INTERACTIONS BETWEEN GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASES AND 2-DEOXY GLYCOSYL DERIVATIVES OF URIDINE SIMULATED BY MOLECULAR DOCKING
|
|
|
- Norman Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 65 No. 6 pp. 735ñ741, 2008 ISSN Polish Pharmaceutical Society INTERACTIONS BETWEEN GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASES AND 2-DEOXY GLYCOSYL DERIVATIVES OF URIDINE SIMULATED BY MOLECULAR DOCKING ILONA WANDZIK* Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Chemistry, Department of Organic Chemistry, Bioorganic Chemistry and Biotechnology, 4 Krzywoustego St., Gliwice, Poland Abstract: The focus of the present work was to investigate interactions between 2-deoxy sugar derivatives of uridine and active sites of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I and β-1,4-galactosyltransferase I. The ligand-protein interactions were simulated with a docking software (GOLD). The results suggest that the synthesized compounds bind the enzyme by a similar mode as the natural substrate. Keywords: inhibitors of glycosyltransferases, molecular docking, structure-based drug design Glycosyltransferases (GTs) of the Leloir pathway (1) catalyze the transfer of a monosaccharide unit from an activated nucleotide sugar donor to the hydroxyl group of an acceptor with complete regioand stereoselectivity. The molecules to which GTs transfer monosaccharide units include oligosaccharides, proteins or lipids. GTs are involved in several metabolic pathways and modulation of their activities by efficient inhibitors has potential for the control of certain cellular functions (2). Compounds that can modulate the biosynthesis of glycoconjugates are of great interest as novel therapeutic agents. They may also find applications in the study of biological pathways and can be valuable tools in the preparative stereoselective synthesis of oligosaccharides (3, 4). Different strategies have been used to design potent inhibitors of GTs (5-8). Identification of potent inhibitors has been developing very rapidly during the last two decades since the 3D structures of several GTs were found (9-11) and catalytic mechanism proposed (12). The use of computeraided structure-based approach have been very useful for the optimization and de novo discovering inhibitors of GTs. Most GTs utilize donors containing uridine pyrophosphate leaving group (UDP). N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I (GnT I) (10) and β-1,4- galactosyltransferase I (β4galt I) (13) are typical examples. They belong to the GT-A superfamily and employ a DxD motif, which is present on the N- terminal domain, to bind a divalent metal, most commonly Mn 2+ cation. The metal ion is essential for catalysis since it interacts with the pyrophosphate group of the UDP-sugar donor in the enzyme active site. A variety of pyrophosphate analogues that can mimic pyrophosphate-metal interactions have been developed. It has been reported that monosaccharide units might act as pyrophosphatemetal ion complex mimetics (14-16). It is likely that complexation with Mn 2+ is feasible with two hydroxyl group of the sugar. Recently, we have synthesized 2-deoxy-hexopyranosyl derivatives of uridine as donor substrate analogues of gluco- and galactosyltransferases (Figure 1) (17). Compounds A-E are composed of uridine and one or two residues of 2-deoxy-hexopyranose and can be synthesized in a totally stereoselective manner using the Falck-Mioskowski protocol (18). In our study the central 2-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranose moiety replacing the key pyrophosphate unit can be linked with terminal 2-deoxyglycosyl moiety through α-(1 3)-, α-(1 4)- and α-(1 6)- linked glycosidic linkages. The stereoselective synthesis of these compounds requires several steps and purification after each step by column chromatography. The synthesized compounds A-E possessed isopropylidene block as a protection of two hydroxyl groups on ribose part. There is a worry that such compounds * Corresponding author: ilona.wandzik@polsl.pl 735
2 736 ILONA WANDZIK Figure 1. 2-Deoxy-O-glycosyl rings as pyrophosphate linkage mimetics. Figure 2. Set of ligands for docking simulations and selected ligands for synthesis.
3 Interactions between glycosyltransferases and 2-deoxy glycosyl Figure 3. a/ The binding interactions of UDP-GlcNAc, b/ the putative interactions of 2-deoxy-α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1 6)-2-deoxy-α-Dglucopyranosy-(1 5)-uridine (9) in the active site of GnT I. will not fit into the active site of the protein because two polar domains are excluded. Removal of isopropylidene groups can be performed in the presence of trifluoroacetic acid or acetic acid. Unfortunately, yield of deprotection was only 25-30% due to small stability of 2-deoxyglycosidic linkage under acidic conditions. Therefore, as a rational design of potent inhibitors of GTs this report focused on comparison studies by molecular docking of two set of ligands (Figure 2): set A containing totally deprotected derivatives and set B containing structures that can be synthesized according to the described procedure (17). The proposed structures are combinations of several 2-deoxy-hexopyranosyl moieties, connected with uridine. The main objective was to investigate interactions between 2-deoxy sugar derivatives of uridine and active sites of GnT I and β4galt I. The structures with the best affinity will be synthesized and subjected to biological studies. Methodology X-ray structure of GnT I complexed with UDP-GlcNAc (PDB 1FOA) (10) and b4galt I (PDB 1O0R) (13), in which all the active site amino acid residues were resolved, were chosen for docking purpose. Before docking simulations ligands were removed from the active sites. Hydrogen atoms were added to protein, all the water molecules present in protein were removed and proper protonation states were assigned for acidic and basic residues of protein using molecular graphics pro-
4 738 ILONA WANDZIK Figure 4. a/ The binding interactions of UDP-Gal, b/ the putative interactions of 2-deoxy-α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1 6)-2-deoxy-α-Dglucopyranosyl-(1 5)-uridine (9) in the active site of β4galt I. gram ñ the Chimera software (UCSF Chimera, for detailed information, see /chimera). The Mn 2+ ion was placed in the active sites of each protein considering octahedral geometry of this ion. Possible geometries of analyzed ligands 1-28 were found using MOPACís AM1 quantum semiempirical method implemented in Chem3D system. Docking simulations were performed using GOLD 3.2 software (19), which does flexible docking using a genetic algorithm. A 10 Å radius active site was defined considering the points: (1.49, 18.82, 11.01) and (10.70, 25.79, 33.14) as the center of the active site for GnT I and β4galt I, respectively. All docking runs were carried out using standard default settings with a population size of 100, a maximum of operations, number of islands as 5, a niche size of 2, and a mutation and crossover rate of 95. Ten orientations of the highest score for each compound were then selected using the score function GoldScore. The resulted top scored orientations of docked ligands 1-28 were inspected visually. Visual inspection of the structures was performed with GoldMine 1.0. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A small but diverse library containing 28 compounds was assembled (Figure 2). Structures in the set possess common uridine motif and two moieties
5 Interactions between glycosyltransferases and 2-deoxy glycosyl Table 1. H-bond interactions and the active site amino acid residues interacting with highly scored ligands. Docking into the active site of GnT I (PDB 1FOA) Entry Ligand Ranking b Hbound His190 Asp144 Distance to Goldscore Other interacting amino acid residues count (Å) d (Å) d Mn (Å) Fitness O2 2.5 N3 Val321, Asp212, Ala114, Cys O4î O6î O2 - Ile113 a, Asp212, Arg117, Gly317, Arg295, Asp291, Leu O3î O2 2.9 N3 Ile113 a, Ala114, Arg117, Gly320 a, Arg318 a 2.1 O3î O2 - Asp212, Asp212, Arg117, Asp213, Asp291, Asp O3î O4î O2 - Asp212, Asp212, Gly317, Asp O3î O4î Docking into the active site of b4galt I (PDB 1O0R) Entry Ligand Ranking c Hbound Arg189 a Arg189 a Other interacting amino acid residues Distance Goldscore count (Å) d (Å) d to Mn (Å) Fitness O2 2.4 N3 Pro187 a, Tyr289, Glu317, Gly316 a, Asp318, 2.2 O3î O2 2.7 N3 Pro187 a, Tyr289, Val253 a, Asp252, Gly315 a, Glu317, 2.0 O3î O2 2.3 N3 Pro187 a, Asp252, Lys279, Tyr289, Asp O3î O2 1.9 N3 Asn353, Gly315 a, Asn353, Asn318, Tyr289, Trp O2 2.4 N3 Pro187 a, Val253 a, Asn353, Gly315 a, Lys279, Asp252, 2.5 O6îí a backbone; b from total 256 solutions; c from total 248 solutions; d hydrogen bond as distance between donor and acceptor.
6 740 ILONA WANDZIK of 2-deoxy sugar connected by α-(1 3)-, α-(1 4)- or α-(1 6)-linked glycosidic linkages. The uridine fragment is supposed to ensure reasonable interactions with enzyme, similar to that of the natural substrate. As a first macromolecular object rabbit GnT I was chosen. It transfers the first N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) residue onto the oligomannose core, all other enzymes in the hybrid and complex pathway depend on its prior action (20). This enzyme plays a fundamental role in mammalian development. In Figure 3a key residues of GnT I that interact with natural substrate UDP-GlcNAc described by nligil at al. (10) are shown. Manganese ion interacts only with Asp213 and two oxygen atom of pyrophosphate moiety. β4galt I was the second target. Human β4galt I plays a role in the biosynthesis of blood groups antigens and is involved in some pathologies such as arthritis and cancer (21). In Figure 4a key residues of b4galt I that interact with natural substrate UDP-Gal are shown (13). In the first experiment, all ligands 1-28 were docked into the active site of GnT I and the bound conformations inside the active site of GnT I were visually examined. From the obtained complexes only those with proper ligand binding mode of uridine moiety were selected for further analysis. The most important criterion was the possibility of an interaction between: uracil nitrogen (N3) of the ligand and Asp144 in the enzyme active site, uracil oxygen (O2) of the ligand and His190 in the enzyme active site, To further validate these models, binding energies of each docked ligand were evaluated. Goldscore fitness function is composed of four components: protein-ligand hydrogen bond energy, protein-ligand van der Waals energy, ligand internal van der Waals energy and ligand torsional strain energy. The fitness score is taken as the negative of the sum of the components energy terms, so that the larger fitness scores are better. The 30 highest scores from 256 solutions obtained for studied ligands were in the range ñ The first three solutions were ìtail to headî and were ruled out from further analysis. None of the ligands from set B was correctly docked in this range. The best scored ligand 21 from set B shown Goldscore fitness H- bond interactions and the active site amino acid residues interacting with the highly scored ligands and GoldScore fitness are collected in Table 1. As an example the putative interactions of ligand 9 inside the active site of GnT I are shown in Figure 3b. The functional heteroatoms of uridine fragment are within hydrogen bonding distance of the protein residues. Uracil oxygen O2 forms hydrogen bond with His 190 (O N distance 2.9 Å). The O2í and O3í hydroxyl groups of ribose form hydrogen bonds with Asp 212 (O2í O and O3í O distance 2.5 Å and 2.3 Å, respectively). In comparison with natural substrate the O3í hydroxyl group of ribose form additional interactions with Arg117 present in the active site (O3îí O distance 2.7 Å). Moreover, other interactions of terminal 2-deoxy sugar ring are noted. Asp291 forms hydrogen bond with O4íî (O4îí O distance 2.8 Å) and O6îí (O4îí O distance 2.8 Å). This interaction is crucial since Asp291 is the binding site for the second acceptortype substrate. Ligand 9 blocks this site against approaching natural substrate. Distances to manganese ion formed by O3î and O4î of ligand 9 are 2.0 and 2.1 Å, respectively. Generally the highest scored ligands possess α-(1-6) glycosidic linkage between two 2-deoxy sugar rings (6, 9, 12) or α-(1-4) glycosidic linkage as in the case of ligand 8. In the second experiment, ligands 1-28 were docked into the active site of b4galt I. Only ligands that formed interactions between the uracil heteroatoms and backbone oxygen and nitrogen of Arg189 were taken into considerations. The 30 highest scores from 248 solutions were between and None of ligands from set B was correctly docked in this range. Similarly to solutions in the first experiment, the highest scored ligands possess α-(1-6) glycosidic linkage between two 2-deoxy sugar rings (6, 9, 12). On the contrary, no favorable interactions were noted for α-(1-4) linked ligands, but α-(1-3) linked ligands 7 and 13 shown reasonable affinity. The putative interactions of ligand 9 are shown as an example in Figure 4b. Eight hydrogen bonds are found, four of them are formed by uridine moiety to backbone of Arg189, Pro187 and Val253 in similar mode to the natural substrate. Moreover, interactions for oxygen O3î are observed to backbone Gly315 and side chain Glu317. Unfortunately, only one oxygen atom of ligands 9 (O3î) is in bonding distance to manganese ion. Visual analysis of the simulated binding modes of ligands 1-28 into active sites of Gnt I and β4galt I suggests that two hydroxyl groups 2-OH and 3-OH in the ribose moiety were crucial for interactions for both targets. Only the ligands from set A could bind the enzymes active site by a similar mode as its natural substrate. The ligands from set B most often were docked ìtail to headî. Currently, five ligands: 6, 7, 9, 12 and 13 are being synthesized and biolog-
7 Interactions between glycosyltransferases and 2-deoxy glycosyl ical evaluations toward commercially available bovine milk b4galt I will be carried out soon. REFERENCES 1. Leloir L.F.: Science 172, 1299 (1971). 2. Koeller K.M., Wong C-H.: Chem. Rev. 100, 4465 (2000). 3. Bertozzi C.R., Kiessling L.L.: Science 291, 2357 (2001). 4. Sears P., Wong C-H.: Science 291, 2344 (2001). 5. Jung K-H., Schmidt R.R.: in Carbohydrate- Based Drug Discovery, Wong C-H. Ed., Vol. 2, pp , Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim Compain P., Martin O.R.: Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9, 3077 (2001). 7. Zou W.: Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 5, 1363 (2005). 8. Kajimoto T., Node M.: J. Synth. Org. Chem. Jpn. 64, 894 (2006). 9. Kikuchi N., Narimatsu H.: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1760, 578 (2006). 10. nligil U. M., Rini J.M. : Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 10, 510 (2000). 11. Breton C., änajdrov L., Jeanneau C., KoËa J., Imberty A.: Glycobiology 16, 29R (2006). 12. Tvoroöka I., AndrÈ I., Carver J.P.: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 8762 (2000). 13. Gastinel L.N., Cambillau C., Bourne Y.: EMBO J. 18, 3546 (1999). 14. Wang R., Steensma D.H., Takaoka Y., Yun J. W., Kajimoto T., Wong C-H.: Bioorg. Med. Chem. 5, 661 (1997). 15. Behr J-B., Gourlain T., Helimi A., Guillerm G.: Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 13, 1713 (2003). 16. Ballell L., Young R.J., Field R.A.: Org. Biomol. Chem. 3, 1109 (2005). 17. Wandzik I., Bieg T.: Bioorg. Chem. 35, 401 (2007). 18. Bolitt V., Mioskowski C., Lee S.-G., Falck J.R.: J. Org. Chem. 55, 5812 (1990). 19. Jones G., Wilett P., Glein R.C., Leach A.R., Taylor R.: J. Mol. Biol. 267, 727 (1997). 20. Schachter H.: Glycobiology 1, 453 (1991). 21. Burkart M.D., Vincent S.P., D ffel A., Murray B.W., Ley S.V., Wong C.-H.: Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8, 1937 (2000).
Ranjit P. Bahadur Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India. 1 st November, 2013
 Hydration of protein-rna recognition sites Ranjit P. Bahadur Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India 1 st November, 2013 Central Dogma of life DNA
Hydration of protein-rna recognition sites Ranjit P. Bahadur Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India 1 st November, 2013 Central Dogma of life DNA
Receptor Based Drug Design (1)
 Induced Fit Model For more than 100 years, the behaviour of enzymes had been explained by the "lock-and-key" mechanism developed by pioneering German chemist Emil Fischer. Fischer thought that the chemicals
Induced Fit Model For more than 100 years, the behaviour of enzymes had been explained by the "lock-and-key" mechanism developed by pioneering German chemist Emil Fischer. Fischer thought that the chemicals
NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile virus NS2B-NS3 protease
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile
Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2
 2 Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2 Overview Viewing the accessible surface Analyzing the properties of proteins containing thousands of atoms is best accomplished by representing
2 Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2 Overview Viewing the accessible surface Analyzing the properties of proteins containing thousands of atoms is best accomplished by representing
Structural Perspectives on Drug Resistance
 Structural Perspectives on Drug Resistance Irene Weber Departments of Biology and Chemistry Molecular Basis of Disease Program Georgia State University Atlanta, GA, USA What have we learned from 20 years
Structural Perspectives on Drug Resistance Irene Weber Departments of Biology and Chemistry Molecular Basis of Disease Program Georgia State University Atlanta, GA, USA What have we learned from 20 years
Biological Macromolecules
 Introduction for Chem 493 Chemistry of Biological Macromolecules Dr. L. Luyt January 2008 Dr. L. Luyt Chem 493-2008 1 Biological macromolecules are the molecules of life allow for organization serve a
Introduction for Chem 493 Chemistry of Biological Macromolecules Dr. L. Luyt January 2008 Dr. L. Luyt Chem 493-2008 1 Biological macromolecules are the molecules of life allow for organization serve a
Structure Investigation of Fam20C, a Golgi Casein Kinase
 Structure Investigation of Fam20C, a Golgi Casein Kinase Sharon Grubner National Taiwan University, Dr. Jung-Hsin Lin University of California San Diego, Dr. Rommie Amaro Abstract This research project
Structure Investigation of Fam20C, a Golgi Casein Kinase Sharon Grubner National Taiwan University, Dr. Jung-Hsin Lin University of California San Diego, Dr. Rommie Amaro Abstract This research project
7.012 Problem Set 1 Solutions
 ame TA Section 7.012 Problem Set 1 Solutions Your answers to this problem set must be inserted into the large wooden box on wheels outside 68120 by 4:30 PM, Thursday, September 15. Problem sets will not
ame TA Section 7.012 Problem Set 1 Solutions Your answers to this problem set must be inserted into the large wooden box on wheels outside 68120 by 4:30 PM, Thursday, September 15. Problem sets will not
Modelling of Possible Binding Modes of Caffeic Acid Derivatives to JAK3 Kinase
 John von Neumann Institute for Computing Modelling of Possible Binding Modes of Caffeic Acid Derivatives to JAK3 Kinase J. Kuska, P. Setny, B. Lesyng published in From Computational Biophysics to Systems
John von Neumann Institute for Computing Modelling of Possible Binding Modes of Caffeic Acid Derivatives to JAK3 Kinase J. Kuska, P. Setny, B. Lesyng published in From Computational Biophysics to Systems
7.012 Problem Set 1. i) What are two main differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
 ame 7.01 Problem Set 1 Section Question 1 a) What are the four major types of biological molecules discussed in lecture? Give one important function of each type of biological molecule in the cell? b)
ame 7.01 Problem Set 1 Section Question 1 a) What are the four major types of biological molecules discussed in lecture? Give one important function of each type of biological molecule in the cell? b)
Computer simulations of protein folding with a small number of distance restraints
 Vol. 49 No. 3/2002 683 692 QUARTERLY Computer simulations of protein folding with a small number of distance restraints Andrzej Sikorski 1, Andrzej Kolinski 1,2 and Jeffrey Skolnick 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Vol. 49 No. 3/2002 683 692 QUARTERLY Computer simulations of protein folding with a small number of distance restraints Andrzej Sikorski 1, Andrzej Kolinski 1,2 and Jeffrey Skolnick 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
It s the amino acids!
 Catalytic Mechanisms HOW do enzymes do their job? Reducing activation energy sure, but HOW does an enzyme catalysis reduce the energy barrier ΔG? Remember: The rate of a chemical reaction of substrate
Catalytic Mechanisms HOW do enzymes do their job? Reducing activation energy sure, but HOW does an enzyme catalysis reduce the energy barrier ΔG? Remember: The rate of a chemical reaction of substrate
Carbohydrate- Protein interac;ons are Cri;cal in Life and Death. Other Cells. Hormones. Viruses. Toxins. Cell. Bacteria
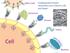 ther Cells Carbohydrate- Protein interac;ons are Cri;cal in Life and Death ormones Viruses Toxins Cell Bacteria ow to Model Protein- ligand interac;ons? Protein Protein Protein DNA/RNA Protein Carbohydrate
ther Cells Carbohydrate- Protein interac;ons are Cri;cal in Life and Death ormones Viruses Toxins Cell Bacteria ow to Model Protein- ligand interac;ons? Protein Protein Protein DNA/RNA Protein Carbohydrate
Packing of Secondary Structures
 7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapy-JPET#172536
 A NEW NON-PEPTIDIC INHIBITOR OF THE 14-3-3 DOCKING SITE INDUCES APOPTOTIC CELL DEATH IN CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA SENSITIVE OR RESISTANT TO IMATINIB Manuela Mancini, Valentina Corradi, Sara Petta, Enza
A NEW NON-PEPTIDIC INHIBITOR OF THE 14-3-3 DOCKING SITE INDUCES APOPTOTIC CELL DEATH IN CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA SENSITIVE OR RESISTANT TO IMATINIB Manuela Mancini, Valentina Corradi, Sara Petta, Enza
Enhancing Specificity in the Janus Kinases: A Study on the Thienopyridine. JAK2 Selective Mechanism Combined Molecular Dynamics Simulation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enhancing Specificity in the Janus Kinases: A Study on the Thienopyridine
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enhancing Specificity in the Janus Kinases: A Study on the Thienopyridine
Volume 12(2)
 Open access www.bioinformation.net Volume 12(2) Hypothesis Insights from molecular modeling, docking and simulation of imidazole nucleus containing chalcones with EGFR kinase domain for improved binding
Open access www.bioinformation.net Volume 12(2) Hypothesis Insights from molecular modeling, docking and simulation of imidazole nucleus containing chalcones with EGFR kinase domain for improved binding
Supplementary Information. Broad Spectrum Anti-Influenza Agents by Inhibiting Self- Association of Matrix Protein 1
 Supplementary Information Broad Spectrum Anti-Influenza Agents by Inhibiting Self- Association of Matrix Protein 1 Philip D. Mosier 1, Meng-Jung Chiang 2, Zhengshi Lin 2, Yamei Gao 2, Bashayer Althufairi
Supplementary Information Broad Spectrum Anti-Influenza Agents by Inhibiting Self- Association of Matrix Protein 1 Philip D. Mosier 1, Meng-Jung Chiang 2, Zhengshi Lin 2, Yamei Gao 2, Bashayer Althufairi
Geometrical Concept-reduction in conformational space.and his Φ-ψ Map. G. N. Ramachandran
 Geometrical Concept-reduction in conformational space.and his Φ-ψ Map G. N. Ramachandran Communication paths in trna-synthetase: Insights from protein structure networks and MD simulations Saraswathi Vishveshwara
Geometrical Concept-reduction in conformational space.and his Φ-ψ Map G. N. Ramachandran Communication paths in trna-synthetase: Insights from protein structure networks and MD simulations Saraswathi Vishveshwara
Other Cells. Hormones. Viruses. Toxins. Cell. Bacteria
 Other Cells Hormones Viruses Toxins Cell Bacteria ΔH < 0 reaction is exothermic, tells us nothing about the spontaneity of the reaction Δ H > 0 reaction is endothermic, tells us nothing about the spontaneity
Other Cells Hormones Viruses Toxins Cell Bacteria ΔH < 0 reaction is exothermic, tells us nothing about the spontaneity of the reaction Δ H > 0 reaction is endothermic, tells us nothing about the spontaneity
Structural biology and drug design: An overview
 Structural biology and drug design: An overview livier Taboureau Assitant professor Chemoinformatics group-cbs-dtu otab@cbs.dtu.dk Drug discovery Drug and drug design A drug is a key molecule involved
Structural biology and drug design: An overview livier Taboureau Assitant professor Chemoinformatics group-cbs-dtu otab@cbs.dtu.dk Drug discovery Drug and drug design A drug is a key molecule involved
7.014 Quiz I Handout
 7.014 Quiz I andout Quiz I announcements: Quiz I: Friday, February 27 12:05 12:55 Walker Gym, rd floor (room 5040) **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Wednesday, February 25 7:00 9:00
7.014 Quiz I andout Quiz I announcements: Quiz I: Friday, February 27 12:05 12:55 Walker Gym, rd floor (room 5040) **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Wednesday, February 25 7:00 9:00
Exam I Answer Key: Summer 2006, Semester C
 1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
*Corresponding Author *K. F.: *T. H.:
 Theoretical Analysis of Activity Cliffs among Benzofuranone Class Pim1 Inhibitors Using the Fragment Molecular Orbital Method with Molecular Mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area (FMO+MM-PBSA) Approach
Theoretical Analysis of Activity Cliffs among Benzofuranone Class Pim1 Inhibitors Using the Fragment Molecular Orbital Method with Molecular Mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area (FMO+MM-PBSA) Approach
Chapter 02 Chemical Composition of the Body
 Chapter 02 Chemical Composition of the Body 1. In an atom, the number of Student: A. Protons always equals the number of neutrons B. Of protons always equals the number of electrons C. Of neutrons always
Chapter 02 Chemical Composition of the Body 1. In an atom, the number of Student: A. Protons always equals the number of neutrons B. Of protons always equals the number of electrons C. Of neutrons always
DOCKING TUTORIAL. A. The docking Workflow
 2 nd Strasbourg Summer School on Chemoinformatics VVF Obernai, France, 20-24 June 2010 E. Kellenberger DOCKING TUTORIAL A. The docking Workflow 1. Ligand preparation It consists in the standardization
2 nd Strasbourg Summer School on Chemoinformatics VVF Obernai, France, 20-24 June 2010 E. Kellenberger DOCKING TUTORIAL A. The docking Workflow 1. Ligand preparation It consists in the standardization
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. PAPER NO: _1_ LOCATION: 173 Robert Schultz Theatre PAGE NO: 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM / MBIO 2770 TIME: 1 HOUR
 THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA 1 November 1, 2016 Mid-Term EXAMINATION PAPER NO: _1_ LOCATION: 173 Robert Schultz Theatre PAGE NO: 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM / MBIO 2770 TIME: 1 HOUR EXAMINATION:
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA 1 November 1, 2016 Mid-Term EXAMINATION PAPER NO: _1_ LOCATION: 173 Robert Schultz Theatre PAGE NO: 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM / MBIO 2770 TIME: 1 HOUR EXAMINATION:
Insights into pneumococcal fratricide from crystal structure of the modular killing factor LytC
 Insights into pneumococcal fratricide from crystal structure of the modular killing factor LytC Inmaculada Pérez-Dorado, Ana González, María Morales, Reyes Sanles, Waldemar Striker, Waldemar Vollmer, Shahriar
Insights into pneumococcal fratricide from crystal structure of the modular killing factor LytC Inmaculada Pérez-Dorado, Ana González, María Morales, Reyes Sanles, Waldemar Striker, Waldemar Vollmer, Shahriar
Conformational Analysis
 Conformational Analysis C01 3 C C 3 is the most stable by 0.9 kcal/mole C02 K eq = K 1-1 * K 2 = 0.45-1 * 0.048 = 0.11 C04 The intermediate in the reaction of 2 has an unfavorable syn-pentane interaction,
Conformational Analysis C01 3 C C 3 is the most stable by 0.9 kcal/mole C02 K eq = K 1-1 * K 2 = 0.45-1 * 0.048 = 0.11 C04 The intermediate in the reaction of 2 has an unfavorable syn-pentane interaction,
Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound ogm-csf and ogm-csf as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine
 Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound and as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine GM-CSF (slate) with bound GM-CSF in the GIF:GM-CSF complex (GIF: green,
Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound and as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine GM-CSF (slate) with bound GM-CSF in the GIF:GM-CSF complex (GIF: green,
Multi-scale approaches in description and design of enzymes
 Multi-scale approaches in description and design of enzymes Anastassia Alexandrova and Manuel Sparta UCLA & CNSI Catalysis: it is all about the barrier The inside-out protocol: Big Aim: development of
Multi-scale approaches in description and design of enzymes Anastassia Alexandrova and Manuel Sparta UCLA & CNSI Catalysis: it is all about the barrier The inside-out protocol: Big Aim: development of
Course Notes: Topics in Computational. Structural Biology.
 Course Notes: Topics in Computational Structural Biology. Bruce R. Donald June, 2010 Copyright c 2012 Contents 11 Computational Protein Design 1 11.1 Introduction.........................................
Course Notes: Topics in Computational Structural Biology. Bruce R. Donald June, 2010 Copyright c 2012 Contents 11 Computational Protein Design 1 11.1 Introduction.........................................
Retrieving hits through in silico screening and expert assessment M. N. Drwal a,b and R. Griffith a
 Retrieving hits through in silico screening and expert assessment M.. Drwal a,b and R. Griffith a a: School of Medical Sciences/Pharmacology, USW, Sydney, Australia b: Charité Berlin, Germany Abstract:
Retrieving hits through in silico screening and expert assessment M.. Drwal a,b and R. Griffith a a: School of Medical Sciences/Pharmacology, USW, Sydney, Australia b: Charité Berlin, Germany Abstract:
BSc and MSc Degree Examinations
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BSc and MSc Degree Examinations 2018-9 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Part I Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BSc and MSc Degree Examinations 2018-9 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Part I Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking
Chemistry Problem Set #9 Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class.
 Chemistry 391 - Problem Set #9 Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class. Name 1. There is a real enzyme called cocaine esterase that is produced in bacteria that live at the base of the coca plant. The enzyme
Chemistry 391 - Problem Set #9 Due on Thursday 11/15/18 in class. Name 1. There is a real enzyme called cocaine esterase that is produced in bacteria that live at the base of the coca plant. The enzyme
COMBINATORIAL CHEMISTRY: CURRENT APPROACH
 COMBINATORIAL CHEMISTRY: CURRENT APPROACH Dwivedi A. 1, Sitoke A. 2, Joshi V. 3, Akhtar A.K. 4* and Chaturvedi M. 1, NRI Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Bhopal, M.P.-India 2, SRM College of Pharmacy,
COMBINATORIAL CHEMISTRY: CURRENT APPROACH Dwivedi A. 1, Sitoke A. 2, Joshi V. 3, Akhtar A.K. 4* and Chaturvedi M. 1, NRI Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Bhopal, M.P.-India 2, SRM College of Pharmacy,
User Guide for LeDock
 User Guide for LeDock Hongtao Zhao, PhD Email: htzhao@lephar.com Website: www.lephar.com Copyright 2017 Hongtao Zhao. All rights reserved. Introduction LeDock is flexible small-molecule docking software,
User Guide for LeDock Hongtao Zhao, PhD Email: htzhao@lephar.com Website: www.lephar.com Copyright 2017 Hongtao Zhao. All rights reserved. Introduction LeDock is flexible small-molecule docking software,
Physiochemical Properties of Residues
 Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Using AutoDock for Virtual Screening
 Using AutoDock for Virtual Screening CUHK Croucher ASI Workshop 2011 Stefano Forli, PhD Prof. Arthur J. Olson, Ph.D Molecular Graphics Lab Screening and Virtual Screening The ultimate tool for identifying
Using AutoDock for Virtual Screening CUHK Croucher ASI Workshop 2011 Stefano Forli, PhD Prof. Arthur J. Olson, Ph.D Molecular Graphics Lab Screening and Virtual Screening The ultimate tool for identifying
Exam III. Please read through each question carefully, and make sure you provide all of the requested information.
 09-107 onors Chemistry ame Exam III Please read through each question carefully, and make sure you provide all of the requested information. 1. A series of octahedral metal compounds are made from 1 mol
09-107 onors Chemistry ame Exam III Please read through each question carefully, and make sure you provide all of the requested information. 1. A series of octahedral metal compounds are made from 1 mol
Identifying Interaction Hot Spots with SuperStar
 Identifying Interaction Hot Spots with SuperStar Version 1.0 November 2017 Table of Contents Identifying Interaction Hot Spots with SuperStar... 2 Case Study... 3 Introduction... 3 Generate SuperStar Maps
Identifying Interaction Hot Spots with SuperStar Version 1.0 November 2017 Table of Contents Identifying Interaction Hot Spots with SuperStar... 2 Case Study... 3 Introduction... 3 Generate SuperStar Maps
interactions and reaction mechansims in peroxidases and aldo-keto reductases Carme Rovira ICREA / Parc Científic de Barcelona Barcelona
 Molecular modeling of enzyme-substrate interactions and reaction mechansims in peroxidases and aldo-keto reductases Carme Rovira ICREA / Parc Científic de Barcelona Barcelona What we do Molecular (atomistic)
Molecular modeling of enzyme-substrate interactions and reaction mechansims in peroxidases and aldo-keto reductases Carme Rovira ICREA / Parc Científic de Barcelona Barcelona What we do Molecular (atomistic)
Sequence Based Bioinformatics
 Structural and Functional Analysis of Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase using Sequence-Based Bioinformatics Barry Sexton 1,2 and Troy Wymore 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department
Structural and Functional Analysis of Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase using Sequence-Based Bioinformatics Barry Sexton 1,2 and Troy Wymore 3 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Department
What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and peptides at aqueous graphene interfaces: Electronic Supplementary
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Supplementary Figure 3 a. Structural comparison between the two determined structures for the IL 23:MA12 complex. The overall RMSD between the two
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biopanningg and clone enrichment of Alphabody binders against human IL 23. Positive clones in i phage ELISA with optical density (OD) 3 times higher than background are shown for
Supplementary Figure 1. Biopanningg and clone enrichment of Alphabody binders against human IL 23. Positive clones in i phage ELISA with optical density (OD) 3 times higher than background are shown for
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
Biomolecules: lecture 10
 Biomolecules: lecture 10 - understanding in detail how protein 3D structures form - realize that protein molecules are not static wire models but instead dynamic, where in principle every atom moves (yet
Biomolecules: lecture 10 - understanding in detail how protein 3D structures form - realize that protein molecules are not static wire models but instead dynamic, where in principle every atom moves (yet
Programme Last week s quiz results + Summary Fold recognition Break Exercise: Modelling remote homologues
 Programme 8.00-8.20 Last week s quiz results + Summary 8.20-9.00 Fold recognition 9.00-9.15 Break 9.15-11.20 Exercise: Modelling remote homologues 11.20-11.40 Summary & discussion 11.40-12.00 Quiz 1 Feedback
Programme 8.00-8.20 Last week s quiz results + Summary 8.20-9.00 Fold recognition 9.00-9.15 Break 9.15-11.20 Exercise: Modelling remote homologues 11.20-11.40 Summary & discussion 11.40-12.00 Quiz 1 Feedback
Other Methods for Generating Ions 1. MALDI matrix assisted laser desorption ionization MS 2. Spray ionization techniques 3. Fast atom bombardment 4.
 Other Methods for Generating Ions 1. MALDI matrix assisted laser desorption ionization MS 2. Spray ionization techniques 3. Fast atom bombardment 4. Field Desorption 5. MS MS techniques Matrix assisted
Other Methods for Generating Ions 1. MALDI matrix assisted laser desorption ionization MS 2. Spray ionization techniques 3. Fast atom bombardment 4. Field Desorption 5. MS MS techniques Matrix assisted
Lecture 15: Realities of Genome Assembly Protein Sequencing
 Lecture 15: Realities of Genome Assembly Protein Sequencing Study Chapter 8.10-8.15 1 Euler s Theorems A graph is balanced if for every vertex the number of incoming edges equals to the number of outgoing
Lecture 15: Realities of Genome Assembly Protein Sequencing Study Chapter 8.10-8.15 1 Euler s Theorems A graph is balanced if for every vertex the number of incoming edges equals to the number of outgoing
A Brief Overview of Biochemistry. And I mean BRIEF!
 A Brief Overview of Biochemistry And I mean BRIEF! Introduction A. Chemistry deals with the composition of substances and how they change. B. A knowledge of chemistry is necessary for the understanding
A Brief Overview of Biochemistry And I mean BRIEF! Introduction A. Chemistry deals with the composition of substances and how they change. B. A knowledge of chemistry is necessary for the understanding
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I. 1. Of the 20 standard amino acids, only is not optically active. The reason is that its side chain.
 Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
Figure 1. Molecules geometries of 5021 and Each neutral group in CHARMM topology was grouped in dash circle.
 Project I Chemistry 8021, Spring 2005/2/23 This document was turned in by a student as a homework paper. 1. Methods First, the cartesian coordinates of 5021 and 8021 molecules (Fig. 1) are generated, in
Project I Chemistry 8021, Spring 2005/2/23 This document was turned in by a student as a homework paper. 1. Methods First, the cartesian coordinates of 5021 and 8021 molecules (Fig. 1) are generated, in
Chemistry in Living Systems. By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt SAC Biology Department
 Chemistry in Living Systems By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt SAC Biology Department Matter and Energy Definitions Types of energy Kinetic vs. potential Forms of energy Chemical Ex: ATP Electrical Ex:
Chemistry in Living Systems By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt SAC Biology Department Matter and Energy Definitions Types of energy Kinetic vs. potential Forms of energy Chemical Ex: ATP Electrical Ex:
NAME. EXAM I I. / 36 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BICH421/621 III. / 38 TOTAL /100
 EXAM I I. / 6 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BIH421/621 III. / 8 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE HOIE (6 points) hoose the BEST answer to the question by circling the appropriate letter. 1. An amino
EXAM I I. / 6 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BIH421/621 III. / 8 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE HOIE (6 points) hoose the BEST answer to the question by circling the appropriate letter. 1. An amino
Problem Set 1
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 1 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 15, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. For each of the following parts, pick
2006 7.012 Problem Set 1 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 15, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. For each of the following parts, pick
2: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE BODY
 1 2: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE BODY Although most students of human physiology have had at least some chemistry, this chapter serves very well as a review and as a glossary of chemical terms. In particular,
1 2: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE BODY Although most students of human physiology have had at least some chemistry, this chapter serves very well as a review and as a glossary of chemical terms. In particular,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES. Figure S1
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1 The substrate for DH domain (2R,3R,4R,6R,7S,8S,9R)-3,7,9-trihydroxy-5-oxo-2,4,6,8 tetramethylundecanoate) was docked as two separate fragments shown in magenta and blue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1 The substrate for DH domain (2R,3R,4R,6R,7S,8S,9R)-3,7,9-trihydroxy-5-oxo-2,4,6,8 tetramethylundecanoate) was docked as two separate fragments shown in magenta and blue
Review. Membrane proteins. Membrane transport
 Quiz 1 For problem set 11 Q1, you need the equation for the average lateral distance transversed (s) of a molecule in the membrane with respect to the diffusion constant (D) and time (t). s = (4 D t) 1/2
Quiz 1 For problem set 11 Q1, you need the equation for the average lateral distance transversed (s) of a molecule in the membrane with respect to the diffusion constant (D) and time (t). s = (4 D t) 1/2
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
Automatic Epitope Recognition in Proteins Oriented to the System for Macromolecular Interaction Assessment MIAX
 Genome Informatics 12: 113 122 (2001) 113 Automatic Epitope Recognition in Proteins Oriented to the System for Macromolecular Interaction Assessment MIAX Atsushi Yoshimori Carlos A. Del Carpio yosimori@translell.eco.tut.ac.jp
Genome Informatics 12: 113 122 (2001) 113 Automatic Epitope Recognition in Proteins Oriented to the System for Macromolecular Interaction Assessment MIAX Atsushi Yoshimori Carlos A. Del Carpio yosimori@translell.eco.tut.ac.jp
Chapter 2. Introduction: Chapter Chemical Basis of Life. Structure of Matter:
 Chapter 2.1-2.2 Read text 2.1 and describe why chemistry is important in understanding life. Read text 2.2 and discuss how atomic structure determines how atoms interact. Also describe the types of chemical
Chapter 2.1-2.2 Read text 2.1 and describe why chemistry is important in understanding life. Read text 2.2 and discuss how atomic structure determines how atoms interact. Also describe the types of chemical
Central Dogma. modifications genome transcriptome proteome
 entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
CHMI 2227 EL. Biochemistry I. Test January Prof : Eric R. Gauthier, Ph.D.
 CHMI 2227 EL Biochemistry I Test 1 26 January 2007 Prof : Eric R. Gauthier, Ph.D. Guidelines: 1) Duration: 55 min 2) 14 questions, on 7 pages. For 70 marks (5 marks per question). Worth 15 % of the final
CHMI 2227 EL Biochemistry I Test 1 26 January 2007 Prof : Eric R. Gauthier, Ph.D. Guidelines: 1) Duration: 55 min 2) 14 questions, on 7 pages. For 70 marks (5 marks per question). Worth 15 % of the final
pharmaceutical industry- drug discovery
 ombinatorial hemistry: molecular diversity "Synthesis and pplications of Small Molecule Libraries." Thompson, L..; llman, J.. hem. ev.,, -00. "esign, Synthesis, and valuation of Small-Molecule Libraries.
ombinatorial hemistry: molecular diversity "Synthesis and pplications of Small Molecule Libraries." Thompson, L..; llman, J.. hem. ev.,, -00. "esign, Synthesis, and valuation of Small-Molecule Libraries.
Supplement information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physil Chemistry Chemil Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 216 Supplement information Fullerenol C 6 (OH) 16 prevents amyloid fibrillization of Aβ
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physil Chemistry Chemil Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 216 Supplement information Fullerenol C 6 (OH) 16 prevents amyloid fibrillization of Aβ
Docking. GBCB 5874: Problem Solving in GBCB
 Docking Benzamidine Docking to Trypsin Relationship to Drug Design Ligand-based design QSAR Pharmacophore modeling Can be done without 3-D structure of protein Receptor/Structure-based design Molecular
Docking Benzamidine Docking to Trypsin Relationship to Drug Design Ligand-based design QSAR Pharmacophore modeling Can be done without 3-D structure of protein Receptor/Structure-based design Molecular
 There are two types of polysaccharides in cell: glycogen and starch Starch and glycogen are polysaccharides that function to store energy Glycogen Glucose obtained from primary sources either remains soluble
There are two types of polysaccharides in cell: glycogen and starch Starch and glycogen are polysaccharides that function to store energy Glycogen Glucose obtained from primary sources either remains soluble
Protein Fragment Search Program ver Overview: Contents:
 Protein Fragment Search Program ver 1.1.1 Developed by: BioPhysics Laboratory, Faculty of Life and Environmental Science, Shimane University 1060 Nishikawatsu-cho, Matsue-shi, Shimane, 690-8504, Japan
Protein Fragment Search Program ver 1.1.1 Developed by: BioPhysics Laboratory, Faculty of Life and Environmental Science, Shimane University 1060 Nishikawatsu-cho, Matsue-shi, Shimane, 690-8504, Japan
NAME IV. /22. I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. (48 points; 2 pts each) Choose the BEST answer to the question by circling the appropriate letter.
 NAME Exam I I. /48 September 25, 2017 Biochemistry I II. / 4 BI/CH 421/621 III. /26 IV. /22 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. (48 points; 2 pts each) Choose the BEST answer to the question by circling the
NAME Exam I I. /48 September 25, 2017 Biochemistry I II. / 4 BI/CH 421/621 III. /26 IV. /22 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. (48 points; 2 pts each) Choose the BEST answer to the question by circling the
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 14, 2018 02:00 pm GMT PDB ID : 3RRQ Title : Crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human PD-1 Authors : Lazar-Molnar, E.; Ramagopal, U.A.; Nathenson,
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 14, 2018 02:00 pm GMT PDB ID : 3RRQ Title : Crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human PD-1 Authors : Lazar-Molnar, E.; Ramagopal, U.A.; Nathenson,
Chemistry in Biology. Section 1. Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
 Section 1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Atoms! Chemistry is the study of matter.! Atoms are the building blocks of matter.! Neutrons and protons are located at the center of the atom.! Protons are positively
Section 1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Atoms! Chemistry is the study of matter.! Atoms are the building blocks of matter.! Neutrons and protons are located at the center of the atom.! Protons are positively
CHEM 3653 Exam # 1 (03/07/13)
 1. Using phylogeny all living organisms can be divided into the following domains: A. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Vertebrate B. Archaea and Eukarya C. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Archaea D. Eukarya and Bacteria
1. Using phylogeny all living organisms can be divided into the following domains: A. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Vertebrate B. Archaea and Eukarya C. Bacteria, Eukarya, and Archaea D. Eukarya and Bacteria
Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis
 Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis Voet & Voet: Pages 496-508 Slide 1 Catalytic Mechanisms Catalysis is a process that increases the rate at which a reaction approaches equilibrium Rate enhancement depends
Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis Voet & Voet: Pages 496-508 Slide 1 Catalytic Mechanisms Catalysis is a process that increases the rate at which a reaction approaches equilibrium Rate enhancement depends
Energy and Cellular Metabolism
 1 Chapter 4 About This Chapter Energy and Cellular Metabolism 2 Energy in biological systems Chemical reactions Enzymes Metabolism Figure 4.1 Energy transfer in the environment Table 4.1 Properties of
1 Chapter 4 About This Chapter Energy and Cellular Metabolism 2 Energy in biological systems Chemical reactions Enzymes Metabolism Figure 4.1 Energy transfer in the environment Table 4.1 Properties of
CHEM J-9 June 2014
 CEM1611 2014-J-9 June 2014 Alanine (ala) and lysine (lys) are two amino acids with the structures given below as Fischer projections. The pk a values of the conjugate acid forms of the different functional
CEM1611 2014-J-9 June 2014 Alanine (ala) and lysine (lys) are two amino acids with the structures given below as Fischer projections. The pk a values of the conjugate acid forms of the different functional
Using Higher Calculus to Study Biologically Important Molecules Julie C. Mitchell
 Using Higher Calculus to Study Biologically Important Molecules Julie C. Mitchell Mathematics and Biochemistry University of Wisconsin - Madison 0 There Are Many Kinds Of Proteins The word protein comes
Using Higher Calculus to Study Biologically Important Molecules Julie C. Mitchell Mathematics and Biochemistry University of Wisconsin - Madison 0 There Are Many Kinds Of Proteins The word protein comes
Conformational Geometry of Peptides and Proteins:
 Conformational Geometry of Peptides and Proteins: Before discussing secondary structure, it is important to appreciate the conformational plasticity of proteins. Each residue in a polypeptide has three
Conformational Geometry of Peptides and Proteins: Before discussing secondary structure, it is important to appreciate the conformational plasticity of proteins. Each residue in a polypeptide has three
Secondary Structure. Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2. Structure and Function of Proteins. Further Reading. Φ, Ψ angles alone determine protein structure
 Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Chemistry. Question Type: Multiple Choice. 1) Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
 Microbiology Principles and Explorations 9th Edition Black TEST BANK Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/microbiology-principles-explorations- 9th-edition-black-test-bank/ Microbiology
Microbiology Principles and Explorations 9th Edition Black TEST BANK Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/microbiology-principles-explorations- 9th-edition-black-test-bank/ Microbiology
Flexibility and Constraints in GOLD
 Flexibility and Constraints in GOLD Version 2.1 August 2018 GOLD v5.6.3 Table of Contents Purpose of Docking... 3 GOLD s Evolutionary Algorithm... 4 GOLD and Hermes... 4 Handling Flexibility and Constraints
Flexibility and Constraints in GOLD Version 2.1 August 2018 GOLD v5.6.3 Table of Contents Purpose of Docking... 3 GOLD s Evolutionary Algorithm... 4 GOLD and Hermes... 4 Handling Flexibility and Constraints
Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life
 Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that has weight and occupies space can be described as A. an atom. B. matter. C. a compound. D. a molecule. #1 Learning Outcome:
Chapter 2 Chemical Aspects of Life Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that has weight and occupies space can be described as A. an atom. B. matter. C. a compound. D. a molecule. #1 Learning Outcome:
Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase Cwc27
 Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Feb 17, 2018 01:16 am GMT PDB ID : 1IFT Title : RICIN A-CHAIN (RECOMBINANT) Authors : Weston, S.A.; Tucker, A.D.; Thatcher, D.R.; Derbyshire, D.J.; Pauptit,
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Feb 17, 2018 01:16 am GMT PDB ID : 1IFT Title : RICIN A-CHAIN (RECOMBINANT) Authors : Weston, S.A.; Tucker, A.D.; Thatcher, D.R.; Derbyshire, D.J.; Pauptit,
Problems from Previous Class
 1 Problems from Previous lass 1. What is K m? What are the units of K m? 2. What is V max? What are the units of V max? 3. Write down the Michaelis-Menten equation. 4. What order of reaction is the reaction
1 Problems from Previous lass 1. What is K m? What are the units of K m? 2. What is V max? What are the units of V max? 3. Write down the Michaelis-Menten equation. 4. What order of reaction is the reaction
Atomic weight = Number of protons + neutrons
 1 BIOLOGY Elements and Compounds Element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. Essential elements are chemical elements required for an organism to survive,
1 BIOLOGY Elements and Compounds Element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. Essential elements are chemical elements required for an organism to survive,
Targeting protein-protein interactions: A hot topic in drug discovery
 Michal Kamenicky; Maria Bräuer; Katrin Volk; Kamil Ödner; Christian Klein; Norbert Müller Targeting protein-protein interactions: A hot topic in drug discovery 104 Biomedizin Innovativ patientinnenfokussierte,
Michal Kamenicky; Maria Bräuer; Katrin Volk; Kamil Ödner; Christian Klein; Norbert Müller Targeting protein-protein interactions: A hot topic in drug discovery 104 Biomedizin Innovativ patientinnenfokussierte,
Computational Protein Design
 11 Computational Protein Design This chapter introduces the automated protein design and experimental validation of a novel designed sequence, as described in Dahiyat and Mayo [1]. 11.1 Introduction Given
11 Computational Protein Design This chapter introduces the automated protein design and experimental validation of a novel designed sequence, as described in Dahiyat and Mayo [1]. 11.1 Introduction Given
B O C 4 H 2 O O. NOTE: The reaction proceeds with a carbonium ion stabilized on the C 1 of sugar A.
 hbcse 33 rd International Page 101 hemistry lympiad Preparatory 05/02/01 Problems d. In the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond, the glycosidic bridge oxygen goes with 4 of the sugar B. n cleavage, 18 from
hbcse 33 rd International Page 101 hemistry lympiad Preparatory 05/02/01 Problems d. In the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond, the glycosidic bridge oxygen goes with 4 of the sugar B. n cleavage, 18 from
Advanced Topics in RNA and DNA. DNA Microarrays Aptamers
 Quiz 1 Advanced Topics in RNA and DNA DNA Microarrays Aptamers 2 Quantifying mrna levels to asses protein expression 3 The DNA Microarray Experiment 4 Application of DNA Microarrays 5 Some applications
Quiz 1 Advanced Topics in RNA and DNA DNA Microarrays Aptamers 2 Quantifying mrna levels to asses protein expression 3 The DNA Microarray Experiment 4 Application of DNA Microarrays 5 Some applications
References on Kinetics and Mechanisms
 References on Kinetics and Mechanisms Excellent reference for all aspects of enzyme kinetics including important elements of Metabolic Control Analysis of relevance to systems analysis of enzyme function
References on Kinetics and Mechanisms Excellent reference for all aspects of enzyme kinetics including important elements of Metabolic Control Analysis of relevance to systems analysis of enzyme function
Chapter 4: Amino Acids
 Chapter 4: Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. lipid polysaccharide enzyme 1940s 1980s. Lipids membrane 1960s. Polysaccharide Are energy metabolites and many of
Chapter 4: Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. lipid polysaccharide enzyme 1940s 1980s. Lipids membrane 1960s. Polysaccharide Are energy metabolites and many of
Supplemental Materials for. Structural Diversity of Protein Segments Follows a Power-law Distribution
 Supplemental Materials for Structural Diversity of Protein Segments Follows a Power-law Distribution Yoshito SAWADA and Shinya HONDA* National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST),
Supplemental Materials for Structural Diversity of Protein Segments Follows a Power-law Distribution Yoshito SAWADA and Shinya HONDA* National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST),
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
17. Biomolecular Interaction
 17. Biomolecular Interaction Methods for characterizing biomolecular interactions Sequence-specific DNA binding ligands Molecular mechanisms of drug action and drug resistance In silico compound design
17. Biomolecular Interaction Methods for characterizing biomolecular interactions Sequence-specific DNA binding ligands Molecular mechanisms of drug action and drug resistance In silico compound design
Bioengineering & Bioinformatics Summer Institute, Dept. Computational Biology, University of Pittsburgh, PGH, PA
 Pharmacophore Model Development for the Identification of Novel Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors Edwin Kamau Dept Chem & Biochem Kennesa State Uni ersit Kennesa GA 30144 Dept. Chem. & Biochem. Kennesaw
Pharmacophore Model Development for the Identification of Novel Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors Edwin Kamau Dept Chem & Biochem Kennesa State Uni ersit Kennesa GA 30144 Dept. Chem. & Biochem. Kennesaw
Introductory Biochemistry
 Introductory Biochemistry Instructors Dr. Nafez Abu Tarboush Dr. Mamoun Ahram Recommended textbooks Biochemistry; Mary K. Campbell and Shawn O. Farrell, Brooks Cole; 6 th edition Recommended electronic
Introductory Biochemistry Instructors Dr. Nafez Abu Tarboush Dr. Mamoun Ahram Recommended textbooks Biochemistry; Mary K. Campbell and Shawn O. Farrell, Brooks Cole; 6 th edition Recommended electronic
Chapter 002 The Chemistry of Biology
 Chapter 002 The Chemistry of Biology Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. Atomic B. Living C. Matter D. Energy E. Space 2. The electrons of an atom are A.
Chapter 002 The Chemistry of Biology Multiple Choice Questions 1. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called A. Atomic B. Living C. Matter D. Energy E. Space 2. The electrons of an atom are A.
Protein Struktur (optional, flexible)
 Protein Struktur (optional, flexible) 22/10/2009 [ 1 ] Andrew Torda, Wintersemester 2009 / 2010, AST nur für Informatiker, Mathematiker,.. 26 kt, 3 ov 2009 Proteins - who cares? 22/10/2009 [ 2 ] Most important
Protein Struktur (optional, flexible) 22/10/2009 [ 1 ] Andrew Torda, Wintersemester 2009 / 2010, AST nur für Informatiker, Mathematiker,.. 26 kt, 3 ov 2009 Proteins - who cares? 22/10/2009 [ 2 ] Most important
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Biology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
