Continuous agglomerate model for identifying the solute- indifferent part of colloid nanoparticle's surface charge
|
|
|
- Berniece Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Continuous agglomerate model for identifying the solute- indifferent part of colloid nanoparticle's surface charge To cite this article: A V Alfimov et al 016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser View the article online for updates and enhancements. This content was downloaded from IP address on 03/09/018 at 0:3
2 Continuous agglomerate model for identifying the soluteindifferent part of colloid nanoparticle s surface charge A V Alfimov, E M Aryslanova and S A Chivilikhin ITMO University, Kronverkskiy, 49, St. Petersburg, , Russia Abstract. This work proposes an explicit analytical model for the surface potential of a colloidal nano-agglomerate. The model predicts that when an agglomerate reaches a certain critical size, its surface potential becomes independent of the agglomerate radius. The model also provides a method for identifying and quantifying the solute-indifferent charge in nanocolloids, that allows to assess the stability of toxicologically significant parameters of the system. 1. Introduction Biocompatibility of inorganic colloidal nanoparticles (NPs) depends greatly on their surface charge. This charge governs the state of agglomeration in nanocolloids, which, in turn, affects internalization, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of NPs in biological systems [1-6]. It was recently reported that the surface charge itself also has an impact on the toxicity of NPs [1,7-9]. Synthesized metal oxide NPs in aqueous solutions can acquire surface charge through a number of mechanisms: adsorption and desorption of protons on surface hydroxyl groups; physical adsorption of ions; reversible and irreversible chemical adsorption of ions; isomorphic substitution [10,11]. Most of these processes are dependent on the ph of the solution. Therefore, the effect of the medium on the surface charge is usually studied by measuring the surface potential of agglomerated NPs in a relevant ph range. However, the part of the surface charge arising due to irreversible chemical adsorption and/or isomorphic substitution can be indifferent to the solution used for titration. When NPs are released into a solution of unknown chemistry, the species responsible for this constant charge may react with the medium, leading to neutralisation of their charge. As a result, the surface potential can significantly deviate from the expected values, presenting a considerable toxicological threat. During experimental studies of colloidal systems, one often observes agglomerates rather than individual particles. We assume that, while for solid particles charging occurs only on the surface, agglomerates, like porous particles, can exhibit volumetric charging. Consequently, it is important to focus theoretical studies of the colloidal charging phenomena not just on individual NPs, but on their agglomerates as well. In the present work, we propose an analytical model of a colloidal nano-agglomerate that allows to identify the presence of the constant solute-indifferent charge (SIC) and study its effect on the surface potential. Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence. Any further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the title of the work, journal citation and DOI. Published under licence by Ltd 1
3 . Methods We consider a spherical agglomerate of metal oxide NPs. The agglomerate is immersed in a solution of a strong inert monovalent electrolyte in deionized water. The solution is isolated from atmospheric CO. The ph of this colloidal solution can be varied using acid-base titration at constant ionic strength I = const. The agglomerate is assumed to be a porous particle. The volume fraction of void space in the agglomerate (porosity Ω ) depends on the ordering of constituent NPs and their hydration. Nanoparticles inside the agglomerate acquire surface charge by protonation and deprotonation of surface hydroxyl groups. They can also carry a SIC originating from isomorphic substitution and/or irreversible chemisorption. Due to the porosity of the agglomerate we assume that the adsorption and desorption of protons on NP surface occurs in the entire volume of the agglomerate. It is now generally agreed that the adsorption and desorption of protons happens on two types of surface hydroxyl groups, basic and acidic in nature respectively [1-16]: M OH b + H +! K b M OH +, (1) M OH a! K a M O + H +, () where M OH b, M OH a - basic and acidic surface OH groups; K b, K a - equilibrium constants for protonation (1) and deprotonation () reactions. We consider the reactive surface hydroxyls to be evenly split between acidic and basic type [13,14]. Surface density of hydroxyl groups for NPs usually lies in the range of γ S = 1 0 nm - [10,1-14,17]. It should be noted that the average density of reactive sites on NPs comprising the agglomerate could be lower than the values for individual NPs. When NPs do not posses the constant charge (SIC), the ph at which the particle s surface charge is zero (point of zero charge) can be found as: PZC 0 = pk + pk b a, (3) where PZC 0 - point of zero charge in absence of SIC; pk b = log 10 ( K b ) and pk a = log 10 ( K a ). Parameters pk b and pk a have the physical meaning of ph values at which half of the basic (acidic) sites are protonated (deprotonated). We can now express: pk b = PZC 0 ΔpK and pk a = PZC 0 + ΔpK, (4) where ΔpK = pk a pk b. Values of ΔpK for metal oxide NPs can span over a wide range of ΔpK = 1 14 [18]. Electrostatic potential ϕ in the described system is governed by the Poisson-Boltzmann equation [10]. A number of assumptions were made to derive an analytical solution to the Poisson-Boltzmann problem for the potential inside and outside of the agglomerate. First, the Debye-Huckel approximation for low potentials in the system is used. According to this approximation, the maximum potential in the system should satisfy the condition: max(ϕ) < kt e ( k - Boltzmann constant; T - temperature; e - elementary charge). Second, we consider only the non-saturated regime of protonation/deprotonation: pk b < ph < pk a. Finally, the internal space of the agglomerate is approximated with continuous distributions of effective volume charge density ρ and dielectric permittivity : ( ) = e 1 Ω ρ r ( ) Z C + P 10 ΔpH 1 eϕ r kt 10ΔpH 1+ eϕ r kt A Ωκ ϕ ( r), (5) = ε NP ( 1 Ω) + ε M Ω, (6) ( )
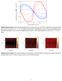
4 where Z C - average charge number of SIC per NP, P = S NP γ S 10 1 ΔpK - charge regulation parameter;, S NP - volume and surface area of primary NPs; κ = I e ε M kt - Debye-Huckel screening parameter of the solution; ε NP, ε M - dielectric permittivities of NPs and the medium (solution); - dielectric constant; r - position vector. By solving the resulting Debye-Huckel problem we obtained the following expression for the surface potential of the agglomerate : [ ] = e 1 Ω Z C + P sinh ln(10) ΔpH α 1+ ε, (7) M κ R +1 α R coth(α R) 1 where R - agglomerate radius; α - effective Debye-Huckel screening parameter of the agglomerate s interior that is given by: e α = kt 1 Ω P cosh[ ln(10) ΔpH] + ( Ωκ ). (8) As follows from (8), the parameter α consists of contributions from the surface charge of constituent NPs (first term) and from ions penetrating the void spaces between the NPs (second term). 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Surface potential as a function of agglomerate size From expressions (7) and (8) it follows that when κ R 1, the surface potential becomes independent of agglomerate radius. This behavior is illustrated in figure 1A. The saturated size-independent surface potential of the agglomerate is given by: Sat = e 1 Ω Z C + P sinh[ ln(10) ΔpH] α 1+ ε M κ (9) α The critical radius above which the agglomerate s surface potential becomes size-independent is defined only by the ionic strength of the solution. This relation is shown in figure 1B. Figure 1. A surface potential as a function of agglomerate radius (normalized to the primary NP radius) at different values of ΔpH ; B dependency of critical agglomerate radius on ionic strength of the solution; filled area corresponds to agglomerate radii above the critical value for which surface potential becomes independent of agglomerate size. 3
5 3.. Effect of solute-indifferent charge on the agglomerate s point of zero charge The model of the agglomerate s surface potential was developed under the Debye-Huckel approximation. Therefore, it is quantitatively valid only at low potentials. This condition is generally not satisfied throughout entire experimental surface potential curves. However, expression (7) is always applicable around the point of zero charge of the agglomerate. Consequently, we can use it to find the condition for zero agglomerate charge in case of non-zero SIC: Z C = sinh[ ln(10) ΔPZC], (10) P where ΔPZC = PZC PZC 0 - shift of point of zero charge in relation to its value in absence of SIC. Equation (10) shows that the presence of SIC shifts the agglomerate s PZC in relation to PZC 0 (point of zero charge when SIC is zero): 1 Z ΔPZC = log C 10 P + Z C +1 P ; (11) this dependency is illustrated in figure A. As a result, it is possible to identify the presence of SIC by detecting such PZC shift. As shown by (3), PZC 0 lies exactly in the middle between pk b and pk a, which signify the onset of protonation and deprotonation saturation correspondingly. We use a numerical non-linear Poisson- Boltzmann model of charged flat surface to demonstrate that non-zero SIC does not alter ph values at which protonation and deprotonation saturate (figure B). It is thus possible to assess the position of PZC 0 as a mid-point between the points of saturation onset. Figure. A point of zero charge shift ( ΔPZC ) as a function of average charge number of SIC per NP ( Z C ) at different values of charge regulation parameter P ; B surface potential as a function of ΔpH predicted by the numerical model of flat surface at different values of surface charge density of SIC Limiting cases of continuous agglomerate model We now consider the interior Debye-Huckel screening parameter α. According to (8), this parameter consists of contributions from NPs surface charge and ions in the inter-particle cavities. In a limiting case when one of these contributions significantly outweighs the other, expression (9) allows for further simplification. 4
6 The interior Debye-Huckel parameter α reduces to just the NP surface charge contribution when the following condition is met: e kt S NP γ S 10 1 ΔpK Ω ε NP + ε M 1 Ω 1 Ωκ. (1) We denote this limit as Case A. For closed-packed agglomerates of NPs with site density γ S = 1 nm - immersed in electrolyte solution with ionic strength I = M, condition (1) is met when primary NPs radius is less or equal to 5 nm and ΔpK 4. The simplified agglomerate s surface potential expression for Case A is given by: Case ϕ A S = kt e Z C + P sinh[ ln(10) ΔpH] P cosh[ ln(10) ΔpH] 1+ ε M κ. (13) α For highly porous agglomerates/particles with large ΔpK in solutions with high ionic strength, the opposite limiting case can be relevant: e kt S NP γ S 10 1 ΔpK Ω ε NP + ε M 1 Ω Ωκ. (14) The interior Debye-Huckel parameter alpha then reduces to just the contribution from ions in agglomerate s cavities. We denote this limit as Case B. For agglomerates with porosity Ω 0.5 composed from NPs with site density γ S = 1 nm - this condition is met in solutions with ionic strength I M when primary NP radius is greater or equal to 5 nm and ΔpK 6. The simplified agglomerate s surface potential expression for Case B is given by: Case e 1 Ω ϕ B S = ( ) Z C + P sinh[ ln(10) ΔpH] (15) κ ε NP Ω 1 Ω 1 ( ) ( ) + ε M Ω + Ω Expressions (13) and (15) explicitly show the dependency of agglomerate s surface potential on the ionic strength of the solution. In both cases the effect of SIC on the potential increases at lower ionic strengths. Moreover, this dependency is suggested to be stronger for the case of highly porous agglomerates/particles (15) Solute-indifferent charge assessment Simplified expressions (13) and (15) are always valid near to the agglomerate s point of zero charge for the same reason as the original formula (7). Therefore, we can use these expressions to find the relation between the model parameters ( Z C and P ) and the first derivative of the surface potential dependency on ph at the point of zero charge. The derivative of the surface potential curve at PZC can be determined experimentally. Then, by differentiating expression (13) or (15) and using the relation (10), we can find the estimate for the SIC charge number per NP Z C and the charge regulation parameter P : Z C = tanh[ ln(10) ΔPZC] Y, (16) P = sech[ ln(10) ΔPZC] Y, (17) where the Y function is specific to the employed limiting case. For the Case A we have: ε M κ ΔPZC Y Case A = ln(10) kt e +ϕ S ΔPZC and for the Case B: [ ] + ε M Ω[ 1 Ω] ε e NP 1 Ω kt 1, (18) 5
7 where ΔPZC ΔPZC Y Case B = ln(10) κ e Ω + Ω ε NP Ω + ε M 1 Ω (19) experimentally determined first derivative of the surface potential dependency on ph at the agglomerate s point of zero charge. Note that this assessment requires the additional knowledge of estimates for the agglomerates porosity Ω and primary NP s volume and dielectric permittivity ε NP. 4. Conclusions We developed an explicit analytical model for the surface potential of a colloidal nano-agglomerate. Analysis of this model suggests that 1) after an agglomerate reaches a certain critical size, its surface potential becomes independent of the agglomerate radius. The value of this critical size is defined solely by the ionic strength of the solution. ) Presence of solute-indifferent charge (SIC) in the agglomerate causes the point of zero charge to shift in relation to its value in absence of SIC. The sign of this shift coincides with the sign of SIC. 3) The effect of SIC on the surface potential increases at lower ionic strength. This correlation is stronger for highly porous agglomerates/particles. 4) It is possible to identify the presence of SIC by comparing the point of zero charge and the midpoint between the ph values corresponding to protonation and deprotonation saturation onsets. The developed agglomerate model provides a method for quantitative assessment of the average amount of SIC per primary nanoparticle. Acknowledgements This work was financially supported by the Government of Russian Federation, Grant 074-U01. References [1] Abdelmonem A M, Pelaz B, Kantner K, Bigall N C, Del Pino P and Parak W J 015 Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry [] Cupi D, Hartmann N B and Baun A 016 Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety [3] Jiang J, Oberdörster G and Biswas P 009 J Nanopart Res [4] Kim K-M et al 01 Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci [5] Berg J M, Romoser A, Banerjee N, Zebda R and Sayes C M 009 Nanotoxicology 3 76 [6] Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E and Oberdörster J 005 Environmental Health Perspectives [7] Barisik M, Atalay S, Beskok A and Qian S 014 J. Phys. Chem. C [8] Chusuei C C et al 013 Chemico-Biological Interactions [9] Schwegmann H, Feitz A J and Frimmel F H 010 J. Colloid Interface Sci [10] Stumm W 199 Chemistry of the solid-water interface (John Wiley & Sons) [11] Cosgrove T 010 Colloid Science (John Wiley & Sons) [1] Fierro J L G 005 Metal Oxides (CRC Press) [13] Tamura H, Mita K, Tanaka A and Ito M 001 J. Colloid Interface Sci [14] Tamura H 1999 J. Colloid Interface Sci [15] Hiemstra T, Van Riemsdijk W H and Bolt G H 1989 J. Colloid Interface Sci [16] Hiemstra T and Van Riemsdijk W H 1991 Colloids and Surfaces 59 7 [17] McCafferty E and Wightman J P 1998 Surface and Interface Analysis [18] Hiemstra T 1989 J. Colloid Interface Sci
Module 8: "Stability of Colloids" Lecture 38: "" The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c )
 The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
Electrical double layer
 Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces
 Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
1044 Lecture #14 of 18
 Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
Colloid Chemistry. La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross.
 Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Effect of Electrolyte Concentration during Solution Plasma on Copper Nanoparticle Size
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of Electrolyte Concentration during Solution Plasma on Copper Nanoparticle Size To cite this article: M H S Al Anbouri
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of Electrolyte Concentration during Solution Plasma on Copper Nanoparticle Size To cite this article: M H S Al Anbouri
Synthesis of ternary chalcogenide colloidal nanocrystals in aqueous medium
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Synthesis of ternary chalcogenide colloidal nanocrystals in aqueous medium To cite this article: D S Mazing et al 28 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 38 25 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Synthesis of ternary chalcogenide colloidal nanocrystals in aqueous medium To cite this article: D S Mazing et al 28 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 38 25 View
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview
 Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Rheological properties of crude oils in Yaregskoye and Yaraktinskoye oil fields
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Rheological properties of crude oils in Yaregskoye and Yaraktinskoye oil fields Related content - Steam-assisted gravity drainage
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Rheological properties of crude oils in Yaregskoye and Yaraktinskoye oil fields Related content - Steam-assisted gravity drainage
(name) Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant. Final Exam
 10.626 Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant Final Exam Instructions. This is a three-hour closed book exam. You are allowed to have five doublesided pages of personal notes during
10.626 Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant Final Exam Instructions. This is a three-hour closed book exam. You are allowed to have five doublesided pages of personal notes during
Lightlike solitons with spin
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Lightlike solitons with spin To cite this article: Alexander A. Chernitskii 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 012016 Related content - On solitons in
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Lightlike solitons with spin To cite this article: Alexander A. Chernitskii 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 678 012016 Related content - On solitons in
The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Resonant solitons in a polydisperse bubble medium
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Resonant solitons in a polydisperse bubble medium To cite this article: I A Ogorodnikov 018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1105 01088 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Resonant solitons in a polydisperse bubble medium To cite this article: I A Ogorodnikov 018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1105 01088 View the article online
On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer
 1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
V. Electrostatics. MIT Student
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
Electrochemical Properties of Materials for Electrical Energy Storage Applications
 Electrochemical Properties of Materials for Electrical Energy Storage Applications Lecture Note 3 October 11, 2013 Kwang Kim Yonsei Univ., KOREA kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 Y 88.91 8 O 16.00 7 N 14.01 34 Se
Electrochemical Properties of Materials for Electrical Energy Storage Applications Lecture Note 3 October 11, 2013 Kwang Kim Yonsei Univ., KOREA kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 Y 88.91 8 O 16.00 7 N 14.01 34 Se
High Performance, Low Operating Voltage n-type Organic Field Effect Transistor Based on Inorganic-Organic Bilayer Dielectric System
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS High Performance, Low Operating Voltage n-type Organic Field Effect Transistor Based on Inorganic-Organic Bilayer Dielectric System To cite this
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS High Performance, Low Operating Voltage n-type Organic Field Effect Transistor Based on Inorganic-Organic Bilayer Dielectric System To cite this
Model of non-ideal detonation of condensed high explosives
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Model of non-ideal detonation of condensed high explosives To cite this article: E B Smirnov et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 774 012076 View the
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Model of non-ideal detonation of condensed high explosives To cite this article: E B Smirnov et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 774 012076 View the
Electrophoretic Deposition. - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode
 Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
MODULE No. 24: Solution Kinetics Part - III
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 6 and PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY-II (Statistical 24 and Solution Kinetics - III CHE_P6_M24 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Primary
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 6 and PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY-II (Statistical 24 and Solution Kinetics - III CHE_P6_M24 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Primary
Features of mathematical model for ignition process of a metallized condensed substance by a local energy source
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Features of mathematical model for ignition process of a metallized condensed substance by a local energy source To cite this article:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Features of mathematical model for ignition process of a metallized condensed substance by a local energy source To cite this article:
The Utility of Zeta Potential Measurements in the Characterization of CMP Slurries David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd
 The Utility of Zeta Potential Measurements in the Characterization of CMP Slurries David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd HORIBA Scientific Webinar June 12 th 2013 Dispersed Systems An interface
The Utility of Zeta Potential Measurements in the Characterization of CMP Slurries David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd HORIBA Scientific Webinar June 12 th 2013 Dispersed Systems An interface
PIC Algorithm with Multiple Poisson Equation Solves During One Time Step
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS PIC Algorithm with Multiple Poisson Equation Solves During One Time Step To cite this article: Junxue Ren et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 640 012033
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS PIC Algorithm with Multiple Poisson Equation Solves During One Time Step To cite this article: Junxue Ren et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 640 012033
Numerical modeling of a cutting torch
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Numerical modeling of a cutting torch To cite this article: B R Mancinelli et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 511 012071 View the article online for updates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Numerical modeling of a cutting torch To cite this article: B R Mancinelli et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 511 012071 View the article online for updates
Numerical Solution of Nonlinear Poisson Boltzmann Equation
 Numerical Solution of Nonlinear Poisson Boltzmann Equation Student: Jingzhen Hu, Southern Methodist University Advisor: Professor Robert Krasny A list of work done extended the numerical solution of nonlinear
Numerical Solution of Nonlinear Poisson Boltzmann Equation Student: Jingzhen Hu, Southern Methodist University Advisor: Professor Robert Krasny A list of work done extended the numerical solution of nonlinear
Metrological Characterization of Hardness Indenter Calibration System
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Metrological Characterization of Hardness Indenter Calibration System To cite this article: Cihan Kuzu et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1065 062014
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Metrological Characterization of Hardness Indenter Calibration System To cite this article: Cihan Kuzu et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1065 062014
An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential. David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd
 An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd Fundamental Parameters that control the Nature and Behavior of all Particulate
An Overview of the Concept, Measurement, Use and Application of Zeta Potential David Fairhurst, Ph.D. Colloid Consultants, Ltd Fundamental Parameters that control the Nature and Behavior of all Particulate
Fermionic matter under the effects of high magnetic fields and its consequences in white dwarfs
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Fermionic matter under the effects of high magnetic fields and its consequences in white dwarfs To cite this article: E Otoniel et al 2015 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Fermionic matter under the effects of high magnetic fields and its consequences in white dwarfs To cite this article: E Otoniel et al 2015 J. Phys.:
 Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
957 Lecture #13 of 18
 Lecture #13 of 18 957 958 Q: What was in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 2 main concepts: Section 2.1 : Section 2.3: Salt; Activity; Underpotential deposition Transference numbers; Liquid junction
Lecture #13 of 18 957 958 Q: What was in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 2 main concepts: Section 2.1 : Section 2.3: Salt; Activity; Underpotential deposition Transference numbers; Liquid junction
Initial position, x p (0)/L
 .4 ) xp().2 ) ( 2L 2 xp Dc ( Displacement, /L.2.4.5.5 Initial position, x p ()/L Supplementary Figure Computed displacements of (red) positively- and (blue) negatively-charged particles at several CO 2
.4 ) xp().2 ) ( 2L 2 xp Dc ( Displacement, /L.2.4.5.5 Initial position, x p ()/L Supplementary Figure Computed displacements of (red) positively- and (blue) negatively-charged particles at several CO 2
 Number of pages in the question paper : 06 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Number of pages in the question paper : 06 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Attraction or repulsion between charged colloids? A connection with Debye Hückel theory
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12 (2000) A263 A267. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(00)07724-9 Attraction or repulsion between charged colloids? A connection with Debye Hückel theory René van Roij H H Wills
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12 (2000) A263 A267. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(00)07724-9 Attraction or repulsion between charged colloids? A connection with Debye Hückel theory René van Roij H H Wills
Application of COMSOL Multiphysics in Nanoscale Electrokinetic Transport
 High Performance Computing Day Application of COMSOL Multiphysics in Nanoscale Electrokinetic Transport Selcuk Atalay, PhD Candidate Advisor: Prof. Shizhi Qian Institute of Micro/Nanotechnology Aerospace
High Performance Computing Day Application of COMSOL Multiphysics in Nanoscale Electrokinetic Transport Selcuk Atalay, PhD Candidate Advisor: Prof. Shizhi Qian Institute of Micro/Nanotechnology Aerospace
Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer
 Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Dry Clay Swollen Clay Repulsive electrostatics control swelling of clays in water LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Separation techniques such as : column
Electrostatic Forces & The Electrical Double Layer Dry Clay Swollen Clay Repulsive electrostatics control swelling of clays in water LiquidSolid Interface; Colloids Separation techniques such as : column
Interaction of static charges in graphene
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Interaction of static charges in graphene To cite this article: V V Braguta et al 5 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 67 7 Related content - Radiative Properties
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Interaction of static charges in graphene To cite this article: V V Braguta et al 5 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 67 7 Related content - Radiative Properties
The Effect of Electrostatic Surface Charges on Photoresist Dissolution
 Sean Burns 4/24/00 Dr. Bonnecaze ChE 385M The Effect of Electrostatic Surface Charges on Photoresist Dissolution Introduction/Motivation It would be very useful and economical to have a fundamental model
Sean Burns 4/24/00 Dr. Bonnecaze ChE 385M The Effect of Electrostatic Surface Charges on Photoresist Dissolution Introduction/Motivation It would be very useful and economical to have a fundamental model
Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation
 Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation Ion:ion interactions What is the free energy of ion:ion interactions ΔG i-i? Consider an ion in a solution
Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation Ion:ion interactions What is the free energy of ion:ion interactions ΔG i-i? Consider an ion in a solution
Title. Author(s)Tamura, Hiroki. CitationJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 279(1): 1- Issue Date Doc URL. Type.
 Title Theorization on ion-exchange equilibria: activity of Author(s)Tamura, Hiroki CitationJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 279(1): 1- Issue Date 2004-11-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/14604
Title Theorization on ion-exchange equilibria: activity of Author(s)Tamura, Hiroki CitationJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 279(1): 1- Issue Date 2004-11-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/14604
Multimedia : Boundary Lubrication Podcast, Briscoe, et al. Nature , ( )
 3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
Density dependence of dielectric permittivity of water and estimation of the electric field for the breakdown inception
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Density dependence of dielectric permittivity of water and estimation of the electric field for the breakdown inception To cite this article: D I
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Density dependence of dielectric permittivity of water and estimation of the electric field for the breakdown inception To cite this article: D I
Quantum phase transition and conductivity of parallel quantum dots with a moderate Coulomb interaction
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Quantum phase transition and conductivity of parallel quantum dots with a moderate Coulomb interaction To cite this article: V S Protsenko and A
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Quantum phase transition and conductivity of parallel quantum dots with a moderate Coulomb interaction To cite this article: V S Protsenko and A
O 3. : Er nanoparticles prospective system for energy convertors
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Interband optical transitions in Gd 2 O 3 : Er nanoparticles prospective system for energy convertors To cite this article: A
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Interband optical transitions in Gd 2 O 3 : Er nanoparticles prospective system for energy convertors To cite this article: A
Simulation of Surface Plasmon Resonance on Different Size of a Single Gold Nanoparticle
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of Surface Plasmon Resonance on Different Size of a Single Gold Nanoparticle To cite this article: Norsyahidah Md Saleh and A. Abdul Aziz
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of Surface Plasmon Resonance on Different Size of a Single Gold Nanoparticle To cite this article: Norsyahidah Md Saleh and A. Abdul Aziz
NaTa0 3. /MCM-48 composites for photocatalytic conversion of organic molecules. Journal of Physics: Conference Series.
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS NaTa0 3 /MCM-48 composites for photocatalytic conversion of organic molecules To cite this article: K Senevirathne et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS NaTa0 3 /MCM-48 composites for photocatalytic conversion of organic molecules To cite this article: K Senevirathne et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Physical chemistry of surfaces
 Physical chemistry of surfaces Nanostructures possess a large fraction of surface atoms per unit volume. The physical and chemical properties of surfaces have great importance when describing general properties
Physical chemistry of surfaces Nanostructures possess a large fraction of surface atoms per unit volume. The physical and chemical properties of surfaces have great importance when describing general properties
A Simple Procedure to Determine Surface Charging Parameters in Aqueous Solutions
 A Simple Procedure to Determine Surface Charging Parameters in Aqueous Solutions Theresa Feltes and Melanie Timmons under the supervision of Dr. John Regalbuto The measurement technique of equilibrium
A Simple Procedure to Determine Surface Charging Parameters in Aqueous Solutions Theresa Feltes and Melanie Timmons under the supervision of Dr. John Regalbuto The measurement technique of equilibrium
On the deformed Einstein equations and quantum black holes
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS On the deformed Einstein euations and uantum black holes To cite this article: E Dil et al 016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 766 01004 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS On the deformed Einstein euations and uantum black holes To cite this article: E Dil et al 016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 766 01004 View the article online
Characterisation of Nanoparticle Structure by High Resolution Electron Microscopy
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Characterisation of Nanoparticle Structure by High Resolution Electron Microscopy To cite this article: Robert D Boyd et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 522
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Characterisation of Nanoparticle Structure by High Resolution Electron Microscopy To cite this article: Robert D Boyd et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 522
Inductance and Current Distribution Analysis of a Prototype HTS Cable
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Inductance and Current Distribution Analysis of a Prototype HTS Cable To cite this article: Jiahui Zhu et al J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 7 7 Recent citations
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Inductance and Current Distribution Analysis of a Prototype HTS Cable To cite this article: Jiahui Zhu et al J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 7 7 Recent citations
Effects of femtosecond laser radiation on the skin
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of femtosecond laser radiation on the skin To cite this article: P Yu Rogov and V G Bespalov 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 735 012032 View the
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of femtosecond laser radiation on the skin To cite this article: P Yu Rogov and V G Bespalov 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 735 012032 View the
Slow viscous flow in a microchannel with similar and different superhydrophobic walls
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Slow viscous flow in a microchannel with similar and different superhydrophobic walls To cite this article: A I Ageev and A N Osiptsov 2018 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Slow viscous flow in a microchannel with similar and different superhydrophobic walls To cite this article: A I Ageev and A N Osiptsov 2018 J. Phys.:
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian. which is given in spherical coordinates by (2)
 1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
Electrical double layer interactions between dissimilar oxide surfaces with charge regulation and Stern Grahame layers
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 296 (2006) 150 158 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis Electrical double layer interactions between dissimilar oxide surfaces with charge regulation and Stern Grahame
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 296 (2006) 150 158 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis Electrical double layer interactions between dissimilar oxide surfaces with charge regulation and Stern Grahame
Surface Charge of Silver Iodide and Several Metal Oxides. Are All Surfaces Nernstian?
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 227, 152 163 (2000) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.6847, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Surface Charge of Silver Iodide and Several Metal Oxides. Are
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 227, 152 163 (2000) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.6847, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Surface Charge of Silver Iodide and Several Metal Oxides. Are
Determination of the Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic Impurity Magnetic Susceptibility in Ge:As near the Metal Insulator phase Transition
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Determination of the Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic Impurity Magnetic Susceptibility in Ge:As near the Metal Insulator phase Transition To cite this
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Determination of the Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic Impurity Magnetic Susceptibility in Ge:As near the Metal Insulator phase Transition To cite this
Theoretische Physik 2: Elektrodynamik (Prof. A-S. Smith) Home assignment 11
 WiSe 22..23 Prof. Dr. A-S. Smith Dipl.-Phys. Matthias Saba am Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Physik I Department für Physik Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg Problem. Theoretische Physik 2:
WiSe 22..23 Prof. Dr. A-S. Smith Dipl.-Phys. Matthias Saba am Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Physik I Department für Physik Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg Problem. Theoretische Physik 2:
1.5 μm InAs/InGaAsP/InP quantum dot laser with improved temperature stability
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS 1.5 μm InAs/InGaAsP/InP quantum dot laser with improved temperature stability To cite this article: F I Zubov et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 741
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS 1.5 μm InAs/InGaAsP/InP quantum dot laser with improved temperature stability To cite this article: F I Zubov et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 741
Coherence of Noisy Oscillators with Delayed Feedback Inducing Multistability
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Coherence of Noisy Oscillators with Delayed Feedback Inducing Multistability To cite this article: Anastasiya V Pimenova and Denis S Goldobin 2016
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Coherence of Noisy Oscillators with Delayed Feedback Inducing Multistability To cite this article: Anastasiya V Pimenova and Denis S Goldobin 2016
A Solution of the Spherical Poisson-Boltzmann Equation
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 1, 018, no. 1, 1-7 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.1988/ijma.018.71155 A Solution of the Spherical Poisson-Boltzmann quation. onseca
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 1, 018, no. 1, 1-7 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.1988/ijma.018.71155 A Solution of the Spherical Poisson-Boltzmann quation. onseca
Research Statement. Shenggao Zhou. November 3, 2014
 Shenggao Zhou November 3, My research focuses on: () Scientific computing and numerical analysis (numerical PDEs, numerical optimization, computational fluid dynamics, and level-set method for interface
Shenggao Zhou November 3, My research focuses on: () Scientific computing and numerical analysis (numerical PDEs, numerical optimization, computational fluid dynamics, and level-set method for interface
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications. CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications
 CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications History of Nanotechnology: Time Line Democritus in ancient Greece: concept of atom 1900 : Rutherford : discovery of atomic nucleus The first TEM was
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications History of Nanotechnology: Time Line Democritus in ancient Greece: concept of atom 1900 : Rutherford : discovery of atomic nucleus The first TEM was
Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants
 Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants Fuquan Tu, Bum Jun Park and Daeyeon Lee*. Description of the term notionally swollen droplets When particles are adsorbed
Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants Fuquan Tu, Bum Jun Park and Daeyeon Lee*. Description of the term notionally swollen droplets When particles are adsorbed
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Electrokinetics in porous media Luong, D.T. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Electrokinetics in porous media Luong, D.T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Luong, D. T. (2014). Electrokinetics in porous media General
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Electrokinetics in porous media Luong, D.T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Luong, D. T. (2014). Electrokinetics in porous media General
Turbulent flow of oil-water emulsions with polymer additives
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Turbulent flow of oil-water emulsions with polymer additives To cite this article: V N Manzhai et al 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Turbulent flow of oil-water emulsions with polymer additives To cite this article: V N Manzhai et al 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
Studies on the concentration dependence of specific rotation of Alpha lactose monohydrate (α-lm) aqueous solutions and growth of α-lm single crystals
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Studies on the concentration dependence of specific rotation of Alpha lactose monohydrate (α-lm) aqueous solutions and growth
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Studies on the concentration dependence of specific rotation of Alpha lactose monohydrate (α-lm) aqueous solutions and growth
Diffusion of silver in silicate glass and clustering in hydrogen atmosphere
 Defect and Diffusion Forum Vols. 7-4 (5) pp. 689-694 online at http://www.scientific.net 5 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Diffusion of silver in silicate glass and clustering in hydrogen atmosphere
Defect and Diffusion Forum Vols. 7-4 (5) pp. 689-694 online at http://www.scientific.net 5 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Diffusion of silver in silicate glass and clustering in hydrogen atmosphere
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015,
 Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
INCLUSION OF ELECTROSTATIC FORCES TO ASSESSMENT OF RATE OF MAGNETIC FORCES IMPACT TO IRON NANOPARTICLE AGGREGATION
 INCLUSION OF ELECTROSTATIC FORCES TO ASSESSMENT OF RATE OF MAGNETIC FORCES IMPACT TO IRON NANOPARTICLE AGGREGATION Dana ROSICKA a, Jan SEMBERA a a Technical University of Liberec, Studentska 2, 461 17
INCLUSION OF ELECTROSTATIC FORCES TO ASSESSMENT OF RATE OF MAGNETIC FORCES IMPACT TO IRON NANOPARTICLE AGGREGATION Dana ROSICKA a, Jan SEMBERA a a Technical University of Liberec, Studentska 2, 461 17
Convex and concave successions of power-law decays in small-angle scattering
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Convex and concave successions of power-law decays in small-angle scattering To cite this article: E M Anitas 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 738 012022
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Convex and concave successions of power-law decays in small-angle scattering To cite this article: E M Anitas 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 738 012022
Measurement of the bending of thin inclined nanowires as a method for determining elastic modulus
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Measurement of the bending of thin inclined nanowires as a method for determining elastic modulus To cite this article: M S Dunaevskiy
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Measurement of the bending of thin inclined nanowires as a method for determining elastic modulus To cite this article: M S Dunaevskiy
Multiscale integral analysis of a HT leakage in a fusion nuclear power plant
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Multiscale integral analysis of a HT leakage in a fusion nuclear power plant To cite this article: M Velarde et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 717
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Multiscale integral analysis of a HT leakage in a fusion nuclear power plant To cite this article: M Velarde et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 717
Applying a cellular automaton model to describing the anomalous relaxation of the metastable states in the disordered porous media
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Applying a cellular automaton model to describing the anomalous relaxation of the metastable states in the disordered porous media o cite this article:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Applying a cellular automaton model to describing the anomalous relaxation of the metastable states in the disordered porous media o cite this article:
Surface interactions part 1: Van der Waals Forces
 CHEM-E150 Interfacial Phenomena in Biobased Systems Surface interactions part 1: Van der Waals Forces Monika Österberg Spring 018 Content Colloidal stability van der Waals Forces Surface Forces and their
CHEM-E150 Interfacial Phenomena in Biobased Systems Surface interactions part 1: Van der Waals Forces Monika Österberg Spring 018 Content Colloidal stability van der Waals Forces Surface Forces and their
Influence of an Electric Field on the Propagation of a Photon in a Magnetic field
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of an Electric Field on the Propagation of a Photon in a Magnetic field To cite this article: V M Katkov 06 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 73 0003
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of an Electric Field on the Propagation of a Photon in a Magnetic field To cite this article: V M Katkov 06 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 73 0003
Particles in aqueous environments
 Lecture 11 Particle-Aqueous Solute Interactions Today 1. Particle types and sizes 2. Particle charges 3. Particle-solute Interactions Next time Please continue to read Manahan Chapter 4. 1. Fresh-salt
Lecture 11 Particle-Aqueous Solute Interactions Today 1. Particle types and sizes 2. Particle charges 3. Particle-solute Interactions Next time Please continue to read Manahan Chapter 4. 1. Fresh-salt
Supporting Information for. Concentration dependent effects of bovine serum albumin on graphene
 Supporting Information for Concentration dependent effects of bovine serum albumin on graphene oxide colloidal stability in aquatic environment Binbin Sun, Yinqing Zhang, Wei Chen, Kunkun Wang, Lingyan
Supporting Information for Concentration dependent effects of bovine serum albumin on graphene oxide colloidal stability in aquatic environment Binbin Sun, Yinqing Zhang, Wei Chen, Kunkun Wang, Lingyan
Chapter 8 - Activity
 Chapter 8 - Activity dilute solution Ions in concentrated solution interact CM 320 Lecture 10 Chap 8 ow do ionized species interact in solution? The charge on the ions attracts or repels other ionic species
Chapter 8 - Activity dilute solution Ions in concentrated solution interact CM 320 Lecture 10 Chap 8 ow do ionized species interact in solution? The charge on the ions attracts or repels other ionic species
An analytical method for the inverse Cauchy problem of Lame equation in a rectangle
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS An analytical method for the inverse Cauchy problem of Lame equation in a rectangle To cite this article: Yu Grigor ev 218 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 991
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS An analytical method for the inverse Cauchy problem of Lame equation in a rectangle To cite this article: Yu Grigor ev 218 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 991
Research Article Surface Potential of Polycrystalline Hematite in Aqueous Medium
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Electrochemistry Volume 2011, Article ID 412731, 6 pages doi:10.4061/2011/412731 Research Article Surface Potential of Polycrystalline Hematite in Aqueous
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Electrochemistry Volume 2011, Article ID 412731, 6 pages doi:10.4061/2011/412731 Research Article Surface Potential of Polycrystalline Hematite in Aqueous
Stability of colloidal systems
 Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Supporting Information for Lysozyme Adsorption in ph-responsive Hydrogel Thin-Films: The non-trivial Role of Acid-Base Equilibrium
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Supporting Information for Lysozyme Adsorption in ph-responsive Hydrogel Thin-Films: The non-trivial
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Supporting Information for Lysozyme Adsorption in ph-responsive Hydrogel Thin-Films: The non-trivial
Interaction of impeller and guide vane in a seriesdesigned
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Interaction of impeller and guide vane in a seriesdesigned axial-flow pump To cite this article: S Kim et al 212 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Interaction of impeller and guide vane in a seriesdesigned axial-flow pump To cite this article: S Kim et al 212 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci.
Shear Flow of a Nematic Liquid Crystal near a Charged Surface
 Physics of the Solid State, Vol. 45, No. 6, 00, pp. 9 96. Translated from Fizika Tverdogo Tela, Vol. 45, No. 6, 00, pp. 5 40. Original Russian Text Copyright 00 by Zakharov, Vakulenko. POLYMERS AND LIQUID
Physics of the Solid State, Vol. 45, No. 6, 00, pp. 9 96. Translated from Fizika Tverdogo Tela, Vol. 45, No. 6, 00, pp. 5 40. Original Russian Text Copyright 00 by Zakharov, Vakulenko. POLYMERS AND LIQUID
Determination of Dynamic Characteristics of the Frame Bearing Structures of the Vibrating Separating Machines
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Determination of Dynamic Characteristics of the Frame Bearing Structures of the Vibrating Separating Machines To cite this article:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Determination of Dynamic Characteristics of the Frame Bearing Structures of the Vibrating Separating Machines To cite this article:
Development of Porosity Measurement Method in Shale Gas Reservoir Rock
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Development of Measurement Method in Shale Gas Reservoir Rock To cite this article: Alita Siswandani and BagusEndar B. Nurhandoko 2016 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Development of Measurement Method in Shale Gas Reservoir Rock To cite this article: Alita Siswandani and BagusEndar B. Nurhandoko 2016 J. Phys.:
Spring 2009 EE 710: Nanoscience and Engineering
 Spring 009 EE 710: Nanoscience and Engineering Part 10: Surface Plasmons in Metals Images and figures supplied from Hornyak, Dutta, Tibbals, and Rao, Introduction to Nanoscience, CRC Press Boca Raton,
Spring 009 EE 710: Nanoscience and Engineering Part 10: Surface Plasmons in Metals Images and figures supplied from Hornyak, Dutta, Tibbals, and Rao, Introduction to Nanoscience, CRC Press Boca Raton,
VI. EIS STUDIES LEAD NANOPOWDER
 VI. EIS STUDIES LEAD NANOPOWDER 74 26. EIS Studies of Pb nanospheres Impedance (valid for both DC and AC), a complex resistance occurs when current flows through a circuit (composed of various resistors,
VI. EIS STUDIES LEAD NANOPOWDER 74 26. EIS Studies of Pb nanospheres Impedance (valid for both DC and AC), a complex resistance occurs when current flows through a circuit (composed of various resistors,
Phenols removal using ozonation-adsorption with granular activated carbon (GAC) in rotating packed bed reactor
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Phenols removal using ozonation-adsorption with granular activated carbon (GAC) in rotating packed bed reactor To cite this article:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Phenols removal using ozonation-adsorption with granular activated carbon (GAC) in rotating packed bed reactor To cite this article:
Integrable Hamiltonian systems generated by antisymmetric matrices
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Integrable Hamiltonian systems generated by antisymmetric matrices To cite this article: Alina Dobrogowska 013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 474 01015 View the
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Integrable Hamiltonian systems generated by antisymmetric matrices To cite this article: Alina Dobrogowska 013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 474 01015 View the
Soft Matter and Biological Physics
 Dr. Ulrich F. Keyser - ufk20 (at) cam.ac.uk Soft Matter and Biological Physics Question Sheet Michaelmas 2011 Version: November 2, 2011 Question 0: Sedimentation Initially consider identical small particles
Dr. Ulrich F. Keyser - ufk20 (at) cam.ac.uk Soft Matter and Biological Physics Question Sheet Michaelmas 2011 Version: November 2, 2011 Question 0: Sedimentation Initially consider identical small particles
The Poisson Boltzmann equation and the charge separation phenomenon at the silica-water interface: A holistic approach
 The Poisson oltzmann equation and the charge separation phenomenon at the silica-water interface: A holistic approach Maijia Liao 1, Li Wan 2, Shixin Xu 3, Chun Liu 4, Ping Sheng 1,* 1 Department of Physics,
The Poisson oltzmann equation and the charge separation phenomenon at the silica-water interface: A holistic approach Maijia Liao 1, Li Wan 2, Shixin Xu 3, Chun Liu 4, Ping Sheng 1,* 1 Department of Physics,
Modelling ph-dependent and Microstructure-Dependent Streaming Potential Coefficient and Zeta Potential of Porous Sandstones
 Transp Porous Med (2018) 124:31 56 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1036-z Modelling ph-dependent and Microstructure-Dependent Streaming Potential Coefficient and Zeta Potential of Porous Sandstones
Transp Porous Med (2018) 124:31 56 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1036-z Modelling ph-dependent and Microstructure-Dependent Streaming Potential Coefficient and Zeta Potential of Porous Sandstones
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Approved Learning Outcomes Approved May 2017 at Departmental Retreat
 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Approved Learning Outcomes Approved May 2017 at Departmental Retreat Chem 101 Critique and give examples of how understanding and applying chemistry is a means
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Approved Learning Outcomes Approved May 2017 at Departmental Retreat Chem 101 Critique and give examples of how understanding and applying chemistry is a means
Surface-enhanced raman scattering from a layer of gold nanoparticles
 VNU Journal of Science, Mathematics - Physics 26 (2010) 187-192 Surface-enhanced raman scattering from a layer of gold nanoparticles Nguyen The Binh *, Nguyen Thanh Dinh, Nguyen Quang Dong, Vu Thi Khanh
VNU Journal of Science, Mathematics - Physics 26 (2010) 187-192 Surface-enhanced raman scattering from a layer of gold nanoparticles Nguyen The Binh *, Nguyen Thanh Dinh, Nguyen Quang Dong, Vu Thi Khanh
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems
 BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Catalysis of environmental reactions Dr. Zifei Liu Catalysis and catalysts Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Catalysis of environmental reactions Dr. Zifei Liu Catalysis and catalysts Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation
Second Quantization Model of Surface Plasmon Polariton at Metal Planar Surface
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Second Quantization Model of Surface Plasmon Polariton at Metal Planar Surface To cite this article: Dao Thi Thuy Nga et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Second Quantization Model of Surface Plasmon Polariton at Metal Planar Surface To cite this article: Dao Thi Thuy Nga et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf.
Classical Models of the Interface between an Electrode and Electrolyte. M.Sc. Ekaterina Gongadze
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 009 Milan Classical Models of the Interface between an Electrode and Electrolyte M.Sc. Ekaterina Gongadze Faculty of Informatics and Electrical Engineering Comsol Conference
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 009 Milan Classical Models of the Interface between an Electrode and Electrolyte M.Sc. Ekaterina Gongadze Faculty of Informatics and Electrical Engineering Comsol Conference
Overview of DLVO Theory
 Overview of DLVO Theory Gregor Trefalt and Michal Borkovec Email. gregor.trefalt@unige.ch, michal.borkovec@unige.ch September 29, 214 Direct link www.colloid.ch/dlvo Derjaguin, Landau, Vervey, and Overbeek
Overview of DLVO Theory Gregor Trefalt and Michal Borkovec Email. gregor.trefalt@unige.ch, michal.borkovec@unige.ch September 29, 214 Direct link www.colloid.ch/dlvo Derjaguin, Landau, Vervey, and Overbeek
