Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
|
|
|
- Ilene Francis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6 Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity آلکن ها: ساختار و واکنش پذیری Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
2 2 Alkene - Hydrocarbon With Carbon-Carbon Double Bond Also called an olefin but alkene is better Includes many naturally occurring materials Flavors, fragrances, vitamins طعم دهنده ها خوشبوکننده ها ویتامین ها سقز از درخت ب ن ه
3 3 Why this Chapter? C=C double bonds are present in most organic and biological molecules To examine consequences of alkene stereoisomerism To focus on general alkene reaction: electrophilic addition
4 4 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes Ethylene and propylene are the most important organic chemicals produced Made by thermal cracking of light alkanes (petroleum)
5 5 6.2 Calculating Degree of Unsaturation محاسبه درجه سیرنشدگی Relates molecular formula to possible structures Degree of unsaturation سیرنشدگی :درجه number of multiple bonds or rings Formula for a saturated acyclic ) خطی )سیرشده compound is C n H 2n+2 Each ring or multiple bond replaces 2 H's سیرشده سیرنشده
6 6 Example: C 6 H 10 MW = 6 x x 1= 82 Saturated is C 6 H 14 Therefore 4 H's are not present This has two degrees of unsaturation Two double bonds? 2 = or two rings? درجه سیرنشدگی or ring and double bond? or triple bond?
7 7 Degree of Unsaturation With Other Elements Organohalogens (X: F, Cl, Br, I) Halogen replaces hydrogen C 4 H 6 Br 2 and C 4 H 8 have one degree of unsaturation Organoxygen compounds (C,H,O) - if connected by single bonds These don't affect the total count of H's
8 8 Organonitrogen compounds Nitrogen has three bonds So if it connects where H was, it adds a connection point Subtract one H for equivalent degree of unsaturation in hydrocarbon
9 Summary - Degree of Unsaturation Method 1 Add the number of halogens to the number of hydrogens. Ignore the number of oxygens. Subtract the number of nitrogens from the number of hydrogens. Method 2 Method 3 H sat 2C 2 X N (ignore O,S) Degree of Unsaturation H sat - H 2 act = درجه سیرنشدگی )2- ظرفیت( تعداد اتم
10 10 :مثال درجه سیرنشدگی = C 20 H 32 ClN = 2 )2- ظرفیت( تعداد اتم (4-2) + 32(1-2) +1(1-2)+1(3-2) 2 Diazepam, marketed as an antianxiety medication under the name Valium, has three rings, eight double bonds, and the formula C 16 H? ClN 2 O. How many hydrogens does diazepam have? (Calculate the answer; don t count hydrogens in the structure.) = 5 No.H + No.X = = 33 - No.N = 33-1 = 32 C n H 2n+2 = C 20 H = / 2 = 5 = 2+16(4-2) +X(1-2)+1(1-2)+2(3-2)+1(2-2) = 11 2 = -X+35 = 11 2 X= 13 C 16 H 13 ClN 2 O
11 6.3 Naming of Alkenes Name the parent hydrocarbon change ending to ene Number carbons in chain so that double bond carbons have lowest possible numbers Alkenes higher priority than alkanes: even shorter chain Multiple C=C are named as diene triene tetraene etc Rings have cyclo prefix double bond always C#1, C#2 11
12 12 Many Alkenes Are Known by Common Names
13 6.4 Cis-Trans Isomerism in Alkenes Carbon atoms in a double bond are sp 2 -hybridized Three equivalent orbitals at 120º separation in plane Fourth orbital is atomic p orbital Combination of electrons in two sp 2 orbitals of two atoms forms bond between them Additive interaction of p orbitals creates a bonding orbital Occupied orbital prevents rotation about -bond Rotation prevented by bond - high barrier, about 268 kj/mole in ethylene 13
14 14 Rotation of Bond Is Prohibitive This prevents rotation about a carbon-carbon double bond (unlike a carbon-carbon single bond). Creates possible alternative structures
15 15 The presence of a carbon-carbon double bond can create two possible structures cis isomer - two similar groups on same side of the double bond trans isomer - similar groups on opposite sides Each carbon must have two different groups for these isomers to occur
16 16 Cis, Trans Isomers Require That End Groups Must Differ in Pairs 180 rotation superposes Bottom pair cannot be superposed without breaking C=C
17 Sequence Rules: The E,Z Designation قواعد ترتیب تقدم : سیستم E, Z نامگذاری Neither compound is clearly cis or trans Substituents on C1 are different than those on C2 We need to define similarity in a precise way to distinguish the two stereoisomers Cis, trans nomenclature only works for disubstituted double bonds E/Z Nomenclature for 3 or 4 substituents
18 E,Z Stereochemical Nomenclature Priority rules )قواعد ترتیب تقدم( of Cahn, Ingold, and Prelog Compare where higher priority groups are with respect to bond and designate as prefix E -entgegen, opposite sides Z - zusammen, together on the same side Hi(C1)-Low(C1)-Hi(C2)-Lo(C2) 18
19
20 Ranking Priorities: Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules RULE 1 Must rank atoms that are connected at comparison point Higher atomic number gets higher priority Br > Cl > S > P > O > N > C > H
21 21 Extended Comparison RULE 2 If atomic numbers are the same, compare at next connection point at same distance Compare until something has higher atomic number Do not combine always compare
22 22 Dealing With Multiple Bonds: RULE 3 Substituent is drawn with connections shown and no double or triple bonds
23
24 Stability of Alkenes پایداری آلکن ها Cis alkenes are less stable than trans alkenes Compare heat given off on hydrogenation: H o Less stable isomer is higher in energy And gives off more heat tetrasubstituted > trisubstituted > disubstituted > monosusbtituted hyperconjugation ) شدن موقت )مزدوج stabilizes ازدحام فضایی 2/8 ناپایدارتر از kj/mol
25 25 Comparing Stabilities of Alkenes Evaluate heat given off when C=C is converted to C-C More stable alkene gives off less heat ( G o cis > G o trans) 2/8 kj/mol
26 trans-butene generates 4 kj less heat than cis-butene CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 but the numbers aren t exactly the same 4 kj/mol (energy difference) 2.8 kj/mole (quilibrium data) for two reasons: 1. There is probably some experimental error, since heats of hydrogenation are difficult to measure accurately. 2. Heats of reaction and equilibrium constants don t measure exactly the same thing. Heats of reaction measure H, equilibrium constants measure G a (slight difference between the two) 26
27 Alkenes become more stable with increasing substitution: As a general rule, alkenes follow the stability order: This order of stability is due to: )مزدوج شدن موقت( Hyperconjugation )قدرت پیوند( bond strength
28 28 )مزدوج شدن موقت( Hyperconjugation Electrons in neighboring filled orbital stabilize vacant antibonding orbital net positive interaction برهم کنش پایدارکننده ای بین اوربیتال ضدپیوندی پرنشده C=C شده پیوند C-H برروی استخالف های مجاور و اوربیتال پر
29 Alkyl groups are better than H 29
30 30 Hyperconjugation involves a sigma orbital component, usually a C-C or C-H bond. Resonance involves pi orbitals Alternative Explanation: )قدرت پیوند( bond strength sp 3 sp 2 bond > sp 3 sp 3 bond
31 6.7 Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes General reaction mechanism: electrophilic addition Attack of electrophile (such as HBr) on bond of alkene Produces carbocation and bromide ion Carbocation is an electrophile, reacting with nucleophilic bromide ion 31
32 32 Electrophilic Addition Energy Path Two step process First transition state is high energy point
33 Electrophilic Addition for preparations The reaction is successful with HCl and with HI as well as HBr HI is generated from KI and phosphoric acid 33
34 6.8 Orientation of Electrophilic Addition: قاعده مارکونیکوف Markovnikov s Rule In an unsymmetrical alkene, HX reagents can add in two different ways, but one way may be preferred over the other If one orientation predominates, the reaction is regiospecific )جهت ویژه( Markovnikov observed in the 19 th century that in the addition of HX to alkene, the H attaches to the carbon with the most H s and X attaches to the other end (to the one with the most alkyl substituents) This is Markovnikov s rule. 34
35 Example of Markovnikov s Rule Addition of HCl to 2-methylpropene Regiospecific one product forms where two are possible جهت ویژه واکنشی که افزایش فقط در یکی از دوجهت ممکن صورت می گیرد If both ends have similar substitution, then not regiospecific 35
36 Markovnikov s Rule )به بیان دیگر( (restated) More highly substituted carbocation forms as intermediate rather than less highly substituted one Tertiary cations and associated transition states are more stable than primary cations 36
37 Carbocation Structure and Stability Carbocations are planar and the tricoordinate carbon is surrounded by only 6 electrons in sp 2 orbitals The fourth orbital on carbon is a vacant p-orbital The stability of the carbocation (measured by energy needed to form it from R-X) is increased by the presence of alkyl substituents (Hyperconjugation stabilizes C+) اوربیتال p خالی از الکترون
38 The stability of carbocation (R + ) can be determined by measuring energy needed to form it from R-X: تعیین پایداری کربوکاتیون می تواند توسط اندازه گیری انرژی الزم برای تشکیل آن از R-X بدست آید R-X R + + :X - 3º alkyl halides dissociate to give R + more easily than 2º and 1º تفکیک هالید نوع سوم بسیار سریع تر نوع اول و دوم است
39 Inductive stabilization of پایداری القایی cation species 39 هرچه تعداد گروههای آلکیل بیشتری به کربن مثبت متصل باشد چگالی الکترونی بیشتر و میزان کم الکترونی کربن مثبت ( رنگ آبی( کاسته می شود Hyperconjugation )مزدوج شدن موقت( هرچه تعداد گروههای آلکیل واقع بر روی کربوکاتیون بیشتر باشد امکان بیشتری برای مزدوج شدن موقت و ایجاد کربوکاتیونی پایدارتر وجود خواهد داشت.
40 The Hammond Postulate پذیره هاموند If carbocation intermediate is more stable than another, why is the reaction through the more stable one faster? چرا پایداری یک کربوکاتیون بر سرعت تشکیل آن اثر گذاشته و ساختار محصول نهایی را تعیین می کند The relative stability of the intermediate is related to an equilibrium constant ( Gº) پایداری نسبی حدواسط کربوکاتیون به وسیله ( Gº) تعیین می شود The relative stability of the transition state (which describes the size of the rate constant) is the activation energy ( G ) اما سرعت واکنش به وسیله انرژی فعال سازی ) ( G بدست می آید The transition state is transient and cannot be examined حاالت گذار حاالت گذرایی هستند و به دلیل عمر بسیار کوتاه خود قابل بررسی نیستند
41 41 Transition State Structures A transition state is the highest energy species in a reaction step یک حالت گذار عبارت از پرانرژی ترین جزء در یک مرحله واکنش است By definition, its structure is not stable enough to exist for one vibration برطبق تعریف ساختار آنها به اندازه کافی پایدار نیست که قابل مشاهده باشند But the structure controls the rate of reaction اما ساختار آنها سرعت واکنش را کنترل می نمایند So we need to be able to guess about its properties in an informed way We classify them in general ways and look for trends in reactivity the conclusions are in the Hammond Postulate The structure of the transition state resembles the structure of the nearest stable species. T.S. for Endergonic steps resemble products. T.S. for Exergonic steps resemble reactants. ساختار یک حالت گذار به ساختار نزدیک ترین گونه شیمیایی پایدار شباهت دارد T.S. مراحل انرژی خواه از لحاظ ساختاری به فرآورده ها و T.S. مراحل انرژی زا از لحاظ ساختاری به واکنش دهندگان شباهت دارد
42 Examination of the Hammond Postulate A transition state should be similar to an intermediate that is close in energy Sequential states on a reaction path that are close in energy are likely to be close in structure - G. S. Hammond واکنش آهسته تر منجر به تولید حدواسط پایدارتری می شود در مرحله انرژی زا ترازهای انرژی حالت گذار و واکنش دهنده مشابه هستند واکنش سریع تر حدواسط پایدارتری تولید می کند در مرحله انرژی خواه ترازهای انرژی حالت گذار و فرآورده مشابه هستند 42
43 43 Competing Reactions and the Hammond Postulate Normal Expectation: Faster reaction gives stable intermediate حدواسط شبیه به حالت گذار Intermediate resembles transition state است تشکیل یک کربوکاتیون با پروتون دار شدن یک آلکن مرحله ای انرژی خواه است. بنابراین حالت گذار پروتون دار شدن آلکن از لحاظ ساختاری باید به حدواسط کربوکاتیونی شباهت داشته باشد
44 Mechanism of Electrophilic Addition: Rearrangements of Carbocations Carbocations undergo structural rearrangements following set patterns 1,2-H and 1,2-alkyl shifts occur Goes to give more stable carbocation Can go through less stable ions as intermediates
45 Alkyl Shifts Can Also Occur 45
Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) Can act as weak nucleophiles
 Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
Alkenes. Structure, Nomenclature, and an introduc1on to Reac1vity Thermodynamics and Kine1cs
 Alkenes Structure, Nomenclature, and an introduc1on to Reac1vity Thermodynamics and Kine1cs 1 Alkene - Hydrocarbon With Carbon- Carbon Double Bond Also called an olefin but alkene is be>er Hydrocarbon
Alkenes Structure, Nomenclature, and an introduc1on to Reac1vity Thermodynamics and Kine1cs 1 Alkene - Hydrocarbon With Carbon- Carbon Double Bond Also called an olefin but alkene is be>er Hydrocarbon
Alkenes and Alkynes 10/27/2010. Chapter 7. Alkenes and Alkynes. Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes CHP6 Problems: 6.1-13, 16-34, 36. CHP7 Problems: 7.1-23, 25-28, 31-34, 37-39, 41-47, 49-56. Alkenes and Alkynes Alkene (or olefin ) Hydrocarbon that contains a carbon-carbon
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes CHP6 Problems: 6.1-13, 16-34, 36. CHP7 Problems: 7.1-23, 25-28, 31-34, 37-39, 41-47, 49-56. Alkenes and Alkynes Alkene (or olefin ) Hydrocarbon that contains a carbon-carbon
Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds.
 Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
1. Root of name depends on longest chain of C containing the double bond; ends in "ene"
 Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
An Overview of Organic Reactions
 5 An Overview of Organic Reactions نگاهی اجمالی به واکنش های شیمیایی Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know:
5 An Overview of Organic Reactions نگاهی اجمالی به واکنش های شیمیایی Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know:
به نام خدا. Organic Chemistry 1. Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran
 به نام خدا 3 Organic Chemistry 1 Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir 3 Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry ترکیبات آلی:
به نام خدا 3 Organic Chemistry 1 Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir 3 Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry ترکیبات آلی:
Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry
 3 Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry ترکیبات آلی: آلکان ها و استریوشیمی آنها Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Why this Chapter Alkanes are unreactive, but provide useful
3 Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry ترکیبات آلی: آلکان ها و استریوشیمی آنها Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Why this Chapter Alkanes are unreactive, but provide useful
Ch.6 Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
 alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases
 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases پیوندهای کوواالنسی قطبی اسیدها و بازها Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition چرا این فصل Description of basic ways chemists account for chemical reactivity.
2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases پیوندهای کوواالنسی قطبی اسیدها و بازها Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition چرا این فصل Description of basic ways chemists account for chemical reactivity.
Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations
 11 Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations واکنش آلکیل هالیدها: جانشینی هسته دوستی و حذف Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir
11 Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations واکنش آلکیل هالیدها: جانشینی هسته دوستی و حذف Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir
به نام خدا. Organic Chemistry 1. Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran
 به نام خدا 8 Organic Chemistry 1 Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir 8 Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis آلکین ها: مقدمه ای
به نام خدا 8 Organic Chemistry 1 Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir 8 Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis آلکین ها: مقدمه ای
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Excluded sections 3.15&3.16
 Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes
 Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
5.1 Alkene Nomenclature
 5.1 Alkene Nomenclature Alkenes Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain a carbon-carbon double bond also called "olefins" characterized by molecular formula n 2n said to be "unsaturated" Alkene Nomenclature
5.1 Alkene Nomenclature Alkenes Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain a carbon-carbon double bond also called "olefins" characterized by molecular formula n 2n said to be "unsaturated" Alkene Nomenclature
Stereochemistry. Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran
 9 Stereochemistry استریوشیمی Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Stereochemistry Some
9 Stereochemistry استریوشیمی Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Stereochemistry Some
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
به نام خدا شیمی آلی 1. Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran
 به نام خدا 4 شیمی آلی 1 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran 4 Organic Compounds: Cycloalkanes and their Stereochemistry ترکیبات آلی: سیکلوآلکان ها و استریوشیمی آنها
به نام خدا 4 شیمی آلی 1 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran 4 Organic Compounds: Cycloalkanes and their Stereochemistry ترکیبات آلی: سیکلوآلکان ها و استریوشیمی آنها
Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
 7 Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis آلکن ها: واکنش ها و سنتز Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7
7 Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis آلکن ها: واکنش ها و سنتز Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Loudon Ch. 4 Review: Alkene Structure/Reactivity Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 5/30/2017
 We already saw in Ch. 1 that π bonds are based on side-on overlap of leftover p orbitals. C atom C=C bond C atom orbital comes from destructive (differentcolor) interference: (note extra node) + 2p 2p
We already saw in Ch. 1 that π bonds are based on side-on overlap of leftover p orbitals. C atom C=C bond C atom orbital comes from destructive (differentcolor) interference: (note extra node) + 2p 2p
Stereochemistry استریوشیمی. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 9 Stereochemistry استریوشیمی Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Stereochemistry Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry) A right-hand
9 Stereochemistry استریوشیمی Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Stereochemistry Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry) A right-hand
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes
 Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Question. Chapter 5 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes (C n H 2n ): Elimination Reactions
 hapter 5 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes ( n 2n ): Elimination Reactions The molecular formula of β-arotene is 40 On catalytic hydrogenation, β-carotene is converted to a saturated hydrocarbon of
hapter 5 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes ( n 2n ): Elimination Reactions The molecular formula of β-arotene is 40 On catalytic hydrogenation, β-carotene is converted to a saturated hydrocarbon of
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Ali Karimpour Aociate Profeor Ferdowi Univerity of Mahhad Lecture Stability analyi Topic to be covered include: Stability of linear control ytem. Bounded input bounded output tability
LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Ali Karimpour Aociate Profeor Ferdowi Univerity of Mahhad Lecture Stability analyi Topic to be covered include: Stability of linear control ytem. Bounded input bounded output tability
and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
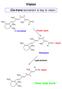 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chapter 13
 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Química Orgânica I. Organic Reactions
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
2/26/18. Practice Questions. Practice Questions B F. How many steps are there in this reaction?
 Practice Questions Practice Questions D B F C E A G How many steps are there in this reaction? 1 Practice Questions D B F C E A G What is the highest-energy transitions state? Practice Questions D B F
Practice Questions Practice Questions D B F C E A G How many steps are there in this reaction? 1 Practice Questions D B F C E A G What is the highest-energy transitions state? Practice Questions D B F
Chapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
 hapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and eactivity overage: 1. Degrees of Unsaturation 2. Nomenclature cis/trans E/Z 3. Alkene Stability 4. Electrophilic Addition eactions/markovinikov s ule 5. The ammond Postulate
hapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and eactivity overage: 1. Degrees of Unsaturation 2. Nomenclature cis/trans E/Z 3. Alkene Stability 4. Electrophilic Addition eactions/markovinikov s ule 5. The ammond Postulate
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems. Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI - 87
 HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY. Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
General Glossary. General Glossary
 General Glossary Absolute configuration The actual three-dimensional structure of a chiral molecule. Absolute configurations are specified verbally by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog R,S convention and are represented
General Glossary Absolute configuration The actual three-dimensional structure of a chiral molecule. Absolute configurations are specified verbally by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog R,S convention and are represented
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
CHAPTER 3 ALKENES, ALKYNES & CONJUGATE DIENES
 CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
C C. sp 2. π M.O. atomic. orbitals. carbon 1. σ M.O. molecular. orbitals. H C C rotate D. D H zero overlap of p orbitals: π bond broken!
 Alkenes Electrophilic Addition 1 Alkene Structures chemistry of double bond σ BDE ~ 80 kcal/mol π = BDE ~ 65 kcal/mol The p-bond is weaker than the sigma-bond The, electrons in the p-bond are higher in
Alkenes Electrophilic Addition 1 Alkene Structures chemistry of double bond σ BDE ~ 80 kcal/mol π = BDE ~ 65 kcal/mol The p-bond is weaker than the sigma-bond The, electrons in the p-bond are higher in
11/5/ Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Heats of Hydrogenation
 8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
مادسیج یعنی دهکده علم و دانش ایران!! مادسیج شبکه آموزشی پژوهشی دانشجویان ایران. Madsg.com
 مادسیج یعنی دهکده علم و دانش ایران!! مادسیج شبکه آموزشی پژوهشی دانشجویان ایران Madsg.com انواع پیوند ها قاعده ی هشتایی )اوکتت( و واکنش پذیری اتم ها هشتایی شدن الکترون های الیه پایدار گاز نجیب معیاری برای
مادسیج یعنی دهکده علم و دانش ایران!! مادسیج شبکه آموزشی پژوهشی دانشجویان ایران Madsg.com انواع پیوند ها قاعده ی هشتایی )اوکتت( و واکنش پذیری اتم ها هشتایی شدن الکترون های الیه پایدار گاز نجیب معیاری برای
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Alkenes. Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents
 Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing.
 Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
Chapter 4. Reactions of alkenes. Addition reactions Carbocations Selectivity of reactions
 Chapter 4 Reactions of alkenes Addition reactions Carbocations Selectivity of reactions Prob 47 p192. Give the reagents that would be required (including catalyst). Ch 4 #2 Electrophilic addition Ch 4
Chapter 4 Reactions of alkenes Addition reactions Carbocations Selectivity of reactions Prob 47 p192. Give the reagents that would be required (including catalyst). Ch 4 #2 Electrophilic addition Ch 4
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Alkenes. Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula C n H 2n. Nomenclature
 Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition. Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i. Chapter 10 Alkenes
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
Alkenes. Bonding and Structure: Carbons in the double bond of butene are sp 2 hybridized. Side on p-p orbital overlap creates a π-bond.
 Alkenes Bonding and Structure: Carbons in the double bond of butene are sp 2 hybridized. Side on p-p orbital overlap creates a π-bond. Angles around the carbons in the double bond are ~ 120º. Thus, all
Alkenes Bonding and Structure: Carbons in the double bond of butene are sp 2 hybridized. Side on p-p orbital overlap creates a π-bond. Angles around the carbons in the double bond are ~ 120º. Thus, all
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- 1
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
OCR AS Chemistry A H032 for first assessment in Complete Tutor Notes. Section: Alkenes Boomer Publications
 OR AS hemistry A 032 for first assessment in 206 omplete Tutor Notes www.boomerchemistry.com Section: 4..3 Alkenes E/Z Isomerism Alkenes Addition polymers 205 Boomer Publications page 43 page 45 page 5
OR AS hemistry A 032 for first assessment in 206 omplete Tutor Notes www.boomerchemistry.com Section: 4..3 Alkenes E/Z Isomerism Alkenes Addition polymers 205 Boomer Publications page 43 page 45 page 5
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
Alkynes Nomenclature of Alkynes
 Chapter 7 Alkynes Alkynes - hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon triple bond (2 bonds) Acyclic alkanes = C n H 2n+2 Alkenes and cyclic alkanes = C n H 2n Alkynes (and cyclic alkenes) = C n H 2n-2 The
Chapter 7 Alkynes Alkynes - hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon triple bond (2 bonds) Acyclic alkanes = C n H 2n+2 Alkenes and cyclic alkanes = C n H 2n Alkynes (and cyclic alkenes) = C n H 2n-2 The
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
H H C C. Alkenes C n H 2n unsaturated hydrocarbons. C 2 H 4 ethylene. Functional group = carbon-carbon double bond
 Alkenes C n H 2n unsaturated hydrocarbons C 2 H 4 ethylene H H C C H H Functional group = carbon-carbon double bond sp 2 hybridization => flat, 120 o bond angles σ bond & π bond => H 2 C=CH 2 No rotation
Alkenes C n H 2n unsaturated hydrocarbons C 2 H 4 ethylene H H C C H H Functional group = carbon-carbon double bond sp 2 hybridization => flat, 120 o bond angles σ bond & π bond => H 2 C=CH 2 No rotation
Lecture 11 Organic Chemistry 1
 EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
Final Exam Sample Questions Signals and Systems Course Fall 91
 1 1. Consider the signal x(t) with the Laplace transform region of convergence a < Real{s} < b where a < 0 < b. Determine the Laplace transform region of convergence for y(t) = x(t)u(t). 2. Given the following
1 1. Consider the signal x(t) with the Laplace transform region of convergence a < Real{s} < b where a < 0 < b. Determine the Laplace transform region of convergence for y(t) = x(t)u(t). 2. Given the following
 Air pollution Sahraei Physics Department Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei پایداری قائم جو اگر بخواهیم پدیده های مهم جوی مانند آشفتگی را درک و پیش بینی کنیم باید برای پایداری حرکت قائم هوا
Air pollution Sahraei Physics Department Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei پایداری قائم جو اگر بخواهیم پدیده های مهم جوی مانند آشفتگی را درک و پیش بینی کنیم باید برای پایداری حرکت قائم هوا
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King I. Conjugation
 Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures
 Isomerism It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures Definition- Structural isomers: same molecular formula different structures (or structural formulae)
Isomerism It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures Definition- Structural isomers: same molecular formula different structures (or structural formulae)
The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature of alkenes.
 Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
240 Chem. Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 6
 240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
Dienes & Polyenes: An overview and two key reactions (Ch )
 Dienes & Polyenes: An overview and two key reactions (h. 14.1-14.5) Polyenes contain more than one double bond and are very common in natural products (ex: carotene). Diene chemistry applies to trienes,
Dienes & Polyenes: An overview and two key reactions (h. 14.1-14.5) Polyenes contain more than one double bond and are very common in natural products (ex: carotene). Diene chemistry applies to trienes,
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Chapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes
 BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
eg ethylene (IUPAC: ethene), C 2
 Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
2. Hydrohalogenation: Propylene reacts with HBr to form 2-bromopropane.
 Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
 CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
Chemistry 110. Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell. Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes.
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chapter 6 H 2 H 3 C C H CH 3 C H H 2 C C CH 3. (b) =2 H 2 C C C H H C H CH 2 C CH 3 H 3 C C C CH 3. (c) =2
 hapter 6 6.1 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the following hydrocarbons: 8 14 ; 5 6 (c) 12 20 (d) 20 32 (e) 40 56 =2 =3 (c) =3 (d) =5 (e) =13 6.2 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the
hapter 6 6.1 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the following hydrocarbons: 8 14 ; 5 6 (c) 12 20 (d) 20 32 (e) 40 56 =2 =3 (c) =3 (d) =5 (e) =13 6.2 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Dr. Mishu Singh Department of chemistry Maharana Pratap Govt.P.G.College Hardoi
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Dr. Mishu Singh Department of chemistry Maharana Pratap Govt.P.G.College Hardoi 1 Recall the electophilic addition of HBr (or Br2) to alkenes H + nu cleophile H Br H
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Dr. Mishu Singh Department of chemistry Maharana Pratap Govt.P.G.College Hardoi 1 Recall the electophilic addition of HBr (or Br2) to alkenes H + nu cleophile H Br H
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Classification of organic compounds
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is very important branch of chemistry and it study the compounds which contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), in general, and may contains other atoms such as oxygen (O),
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is very important branch of chemistry and it study the compounds which contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), in general, and may contains other atoms such as oxygen (O),
Organic Chemistry. Why are these compounds called Organic. What is a Hydrocarbon? Questions: P167 Read
 Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
5. Reactions of Alkenes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
Chem 341 Organic Chemistry I Lecture Summary 16 October 01, 2007
 hem 341 Organic hemistry I Lecture Summary 16 October 01, 2007 hapter 6 - Alkenes: Structure and eactivity Nomenclature Double bond geometry is important in biology. For example, the trans to cis isomerization
hem 341 Organic hemistry I Lecture Summary 16 October 01, 2007 hapter 6 - Alkenes: Structure and eactivity Nomenclature Double bond geometry is important in biology. For example, the trans to cis isomerization
Advanced Inorganic Chemistry. نیم سال اول Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 Advanced Inorganic Chemistry ماتریس matrix ماتریس آرایه ای مستطیلی از اعداد یا عالئم می باشد عضو های قطری 2 ماتریس واحد 3 جمع و تفریق ماتریس ها 4 جمع و تفریق ماتریس ها 5 نکته 6 تمرین جمع و تفریق ماتریس
Advanced Inorganic Chemistry ماتریس matrix ماتریس آرایه ای مستطیلی از اعداد یا عالئم می باشد عضو های قطری 2 ماتریس واحد 3 جمع و تفریق ماتریس ها 4 جمع و تفریق ماتریس ها 5 نکته 6 تمرین جمع و تفریق ماتریس
Organic Chemistry. Alkenes (2)
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkenes (2) by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkenes (2) by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides"
 Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides The (E)-(Z) System for Designating Alkene Diastereomers The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention is used to assign
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides The (E)-(Z) System for Designating Alkene Diastereomers The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention is used to assign
General formula is CnH2n. Propene. But-1-ene. C-C pi bond. Formation of π bond in alkenes p orbitals Rotation can occur around a sigma bond
 4.1.3 Alkenes Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons General formula is n2n Alkenes contain a carboncarbon double bond somewhere in their structure Ethene Propene Numbers need to be added to the name when
4.1.3 Alkenes Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons General formula is n2n Alkenes contain a carboncarbon double bond somewhere in their structure Ethene Propene Numbers need to be added to the name when
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds
 1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
Dynamic meteorology 1
 Dynamic meteorology 1 Lecture Sahraei Physics Department Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei متغیرهای فیزیکی Physical Variables وابسته مستقل T - وابسته: )یا نرده ای است مانند فشار هوا P سرعت
Dynamic meteorology 1 Lecture Sahraei Physics Department Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei متغیرهای فیزیکی Physical Variables وابسته مستقل T - وابسته: )یا نرده ای است مانند فشار هوا P سرعت
Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions
 Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C 3 C C 3 bond length bond strength 2 C C 2 a C=C double bond is stronger than a C C single
Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C 3 C C 3 bond length bond strength 2 C C 2 a C=C double bond is stronger than a C C single
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
