring electrons
Learning Model Answers Year 11 Double Chemistry
 1 Describe ionic bonding Describe covalent bonding Occurs between metals and non-metals. Electrons are transferred. There is an electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions. Occurs
1 Describe ionic bonding Describe covalent bonding Occurs between metals and non-metals. Electrons are transferred. There is an electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions. Occurs
Le Lycee Mauricien. Proposed Syllabus Chemistry (5070) - Form 5
 Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Keywords
 Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Respiration. Know that respiration in living organisms can be aerobic or anaerobic The word equation for aerobic respiration The process of anaerobic respiration
Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Respiration. Know that respiration in living organisms can be aerobic or anaerobic The word equation for aerobic respiration The process of anaerobic respiration
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
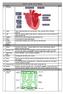 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
In the event of snow:
 BIOLOGY Units Learning Objectives: Pupils should be taught (underlined = level 2 only) YEAR 7 Cells and Cell Functions 1a-e Nutrition and movement 2a-e Reproduction 2f-h Breathing and Respiration 2i-l
BIOLOGY Units Learning Objectives: Pupils should be taught (underlined = level 2 only) YEAR 7 Cells and Cell Functions 1a-e Nutrition and movement 2a-e Reproduction 2f-h Breathing and Respiration 2i-l
Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science magnification tur tur magnification ell Struc ell Struc ells ells Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science
 Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
AQA GCSE (9-1) Combined Chemistry Three Year Scheme of Work
 Year 9 Term 1 1/2 1.1 Elements and compounds Year 9 Term 1 1/2 1.2 Atoms, formulae and equations Chapter 1: Atomic structure and the periodic table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table
Year 9 Term 1 1/2 1.1 Elements and compounds Year 9 Term 1 1/2 1.2 Atoms, formulae and equations Chapter 1: Atomic structure and the periodic table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table
In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium salt to produce potassium
 Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
Cambridge IGCSE Science. Syllabus 0654 for 2016 Exam
 Cambridge IGCSE Science Syllabus 0654 for 2016 Exam What is in this revision guide? 1. A topic checklist: here you can find the names of all of the topics we cover. You can tick them off when we do them
Cambridge IGCSE Science Syllabus 0654 for 2016 Exam What is in this revision guide? 1. A topic checklist: here you can find the names of all of the topics we cover. You can tick them off when we do them
Chemistry Unit 1 C1 C2 C3
 hemistry Unit 1 1 2 3 GRADE HEKERS 1 Revision - arbon hemistry Go to http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/ocr_gateway/carbon_chemistry/. This is the link for the 1 unit on OR Gateway hemistry.
hemistry Unit 1 1 2 3 GRADE HEKERS 1 Revision - arbon hemistry Go to http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/ocr_gateway/carbon_chemistry/. This is the link for the 1 unit on OR Gateway hemistry.
Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview
 Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 Hypothesis
Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 Hypothesis
GCSE Science: Progression in key ideas
 The Collins GCSE Science (9-1) Five Year Scheme of Work: Identifies ten key scientific concepts Outlines the development of students understanding in these concepts over the five years from age 11 to 16
The Collins GCSE Science (9-1) Five Year Scheme of Work: Identifies ten key scientific concepts Outlines the development of students understanding in these concepts over the five years from age 11 to 16
Curriculum overview Key Stage 2 Living things and their habitats: Animals: Properties and changes of materials: Earth and Space: Forces: Evolution:
 Curriculum overview: Science (Foundation) Key Stage 2 Living things and their habitats: Life cycles of a mammal, an amphibian, an insect and a bird Reproduction in some plants and animals. Classification
Curriculum overview: Science (Foundation) Key Stage 2 Living things and their habitats: Life cycles of a mammal, an amphibian, an insect and a bird Reproduction in some plants and animals. Classification
Atomic Structure. Same atomic number Different mass number
 Mass number Number of protons and neutrons Atomic number Number of protons Atomic Structure Cl 35 17 Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons - these atoms are called isotopes of
Mass number Number of protons and neutrons Atomic number Number of protons Atomic Structure Cl 35 17 Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons - these atoms are called isotopes of
- know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues can be massed together to form organs
 Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Combined Science: Trilogy
 Co-teaching GCSE Chemistry and GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy This high level co-teaching guide will help you plan your route through the course. You ll be able to see what common themes and topics span
Co-teaching GCSE Chemistry and GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy This high level co-teaching guide will help you plan your route through the course. You ll be able to see what common themes and topics span
UNIT 9A Inheritance and Selection
 UNIT 9A Inheritance and Selection Know what inheritance means Know what characteristics are Know that sexual reproduction needs two parents Know that animals and plants can be bred for their characteristics
UNIT 9A Inheritance and Selection Know what inheritance means Know what characteristics are Know that sexual reproduction needs two parents Know that animals and plants can be bred for their characteristics
C2 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you)
 Name: C2 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you) Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths and working scientifically questions PRACTICE ALL THESE QUESTIONS! Maths and Science Skills
Name: C2 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you) Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths and working scientifically questions PRACTICE ALL THESE QUESTIONS! Maths and Science Skills
Atomic Structure. Same atomic number Different mass number
 Mass number Number of protons and neutrons Atomic number Number of protons Atomic Structure Cl 35 17 Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons - these atoms are called isotopes of
Mass number Number of protons and neutrons Atomic number Number of protons Atomic Structure Cl 35 17 Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons - these atoms are called isotopes of
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE)
 Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
Year 7 Science Assessment Criteria Energy
 Year 7 Science Assessment Criteria Energy To be able to explain the difference between an energy transfer and an energy transformation To be able to draw more complex energy transfer diagrams and explain
Year 7 Science Assessment Criteria Energy To be able to explain the difference between an energy transfer and an energy transformation To be able to draw more complex energy transfer diagrams and explain
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Combined Science Trilogy) 15 Week Revision Timetable
 Exam advice o READ THE WHOLE QUESTION CAREFULLY before starting to write an answer. o Make sure you have all the necessary equipment o It s ok to draw diagrams even if there are lines for writing. Don
Exam advice o READ THE WHOLE QUESTION CAREFULLY before starting to write an answer. o Make sure you have all the necessary equipment o It s ok to draw diagrams even if there are lines for writing. Don
GCSE Additional Science
 GCSE Additional Science Module C5 Chemicals of the Natural Environment: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this
GCSE Additional Science Module C5 Chemicals of the Natural Environment: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this
C2 REVISION CHAPTER 1 STRUCTURES & BONDING
 C2 REVISION CHAPTER 1 STRUCTURES & BONDING Draw the symbol for sodium include its mass number and atomic number (what do they tell us) Complete the table Relative Charge Relative Mass Use pictures and
C2 REVISION CHAPTER 1 STRUCTURES & BONDING Draw the symbol for sodium include its mass number and atomic number (what do they tell us) Complete the table Relative Charge Relative Mass Use pictures and
All you need to know about Additional Science
 All you need to know about Additional Science Chapters in this unit 1. Structures and bonding 2. Structures and properties 3. How much? 4. Rates of reaction 5. Energy and reactions 6. Electrolysis 7. Acids,
All you need to know about Additional Science Chapters in this unit 1. Structures and bonding 2. Structures and properties 3. How much? 4. Rates of reaction 5. Energy and reactions 6. Electrolysis 7. Acids,
Proficiency Review #1
 Proficiency Review #1 What is the best way to determine how two people are most closely DNA related? What best measures a liquid? Graduated Cylinder A hydro-electric generator converts mechanical energy
Proficiency Review #1 What is the best way to determine how two people are most closely DNA related? What best measures a liquid? Graduated Cylinder A hydro-electric generator converts mechanical energy
8 th Grade Integrated Science Curriculum
 Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the curriculum, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. 8.1 Scientific Thinking and Practice 1. Use scientific methods to develop
Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the curriculum, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. 8.1 Scientific Thinking and Practice 1. Use scientific methods to develop
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (double award)
 EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (double award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the three states of matter in terms of the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (double award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the three states of matter in terms of the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles
AQA GCSE (9-1) Chemistry Three Year Scheme of Work
 This 3-Year Scheme of Work offers a flexible approach for KS4. It is based on three science lessons per fortnight (assuming a two week timetable of two lessons one week and one lesson in the other). Lessons
This 3-Year Scheme of Work offers a flexible approach for KS4. It is based on three science lessons per fortnight (assuming a two week timetable of two lessons one week and one lesson in the other). Lessons
CHEMISTRY 2b SUMMARY
 CHEMISTRY 2b SUMMARY Items in ITALLICS are HIGHER TIER NLY C2.4.1 RATES F REACTIN Speeding up, or slowing down, chemical reactions is important in everyday life and in industry The rate of a chemical reaction
CHEMISTRY 2b SUMMARY Items in ITALLICS are HIGHER TIER NLY C2.4.1 RATES F REACTIN Speeding up, or slowing down, chemical reactions is important in everyday life and in industry The rate of a chemical reaction
