Theoretical study of the first step of SPLET mechanism: O H bond cleavage in the mono-substituted benzoic acids
|
|
|
- Dominick Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Theoretical study of the first step of SPLET mechanism: O H bond cleavage in the mono-substituted benzoic acids Martin Michalík, Peter Škorňa, Vladimír Lukeš Department of Chemical Physics, Faculty of Chemical and Food Technology, Slovak University of Technology, Radlinského 9, SK Bratislava, Slovakia xmichalikm@stuba.sk Abstract: The first step of SPLET mechanism in solution phase for 15 benzoic acid derivatives was studied from the thermodynamic point of view. For this purpose, proton affinities (PAs) of corresponding carboxylate or phenoxide anions were computed by means of DFT method employing B3LYP and M062X functionals with G** basis set and SMD or IEF-PCM solvent model. The substituent effect on PAs was analyzed in terms of Hammett constants, σ p. Found dependences exhibit satisfactory linearity and enable quick estimation of solution phase PAs from the Hammett constants. Keywords: Proton affinity, B3LYP, M062X, IEF-PCM, SMD, benzoic acid derivatives Introduction Protonation or deprotonation is the first step in many important chemical reactions. The ability of a molecule to abstract a proton is characterized, from thermodynamical point of view, by proton affinity (PA) of the corresponding anion. PA is useful as a measure of the correlations between the acidity of organic compounds and their structure. Comparison of the PA values with pka values of the respective acids in solution gives information about the solvation effects on the acidity of studied molecules. From the practical point of view, it can help to rationalize the fragmentation pathways of compounds of interest. Like numerous other natural phenolic compounds, hydroxybenzoic acids exhibit antioxidative properties as free radical scavengers and metal ion chelators (Andjelkovic, 2006). The structure of phenolic compounds, especially the number and position of OH groups, seems to play the crucial role in their antioxidant, antiproliferative, cytotoxic and enzyme inhibition activities (Pietta, 2000). Many of the health-promoting activities of phenolic compounds are ascribed to their antioxidant activities as well as to their ability to modify cellular signaling pathways. Most ingested flavonoids are extensively degraded to various hydroxybenzoic acids, some of which possess high radical scavenging ability (Cuvelier, 1992; Duenas, 2011). The hydroxybenzoic acids occur mainly in the form of glycosides and are rarely free in edible plants, such as rosaceous fruits (strawberry, blackberry, blackcurrant and raspberry), potatoes, black radishes, grape seeds, onions, wines, and teas. As conjugates, hydroxybenzoics are components of plant complex polyphenolic structures, such as lignins and hydrolysable tannins (Barberan, 2000; Herrmann, 1989; Manach, 2004). Hydroxybenzoic acids are present in red wine as cofactors of the anthocyanin pigments (Zhang, 2015). In this work we investigate the first step of sequential proton-loss electron-transfer (SPLET) mechanism. ArX H ArX + H + (1) The reaction enthalpy of this step is proton affinity (PA). From the thermodynamic point of view, entering SPLET mechanism is the most probable process in water, where PAs are frequently considerably lower than bond dissociation enthalpies (Klein, 2009). PA values can be experimentally or theoretically determined. Experimental determination is possible only in the gas phase. Proton afinity also depends on the position of substituents at the aromatic ring (Bordwell et al., 1994; Klein and Lukeš, 2006). Because the SPLET mechanism is relevant mainly in the solution phase, the main aim of this work is to calculate the O H proton affinities of monosubstituted benzoic acids in solution phase. This paper extends the work commenced in Škorňa et al., Reliability of the obtained values was assessed by means of their comparison with available experimental and theoretical data. Furthermore, the substituent effect was assessed for the reaction enthalpy of a set of 14 para-substituted benzoic acids. 120 Acta Chimica Slovaca, Vol. 8, No. 2, 2015, pp , DOI: /acs
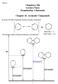
2 Computational details The calculations were carried out using the Gaussian 09 program package (Frisch et al., 2009). All geometries were fully optimized by minimizing the energy with respect to all geometrical variables using DFT method employing the widely used B3LYP (Becke,1988; Lee et al., 1988; Frisch et al., 2009) and M062X functional (Zhao et al., 2008) without any constraints (energy cut-off of 10 5 kj mol 1, final RMS energy gradient below 0.01 kj mol 1 Å 1 ). For species having several conformers all the conformers were investigated and the conformers with the lowest electronic energy were used. Calculations were performed in the standard G** basis set of Pople (Krishnan et al., 1980; McLean and Chandler, 1980; Curtiss et al., 1995). This level of theory was found to outperform more expensive wave function-based methods for calculations of absolute proton affinities, thus comforting us in this choice. (Dumont, 2009). The optimized structures were confirmed to be true minima by the vibration analysis (no imaginary frequency). All enthalpies were calculated for K. Proton affinities (PA) were calculated from the total enthalpies as follows: PA = H(ArX ) + H(H + ) H(ArX H) (2) The influence of the water as a solvent was approximated by the continuum Solvation Model based on the quantum mechanical charge Density, SMD (Marenich et al., 2009) of a solute molecule interacting with a continuum description of the solvent and Integral Equation Formalism Polarized Continuum Model, IEF-PCM (Cances et al., 1997). Total proton enthalpies in water reached the following values: kj mol 1 (B3LYP/IEF-PCM), (B3LYP/SMD), (M062X/IEF-PCM) and kj mol 1 (M062X/SMD). Available experimental value of proton solvation enthalpy is its hydration enthalpy, Δ hydr H(H + ) = 1090 kj mol 1 (Atkins, 1998). For hydroxybenzoic acids full torsion scans of carboxyl group were performed with 15 steps and subsequent geometry relaxation. Results and discussion Proton affinities of hydroxybenzoic acid The term protomers has been suggested for species differing exclusively in the binding site of a proton (Galaverna, 2015). Figure 1 depicts the stable protomers of ortho- (salicylic acid) and meta- substituted benzoic acid. Theoretical calculations in solvent, using DFT level of theory with IEF-PCM or SMD models was employed to indicate the energy difference of the stable species. Negligible difference at the level of standard deviation (0.1 kj mol 1 ) was found for para-hydroxy protomers having O H and C=O bonds in anti or sym position to each other. In gas phase a similar difference (0.2 kj mol 1 ) was found (Aarset, 2008). Despite the difference in geometries, carboxyl group remained coplanar with the phenyl ring in all studied isomers. To evaluate energy barrier for the rotation of the carboxyl group, torsion scans were performed with 15 steps and subsequent geometry relaxations, starting from the geometry of the energy minima, depicted in Fig. 3. The highest energy barrier (nearly 40 kj mol 1 ) was observed in ortho-hydroxy benzoic acid. Para-hydroxy isomer shows 27 kj mol 1 energy barrier and meta-hydroxy benzoic acid has the lowest 21 kj mol 1 energy barrier. The two viable ways of deprotonating hydroxybenzoic acids are presented in Figure 1. The calculated PA values are summarized in Table 1. Only in the case of ortho-isomer, OH group deprotonation was found to be thermodynamically preferred. In gas phase hydroxyl group deprotonation was favored in para-isomer (Škorňa, 2015). Chen et al. found (B3LYP/ G**) for phenoxide anion of salicylic acid in water the PA value of 194 kj mol 1. Considering that proton can be abstracted from any site, PAs of these isomers were in the following descending order: ortho- < meta- < para-, which can be correlated with known experimental pka values (2.9, 4.0, 4.5) (Abramson 2013). Fig. 1. Formation of deprotonated species from hydroxybenzoic acid. 121
3 Tab. 1. B3LYP and M062X/ G** proton affinities of ortho-, meta- and para-substituted hydroxybenzoic adic using IEF-PCM and SMD solvent models. Functional/solvent Carboxylate anion PA/kJ mol 1 Phenoxide anion PA/kJ mol 1 model Ortho Meta Para Ortho Meta Para B3LYP/IEF-PCM M062X/IEF-PCM B3LYP/SMD M062X/SMD Ortho-1, E = 0 kj mol 1 Ortho-2, E = 9 kj mol 1 Ortho-3, E = 19 kj mol 1 Meta-1, E = 0 kj mol 1 Meta-2, E = 1 kj mol 1 Para Fig. 2. Stable isomers of hydroxybenzoic acid, E represents the energy difference between the protomers. Para-substituted benzoic acids Tables 2 and 3 present proton affinities of 14 parasubstituted benzoic acid derivatives in the aqueous solution. Employing IEF-PCM and SMD solvation models, the found PAs were in the range up to 33 kj mol 1 for both solvation models. Unfor- tunately, experimental PAs for para-substituted benzoic acids are rather scarce and limited to the gas phase only. In comparison with the theoretical gas phase PA data presented by Škorňa et al., our calculations are lower by ca 1200 kj mol 1. Gas phase PA values are in the wide range from 122
4 Fig. 3. Relative energies ( E) and energy barriers for the torsion scans performed (15 steps) kj mol 1 (para-no 2 ) to 1438 kj mol 1 (para- NMe 2 ). It is well-known fact that solvents, in contrast to the gas phase, tend to attenuate PA values with the increase of their po larity. Moreover gas phase PAs are significantly higher than the solution phase ones, which is mainly due to the large enthalpy of H + hydration (Klein, 2009; Taft, 1983). Nevertheless the electron-donating or electronwithdrawing nature of the substituent has a nonnegligible influence on thermochemical properties. In comparison with non-substituted benzoic acid, electron-donating substituents induce the PA increase. On the other hand, electron-withdrawing groups decrease PA values, thus increasing the acidity of the carboxyl group. Such trend is clearly obeyed by substituents with strong effects and is Tab. 2. M062X/ G** proton affinities of para-substituted benzoic acid derivatives using IEF-PCM and SMD solvent models and the corresponding Hammett constants, σ p. Substituent M062X/IEF-PCM M062X/SMD PA/kJ mol 1 PA/kJ mol 1 PA/kJ mol 1 PA/kJ mol 1 H NMe NH MeO t-bu Me Ph F Br Cl MeCO CF CN MeSO NO σ p 123
5 Tab. 3. B3LYP/ G** proton affinities of para-substituted benzoic acid derivatives using IEF-PCM and SMD solvent models and the corresponding Hammett constants, σ p. Substituent B3LYP/IEF-PCM B3LYP/SMD PA/kJ mol 1 PA/kJ mol 1 PA/kJ mol 1 PA/kJ mol 1 H NMe NH MeO t-bu Me Ph F Br Cl MeCO CF CN MeSO NO σ p Fig 4. Correlation of the PAs with Hammett constants, σ p. evident from the Tables 2 and 3 displaying also PA values, where PA = PA(Y ArCOOH) PA(ArCOOH) (3) Measure of a substituent effect is usually effectively predicted by Hammett constants (Hammett, 1937). Fig. 4 shows PA = f(σ p ) dependence, where σ p are Hammett constants. The Hammett equation (and its extended forms) represents one of the most widely used means for the study and interpretation of organic reactions and their mechanisms. (Hansch et al., 1991; Krygowski and Stępień, 2005). Linear regression provided these equations: PA(B3LYP/IEF-PCM)/kJ mol 1 = = σ p (4) PA(B3LYP/SMD)/kJ mol 1 = σ p (5) 124
6 PA(M062X/IEF-PCM)/kJ mol 1 = = σ p (6) PA(M062X/SMD)/kJ mol 1 = σ p (7) with the correlation coefficients for B3LYP/IEF- PCM of and B3LYP/SMD 0.989, for M062X/ IEF-PCM of and M062X/SMD Correlation of Hammett constants with gas phase PAs of para-substituted benzoic acids yielded correlation coefficient In the present case, the selection of the functional led to only small changes of the intercept, which is much more sensitive to the choice of the solvation model. SMD model provides ca 80 kj mol 1 lower PAs in water than IEF-PCM model. Obtained intercepts as well as line slopes are lower than those found for the gas phase. Thus we can assume that aqueous solution induces considerable changes in the substituent effect in comparison to the gas phase. Conclusion In this paper the first step of SPLET mechanism was investigated for 15 selected monosubstitued benzoic acid derivatives in solution phase. Therefore the corresponding reaction enthalpy, proton affinity (PA), was evaluated for the carboxylate or phenoxide anions. Employing M062X and B3LYP functional in combination with the G** basis set and IEF-PCM or SMD solvation models we were able to find that the theoretical PA values are more influenced by the choice of the solvation model. The presence of electron-donating substituents resulted, in general, in higher PA values while electron-withdrawing groups cause the decrease of PAs. Linearity for all functional and solvation model combinations of the corresponding Hammett type dependencies can be considered satisfactorily. In terms of the obtained PA values, OH group deprotonation was found to be thermodynamically preferred in salicylic acid. Future studies will investigate solution phase PAs of additional species employing a chemical microsolvation method. References Abramson R, Baldridge A, Kim K (2013) Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 9: Andjelković M et al. (2006) Food Chemistry 98: Atkins PW (1998) Physical chemistry, 6 th ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford. Barberán FA, Clifford MN (2000) Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 80: Bordwell FG et al. (1994) Journal of the American Chemical Society 116: Cances E, Mennucci B, Tomasi J (1997) J. Chem. Phys 107: Cuvelier M-E, Richard H, Berset C (1992) Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 56: Dueñas M et al. (2011) European Food Research and Technology 232: Dumont E, Chaquin P (2009) The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 113: Galaverna RS et al. (2015) European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2015: Hammett LP (1937) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 59: Herrmann K, Nagel CW (1989) Critical Reviews in Food Science & Nutrition 28: Klein E, Lukeš V (2006) The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 110: Klein E, Rimarčík J, Lukeš V (2009) Acta Chim. Slovaca 2: Manach C et al. (2004) The American journal of clinical nutrition 79: Marenich AV, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2009) The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 113: Pietta P-G (2000) Journal of natural products 63: Škorňa P et al. (2015) Acta Chimica Slovaca 8: Taft RW (1983) Prog. Phys. Org. Chem 14: Zhang B et al. (2015) Food chemistry 170: Zhao Y, Truhlar DG (2008) Theor. Chem. Acc. 120:
Water effect on the bond dissociation energy of O H and N H bonds in phenol and aniline: The testing of simple molecular dynamics model
 Water effect on the bond dissociation energy of O H and N H bonds in phenol and aniline: The testing of simple molecular dynamics model Martin Michalík a, Adam Vagánek b, Peter Poliak a a Department of
Water effect on the bond dissociation energy of O H and N H bonds in phenol and aniline: The testing of simple molecular dynamics model Martin Michalík a, Adam Vagánek b, Peter Poliak a a Department of
A Theoretical Study on the Enthalpies of Homolytic and Heterolytic N H Bond Cleavage in Substituted Melatonins in the Gas Phase and Aqueous Solution
 43 Scientific paper A Theoretical Study on the Enthalpies of Homolytic and Heterolytic N H Bond Cleavage in Substituted Melatonins in the Gas Phase and Aqueous Solution Meysam Najafi, 1 Davood Farmanzadeh,
43 Scientific paper A Theoretical Study on the Enthalpies of Homolytic and Heterolytic N H Bond Cleavage in Substituted Melatonins in the Gas Phase and Aqueous Solution Meysam Najafi, 1 Davood Farmanzadeh,
Theoretical study of the energetics of carboxylic O H bond cleavage in the para- and meta-substituted benzoic acid derivatives
 Theoretical study of the energetics of caroxylic O H ond cleavage in the para- and meta-sustituted enzoic acid derivatives Peter Škorňa 1, Adam Vagánek 2, Peter Poliak 1, Erik Klein 1 1 Institute of Physical
Theoretical study of the energetics of caroxylic O H ond cleavage in the para- and meta-sustituted enzoic acid derivatives Peter Škorňa 1, Adam Vagánek 2, Peter Poliak 1, Erik Klein 1 1 Institute of Physical
S H Bond Dissociation Enthalpies in para- and meta- Substituted Thiophenols: Correlation with Thiophenolic C S Bond Length
 S H Bond Dissociation Enthalpies in para- and meta- Substituted Thiophenols: Correlation with Thiophenolic C S Bond Length Lenka Rottmannová, Adam Vagánek, Ján Rimarčík, Vladimír Lukeš, Erik Klein Institute
S H Bond Dissociation Enthalpies in para- and meta- Substituted Thiophenols: Correlation with Thiophenolic C S Bond Length Lenka Rottmannová, Adam Vagánek, Ján Rimarčík, Vladimír Lukeš, Erik Klein Institute
Gallic acid: thermodynamics of the homolytic and heterolytic phenolic O H bonds splitting-off
 Gallic acid: thermodynamics of the homolytic and heterolytic phenolic O H bonds splitting-off Peter Škorňa, Martin Michalík, Erik Klein Institute of Physical Chemistry and Chemical Physics, Slovak University
Gallic acid: thermodynamics of the homolytic and heterolytic phenolic O H bonds splitting-off Peter Škorňa, Martin Michalík, Erik Klein Institute of Physical Chemistry and Chemical Physics, Slovak University
Theoretical 1 H(Se H) NMR shifts in meta-substituted Ph XH (X = O, S, Se)
 Theoretical 1 H(Se H) NMR shifts in meta-substituted Ph XH (X = O, S, Se) Vladimir Sladek, Lenka Rottmannová, Peter Škorňa, Michal Ilčin and Vladimír Lukeš Institute of Physical Chemistry and Chemical
Theoretical 1 H(Se H) NMR shifts in meta-substituted Ph XH (X = O, S, Se) Vladimir Sladek, Lenka Rottmannová, Peter Škorňa, Michal Ilčin and Vladimír Lukeš Institute of Physical Chemistry and Chemical
Supplemental Information: Photobasicity in. Quinolines: Origin and Tunability via the. Substituents Hammett Parameters
 Supplemental Information: Photobasicity in Quinolines: Origin and Tunability via the Substituents Hammett Parameters Eric Driscoll, Jonathan Ryan Hunt, and Jahan M Dawlaty University of Southern California
Supplemental Information: Photobasicity in Quinolines: Origin and Tunability via the Substituents Hammett Parameters Eric Driscoll, Jonathan Ryan Hunt, and Jahan M Dawlaty University of Southern California
Comparison of molecular structure of alkali metal ortho substituted benzoates
 Spectroscopy 24 (2010) 439 443 439 DOI 10.3233/SPE-2010-0444 IOS Press Comparison of molecular structure of alkali metal ortho substituted benzoates R. Świsłocka Department of Chemistry, Biatystok Technical
Spectroscopy 24 (2010) 439 443 439 DOI 10.3233/SPE-2010-0444 IOS Press Comparison of molecular structure of alkali metal ortho substituted benzoates R. Świsłocka Department of Chemistry, Biatystok Technical
Conformational Studies on Aryl-cyclopentadienylidenes: Electronic Effects of Aryl Groups
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol., No. (010), 888-89 Conformational Studies on Aryl-cyclopentadienylidenes: Electronic Effects of Aryl roups E. VESSALLY Islamic Azad University, Miyaneh Branch, Miyaneh,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol., No. (010), 888-89 Conformational Studies on Aryl-cyclopentadienylidenes: Electronic Effects of Aryl roups E. VESSALLY Islamic Azad University, Miyaneh Branch, Miyaneh,
CHAPTER 3. Vibrational Characteristics of PTP-1B Inhibitors
 CHAPTER 3 Vibrational Characteristics of PTP-1B Inhibitors 3.1 Preface Theoretical Frequency calculations were performed on the molecules chosen in this study. Initially all the geometries were optimized
CHAPTER 3 Vibrational Characteristics of PTP-1B Inhibitors 3.1 Preface Theoretical Frequency calculations were performed on the molecules chosen in this study. Initially all the geometries were optimized
Mechanism of Hydrogen Evolution in Cu(bztpen)-Catalysed Water Reduction: A DFT Study
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information to Mechanism of Hydrogen Evolution in Cu(bztpen)-Catalysed Water
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information to Mechanism of Hydrogen Evolution in Cu(bztpen)-Catalysed Water
Torsional deformation effect on the N H bond dissociation energy in diphenylamine
 Torsional deformation effect on the N H bond dissociation energy in diphenylamine Peter Poliak, Adam Vagánek Institute of Physical Chemistry and Chemical Physics, Slovak University of Technology, Radlinského
Torsional deformation effect on the N H bond dissociation energy in diphenylamine Peter Poliak, Adam Vagánek Institute of Physical Chemistry and Chemical Physics, Slovak University of Technology, Radlinského
Groups to the Extractability of
 129 Contribution of Substituent Phenols and Benzoic Acids Groups to the Extractability of Takuyuki HAGIWARA and Shoji MOTOMIzu Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,Okayama University, Tsushimanaka,
129 Contribution of Substituent Phenols and Benzoic Acids Groups to the Extractability of Takuyuki HAGIWARA and Shoji MOTOMIzu Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,Okayama University, Tsushimanaka,
Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds
 Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds 1 Structure of Benzene H H C C C H C 6 H 6 H C C C H H A cyclic conjugate molecule Benzene is a colourless odourless liquid, boiling at 80 o C and melting at 5 o C. It is
Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds 1 Structure of Benzene H H C C C H C 6 H 6 H C C C H H A cyclic conjugate molecule Benzene is a colourless odourless liquid, boiling at 80 o C and melting at 5 o C. It is
Keto-Enol Thermodynamics of Breslow Intermediates
 Keto-Enol Thermodynamics of Breslow Intermediates Mathias Paul, Martin Breugst, Jörg-Martin Neudörfl, Raghavan B. Sunoj, and Albrecht Berkessel Computational Section of the Supporting Information 1 Computational
Keto-Enol Thermodynamics of Breslow Intermediates Mathias Paul, Martin Breugst, Jörg-Martin Neudörfl, Raghavan B. Sunoj, and Albrecht Berkessel Computational Section of the Supporting Information 1 Computational
and Stereochemistry) PAPER 1: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- I (Nature of Bonding and Stereochemistry) MODULE 4: Applications of Electronic Effects
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 1: ORGANIC - I (Nature of Bonding Module 4: Applications of Electronic Effects CHE_P1_M4 PAPER 1: ORGANIC - I (Nature of Bonding
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 1: ORGANIC - I (Nature of Bonding Module 4: Applications of Electronic Effects CHE_P1_M4 PAPER 1: ORGANIC - I (Nature of Bonding
Quantum Mechanical Study on the Adsorption of Drug Gentamicin onto γ-fe 2
 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-00 X CODEN: OJCHEG 015, Vol. 31, No. (3): Pg. 1509-1513 Quantum Mechanical
ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-00 X CODEN: OJCHEG 015, Vol. 31, No. (3): Pg. 1509-1513 Quantum Mechanical
Chapter 23 Phenols CH. 23. Nomenclature. The OH group takes precedence as the parent phenol.
 CH. 23 Chapter 23 Phenols Nomenclature The OH group takes precedence as the parent phenol. Carboxyl and acyl groups take precedence over the OH group. The OH group is a strong electron-donating group through
CH. 23 Chapter 23 Phenols Nomenclature The OH group takes precedence as the parent phenol. Carboxyl and acyl groups take precedence over the OH group. The OH group is a strong electron-donating group through
A theoretical investigation of the relative stability of hydrated glycine and methylcarbamic acid from water clusters to interstellar icesw
 PCCP Dynamic Article Links Cite this: Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 4942 4958 www.rsc.org/pccp PAPER A theoretical investigation of the relative stability of hydrated glycine and methylcarbamic acid
PCCP Dynamic Article Links Cite this: Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 4942 4958 www.rsc.org/pccp PAPER A theoretical investigation of the relative stability of hydrated glycine and methylcarbamic acid
Acid-Base Strength. Chapter 6. Monday, November 2, 2015
 Acid-Base Strength Chapter 6 Monday, November 2, 2015 Acid-Base Strength We ve seen that the reactivity of acids and bases can be viewed through the HSAB Model or the EC Model. Both of these models try
Acid-Base Strength Chapter 6 Monday, November 2, 2015 Acid-Base Strength We ve seen that the reactivity of acids and bases can be viewed through the HSAB Model or the EC Model. Both of these models try
Journal of the Mexican Chemical Society ISSN: X Sociedad Química de México México
 Journal of the Mexican Chemical Society ISSN: 1870-249X editor.jmcs@gmail.com Sociedad Química de México México Najafi, Meysam On the Antioxidant Activity of the Ortho and Meta Substituted Daidzein Derivatives
Journal of the Mexican Chemical Society ISSN: 1870-249X editor.jmcs@gmail.com Sociedad Química de México México Najafi, Meysam On the Antioxidant Activity of the Ortho and Meta Substituted Daidzein Derivatives
Substituent Effects on the Binding Energies of Benzyl Alcohol-H 2 O Clusters: Ab initio Study
 262 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2002, Vol. 23, No. 2 Doo-Sik Ahn and Sungyul Lee Substituent Effects on the Binding Energies of Benzyl Alcohol-H 2 O Clusters: Ab initio Study Doo-Sik Ahn and Sungyul Lee *
262 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2002, Vol. 23, No. 2 Doo-Sik Ahn and Sungyul Lee Substituent Effects on the Binding Energies of Benzyl Alcohol-H 2 O Clusters: Ab initio Study Doo-Sik Ahn and Sungyul Lee *
Lecture 12 (2/17/17) Phenols. Chapter 18 in Loudon, M.; Parise, J. Organic Chemistry, 6th Ed. W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, 2016
 J. G. Rudick CHE 322: rganic Chemistry IIA Lecture 12 (2/17/17) Phenols Chapter 18 in Loudon, M.; Parise, J. rganic Chemistry, 6th Ed. W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, 2016 Prof. Jon Rudick ffice Hours: CHEM
J. G. Rudick CHE 322: rganic Chemistry IIA Lecture 12 (2/17/17) Phenols Chapter 18 in Loudon, M.; Parise, J. rganic Chemistry, 6th Ed. W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, 2016 Prof. Jon Rudick ffice Hours: CHEM
Module 2 Acids and Bases. Lecture 3 Acids and Bases
 Module 2 Acids and Bases Lecture 3 Acids and Bases 2.1 Concepts A compound is classified as an acid or a base based on certain properties. At present there are several theories which define the concepts
Module 2 Acids and Bases Lecture 3 Acids and Bases 2.1 Concepts A compound is classified as an acid or a base based on certain properties. At present there are several theories which define the concepts
Chapter 8. Acidity, Basicity and pk a
 Chapter 8 Acidity, Basicity and pk a p182 In this reaction water is acting as a base, according to our definition above, by accepting a proton from HCl which in turn is acting as an acid by donating a
Chapter 8 Acidity, Basicity and pk a p182 In this reaction water is acting as a base, according to our definition above, by accepting a proton from HCl which in turn is acting as an acid by donating a
Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy
 Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy Chromophore The part of a molecule responsible for imparting color, are called as chromospheres. OR The functional groups containing multiple bonds capable of absorbing
Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy Chromophore The part of a molecule responsible for imparting color, are called as chromospheres. OR The functional groups containing multiple bonds capable of absorbing
Characteristic Effects of 4,5-Disubstituted Pyridazin-3-one Derivatives with Various Functional Groups: Ab initio Study
 Structural and Electronic Effects Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, Vol. 28, No. 8 1363 Characteristic Effects of 4,5-Disubstituted Pyridazin-3-one Derivatives with Various Functional Groups: Ab initio Study
Structural and Electronic Effects Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, Vol. 28, No. 8 1363 Characteristic Effects of 4,5-Disubstituted Pyridazin-3-one Derivatives with Various Functional Groups: Ab initio Study
A Theoretical Study of Oxidation of Phenoxy and Benzyl Radicals by HO 2
 A Theoretical Study of xidation of Phenoxy and Benzyl adicals by 2 S. Skokov, A. Kazakov, and F. L. Dryer Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 We
A Theoretical Study of xidation of Phenoxy and Benzyl adicals by 2 S. Skokov, A. Kazakov, and F. L. Dryer Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 We
Chemistry 204: Benzene and Aromaticity
 Chemistry 204: Benzene and Aromaticity Structure of and Bonding in Benzene benzene, C 6 H 6, was first isolated in 1825 (Michael Faraday), but it was not until more than 100 years later that an adequate
Chemistry 204: Benzene and Aromaticity Structure of and Bonding in Benzene benzene, C 6 H 6, was first isolated in 1825 (Michael Faraday), but it was not until more than 100 years later that an adequate
Structure, Electronic and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Furyloxazoles and Thienyloxazoles
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structure, Electronic and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Furyls and Thienyls To cite this article: Ozlem Dagli et al 6 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 77 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structure, Electronic and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Furyls and Thienyls To cite this article: Ozlem Dagli et al 6 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 77 View
CHAPTER-IV. FT-IR and FT-Raman investigation on m-xylol using ab-initio HF and DFT calculations
 4.1. Introduction CHAPTER-IV FT-IR and FT-Raman investigation on m-xylol using ab-initio HF and DFT calculations m-xylol is a material for thermally stable aramid fibers or alkyd resins [1]. In recent
4.1. Introduction CHAPTER-IV FT-IR and FT-Raman investigation on m-xylol using ab-initio HF and DFT calculations m-xylol is a material for thermally stable aramid fibers or alkyd resins [1]. In recent
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2005, 6, International Journal of
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2005, 6, 11-17 International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 2005 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/ijms/ Substituent Effects in the 13 C-NMR Spectra of Six-Membered Nitrogen Heteroaromatic
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2005, 6, 11-17 International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 2005 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/ijms/ Substituent Effects in the 13 C-NMR Spectra of Six-Membered Nitrogen Heteroaromatic
Elucidating the structure of light absorbing styrene. carbocation species formed within zeolites SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Elucidating the structure of light absorbing styrene carbocation species formed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Elucidating the structure of light absorbing styrene carbocation species formed
Chapter 3 Results. 3.1 Accurate pk a computation pk a values for a heterogeneous group of organic molecules
 69 Chapter 3 Results 3.1 Accurate pk a computation Single molecule studies to compute pk a values, PA values (for a definition of PA values see: eq. 2.1) and the electrostatic solvation free energies were
69 Chapter 3 Results 3.1 Accurate pk a computation Single molecule studies to compute pk a values, PA values (for a definition of PA values see: eq. 2.1) and the electrostatic solvation free energies were
11/30/ Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions. Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions
 Chapter 9 Problems: 9.1-29, 32-34, 36-37, 39-45, 48-56, 58-59, 61-69, 71-72. 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic
Chapter 9 Problems: 9.1-29, 32-34, 36-37, 39-45, 48-56, 58-59, 61-69, 71-72. 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic
Key ideas: In EAS, pi bond is Nu and undergoes addition.
 Objective 7. Apply addition and elimination concepts to predict electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (EAS) of benzene and monosubstituted benzenes. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features
Objective 7. Apply addition and elimination concepts to predict electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (EAS) of benzene and monosubstituted benzenes. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features
Notes. Rza Abbasoglu*, Abdurrahman Atalay & Ahmet Şenocak. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 53A, March, 2014, pp
 Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 53A, March, 2014, pp. 288-293 Notes DFT investigations of the Diels-Alder reaction of fulvene with tetracyclo[6.2.2.1 3,6.0 2,7 ]trideca-4,9,11-triene- 9,10-dicarboxylic
Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 53A, March, 2014, pp. 288-293 Notes DFT investigations of the Diels-Alder reaction of fulvene with tetracyclo[6.2.2.1 3,6.0 2,7 ]trideca-4,9,11-triene- 9,10-dicarboxylic
Electronic Structure. Hammett Correlations. Linear Free Energy Relationships. Quantitative Structure Activity Relationships (QSAR)
 Electronic Structure ammett Correlations Quantitative Structure Activity Relationships (QSAR) Quantitative Structure Activity Relationships (QSAR) We have already seen that by changing groups in a drug
Electronic Structure ammett Correlations Quantitative Structure Activity Relationships (QSAR) Quantitative Structure Activity Relationships (QSAR) We have already seen that by changing groups in a drug
CHEMISTRY. Module No and Title Module-, Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: The ortho/para ipso attack, orientation in other ring systems.
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Paper-5, Organic Chemistry-II Module No and Title Module-, Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: The ortho/para Module Tag CHE_P5_M29 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Paper-5, Organic Chemistry-II Module No and Title Module-, Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: The ortho/para Module Tag CHE_P5_M29 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes
Electron Affinities of Selected Hydrogenated Silicon Clusters (Si x H y, x ) 1-7, y ) 0-15) from Density Functional Theory Calculations
 J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 6083-6087 6083 Electron Affinities of Selected Hydrogenated Silicon Clusters (Si x H y, x ) 1-7, y ) 0-15) from Density Functional Theory Calculations Mark T. Swihart Department
J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 6083-6087 6083 Electron Affinities of Selected Hydrogenated Silicon Clusters (Si x H y, x ) 1-7, y ) 0-15) from Density Functional Theory Calculations Mark T. Swihart Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Computer-aided molecular design of solvents for accelerated reaction kinetics Heiko Struebing, Zara Ganase, Panagiotis G. Karamertzanis, Eirini Siougkrou, Peter Haycock, Patrick Piccione, Alan Armstrong,
Computer-aided molecular design of solvents for accelerated reaction kinetics Heiko Struebing, Zara Ganase, Panagiotis G. Karamertzanis, Eirini Siougkrou, Peter Haycock, Patrick Piccione, Alan Armstrong,
Important Note: We will NOT accept papers written in pencil back for re-marking after they have been returned to you. Please do not ask!
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 15, 2012; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 15, 2012; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
1 The Hammett cp relationship
 1 The Hammett cp relationship 1.1. Introduction. The student of organic chemistry is introduced early to the theory of two distinct and apparently mutually independent modes for transmission of electronic
1 The Hammett cp relationship 1.1. Introduction. The student of organic chemistry is introduced early to the theory of two distinct and apparently mutually independent modes for transmission of electronic
Chapter 16: Aromatic Compounds
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes xamination 2 Materials Chapter 16: Aromatic Compounds Benzene, the Most Commonly Known Aromatic Compound: The aromatic nature of benzene stabilizes it 36 kcal.mol 1.
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes xamination 2 Materials Chapter 16: Aromatic Compounds Benzene, the Most Commonly Known Aromatic Compound: The aromatic nature of benzene stabilizes it 36 kcal.mol 1.
Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives
COMPUTATIONAL STUDY OF H-A-X (A = GROUP TWO ATOMS, X = F, Cl, Br) MOLECULES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(2), 2010, 914-922 COMPUTATIONAL STUDY OF H-A-X (A = GROUP TWO ATOMS, X = F, Cl, Br) MOLECULES C. YOHANNAN PANICKER *, S. DEEPTHI, HEMA TRESA VARGHESE a and Y. SHEENA MARY a Department
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(2), 2010, 914-922 COMPUTATIONAL STUDY OF H-A-X (A = GROUP TWO ATOMS, X = F, Cl, Br) MOLECULES C. YOHANNAN PANICKER *, S. DEEPTHI, HEMA TRESA VARGHESE a and Y. SHEENA MARY a Department
Physical Organic Chemistry (15 h)
 Course code : CEM 43244 Course title : Advanced rganic Chemistry I Physical rganic Chemistry (15 h) Dr. Dinesh Pandithavidana E-mail: dinesh@kln.ac.lk Mobile: 0777-745-720 ffice: B1 222/3 Stereochemical
Course code : CEM 43244 Course title : Advanced rganic Chemistry I Physical rganic Chemistry (15 h) Dr. Dinesh Pandithavidana E-mail: dinesh@kln.ac.lk Mobile: 0777-745-720 ffice: B1 222/3 Stereochemical
CHM A Look at the Dissociation Pathways of Acetone and Tri-fluoroacetone
 CHM 7440 COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY PROJECT A Look at the Dissociation Pathways of Acetone and Tri-fluoroacetone By Smriti Anand & Muhannad Zamari April 26 th / 2001 Introduction: One of the papers that was
CHM 7440 COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY PROJECT A Look at the Dissociation Pathways of Acetone and Tri-fluoroacetone By Smriti Anand & Muhannad Zamari April 26 th / 2001 Introduction: One of the papers that was
Solvent & geometric effects on non-covalent interactions
 Solvent & geometric effects on non-covalent interactions Scott L. Cockroft PhysChem Forum 10, Syngenta, Jealott s Hill, 23 rd March 11 QSAR & Physical Organic Chemistry Quantifiable Physicochemical Properties
Solvent & geometric effects on non-covalent interactions Scott L. Cockroft PhysChem Forum 10, Syngenta, Jealott s Hill, 23 rd March 11 QSAR & Physical Organic Chemistry Quantifiable Physicochemical Properties
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols
 Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
Computational Studies of the Photoreceptor Rhodopsin. Scott E. Feller Wabash College
 Computational Studies of the Photoreceptor Rhodopsin Scott E. Feller Wabash College Rhodopsin Photocycle Dark-adapted Rhodopsin hn Isomerize retinal Photorhodopsin ~200 fs Bathorhodopsin Meta-II ms timescale
Computational Studies of the Photoreceptor Rhodopsin Scott E. Feller Wabash College Rhodopsin Photocycle Dark-adapted Rhodopsin hn Isomerize retinal Photorhodopsin ~200 fs Bathorhodopsin Meta-II ms timescale
Torsional Potentials of Mono- and Fluoro-halooxopropenolates
 1st WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY, Cairo, Egypt, December 29-31, 7 19 Torsional Potentials of Mono- and Fluoro-halooxopropenolates A. VONGACHARIYA, S. TANTIWATTANAKUL, AND V. PARASUK Department
1st WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY, Cairo, Egypt, December 29-31, 7 19 Torsional Potentials of Mono- and Fluoro-halooxopropenolates A. VONGACHARIYA, S. TANTIWATTANAKUL, AND V. PARASUK Department
Carboxylic Acids. Draw structures corresponding to each of the following IUPAC names propylpentanoic acid. Answer: O. 2. m-chlorobenzoic acid
 arboxylic Acids Draw structures corresponding to each of the following IUPA names. 1. 2-propylpentanoic acid H 2. m-chlorobenzoic acid l H 3. H(H 2 ) 3 H glutaric acid pentanedioic acid 4. H salicylic
arboxylic Acids Draw structures corresponding to each of the following IUPA names. 1. 2-propylpentanoic acid H 2. m-chlorobenzoic acid l H 3. H(H 2 ) 3 H glutaric acid pentanedioic acid 4. H salicylic
Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Chapter 3- SAR and QSAR
 Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Chapter 3- SAR and QSAR Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) - similar
Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Chapter 3- SAR and QSAR Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) - similar
I5 ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTIONS OF
 Section I Aromatic chemistry I5 ELECTPILIC SUBSTITUTINS F MN-SUBSTITUTED AMATIC INGS Key Notes ortho, meta and para substitution Substituent effect eaction profile Activating groups inductive o/p Deactivating
Section I Aromatic chemistry I5 ELECTPILIC SUBSTITUTINS F MN-SUBSTITUTED AMATIC INGS Key Notes ortho, meta and para substitution Substituent effect eaction profile Activating groups inductive o/p Deactivating
Chap. 8 Substitution Reactions
 Chap. 8 Substitution Reactions Y + R X R' Y + X Nucleophilic not necessarily the same as R Electrophilic S N 1 slow (C 3 ) 3 CCl (C + Cl - 3 ) 3 C + (C 3 ) 3 C + OC 2 C 3 C 3 C 2 O C 3 C 2 O d[( C ) 3CCl]
Chap. 8 Substitution Reactions Y + R X R' Y + X Nucleophilic not necessarily the same as R Electrophilic S N 1 slow (C 3 ) 3 CCl (C + Cl - 3 ) 3 C + (C 3 ) 3 C + OC 2 C 3 C 3 C 2 O C 3 C 2 O d[( C ) 3CCl]
5. (6 pts) Show how the following compound can be synthesized from the indicated starting material:
 Exam 2 Name CHEM 212 1. (36 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Exam 2 Name CHEM 212 1. (36 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Quantum chemical studies on the structures of some heterocyclic azo disperse dyes
 Quantum chemical studies on the structures of some heterocyclic azo disperse dyes Nesrin Tokay, a* Zeynel Seferoğlu, b Cemil Öğretir, c and Nermin Ertan b a Hacettepe University, Faculty of Science, Chemistry
Quantum chemical studies on the structures of some heterocyclic azo disperse dyes Nesrin Tokay, a* Zeynel Seferoğlu, b Cemil Öğretir, c and Nermin Ertan b a Hacettepe University, Faculty of Science, Chemistry
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Substituent Effects on the Physical Properties and pk a of Aniline. Department of Chemistry, Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio 45435
 Substituent Effects on the Physical Properties and pk a of Aniline KEVIN C. GROSS, PAUL G. SEYBOLD Department of Chemistry, Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio 45435 Received 29 February 2000; accepted
Substituent Effects on the Physical Properties and pk a of Aniline KEVIN C. GROSS, PAUL G. SEYBOLD Department of Chemistry, Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio 45435 Received 29 February 2000; accepted
Performance of B3PW91, PBE1PBE and OPBE Functionals in Comparison to B3LYP for 13C NMR Chemical Shift Calculations
 Journal of Science and Technology Ubon Ratchathani University : Special Issue November 17 Performance of B3PW91, PBE1PBE and OPBE Functionals in Comparison to B3LYP for 13C NMR Chemical Shift Calculations
Journal of Science and Technology Ubon Ratchathani University : Special Issue November 17 Performance of B3PW91, PBE1PBE and OPBE Functionals in Comparison to B3LYP for 13C NMR Chemical Shift Calculations
Uptake of OH radical to aqueous aerosol: a computational study
 Uptake of OH radical to aqueous aerosol: a computational study Grigory Andreev Karpov Institute of Physical Chemistry 10 Vorontsovo pole, Moscow, 105064, Russia Institute of Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry
Uptake of OH radical to aqueous aerosol: a computational study Grigory Andreev Karpov Institute of Physical Chemistry 10 Vorontsovo pole, Moscow, 105064, Russia Institute of Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY
 4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
Exam (6 pts) Show which starting materials are used to produce the following Diels-Alder products:
 Exam 1 Name CHEM 212 1. (18 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Exam 1 Name CHEM 212 1. (18 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Dr. Zainab M Almarhoon 2 Learning Objectives By the end of chapter four the students will: Understand the resonance description of structure of benzene Understand the hybridization
BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Dr. Zainab M Almarhoon 2 Learning Objectives By the end of chapter four the students will: Understand the resonance description of structure of benzene Understand the hybridization
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 3 A SCALED QUANTUM MECHANICAL APPROACH OF VIBRATIONAL ANALYSIS OF O-TOLUNITRILE BASED ON FTIR AND FT RAMAN SPECTRA, AB INITIO, HARTREE FOCK AND DFT METHODS 3.1. INTRODUCTION o-tolunitrile or ortho
CHAPTER 3 A SCALED QUANTUM MECHANICAL APPROACH OF VIBRATIONAL ANALYSIS OF O-TOLUNITRILE BASED ON FTIR AND FT RAMAN SPECTRA, AB INITIO, HARTREE FOCK AND DFT METHODS 3.1. INTRODUCTION o-tolunitrile or ortho
CHEM1902/ N-8 November Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E.
 CEM1902/4 2014--8 ovember 2014 Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E. 6 ame compounds E and G. E: propionic acid G: methyl propionate Propose structures for compounds
CEM1902/4 2014--8 ovember 2014 Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E. 6 ame compounds E and G. E: propionic acid G: methyl propionate Propose structures for compounds
Organic Chemistry. Second Edition. Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions. David Klein. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e
 Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 19.1 Introduction to Electrophilic
Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 19.1 Introduction to Electrophilic
Practice Hour Examination # 1-1
 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Monday,
CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Monday,
Lecture 10. More Aromatics. February 18, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 18, 2016 eterocyclic Aromatic Compounds N N O S Pyridine Pyrrole Furan Thiophene ückel and Pyridine ückel and Pyrrole uckel and Furan Recognizing Aromatic Compounds Be
Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 18, 2016 eterocyclic Aromatic Compounds N N O S Pyridine Pyrrole Furan Thiophene ückel and Pyridine ückel and Pyrrole uckel and Furan Recognizing Aromatic Compounds Be
2. Which of the following is NOT an electrophile in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction? A) NO 2
 Name: CHEM 226 Practice Quiz 3 Chapter 4-Aromatic Compounds and Chapter 7- Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols Attempt all questions showing your answers and work clearly for full and partial credits 1. Which
Name: CHEM 226 Practice Quiz 3 Chapter 4-Aromatic Compounds and Chapter 7- Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols Attempt all questions showing your answers and work clearly for full and partial credits 1. Which
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes
 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
Modeling Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
 University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Theses and Dissertations 8-2013 Modeling Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Osman Uner University of Arkansas, Fayetteville Follow this and additional
University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Theses and Dissertations 8-2013 Modeling Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Osman Uner University of Arkansas, Fayetteville Follow this and additional
Minnesota Density Functionals
 Main Group Thermochemistry Minnesota Density Functionals D e 2 oncovalent Interactions M06-ass Functionals Long-range Charge Transfer Thermochemical Kinetics Transition Metal Chemistry We have developed
Main Group Thermochemistry Minnesota Density Functionals D e 2 oncovalent Interactions M06-ass Functionals Long-range Charge Transfer Thermochemical Kinetics Transition Metal Chemistry We have developed
Acid Dissociation Constant
 CE 131 Lecture 37 Lewis Acids and Bases Chapter 16: pp. 800-802. Acid Dissociation Constant C 2 3 2 + 2 3 + + C 2 3-2 [ 3 + ][C 2 3-2 ] K = [ 2 ][C 2 3 2 ] [ 3 + ][C 2 3-2 ] K a = K [ 2 ] = [C 2 3 2 ]
CE 131 Lecture 37 Lewis Acids and Bases Chapter 16: pp. 800-802. Acid Dissociation Constant C 2 3 2 + 2 3 + + C 2 3-2 [ 3 + ][C 2 3-2 ] K = [ 2 ][C 2 3 2 ] [ 3 + ][C 2 3-2 ] K a = K [ 2 ] = [C 2 3 2 ]
CHEM1902/ N-8 November Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E.
 CHEM1902/4 2014-N-8 November 2014 Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E. 6 Name compounds E and G. E: G: Propose structures for compounds F, H and J. F H J Propose
CHEM1902/4 2014-N-8 November 2014 Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E. 6 Name compounds E and G. E: G: Propose structures for compounds F, H and J. F H J Propose
The Electronic Structure Studies of Hydroxyl Substituted Benzoic Acids
 Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology Volume 12,Number2(1999) 331-338 1999TAPJ i The Electronic Structure Studies of Hydroxyl Substituted Benzoic Acids Wang Liyuan and Yu Shangxian Department
Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology Volume 12,Number2(1999) 331-338 1999TAPJ i The Electronic Structure Studies of Hydroxyl Substituted Benzoic Acids Wang Liyuan and Yu Shangxian Department
Supporting Information For. metal-free methods for preparation of 2-acylbenzothiazoles and. dialkyl benzothiazole-2-yl phosphonates
 Supporting Information For Peroxide as switch of dialkyl H-phosphonate: two mild and metal-free methods for preparation of 2-acylbenzothiazoles and dialkyl benzothiazole-2-yl phosphonates Xiao-Lan Chen,*,
Supporting Information For Peroxide as switch of dialkyl H-phosphonate: two mild and metal-free methods for preparation of 2-acylbenzothiazoles and dialkyl benzothiazole-2-yl phosphonates Xiao-Lan Chen,*,
Cethrene: The Chameleon of Woodward Hoffmann Rules
 Supporting Information Cethrene: The Chameleon of Woodward Hoffmann Rules Tomáš Šolomek,*, Prince Ravat,, Zhongyu Mou, Miklos Kertesz, and Michal Juríček*,, Department of Chemistry, University of Basel,
Supporting Information Cethrene: The Chameleon of Woodward Hoffmann Rules Tomáš Šolomek,*, Prince Ravat,, Zhongyu Mou, Miklos Kertesz, and Michal Juríček*,, Department of Chemistry, University of Basel,
Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids
 Carboxylic acids have the formula RCO2H. Nomenclature Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids For the parent alkane, drop the terminal e and add the suffix oic acid. The parent alkane is the longest continuous chain
Carboxylic acids have the formula RCO2H. Nomenclature Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids For the parent alkane, drop the terminal e and add the suffix oic acid. The parent alkane is the longest continuous chain
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
CHEM Chapter 20. Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles (homework) W
 CHEM 2425. Chapter 20. Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles (homework) W Short Answer Drawing Instructions: Draw structures corresponding to each of the given names. 1. Draw: 2-propylpentanoic acid 2. Draw: cis-1,3-cyclopentanedicarboxylic
CHEM 2425. Chapter 20. Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles (homework) W Short Answer Drawing Instructions: Draw structures corresponding to each of the given names. 1. Draw: 2-propylpentanoic acid 2. Draw: cis-1,3-cyclopentanedicarboxylic
Acid-Base Chemistry. Chapter Brønsted Acid-Base Chemistry R P
 Chapter 5 Acid-Base Chemistry 5.1 Brønsted Acid-Base Chemistry R P The equilibrium constant (K eq ) gives quick insight into whether the reactant or product is more stable, and the extent to which the
Chapter 5 Acid-Base Chemistry 5.1 Brønsted Acid-Base Chemistry R P The equilibrium constant (K eq ) gives quick insight into whether the reactant or product is more stable, and the extent to which the
AB INITIO MODELING OF THE STRUCTURAL DEFECTS IN AMIDES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(4), 2011, 1564-1568 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com AB INITIO MODELING OF THE STRUCTURAL DEFECTS IN AMIDES M. FATHIMA BEGUM, HEMA TRESA VARGHESE a, Y. SHEENA MARY a, C.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(4), 2011, 1564-1568 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com AB INITIO MODELING OF THE STRUCTURAL DEFECTS IN AMIDES M. FATHIMA BEGUM, HEMA TRESA VARGHESE a, Y. SHEENA MARY a, C.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Synthesis and Properties of the THF Solvates of Extremely Soluble Bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)calcium and Tris(2,6-dimethoxyphenyl)dicalcium
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Synthesis and Properties of the THF Solvates of Extremely Soluble Bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)calcium and Tris(2,6-dimethoxyphenyl)dicalcium
Basic radical reactions in water treatment by ionizing radiation
 Basic radical reactions in water treatment by ionizing radiation By: László Wojnárovits Selectivity, rate constants, main reactions Do up the buttons again Gomboljuk újra a kabátot! 1 General believes:
Basic radical reactions in water treatment by ionizing radiation By: László Wojnárovits Selectivity, rate constants, main reactions Do up the buttons again Gomboljuk újra a kabátot! 1 General believes:
Organic Chemistry II KEY March 27, Which of the following reaction intermediates will form the fastest in the reaction below?
 rganic Chemistry II KEY March 27, 2013 Exam 2: VERSI D 1. Which of the following reaction intermediates will form the fastest in the reaction below? C 1 equiv a 2 a) IV b) III c) II d) II & III e) I I.
rganic Chemistry II KEY March 27, 2013 Exam 2: VERSI D 1. Which of the following reaction intermediates will form the fastest in the reaction below? C 1 equiv a 2 a) IV b) III c) II d) II & III e) I I.
Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides
 Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides Ethers (R-O-R ) are compounds with two organic groups attached to an sp 3 oxygen. Epoxides are cyclic ethers where the sp 3 O is a part of a 3-membered ring. Thiols (R-S-H ) and
Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides Ethers (R-O-R ) are compounds with two organic groups attached to an sp 3 oxygen. Epoxides are cyclic ethers where the sp 3 O is a part of a 3-membered ring. Thiols (R-S-H ) and
1. Introduction T = T! " T +T! (1)
 Thymine dimer repair by electron transfer from photo-excited 2!,3!,5!-tri- -acetyl-8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanosine or 2!,3!,5!-tri--acetyl-ribosyluric acid- a theoretical study Marzena Marchaj 1, Iwona Sieradzan
Thymine dimer repair by electron transfer from photo-excited 2!,3!,5!-tri- -acetyl-8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanosine or 2!,3!,5!-tri--acetyl-ribosyluric acid- a theoretical study Marzena Marchaj 1, Iwona Sieradzan
pka Prediction for Organic Acids and Bases
 pka Prediction for Organic Acids and Bases pka Prediction for Organic Acids and Bases D. D. Perrin John Curtin School of Medical Research Australian National Universi~oy Canberra Boyd Dempsey and E. P.
pka Prediction for Organic Acids and Bases pka Prediction for Organic Acids and Bases D. D. Perrin John Curtin School of Medical Research Australian National Universi~oy Canberra Boyd Dempsey and E. P.
Notes of Dr. Anil Mishra at 1
 Introduction Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships QSPR Quantitative Structure-Property Relationships What is? is a mathematical relationship between a biological activity of a molecular system
Introduction Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships QSPR Quantitative Structure-Property Relationships What is? is a mathematical relationship between a biological activity of a molecular system
Quantitative Understanding of Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Treatment of Emerging Contaminants
 Quantitative Understanding of Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Treatment of Emerging Contaminants Daisuke Minakata and John Crittenden School of Civil and Environmental Engineering Brook Byers Institute
Quantitative Understanding of Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Treatment of Emerging Contaminants Daisuke Minakata and John Crittenden School of Civil and Environmental Engineering Brook Byers Institute
Mutual Interplay Between -Electron Interactions and Simultaneous σ-hole Interactions: A Computational Study. M. Solimannejad* and A.R.
 Regular Article PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY RESEARCH Published by the Iranian Chemical Society www.physchemres.org info@physchemres.org Phys. Chem. Res., Vol. 2, No. 1, 1-10, June 2014. DOI: 10.22036/pcr.2014.3817
Regular Article PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY RESEARCH Published by the Iranian Chemical Society www.physchemres.org info@physchemres.org Phys. Chem. Res., Vol. 2, No. 1, 1-10, June 2014. DOI: 10.22036/pcr.2014.3817
March 08 Dr. Abdullah Saleh
 March 08 Dr. Abdullah Saleh 1 Effects of Substituents on Reactivity and Orientation The nature of groups already on an aromatic ring affect both the reactivity and orientation of future substitution Activating
March 08 Dr. Abdullah Saleh 1 Effects of Substituents on Reactivity and Orientation The nature of groups already on an aromatic ring affect both the reactivity and orientation of future substitution Activating
Chem 3719 Klein Chapter Practice Problems
 Chem 379 Klein Chapter Practice Problems Dr. Peter Norris, 208 Klein Chapter Problems : Review of General Chemistry. Draw viable structures for molecules with the following molecular formulae. Remember
Chem 379 Klein Chapter Practice Problems Dr. Peter Norris, 208 Klein Chapter Problems : Review of General Chemistry. Draw viable structures for molecules with the following molecular formulae. Remember
Towards a Molecular Understanding of Energetics in Li-S Batteries using Non-Aqueous Electrolytes: A High-level Quantum Chemical Study
 Supporting Information Towards a Molecular Understanding of Energetics in Li-S Batteries using Non-Aqueous Electrolytes: A High-level Quantum Chemical Study Rajeev S. Assary a,b*, Larry A. Curtiss a,b,*,
Supporting Information Towards a Molecular Understanding of Energetics in Li-S Batteries using Non-Aqueous Electrolytes: A High-level Quantum Chemical Study Rajeev S. Assary a,b*, Larry A. Curtiss a,b,*,
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Applications of Computational Chemistry to the Reactions of Lignin
 Applications of Computational Chemistry to the Reactions of Lignin Thomas Elder USDA-Forest Service Southern Research Station ctober 30-ovember 2, 2012 Frontiers in Biorefining, Chemicals and Products
Applications of Computational Chemistry to the Reactions of Lignin Thomas Elder USDA-Forest Service Southern Research Station ctober 30-ovember 2, 2012 Frontiers in Biorefining, Chemicals and Products
