Amides, Amino acids and Chirality
|
|
|
- Doris Willis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 R hemistry A 432 Amides, Amino Acids & hirality Amides, Amino acids and hirality aming of Amides The amide functional group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to the nitrogen of an amine. Like amines, amides are classified by the number of carbons attached to the nitrogen. A primary amide is therefore one in which both of the other atoms bonded to the nitrogen are hydrogens: propanamide (note that the carbon of the carbonyl group is counted in the longest chain, and that they stem is propan- not propyl-) A secondary amide is a linking group (biologists may refer to this as a peptide link) with the form - forming the link methylpropanamide A tertiary amide has the carbonyl group and two other carbon atoms attached to the ( 2 5 ) 2,-diethylmethanamide ote that this type of hybrid between a displayed and a structural formula is K if you are only required to draw a molecule unambiguously, but T if the type of formula is specified in the question as displayed Production of amides Amides are produced by the reaction of acyl chlorides (or acid anhydrides) with ammonia or amines. The ammonia or amide acts as a nucleophile, donating the lone pair on the nitrogen to form a dative bond to the δ+ carbon of the acyl chloride. Primary amides are produced in the reaction with ammonia: 3 l + 2 3! l ethanoyl chloride ethanamide Secondary amides are produced in the reaction with a primary amine: 3 2 l ! l - propanoyl chloride methylamine -methylpropanamide methylammonium chloride Page 1
2 R hemistry A 432 Amides, Amino Acids & hirality Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks for biological molecules called peptides, and for proteins (polypeptides). The body has 20 different amino acids from which to assemble proteins. Structure An amino acid contains the functional groups 2 and (amine and carboxylic acid). In an -amino acid (such as the 20 the body uses to make proteins) the 2 and groups are both bonded to the same carbon atom. The general formula of an -amino acid can therefore be written as: or R( 2 ) The R-group is usually an alkyl group but can contain, -S, - or 2 groups. Example of -amino acids: glycine glutamic acid alanine serine (aminoethanoic acid) (2-aminopropanoic acid) (2-aminopentanedioic acid) (2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid) EXTESI MATERIAL T SPEIFIATI Zwitterions The acidic carboxylic acid group can donate a proton to the basic amine group. The result is an internal salt (a molecule having both a positive and a negative charge on different parts of the same molecule) known as a zwitterion. A zwitterion has no overall charge.! Page 2
3 R hemistry A 432 Amides, Amino Acids & hirality Each amino acid has a characteristic p called the ISELETRI PIT at which it exists as a zwitterion. The exact value of p depends on the nature of the R- group. The presence of an acidic group such as in the R-group shifts the isoelectric point to a lower (more acidic) p, while the presence of a basic group such as 2 in the R- group shifts the isoelectric point to higher (more alkaline) p. Amphoteric properties of amino acids Amino acids are amphoteric which means they can react with both acids and bases. The 2 group, like any amine, is able to act as a base by using the lone pair on the atom to accept a proton. It can therefore neutralise acids, forming salts. l + l - The group, as in carboxylic acid, can act as a proton donor. The carboxylic acid group in an amino acid therefore can form salts when reacted with alkalis, 3 3 a 2 a and form esters when heated with an alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid as a catalyst ote that because this reaction is carried out under acidic conditions, the a mine group in the amino acid (which is a base) will also react with the acid and become protonated Page 3
4 R hemistry A 432 Amides, Amino Acids & hirality hirality and ptical Isomerism We have already met stereoisomerism in the form of E/Z (and the more specific cistrans) isomerism. ere the restricted rotation around double bond results in two isomers. These two isomers may have different chemical properties why might this be? The acid = can be extracted from unripe tomatoes and apples, and also from the wild flower Fumaria officinalis. When heated, the acid obtained from unripe tomatoes or apples reacts, forming a cyclic acid anhydride. The acid from the wild flower, however, does not react. The explanation for this, that the acid from the tomatoes or apples has the acid functional groups on the same side of the double bond where they can react, while the acid from the wild flower has the acid groups on opposite sides of the double bond where restricted rotation around the bond prevents them from reacting, gained van t off the first obel Prize in hemistry for his contribution of the ideas of cis- and transisomers in stereochemistry. With the exception of glycine, amino acids are examples of molecules that show a different type of stereoisomerism: optical isomerism. This occurs when a carbon atom in a molecule has four different groups attached to it. For example, the in an alanine molecule has, - 3, - 2 and attached to it. We call such a carbon atom chiral. Because of the tetrahedral arrangement of groups around a carbon with four single bonds, there are two possible arrangements for these groups. They are mirror images of one another. Rotations of the molecule about the carbon atom cannot make one optical isomer the same as the other. Definition: optical isomerism occurs when a molecule has non-superimposable mirror images about a chiral centre. ptical isomers are also referred to as enantiomers. ptical isomers are chemically identical, although they have different physical properties, in that they rotate plane-polarised light in different directions. A molecule can have more than one chiral centre. Each produces two optical isomers, so if a molecule has two chiral carbon atoms it will have two pairs of isomers (i.e. four optical isomers). Page 4
5 R hemistry A 432 Amides, Amino Acids & hirality Identifying optical isomers We find a chiral centre anywhere the four groups attached to a carbon atom are different. This sounds straight forward, but can be made difficult in two ways: i) when the molecule is presented skeletally (and so hydrogen atoms are hidden) l in 2-chloro-5-ethyloctane there are two chiral carbons, indicated with. int: it is easier to see chiral carbons if you re-draw the molecule displayed. ii) when the molecule is large or contains rings - the points of difference can be quite a distance from the chiral carbon, and the whole of the molecule has to be considered. this molecule only has one chiral centre, indicated with. You need to be sure you understand both why this carbon is chiral, and why the others aren t especially the carbon two to the right of the chiral one. Practice: Which of the following molecules has chiral centers, and where are they: no 3 2 ( 2 ) 3 3 l 3 3 ()Br - yes 3 rd from the left is chiral - no - yes 2 nd from left is chiral - yes, four of them shown with Page 5
6 R hemistry A 432 Amides, Amino Acids & hirality Drawing the optical isomers Structures must be drawn around a correctly-drawn 3D tetrahedral carbon centre Each enantiomer is then drawn as the mirror image of the other one Structural formulae may be used for attached groups if convenient (and unless told otherwise in the question) Use a vertical dotted line to show the mirror plane between the two molecules Remember to draw the connecting bonds to the correct atoms on the four groups Significance of ptical Isomerism ptical activity is important in biological systems where frequently only one of the optical isomers is biologically active only one of the optical isomers will interact with an enzyme due to the specific geometry of the receptor sites on enzymes we call this being stereospecific. This can result in them having different sensory effects or medical effects. leucine an amino acid with R = - 2 ( 3 ) 2 ne optical isomer tastes sweet, the other tastes bitter and is used as a food additive. Thalidomide (1954) prescribed to prevent morning-sickness in pregnant women drug was later found to be chiral only one enantiomer had the required thereputic effect the drug was not marketed in the US because the FDA demanded further testing before licensing, and during this process the activity of the other enantiomer was discovered the other optical isomer led to deformities in developing babies some 10,000 were affected in Europe Seldane one of the first antihistamines used to relieve hayfever symptoms chiral with one enantiomer having the required thereputic effect after testing and licensing, it was found that the inactive isomer caused a potentially fatal heart condition in some patients Page 6
7 R hemistry A 432 Amides, Amino Acids & hirality Ibuprofen one active optical isomer controls pain effectively by blocking messages to the brain and reducing swelling and inflammation the other isomer is inactive, but is fortuitously converted into the active isomer in the body, so the whole dose is active Page 7
3.7 Organic naming and Isomerism continued
 3.7 rganic naming and Isomerism continued See chapter 3.1 for basic naming of organic molecules. This chapter extends the naming for functional groups met in next few chapters homologous series functional
3.7 rganic naming and Isomerism continued See chapter 3.1 for basic naming of organic molecules. This chapter extends the naming for functional groups met in next few chapters homologous series functional
Q.1 Draw structures for all amines of molecular formula C 4 H 11 N. Classify them as primary, secondary or tertiary amines.
 1 AMIES Structure ontain the 2 group. lassification primary (1 ) amines secondary (2 ) amines tertiary (3 ) amines quarternary (4 ) ammonium salts + 1 2 3 4 Aliphatic Aromatic methylamine, ethylamine,
1 AMIES Structure ontain the 2 group. lassification primary (1 ) amines secondary (2 ) amines tertiary (3 ) amines quarternary (4 ) ammonium salts + 1 2 3 4 Aliphatic Aromatic methylamine, ethylamine,
Organic: module 4 revision guide. Basic definitions to know. Drawing Displayed formulae
 opyright Goalby Bancroft's School rganic: module 4 revision guide ydrocarbon is a compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon only Basic definitions to know Saturated: ontain single carbon-carbon bonds
opyright Goalby Bancroft's School rganic: module 4 revision guide ydrocarbon is a compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon only Basic definitions to know Saturated: ontain single carbon-carbon bonds
Chem!stry. Optical Isomerism
 hem!stry ame: ( ) lass: Date: / / ptical Isomerism ptical isomers are compounds that share the same molecular formula, but which rotate plane polarised light in opposite directions, either clockwise or
hem!stry ame: ( ) lass: Date: / / ptical Isomerism ptical isomers are compounds that share the same molecular formula, but which rotate plane polarised light in opposite directions, either clockwise or
OPTICAL ISOMERISM UNIT-1
 OPTICAL ISOMERISM UNIT-1 K.Anita priyadharshini, Lecturer, Dept.of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, SRM College of Pharmacy TYPES OF ISOMERISM CHAIN ISOMERISM STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM Same molecular formula but different
OPTICAL ISOMERISM UNIT-1 K.Anita priyadharshini, Lecturer, Dept.of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, SRM College of Pharmacy TYPES OF ISOMERISM CHAIN ISOMERISM STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM Same molecular formula but different
ISOMERISM - A general survey
 Isomerism 1 ISOMERISM - A general survey STRUTURAL ISOMERS have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae They occur due to variations in... the carbon skeleton AIN ISOMERISM 2 2 positions
Isomerism 1 ISOMERISM - A general survey STRUTURAL ISOMERS have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae They occur due to variations in... the carbon skeleton AIN ISOMERISM 2 2 positions
It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures
 Isomerism It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures Definition- Structural isomers: same molecular formula different structures (or structural formulae)
Isomerism It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures Definition- Structural isomers: same molecular formula different structures (or structural formulae)
Topic 4.8 AMINO ACIDS. Structure Acid-Base Properties Condensation Reactions Proteins
 Topic 4.8 AMI AIDS Structure Acid-Base Properties ondensation eactions Proteins STUTUE F AMI AIDS Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group and a carboxylic acid group. aturally occurring amino
Topic 4.8 AMI AIDS Structure Acid-Base Properties ondensation eactions Proteins STUTUE F AMI AIDS Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group and a carboxylic acid group. aturally occurring amino
Nitrogen Compounds - MS 1. (a) (i) is an amine and a carboxylic acid / contains both NH2 and COOH functional groups (1) AW 1
 itrogen ompounds - MS. (a) (i) is an amine and a carboxylic acid / contains both and functional groups () AW (c) R( ) () R Does not fit the formula because and are not attached to the same carbon () AW
itrogen ompounds - MS. (a) (i) is an amine and a carboxylic acid / contains both and functional groups () AW (c) R( ) () R Does not fit the formula because and are not attached to the same carbon () AW
Empirical formula: shows the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in the compound
 3.7 rganic naming and Isomerism ydrocarbon is a compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon only Basic definitions to know Saturated: ontain single carbon-carbon bonds only Unsaturated : ontains a = double
3.7 rganic naming and Isomerism ydrocarbon is a compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon only Basic definitions to know Saturated: ontain single carbon-carbon bonds only Unsaturated : ontains a = double
2/25/2015. Chapter 4. Introduction to Organic Compounds. Outline. Lecture Presentation. 4.1 Alkanes: The Simplest Organic Compounds
 Lecture Presentation Outline Chapter 4 Introduction to Organic Compounds 4.2 Representing Structures of Organic Compounds Julie Klare Fortis College Smyrna, GA Alkanes are structurally simple organic compounds
Lecture Presentation Outline Chapter 4 Introduction to Organic Compounds 4.2 Representing Structures of Organic Compounds Julie Klare Fortis College Smyrna, GA Alkanes are structurally simple organic compounds
Optical Isomerism. Types of isomerism. chemrevise.org 20/08/2013. N Goalby Chemrevise.org. Isomerism. Structural isomerism.
 ptical Isomerism N Goalby hemrevise.org Types of isomerism Isomerism Structural isomerism Stereoisomerism Geometric isomerism ptical isomerism 1 ptical Isomerism ptical isomerism occurs in carbon compounds
ptical Isomerism N Goalby hemrevise.org Types of isomerism Isomerism Structural isomerism Stereoisomerism Geometric isomerism ptical isomerism 1 ptical Isomerism ptical isomerism occurs in carbon compounds
The simplest amino acid is glycine, where the R is an H NH 2 CO2H NH2
 3.13 Amino Acids, roteins and DA General structure of an α amino acid 2 2 The simplest amino acid is glycine, where the is an 2 2 2 The group can be a variety of different things depending on what amino
3.13 Amino Acids, roteins and DA General structure of an α amino acid 2 2 The simplest amino acid is glycine, where the is an 2 2 2 The group can be a variety of different things depending on what amino
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry
 UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
Topic 5 Stereochemistry and optical isomers Isomerism
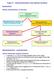 Topic 5 Stereochemistry and optical isomers Isomerism Recap lassification of isomers same molecular formula onstitutional Different nature/sequence of bonds Stereoisomers Different arrangement of groups
Topic 5 Stereochemistry and optical isomers Isomerism Recap lassification of isomers same molecular formula onstitutional Different nature/sequence of bonds Stereoisomers Different arrangement of groups
Organic and Biochemical Molecules. 1. Compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons.
 Organic and Biochemical Molecules 1. Compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. 2. A compound is said to be saturated if it contains only singly bonded carbons. Such hydrocarbons
Organic and Biochemical Molecules 1. Compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. 2. A compound is said to be saturated if it contains only singly bonded carbons. Such hydrocarbons
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
The simplest amino acid is glycine, where the R is an H NH 2 CO2H NH2
 6.11 Amino Acids, roteins and DA General structure of an α amino acid 2 2 The simplest amino acid is glycine, where the is an 2 2 2 The group can be a variety of different things depending on what amino
6.11 Amino Acids, roteins and DA General structure of an α amino acid 2 2 The simplest amino acid is glycine, where the is an 2 2 2 The group can be a variety of different things depending on what amino
Properties of Amino Acids
 Biochemistry Department Date:19/9/ 2017 Properties of Amino Acids Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1 Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs) By the end of this lecture,
Biochemistry Department Date:19/9/ 2017 Properties of Amino Acids Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1 Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs) By the end of this lecture,
Chemistry M11 Spring 2010 Examination #3 ANSWER KEY pp. 1
 Chemistry M11 Spring 2010 Examination #3 ASWER KEY pp. 1 or Questions 1 2, consider the hydrogenation of trans-3-methyl-2-pentene in the presence of a transition metal catalyst. 1. C Determine the major
Chemistry M11 Spring 2010 Examination #3 ASWER KEY pp. 1 or Questions 1 2, consider the hydrogenation of trans-3-methyl-2-pentene in the presence of a transition metal catalyst. 1. C Determine the major
Introduction to Organic Chemistry, Unit 3: Chirality at Carbon Centers Bring your model kits to class!
 Introduction to rganic hemistry, Unit 3: hirality at arbon enters Bring your model kits to class! rganic hemistry #3 1 bjectives: by the end of this unit, you should be able to... Identify the chiral centres
Introduction to rganic hemistry, Unit 3: hirality at arbon enters Bring your model kits to class! rganic hemistry #3 1 bjectives: by the end of this unit, you should be able to... Identify the chiral centres
Enantiomers. nonsuperimposable mirror image Both Configuration will be opposite. Both Configuration will be opposite
 Optical Isomerism Isomerism of Organic Molecules: Two chiral centers Many organic compounds have more than one asymmetric carbon. The more asymmetric carbons a compound has, the more number of stereoisomers
Optical Isomerism Isomerism of Organic Molecules: Two chiral centers Many organic compounds have more than one asymmetric carbon. The more asymmetric carbons a compound has, the more number of stereoisomers
O N N. electrons in ring
 ame I. ( points) Page 1 A. The compound shown below is a commonly prescribed antifungal drug. It belongs to a category of compounds known as triazoles. Analyze the geometry and other properties for various
ame I. ( points) Page 1 A. The compound shown below is a commonly prescribed antifungal drug. It belongs to a category of compounds known as triazoles. Analyze the geometry and other properties for various
Chapter 24 From Petroleum to Pharmaceuticals
 hapter 24 From Petroleum to Pharmaceuticals 24.1 Petroleum Refining and the ydrocarbons 24.2 Functional Groups and Organic Synthesis 24.3 Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals IR Tutor and Infrared Spectroscopy
hapter 24 From Petroleum to Pharmaceuticals 24.1 Petroleum Refining and the ydrocarbons 24.2 Functional Groups and Organic Synthesis 24.3 Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals IR Tutor and Infrared Spectroscopy
CHEM 261 Feb. 2, Stereochemistry and Chirality
 70 EM 261 eb. 2, 2017 Stereochemistry and hirality hiral object or molecule: has a non-superimposable mirror image Achiral object: not chiral, has a superimposable mirror image 1848 - Louis Pasteur separated
70 EM 261 eb. 2, 2017 Stereochemistry and hirality hiral object or molecule: has a non-superimposable mirror image Achiral object: not chiral, has a superimposable mirror image 1848 - Louis Pasteur separated
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to form long chains. Without this property, large biomolecules such as proteins,
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to form long chains. Without this property, large biomolecules such as proteins,
CH 3 C 2 H 5. Tetrahedral Stereochemistry
 Ch 5 Tetrahedral Stereochemistry Enantiomers - Two non-superimposable mirror image molecules - They are stereoisomers with the same atoms and bonds, but different spatial geometries. - The two molecules
Ch 5 Tetrahedral Stereochemistry Enantiomers - Two non-superimposable mirror image molecules - They are stereoisomers with the same atoms and bonds, but different spatial geometries. - The two molecules
2A - Amines. 2 H atoms replaced: 2 attached C's to N. 3 H atom replaced: 3 attached C's to N Ammonia, NH3 Primary amine Secondary amine Tertiary amine
 2A - Amines Something fishy about amines: Have an NH 2, amine group. Amines are derivatives of ammonia: 3 H atoms 1 H atom replaced: 1 attached C to N 2 H atoms replaced: 2 attached C's to N 3 H atom replaced:
2A - Amines Something fishy about amines: Have an NH 2, amine group. Amines are derivatives of ammonia: 3 H atoms 1 H atom replaced: 1 attached C to N 2 H atoms replaced: 2 attached C's to N 3 H atom replaced:
Lecture 4: 12.4 Isomerism
 Lecture 4: 12.4 Isomerism Learning Outcomes: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to : Define isomerism. Explain constitutional isomerism. chain isomers positional isomers functional group
Lecture 4: 12.4 Isomerism Learning Outcomes: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to : Define isomerism. Explain constitutional isomerism. chain isomers positional isomers functional group
Worksheet Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary
 Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
Chapter 5: Stereoisomerism
 hapter 5: Stereoisomerism [Sections: 5.1-5.9] 1. dentifying Types of somers Same MolecularFormula? A B compounds are not isomers Same onnectivity? D E constitutional isomers have different names (parent
hapter 5: Stereoisomerism [Sections: 5.1-5.9] 1. dentifying Types of somers Same MolecularFormula? A B compounds are not isomers Same onnectivity? D E constitutional isomers have different names (parent
QUESTION 1 Which two functional groups react to form the peptide link found in proteins?
 QUESTION 1 Which two functional groups react to form the peptide link found in proteins? NH and NH and NH2 and and NH2 A 2 B 2 C D OH COOH OH COOH QUESTION 2 The elements present in proteins are A B C
QUESTION 1 Which two functional groups react to form the peptide link found in proteins? NH and NH and NH2 and and NH2 A 2 B 2 C D OH COOH OH COOH QUESTION 2 The elements present in proteins are A B C
Chapter 3 The Chemistry of Carbon
 Complex molecules assembled like TinkerToys Chapter 3 The Chemistry of Carbon Why study Carbon? All living things are made of cells Cells ~72% H 2 O ~3% salts (Na, Cl, K ) ~25% carbon compounds carbohydrates
Complex molecules assembled like TinkerToys Chapter 3 The Chemistry of Carbon Why study Carbon? All living things are made of cells Cells ~72% H 2 O ~3% salts (Na, Cl, K ) ~25% carbon compounds carbohydrates
12.1 The Nature of Organic molecules
 12.1 The Nature of Organic molecules Organic chemistry: : The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon is tetravalent; it always form four bonds. Prentice Hall 2003 Chapter One 2 Organic molecules have covalent
12.1 The Nature of Organic molecules Organic chemistry: : The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon is tetravalent; it always form four bonds. Prentice Hall 2003 Chapter One 2 Organic molecules have covalent
Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from:
 Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from: Blackman, Bottle, Schmid, Mocerino and Wille, hemistry, 2007 (John Wiley) ISBN: 9 78047081 0866 1 hemistry 1B EM1002 Lecture
Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from: Blackman, Bottle, Schmid, Mocerino and Wille, hemistry, 2007 (John Wiley) ISBN: 9 78047081 0866 1 hemistry 1B EM1002 Lecture
Summary of mechanisms. Type of reaction: Nucleophilic subsitution/hydrolysis
 S Summary of mechanisms S Summary of mechanisms electrophilic addition Electrophiles: H δ in H (Ni catalyst needed), H δ in H-X; X δ in X ; H δ in H O (g) (conc H 3 PO 4 cat needed); H δ in NH 3 ; H δ
S Summary of mechanisms S Summary of mechanisms electrophilic addition Electrophiles: H δ in H (Ni catalyst needed), H δ in H-X; X δ in X ; H δ in H O (g) (conc H 3 PO 4 cat needed); H δ in NH 3 ; H δ
E30 ENANTIOMERS Chirality in organic chemistry
 E30 ENANTIMERS hirality in organic chemistry TE TASK To investigate the nature of chirality in organic chemistry. TE SKILLS By the end of the experiment you should be able to: use molecular modelling kits
E30 ENANTIMERS hirality in organic chemistry TE TASK To investigate the nature of chirality in organic chemistry. TE SKILLS By the end of the experiment you should be able to: use molecular modelling kits
University of Sydney Chemistry 1B (CHEM1102) Organic Chemistry Lecture Notes
 University of Sydney hemistry 1B (EM1102) rganic hemistry Lecture Notes Topic 1 Introduction & isomers 2 Topic 2 Alkenes, alkynes, arenes 20 Topic 3 Structure determination 27 Topic 4 Alcohols and amines
University of Sydney hemistry 1B (EM1102) rganic hemistry Lecture Notes Topic 1 Introduction & isomers 2 Topic 2 Alkenes, alkynes, arenes 20 Topic 3 Structure determination 27 Topic 4 Alcohols and amines
CHEM J-10 June The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below.
 CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
Bio-elements. Living organisms requires only 27 of the 90 common chemical elements found in the crust of the earth, to be as its essential components.
 Bio-elements Living organisms requires only 27 of the 90 common chemical elements found in the crust of the earth, to be as its essential components. Most of the chemical components of living organisms
Bio-elements Living organisms requires only 27 of the 90 common chemical elements found in the crust of the earth, to be as its essential components. Most of the chemical components of living organisms
Unit 5: Organic Chemistry
 Unit 5: Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry: discipline in chemistry focussing strictly on the study of hydrocarbons compounds made up of carbon & hydrogen Organic compounds can contain other elements
Unit 5: Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry: discipline in chemistry focussing strictly on the study of hydrocarbons compounds made up of carbon & hydrogen Organic compounds can contain other elements
Unit One Part 8: stereochemistry
 Unit ne Part 8: stereochemistry 1 Describe the difference between stereoisomers & structural isomers omenclature used for double bonds (cis-trans or E-Z) Predict conformations of cyclohexanes Define chirality
Unit ne Part 8: stereochemistry 1 Describe the difference between stereoisomers & structural isomers omenclature used for double bonds (cis-trans or E-Z) Predict conformations of cyclohexanes Define chirality
CHEM J-8 June Complete the following table. Make sure you give the name of the starting material where indicated. REAGENTS/ CONDITIONS
 CEM1102 2014-J-8 June 2014 Complete the following table. Make sure you give the name of the starting material where indicated. STARTIG MATERIAL REAGETS/ CDITIS STRUCTURAL FRMULA(S) F MAJR RGAIC PRDUCT(S)
CEM1102 2014-J-8 June 2014 Complete the following table. Make sure you give the name of the starting material where indicated. STARTIG MATERIAL REAGETS/ CDITIS STRUCTURAL FRMULA(S) F MAJR RGAIC PRDUCT(S)
Chirality, Carbonyls and Carboxylic Acids
 hirality, arbonyls and arboxylic Acids Questions on this unit may include material from UNIT 2 see syllabus Isomerism Structural isomerism. Structural isomerism was dealt with in UNIT 2. All isomers are
hirality, arbonyls and arboxylic Acids Questions on this unit may include material from UNIT 2 see syllabus Isomerism Structural isomerism. Structural isomerism was dealt with in UNIT 2. All isomers are
02/07/2017. Isomerism. Structural isomerism. 1. Structural isomerism different linkages of atoms. Same molecular formula Different structural formulae
 hain isomerism Position isomerism Metamerism Tautomerism Functional group isomerism Geometrical isomerism Optical isomerism 02/07/2017 Isomerism The presence of two or more compounds which has the same
hain isomerism Position isomerism Metamerism Tautomerism Functional group isomerism Geometrical isomerism Optical isomerism 02/07/2017 Isomerism The presence of two or more compounds which has the same
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features We shall survey the nature of the compounds in a tour of the families
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features We shall survey the nature of the compounds in a tour of the families
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
10/4/2010. Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration. Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration. 5.5 Sequence Rules for Specifying.
 5.5 Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration Configuration The three-dimensional arrangement of substituents at a chirality center Sequence rules to specify the configuration of a chirality center:
5.5 Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration Configuration The three-dimensional arrangement of substituents at a chirality center Sequence rules to specify the configuration of a chirality center:
2.0 h; 240 points please print clearly Dr. Kathleen Nolta Signature. Problem Points Score GSI I 42 II 35 III 36 IV 46 V 42 VI 39 Total 240
 hemistry 10 irst ame inal Examination Last ame.0 h; 0 points please print clearly Dr. Kathleen olta ignature UM ID # Problem Points core GI I II 5 III IV V VI 9 Total 0 Precision in drawing counts. heck
hemistry 10 irst ame inal Examination Last ame.0 h; 0 points please print clearly Dr. Kathleen olta ignature UM ID # Problem Points core GI I II 5 III IV V VI 9 Total 0 Precision in drawing counts. heck
OXFORD H i g h e r E d u c a t i o n Oxford University Press, All rights reserved.
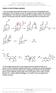 Patrick, An Introduction to dicinal hemistry 4e Answers to end-of-chapter questions 1) The mechanism below shows the release of one molecule of formaldehyde from methenamine. The mechanism can then be
Patrick, An Introduction to dicinal hemistry 4e Answers to end-of-chapter questions 1) The mechanism below shows the release of one molecule of formaldehyde from methenamine. The mechanism can then be
3.1 Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 3.1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Organic hemistry is the study of carbon chemistry as carbon has the ability to join together in chains, rings, balls etc. arbon also joins with other elements easily
3.1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Organic hemistry is the study of carbon chemistry as carbon has the ability to join together in chains, rings, balls etc. arbon also joins with other elements easily
Chemistry of Carbon. Building Blocks of Life
 Chemistry of Carbon Building Blocks of Life 2007-2008 Why study Carbon? All of life is built on carbon Cells ~72% H2O ~25% carbon compounds carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic acids ~3% salts Na, Cl,
Chemistry of Carbon Building Blocks of Life 2007-2008 Why study Carbon? All of life is built on carbon Cells ~72% H2O ~25% carbon compounds carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic acids ~3% salts Na, Cl,
GCE A level 1094/01 CHEMISTRY CH4
 Surname ther Names Centre 2 Candidate GCE A level 1094/01 CHEMISTRY CH4 P.M. MNDAY, 14 January 2013 1¾ hours ADDITINAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination paper, you will need: Data Sheet Periodic
Surname ther Names Centre 2 Candidate GCE A level 1094/01 CHEMISTRY CH4 P.M. MNDAY, 14 January 2013 1¾ hours ADDITINAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination paper, you will need: Data Sheet Periodic
5. Stereochemical Analysis. 7. Dipole Moments and Inductive versus Resonance Effects. 8. Types of isomers from a given formula. 9. Physical Properties
 hem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp ame Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 2. Lewis Structures, Resonance, Formal harge 3. yclohexane onformations, 2 substituents, ewman
hem 201 Sample Midterm Beauchamp ame Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 2. Lewis Structures, Resonance, Formal harge 3. yclohexane onformations, 2 substituents, ewman
Chapter 15 Amines. Amines contain one or more organic groups bonded to nitrogen the compounds have these general formulas:
 Chapter 15 Amines Amines have single bonds of Carbon bound to Nitrogen. Many of the molecules that carry chemical messages (such as neurotransmitters) are amines. They are present in many kinds of essential
Chapter 15 Amines Amines have single bonds of Carbon bound to Nitrogen. Many of the molecules that carry chemical messages (such as neurotransmitters) are amines. They are present in many kinds of essential
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life CHAPTER 4
 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life CHAPTER 4 1 Carbon: The Backbone of Life Although cells are 70 95% water, the rest consists mostly of carbon-based compounds Carbon is unparalleled in its ability
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life CHAPTER 4 1 Carbon: The Backbone of Life Although cells are 70 95% water, the rest consists mostly of carbon-based compounds Carbon is unparalleled in its ability
Chem 263 Nov 24, Properties of Carboxylic Acids
 Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Stereochemistry Structural or constitutional isomers... have the same molecular formula but different connectivity (skeletal, positional, functional)
 Stereochemistry Structural or constitutional isomers... have the same molecular formula but different connectivity (skeletal, positional, functional) Stereoisomers... have the same connectivity but a different
Stereochemistry Structural or constitutional isomers... have the same molecular formula but different connectivity (skeletal, positional, functional) Stereoisomers... have the same connectivity but a different
CARBONYLS CARBONYLS CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY CARBONYLS CARBONYLS CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY
 CRBONYLS CRBONYLS Outline mechanism for reaction methanol with propanoyl chloride. Clearly start curly arrow from middle lone pair or middle a bond. CRBONYLS CRBONYLS display formula butanoic anhydride.
CRBONYLS CRBONYLS Outline mechanism for reaction methanol with propanoyl chloride. Clearly start curly arrow from middle lone pair or middle a bond. CRBONYLS CRBONYLS display formula butanoic anhydride.
Name/CG: 2012 Term 2 Organic Chemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question
 Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
CHERRY HILL TUITION OCR A CHEMISTRY A2 PAPER 19 MARK SCHEME ANNOTATIONS MUST BE USED CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 H + correct products
 ERRY ILL TUITIN R A EMISTRY A2 PAPER 19 MARK SEME ALLW Kekulé structures throughout 1 (a) ANNTATINS MUST BE USED ALLW skeletal ALLW + + N 2 R N 2 ALLW 1st curly arrow from the ring R from within the ring
ERRY ILL TUITIN R A EMISTRY A2 PAPER 19 MARK SEME ALLW Kekulé structures throughout 1 (a) ANNTATINS MUST BE USED ALLW skeletal ALLW + + N 2 R N 2 ALLW 1st curly arrow from the ring R from within the ring
Experiment 10: Molecular Models
 B hemistry 162 Laboratory Manual Name Section Experiment 10: Molecular Models Modeling the shape of small organic molecules Previously we have considered molecules and ions for which one chemical formula
B hemistry 162 Laboratory Manual Name Section Experiment 10: Molecular Models Modeling the shape of small organic molecules Previously we have considered molecules and ions for which one chemical formula
10. Amines (text )
 2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western Ontario 10.1 10. Amines (text 10.1 10.6) A. Structure and omenclature Amines are derivatives of ammonia (H 3 ), where one or more H atoms has been
2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western Ontario 10.1 10. Amines (text 10.1 10.6) A. Structure and omenclature Amines are derivatives of ammonia (H 3 ), where one or more H atoms has been
Stereochemistry. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition
 Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry! Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry)! A right-hand glove
Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry! Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry)! A right-hand glove
Chapter 22. Organic and Biological Molecules
 Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
This section will involve expanding your knowledge of different types of ISOMERS.
 This section will involve expanding your knowledge of different types of ISOMERS. Isomerism arises whenever there is more than one way to organise a given number of atoms. It is very common in organic
This section will involve expanding your knowledge of different types of ISOMERS. Isomerism arises whenever there is more than one way to organise a given number of atoms. It is very common in organic
1 The repeat unit for poly(propenamide) is H H H O N C C C N C C C H H NH 2. (Total for Question = 1 mark) PhysicsAndMathsTutor.
 1 The repeat unit for poly(propenamide) is 2 2 2 The structures of three amino acids are shown in the table. mino acid cysteine glycine threonine Structure S 2 ( 2 ) 2 2 3 ()( 2 ) The tripeptide glycine-cysteine-threonine
1 The repeat unit for poly(propenamide) is 2 2 2 The structures of three amino acids are shown in the table. mino acid cysteine glycine threonine Structure S 2 ( 2 ) 2 2 3 ()( 2 ) The tripeptide glycine-cysteine-threonine
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
 Chapter 4 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Carbon and the Molecular Diversity
Chapter 4 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Carbon and the Molecular Diversity
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
 Chapter 4 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Carbon and the Molecular Diversity
Chapter 4 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Carbon and the Molecular Diversity
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
Lecture Notes Chemistry 342 Mukund P. Sibi Lecture 33 Amines
 Lecture otes Chemistry 342 Mukund P. Sibi Amines Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia. The nitrogen in amines contains a lone pair of electrons. The presence of this lone pair of electrons
Lecture otes Chemistry 342 Mukund P. Sibi Amines Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia. The nitrogen in amines contains a lone pair of electrons. The presence of this lone pair of electrons
Amino Acids and Peptides
 Amino Acids Amino Acids and Peptides Amino acid a compound that contains both an amino group and a carboxyl group α-amino acid an amino acid in which the amino group is on the carbon adjacent to the carboxyl
Amino Acids Amino Acids and Peptides Amino acid a compound that contains both an amino group and a carboxyl group α-amino acid an amino acid in which the amino group is on the carbon adjacent to the carboxyl
Stereochemistry CHAPTER SUMMARY
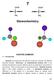 2 7 2 7. Introduction APTER SUMMARY Isomers are compounds with identical molecular formulas but different structural formulas. Structural or constitutional isomers differ in the bonding arrangement of
2 7 2 7. Introduction APTER SUMMARY Isomers are compounds with identical molecular formulas but different structural formulas. Structural or constitutional isomers differ in the bonding arrangement of
(a) (i) Give the equation representing the overall reaction. (1) Give the equation representing the formation of the electrophile.
 1. Benzene reacts with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid at about 50 º in an electrophilic substitution reaction to give nitrobenzene. (a) Give the equation representing
1. Benzene reacts with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid at about 50 º in an electrophilic substitution reaction to give nitrobenzene. (a) Give the equation representing
ANNOTATIONS MUST BE USED
 1 (a) ATATIS MUST BE USED ALLW skeletal ALLW R ALLW 1st curly arrow from the ring R from within the ring to any part of the 2 including the charge H D T ALLW intermediate with broken ring less than halfway
1 (a) ATATIS MUST BE USED ALLW skeletal ALLW R ALLW 1st curly arrow from the ring R from within the ring to any part of the 2 including the charge H D T ALLW intermediate with broken ring less than halfway
3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 3 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto 1 Families of Organic Compounds!
3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 3 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto 1 Families of Organic Compounds!
MOLECULAR REPRESENTATIONS AND INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY
 MOLEULAR REPRESENTATIONS AND INFRARED SPETROSOPY A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Given a Lewis (dash or dot), condensed, bond-line, or wedge formula of a compound draw the other representations. 2. Give
MOLEULAR REPRESENTATIONS AND INFRARED SPETROSOPY A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Given a Lewis (dash or dot), condensed, bond-line, or wedge formula of a compound draw the other representations. 2. Give
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Chapter 3 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Two types Saturated hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons 3.1 Alkanes Also referred as aliphatic hydrocarbons General formula: CnH2n+2 (straight chain) and CnH2n (cyclic)
Chapter 3 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Two types Saturated hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons 3.1 Alkanes Also referred as aliphatic hydrocarbons General formula: CnH2n+2 (straight chain) and CnH2n (cyclic)
Solutions In each case, the chirality center has the R configuration
 CAPTER 25 669 Solutions 25.1. In each case, the chirality center has the R configuration. C C 2 2 C 3 C(C 3 ) 2 D-Alanine D-Valine 25.2. 2 2 S 2 d) 2 25.3. Pro,, Trp, Tyr, and is, Trp, Tyr, and is Arg,
CAPTER 25 669 Solutions 25.1. In each case, the chirality center has the R configuration. C C 2 2 C 3 C(C 3 ) 2 D-Alanine D-Valine 25.2. 2 2 S 2 d) 2 25.3. Pro,, Trp, Tyr, and is, Trp, Tyr, and is Arg,
Figure 20.3 Molecular Models Representing an Enantiomeric Pair in a Chiral Molecule
 Topic 20 Additional igher Level 2. ptical Isomerism ptical isomerism occurs in molecules which have at least one carbon atom which is bonded to four different atoms or groups. A carbon bonded to four different
Topic 20 Additional igher Level 2. ptical Isomerism ptical isomerism occurs in molecules which have at least one carbon atom which is bonded to four different atoms or groups. A carbon bonded to four different
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
 Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: Carbon The Backbone of Biological Molecules
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: Carbon The Backbone of Biological Molecules
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS TOPIC 4.11 STRUCTURE DETERMINATION BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS TOPIC 4.11 STRUCTURE DETERMINATION BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1 1. Consider the following reaction sequence. CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 Step 1
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS TOPIC 4.11 STRUCTURE DETERMINATION BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1 1. Consider the following reaction sequence. CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 Step 1
STEREOCHEMISTRY A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOCHEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define the following terms, and give examples of pairs
A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOCHEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define the following terms, and give examples of pairs
Q1. The following pairs of compounds can be distinguished by simple test tube reactions.
 Q1. The following pairs of compounds can be distinguished by simple test tube reactions. For each pair of compounds, give a reagent (or combination of reagents) that, when added separately to each compound,
Q1. The following pairs of compounds can be distinguished by simple test tube reactions. For each pair of compounds, give a reagent (or combination of reagents) that, when added separately to each compound,
4.4, 4.5 HW MS 1. (a) nucleophilic addition 1 M2. (b) (i) 2-hydroxybutanenitrile 1 (ii) 2 H 3C O H
 4.4, 4.5 W MS 1. (a) nucleophilic addition 1 M N N M1 M M4 4 (b) (i) -hydroxybutanenitrile 1 (ii) N (allow 1 for amide even if not 4 7 N, i.e. RN ) (if not amide, allow one for any isomer of 4 7 N which
4.4, 4.5 W MS 1. (a) nucleophilic addition 1 M N N M1 M M4 4 (b) (i) -hydroxybutanenitrile 1 (ii) N (allow 1 for amide even if not 4 7 N, i.e. RN ) (if not amide, allow one for any isomer of 4 7 N which
Chapter 2: An Introduction to Organic Compounds
 Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
Number of d electrons CO 2 carbon dioxide +IV or +4 0
 CEM1611 2007-J-2 June 2007 Complete the following table. Give, as required, the formula, the systematic name, the oxidation number of the underlined atom and, where indicated, the number of d electrons
CEM1611 2007-J-2 June 2007 Complete the following table. Give, as required, the formula, the systematic name, the oxidation number of the underlined atom and, where indicated, the number of d electrons
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
 Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Dr. Wendy Sera Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 4: 1. Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds 2. Carbon atoms
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Dr. Wendy Sera Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 4: 1. Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds 2. Carbon atoms
QUESTIONSHEETS TEST QUESTION ON ISOMERISM STRUCTURES OF CYCLOALKENES BOND TYPE AND REACTIVITY REACTION CONDITIONS AND PRODUCT
 CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSHEETS A2 Level A2 TOPIC 23 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (INTRODUCTION AND REACTIONS) Questionsheet 1 Questionsheet 2 Questionsheet 3 Questionsheet 4 Questionsheet 5 Questionsheet 6 Questionsheet
CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSHEETS A2 Level A2 TOPIC 23 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (INTRODUCTION AND REACTIONS) Questionsheet 1 Questionsheet 2 Questionsheet 3 Questionsheet 4 Questionsheet 5 Questionsheet 6 Questionsheet
Two enantiomers of a racemic carboxylic acid (to be separated)
 7.8 FISCER PRJECTINS 237 (R)-RC 2 (S)-RC 2 Two enantiomers of a racemic carboxylic acid (to be separated) Figure 7.5 RESLUTIN F A RACEMIC CARBYLIC ACID. (S)-RN 2 ne enantiomer of a chiral amine + (R)-RC
7.8 FISCER PRJECTINS 237 (R)-RC 2 (S)-RC 2 Two enantiomers of a racemic carboxylic acid (to be separated) Figure 7.5 RESLUTIN F A RACEMIC CARBYLIC ACID. (S)-RN 2 ne enantiomer of a chiral amine + (R)-RC
Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model stand for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion and predicts the 3D shape of molecules that are formed in bonding.
 Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model stand for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion and predicts the 3D shape of molecules that are formed in bonding. Sigma and Pi Bonds: All single bonds are sigma(σ), that
Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model stand for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion and predicts the 3D shape of molecules that are formed in bonding. Sigma and Pi Bonds: All single bonds are sigma(σ), that
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY 2
 ADVANCED CHEMISTRY 2 Philip Matthews ±m±l CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Acknowledgements How to use this book INORGANIC CHEMISTRY 88 Periodicity of physical properties 88.1 Periodicity of ionisation energies
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY 2 Philip Matthews ±m±l CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Acknowledgements How to use this book INORGANIC CHEMISTRY 88 Periodicity of physical properties 88.1 Periodicity of ionisation energies
Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins. An -amino acid is a carboxylic acid which has an amino group attached to the carbon to the COOH.
 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins An -amino acid is a carboxylic acid which has an amino group attached to the carbon to the OO. Polypeptides and proteins are composed, either completely or partially,
Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins An -amino acid is a carboxylic acid which has an amino group attached to the carbon to the OO. Polypeptides and proteins are composed, either completely or partially,
Stereochemistry. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects.
 Stereochemistry This is study of the 3 dimensional arrangement in space of molecules. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects. E.g. the isomers
Stereochemistry This is study of the 3 dimensional arrangement in space of molecules. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects. E.g. the isomers
Carboxylic acid derivatives
 arboxylic acid derivatives Acyl hlorides and Acid Anhydrides N Goalby hemrevise.org arboxylic acid derivatives carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid) 3 l Acyl hloride (ethanoyl chloride) key 3 3 Acid Anhydride
arboxylic acid derivatives Acyl hlorides and Acid Anhydrides N Goalby hemrevise.org arboxylic acid derivatives carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid) 3 l Acyl hloride (ethanoyl chloride) key 3 3 Acid Anhydride
Chapter 3: Stereochemistry & Chirality
 Chapter 3: Stereochemistry & Chirality 1. Chiral & Achiral Compounds - Identifying Stereocenters 2. Assigning R & S configurations 3. Diastereomers - Molecules with two or more stereocenters 4. Properties
Chapter 3: Stereochemistry & Chirality 1. Chiral & Achiral Compounds - Identifying Stereocenters 2. Assigning R & S configurations 3. Diastereomers - Molecules with two or more stereocenters 4. Properties
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity
CHEMpossible. 261 Exam 1 Review
 CHEMpossible 261 Exam 1 Review A. Rank the following carboxylic acids from least acidic to most acidic: B. Draw the line-angle formulas for three acylic (non-cyclic) esters with the molecular formula C
CHEMpossible 261 Exam 1 Review A. Rank the following carboxylic acids from least acidic to most acidic: B. Draw the line-angle formulas for three acylic (non-cyclic) esters with the molecular formula C
Organic Chemistry. Unit 10
 Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
Fall Organic Chemistry Experiment #6 Fractional Crystallization (Resolution of Enantiomers)
 Suggested Reading: Fall Organic Chemistry Experiment #6 Fractional Crystallization (Resolution of Enantiomers) Jones Section 4.9 Physical Properties of Diastereomers: Optical Resolution pages 176-178 Introduction
Suggested Reading: Fall Organic Chemistry Experiment #6 Fractional Crystallization (Resolution of Enantiomers) Jones Section 4.9 Physical Properties of Diastereomers: Optical Resolution pages 176-178 Introduction
