THEORETICAL STUDY OF THE REGIOSELECTIVITY OF THE ADDITION OF THE TRIPLET OXYGEN ATOM TO UNSYMMETRICAL SUBSTITUTED ALKENES
|
|
|
- Kelley Myron Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Theoretical and Computational Chemistry Vol. 11, No. 3 (2012) #.c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: /S THEORETICAL STUDY OF THE REGIOSELECTIVITY OF THE ADDITION OF THE TRIPLET OXYGEN ATOM TO UNSYMMETRICAL SUBSTITUTED ALKENES BOULANOUAR MESSAOUDI and SIDI MOHAMED MEKELLECHE* Laboratory of Applied Thermodynamics and Molecular Modeling Department of Chemistry, University of Tlemcen PB 119, Tlemcen, 13000, Algeria *sm_mekelleche@mail.univ-tlemcen.dz NELAINE MORA-DIEZ Department of Chemistry, Thompson Rivers University 900 McGill Road, Kamloops, BC, V2C 0C8, Canada Received 7 September 2011 Accepted 26 September 2011 A theoretical study of the reactivity and regioselectivity of the addition of the triplet oxygen atom O( 3 P) to a series of unsymmetrical substituted alkenes has been performed at the PMP2/ 6-311þþG (d,p) level of theory. Two reaction pathways, namely, the addition to the substituted carbon atom (-site) and addition to the non-substituted carbon atom (-site), have been studied. Our calculations show that the -addition products are kinetically more favored; whereas the -addition products are found to be thermodynamically more stable. The regioselectivity ð vs. Þ of the addition of the O( 3 P) to the carbon carbon double bond is predicted by means of the relative energies of the localized transition states and also by the calculation of spin densities of the 3 states of reactants and Fukui indices corresponding to the radical attack to alkenes. Our calculations are in good agreement with experimental outcomes. Keywords: Atmospheric reactions; substituted alkenes; O( 3 P) atoms; regioselectivity; ab initio calculations. 1. Introduction Unsaturated compounds possessing a carbon carbon double bond react with various active species in the atmosphere, such as OH and NO 3 radicals, O 3 molecules, Cl, and O atoms. 1 4 More attention has been paid to the reactions of triplet oxygen atom, denoted O( 3 P), with olefins for their importance in our understanding of combustion processes and oxidation mechanisms of hydrocarbons. 5,6 According to Cvetanovic, 6,7 the O( 3 P) atom, when allowed to react with olefins, first adds to one of the olefinic carbons to give a triplet diradical, which is a key step for the atmospheric degradation of unsaturated compounds (see Scheme 1). 527
2 528 B. Messaoudi, S. M. Mekelleche & N. Mora-Diez Scheme 1. The two possible channels of the O( 3 P) addition on the carbon carbon double bond. Radical addition to alkenes has been extensively investigated since it is a powerful synthetic tool for the formation of intermolecular bonds. A great amount of experimental and theoretical studies devoted to the radical additions to unsymmetrical substituted alkenes can be found in the literature The normal pathway is the radical attack, essentially, at the less substituted carbon atom, namely the position, although the radical attack at the position is also experimentally observed Using theoretical approaches, Sekusak et al. have investigated the reactivity and regioselectivity of the addition of hydroxyl radical to halogenated ethenes and found that the radical attack takes place preferentially on the unsubstituted site. 27 Recently, El-Nahas et al. have studied theoretically the relative reactivity and regioselectivity of halogen-substituted ethenes and propene toward the addition of OH radical or O( 3 P) atom, and found that the -addition products are kinetically more favored whereas the -addition products are thermodynamically more favored. 28 Our aim in this work is to perform a theoretical study of the addition of the O( 3 P) atoms to a series of substituted propene and 1-butene compounds (see Scheme 1). The alkene systems under investigation are all unsymmetrical and consequently two reaction pathways can be investigated: (i) the -addition of the O( 3 P) to the substituted carbon atom of the double bond, (ii) the -addition of the O( 3 P) to the non-substituted carbon atom of the double bond. The kinetic control of the additions has been put in evidence by calculations of activation energies corresponding to the two reaction pathways while the thermodynamic control of the additions has been predicted by calculations of reaction enthalpies corresponding to the two possible additions. The positional selectivity,
3 Regioselectivity of the Addition of O( 3 P) to Unsymmetrical Substituted Alkenes 529 namely or, of addition of the O( 3 P) to the carbon-carbon double bond is predicted by means of the calculation of the difference of activation energies and Mulliken spin densities of the triplet state of the alkene systems and also by the calculation of the Fukui indices corresponding to the radical attack on the and the carbon site of the alkene. 2. Computational Details Ab initio calculations were carried out with the Gaussian 03 suite of programs. 29 Using Møller-Plesset perturbation theory truncated at the second-order 30 in conjunction with the 6-311þþG(d,p) basis set, we performed full geometry optimizations for the reactants, products, and transition states (TSs) for the addition of O( 3 P) atom to alkene molecules. Restricted (RMP2) and unrestricted (UMP2) methods were used for the closed and open-shell systems, respectively. Spin contamination of the open-shell systems in this study was small. For the doublet radicals and the triplet biradicals, the expectation values of the total spin S 2 were less than 0.76 and 2.01, respectively, after spin annihilations. For the transition states, spin contamination was slightly larger than in the stable radicals; however, all values of S 2 were less than 0.76 and 2.01 after spin annihilations. For each stationary point, we carried out vibrational frequency calculations and examined the vibrational modes by using the GaussView program. Mulliken spin densities 31 and Fukui indices were calculated in order to predict the regioselectivity of the radical attack. The Fukui function is defined as the first derivative of the electronic density ðrþ of a system with respect to the number of electrons N at a constant external potential vðrþ. 32 fðrþ ¼ : vðrþ vðrþ N Using left and right derivatives with respect to the number of electrons, electrophilic and nucleophilic Fukui functions for a site k in a molecule can be defined. 33 f k þ ¼½ k ðn þ 1Þ k ðnþš; for nucleophilic attack ð2aþ f k ¼½ k ðnþ k ðn 1ÞŠ; for electrophilic attack ð2bþ f k 0 ¼½ k ðn þ 1Þ k ðn 1ÞŠ=2; for radical attack ð2cþ where k ðnþ; k ðn 1Þ and k ðn þ 1Þ are the gross electronic populations of the site k in neutral, cationic, and anionic systems, respectively. 3. Results and Discussion Table 1 summarizes the MP2/6-311þþG(d, p) optimized bond lengths of reactants, transition states, and diradical products corresponding to the addition of the O( 3 P) atom to a series of substituted alkenes.
4 530 B. Messaoudi, S. M. Mekelleche & N. Mora-Diez Table 1. Bond lengths (A) for reactants, transition states, and products. Transition state Product Entry # Substrate -Addition -Addition -Addition -Addition 1 C1-C C2-C C-O C1-C C2-C C-F C-O C1-C C2-C C2-C C-O C1-C C2-C C3-C C-O C1-C C2-C C2-C C4-C C-O C1-C C2-C C3-C C3-C C-O Addition of O( 3 P) atom to the carbon carbon double bond leads to a change of the hybridization of carbon atoms of the parent molecules; the sp 2 carbon atoms become sp 3. On going from the parent alkene molecules to the radical products, the bond length between the carbon atoms is increased and, correspondingly, the carbon carbon bonds are longer for diradical products in comparison with the parent alkene. For instance, O( 3 P) radical addition to 1-butene substrate lengthens the carbon carbon bond from A to and A in the - and-addition radical products, respectively. We note that the C 1 C 2 bonds for -products are longer than those of -products. Inversely, the C O bonds for -products are shorter in comparison with -products. Tables 2 and 3 report the total and relative Gibbs free energies of TSs and products corresponding to the two reaction pathways ð=þ of the addition of the triplet oxygen atom on alkene systems. Comparison between the - and -additions is quite interesting: (i) Both the and additions of the oxygen atom are highly exothermic (H < 0) and the G of the reaction ranges from to 5.73 kcal/mol.
5 Regioselectivity of the Addition of O( 3 P) to Unsymmetrical Substituted Alkenes 531 Table 2. PMP2/ G(d,p) Gibb free energies (in a.u) of reactants and transition states [the Gibbs free energy of the O( 3 P) atom is 74:93832 a.u] and energy differences are in kcal/mol. Transition states Entry # Reactants -addition G # -addition G # The PMP2 Gibbs free energy values do not indicate a stable pattern when comparing the thermodynamic stability of the -and-addition products. A higher level of theory might need to be used for this. (ii) The TSs corresponding to the -addition are lower in energy in comparison with the -TSs. The energy difference ranges from 0.55 kcal/mol (for reaction #6) to 1.64 kcal/mol (for reaction #2). Consequently, the -additions are found to be kinetically more favored than the -additions for all reactions under investigation. In order to confirm the regioselectivity of the additions of O( 3 P) to substituted alkene systems, we have calculated Mulliken spin densities (MSD) at the and sites of the 3 triplet state of alkenes. 27,34 36 The MSD is defined as the difference of the Mulliken charges of spin-up and spin-down electrons. The sum over the Mulliken spin densities equals the total spin of the system. The importance of the relative spin densities in the triplet state in directing the regiochemistry for radical addition could be rationalized considering the state correlation diagram (SCD) model that belongs to the general approach of curve crossing diagrams. 34 The main electronic interactions during radical addition to a double bond can be described as the spin density interactions between the radical and the alkene Table 3. PMP2/6-311 þþg(d,p) Gibbs free energies (in a.u) of reactants and products [the Gibbs free energy of the O( 3 P) atom is 74:93832 a.u] and energy differences are in kcal/mol. Products Entry # Reactants -addition G -addition G
6 532 B. Messaoudi, S. M. Mekelleche & N. Mora-Diez Fig. 1. MP2/6-311þþGðd; pþ optimized structures of the substrate, transition states and product adducts for the reactions of propene (1), 3,3,3-trifluoropropene (2) and 2-methylpropene (3). molecules. For the parent alkene molecule, the triplet 3 state is described with one unpaired electron on each carbon atom. Substitution in the alkene molecule disturbs the symmetry of the electronic spin density and a carbon atom with higher spin density will be more reactive for radical addition. Figure 1 displays MP2/6-311þþG(d,p) optimized structures of the substrate, TSs and product adducts for the reactions of propene 1, 3,3,3-trifluoropropene 2 and 2-methylpropene 3. Figure 2 displays the MP2/6-311þþG(p,d) optimized structures of the substrate transition states and product adducts for the reactions of 1-butene 4, 2-methyl-1- butene 5 and 3-methyl-1-butene 6. According to the frontier molecular orbital (FMO) picture, the major orbital interactions in the transition states will occur between the and orbitals of the Fig. 2. MP2/6-311þþGðd; pþ optimized structures of the substrate, transition states and product adducts for the reactions of: 1-butene (4), 2-methyl-1-butene (5), 3-methyl-1-butene (6).
7 Regioselectivity of the Addition of O( 3 P) to Unsymmetrical Substituted Alkenes 533 Table 4. Relative spin densities in the state 3 * and values for the Fukui functions. Highest values are given in bold. f þ f f Substrate 3 * state Spin density MPA NPA MPA NPA MPA NPA 1 CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ CðÞ alkene molecule and the SOMO of the O( 3 P) atom. The calculated spin densites corresponding to and sites of the 3 state of alkenes are given in Table 4. It turns out that the spin density at the site is higher than the spin density at the site for all triplet states of the alkenes, indicating, that the radical attack of the O( 3 P) atom is more favored on the site. The regioselectivity of the additions of O( 3 P) atoms to substituted alkene systems could also be rationalized using Fukui indices, f 0, corresponding to the radical attack defined in Eq. (2c). The values of Fukui indices for radical attacks on the and sites are reported in Table 4. The atomic gross electron densities were calculated using both Mulliken (MPA) and natural (NPA) population analyses. The tabulated values show that Fukui indices corresponding to the sites are larger than those corresponding to sites for all alkene systems except for 3-methyl-1- butene system. In conclusion both calculated spin densities and condensed Fukui functions show that the regioselectivity is favored over the regioselectivity. Indeed, according to the pioneering experimental works by Cvetanovic as well as the recent studies by Washida et al., 40 and Quandt et al., 41 the initial attack of the oxygen atom occurs, preferably, at the lesser substituted position of the double bond, as a consequence of the electron-releasing character of the alkyl groups, which promotes electron density on the non-substituted beta carbon atom. 4. Conclusions We have carried out ab initio calculations on the addition of O( 3 P) to a series of substituted alkenes. The potential energy surfaces corresponding to the two reaction channels and were studied at the PMP2/6-311þþG(d,p) computational level. Our calculations show that these additions are all exothermic. On the other hand,
8 534 B. Messaoudi, S. M. Mekelleche & N. Mora-Diez the calculated activation barriers show that the -additions are kinetically more favored than the -additions. The calculated spin densities and Fukui indices show that the attack of the triplet oxygen atom takes place preferentially on the least alkyl-substituted site of the double bond of the alkene system. We note that the regioselectivity for O( 3 P) atom addition to substituted alkenes is not governed by the thermodynamic control (products stability) but by the kinetic control (reaction rates). References 1. Atkinson R, Atmos Environ 24A:1, Atkinson R, Arey J, Chem Rev 103:4605, Wayne RP, Chemistry of Atmospheres, 3 rd ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford, Finlayson-Pitts BJ, Pitts Jr JN, Chemistry of the Upper and Lower Atmosphere: Theory, Experiments, and Applications, Academic Press, Saunders D, Heicklen J, J Phys Chem 70:1950, Cvetanovic RJ, Adv Photochem 1:115, Cvetanovic RJ, J Phys Chem 74:2730, Schlegel HB, Sosa C, J Phys Chem 88:1141, Canadell E, Eisenstein O, Ohanessian G, Poblet JM, J Phys Chem 89:4856, Delbecq F, Ilavasky D, Anh NT, Lefour JM, J Am Chem Soc 107:1623, Arnaud R, Subra R, Barone V, Lelj F, Olivella S, Sole A, Russo N, J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 2:1517, Clark T, J Chem Soc Chem Commun 24:1774, Zipse H, He J, Houk KN, Giese B, J Am Chem Soc 113:4324, Tozer DJ, Andrews JS, Amos RD, Handy NC, Chem Phys Lett 199:229, Schmidt C, Warken M, Handy NC, Chem Phys Lett 211:272, Arnaud R, Vidal S, New J Chem 16:471, Wong MW, Pross A, Radom L, Isr J Chem 33:415, Wong MW, Pross A, Radom L, J Am Chem Soc 115:11050, Wong MW, Pross A, Radom L, J Am Chem Soc 116:11938, Wong MW, Pross A, Radom L, J Am Chem Soc 116:6284, Sosa C, Schlegel HB, Int J Quantum Chem 29:1001, Gonzalez C, Sosa C, Schlegel HB, J Phys Chem 93:2435, Houk KN, Paddon-Row MN, Spellmeyer DC, Rondan NG, Nagase S, J Org Chem 51:2874, Tedder JM, Walton C, Tetrahedron 36:701, Tedder JM, Angew Chem Int Ed 21:401, Giese B, Angew Chem Int Ed 22(10):753, Sekusak S, Liedl KR, Sabljic A, J Phys Chem A 102:1583, El-Nahas AM, Uchimaru T, Sugie M, Tokuhashi K, Sekiya A, J Mol Struct 770:59, Frisch MJ et al., Gaussian 03, Revision C.02, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, Møller C, Plesset MS, Phys Rev 46:618, Mulliken RS, Rieke CA, Orloff D, Orloff H, J Chem Phys 17:1248, Parr RG, Yang W, J Am Chem Soc 106:4049, Yang W, Mortier WJ, J Am Chem Soc 108:5708, Shaik SS, Canadell E, J Am Chem Soc 112:1446, Arnaud R, Vetere V, Barone V, Chem Phys Lett 293:295, 1998.
9 Regioselectivity of the Addition of O( 3 P) to Unsymmetrical Substituted Alkenes Arnaud R, Vetere V, Barone V, J Comput Chem 21:675, Cvetanovic RJ, J Chem Phys 25:376, Cvetanovic RJ, Can J Chem 36(4):623, Cvetanovic RJ, Singleton DL, Rev Chem Intermed 5:183, Washida N, Inomata S, Furubayashi M, J Phys Chem A 102:7924, Quandt R, Min Z, Wang X, Bershon R, J Phys Chem A 102:60, 1998.
Theoretical investigation of mechanism for the gas-phase reaction of OH radical and ethane
 J. At. Mol. Sci. doi: 10.4208/jams.122810.011811a Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 225-233 August 2011 Theoretical investigation of mechanism for the gas-phase reaction of OH radical and ethane Xiao-Ping Hu a, Bing-Xing
J. At. Mol. Sci. doi: 10.4208/jams.122810.011811a Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 225-233 August 2011 Theoretical investigation of mechanism for the gas-phase reaction of OH radical and ethane Xiao-Ping Hu a, Bing-Xing
Molecular Orbital Theory. Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, not held in discrete regions between two bonded atoms
 Molecular Orbital Theory Valence Bond Theory: Electrons are located in discrete pairs between specific atoms Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, not held in discrete regions
Molecular Orbital Theory Valence Bond Theory: Electrons are located in discrete pairs between specific atoms Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, not held in discrete regions
Formation of CO precursors during char gasification with O 2,CO 2 and H 2 O
 Fuel Processing Technology 77 78 (2002) 125 130 www.elsevier.com/locate/fuproc Formation of CO precursors during char gasification with O 2,CO 2 and H 2 O Alejandro Montoya a, *, Fanor Mondragón a, Thanh
Fuel Processing Technology 77 78 (2002) 125 130 www.elsevier.com/locate/fuproc Formation of CO precursors during char gasification with O 2,CO 2 and H 2 O Alejandro Montoya a, *, Fanor Mondragón a, Thanh
Ab initio study on the paths of oxygen abstraction of hydrogen trioxide (HO 3 ) molecule in the HO 3 + SO 2 reaction
 J. Chem. Sci. Vol. 125, No. 4, July 2013, pp. 927 932. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Ab initio study on the paths of oxygen abstraction of hydrogen trioxide (HO 3 ) molecule in the HO 3 + SO 2 reaction
J. Chem. Sci. Vol. 125, No. 4, July 2013, pp. 927 932. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Ab initio study on the paths of oxygen abstraction of hydrogen trioxide (HO 3 ) molecule in the HO 3 + SO 2 reaction
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes
 Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Journal of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry
 Journal of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry of Islamic Azad University of Iran, 8 (1) 1-9: Spring 2011 (J. Phys. Theor. Chem. IAU Iran) ISSN: 1735-2126 Ab initio Study of Simple -Ene Reactions of Propenyl
Journal of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry of Islamic Azad University of Iran, 8 (1) 1-9: Spring 2011 (J. Phys. Theor. Chem. IAU Iran) ISSN: 1735-2126 Ab initio Study of Simple -Ene Reactions of Propenyl
Ab Initio Molecular Orbital Calculations of Electronic Effects on the Kinetics of Cyclopropylcarbinyl Radical Ring Openings
 3618 J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 3618-3623 Ab Initio Molecular Orbital Calculations of Electronic Effects on the Kinetics of Cyclopropylcarbinyl Radical Ring Openings Felix N. Martinez, H. Bernhard Schlegel,*
3618 J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 3618-3623 Ab Initio Molecular Orbital Calculations of Electronic Effects on the Kinetics of Cyclopropylcarbinyl Radical Ring Openings Felix N. Martinez, H. Bernhard Schlegel,*
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature of alkenes.
 Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Reactions of superelectrophilic BH2 +, BCl2 + and AlCl2 + with carbonyl compounds and alkenes 1
 Issue in Honor of Prof.. D. Nenitzescu ARKIV 2002 (ii) 7-18 Reactions of superelectrophilic H2, l2 and All2 with carbonyl compounds and alkenes 1 George. A. lah*, G. K. Surya Prakash, and Golam Rasul Loker
Issue in Honor of Prof.. D. Nenitzescu ARKIV 2002 (ii) 7-18 Reactions of superelectrophilic H2, l2 and All2 with carbonyl compounds and alkenes 1 George. A. lah*, G. K. Surya Prakash, and Golam Rasul Loker
Conjugated Systems. With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn
 Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Conformational energy analysis
 Lab 3 Conformational energy analysis Objective This computational project deals with molecular conformations the spatial arrangement of atoms of molecules. Conformations are determined by energy, so the
Lab 3 Conformational energy analysis Objective This computational project deals with molecular conformations the spatial arrangement of atoms of molecules. Conformations are determined by energy, so the
5. Reactions of Alkenes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
A Theoretical Study of Oxidation of Phenoxy and Benzyl Radicals by HO 2
 A Theoretical Study of xidation of Phenoxy and Benzyl adicals by 2 S. Skokov, A. Kazakov, and F. L. Dryer Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 We
A Theoretical Study of xidation of Phenoxy and Benzyl adicals by 2 S. Skokov, A. Kazakov, and F. L. Dryer Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 We
The Use of Relative Magnitudes of Steric Effects to Explore Reactions of Molecular Halogens With Representative Acyclic
 The Use of Relative Magnitudes of Steric Effects to Explore Reactions of Molecular Halogens With Representative Acyclic Alkenes Donna J. Nelson and Tamy Perng Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
The Use of Relative Magnitudes of Steric Effects to Explore Reactions of Molecular Halogens With Representative Acyclic Alkenes Donna J. Nelson and Tamy Perng Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
Organic Chemistry. Why are these compounds called Organic. What is a Hydrocarbon? Questions: P167 Read
 Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito
 1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
Notes. Rza Abbasoglu*, Abdurrahman Atalay & Ahmet Şenocak. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 53A, March, 2014, pp
 Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 53A, March, 2014, pp. 288-293 Notes DFT investigations of the Diels-Alder reaction of fulvene with tetracyclo[6.2.2.1 3,6.0 2,7 ]trideca-4,9,11-triene- 9,10-dicarboxylic
Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 53A, March, 2014, pp. 288-293 Notes DFT investigations of the Diels-Alder reaction of fulvene with tetracyclo[6.2.2.1 3,6.0 2,7 ]trideca-4,9,11-triene- 9,10-dicarboxylic
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
An ab initio study of the mechanism of the cycloaddition reaction forming bicyclic compounds between vinylidene (H 2 C=C:) and ethylene
 J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 76 (5) 743 749 (2011) UDC 547.313.2+541.124: JSCS 4155 66.095.252.091.7:536.722 Original scientific paper An ab initio study of the mechanism of the cycloaddition reaction forming bicyclic
J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 76 (5) 743 749 (2011) UDC 547.313.2+541.124: JSCS 4155 66.095.252.091.7:536.722 Original scientific paper An ab initio study of the mechanism of the cycloaddition reaction forming bicyclic
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
The Cycloaddition Reactions of Angle Strained Cycloalkynes. A Theoretical Study
 Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2005, 52, 599-624 599 The Cycloaddition Reactions of Angle Strained Cycloalkynes. A Theoretical Study Ming-Der Su* ( ) School of Medicinal and Applied Chemistry,
Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2005, 52, 599-624 599 The Cycloaddition Reactions of Angle Strained Cycloalkynes. A Theoretical Study Ming-Der Su* ( ) School of Medicinal and Applied Chemistry,
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Excluded sections 3.15&3.16
 Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
1. Root of name depends on longest chain of C containing the double bond; ends in "ene"
 Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds
 hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
Bottlenecks in the prediction of regioselectivity of [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions: An assessment of reactivity descriptors
![Bottlenecks in the prediction of regioselectivity of [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions: An assessment of reactivity descriptors Bottlenecks in the prediction of regioselectivity of [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions: An assessment of reactivity descriptors](/thumbs/95/124122018.jpg) J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 117, No. 5, September 2005, pp. 573 582. Indian Academy of Sciences. Bottlenecks in the prediction of regioselectivity of [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions: An assessment of reactivity
J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 117, No. 5, September 2005, pp. 573 582. Indian Academy of Sciences. Bottlenecks in the prediction of regioselectivity of [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions: An assessment of reactivity
Ab Initio MO and TST Calculations for the Rate Constant of the HNO NO : HONO NO
 Ab Initio M and TST Calculations for the Rate Constant of the N N : N N 2 Reaction A. M. MEBEL,* M. C. LIN, K. MRKUMA Cherry L. Emerson Center for Scientific Computation and Department of Chemistry, Emory
Ab Initio M and TST Calculations for the Rate Constant of the N N : N N 2 Reaction A. M. MEBEL,* M. C. LIN, K. MRKUMA Cherry L. Emerson Center for Scientific Computation and Department of Chemistry, Emory
Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides (NO x ) by Superalkalis
 Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides (NO x ) by Superalkalis Ambrish Kumar Srivastava P. G. Department of Physics, Veer Kunwar Singh University, Ara-802301, Bihar, India E-mail: ambrishphysics@gmail.com 1 Abstract
Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides (NO x ) by Superalkalis Ambrish Kumar Srivastava P. G. Department of Physics, Veer Kunwar Singh University, Ara-802301, Bihar, India E-mail: ambrishphysics@gmail.com 1 Abstract
Synthesis, Mechanism, and Properties of Cyclopenta-fused Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Chaolumen. Introduction
 March 22, 2018 Synthesis, Mechanism, and Properties of Cyclopenta-fused Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Reaxys Prize Club Symposium in Japan 2018 Chaolumen Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University
March 22, 2018 Synthesis, Mechanism, and Properties of Cyclopenta-fused Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Reaxys Prize Club Symposium in Japan 2018 Chaolumen Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Density Functional Theory Study on Mechanism of Forming Spiro-Geheterocyclic Ring Compound from Me 2 Ge=Ge: and Acetaldehyde
 CHINESE JURNAL F CHEMICAL PHYSICS VLUME 26, NUMBER 1 FEBRUARY 27, 2013 ARTICLE Density Functional Theory Study on Mechanism of Forming Spiro-Geheterocyclic Ring Compound from Me 2 Ge=Ge: and Acetaldehyde
CHINESE JURNAL F CHEMICAL PHYSICS VLUME 26, NUMBER 1 FEBRUARY 27, 2013 ARTICLE Density Functional Theory Study on Mechanism of Forming Spiro-Geheterocyclic Ring Compound from Me 2 Ge=Ge: and Acetaldehyde
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 31, April 12, 2006
 Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 31, April 12, 2006 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 31, April 12, 2006 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
Competition between Alkalide Characteristics and Nonlinear Optical Properties in OLi 3 M Li 3 O (M = Li, Na, and K) Complexes
 Competition between Alkalide Characteristics and Nonlinear Optical Properties in OLi 3 M Li 3 O (M = Li, Na, and K) Complexes Ambrish Kumar Srivastava and Neeraj Misra * Department of Physics, University
Competition between Alkalide Characteristics and Nonlinear Optical Properties in OLi 3 M Li 3 O (M = Li, Na, and K) Complexes Ambrish Kumar Srivastava and Neeraj Misra * Department of Physics, University
LECTURE #12 Thurs., Oct.13, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2,
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #12 Thurs., Oct.13, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6 How alkenes react: curved arrows to show
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #12 Thurs., Oct.13, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6 How alkenes react: curved arrows to show
CHM 5423 Atmospheric Chemistry Notes on reactions of organics in the troposphere (Chapter 5)
 CHM 5423 Atmospheric Chemistry Notes on reactions of organics in the troposphere (Chapter 5) 5.1 Introduction In general, the lifetime of a molecule in the troposphere is governed by a variet of processes.
CHM 5423 Atmospheric Chemistry Notes on reactions of organics in the troposphere (Chapter 5) 5.1 Introduction In general, the lifetime of a molecule in the troposphere is governed by a variet of processes.
3 - CONJUGATION. More than one double bond can be in a given compound: n=0
 3 - NJUGATIN 1. Terminology and Nomenclature (SF 13.1 13.6; SFS 13.1 13.6) A compound containing a double bond is called an alkene, olefin or maybe simply "ene". There are often other names associated
3 - NJUGATIN 1. Terminology and Nomenclature (SF 13.1 13.6; SFS 13.1 13.6) A compound containing a double bond is called an alkene, olefin or maybe simply "ene". There are often other names associated
Study of Chemical Reactions
 Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Kinetics of nitric oxide desorption from carbonaceous surfaces
 Fuel Processing Technology 77 78 (2002) 453 458 www.elsevier.com/locate/fuproc Kinetics of nitric oxide desorption from carbonaceous surfaces Alejandro Montoya a, Fanor Mondragón a, Thanh N. Truong b,
Fuel Processing Technology 77 78 (2002) 453 458 www.elsevier.com/locate/fuproc Kinetics of nitric oxide desorption from carbonaceous surfaces Alejandro Montoya a, Fanor Mondragón a, Thanh N. Truong b,
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling
 CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Day 1 all calculation data obtained from Gaussian09 using B3LYP/6-31G(d) unless otherwise noted.
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Day 1 all calculation data obtained from Gaussian09 using B3LYP/6-31G(d) unless otherwise noted.
L.7. Mass Spectrum Interpretation
 L.7. Mass Spectrum Interpretation Fragmentation reactions Spectrum interpretation Confirmation of ion structural assignment Biomolecule dissociation Fragmentation reactions 1. Fragmentation reactions of
L.7. Mass Spectrum Interpretation Fragmentation reactions Spectrum interpretation Confirmation of ion structural assignment Biomolecule dissociation Fragmentation reactions 1. Fragmentation reactions of
An Overview of Organic Reactions
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
Andrew Zahrt Denmark Group Meeting
 Andrew Zahrt Denmark Group Meeting 4.28.15 Introduction Early Publications/Hypotheses: Thermodynamic Product Stability Ground State Destabilization Transition State Stabilization Solvent Effects Gas Phase
Andrew Zahrt Denmark Group Meeting 4.28.15 Introduction Early Publications/Hypotheses: Thermodynamic Product Stability Ground State Destabilization Transition State Stabilization Solvent Effects Gas Phase
Advanced Organic Chemistry
 D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination
 Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination 1. What is β elimination? 2. Alkenes: structure, steroisomerism and stability 3. Elimination Reactions o E2 Mechanism o E1 Mechanism
Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination 1. What is β elimination? 2. Alkenes: structure, steroisomerism and stability 3. Elimination Reactions o E2 Mechanism o E1 Mechanism
What are radicals? H. Cl. Chapter 10 Radical Reactions. Production of radicals. Reactions of radicals. Electronic structure of methyl radical
 What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) Can act as weak nucleophiles
 Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds.
 Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
Dr. P. Wipf Chem /26/2007
 I. Basic Principles I-L. Radicals & Carbenes Features of Radical Reactions Review: Curran, D. P. In Comprehensive Organic Synthesis; B. M. Trost and I. Fleming, Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, 1991; Vol.
I. Basic Principles I-L. Radicals & Carbenes Features of Radical Reactions Review: Curran, D. P. In Comprehensive Organic Synthesis; B. M. Trost and I. Fleming, Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, 1991; Vol.
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Description
 CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry
 CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 5 Alkene: Introduction Thermodynamics and Kinetics Midterm 2... Grades will be posted on Tuesday, Feb. 27 th.
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 5 Alkene: Introduction Thermodynamics and Kinetics Midterm 2... Grades will be posted on Tuesday, Feb. 27 th.
Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes
 1 Literature Seminar Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes 2016. 7. 23. Nagashima Nozomu 2 C-H functionalization by enzymes Enzymes enable aliphatic C-H functionalization 3 P450 oxidation
1 Literature Seminar Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes 2016. 7. 23. Nagashima Nozomu 2 C-H functionalization by enzymes Enzymes enable aliphatic C-H functionalization 3 P450 oxidation
DE-MAN HAN, GUO-LIANG DAI*, ZHEN-ZHONG YAN, CHUAN-FENG WANG, AI-GUO ZHONG
 J. Chil. Chem. Soc., 55, Nº 1 (010) CARBON DIOXIDE ACTIVATION BY Y ATOM AND Y + CATION IN THE GAS PHASE: A DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORETICAL STUDY DE-MAN HAN, GUO-LIANG DAI*, ZHEN-ZHONG YAN, CHUAN-FENG WANG,
J. Chil. Chem. Soc., 55, Nº 1 (010) CARBON DIOXIDE ACTIVATION BY Y ATOM AND Y + CATION IN THE GAS PHASE: A DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORETICAL STUDY DE-MAN HAN, GUO-LIANG DAI*, ZHEN-ZHONG YAN, CHUAN-FENG WANG,
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 The controversial reaction mechanism of Stevens rearrangement: A review Soumendranath
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 The controversial reaction mechanism of Stevens rearrangement: A review Soumendranath
Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1. Oxidative Addition
 Oxidative Addition Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1 An oxidative addition reaction is one in which (usually) a neutral ligand adds to a metal center and in doing so oxidizes the metal, typically
Oxidative Addition Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1 An oxidative addition reaction is one in which (usually) a neutral ligand adds to a metal center and in doing so oxidizes the metal, typically
4. Organic photosynthetic reactions
 4. rganic photosynthetic reactions 100 4.1 eactions of ethenes and aromatic compounds Photoreactivity of ethenes E Geometrical isomerization In π-π* excited states, there is effectively no π bond and so
4. rganic photosynthetic reactions 100 4.1 eactions of ethenes and aromatic compounds Photoreactivity of ethenes E Geometrical isomerization In π-π* excited states, there is effectively no π bond and so
Introduction to Chemical Kinetics AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch
 Introduction to Chemical Kinetics AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Goals for today: Loose ends from last lecture Overview of Chemical Kinetics
Introduction to Chemical Kinetics AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Goals for today: Loose ends from last lecture Overview of Chemical Kinetics
Reaction Mechanism of Polar Diels-Alder Reactions between 3-Nitrofuran and different Dienes. A Theoretical Study.
 Reaction Mechanism of Polar Diels-Alder Reactions between 3-Nitrofuran and different Dienes. A Theoretical Study. MAUR CAINELLI, CARLA RMACHEA, PEDR MANCINI, MARÍA KNEETEMAN* Área Química rgánica Departamento
Reaction Mechanism of Polar Diels-Alder Reactions between 3-Nitrofuran and different Dienes. A Theoretical Study. MAUR CAINELLI, CARLA RMACHEA, PEDR MANCINI, MARÍA KNEETEMAN* Área Química rgánica Departamento
1 Which of the compounds shown are in the same homologous series? 1 CH 3 OH 2 CH 3 CH 2 OH 3 CH 3 COOH C 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH
 1 Which of the compounds shown are in the same homologous series? 1 3 2 3 2 3 3 4 3 2 2 1, 2 and 3 1, 2 and 4 1, 3 and 4 2, 3 and 4 2 Which compound is not an alkane, n 2n+2? 3 2 2 3 ( 3 ) 2 3 3 3 ( 3
1 Which of the compounds shown are in the same homologous series? 1 3 2 3 2 3 3 4 3 2 2 1, 2 and 3 1, 2 and 4 1, 3 and 4 2, 3 and 4 2 Which compound is not an alkane, n 2n+2? 3 2 2 3 ( 3 ) 2 3 3 3 ( 3
and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing.
 Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions
 Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Chapter 10 Free Radicals
 hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
 CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
Radical Reactions. Radical Stability!!! bond dissociation energies X Y X + Y. bond BDE (kcal/mol) bond BDE (kcal/mol) CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 95 O H R 2 C H
 adical eactions adical Stability!!! bond dissociation energies X Y X Y bond BDE (kcal/mol) bond BDE (kcal/mol) C 3 104 108 C 3 C 2 98 110 95 2 C 102 (-) 93 (C-) 92 C 3 C 3 36 89 85 C 3 C 3 80 adical eactions
adical eactions adical Stability!!! bond dissociation energies X Y X Y bond BDE (kcal/mol) bond BDE (kcal/mol) C 3 104 108 C 3 C 2 98 110 95 2 C 102 (-) 93 (C-) 92 C 3 C 3 36 89 85 C 3 C 3 80 adical eactions
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
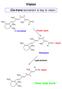 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling
 CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Part 1: Molecular Orbital Theory, Hybridization, & Formal Charge * all calculation data obtained
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Part 1: Molecular Orbital Theory, Hybridization, & Formal Charge * all calculation data obtained
Theoretical study of the complex reaction of O( 3 P) with cis-2-butene
 Theor Chem Acc (201) 12:194 DOI 10.1007/s00214-01-194-0 REGULAR ARTICLE Theoretical study of the complex reaction of O( P) with cis-2-butene Boulanouar Messaoudi Sidi Mohamed Mekelleche Nelaine Mora-Diez
Theor Chem Acc (201) 12:194 DOI 10.1007/s00214-01-194-0 REGULAR ARTICLE Theoretical study of the complex reaction of O( P) with cis-2-butene Boulanouar Messaoudi Sidi Mohamed Mekelleche Nelaine Mora-Diez
Calculation of Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity of Molecule of Hydro- and Fluorinefullerenes C 60 H(F) n (0 n 60)
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 FULLERENES, NANOTUBES, AND CARBON NANOSTRUCTURES Vol. 12, No. 1, pp. 513 519, 2004 Calculation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 FULLERENES, NANOTUBES, AND CARBON NANOSTRUCTURES Vol. 12, No. 1, pp. 513 519, 2004 Calculation
N-Heterocyclic Carbenes
 N-Heterocyclic Carbenes References 1. "N-Heterocyclic Carbenes as Organocatalysts." Marion, N.; Diez- Gonzalez, S.; Nolan, S.P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 26, 2988. (general review) 2. "Stable Carbenes."
N-Heterocyclic Carbenes References 1. "N-Heterocyclic Carbenes as Organocatalysts." Marion, N.; Diez- Gonzalez, S.; Nolan, S.P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 26, 2988. (general review) 2. "Stable Carbenes."
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
Química Orgânica I. Organic Reactions
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Chapter 13. Conjugated Unsaturated Systems. +,., - Allyl. What is a conjugated system? AllylicChlorination (High Temperature)
 What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A
 An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems. Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Electron Affinities of Selected Hydrogenated Silicon Clusters (Si x H y, x ) 1-7, y ) 0-15) from Density Functional Theory Calculations
 J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 6083-6087 6083 Electron Affinities of Selected Hydrogenated Silicon Clusters (Si x H y, x ) 1-7, y ) 0-15) from Density Functional Theory Calculations Mark T. Swihart Department
J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 6083-6087 6083 Electron Affinities of Selected Hydrogenated Silicon Clusters (Si x H y, x ) 1-7, y ) 0-15) from Density Functional Theory Calculations Mark T. Swihart Department
Essential Organic Chemistry. Chapter 9
 Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition. Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i. Chapter 10 Alkenes
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
17.3 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC ANIONS
 798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch Handouts 1
 Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
Ch.6 Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
 alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry. Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School
 Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
*Assignments could be reversed. *
 Name Key 5 W-Exam No. Page I. (6 points) Identify the indicated pairs of hydrogens in each of the following compounds as (i) homotopic, (ii) enantiotopic, or (iii) diastereotopic s. Write the answers as
Name Key 5 W-Exam No. Page I. (6 points) Identify the indicated pairs of hydrogens in each of the following compounds as (i) homotopic, (ii) enantiotopic, or (iii) diastereotopic s. Write the answers as
Introduction to Alkenes. Structure and Reactivity
 4 4 Introduction to Alkenes. Structure and Reactivity Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain one or more carbon carbon double bonds. Alkenes are sometimes called olefins, particularly in the chemical industry.
4 4 Introduction to Alkenes. Structure and Reactivity Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain one or more carbon carbon double bonds. Alkenes are sometimes called olefins, particularly in the chemical industry.
Organic Chemistry. Radical Reactions
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Are the Bader Laplacian and the Bohm Quantum Potential Equivalent?
 Are the Bader Laplacian and the Bohm Quantum Potential Equivalent? Creon Levit & Jack Sarfatti NASA Ames Research Center, creon@nas.nasa.gov Internet Science Eductaion Project, sarfatti@well.com ABSTRACT
Are the Bader Laplacian and the Bohm Quantum Potential Equivalent? Creon Levit & Jack Sarfatti NASA Ames Research Center, creon@nas.nasa.gov Internet Science Eductaion Project, sarfatti@well.com ABSTRACT
CHEMISTRY 332 FALL 08 EXAM II October 22-23, 2008
 First Three Letters of Last Name NAME Network ID CHEMISTRY 332 FALL 08 EXAM II October 22-23, 2008 The following materials are permissible during the exam: molecular model kits, course notes (printed,
First Three Letters of Last Name NAME Network ID CHEMISTRY 332 FALL 08 EXAM II October 22-23, 2008 The following materials are permissible during the exam: molecular model kits, course notes (printed,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Formation of Ruthenium Carbenes by gem-hydrogen Transfer to Internal Alkynes: Implications for Alkyne trans-hydrogenation Markus Leutzsch, Larry M. Wolf, Puneet Gupta, Michael Fuchs,
Supporting Information Formation of Ruthenium Carbenes by gem-hydrogen Transfer to Internal Alkynes: Implications for Alkyne trans-hydrogenation Markus Leutzsch, Larry M. Wolf, Puneet Gupta, Michael Fuchs,
A Summary of Organometallic Chemistry
 A Summary of Organometallic Chemistry Counting valence electrons (v.e.) with the ionic model 1. Look at the total charge of the complex Ph 3 P Cl Rh Ph 3 P PPh 3 OC CO 2 Fe OC CO Co + charge:0 charge:
A Summary of Organometallic Chemistry Counting valence electrons (v.e.) with the ionic model 1. Look at the total charge of the complex Ph 3 P Cl Rh Ph 3 P PPh 3 OC CO 2 Fe OC CO Co + charge:0 charge:
