The thermal degradation of poly(iso-butyl methacrylate) and poly(sec-butyl methacrylate)
|
|
|
- Linda Ashlynn Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 65(12) (2000) UDC : JSCS 2814 Original scientific paper The thermal degradation of poly(iso-butyl methacrylate) and poly(sec-butyl methacrylate) KATARINA NOVAKOVI] #, LYNNE KATSIKAS and IVANKA G. POPOVI] # Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy, University of Belgrade, Karnegijeva 4, Belgrade, Yugoslavia (Received 17 July 2000) The non-oxidative thermal degradation of poly(iso-butyl methacrylate) and poly(sec-butyl methacrylate) was investigated by studying changes in the polymer residue. Due to the different number of β-hydrogens in their ester substituents, these two polymeric isomers behave differently when subjected to elevated temperatures. Poly(iso-butyl methacrylate) degrades quantitatively by depolymerisation with zip lengths of the same order of magnitude as those of poly(methyl methacrylate). Poly(sec-butyl methacrylate) degrades by a combined degradation mechanism of depolymerisation and de-esterification. De-esterification becomes a significant thermolysis route at temperatures higher than 240 ºC. Keywords: poly(butyl methacrylate), isomers, thermal degradation, mechanism, depolymerisation, de-esterification. INTRODUCTION It is generally considered that most polymethacrylates thermally degrade by depolymerisation. Grassie and his co-workers initiated and carried out investigations of thermal degradation of numerous polymethacrylates, placing most emphasis on the major represen- Scheme 1. The de-esterification of a polymethacrylate with 2β-hydrogens # Serbian Chemical Society active member. 867
2 868 NOVAKOVI], KATSIKAS and POPOVI] tative of this class of compounds, poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA). 1 4 Although PMMA degrades practically quantitatively to its monomer, the thermolysis mechanism of other polymethacrylates is not that simple and is determined predominantly by the structure of the ester substituent. If there are β-hydrogen atoms present in the substituent, de-esterification may and does occur (Scheme 1). The influence of β-hydrogens on the thermolysis mechanism of polymethacrylates is shown in Table I. 3 De-esterification competes with depolymerisation as a relevant degradation path when the monomer unit has five or more β-hydrogens. Consequently, isomeric structures such as poly(iso-, n-, sec- and tert-butyl methacrylate) (PiBMA, PnBMA, PsBMA and PtBMA) have different thermolysis mechanisms. Grassie studied the thermal degradation of PnBMA nad PtBMA and found that the former predominantly degraded by depolymerisation 2 and the latter by de-esterification. 5 TABLE I. The influence of β-hydrogens on the thermal degradation mechanism of polymethacrylates 3 Depolymerisation Mostly depolymerisation De-esterification Substituent No. of β-hs Substituent No. of β-hs Substituent No. of β-hs Methyl 0 Ethyl 3 iso-propyl 6 Neopentyl 0 n-propyl 2 sec-butyl 5 iso-butyl 1 n-butyl 2 tert-butyl 9 Ethoxyethyl 2 n-hexyl 2 n-heptyl 2 n-octyl 2 The goal of this study was to investigate the thermal degradation of PiBMA (Structure I) and PsBMA (Structure II) and determine their basic thermolysis mechanisms by studying changes in the polymer residue. Stucture I Stucture II EXPERIMENTAL The monomers, iso-butyl methacrylate and sec-butyl methacrylate, were synthesised by the standard acid catalysed esterification of methacrylic acid (Aldrich, p.a.) with iso-butanol (Kemika, p.a.) and sec-butanol (Kemika, p.a), respectively. After the normal work-up procedure, the monomers were vacuum distilled immediately prior to polymerisation. The polymerisations were performed in bulk at 50 ºC in glass ampoules sealed under high vacuum using 0.5 mol % α,α'-azo-
3 THERMAL DEGRADATION 869 bisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as the initiator. The polymers were isolated by precipitation with methanol (Zorka Pharma, p.a.) containing about 5 % water and freed of residual monomer by repeated precipitation from acetone (Zorka Pharma, p.a.) solutions using methanol containing 5 % water. The polymers were dried to constant mass at room temperature. The values of the limiting viscosity numbers (LVN) of the samples were determined in acetone at 25 ºC using an Ubbelohde viscometer; LVN PiBMA = m 3 /kg and LVN PsBMA = m 3 /kg. The mean number-average molar mass, M n of PiBMA was calculated from the obtained LVN value using the Kuhn-Mark-Houwink-Sakurada equation and literature values for the coefficients K and a 6 ; M n = g/mol. Thermal degradation experiments were performed using a small furnace, the temperature of which was controlled by a rheostat. The temperature of the furnace, measured by a Ni-NiCd thermocouple, was kept constant to ±1ºC. Experiments were performed in the range ºC for PiBMA and ºC for PsBMAunder a nitrogen flow of 50 cm 3 /min for 5 to 30 min. The sample masses were about 120 mg. After determining the mass loss, the PiBMA residues were analysed by measuring the LVN. The content of free acid groups in degraded PsBMA samples was determined by dissolving or swelling the residue in methanol, adding a known amount of methanolic 0.1 mol/dm 3 NaOH solution and back titrating the excess alkali with 0.1 mol/dm 3 aqueous HCl using phenolphthalein as indicator. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Thermal degradation of PiBMA The isothermal mass loss of PiBMA as a function of degradation time at various thermolysis temperatures is shown in Fig. 1. Significant mass loss can be noticed at longer degradation times and at 200 ºC. Based on the fact that PiBMAhas one β-hydrogen in its ester substituent, it may be assumed that depolymerisation is the main thermal degradation mechanism. This assumption was confirmed by thermal volatilisation analysis (TVA), which indicated almost quantitative degradation to monomer. 7 Therefore, it is interesting to follow changes in the molar mass of the residue during thermal degradation, Fig. 2. The molar mass of PiBMA decreases considerably during degradation. Fig. 1. The dependence of PiBMA mass loss on time at various degradation temperatures.
4 870 NOVAKOVI], KATISKAS and POPOVI] Fig. 2. The change in M n of PiBMA degraded at various temperatures. The number of main chain scissions per monomer unit can be determined on the basis of changes in the mass and molar mass of the degraded sample. 8 The number of bond scissions per monomer unit, s/p 0, may be calculated from the equation: s P 1 x 1 = P P 0 t 0 where s is the number of scissions, x the fraction of evaporated thermal degradation volatiles, and P 0 and P t the degrees of polymerisation of the initial and degraded polymer, respectively. The results of this calculation are shown in Fig. 3 where s/p 0 is plotted against time at various temperatures. It may be noticed that the values of (1) Fig. 3. Dependence of the number of bonds broken per monomer unit of PiBMA, s/p 0, on time at various degradation temperatures.
5 THERMAL DEGRADATION 871 s/p 0 tend toward constant values at longer degradation times. As expected, higher values of s/p 0 are observed at higher degradation temperatures. The relative change in the molar mass of the polymer residues, M n /M n0,asafunction of mass loss is shown in Fig. 4. The shape of the M n /M n0 vs. conversion curve indicates the occurrence of random main chain scission, which initiates depolymerisation, and/or that the zip length of depropagation, Z, is smaller than the degree of polymerisation of the polymer. 8 An attempt was made to determine the zip length of depropagation by the equation proposed by Kashiwagi et al.: 9 W W 0 2 Pt = P 2 0 Z + P0 Z + P t where W/W 0 is the ratio of the mass of the residue and the mass of the initial polymer. The results of the calculation are shown in Fig. 5. The value of Z increases with degradation temperature. Also, as expected from the shape of the dependence M n /M n0 vs. mass loss, the values of Z are lower than the initial degree of polymerisation of PiBMA, P 0 = Similar calculations for PMMA degraded in the temperature range ºC yielded Z values between 1000 and The values for PiBMAare lower most probably because they were derived from data obtained at lower thermolysis temperatures. If one extrapolates the obtained depencence of Zvs. degradation temperature to the temperatures 260 and 300 ºC, one obtains Z values of 1455 and 2080, respectively, which compare very well with the values determined for PMMAand indicate the similar depropagation behaviour of PMMA and PiBMA. However, detailed results obtained for the thermolysis of the structurally similar isomeric butyl diesters of poly(itaconic acid) showed that although depolymerisation 2 Fig. 4. The relative change of PiBMA molar mass, M n /M n0, as a function of mass loss after thermal treatment. (2)
6 872 NOVAKOVI], KATSIKAS and POPOVI] Fig. 5. The depencence of the depolymerisation zip length Z on temperature after a degradation time of 30 min. was the main degradation mechanism of poly(di-isobutyl itaconate) (PDiBI) more alkene was evolved than was the case of poly(di-n-butyl itaconate) (PDnBI). 10 This is contrary to the assumption that the amount of ester decomposition is dependent on the number of β-hydrogen atoms. This fact was explained by the special lability of the lone tertiary hydrogen atom present in the ester substituents of PDiBI. This mechanism is also likely to accur in the thermal degradation of PiBMA. Furher results would be necessary to confirm this assumption. Thermal degradation of PsBMA The isothermal mass loss of PsBMA as a function of degradation time at various thermolysis temperatures is shown in Fig. 6. Significant mass loss can be noticed at 220 ºC. Fig. 6. The dependence of PsBMA mass loss on time at various degradation temperatures.
7 THERMAL DEGRADATION 873 Compared to PiBMA, PsBMA seems to be more thermally stable (the mass loss of PiBMA after 30 min at 200 ºC is 55.2 % and for PsBMA 7.4 %). As PsBMA has five β-hydrogens in the ester substituent, it may be assumed that de-esterification significantly competes with depolymerisation as the main thermal degradation mechanism. Attempts to determine the LVN of degraded PsBMAwere not successful as η sp /c increased with decreasing polymer concentration. Such behaviour indicates that the structure of the polymer residue changes during thermal degradation implying that depropagation is not the only degradation mechanism and that the residue has ionometric properties in dilute solution. The ionomeric properties can only result from the existence of free acid or anhydride groups in the polymer residue. Fig. 7. The dependence of the number of COOH groups evolved per monomer unit of PsBMA as a function of time at various thermolysis temperatures. Fig. 8. The depencence of the number of COOH groups evolved per monomer unit of PsBMA as a function of temperature, degradation time 30 min.
8 874 NOVAKOVI], KATSIKAS and POPOVI] The acid gropus formed in the PsBMAresidue were determined quantitatively by acid-base titrations of the residues. The determined amounts of acid groups, expressed as mol COOH per mol monomer unit, are shown as a function of time and temperature of degradation in Figs. 7 and 8, respectively. The number of evolved COOH groups increases exponentially with degradation temperature indicating that de-esterification is a relevant degradation route at temperatures higher than 240 ºC. These data agree well with the TVA data of McNeill on the evolution of 1- and 2-butene during thermolysis. 7 Similar behaviour was found for the thermal degradation of the structurally similar poly(di-sec-butyl itaconate). 10 CONCLUSIONS On the basis of our own findings and the TVA work of McNeill, 7 it may be concluded that the assumptions made by Grassie and coworkers 1 4 concerning the mechanism of thermal degradation of polymethacrylates were generally correct, although the importance of the lone tertiary hydrogen atom in the ester substituent structures still needs to be established. Poly(iso-butyl methacrylate) degrades quantitatively by depolymerisation with zip lengths of the same order of magnitude as those of PMMA. Poly(sec-butyl methacrylate) degrades by a combined degradation mechanism of depolymerisation and de-esterification. De-esterification becomes a significant thermolysis route at temperatures higher than 240 ºC. IZVOD TERMI^KA DEGRADACIJA POLI(iso-BUTIL METAKRILATA) I POLI(sec-BUTIL METAKRILATA) KATARINA NOVAKOVI], LYNNE KATSIKAS i IVANKA G. POPOVI] Tehnolo{ko-metalur{ki fakultet, Univerzitet u Beogradu, Karnegijeva 4, Beograd Neoksidativna termi~ka degradacija poli(iso-butil metakrilata) i poli(sec-butil metakrilata) ispitana je pra}ewem promena u polimernom ostatku. Zbog razli~itog broja β-vodonika u estarskom supstituentu, ova dva polimerna izomera se razli~ito pona{aju prilikom izlagawa povi{enim temperaturama. Poli(iso-butil metakrilat) degradira kvantitativno depolimerizacijom do svog monomera sa kineti~kim du`inama depropagacije istog reda veli~ine kao kod degradacije poli(metil metakrilata). Poli(sec-butil metakrilat) degradira kombinovanim mehanizmom degradacije: depolimerizacijom i deesterifikacijom. Deestirifikacija postaje zna~ajna reakcija termolize na temperaturama vi{im od 240 ºC. (Primqeno 17. jula 2000) REFERENCES 1. N. Grassie, H. W. Melville, Proc. Roy. Soc. Ser. A 199 (1949) N. Grassie, J. R. MacCallum, J. Polym. Sci. A2 (1964) N. Grassie, Pure Appl. Chem. 30 (1972) I. C. McNeill, Thermal Degradation in Comprehensive Polymer Science, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1989, Vol. 6, pp
9 THERMAL DEGRADATION D. H. Grant, N. Grassie, Polymer 1 (1960) M. Kurata, Y. Tsunashima, M. Iwama, K. Kamada, Viscosity - Molecular Weight Relationships and Unperturbed Dimensions of Linear Chain Molecules in Polymer Handbook, J. Brandrup, E. H. Immergut, Eds., Wiley, New York, 1975, p. IV I. C. McNeill, private communication 8. N. Grassie, G. Scott, Polymer Degradation and Stabilisation, Cambridge University Press, Cambrigde, T. Kashiwagi, T. Hirata, J. E. Brown, Macromolecules 18 (1985) S. J. Velickovi}, L. Katsikas, I. G. Popovi}, Yugoslav Congress of Plastics and Rubber Engineers YU-POLIMERI 98, Jagodina, 1998, Conference Proceedings, pp
PHOTODEGRADATION OF METHACRYLATE/ACRYLATE COPOLYMERS. The various contributions to this symposium have demonstrated the
 PHOTODEGRADATION OF METHARYLATE/ARYLATE OPOLYMERS N. GRASSIE Department of hemistry, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G12 8QQ. Scotland ABSTRAT Although the effects of u.v. radiation on poly(methyl methacrylate)
PHOTODEGRADATION OF METHARYLATE/ARYLATE OPOLYMERS N. GRASSIE Department of hemistry, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G12 8QQ. Scotland ABSTRAT Although the effects of u.v. radiation on poly(methyl methacrylate)
Characterisation of Viscosity and Molecular Weight of Fractionated NR
 Characterisation of Viscosity and Molecular Weight of Fractionated NR ENG A.H. Science & Technology Innovation Centre, Ansell Shah Alam, Malaysia (e-mail: engah@ap.ansell.com) Abstract Viscosity of a rubber
Characterisation of Viscosity and Molecular Weight of Fractionated NR ENG A.H. Science & Technology Innovation Centre, Ansell Shah Alam, Malaysia (e-mail: engah@ap.ansell.com) Abstract Viscosity of a rubber
RECENT WORK ON THE THERMAL DEGRADATION HOMOPOLYMERS AND COPOLYMERS
 REENT WORK ON THE THERMAL DEGRADATION OF ARYLATE AND METHARYLATE HOMOPOLYMERS AND OPOLYMERS N. GRASSIE Department of hemistry, University of Glasgow, Glasgow W2, Scotland ABSTRAT The principal degradation
REENT WORK ON THE THERMAL DEGRADATION OF ARYLATE AND METHARYLATE HOMOPOLYMERS AND OPOLYMERS N. GRASSIE Department of hemistry, University of Glasgow, Glasgow W2, Scotland ABSTRAT The principal degradation
Structural Relaxation and Refractive Index of Low-Loss Poly(methyl methacrylate) Glass
 Polymer Journal, Vol. 34, No. 6, pp 466 470 (2002) NOTES Structural Relaxation and Refractive Index of Low-Loss Poly(methyl methacrylate) Glass Norihisa TANIO Faculty of Photonics Science and Technology,
Polymer Journal, Vol. 34, No. 6, pp 466 470 (2002) NOTES Structural Relaxation and Refractive Index of Low-Loss Poly(methyl methacrylate) Glass Norihisa TANIO Faculty of Photonics Science and Technology,
An alcohol is a compound obtained by substituting a hydoxyl group ( OH) for an H atom on a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon group.
 Derivatives of Hydrocarbons A functional group is a reactive portion of a molecule that undergoes predictable reactions. All other organic compounds can be considered as derivatives of hydrocarbons (i.e.,
Derivatives of Hydrocarbons A functional group is a reactive portion of a molecule that undergoes predictable reactions. All other organic compounds can be considered as derivatives of hydrocarbons (i.e.,
The temperature dependence of the disproportionation reaction of iodous acid in aqueous sulfuric acid solutions
 J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 67(5)347 351(2002) UDC 542.9:546.155+535.243:536.5 JSCS-2955 Original scientific paper The temperature dependence of the disproportionation reaction of iodous acid in aqueous sulfuric
J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 67(5)347 351(2002) UDC 542.9:546.155+535.243:536.5 JSCS-2955 Original scientific paper The temperature dependence of the disproportionation reaction of iodous acid in aqueous sulfuric
AS Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds. Collated Polymer questions
 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds Collated Polymer questions (2017) (a) Polyvinyl chloride (polychloroethene) is often used to make artificial leather.
AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds Collated Polymer questions (2017) (a) Polyvinyl chloride (polychloroethene) is often used to make artificial leather.
Electronegativity Scale F > O > Cl, N > Br > C, H
 Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
Esterification of Hydroxylated Polymers with 2-Sulfobenzoic Acid Cyclic Anhydride
 Esterification of Hydroxylated Polymers with 2-Sulfobenzoic Acid Cyclic Anhydride Peter D. Iddon, Duan C. Vo, and Steven P. Armes Department of Chemistry, University of Sheffield, UK Macro Group Meeting,
Esterification of Hydroxylated Polymers with 2-Sulfobenzoic Acid Cyclic Anhydride Peter D. Iddon, Duan C. Vo, and Steven P. Armes Department of Chemistry, University of Sheffield, UK Macro Group Meeting,
video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10
 video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10 Butane Methylpropane 1 match the isomers drawing an isomer
video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10 Butane Methylpropane 1 match the isomers drawing an isomer
Organic and Biochemical Molecules. 1. Compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons.
 Organic and Biochemical Molecules 1. Compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. 2. A compound is said to be saturated if it contains only singly bonded carbons. Such hydrocarbons
Organic and Biochemical Molecules 1. Compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. 2. A compound is said to be saturated if it contains only singly bonded carbons. Such hydrocarbons
AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM USING TEMPERATURE BASED SAMPLING FOR POLYMER CHARACTERIZATION
 AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM USING TEMPERATURE BASED SAMPLING FOR POLYMER CHARACTERIZATION Paper # 164-8P Pittsburgh Conference 24 T. Wampler, C. Zawodny, L. Mancini CDS Analytical, Inc 465 Limestone Road, Oxford,
AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM USING TEMPERATURE BASED SAMPLING FOR POLYMER CHARACTERIZATION Paper # 164-8P Pittsburgh Conference 24 T. Wampler, C. Zawodny, L. Mancini CDS Analytical, Inc 465 Limestone Road, Oxford,
Macromolecular Chemistry
 Macromolecular Chemistry N N N Cu + BR - N Lecture 7 Decomposition of Thermal Initiator k d I 2 R Efficiency factor ( f ): CN N N CN di-tert-butylperoxide AIBN di-tert-butylperoxalate f = 0.65 f = 0.75
Macromolecular Chemistry N N N Cu + BR - N Lecture 7 Decomposition of Thermal Initiator k d I 2 R Efficiency factor ( f ): CN N N CN di-tert-butylperoxide AIBN di-tert-butylperoxalate f = 0.65 f = 0.75
Chemistry 2.5 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence Working to Excellence
 Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics. Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi
 Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
Chemistry 131 Lectures 3: The Shapes of Organic Molecules, Naming Alkanes Sections in McMurry, Ballantie, et. al.
 Chemistry 131 Lectures 3: The Shapes of Organic Molecules, Naming Alkanes Sections 12.5 12.6 in McMurry, Ballantie, et. al. 7 th edition HW #1: 12.30, 12.32, 12.34, 12.44, 12.48, 12.52, 12.64, 12.66, 12.68,
Chemistry 131 Lectures 3: The Shapes of Organic Molecules, Naming Alkanes Sections 12.5 12.6 in McMurry, Ballantie, et. al. 7 th edition HW #1: 12.30, 12.32, 12.34, 12.44, 12.48, 12.52, 12.64, 12.66, 12.68,
The influence of some factors on the electrical conductivity and particle size of core/shell polystyrene/polyaniline composites
 J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 70 (11) 1263 1271 (2005) UDC 678.746:66.095.24+6. 78.652 JSCS 3366 Original scientific paper The influence of some factors on the electrical conductivity and particle size of core/shell
J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 70 (11) 1263 1271 (2005) UDC 678.746:66.095.24+6. 78.652 JSCS 3366 Original scientific paper The influence of some factors on the electrical conductivity and particle size of core/shell
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
2A - Amines. 2 H atoms replaced: 2 attached C's to N. 3 H atom replaced: 3 attached C's to N Ammonia, NH3 Primary amine Secondary amine Tertiary amine
 2A - Amines Something fishy about amines: Have an NH 2, amine group. Amines are derivatives of ammonia: 3 H atoms 1 H atom replaced: 1 attached C to N 2 H atoms replaced: 2 attached C's to N 3 H atom replaced:
2A - Amines Something fishy about amines: Have an NH 2, amine group. Amines are derivatives of ammonia: 3 H atoms 1 H atom replaced: 1 attached C to N 2 H atoms replaced: 2 attached C's to N 3 H atom replaced:
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E.
 MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - I-SET -B 008 Sulphuric acid, Ammonia, Analytical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry HCl, Nitric acid, Metallurgy Chemistry SCIENCE
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - I-SET -B 008 Sulphuric acid, Ammonia, Analytical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry HCl, Nitric acid, Metallurgy Chemistry SCIENCE
ORGANIC REACTIONS 14 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes
 ORGANIC REACTIONS 14 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes 1. Combustion Alkanes are very important fossil fuels. The combustion of alkanes is very exothermic and carbon dioxide and water are produced. General
ORGANIC REACTIONS 14 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes 1. Combustion Alkanes are very important fossil fuels. The combustion of alkanes is very exothermic and carbon dioxide and water are produced. General
CYCLOALKANES, POLYMERS, ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS Home Assignment
 CYCLOALKANES, POLYMERS, ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS Home Assignment 1. The tendency of cylopropane (I), Cyclobutane (II), cyclopentane (III) to form addition compounds is in the order : a) I > II > III b) I =
CYCLOALKANES, POLYMERS, ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS Home Assignment 1. The tendency of cylopropane (I), Cyclobutane (II), cyclopentane (III) to form addition compounds is in the order : a) I > II > III b) I =
Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 13: Amines Top concepts
 Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 13: Amines Top concepts 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification
Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 13: Amines Top concepts 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification
(07) 3 (e) Calculate the ph of this buffer solution at 298 K. Give your answer to 2 decimal places
 7 3 (e) An acidic buffer solution is formed when 10.0 cm3 of 0.125 mol dm 3 aqueous sodium hydroxide are added to 15.0 cm3 of 0.174 mol dm 3 aqueous HX. The value of Ka for the weak acid HX is 3.01 10
7 3 (e) An acidic buffer solution is formed when 10.0 cm3 of 0.125 mol dm 3 aqueous sodium hydroxide are added to 15.0 cm3 of 0.174 mol dm 3 aqueous HX. The value of Ka for the weak acid HX is 3.01 10
Basic Organic Chemistry Nomenclature CHEM 104 B
 Basic Organic Chemistry Nomenclature CHEM 104 B I have gone ahead and compiled all of the basic naming rules that we will be dealing with into one worksheet. I hope this will be helpful to you as you work
Basic Organic Chemistry Nomenclature CHEM 104 B I have gone ahead and compiled all of the basic naming rules that we will be dealing with into one worksheet. I hope this will be helpful to you as you work
Atoms, Elements, Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures. Compounds and Mixtures. Atoms and the Periodic Table. Atoms and the.
 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Introduction Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of radicals (also called free radicals) Radicals are highly reactive, short-lived species Single-barbed arrows are
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Introduction Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of radicals (also called free radicals) Radicals are highly reactive, short-lived species Single-barbed arrows are
SAMPLE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS MIXTURE OF UNIT 3 & 4 MATERIALS
 SAMPLE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS MIXTURE OF UNIT 3 & 4 MATERIALS QUESTION 1 The equation describing the production of butyl ethanoate is given below. Catalyst C4H 9OH CH 3COOH CH 3COOC 4H 9 H 2O( l ) 0.0500
SAMPLE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS MIXTURE OF UNIT 3 & 4 MATERIALS QUESTION 1 The equation describing the production of butyl ethanoate is given below. Catalyst C4H 9OH CH 3COOH CH 3COOC 4H 9 H 2O( l ) 0.0500
CHM1 Review for Exam 15
 Topics 1. Organic Compounds a. Hydrocarbons i. Saturated alkanes (all single bonds) ii. Unsaturated alkenes and alkynes b. Functional Groups i. Alcohols ii. Organic Acids iii. Esters iv. Ethers v. Aldehydes
Topics 1. Organic Compounds a. Hydrocarbons i. Saturated alkanes (all single bonds) ii. Unsaturated alkenes and alkynes b. Functional Groups i. Alcohols ii. Organic Acids iii. Esters iv. Ethers v. Aldehydes
# C Name Structural Diagram The simplest hydrocarbon has one carbon atom.
 Organic Chem Class notes name: 1. is the first atom of organic chemistry. 2. Carbon can make bonds to other carbon atoms. 3. There are metals in organic chem 4. Count out loud to ten in organic prefixes
Organic Chem Class notes name: 1. is the first atom of organic chemistry. 2. Carbon can make bonds to other carbon atoms. 3. There are metals in organic chem 4. Count out loud to ten in organic prefixes
Suggest TWO aspects to show approach II is considered to be a greener method than using approach I.
 1. (a) Answer the following short questions Nowadays, products manufactured from industrial process emphasize on a green approach. An organic compound is manufactured by two different approaches as shown
1. (a) Answer the following short questions Nowadays, products manufactured from industrial process emphasize on a green approach. An organic compound is manufactured by two different approaches as shown
Page 2. Q1.Which one of the following is not a correct general formula for the non-cyclic compounds listed? alcohols C nh 2n+2O. aldehydes C nh 2n+1O
 Q1.Which one of the following is not a correct general formula for the non-cyclic compounds listed? A B alcohols C nh 2n+2O aldehydes C nh 2n+1O C esters C nh 2nO 2 C primary amines C nh 2n+3N (Total 1
Q1.Which one of the following is not a correct general formula for the non-cyclic compounds listed? A B alcohols C nh 2n+2O aldehydes C nh 2n+1O C esters C nh 2nO 2 C primary amines C nh 2n+3N (Total 1
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Efficient Temperature Sensing Platform Based on Fluorescent Block Copolymer Functionalized Graphene Oxide Hyunseung Yang, Kwanyeol Paek, and Bumjoon J. Kim * : These authors contributed
Supporting Information Efficient Temperature Sensing Platform Based on Fluorescent Block Copolymer Functionalized Graphene Oxide Hyunseung Yang, Kwanyeol Paek, and Bumjoon J. Kim * : These authors contributed
Chem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp
 hem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp Exams are designed so that no one question will make or break you. The best strategy is to work steadily, starting with those problems you understand best. Partial credit
hem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp Exams are designed so that no one question will make or break you. The best strategy is to work steadily, starting with those problems you understand best. Partial credit
Physical Sciences P2 1 September 2014 Preparatory Examination NSC. Basic Education
 Physical Sciences P2 1 September 2014 Preparatory Examination Basic Education KwaZulu-Natal Department of Basic Education REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY (P2) PREPARATORY EXAMINATION
Physical Sciences P2 1 September 2014 Preparatory Examination Basic Education KwaZulu-Natal Department of Basic Education REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY (P2) PREPARATORY EXAMINATION
Microwave dielectric relaxation study of poly (methyl methacrylate) and polysulphone in dilute solutions
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 44, July 006, pp. 548-553 Microwave dielectric relaxation study of poly (methyl methacrylate) and polysulphone in dilute solutions A Tanwar, K K Gupta, P J
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 44, July 006, pp. 548-553 Microwave dielectric relaxation study of poly (methyl methacrylate) and polysulphone in dilute solutions A Tanwar, K K Gupta, P J
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
 SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Q1. An organic liquid (A), containing C, H and O with boiling point: 78 o C, and possessing a rather pleasant odour, on heating with concentrated sulphuric
SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Q1. An organic liquid (A), containing C, H and O with boiling point: 78 o C, and possessing a rather pleasant odour, on heating with concentrated sulphuric
Colombo, Sri Lanka) 3 (Department of Chemistry / University of Sri Jayewardenepura, Sri Lanka) (1)
 International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 2, Issue 4(April 2013), PP.11-16 Mechanical Properties And Kinetics Of Weight Loss Of
International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 2, Issue 4(April 2013), PP.11-16 Mechanical Properties And Kinetics Of Weight Loss Of
Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes
 Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons generally fall into 2 general groupings, aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatic hydrocarbons contain chains and rings of hydrocarbons,
Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons generally fall into 2 general groupings, aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatic hydrocarbons contain chains and rings of hydrocarbons,
17 Alcohols H H C C. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 H H. Bond angles in Alcohols. Boiling points. Different types of alcohols H 2 C CH 2 CH 2
 17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
Lab Activity 9: Introduction to Organic Chemical Reactivity, Lab 5 Prelab, Reflux
 Lab Activity 9: Introduction to Organic Chemical Reactivity, Lab 5 Prelab, Reflux Objectives 1. Identify structural features (pi bonds, bond polarity, lone pairs) of a compound 2. Determine whether a structural
Lab Activity 9: Introduction to Organic Chemical Reactivity, Lab 5 Prelab, Reflux Objectives 1. Identify structural features (pi bonds, bond polarity, lone pairs) of a compound 2. Determine whether a structural
AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 3) Multiple Choice and FIB (40%)
 AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 3) Class Set Multiple Choice and FIB (40%) 1) A chemistry student is filtering and drying a precipitate that formed from two solutions reacting. Which one is most likely about
AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 3) Class Set Multiple Choice and FIB (40%) 1) A chemistry student is filtering and drying a precipitate that formed from two solutions reacting. Which one is most likely about
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL
 Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Synthesis and Characterization of Alkyl Methacrylate-based Microgels by Experimental Design Method
 Synthesis of Alkyl Methacrylate-based Microgels Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, Vol. 28, No. 9 1493 Synthesis and Characterization of Alkyl Methacrylate-based Microgels by Experimental Design Method Young
Synthesis of Alkyl Methacrylate-based Microgels Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, Vol. 28, No. 9 1493 Synthesis and Characterization of Alkyl Methacrylate-based Microgels by Experimental Design Method Young
TOPIC 13 ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
 Title Heterogeneous Mixture of Metals and Initiator for Vinl Polymerization Author(s) Furukawa, Junji; Fueno, Takayuki Citation Bulletin of the Institute for Chemi University (1959), 37(4): 260-266 Issue
Title Heterogeneous Mixture of Metals and Initiator for Vinl Polymerization Author(s) Furukawa, Junji; Fueno, Takayuki Citation Bulletin of the Institute for Chemi University (1959), 37(4): 260-266 Issue
9. Which compound is an alcohol? A) methanol C) butane B) ethyne D) propanal
 1. Given the structural formulas for two organic compounds: The differences in their physical and chemical properties are primarily due to their different A) number of hydrogen atoms B) number of carbon
1. Given the structural formulas for two organic compounds: The differences in their physical and chemical properties are primarily due to their different A) number of hydrogen atoms B) number of carbon
Supplementary Information. Rational Design of Soluble and Clickable Polymers Prepared by. Conventional Free Radical Polymerization of
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Rational Design of Soluble and Clickable Polymers Prepared by
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Rational Design of Soluble and Clickable Polymers Prepared by
Branching in Radical Polymerization of Acrylamide
 Iranian Polymer Journal/ Volume 7 Number 1 (1998) ISSN: 1026-,265178 Branching in Radical Polymerization of Acrylamide M. Hossein Rafi'ee Fanood Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, University
Iranian Polymer Journal/ Volume 7 Number 1 (1998) ISSN: 1026-,265178 Branching in Radical Polymerization of Acrylamide M. Hossein Rafi'ee Fanood Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, University
Thermal Degradation of Poly(Dimethyl Itaeonate)
 ROATA HEMA ATA AAA 60 (1) 173-183 (1987) A-1715 YU SSN 0011-1643 UD 547+541.64 Original Scientific Paper Thermal Degradation of Poly(Dimethyl taeonate) Jovan Veličković and vanka Popović Department of
ROATA HEMA ATA AAA 60 (1) 173-183 (1987) A-1715 YU SSN 0011-1643 UD 547+541.64 Original Scientific Paper Thermal Degradation of Poly(Dimethyl taeonate) Jovan Veličković and vanka Popović Department of
Prerna Tower, Road No - 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur-01, Phone : ,
 hemistry Paper- I Jee Advance 2014 PART II - EMISTRY SETI - I (ne or More ptions orrect Type) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A) (B) () and (D) out of
hemistry Paper- I Jee Advance 2014 PART II - EMISTRY SETI - I (ne or More ptions orrect Type) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A) (B) () and (D) out of
J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 69 (11) (2004) UDC :54 325:
 J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 69 (11) 949 953 (2004) UDC 531.3+541.124:54 325:547.564.8 JSCS 3222 Short communication SHORT COMMUNICATION Kinetics of the reaction of 5-substituted orotic acids with diazodiphenylmethane
J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 69 (11) 949 953 (2004) UDC 531.3+541.124:54 325:547.564.8 JSCS 3222 Short communication SHORT COMMUNICATION Kinetics of the reaction of 5-substituted orotic acids with diazodiphenylmethane
The particle size and shape of polyaniline in aqueous solutions of poly-(n-vinylpyrrolidone)
 Plasticheskie Massy, No. 1, 2013, pp. 10 14 The particle size and shape of polyaniline in aqueous solutions of poly-(n-vinylpyrrolidone) S.V. Osadchenko, Ya.O. Mezhuev, Yu.V. Korshak, and M.I. Shtil man
Plasticheskie Massy, No. 1, 2013, pp. 10 14 The particle size and shape of polyaniline in aqueous solutions of poly-(n-vinylpyrrolidone) S.V. Osadchenko, Ya.O. Mezhuev, Yu.V. Korshak, and M.I. Shtil man
Quantitative Chemistry. AQA Chemistry topic 3
 Quantitative Chemistry AQA Chemistry topic 3 3.1 Conservation of Mass and Balanced Equations Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is when atoms are basically rearranged into something different. For
Quantitative Chemistry AQA Chemistry topic 3 3.1 Conservation of Mass and Balanced Equations Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is when atoms are basically rearranged into something different. For
Name: Regents Chemistry Review Packet B1
 Name: Regents Chemistry Review Packet B1 1. Compared to an electron, which particle has a charge that is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign? an alpha particle a beta particle a neutron a proton 2.
Name: Regents Chemistry Review Packet B1 1. Compared to an electron, which particle has a charge that is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign? an alpha particle a beta particle a neutron a proton 2.
5.12. A. Properties. Hydrocarbon - molecule with only C-C and C-H bonds. C n H 2n+2. saturated hydrocarbon - maximum number of C-H bonds. H 2, cat.
 5.12 V. Alkanes A. Properties Pset #1 Due Tomorrow at 4:00! B. eactivity ecitations finalized by Friday C. Uses D. Structure and Isomerism Build a model of cyclohexane and E. Nomenclature bring it to class
5.12 V. Alkanes A. Properties Pset #1 Due Tomorrow at 4:00! B. eactivity ecitations finalized by Friday C. Uses D. Structure and Isomerism Build a model of cyclohexane and E. Nomenclature bring it to class
CHMA2000 EXPT 7: The Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols
 CHMA2000 EXPT 7: The Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols Objectives: At the end of this experiment you should be able to: 1. Understand the physical and chemical properties of alcohols 2. Understand
CHMA2000 EXPT 7: The Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols Objectives: At the end of this experiment you should be able to: 1. Understand the physical and chemical properties of alcohols 2. Understand
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Part. Description on materials used in the present work Table S Details of the materials used in the experiments Chemicals Abbreviation in the text Grade of materials Manufacturer
Supporting Information Part. Description on materials used in the present work Table S Details of the materials used in the experiments Chemicals Abbreviation in the text Grade of materials Manufacturer
Emulsifier and Initiator Effects on the Emulsion Copolymerization of Styrene with Butyl Acrylate
 Emulsifier and Initiator Effects on the Emulsion Copolymerization of Styrene with Butyl Acrylate V. CHRÁSTOVÁ, S. ĎURAČKOVÁ, J. MRENICA, and Ľ. ČERNÁKOVÁ Department of Plastics and Rubber, Faculty of Chemical
Emulsifier and Initiator Effects on the Emulsion Copolymerization of Styrene with Butyl Acrylate V. CHRÁSTOVÁ, S. ĎURAČKOVÁ, J. MRENICA, and Ľ. ČERNÁKOVÁ Department of Plastics and Rubber, Faculty of Chemical
Investigation into the mechanism of photo-mediated RAFT polymerization involving the reversible photolysis of the chain-transfer agent
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Investigation into the mechanism of photo-mediated RAFT polymerization involving the reversible
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Investigation into the mechanism of photo-mediated RAFT polymerization involving the reversible
AS Paper 1 and 2 Kc and Equilibria
 AS Paper 1 and 2 Kc and Equilibria Q1.When one mole of ammonia is heated to a given temperature, 50 per cent of the compound dissociates and the following equilibrium is established. NH 3(g) ½ N 2 (g)
AS Paper 1 and 2 Kc and Equilibria Q1.When one mole of ammonia is heated to a given temperature, 50 per cent of the compound dissociates and the following equilibrium is established. NH 3(g) ½ N 2 (g)
5.1 Module 1: Rates, Equilibrium and ph
 5.1 Module 1: Rates, Equilibrium and ph 5.1.1 How Fast? The rate of reaction is defined as the change in concentration of a substance in unit time Its usual unit is mol dm 3 s 1 When a graph of concentration
5.1 Module 1: Rates, Equilibrium and ph 5.1.1 How Fast? The rate of reaction is defined as the change in concentration of a substance in unit time Its usual unit is mol dm 3 s 1 When a graph of concentration
A Level Chemistry. Ribston Hall High School. Pre Course Holiday Task. Name: School: ii) Maths:
 A Level Chemistry Ribston Hall High School Pre Course Holiday Task Name: School: GCSE Grades in i) Chemistry or Science: ii) Maths: 1 The following are a series of questions on topics you have covered
A Level Chemistry Ribston Hall High School Pre Course Holiday Task Name: School: GCSE Grades in i) Chemistry or Science: ii) Maths: 1 The following are a series of questions on topics you have covered
5.1.3 Acids, Bases and Buffers
 5..3 Acids, Bases and Buffers BronstedLowry Definition of Acid Base behaviour A BronstedLowry acid is defined as a substance that can donate a proton. A BronstedLowry base is defined as a substance that
5..3 Acids, Bases and Buffers BronstedLowry Definition of Acid Base behaviour A BronstedLowry acid is defined as a substance that can donate a proton. A BronstedLowry base is defined as a substance that
Chem 124 Exam 1 Spring 2016 Version 1 Name
 Chem 124 Exam 1 Spring 2016 Version 1 Name TOTAL POINTS - 116 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.4 POINTS EACH 1) A molecule containing a central atom with sp 3 hybridization has a(n) electron geometry. A) linear B) tetrahedral
Chem 124 Exam 1 Spring 2016 Version 1 Name TOTAL POINTS - 116 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1.4 POINTS EACH 1) A molecule containing a central atom with sp 3 hybridization has a(n) electron geometry. A) linear B) tetrahedral
IUPAC Nomenclature Chem12A, Organic Chemistry I
 IUPAC Nomenclature ChemA, rganic Chemistry I IUPAC PEFIXES Prefix Substituent Group Number of Carbons meth- methyl eth- ethyl prop- propyl but- butyl pent- pentyl hex- hexyl hept- heptyl 7 oct- octyl 8
IUPAC Nomenclature ChemA, rganic Chemistry I IUPAC PEFIXES Prefix Substituent Group Number of Carbons meth- methyl eth- ethyl prop- propyl but- butyl pent- pentyl hex- hexyl hept- heptyl 7 oct- octyl 8
Chemistry 12 Exam 1 September 27, 2000 Form A
 hemistry 12 Exam 1 September 27, 2000 Form A 1. The chemical formula for sodium phosphate is: A. S 3P 4 B. NaP 3. Na 3P 4 D. S 2P 3 E. Na 2P 4 2. ow many protons, neutrons and electrons does 201 g 2+ have?
hemistry 12 Exam 1 September 27, 2000 Form A 1. The chemical formula for sodium phosphate is: A. S 3P 4 B. NaP 3. Na 3P 4 D. S 2P 3 E. Na 2P 4 2. ow many protons, neutrons and electrons does 201 g 2+ have?
Name/CG: 2012 Term 2 Organic Chemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question
 Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
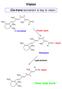 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
# Ans Workings / Remarks
 # Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
# Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
Supporting Information. Surface Functionalized Polystyrene Latexes using Itaconate based Surfmers
 Supporting Information Surface Functionalized Polystyrene Latexes using Itaconate based Surfmers Saheli Chakraborty and S Ramakrishnan* Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Indian Institute of
Supporting Information Surface Functionalized Polystyrene Latexes using Itaconate based Surfmers Saheli Chakraborty and S Ramakrishnan* Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Indian Institute of
Problems Points Credit
 Chem 201 Midterm Winter, 2018 Beauchamp ame Problems Points Credit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 30 2. Resonance, Formal Charge, Arrows 18 3. Properties of Atoms, Logic Arguments
Chem 201 Midterm Winter, 2018 Beauchamp ame Problems Points Credit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 30 2. Resonance, Formal Charge, Arrows 18 3. Properties of Atoms, Logic Arguments
Synthesis of hydrophilic monomer, 1,4-dibromo-2,5-di[4-(2,2- dimethylpropoxysulfonyl)phenyl]butoxybenzene (Scheme 1).
![Synthesis of hydrophilic monomer, 1,4-dibromo-2,5-di[4-(2,2- dimethylpropoxysulfonyl)phenyl]butoxybenzene (Scheme 1). Synthesis of hydrophilic monomer, 1,4-dibromo-2,5-di[4-(2,2- dimethylpropoxysulfonyl)phenyl]butoxybenzene (Scheme 1).](/thumbs/95/126008833.jpg) Supporting Information Materials. Hydroquinone, potassium carbonate, pyridine, tetrahydrofuran (THF for organic synthesis) were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd and used as received. Chlorosulfuric
Supporting Information Materials. Hydroquinone, potassium carbonate, pyridine, tetrahydrofuran (THF for organic synthesis) were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd and used as received. Chlorosulfuric
Organic Chemistry. A brief introduction
 Organic Chemistry A brief introduction Organic Chemistry the study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties excluding: CO, CO 2, CS 2, carbonates and cyanides eight million known organic compounds
Organic Chemistry A brief introduction Organic Chemistry the study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties excluding: CO, CO 2, CS 2, carbonates and cyanides eight million known organic compounds
MODIFICATION WITH A SULFONATE MONOMER
 Thesis - MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONAL MODIFICATIONS OF POLY(VINYL ALCOHOL) CHAPTER 8 BY TOHEI MORITANI MODIFICATION WITH A SULFONATE MONOMER A functional monomer containing sodium sulfonate group,
Thesis - MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONAL MODIFICATIONS OF POLY(VINYL ALCOHOL) CHAPTER 8 BY TOHEI MORITANI MODIFICATION WITH A SULFONATE MONOMER A functional monomer containing sodium sulfonate group,
Chapter 13. Alcohols, Diols, and Ethers
 hem 215 F07 otes Dr. Masato Koreeda - Page 1 of 5. Date: September 12, 2007 hapter 13. lcohols, Diols, and Ethers verview: hemistry and reactions of sp 3 oxygen groups, particularly oxidation of an alcohol,
hem 215 F07 otes Dr. Masato Koreeda - Page 1 of 5. Date: September 12, 2007 hapter 13. lcohols, Diols, and Ethers verview: hemistry and reactions of sp 3 oxygen groups, particularly oxidation of an alcohol,
Unit - 2 SOLUTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. Give an example of liquid in solid type solution.
 Unit - 2 SOLUTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. Give an example of liquid in solid type solution. 2. Which type of solid solution will result by mixing two solid components with large difference
Unit - 2 SOLUTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. Give an example of liquid in solid type solution. 2. Which type of solid solution will result by mixing two solid components with large difference
Reaction Kinetics for the Synthesis of Oligomeric Poly(lactic acid)
 Macromolecular Research, Vol. 13, No. 1, pp 68-72 (2005) Reaction Kinetics for the Synthesis of Oligomeric Poly(lactic acid) Dong Keun Yoo and Dukjoon Kim* Department of Chemical Engineering, Polymer Technology
Macromolecular Research, Vol. 13, No. 1, pp 68-72 (2005) Reaction Kinetics for the Synthesis of Oligomeric Poly(lactic acid) Dong Keun Yoo and Dukjoon Kim* Department of Chemical Engineering, Polymer Technology
CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer Instructor: Paul J. Bracher. Quiz # 3. Monday, July 21 st, :30 a.m.
 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Quiz # 3 Solutions Key Page 1 of 9 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 3 Monday, July 21 st,
CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Quiz # 3 Solutions Key Page 1 of 9 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 3 Monday, July 21 st,
1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? A) ketone B) aldehyde C) amine D) ester E) carboxylic acid
 1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? ketone aldehyde amine ester carboxylic acid 2) Which functional group contains a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group bonded to the same carbon
1) Which type of compound does not contain a carbonyl group? ketone aldehyde amine ester carboxylic acid 2) Which functional group contains a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group bonded to the same carbon
DO NOT OPEN THE EXAMINATION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD BY THE SUPERVISOR TO BEGIN CHEMISTRY 2202 FINAL EXAMINATION. Value: 100% Time: 2 hours
 Name: Teacher: DO NOT OPEN THE EXAMINATION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD BY THE SUPERVISOR TO BEGIN CHEMISTRY 2202 FINAL EXAMINATION Value: 100% Time: 2 hours General Instructions This examination consists
Name: Teacher: DO NOT OPEN THE EXAMINATION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD BY THE SUPERVISOR TO BEGIN CHEMISTRY 2202 FINAL EXAMINATION Value: 100% Time: 2 hours General Instructions This examination consists
Paper Reference. (including synoptic assessment) Monday 23 January 2006 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6245/01 Edexcel GCE Chemistry Paper Reference 6 2 4 5 0 1 Advanced Unit Test 5 (including synoptic assessment) Monday 23 January 2006 Morning Time: 1 hour 30
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6245/01 Edexcel GCE Chemistry Paper Reference 6 2 4 5 0 1 Advanced Unit Test 5 (including synoptic assessment) Monday 23 January 2006 Morning Time: 1 hour 30
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2009
 1. Materials: Styrene (St), methyl methacrylate (MMA) and acrylic acid (AA) (Lingfeng Chemical reagent Co. Ltd, Shanghai, China) were distilled and stored at 4 ºC if not used immediately, ammonium persulfate
1. Materials: Styrene (St), methyl methacrylate (MMA) and acrylic acid (AA) (Lingfeng Chemical reagent Co. Ltd, Shanghai, China) were distilled and stored at 4 ºC if not used immediately, ammonium persulfate
Note: Brief explanation should be no more than 2 sentences.
 Her \Hmher UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING FINAL EXAMINATION, April 26, 2017 DURATION: 2 and /2 hrs MSE245 - HiS - Second Year - MSE Organic Material Chemistry & Processing
Her \Hmher UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING FINAL EXAMINATION, April 26, 2017 DURATION: 2 and /2 hrs MSE245 - HiS - Second Year - MSE Organic Material Chemistry & Processing
 Top concepts Chapter: Amines 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification of amines: 3. Preparation
Top concepts Chapter: Amines 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification of amines: 3. Preparation
Supporting Information for Polybenzimidazolium Salts: A New Class of. Anion-Conducting Polymer
 Supporting Information for Polybenzimidazolium Salts: A ew Class of Anion-Conducting Polymer Owen D. Thomas, Kristen J. W. Y. Soo, Timothy J. Peckham, Mahesh P. Kulkarni and Steven Holdcroft* Department
Supporting Information for Polybenzimidazolium Salts: A ew Class of Anion-Conducting Polymer Owen D. Thomas, Kristen J. W. Y. Soo, Timothy J. Peckham, Mahesh P. Kulkarni and Steven Holdcroft* Department
Styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer grafted with phosphonic acid dialkylesters
 J. Serb. Che. Soc. 69 (12) 43 51 (2004) UDC 547.538+678 13+547.315.2:543.216.185 JSCS-3232 Original scientific paper Styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer grafted with phosphonic acid dialkylesters GHEORGHE
J. Serb. Che. Soc. 69 (12) 43 51 (2004) UDC 547.538+678 13+547.315.2:543.216.185 JSCS-3232 Original scientific paper Styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer grafted with phosphonic acid dialkylesters GHEORGHE
Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCE Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Tuesday 15 May 2012 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCE Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Tuesday 15 May 2012 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com. Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Friday 27 May
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Friday 27 May
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
Xiangxiong Chen, Mohd Yusuf Khan and Seok Kyun Noh* School of Chemical Engineering, Yeungnam University, Dae-dong, Gyeongsan,
 Electronic Supplementary Information For M Amount of Fe (III)-mediated ATR of MMA with hosphorus Containing Ligands in the Absence of Any Additives Xiangxiong Chen, Mohd Yusuf Khan and Seok Kyun Noh* School
Electronic Supplementary Information For M Amount of Fe (III)-mediated ATR of MMA with hosphorus Containing Ligands in the Absence of Any Additives Xiangxiong Chen, Mohd Yusuf Khan and Seok Kyun Noh* School
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certifi cate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certifi cate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level *1536187828* CHEMISTRY 9701/23 Paper 2 Structured Questions AS Core May/June
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certifi cate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level *1536187828* CHEMISTRY 9701/23 Paper 2 Structured Questions AS Core May/June
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Supramolecular design for polymer/titanium oxo-cluster hybrids: An open door to new organic-inorganic dynamers Fabien Périneau, Sandrine Pensec, Clément Sanchez, Costantino Creton,
Supporting Information Supramolecular design for polymer/titanium oxo-cluster hybrids: An open door to new organic-inorganic dynamers Fabien Périneau, Sandrine Pensec, Clément Sanchez, Costantino Creton,
CHEMISTRY (SALTERS) Chemistry of Materials. OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced GCE
 XFRD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATINS Advanced GCE CHEMISTRY (SALTERS) Chemistry of Materials 2849 Monday 19 JUNE 2006 Afternoon 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates answer on the question paper. Additional materials:
XFRD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATINS Advanced GCE CHEMISTRY (SALTERS) Chemistry of Materials 2849 Monday 19 JUNE 2006 Afternoon 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates answer on the question paper. Additional materials:
Page 2. The tripeptide shown is formed from the amino acids alanine, threonine and lysine.
 Q1.(a) The tripeptide shown is formed from the amino acids alanine, threonine and lysine. Draw a separate circle around each of the asymmetric carbon atoms in the tripeptide. Draw the zwitterion of alanine.
Q1.(a) The tripeptide shown is formed from the amino acids alanine, threonine and lysine. Draw a separate circle around each of the asymmetric carbon atoms in the tripeptide. Draw the zwitterion of alanine.
Excess molar volume of acetonitrile + alcohol systems at K. Part II: Correlation by cubic equation of state
 J.Serb.Chem.Soc. 68(1)47 56(2003) UDC 547.261/.262+547.239:541.24/.25 JSCS 3019 Original scientific paper Excess molar volume of acetonitrile + alcohol systems at 298.15 K. Part II: Correlation by cubic
J.Serb.Chem.Soc. 68(1)47 56(2003) UDC 547.261/.262+547.239:541.24/.25 JSCS 3019 Original scientific paper Excess molar volume of acetonitrile + alcohol systems at 298.15 K. Part II: Correlation by cubic
THE CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN AFRICA A. M. E. C. E. A
 THE CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN AFRICA A. M. E. C. E. A MAIN EXAMINATION P.O. Box 62157 00200 Nairobi - KENYA Telephone: 891601-6 Fax: 254-20-891084 E-mail:academics@cuea.edu JANUARY APRIL 2014 TRIMESTER
THE CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN AFRICA A. M. E. C. E. A MAIN EXAMINATION P.O. Box 62157 00200 Nairobi - KENYA Telephone: 891601-6 Fax: 254-20-891084 E-mail:academics@cuea.edu JANUARY APRIL 2014 TRIMESTER
CHAPTER IV HOFMANN REARRANGEMENT IN CROSSLINKED POLYMERIC MATRICES
 CHAPTER IV HOFMANN REARRANGEMENT IN CROSSLINKED POLYMERIC MATRICES The Hofmann degradation reaction has been used as a synthetic route for the preparation of amines 180-187 Tanaka and Senju reported the
CHAPTER IV HOFMANN REARRANGEMENT IN CROSSLINKED POLYMERIC MATRICES The Hofmann degradation reaction has been used as a synthetic route for the preparation of amines 180-187 Tanaka and Senju reported the
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information UCST or LCST? Composition-Dependent Thermoresponsive Behavior of Poly(N-Acryloylglycinamide-co-Diacetone Acrylamide) Wenhui Sun, Zesheng An*, Peiyi Wu * Experimental Materials Glycinamide
Supporting Information UCST or LCST? Composition-Dependent Thermoresponsive Behavior of Poly(N-Acryloylglycinamide-co-Diacetone Acrylamide) Wenhui Sun, Zesheng An*, Peiyi Wu * Experimental Materials Glycinamide
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
