CH301 Vanden Bout/LaBrake Fall LM18 Posted DUE TH 9AM Study Ionic and Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature on Fundamentals Nomenclature Quiz Th
|
|
|
- Colin Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 1 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Monday, September 30, :30 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 ELECTRON CONFIGURATION and BONDING Where did all that salt come from? UNIT 2 Day 4 Important Information LM18 Posted DUE TH 9AM Study Ionic and Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature on Fundamentals Nomenclature Quiz Th Laude LM Lecture 7 CH301 Vanden Bout/LaBrake Spring 2013
2 What are we going to learn today? Electron Configuration and Bonding Relate the valence shell electron configuration to bonding Understand the similarities and differences between ionic and covalent bonding Recognize and name compounds based on elemental composition QUIZ: CLICKER QUESTION 1 The trend on the periodic table is that atomic radii: a) Increases as you move from L to R across b) Decreases as you move from R to L across c) Increases as you move from T to B down d) Increases as you move from B to T up e) Both b and c QUIZ: CLICKER QUESTION 2 Which of the following symbols does not match the elemental name? A.Fe - Iron B.As Arsenic C.Co Copper D.Sn Tin Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 2
3 match the elemental name? Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 3 A.Fe - Iron B.As Arsenic C.Co Copper D.Sn Tin E.V - Vanadium QUIZ: CLICKER QUESTION 3 At the end of the last class period we saw a demo. Two metals were tossed into water and something happened. a)the metals sank to the bottom of the bucket b)the metals floated in the bucket c)the metals spun around the surface of the water and then burst into flames d)this is not true, just a trick question for the 75 people who were absent Thursday
4 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 4 Where are the electrons in Ne? 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 very stable gas Z=10 Where are the electrons in Na? [Ne]3s 1 not so stable metal Z=11 Where are the electrons in K? [Ar]4s 1 more, not so stable metal Z=19 Shielding and Effective Nuclear Charge Left to Right Z eff is increasing Top to Bottom Z eff is similar Top to Bottom. Electron in higher in Energy. Farther from the nucleus THIS CAN EXPLAIN A LOT ABOUT THE PERIODIC TABLE Trend: Atomic Radii
5 Atomic Radii Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 5 CH302 Vanden Bout/LaBrake Fall 2012 EXPLAIN SPIKE IN IONIZATION ENERGY! CH302 Vanden Bout/LaBrake Fall 2013
6 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 6 Based on this trend in ionization energies this element is A. argon B. carbon C. magnesium D. sulfur SHOW SOME ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS OF IONS
7 2Na(s) + Cl (g) Unit2Day4-VandenBout 2NaCl(s) Page 7 CH302 Vanden Bout/LaBrake Fall 2012 POLL: CLICKER QUESTION 4 Where did this guy get all of that salt (NaCl)? a)it formed from Na + and Cl - ions in the water b)he first pitch a few block of Na metal into a pool and then bubbled in Cl 2 gas. c)he add the Cl 2 gas to the water that already had Na + ions. d)he added Na metal to the water that already had Cl - ions. ELECTRON LEAVES.. WHERE DOES IT GO? Metals tend to give up electrons to nonmetals, in each case the valence is satisfied Sometimes is complicated eg in the sodium in water demo Sometimes is more obvious
8 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 8 Sometimes is complicated eg in the sodium in water demo Sometimes is more obvious 2Na(s) + Cl 2 (g) 2NaCl(s) Sometimes they are already gone! Formation of Ionic Compound Downhill in Energy Ionic Compound downhill in energy..
9 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 9 Ionic Compounds Not a discrete pair of ions it is a whole collection POLL: CLICKER QUESTION 5 Coulomb s Law Lattice energy depends on Coulomb s Law and the crystal structure (the way the ions are packed together). Assuming the same crystal structure, which do you think would have the larger lattice energy: a)naf b)nabr? Ionic Radius
10 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 10 Polyatomic Ions Calcium Carbonate Ca 2+ CO 3 2- Know the names and formulas for all the common polyatomic ions. See the Data & Tables under more on the ebook
11 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 11 POLL: CLICKER QUESTION 6 Naming Ionic Compounds Choose the formula that corresponds to: sodium oxide a)nao b)nao 2 c)na 2 O d)na 2 O 2 Naming Ionic Compounds You need to be able to name common ionic compounds and with elemental ions and polyatomic ions. WEBSITE FUNDAMENTALS DO THE WORKSHEETS What about compounds that aren t ionic.. Covalent? How are they formed? Are electrons lost???? No.. They are shared (two non-metals two elements with similar electronegativities)
12 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 12 No.. They are shared (two non-metals two elements with similar electronegativities) Covalent Compounds Characterize the bond. Bond Length Bond Strength Electron Pair Shared Equally? YES PURE COVALENT NO POLAR COVALENT SHOW THE SIMULATOR..
13 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 13 Electronegativity-electron pulling power of an atom when it is part of a molecule When one atom is more electronegative than another in a bond, a polar covalent bond is formed. Degree of polarity is dependent on difference in electronegativities.
14 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 14 Ionic vs Covalent Bonds All bonds can be viewed as hybrids between purely ionic and purely covalent When two identical atoms are bound, it is purely covalent. When two different atoms are bound, one may have a greater attraction for electrons, and have a partial negative charge. Polar covalent bond degree is measured as dipole moment When one atom has a much stronger attraction to the electrons than the other, an electron may be donated yielding an ionic bond. Covalent Compounds - Naming
15 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 15 Covalent Compounds What is attached to what? Valence electrons Lewis symbols Lewis Structure Satisfy the Octet H 2 CH 4 What have we learned? NUCLEAR CHARGE FELT BY VALENCE ELECTRONS IS SHIELDED BY THE CORE ELECTRONS ATOMS BEHAVE IN CERTAIN PREDICTABLE WAYS WHICH CAN BE CORRELATED TO THE ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS IONIC BONDS TEND TO FORM BETWEEN METALS AND NONMETALS COVALENT BONDS TEND TO FORM BETWEEN NONMETALS AND NONMETALS NAMING COMPOUNDS IS IMPORTANT AND NECESSARY
16 Unit2Day4-VandenBout Page 16 Learning Outcomes Identify metals and non-metals and predict types of compounds (ionic/covalent) Between different elements Relate coulombs law and lattice energy Name basic binary ionic compounds including polyatomic ions Name basic covalent compounds containing two elements Explain the trends in electro-negativity on the periodic table Differentiate between pure covalent and polar covalent bonds
Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301
 Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 ELECTRON CONFIGURATION and BONDING UNIT 2 Day 4 Important InformaIon EXAM WRAPPER POSTED- 20 BONUS POINTS LM18 Posted DUE TH 9AM (NGLM10- Ionic- Covalent Compounds & NGLM11- Nomenclature)
Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 ELECTRON CONFIGURATION and BONDING UNIT 2 Day 4 Important InformaIon EXAM WRAPPER POSTED- 20 BONUS POINTS LM18 Posted DUE TH 9AM (NGLM10- Ionic- Covalent Compounds & NGLM11- Nomenclature)
Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford. ELECTRONS and COMPOUNDS. Important Information. HW06 Posted Due Tue 9AM. LM19 Posted DUE Tue 9AM
 Unit2Day5-VandenBout Page 1 Unit2Day5-VandenBout Tuesday, October 01, 2013 2:58 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 ELECTRONS and COMPOUNDS UNIT 2 Day 5 Important Information HW06 Posted Due Tue 9AM
Unit2Day5-VandenBout Page 1 Unit2Day5-VandenBout Tuesday, October 01, 2013 2:58 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 ELECTRONS and COMPOUNDS UNIT 2 Day 5 Important Information HW06 Posted Due Tue 9AM
Important Information
 Unit2Day6-LaBrake Monday, October 07, 2013 3:35 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 ELECTRONS and BONDING WRAP UNIT 2 Day 6 Important Information EXAM WEDNESDAY 7PM 9PM CH301 Vanden Bout/LaBrake Spring
Unit2Day6-LaBrake Monday, October 07, 2013 3:35 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 ELECTRONS and BONDING WRAP UNIT 2 Day 6 Important Information EXAM WEDNESDAY 7PM 9PM CH301 Vanden Bout/LaBrake Spring
Vanden Bout/LaBrake. ELECTRONS and BONDING WRAP. Important Information. EXAM REVIEW TUES 4PM Jester A 121A
 UNIT2DAY6-LaB Page 1 UNIT2DAY6-LaB Monday, October 08, 2012 10:00 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 ELECTRONS and BONDING WRAP UNIT 2 Day 6 Important Information EXAM REVIEW TUES 4PM Jester A 121A EXAM WEDNESDAY
UNIT2DAY6-LaB Page 1 UNIT2DAY6-LaB Monday, October 08, 2012 10:00 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 ELECTRONS and BONDING WRAP UNIT 2 Day 6 Important Information EXAM REVIEW TUES 4PM Jester A 121A EXAM WEDNESDAY
WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? Important Information EXAMS SHOULD BE GRADED BY MIDDAY SATURDAY HW. DEPENDS ON HOW DAY GOES.
 Unit3Day1-Crawford Page 1 Unit3Day1-Crawford Tuesday, October 08, 2013 3:43 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? UNIT 3 Day 1 Important Information EXAMS SHOULD BE GRADED
Unit3Day1-Crawford Page 1 Unit3Day1-Crawford Tuesday, October 08, 2013 3:43 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? UNIT 3 Day 1 Important Information EXAMS SHOULD BE GRADED
Sparks CH301 EFFECTIVE NUCLEAR CHARGE AND PERIODIC TRENDS. Why is strontium so dangerous? UNIT 2 Day 5
 Sparks CH301 EFFECTIVE NUCLEAR CHARGE AND PERIODIC TRENDS Why is strontium so dangerous? UNIT 2 Day 5 How many electrons in Na have l=0? QUIZ QUESTION: INDIVIDUAL WORK, NO TALKING What are we going to
Sparks CH301 EFFECTIVE NUCLEAR CHARGE AND PERIODIC TRENDS Why is strontium so dangerous? UNIT 2 Day 5 How many electrons in Na have l=0? QUIZ QUESTION: INDIVIDUAL WORK, NO TALKING What are we going to
CH301 Fall 2012 Name: KEY VandenBout/LaBrake UNIT 2 READINESS ASSESSMENT QUIZ (RAQ) THIS QUIZ WILL BE PACED WITH CLICKER QUESTIONS
 CH301 Fall 2012 Name: KEY VandenBout/LaBrake UNIT 2 READINESS ASSESSMENT QUIZ (RAQ) THIS QUIZ WILL BE PACED WITH CLICKER QUESTIONS 1. A laser pulse shines for 10 s delivering a total energy of 4 mj of
CH301 Fall 2012 Name: KEY VandenBout/LaBrake UNIT 2 READINESS ASSESSMENT QUIZ (RAQ) THIS QUIZ WILL BE PACED WITH CLICKER QUESTIONS 1. A laser pulse shines for 10 s delivering a total energy of 4 mj of
Unit3Day4-LaBrake. Important Information. Is the molecule CH 2 Cl 2? Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301
 Unit3Day4-LaBrake Page 1 Unit3Day4-LaBrake Monday, October 21, 2013 11:32 AM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 WHY DOES A FROG FLOAT IN A MAGNETIC FIELS? MORE ON BONDING THEORIES UNIT 3 Day 4 Important
Unit3Day4-LaBrake Page 1 Unit3Day4-LaBrake Monday, October 21, 2013 11:32 AM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 WHY DOES A FROG FLOAT IN A MAGNETIC FIELS? MORE ON BONDING THEORIES UNIT 3 Day 4 Important
Electronic Structure and Bonding Review
 Name: Band: Date: Electronic Structure and Bonding Review 1. For electrons: a. What is the relative charge? b. What is the relative mass? c. What is the symbol? d. Where are they located in the modern
Name: Band: Date: Electronic Structure and Bonding Review 1. For electrons: a. What is the relative charge? b. What is the relative mass? c. What is the symbol? d. Where are they located in the modern
Quarter 1 Section 1.2
 Quarter 1 Section 1.2 Opening Activity: Use your periodic table 1. How many protons are in an atom of Carbon? 2. How many electrons are in an atom of Carbon? 3. How many neutrons are in an atom of Carbon?
Quarter 1 Section 1.2 Opening Activity: Use your periodic table 1. How many protons are in an atom of Carbon? 2. How many electrons are in an atom of Carbon? 3. How many neutrons are in an atom of Carbon?
What is Bonding? The Octet Rule. Getting an Octet. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Shapes. (Chapter Three, Part Two)
 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Shapes (Chapter Three, Part Two) What is Bonding? Bonding describes how atoms interact with each other in an attractive sense. There are three types of bonding: Ionic bonding
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Shapes (Chapter Three, Part Two) What is Bonding? Bonding describes how atoms interact with each other in an attractive sense. There are three types of bonding: Ionic bonding
Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301
 Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 ELECTRON CONFIGURATION and PERIODIC TABLE UNIT 2 Day 3 Important InformaIon EXAM WRAPPER POSTED- 20 BONUS POINTS HW05 POSTED DUE Tue 9AM LM17 Posted DUE Tue 9AM (NGLM07- Periodic
Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 ELECTRON CONFIGURATION and PERIODIC TABLE UNIT 2 Day 3 Important InformaIon EXAM WRAPPER POSTED- 20 BONUS POINTS HW05 POSTED DUE Tue 9AM LM17 Posted DUE Tue 9AM (NGLM07- Periodic
POGIL 6 Key Periodic Table Trends (Part 2)
 Honors Chem Block Name POGIL 6 Key Periodic Table Trends (Part 2) is a measure of the ability of an atom s nucleus to attract electrons from a different atom within a covalent bond. A higher electronegativity
Honors Chem Block Name POGIL 6 Key Periodic Table Trends (Part 2) is a measure of the ability of an atom s nucleus to attract electrons from a different atom within a covalent bond. A higher electronegativity
Li or Na Li or Be Ar or Kr Al or Si
 Pre- AP Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory V Name: Date: Block: 1. Atomic Radius/Size 2. Ionization Energy 3. Electronegativity 4. Chemical Bonding Atomic Radius Effective Nuclear Charge (Z eff) Ø Net positive
Pre- AP Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory V Name: Date: Block: 1. Atomic Radius/Size 2. Ionization Energy 3. Electronegativity 4. Chemical Bonding Atomic Radius Effective Nuclear Charge (Z eff) Ø Net positive
Periodic Trends. Atomic Radius: The distance from the center of the nucleus to the outer most electrons in an atom.
 Periodic Trends Study and learn the definitions listed below. Then use the definitions and the periodic table provided to help you answer the questions in the activity. By the end of the activity you should
Periodic Trends Study and learn the definitions listed below. Then use the definitions and the periodic table provided to help you answer the questions in the activity. By the end of the activity you should
Valence Electrons. Periodic Table and Valence Electrons. Group Number and Valence Electrons. Learning Check. Learning Check.
 Chapter 5 Lecture Chapter 5 Electronic Structure and Periodic Trends 5.6 Trends in Periodic Properties Learning Goal Use the electron configurations of elements to explain the trends in periodic properties.
Chapter 5 Lecture Chapter 5 Electronic Structure and Periodic Trends 5.6 Trends in Periodic Properties Learning Goal Use the electron configurations of elements to explain the trends in periodic properties.
Name: Block: Date: Atomic Radius: the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outer most electrons in an atom.
 Name: Block: Date: Chemistry 11 Trends Activity Assignment Atomic Radius: the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outer most electrons in an atom. Ionic Radius: the distance from the center
Name: Block: Date: Chemistry 11 Trends Activity Assignment Atomic Radius: the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outer most electrons in an atom. Ionic Radius: the distance from the center
Chapter 9 Ionic and Covalent Bonding
 Chem 1045 Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 8th Edition Last Update: 06-April-2009 Chapter 9 Ionic and Covalent Bonding These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do
Chem 1045 Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 8th Edition Last Update: 06-April-2009 Chapter 9 Ionic and Covalent Bonding These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do
Chapter 7 Ionic And Metallic Bonding Answer Key Pearson Education
 Chapter 7 Ionic And Metallic Bonding Answer Key Pearson Education CHAPTER 7 IONIC AND METALLIC BONDING ANSWER KEY PEARSON EDUCATION PDF - Are you looking for chapter 7 ionic and metallic bonding answer
Chapter 7 Ionic And Metallic Bonding Answer Key Pearson Education CHAPTER 7 IONIC AND METALLIC BONDING ANSWER KEY PEARSON EDUCATION PDF - Are you looking for chapter 7 ionic and metallic bonding answer
Chem 115: Chapter 9 Dr. Babb
 Periodic Properties of the Atom Properties that depend on position of element in the periodic table. Factors that affect the periodic properties: 1. Principal quantum number of valence shell (n valence
Periodic Properties of the Atom Properties that depend on position of element in the periodic table. Factors that affect the periodic properties: 1. Principal quantum number of valence shell (n valence
Types of bonding: OVERVIEW
 1 of 43 Boardworks Ltd 2009 Types of bonding: OVERVIEW 2 of 43 Boardworks Ltd 2009 There are three types of bond that can occur between atoms: an ionic bond occurs between a metal and non-metal atom (e.g.
1 of 43 Boardworks Ltd 2009 Types of bonding: OVERVIEW 2 of 43 Boardworks Ltd 2009 There are three types of bond that can occur between atoms: an ionic bond occurs between a metal and non-metal atom (e.g.
Ionic and Covalent Bonds
 Chapter 6 Lecture Chapter 6 Ionic and Molecular Compounds 6.1 Ions: Transfer of Electrons Learning Goal Write the symbols for the simple ions of the representative elements. Fifth Edition Octet Rule An
Chapter 6 Lecture Chapter 6 Ionic and Molecular Compounds 6.1 Ions: Transfer of Electrons Learning Goal Write the symbols for the simple ions of the representative elements. Fifth Edition Octet Rule An
Worksheet 5 - Chemical Bonding
 Worksheet 5 - Chemical Bonding The concept of electron configurations allowed chemists to explain why chemical molecules are formed from the elements. In 1916 the American chemist Gilbert Lewis proposed
Worksheet 5 - Chemical Bonding The concept of electron configurations allowed chemists to explain why chemical molecules are formed from the elements. In 1916 the American chemist Gilbert Lewis proposed
CHEM 1305 Introductory Chemistry
 CHEM 1305 Introductory Chemistry Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking 7 th Edition, Charles H. Corwin Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding Modified by: Dr. Violeta F. Coarfa 1 Chemical Bond Concept
CHEM 1305 Introductory Chemistry Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking 7 th Edition, Charles H. Corwin Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding Modified by: Dr. Violeta F. Coarfa 1 Chemical Bond Concept
Goals for Today. 0 Be able to draw Lewis Dot Diagrams for atoms, ions and ionic compounds. 0 Be able to write the names of ionic compounds
 Goals for Today 0 Be able to draw Lewis Dot Diagrams for atoms, ions and ionic compounds 0 Be able to write the names of ionic compounds 0 Be able to write the formulas for ionic compounds 0 Today we are
Goals for Today 0 Be able to draw Lewis Dot Diagrams for atoms, ions and ionic compounds 0 Be able to write the names of ionic compounds 0 Be able to write the formulas for ionic compounds 0 Today we are
Trends in the Periodic Table
 Trends in the Periodic Table Effective nuclear charge: < effective nuclear charge is the attraction felt by the valence electrons from the nucleus < increases across a period : increases across because
Trends in the Periodic Table Effective nuclear charge: < effective nuclear charge is the attraction felt by the valence electrons from the nucleus < increases across a period : increases across because
Chapter 8 The Concept of the Chemical Bond
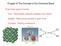 Chapter 8 The Concept of the Chemical Bond Three basic types of bonds: Ionic - Electrostatic attraction between ions (NaCl) Metallic - Metal atoms bonded to each other Covalent - Sharing of electrons Ionic
Chapter 8 The Concept of the Chemical Bond Three basic types of bonds: Ionic - Electrostatic attraction between ions (NaCl) Metallic - Metal atoms bonded to each other Covalent - Sharing of electrons Ionic
Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford. Why are there no blue fireworks? LIGHT, ELECTRONS & QUANTUM MODEL. Important Information
 Unit2Day2-Crawford Page 1 Unit2Day2-Crawford Monday, September 23, 2013 4:15 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 Why are there no blue fireworks? LIGHT, ELECTRONS & QUANTUM MODEL UNIT 2 Day 2 CH302 Vanden
Unit2Day2-Crawford Page 1 Unit2Day2-Crawford Monday, September 23, 2013 4:15 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 Why are there no blue fireworks? LIGHT, ELECTRONS & QUANTUM MODEL UNIT 2 Day 2 CH302 Vanden
Chapter 8: Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8: Concepts of Chemical Bonding Learning Outcomes: Write Lewis symbols for atoms and ions. Define lattice energy and be able to arrange compounds in order of increasing lattice energy based on
Chapter 8: Concepts of Chemical Bonding Learning Outcomes: Write Lewis symbols for atoms and ions. Define lattice energy and be able to arrange compounds in order of increasing lattice energy based on
Periodic Table trends
 2017/2018 Periodic Table trends Mohamed Ahmed Abdelbari Atomic Radius The size of an atom is defined by the edge of its orbital. However, orbital boundaries are fuzzy and in fact are variable under different
2017/2018 Periodic Table trends Mohamed Ahmed Abdelbari Atomic Radius The size of an atom is defined by the edge of its orbital. However, orbital boundaries are fuzzy and in fact are variable under different
Atom the smallest unit of matter indivisible. Helium atom
 Atom the smallest unit of matter indivisible Helium atom electron shells a) Atomic number = number of Electrons a) Electrons vary in the amount of energy they possess, and they occur at certain energy
Atom the smallest unit of matter indivisible Helium atom electron shells a) Atomic number = number of Electrons a) Electrons vary in the amount of energy they possess, and they occur at certain energy
Trends in the Periodic Table
 Trends in the Periodic Table OBJECTIVES FOR TODAY: Fall in love with the Periodic Table, Interpret group and period trends in atomic radii, ionization energies and electronegativity The Periodic Table
Trends in the Periodic Table OBJECTIVES FOR TODAY: Fall in love with the Periodic Table, Interpret group and period trends in atomic radii, ionization energies and electronegativity The Periodic Table
Sparks CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? UNIT 3 Day 1
 Sparks CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? UNIT 3 Day 1 What are we going to learn today? Think about why matter is so diverse Attractive and Repulsive Electrostatic Forces Dipole Moment POLL: CLICKER
Sparks CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? UNIT 3 Day 1 What are we going to learn today? Think about why matter is so diverse Attractive and Repulsive Electrostatic Forces Dipole Moment POLL: CLICKER
SPARKS CH301. ELECTRONS and COMPOUNDS. UNIT 2 Day 8
 SPARKS CH301 ELECTRONS and COMPOUNDS UNIT 2 Day 8 What are we going to learn today? Electron Configuration and Bonding Employ the concept of resonance Use formal charge to help predict best possible Lewis
SPARKS CH301 ELECTRONS and COMPOUNDS UNIT 2 Day 8 What are we going to learn today? Electron Configuration and Bonding Employ the concept of resonance Use formal charge to help predict best possible Lewis
me YouTube link, share with me through Google Drive, or bring flash drive
 Bonding Unit 3 Element Commercial Due tomorrow Each member must have own copy of fact sheet Email me YouTube link, share with me through Google Drive, or bring flash drive Tomorrow there will be a short
Bonding Unit 3 Element Commercial Due tomorrow Each member must have own copy of fact sheet Email me YouTube link, share with me through Google Drive, or bring flash drive Tomorrow there will be a short
CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS
 CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS July 16, 2011 Robert Iafe Office Hours 2 July 18-July 22 Monday: 2:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Tuesday-Thursday: 3:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Chapter 2 Overview 3 Ionic Bonds Covalent
CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS July 16, 2011 Robert Iafe Office Hours 2 July 18-July 22 Monday: 2:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Tuesday-Thursday: 3:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Chapter 2 Overview 3 Ionic Bonds Covalent
CHEM 121 Introduction to Fundamental Chemistry. Summer Quarter 2008 SCCC. Lecture 5.
 CHEM 121 Introduction to Fundamental Chemistry Summer Quarter 2008 SCCC Lecture 5 http://seattlecentral.edu/faculty/lcwest/che121 Forces Between Particles Noble Gas Configurations Ionic Bonding Ionic Compounds
CHEM 121 Introduction to Fundamental Chemistry Summer Quarter 2008 SCCC Lecture 5 http://seattlecentral.edu/faculty/lcwest/che121 Forces Between Particles Noble Gas Configurations Ionic Bonding Ionic Compounds
Section IV: Moving Electrons
 Section IV: Moving Electrons Lesson 17 Technicolor Atoms Lesson 18 Life on the Edge Lesson 19 Noble Gas Envy Lesson 20 Getting Connected Lesson 21 Salty Eights Lesson 22 Isn t It Ionic? Lesson 23 Alchemy
Section IV: Moving Electrons Lesson 17 Technicolor Atoms Lesson 18 Life on the Edge Lesson 19 Noble Gas Envy Lesson 20 Getting Connected Lesson 21 Salty Eights Lesson 22 Isn t It Ionic? Lesson 23 Alchemy
Name PRACTICE Unit 3: Periodic Table
 1. Compared to the atoms of nonmetals in Period 3, the atoms of metals in Period 3 have (1) fewer valence electrons (2) more valence electrons (3) fewer electron shells (4) more electron shells 2. On the
1. Compared to the atoms of nonmetals in Period 3, the atoms of metals in Period 3 have (1) fewer valence electrons (2) more valence electrons (3) fewer electron shells (4) more electron shells 2. On the
Why is it called a periodic table?
 The Periodic Table Why is it called a periodic table? The properties of the elements in the table repeat in a "periodic" way (specific pattern). Periodic law: There is a periodic repetition of chemical
The Periodic Table Why is it called a periodic table? The properties of the elements in the table repeat in a "periodic" way (specific pattern). Periodic law: There is a periodic repetition of chemical
1. Atomic and Ionic radius 2. Ionization energy 3. Electronegativity 4. Electron Affinity PERIODIC TRENDS
 PERIODIC TRENDS Nov 11 9:05 PM Periodic trends that change in a predictable way: 1. Atomic and Ionic radius 2. Ionization energy 3. Electronegativity 4. Electron Affinity Nov 11 8:20 PM 1 Atomic Radius
PERIODIC TRENDS Nov 11 9:05 PM Periodic trends that change in a predictable way: 1. Atomic and Ionic radius 2. Ionization energy 3. Electronegativity 4. Electron Affinity Nov 11 8:20 PM 1 Atomic Radius
Properties of substances are largely dependent on the bonds holding the material together.
 Basics of Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Properties of substances are largely dependent on the bonds holding the material together. Basics of Bonding A chemical bond occurs when atoms or
Basics of Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Properties of substances are largely dependent on the bonds holding the material together. Basics of Bonding A chemical bond occurs when atoms or
Bonding in Chemistry. Chemical Bonds All chemical reactions involve breaking of some bonds and formation of new ones where new products are formed.
 CHEMICAL BONDS Atoms or ions are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds. The type and number of electrons in the outer electronic shells of atoms or ions are instrumental in how atoms
CHEMICAL BONDS Atoms or ions are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds. The type and number of electrons in the outer electronic shells of atoms or ions are instrumental in how atoms
Atom the smallest unit of matter indivisible. Helium atom
 Atom the smallest unit of matter indivisible Helium atom electron shells a) Atomic number = number of Electrons b) Electrons vary in the amount of energy they possess, and they occur at certain energy
Atom the smallest unit of matter indivisible Helium atom electron shells a) Atomic number = number of Electrons b) Electrons vary in the amount of energy they possess, and they occur at certain energy
Chemical Bonds & Lattice Energy
 Chemical Bonds & Chemical bonds form when individual atoms become attached to other atoms. This happens when the electrons in each atom s outer energy level become filled. This is known as a stable octet.
Chemical Bonds & Chemical bonds form when individual atoms become attached to other atoms. This happens when the electrons in each atom s outer energy level become filled. This is known as a stable octet.
Chapter 7. Ionic & Covalent Bonds
 Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Unit3Day7-LaBrake. Important Information. Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301. WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? Gas, Liquid or Solid?
 Unit3Day7-LaBrake Page 1 Unit3Day7-LaBrake Monday, October 28, 2013 9:38 AM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? Gas, Liquid or Solid? UNIT 3 Day 7 Important Information HW09
Unit3Day7-LaBrake Page 1 Unit3Day7-LaBrake Monday, October 28, 2013 9:38 AM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? Gas, Liquid or Solid? UNIT 3 Day 7 Important Information HW09
Its Bonding Time. Chemical Bonds CH 12
 Its Bonding Time Chemical Bonds CH 12 What is a chemical bond? Octet Rule: Chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom, by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons, has an octet of electrons in its
Its Bonding Time Chemical Bonds CH 12 What is a chemical bond? Octet Rule: Chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom, by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons, has an octet of electrons in its
sharing or transferring electrons between atoms covalent ionic polar covalent Quantitative description: Quantum mechanics
 Chapter. 3 Chemical Bonding: The Classical Description Two or more atoms approach -> their electrons interact and form new arrangements of electrons with lower total potential energy than isolated atoms
Chapter. 3 Chemical Bonding: The Classical Description Two or more atoms approach -> their electrons interact and form new arrangements of electrons with lower total potential energy than isolated atoms
Periodic Relationships
 Periodic Relationships 1 Tabulation of Elements Mendeleev (1869) Arranged by mass Tabulation by chem.& physical properties Predicted missing elements and properties 2 Modern Periodic Table Argon vs. potassium
Periodic Relationships 1 Tabulation of Elements Mendeleev (1869) Arranged by mass Tabulation by chem.& physical properties Predicted missing elements and properties 2 Modern Periodic Table Argon vs. potassium
SBI4U BIOCHEMISTRY. Atoms, Bonding & Molecular Polarity
 SBI4U BIOCHEMISTRY Atoms, Bonding & Molecular Polarity 6 types of atoms make up 99% of all living organisms Naturally Occurring Elements in the Human Body Element Symbol Atomic # % of human body weight
SBI4U BIOCHEMISTRY Atoms, Bonding & Molecular Polarity 6 types of atoms make up 99% of all living organisms Naturally Occurring Elements in the Human Body Element Symbol Atomic # % of human body weight
Chemical Bonding I: Covalent Bonding. How are atoms held together in compounds?
 I: Covalent Bonding How are atoms held together in compounds? IONIC or COVALENT bonds or forces For most atoms, a filled outer shell contains 8 electrons ----- an octet Atoms want to form octets when they
I: Covalent Bonding How are atoms held together in compounds? IONIC or COVALENT bonds or forces For most atoms, a filled outer shell contains 8 electrons ----- an octet Atoms want to form octets when they
Name: 1. The mass of a proton is approximately equal to the mass of (1) an alpha particle (2) a beta particle (3) a positron (4) a neutron
 Chemistry Section Name: MID TERM STUDY GUIDE Date: A. Multiple Choice. 1. The mass of a proton is approximately equal to the mass of (1) an alpha particle (2) a beta particle (3) a positron (4) a neutron
Chemistry Section Name: MID TERM STUDY GUIDE Date: A. Multiple Choice. 1. The mass of a proton is approximately equal to the mass of (1) an alpha particle (2) a beta particle (3) a positron (4) a neutron
Chemical Bonds. A chemical bond is the force of attraction holding atoms together due to the transfer or sharing of valence electrons between them.
 Chemical Bonds A chemical bond is the force of attraction holding atoms together due to the transfer or sharing of valence electrons between them. Atoms will either gain, lose or share electrons in order
Chemical Bonds A chemical bond is the force of attraction holding atoms together due to the transfer or sharing of valence electrons between them. Atoms will either gain, lose or share electrons in order
Unit1Day4-LaBrake. Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301. Day 4. Important Information. LM 08 & 09 DUE Th 9AM HW2 & LM06&07 WERE DUE THIS MORNING 9AM
 Unit1Day4-LaBrake Monday, September 09, 2013 5:09 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 Kinetic Theory of Gases How fast do gases move? Day 4 Important Information LM 08 & 09 DUE Th 9AM HW2 & LM06&07 WERE
Unit1Day4-LaBrake Monday, September 09, 2013 5:09 PM Vanden Bout/LaBrake/Crawford CH301 Kinetic Theory of Gases How fast do gases move? Day 4 Important Information LM 08 & 09 DUE Th 9AM HW2 & LM06&07 WERE
What are we going to learn today?
 UNIT3DAY4-LaB Page 1 UNIT3DAY4-LaB Tuesday, October 23, 2012 8:29 AM Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? MORE ON BONDING THEORIES UNIT 3 Day 4 Important Information LM22 DUE Th 9AM
UNIT3DAY4-LaB Page 1 UNIT3DAY4-LaB Tuesday, October 23, 2012 8:29 AM Vanden Bout/LaBrake CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? MORE ON BONDING THEORIES UNIT 3 Day 4 Important Information LM22 DUE Th 9AM
Unit 1 Review: Matter and Chemical Bonding
 Unit 1 Review: Matter and Chemical Bonding 1. Do you think DHMO should be banned? Justify your answer. Write the formula for dihydrogen monoxide. H 2 O 2. Name these groups on the periodic table: 1, 2,
Unit 1 Review: Matter and Chemical Bonding 1. Do you think DHMO should be banned? Justify your answer. Write the formula for dihydrogen monoxide. H 2 O 2. Name these groups on the periodic table: 1, 2,
Why are electrons important?
 Why are electrons important? Chemical bonding involves electrons in the outermost energy level (valence electrons). When chemical bonds are formed, atoms gain, lose or share electrons to have 8 electrons
Why are electrons important? Chemical bonding involves electrons in the outermost energy level (valence electrons). When chemical bonds are formed, atoms gain, lose or share electrons to have 8 electrons
3. Determine the total charge of an oxygen nucleus: Valence electrons are ELECTRONS on the outer most electron shell (principle energy level).
 Name: Period: Date: Hybrid Chemistry Regents Prep Ms. Hart/Mr. Kuhnau UNIT 2: Bonding Lesson 2.1: Ions and Ionic Bonding By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How do metals and non- metals bond
Name: Period: Date: Hybrid Chemistry Regents Prep Ms. Hart/Mr. Kuhnau UNIT 2: Bonding Lesson 2.1: Ions and Ionic Bonding By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How do metals and non- metals bond
Covalent Bonding. a. O b. Mg c. Ar d. C. a. K b. N c. Cl d. B
 Covalent Bonding 1. Obtain the number of valence electrons for each of the following atoms from its group number and draw the correct Electron Dot Notation (a.k.a. Lewis Dot Structures). a. K b. N c. Cl
Covalent Bonding 1. Obtain the number of valence electrons for each of the following atoms from its group number and draw the correct Electron Dot Notation (a.k.a. Lewis Dot Structures). a. K b. N c. Cl
Trends in Atomic Size. Atomic Radius-one half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined
 Periodic trends Trends in Atomic Size Atomic Radius-one half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined Trends in Atomic Size Group Trend: Atomic radii of
Periodic trends Trends in Atomic Size Atomic Radius-one half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined Trends in Atomic Size Group Trend: Atomic radii of
1. Ionic bonding - chemical bond resulting from the attraction of positive and negative ions
 Bonding Bonding can occur in 2 ways: 1. Electron transfer (ionic) 2. Electron sharing (covalent) 1. Ionic bonding - chemical bond resulting from the attraction of positive and negative ions Cation- positive
Bonding Bonding can occur in 2 ways: 1. Electron transfer (ionic) 2. Electron sharing (covalent) 1. Ionic bonding - chemical bond resulting from the attraction of positive and negative ions Cation- positive
Periodic Trends. The trends we will study all have to do with the valence electrons in one way or another. Two key ideas:
 Periodic Trends The trends we will study all have to do with the valence electrons in one way or another. Two key ideas: Nuclear Charge = the number of protons in the nucleus. This is the positive charge
Periodic Trends The trends we will study all have to do with the valence electrons in one way or another. Two key ideas: Nuclear Charge = the number of protons in the nucleus. This is the positive charge
UNIT 7 DAY 1. Ionic Bonding Basics; Dot diagrams
 UNIT 7 DAY 1 Ionic Bonding Basics; Dot diagrams U7D1: Ionic Bonding Basics HW: See Schedule; Lab Due Thursday Do Now: 1.Write your name, date and period on all packets. 2.Look through schedule 3. answer
UNIT 7 DAY 1 Ionic Bonding Basics; Dot diagrams U7D1: Ionic Bonding Basics HW: See Schedule; Lab Due Thursday Do Now: 1.Write your name, date and period on all packets. 2.Look through schedule 3. answer
Periodic Relationships
 Periodic Relationships 1 Tabulation of Elements Mendeleev (1869) Arranged by mass Tabulation by chem.& physical properties Predicted missing elements and properties 2 Modern Periodic Table Argon vs. potassium
Periodic Relationships 1 Tabulation of Elements Mendeleev (1869) Arranged by mass Tabulation by chem.& physical properties Predicted missing elements and properties 2 Modern Periodic Table Argon vs. potassium
Bond Atoms Electron behavior Ionic Metal + nonmetal Electrons transferred Covalent Nonmetal + nonmetal Electrons shared
 ch9blank Page 1 Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Three types of chemical bonding: Bond Atoms Electron behavior Ionic Metal + nonmetal Electrons transferred Covalent Nonmetal + nonmetal Electrons
ch9blank Page 1 Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Three types of chemical bonding: Bond Atoms Electron behavior Ionic Metal + nonmetal Electrons transferred Covalent Nonmetal + nonmetal Electrons
Three types of chemical bonding: Recall that we can use dots to show valence electrons - these are called Lewis electron-dot structures:
 Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Three types of chemical bonding: Bond Atoms Electron behavior Ionic Metal + nonmetal Electrons transferred Covalent Nonmetal + nonmetal Electrons shared Metallic
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Three types of chemical bonding: Bond Atoms Electron behavior Ionic Metal + nonmetal Electrons transferred Covalent Nonmetal + nonmetal Electrons shared Metallic
What is this? Electrons: charge, mass? Atom. Negative charge(-), mass = 0. The basic unit of matter. Made of subatomic particles:
 Chemical Bonds What is this? Atom The basic unit of matter. Electrons: charge, mass? Negative charge(-), mass = 0 Made of subatomic particles: Protons: charge, mass? Positive charge (+), mass = 1 Neutrons:
Chemical Bonds What is this? Atom The basic unit of matter. Electrons: charge, mass? Negative charge(-), mass = 0 Made of subatomic particles: Protons: charge, mass? Positive charge (+), mass = 1 Neutrons:
Week 8/Tu: Lecture Unit 19
 Week 8/Tu: Lecture Unit 19 Unit 18: Periodicity -- electron configurations -- periodicity of elements -- radii, ionization, affinity -- electronegativity Unit 19: Chemical Bonding -- Basis of bonding --
Week 8/Tu: Lecture Unit 19 Unit 18: Periodicity -- electron configurations -- periodicity of elements -- radii, ionization, affinity -- electronegativity Unit 19: Chemical Bonding -- Basis of bonding --
Atomic Structure and Periodicity
 Atomic Structure and Periodicity Atoms and isotopes: Isotopes-#p + same for all but mass number is different b/c of # n o Average atomic mass is weighted average of all the isotopes for an element Average
Atomic Structure and Periodicity Atoms and isotopes: Isotopes-#p + same for all but mass number is different b/c of # n o Average atomic mass is weighted average of all the isotopes for an element Average
Conceptual Integrated Science
 Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 12 THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL BONDS Electron Shells Atoms bond together through their electrons. To learn about bonding, therefore, we need to
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 12 THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL BONDS Electron Shells Atoms bond together through their electrons. To learn about bonding, therefore, we need to
Chapter 7. Part 1 Slides
 Chapter 7 Part 1 Slides Warm Up! Radium was formerly used in self-luminous paints for watches, nuclear panels, aircraft switches, clocks, and instrument dials. This practice stopped because radium is treated
Chapter 7 Part 1 Slides Warm Up! Radium was formerly used in self-luminous paints for watches, nuclear panels, aircraft switches, clocks, and instrument dials. This practice stopped because radium is treated
Thinking Like a Chemist About Dissolution. Unit 5 Day 4
 Thinking Like a Chemist About Dissolution Unit 5 Day 4 What are we going to learn today? Thinking Like a Chemist in the Context of the Dissolution Process. Macro Modeling Micro Modeling Energy of the change
Thinking Like a Chemist About Dissolution Unit 5 Day 4 What are we going to learn today? Thinking Like a Chemist in the Context of the Dissolution Process. Macro Modeling Micro Modeling Energy of the change
Atomic Radius. Atomic Radius. Atomic Radius 10/17/18. Monday October AGENDA YOYO. AIM What are periodic table trends?
 10/17/18 Monday October AGENDA 15 2018 YOYO PUT EVERYTHING AWAY QUIZ TIME! YOYO AIM What are periodic table trends? Quiz Periodic Trend Activity AFTER QUIZ Turn in Quiz and take and start working on Periodic
10/17/18 Monday October AGENDA 15 2018 YOYO PUT EVERYTHING AWAY QUIZ TIME! YOYO AIM What are periodic table trends? Quiz Periodic Trend Activity AFTER QUIZ Turn in Quiz and take and start working on Periodic
Regan & Johnston Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period
 Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
The boundaries of an atom are fuzzy, and an atom s radius can vary under different conditions.
 Atomic Radii The boundaries of an atom are fuzzy, and an atom s radius can vary under different conditions. To compare different atomic radii, they must be measured under specified conditions. Atomic radius
Atomic Radii The boundaries of an atom are fuzzy, and an atom s radius can vary under different conditions. To compare different atomic radii, they must be measured under specified conditions. Atomic radius
Regan & Johnston Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period
 Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends - Chapter 5 section 3 Guided Notes
 Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends - Chapter 5 section 3 Guided Notes There are several important atomic characteristics that show predictable that you should know. Atomic Radius The first and
Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends - Chapter 5 section 3 Guided Notes There are several important atomic characteristics that show predictable that you should know. Atomic Radius The first and
A. Features of Atoms in the Periodic Table Atomic Radius Difficult to measure, since atoms have electron. down a group across a period
 [3.2A Periodicity: Trends in the Periodic Table] pg. 1 of 5 Curriculum: Vertical and horizontal trends in the periodic table exist for atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity
[3.2A Periodicity: Trends in the Periodic Table] pg. 1 of 5 Curriculum: Vertical and horizontal trends in the periodic table exist for atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity
How do Elements Combine to Form Compounds?
 How do Elements Combine to Form Compounds? ACTIVITY What is it made of? Think about the calcium atom vs the calcium ion Compounds account for the huge variety of matter on Earth All the compounds that
How do Elements Combine to Form Compounds? ACTIVITY What is it made of? Think about the calcium atom vs the calcium ion Compounds account for the huge variety of matter on Earth All the compounds that
Chemical Bonding -- Lewis Theory (Chapter 9)
 Chemical Bonding -- Lewis Theory (Chapter 9) Ionic Bonding 1. Ionic Bond Electrostatic attraction of positive (cation) and negative (anion) ions Neutral Atoms e - transfer (IE and EA) cation + anion Ionic
Chemical Bonding -- Lewis Theory (Chapter 9) Ionic Bonding 1. Ionic Bond Electrostatic attraction of positive (cation) and negative (anion) ions Neutral Atoms e - transfer (IE and EA) cation + anion Ionic
Unit 11 Bonding. Identifying the type of bonding involved in a molecule will allow us to predict certain general properties of a compound.
 Unit 11 Bonding INTRODUCTION Within molecules, there are forces that hold atoms together These forces are called bonds There are different types of bonds, or more correctly, variations Identifying the
Unit 11 Bonding INTRODUCTION Within molecules, there are forces that hold atoms together These forces are called bonds There are different types of bonds, or more correctly, variations Identifying the
Topic 4: Chemical Bonds. IB Chemistry SL Ms. Kiely Coral Gables Senior High
 Topic 4: Chemical Bonds IB Chemistry SL Ms. Kiely Coral Gables Senior High 5th PERIOD Bell Ringer - review of 4.1 Quiz (revised) 1. What is the formula of a compound formed by magnesium and phosphate?
Topic 4: Chemical Bonds IB Chemistry SL Ms. Kiely Coral Gables Senior High 5th PERIOD Bell Ringer - review of 4.1 Quiz (revised) 1. What is the formula of a compound formed by magnesium and phosphate?
Atomic Theory and Periodic Trends Practice AP Chemistry Questions
 AP Chemistry/1516 Atomic Theory and Periodic Trends Practice AP Chemistry Questions 1. 2007 B, question #2 Answer the following problems about gases. (b) A major line in the emission spectrum of neon corresponds
AP Chemistry/1516 Atomic Theory and Periodic Trends Practice AP Chemistry Questions 1. 2007 B, question #2 Answer the following problems about gases. (b) A major line in the emission spectrum of neon corresponds
Ionic Bonding Ionic bonding occurs when metals and nonmetals trade one or more electrons and the resulting opposite charges attract each other. Metals
 Chemical Bonding Now that we know what atoms look like A very small (less than 0.001% of the volume) and massive (more than 99.99% of the mass) nucleus with protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) and electrons
Chemical Bonding Now that we know what atoms look like A very small (less than 0.001% of the volume) and massive (more than 99.99% of the mass) nucleus with protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) and electrons
Chemistry of Life 9/16/15. Chemistry s Building Block: The Atom. Ch 2 BIOL 160
 Ch 2 Chemistry of Life BIOL 160 1 Chemistry s Building Block: The Atom Structural Hierarchy (reviewed) Atom Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ The atom is the fundamental unit of matter. Elements Chemistry
Ch 2 Chemistry of Life BIOL 160 1 Chemistry s Building Block: The Atom Structural Hierarchy (reviewed) Atom Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ The atom is the fundamental unit of matter. Elements Chemistry
Chemistry Unit: Chemical Bonding (chapter 7 and 8) Notes
 Name: Period: Due Date: 1-18-2019 / 100 Formative pts. Chemistry Unit: Chemical Bonding (chapter 7 and 8) Notes Topic-1: Review: 1. Valence electrons: The electrons in the outermost of an atom Valence
Name: Period: Due Date: 1-18-2019 / 100 Formative pts. Chemistry Unit: Chemical Bonding (chapter 7 and 8) Notes Topic-1: Review: 1. Valence electrons: The electrons in the outermost of an atom Valence
Chapter 6: Ionic and Molecular Compounds
 Chapter 6: Ionic and Molecular Compounds 1. Recall that the group number indicates the number of valence electrons for any element in that group. Each noble gas has eight valence electrons (except helium,
Chapter 6: Ionic and Molecular Compounds 1. Recall that the group number indicates the number of valence electrons for any element in that group. Each noble gas has eight valence electrons (except helium,
Chemical bonding & structure
 Chemical bonding & structure Ionic bonding and structure Covalent bonding Covalent structures Intermolecular forces Metallic bonding Ms. Thompson - SL Chemistry Wooster High School Topic 4.1 Ionic bonding
Chemical bonding & structure Ionic bonding and structure Covalent bonding Covalent structures Intermolecular forces Metallic bonding Ms. Thompson - SL Chemistry Wooster High School Topic 4.1 Ionic bonding
Ionic Compounds: Chapter 8
 Ionic Compounds: Chapter 8 Bonding between atoms: As you know, atoms bond with each other to form chemical compounds. Usually, this process takes place easily. Why? THE OCTET RULE! All elements want to
Ionic Compounds: Chapter 8 Bonding between atoms: As you know, atoms bond with each other to form chemical compounds. Usually, this process takes place easily. Why? THE OCTET RULE! All elements want to
Biotech 2: Atoms and Molecules OS Text Reading pp Electron cloud Atoms & Nucleus 2e Subatomic Particles Helium Electron cloud
 9/4/017 Biotech : Atoms and Molecules OS Text Reading pp. 34-4 Atoms & Subatomic Particles Nucleus Helium e cloud cloud e Protons Neutrons Mass number = 4 s Nucleus Carbon atomic number = # of protons
9/4/017 Biotech : Atoms and Molecules OS Text Reading pp. 34-4 Atoms & Subatomic Particles Nucleus Helium e cloud cloud e Protons Neutrons Mass number = 4 s Nucleus Carbon atomic number = # of protons
What is an ion? An ion is an atom (or group of atoms) that has a positive or negative charge
 What is an ion? An ion is an atom (or group of atoms) that has a positive or negative charge Cations (+) Formed when an atom LOSES electrons Usually happens to metals in a reaction Anions (-) Formed when
What is an ion? An ion is an atom (or group of atoms) that has a positive or negative charge Cations (+) Formed when an atom LOSES electrons Usually happens to metals in a reaction Anions (-) Formed when
Chapter: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonds
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonds Section 1: Why do atoms combine? Section 2: How Elements Bond Table of Contents Chapter: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonds Section 1: Why
Table of Contents Chapter: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonds Section 1: Why do atoms combine? Section 2: How Elements Bond Table of Contents Chapter: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonds Section 1: Why
Notes: Electrons and Periodic Table (text Ch. 4 & 5)
 Name Per. Notes: Electrons and Periodic Table (text Ch. 4 & 5) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to
Name Per. Notes: Electrons and Periodic Table (text Ch. 4 & 5) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to
Unit 2: Chemical Bonds. Pre-IB Chemistry Ms. Kiely Coral Gables Senior High
 Unit 2: Chemical Bonds Pre-IB Chemistry Ms. Kiely Coral Gables Senior High QUIZ! Take out a PEN Sit in Quiz seats :) Timed 20 minutes Bell-Ringer Which types of elements combine chemically to make an ionic
Unit 2: Chemical Bonds Pre-IB Chemistry Ms. Kiely Coral Gables Senior High QUIZ! Take out a PEN Sit in Quiz seats :) Timed 20 minutes Bell-Ringer Which types of elements combine chemically to make an ionic
Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms.
 7.1 Periodic Trends > Valence Electrons Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms. 1 of 31 Periodic Trends > 2 of 31 Periodic Trends > 3 of 31 7.1 Periodic
7.1 Periodic Trends > Valence Electrons Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms. 1 of 31 Periodic Trends > 2 of 31 Periodic Trends > 3 of 31 7.1 Periodic
Periodic Trends. 1. Why is it difficult to measure the size of an atom? 2. What does the term atomic radius mean? 3. What is ionization energy?
 Periodic Trends 1. Why is it difficult to measure the size of an atom? 2. What does the term atomic radius mean? 3. What is ionization energy? 4. What periodic trends exist for ionization energy? 5. What
Periodic Trends 1. Why is it difficult to measure the size of an atom? 2. What does the term atomic radius mean? 3. What is ionization energy? 4. What periodic trends exist for ionization energy? 5. What
Chapter 6 Test. name. The Structure of Matter
 Chapter 6 Test The Structure of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE. Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question on the answer sheet provided. 1. A compound
Chapter 6 Test The Structure of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE. Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question on the answer sheet provided. 1. A compound
Periodic Trends. 1. (#2 3a) I can determine how gaining or losing electrons affects the atomic
 Periodic Trends objectives: (#2 3) How do the properties of electrons and the electron shells contribute to the periodic trends? 1. (#2 3a) I can determine how gaining or losing electrons affects the atomic
Periodic Trends objectives: (#2 3) How do the properties of electrons and the electron shells contribute to the periodic trends? 1. (#2 3a) I can determine how gaining or losing electrons affects the atomic
Big Idea: Ionic Bonds: Ionic Bonds: Metals: Nonmetals: Covalent Bonds: Ionic Solids: What ions do atoms form? Electron Electron
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
