Division: Rhodophyta. Division: Rhodophyta species Class: Florideophycidae-6199 species
|
|
|
- Simon Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Division: Rhodophyta Division: Rhodophyta species Class: Florideophycidae-6199 species - advanced reds - always multicellular: filaments or psuedoparenchymat ous -marine, freshwater -almost always multinucleate -many discoid chloroplasts -primary and secondary pit plugs - triphasic life history Part II 1 2 1N gametophytes 2N carposporophyte on Triphasic Life Histories :Terminology mitosis 1N Multiple produced through mitosis in gominoblast filaments Connecting filament or Ooblast filament = tube that carries the zygote nucleus from fertilized egg to internal auxiliary cell where it is cloned and differentiates into carpospores (in some Orders!) Carpogonium on a carpogonial branch 1N 2N Auxiliary cell = vegetative cell (N) that receives the 2N zygote nucleus after fertilization (in some Orders!) Gonimoblast = 2N filaments bearing carposporangia in the carposporophyte (ALL Florideophyceans have this) 1N growth meiosis 1N tetraspores 2N 2N tetrasporophyte 3 4 1
2 Post- fertilization Events Distinguishing between Orders of Florideophycidae Division: Rhodophyta species Auxiliary cell absent Gominoblast initiated from carpogonium cp oo Auxiliary cell present Ooblast filament transfers zygote nucleus to auxiliary cell Auxiliary cell present Auxiliary branch & carpogonial branch arise from same supporting cell Gominoblast initiated from a fused carpogonium & auxiliary cell Order: 29 orders but we will focus on 5 1. Nemaliales -255 species 2. Rhodomeniales-357 species 3. Ceramiales species 4. Gigartinales- 806 species 5. Corallinales- 649 species Gominoblast initiated from auxiliary cell Order: Nemaliales Auxiliary cell absent Gominoblasts initiated from carpogonium Pit plugs characterized by 2 cap layers 3.Class: Florideophycidae 1.Order Nemaliales Genus: Cumagloia Carpogonium Tricogyne Spermatium on gonimoblast filaments - cylindrical with branchlets - multiaxial - saxicolous - intertidal Carpogonial branch 2N carposporophyte on 7 8 2
3 2.Order: Rhodymeniales Auxiliary cell formed before fertilization Auxiliary branch & carpogonial branch arise from same supporting cell Gominoblast initiated from a fused carpogonium & auxiliary cell 3.Class: Florideophycidae 2. OrderRhodomeniales Genus: Rhodomenia Spermatium Carpogonium Carpogonial branch on gonimoblast filaments S A S Supporting Cell Auxiliary Cell -Subtidal, saxicolous - Associated with juvenile fish - Dichotomous branching 2N carposporophyte on 9 - Multiaxial 10 3.Class: Florideophycidae 2. OrderRhodomeniales Genus: Botryocladia 3.Order: Ceramiales Auxiliary cell develops from supporting cell of carpogonial branch after fertilization Ooblast filament forms between carpogonium & auxiliary cell Gominoblast initiated from axiliary cell -Subtidal, saxicolous - Mucus-filled sacs - Multiaxial - sea grapes Carpogonium Carpogonial Branch Tricogyne Spermatium After fertilization S S A S A 11 Supporting cell Ooblast filament trasfers zygote nucleus 2N carposporophyte on on gonimoblast filaments 12 3
4 3.Class: Florideophycidae 3. Order Ceramiales Genus Polysiphonia 3.Class: Florideophycidae 3. Order Ceramiales Genus Ceramium - Prominent trichoblasts which leave scars after they fall off. - Number of pericentral cells helps to identify to species - Polysiphonous 13 - saxicolous or ephiphytic -fully or partially corticated - uniaxial 14 3.Class: Florideophycidae 3. Order Ceramiales Genus Microcladia - saxicolous or epiphytic - fully corticated - distichous - uniaxial 4.Order: Gigartinales (former Cryptonemiales) Auxiliary cell present BEFORE fertilization but on a distant branch Ooblast filament transfers zygote nucleus to auxiliary cell Gominoblast initiated from auxiliary cell Spermatium Ooblast filament trasfers zygote nucleus alternate Supporting Cell A Auxiliary Cell A 2N carposporophyte on on gonimoblast filaments pectinate
5 4. Order Gigartinales- 806 species Genera Mazzaella 4. Order Gigartinales- 806 species Genera Mazzaella Common local species: M. flaccida yellow/green; mid to upper intertidal M. splendens red/purple; low intertidal Iridescence Proteinaceous cuticle Multiple layers Alternating opaque and translucent layers Layering produces light interference patterns that give iridescent appearance when submerged Adaptive advantage unknown - multiaxial - filamentous medulla Gametophyte Carposporophyte Tetrasporophyte 4. Order Gigartinales- 806 species Genus Mastocarpus species complex 1N gametophytes 2N carposporophytes on female gametophyte 4. Order Gigartinales- 806 species Genus Prionitis - multiaxial - filamentous medulla - smells like chlorine (antiherbivory) - often has epiphytes 2N tetrasporophyte
6 4. Order Gigartinales- 806 species Genus Endocladia - uniaxial - thallus covered with bumps (antiherbivory) - very high intertidal - saxicolous - can facilitate recruitment of other algae (Fucoids) Division: Rhodophyta species 5. Order Corallinales- 649 species Cell walls impregnated with CaCO3 Isomorphic alternation of generation Reproductive structures in conceptacles Ecological importance: stabilize reefs, induce invert settlement How do coralline algae become calcified? What is known: Sequestering of Calcium ions from the water column, synthesis of calcium carbonate (CaC0 3) in cell wall Synthesis of calcium carbonate(precipitation) requires a high ph High rates of photosynthesis correlated with high rates of calcification Coralline Algae and Global Warming Carbon reaction in seawater: CO2 + H20 H2C03 HCO3 + H+ CO3 + H+ Carbonic acid more acidic Bicarbonate Increasing CO2 pushes RXN in this direction 2 Carbonate more basic Calcification 2-3x faster in light than dark Global warming likely to lead to a lower in ph (raise in acidity of the world s oceans Highest in young tissue Photosynthesis may raise the ph immediately outside a cell 23 Acidic environment is bad for calcification process big (complicated) trouble for calcified critters and algae!! Lots of current research on this 24 6
7 Order: Corallinales (used to part of Cryptonemiales) Supporting cell acts as an auxiliary cell Carpogonial branches located in conceptacles Gominoblast initiated from a fusion of cells in carpogonial branch Supporting Cell Spermatium on gonimoblast filaments Geniculate corallines upright articulated Non-geniculate corallines Crustose or Unattached Encrusting Branching Geniculum (flexible joint) Intergeniculum (hard part between genicula) Carpogonial Branch Tricogyne Carpogonium 2N carposporophyte on Order Corallinales- 649 species Genera Corallina 5. Order Corallinales- 649 species Genus Bossiella - Common intertidally - Conceptacles on tips -Finely branched, more so than Bossiella or Calliarthron - Intergenicula are thin and tubular and smaller than those on Bossiella or Calliarthron - Common intertidaly - Intergenicula typically heartshaped - Conceptacles in pairs on the face of a segment, not margins - Intergenicula are larger than Corallina
8 5. Order Corallinales- 649 species Genus Caliarthron -Common intertidally -Intergenicula typically wingnut-shaped 5. Order Corallinales- 649 species Genus Lithothamnion rhodolith unattached free-living non- geniculate form biogenic habitat for lots of inverts! - Conceptacles mainly on margins of segments - Calcareous sections are larger than Corallina World Rhodolith Distribution Distributional Limits Depth -light limited in deep, dessicated in shallows Water motion-need intermediate amount of hydraulic energy Sedimentation -smothered by fine sediments low DISTURBANCE high Rhodolith Beds New Report Foster 2001 buried by siltation intact rhodolith bed reduced size, cover sand 8
9 Biogenic Ecosystems Foundation Species Rhodolith beds, reefs that rock and roll Kelp Forests Coral Reefs Seagrass Meadows Rhodolith Beds What are other important features of rhodolith beds? Form complex habitat for a variety of orgamisms Rhodolith Bed Community Cryptofauna/Infauna Epifauna/Epiflora Cover extensive ares of the seafloor, globally distributed hard bottom species soft bottom species 9
10 Longitud (mm) Seasonal Macroalgal Species Scinaia confusa Halymenia hollenbergii Sporochnus bolleanus Kallymenia pertursa Growth Rate L. muellerii 0.6 mm/yr L. margaritae 5.6 mm/yr S. trichotomum 7-8 mm/yr Internal Banding 30 Catalina rhodoliths 1.6 mm/yr New growth Lcal= (X) r2= 0.86 P= Número de bandas 10
11 Coralline algae as global palaeothermometers Banding reflects sea surface temperature signal using SrCO 3 and MgCO 3 Baja California They are found in Pleistocene and Pleiocene fossil deposits Lithothamnion glaciale Kamenos et al Post-fertilization in a nutshell auxiliary cell? Before Yes After Ceramiales Ooblast? (has ooblast) Yes. Gigartinales Auxiliary cell is anywhere in thallus No. Rhodymeniales Fusion with carpegonium No Nemaliales Gonimoblasts from carpegonium Corallinales Fusion of carpegonium with carpegonial branch * Supporting cell acts as auxiliary cell 43 11
0.9 bya = first multicellular algae!
 8/12/14 Photosynthetic organisms on earth 3.45 bya = Cyanobacteria appear and introduce photosynthesis 1.5 bya = first Eukaryotes appeared (nuclear envelope and ER thought to come from invagination of
8/12/14 Photosynthetic organisms on earth 3.45 bya = Cyanobacteria appear and introduce photosynthesis 1.5 bya = first Eukaryotes appeared (nuclear envelope and ER thought to come from invagination of
CLASS: RHODOPHYCEAE SUB-CLASS: BANGIOPHYCIDEAE FLORIDEOPHYCIDEAE
 balumcc@gmail.com CLASS: RHODOPHYCEAE SUB-CLASS: BANGIOPHYCIDEAE FLORIDEOPHYCIDEAE CHLOROPHYLL A, D PHYCOCYANIN AND PHYCOERYTHRIN α & β CAROTENES FLORIDEAN STARCH CELLULOSIC CELL WALL XYLAN IN BANGIOPHYCIDAE
balumcc@gmail.com CLASS: RHODOPHYCEAE SUB-CLASS: BANGIOPHYCIDEAE FLORIDEOPHYCIDEAE CHLOROPHYLL A, D PHYCOCYANIN AND PHYCOERYTHRIN α & β CAROTENES FLORIDEAN STARCH CELLULOSIC CELL WALL XYLAN IN BANGIOPHYCIDAE
Algal Morphology. Unicells- solitary cells can be motile or non motile ex. Chlamydomonas
 Algal Morphology I. Internal thallus morphologies II. External thallus morphologies III.Algal Growth Unicells- solitary cells can be motile or non motile ex. Chlamydomonas Colony- an assemblage of individual
Algal Morphology I. Internal thallus morphologies II. External thallus morphologies III.Algal Growth Unicells- solitary cells can be motile or non motile ex. Chlamydomonas Colony- an assemblage of individual
The Rhodophytes Class Rhodymeniophycedae Order Ceramiales
 The Rhodophytes Red algae are red because of the presence of the pigment phycoerythrin. This pigment reflects red light and absorbs blue light. Because blue light penetrates water to a greater depth than
The Rhodophytes Red algae are red because of the presence of the pigment phycoerythrin. This pigment reflects red light and absorbs blue light. Because blue light penetrates water to a greater depth than
Plantae. Division: Rhodophyta. Glaucophytes Rhodophyta Chlorophytes Charophytes Land Plants
 Division: Rhodophyta DOMAIN Groups (Kingdom) 1.Bacteria- cyanobacteria (blue green algae) 2.Archae 3.Eukaryotes 1. Alveolates- dinoflagellates 2. Stramenopiles- diatoms, Ochrophyta 3. Rhizaria- unicellular
Division: Rhodophyta DOMAIN Groups (Kingdom) 1.Bacteria- cyanobacteria (blue green algae) 2.Archae 3.Eukaryotes 1. Alveolates- dinoflagellates 2. Stramenopiles- diatoms, Ochrophyta 3. Rhizaria- unicellular
Biology. Slide 1of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
What creates a coral reef? Why are corals able to form huge reefs?
 Marine ecosystems 5: Coral Reefs Unique features The foundation of the ecosystem is produced by living things Reef-building corals Similarities with tropical rain forests Richness and complexity 3-dimensional
Marine ecosystems 5: Coral Reefs Unique features The foundation of the ecosystem is produced by living things Reef-building corals Similarities with tropical rain forests Richness and complexity 3-dimensional
Major groups of algae
 Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Physiological changes in crustose coralline algae alter competitive interactions in response to acidification
 Physiological changes in crustose coralline algae alter competitive interactions in response to acidification Sophie J. McCoy, Robert T. Paine, Catherine A. Pfister, and J.Timothy Wootton Third International
Physiological changes in crustose coralline algae alter competitive interactions in response to acidification Sophie J. McCoy, Robert T. Paine, Catherine A. Pfister, and J.Timothy Wootton Third International
Dr.Ayad M.J. Lecture 8 Algae Rhodophyta
 Rhodophyta 1-2 General characteristics phylum (division) of the kingdom Protista consisting of the photosynthetic organisms commonly known as red algae. Most of the world's seaweeds belong to this group.
Rhodophyta 1-2 General characteristics phylum (division) of the kingdom Protista consisting of the photosynthetic organisms commonly known as red algae. Most of the world's seaweeds belong to this group.
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014
 Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring Protist Phylogeny. Meet the algae. Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis. Endosymbiosis. Secondary Endosymbiosis
 Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Glaucophyta. Glaucophyta
 Glaucophyta The Glaucophyta include those algae that have endosymbiotic cyanobacteria in the cytoplasm instead of chloroplasts. Because of the nature of their symbiotic association, they are thought to
Glaucophyta The Glaucophyta include those algae that have endosymbiotic cyanobacteria in the cytoplasm instead of chloroplasts. Because of the nature of their symbiotic association, they are thought to
4 Marine Biology Notes. Multi-cellular Primary Producers: Seaweeds and Plants
 4 Marine Biology Notes Multi-cellular Primary Producers: Seaweeds and Plants Marine Algae Marine algae are important primary producers (photosynthetic) These algae are called by a generic term seaweeds
4 Marine Biology Notes Multi-cellular Primary Producers: Seaweeds and Plants Marine Algae Marine algae are important primary producers (photosynthetic) These algae are called by a generic term seaweeds
Significant Ecological Marine Area Assessment Sheet
 Significant Ecological arine Area Assessment Sheet Name: Eastern Bay of Island Biogenic Soft Sediment Complex Summary: The semi-sheltered areas between the central islands of the Eastern Bay of Islands
Significant Ecological arine Area Assessment Sheet Name: Eastern Bay of Island Biogenic Soft Sediment Complex Summary: The semi-sheltered areas between the central islands of the Eastern Bay of Islands
Figure 65: Reservoir in a steady state condition where the input flux is equal to the output flux and the reservoir size remains constant.
 7. The carbon cycle 7.1. Box model of the carbon cycle Without the greenhouse effect, our planet would experience a permanent ice age and life as we know it would not be possible. The main contributors
7. The carbon cycle 7.1. Box model of the carbon cycle Without the greenhouse effect, our planet would experience a permanent ice age and life as we know it would not be possible. The main contributors
Part II: Species and species groups. Chapter 7. Vulnerability of macroalgae of the Great Barrier Reef to climate change
 Chapter 7 Vulnerability of macroalgae of the Great Barrier Reef to climate change Guillermo Diaz-Pulido, Laurence J McCook, Anthony WD Larkum, Heike K Lotze, John A Raven, Britta Schaffelke, Jennifer E
Chapter 7 Vulnerability of macroalgae of the Great Barrier Reef to climate change Guillermo Diaz-Pulido, Laurence J McCook, Anthony WD Larkum, Heike K Lotze, John A Raven, Britta Schaffelke, Jennifer E
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND. Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution
 CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
THE INTERTIDAL ZONE AND BENTHIC ORGANISMS
 THE INTERTIDAL ZONE AND BENTHIC ORGANISMS EPSS 15 Lab #8 OUTLINE I. Intertidal zonation Tides Biotic zonation Physical conditions & biotic interactions II. Intertidal organisms & adaptations Snails Mussels
THE INTERTIDAL ZONE AND BENTHIC ORGANISMS EPSS 15 Lab #8 OUTLINE I. Intertidal zonation Tides Biotic zonation Physical conditions & biotic interactions II. Intertidal organisms & adaptations Snails Mussels
GREEN ALGAE DIVISION CHLOROPHYTA
 GREEN ALGAE DIVISION CHLOROPHYTA Introduction Of the approximately 16,000 species of green algae, 90% are restricted to the freshwater environment: damp soil, rivers, lakes, ponds, puddles, tree bark,
GREEN ALGAE DIVISION CHLOROPHYTA Introduction Of the approximately 16,000 species of green algae, 90% are restricted to the freshwater environment: damp soil, rivers, lakes, ponds, puddles, tree bark,
RED LIST OF EUROPEAN HABITATS. Marine Results Presentation 24 th May, 2016
 RED LIST OF EUROPEAN HABITATS Marine Results Presentation 24 th May, 2016 Geographical scope of the project Habitat Typology One typology for marine and terrestrial At the same time... revision of EUNIS
RED LIST OF EUROPEAN HABITATS Marine Results Presentation 24 th May, 2016 Geographical scope of the project Habitat Typology One typology for marine and terrestrial At the same time... revision of EUNIS
Multicellular Algae. Multicellular Algae 2/11/2015. Chapter 7 Multicellular Primary Producers
 Chapter 7 Multicellular Primary Producers Karleskint Turner Small Multicellular Algae Most primary production in marine ecosystems takes place by phytoplankton but seaweed and flowering plants contribute
Chapter 7 Multicellular Primary Producers Karleskint Turner Small Multicellular Algae Most primary production in marine ecosystems takes place by phytoplankton but seaweed and flowering plants contribute
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Nonvascular Plants. Believed to have evolved from green-algae. Major adaptations in going from water to land. Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids
 Nonvascular Plants Believed to have evolved from green-algae Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids Store starch within chloroplasts Cell wall made up mostly of cellulose Major adaptations in going from water
Nonvascular Plants Believed to have evolved from green-algae Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids Store starch within chloroplasts Cell wall made up mostly of cellulose Major adaptations in going from water
-plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem. -spores with tough walls. -life history of alternation of generations
 Chapter 21-Seedless Plants Major modern plant groups All groups of land-adapted plants have a common set of characteristics: -plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem -spores with
Chapter 21-Seedless Plants Major modern plant groups All groups of land-adapted plants have a common set of characteristics: -plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem -spores with
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta
 Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls
 1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
What is a Plant? Plant Life Cycle. What did they evolve from? Original Habitat 1/15/2018. Plant Life Cycle Alternation of Generations
 What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
Some History: In the life cycle of the kelp Laminaria. One way to separate algae from protozoa is that. Rocks of Cambrian Age (ca.
 One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
Protist Classification the Saga Continues
 Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants. Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR
 Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Divergence time estimates and the evolution of major lineages in the florideophyte red algae
 Divergence time estimates and the evolution of major lineages in the florideophyte red algae The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Divergence time estimates and the evolution of major lineages in the florideophyte red algae The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land
 Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
Eelgrass biomass and production
 Eelgrass biomass and production Objectives To introduce methods for assessing basic parameters fundamental to many seagrass studies such as shoot size and stand structure expressed as biomass and shoot
Eelgrass biomass and production Objectives To introduce methods for assessing basic parameters fundamental to many seagrass studies such as shoot size and stand structure expressed as biomass and shoot
Marine Red Algae (Rhodophyta) in the Intertidal Areas of Siquijor, Philippines 1
 Marine Red Algae (Rhodophyta) in the Intertidal Areas of Siquijor, Philippines 1 Denny Jane Tuastumban, 2* Venus Kinamot Abstract Red algae are known for its ecological role in coral reefs, a primary producer
Marine Red Algae (Rhodophyta) in the Intertidal Areas of Siquijor, Philippines 1 Denny Jane Tuastumban, 2* Venus Kinamot Abstract Red algae are known for its ecological role in coral reefs, a primary producer
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14. Essentials of Geology, 8e. Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College
 The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
Ocean Acidification the other CO2 problem..
 Ocean Acidification the other CO2 problem.. Recall: Atm CO 2 already above recent planetary history CO 2 Today: What does this do to ocean water? Main Outline: 1. Chemistry. How does ocean absorb CO 2,
Ocean Acidification the other CO2 problem.. Recall: Atm CO 2 already above recent planetary history CO 2 Today: What does this do to ocean water? Main Outline: 1. Chemistry. How does ocean absorb CO 2,
Title. Author(s)YOSHIDA, Tadao; YOSHIDA, Meiko. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information. (Rhodophyta,Rhodomelaceae)
 Title Observations on Ditria zonaricola (OKAMURA) comb.nov (Rhodophyta,Rhodomelaceae) Author(s)YOSHIDA, Tadao; YOSHIDA, Meiko CitationJournal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido Universi Issue Date 1983
Title Observations on Ditria zonaricola (OKAMURA) comb.nov (Rhodophyta,Rhodomelaceae) Author(s)YOSHIDA, Tadao; YOSHIDA, Meiko CitationJournal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido Universi Issue Date 1983
Vegetative and reproductive morphology of Kallymenia patens (Kallymeniaceae, Rhodophyta) in the Mediterranean Sea
 Botanica Marina 49 (2006): 310 314 2006 by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/BOT.2006.038 Vegetative and reproductive morphology of Kallymenia patens (Kallymeniaceae, Rhodophyta) in the Mediterranean
Botanica Marina 49 (2006): 310 314 2006 by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/BOT.2006.038 Vegetative and reproductive morphology of Kallymenia patens (Kallymeniaceae, Rhodophyta) in the Mediterranean
Biological survey of species diversity of sea grass beds in selected sites of southern Sri-Lanka.
 Biological survey of species diversity of sea grass beds in selected sites of southern Sri-Lanka. Hikkaduwa,Weligama,Polhena. Harishcandra K.A.D.A.T FS/2006/010 Introduction. 1.What are Sea grasses? 2.Distribution
Biological survey of species diversity of sea grass beds in selected sites of southern Sri-Lanka. Hikkaduwa,Weligama,Polhena. Harishcandra K.A.D.A.T FS/2006/010 Introduction. 1.What are Sea grasses? 2.Distribution
Characteristics of Echinoderms
 Characteristics of Echinoderms Adult echinoderms have a body plan with five parts organized symmetrically around a center Does not have an anterior nor posterior end or a brain Most echinoderms are two
Characteristics of Echinoderms Adult echinoderms have a body plan with five parts organized symmetrically around a center Does not have an anterior nor posterior end or a brain Most echinoderms are two
Kingdom Protista. The following organisms will be examined in the lab today: Volvox, Oedogonium, Spirogyra, Ulva
 Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
CHAPTERS 16 & 17: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 2012 PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES. Fig Lived alone on Earth for over 1 billion years
 CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
Coral Reefs. Organisms and Ecology
 Coral Reefs Organisms and Ecology General Characteristics: Rival tropical rainforests for beauty, richness, complexity Basic structure is made by organisms 3 Dimensional framework home to incredible assortment
Coral Reefs Organisms and Ecology General Characteristics: Rival tropical rainforests for beauty, richness, complexity Basic structure is made by organisms 3 Dimensional framework home to incredible assortment
Name Hour Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages ) Generation Description Haploid or Diploid? Gamete-producing plant Spore-producing plant
 Name Hour Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551-555) What Is a Plant? (page 551) 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about plants. a. Plants are multicellular prokaryotes. b. Plants
Name Hour Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551-555) What Is a Plant? (page 551) 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about plants. a. Plants are multicellular prokaryotes. b. Plants
Lab #5 Multicellular Marine Primary Producers. Part 1: Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments
 Lab #5 Multicellular Marine Primary Producers Part 1: Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments Introduction Photosynthesis is a fundamental life process upon which all living things depend. Organisms
Lab #5 Multicellular Marine Primary Producers Part 1: Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments Introduction Photosynthesis is a fundamental life process upon which all living things depend. Organisms
Plantae. Rhodophyta Chlorophytes Charophytes Land Plants. II. Algal taxonomy. Division: Chlorophyta (green algae)
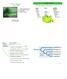 Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Distinguishing Classes III. Morphology IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Distinguishing Classes III. Morphology IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Division: Ochrophyta Or (Heterokontophyta, Chromophyta, Phaeophyta)
 Division: Ochrophyta Or (Heterokontophyta, Chromophyta, Phaeophyta) Algal Evolution: 3.9 bya = Cyanobacteria appear and introduce photosynthesis 2.5 bya = Eukaryotes appeared (nuclear envelope and ER thought
Division: Ochrophyta Or (Heterokontophyta, Chromophyta, Phaeophyta) Algal Evolution: 3.9 bya = Cyanobacteria appear and introduce photosynthesis 2.5 bya = Eukaryotes appeared (nuclear envelope and ER thought
Larvae. Juvenile. Adult. Bipartite life cycle of benthic marine fishes with pelagic larvae. Pelagic Environment. settlement.
 13 - Marine Ecology Bipartite life cycle of benthic marine fishes with pelagic larvae Larvae survive, grow, develop, disperse reproduce Pelagic Environment Benthic Environment settlement Adult Juvenile
13 - Marine Ecology Bipartite life cycle of benthic marine fishes with pelagic larvae Larvae survive, grow, develop, disperse reproduce Pelagic Environment Benthic Environment settlement Adult Juvenile
Growth rate and potential climate record from a rhodolith using 14 C accelerator mass spectrometry
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1773 1777 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Growth rate and potential climate record from a rhodolith using C accelerator mass spectrometry
Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1773 1777 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Growth rate and potential climate record from a rhodolith using C accelerator mass spectrometry
"The Relationship Between Seagrass Cover and Species- richness of Invertebrates"
 "The Relationship Between Seagrass Cover and Species- richness of Invertebrates" SCIE 2204: Marine Systems The Cottesloe Marine Ecosystem Research Project 2014 By Baronie Shaw, K., Bortoloso, T., Cargill,
"The Relationship Between Seagrass Cover and Species- richness of Invertebrates" SCIE 2204: Marine Systems The Cottesloe Marine Ecosystem Research Project 2014 By Baronie Shaw, K., Bortoloso, T., Cargill,
Lecture-1- Introduction to Algae
 Lecture-1- Introduction to 1-General Characteristics 1-Size Criterion: picoplankton ( 20 mm) 2- Most reproduce asexually 3- Both heterotrophic and autotrophic
Lecture-1- Introduction to 1-General Characteristics 1-Size Criterion: picoplankton ( 20 mm) 2- Most reproduce asexually 3- Both heterotrophic and autotrophic
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Division Ochrophyta (Chromophyta)
 Division Ochrophyta (Chromophyta) I. General characteristic of the Ochrophyta II. Class Pheophyceae III. Class Bacillariophyceae Division Ochrophyta General Characteristics: na cos from ocher color chl
Division Ochrophyta (Chromophyta) I. General characteristic of the Ochrophyta II. Class Pheophyceae III. Class Bacillariophyceae Division Ochrophyta General Characteristics: na cos from ocher color chl
Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies:
 Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Announcements. Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology. Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers
 Announcements Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers Movie: Sexual Encounters of the Floral Kind Intro to Keying/Greenhouse
Announcements Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers Movie: Sexual Encounters of the Floral Kind Intro to Keying/Greenhouse
Cycles in the Phanerozoic
 Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Coralline and fleshy algae volume density on epifaunal communities
 Coralline and fleshy algae volume density on epifaunal communities Samuel J. Field & Christopher D. Gani Oregon State University - Department of Biology Abstract Carbon dioxide emissions greatly affect
Coralline and fleshy algae volume density on epifaunal communities Samuel J. Field & Christopher D. Gani Oregon State University - Department of Biology Abstract Carbon dioxide emissions greatly affect
Ulva lactuca Sea lettuce
 Ulva lactuca Sea lettuce S. Donovan Photo : http://www.cryptogamicbotany.com/images/oa_chloro/ulva_lactuca_01_05_09_a_324x550.jpg Ulva lactuca: Sea lettuce Domain: Kingdom: Phylum: Class: Order: Family:
Ulva lactuca Sea lettuce S. Donovan Photo : http://www.cryptogamicbotany.com/images/oa_chloro/ulva_lactuca_01_05_09_a_324x550.jpg Ulva lactuca: Sea lettuce Domain: Kingdom: Phylum: Class: Order: Family:
Treasure Coast Science Scope and Sequence
 Course: Marine Science I Honors Course Code: 2002510 Quarter: 3 Topic(s) of Study: Marine Organisms and Ecosystems Bodies of Knowledge: Nature of Science and Life Science Standard(s): 1: The Practice of
Course: Marine Science I Honors Course Code: 2002510 Quarter: 3 Topic(s) of Study: Marine Organisms and Ecosystems Bodies of Knowledge: Nature of Science and Life Science Standard(s): 1: The Practice of
Meiosis. What is meiosis? How is it different from mitosis? Stages Genetic Variation
 Meiosis What is meiosis? How is it different from mitosis? Stages Genetic Variation Reproduction Asexual reproduction resulting from mitosis (or a similar process) that involves only one parent; the offspring
Meiosis What is meiosis? How is it different from mitosis? Stages Genetic Variation Reproduction Asexual reproduction resulting from mitosis (or a similar process) that involves only one parent; the offspring
6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items S6E3c.
 Composition 6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items Ocean water differs from freshwater in that it has. A. a lower temperature B. a higher temperature C. a higher concentration of silicon dioxide D.
Composition 6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items Ocean water differs from freshwater in that it has. A. a lower temperature B. a higher temperature C. a higher concentration of silicon dioxide D.
Marine Sediments EPSS15 Spring 2017 Lab 4
 Marine Sediments EPSS15 Spring 2017 Lab 4 Why Sediments? Record of Earth s history - Tectonic plate movement - Past changes in climate - Ancient ocean circulation currents - Cataclysmic events 1 Classification
Marine Sediments EPSS15 Spring 2017 Lab 4 Why Sediments? Record of Earth s history - Tectonic plate movement - Past changes in climate - Ancient ocean circulation currents - Cataclysmic events 1 Classification
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Symbiosis. Symbiosis is a close association between of two or more organisms. Endosymbiosis living within another
 PROTISTS Protists constitute several kingdoms within the domain Eukarya Protists obtain their nutrition in a variety of ways Algae are autotrophic protists Protozoans are heterotrophic protists Fungus
PROTISTS Protists constitute several kingdoms within the domain Eukarya Protists obtain their nutrition in a variety of ways Algae are autotrophic protists Protozoans are heterotrophic protists Fungus
Introduction to Bryophyta
 Introduction to Bryophyta Botany Department, Brahmanand PG College, Bryophyta (Greek Bryon = Moss, phyton = plants) is a group of simplest and primitive plants of the class Embryophyta. The group is represented
Introduction to Bryophyta Botany Department, Brahmanand PG College, Bryophyta (Greek Bryon = Moss, phyton = plants) is a group of simplest and primitive plants of the class Embryophyta. The group is represented
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants
 Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
Long-term Climate Change. We are in a period of relative warmth right now but on the time scale of the Earth s history, the planet is cold.
 Long-term Climate Change We are in a period of relative warmth right now but on the time scale of the Earth s history, the planet is cold. Long-term Climate Change The Archean is thought to have been warmer,
Long-term Climate Change We are in a period of relative warmth right now but on the time scale of the Earth s history, the planet is cold. Long-term Climate Change The Archean is thought to have been warmer,
Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants
 Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants Distinguishing Characteristics: Photosynthetic Live in aqueous environments (ie. In or near water) Lack internal tubes to move water and materials from one part of the
Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants Distinguishing Characteristics: Photosynthetic Live in aqueous environments (ie. In or near water) Lack internal tubes to move water and materials from one part of the
CLIMATE CHANGE AND OIL IN THE ARCTIC
 CLIMATE CHANGE AND OIL IN THE ARCTIC What is Climate Change? Rising temperatures Changes in weather Warm acidic oceans Melting ice caps Rising sea levels Photo from uab.edu A Way Forward: Facing Climate
CLIMATE CHANGE AND OIL IN THE ARCTIC What is Climate Change? Rising temperatures Changes in weather Warm acidic oceans Melting ice caps Rising sea levels Photo from uab.edu A Way Forward: Facing Climate
Marine Plants. Marine Ecology. Activity 2
 Marine Plants The ocean contains many plants and plantlike organisms. Some are similar to plants we see on land while others are very different. All of these plants have one thing in common they are primary
Marine Plants The ocean contains many plants and plantlike organisms. Some are similar to plants we see on land while others are very different. All of these plants have one thing in common they are primary
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline)
 Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Evolution and Life in the Ocean
 Characteristics of All Living Things Contain matter in a highly organized state Capture, store and transmit energy; all organisms require energy Capable of reproduction Change through time and adapt to
Characteristics of All Living Things Contain matter in a highly organized state Capture, store and transmit energy; all organisms require energy Capable of reproduction Change through time and adapt to
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Investigating the contribution of allochthonous subsidies to kelp forests in central California
 Investigating the contribution of allochthonous subsidies to kelp forests in central California melissa m foley UCSC Institute of Marine Science and Center for Ocean Solutions system connectivity rivers
Investigating the contribution of allochthonous subsidies to kelp forests in central California melissa m foley UCSC Institute of Marine Science and Center for Ocean Solutions system connectivity rivers
BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY
 BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY AN INTRODUCTION 0 ^ J ty - y\ 2 S CAROL M. LALLI and TIMOTHY R. PARSONS University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada PERGAMON PRESS OXFORD NEW YORK SEOUL TOKYO ABOUT THIS VOLUME
BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY AN INTRODUCTION 0 ^ J ty - y\ 2 S CAROL M. LALLI and TIMOTHY R. PARSONS University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada PERGAMON PRESS OXFORD NEW YORK SEOUL TOKYO ABOUT THIS VOLUME
UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land
 Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
ALGAE. Biol 165: Diversity of Life :24 PM
 Biol 165: Diversity of Life 2013-04-21 9:24 PM ALGAE Introduction Eukaryotic Algae are members of the Kingdom Protoctista Cyanobacteria is a Prokaryotic bacterial Algae, and part of the Domain Bacteria,
Biol 165: Diversity of Life 2013-04-21 9:24 PM ALGAE Introduction Eukaryotic Algae are members of the Kingdom Protoctista Cyanobacteria is a Prokaryotic bacterial Algae, and part of the Domain Bacteria,
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
200 Meters Down Topic: Ocean Zones (5 th 8 th grade)
 200 Meters Down Topic: Ocean Zones (5 th 8 th grade) by Lodge 200 Meters Down Have you people heard about the plankton? Just tiny algae and it s floating, right What about the nekton like jellyfish? They
200 Meters Down Topic: Ocean Zones (5 th 8 th grade) by Lodge 200 Meters Down Have you people heard about the plankton? Just tiny algae and it s floating, right What about the nekton like jellyfish? They
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis. Genetics Terminology: Homologous chromosomes
 For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
Name Hour. Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages )
 Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
2. Which of the following is an organism that is made of only one cell? A. a larva B. an oyster C. an amoeba D. a mold
 1. I am the barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell. I allow food, oxygen, and other needed materials to enter the cell. I am a part of animal and plant cells. A. cell membrane B. cell wall
1. I am the barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell. I allow food, oxygen, and other needed materials to enter the cell. I am a part of animal and plant cells. A. cell membrane B. cell wall
Environmental Science
 Environmental Science A Study of Interrelationships Cui Jiansheng Hebei University of Science and Technology CH06 Kinds of Ecosystems and Communities Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you
Environmental Science A Study of Interrelationships Cui Jiansheng Hebei University of Science and Technology CH06 Kinds of Ecosystems and Communities Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you
Life on Earth
 Life on Earth By feeding, i.e. source of energy a) Autotrophs, self-feeding, e.g. plants (phyto-) b) Heterotrophs, eat others, e.g. animals (zoo-) By feeding, i.e. source of energy a) Autotrophs b)
Life on Earth By feeding, i.e. source of energy a) Autotrophs, self-feeding, e.g. plants (phyto-) b) Heterotrophs, eat others, e.g. animals (zoo-) By feeding, i.e. source of energy a) Autotrophs b)
Topic 14. Algae. Raven Chap. 12 regarding Cyanobacteria (pp ), Chap 15 regarding algae (pp )
 Topic 14 Algae Raven Chap. 12 regarding Cyanobacteria (pp. 263 266), Chap 15 regarding algae (pp. 317 358) I. What is an alga? A. Any* photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae
Topic 14 Algae Raven Chap. 12 regarding Cyanobacteria (pp. 263 266), Chap 15 regarding algae (pp. 317 358) I. What is an alga? A. Any* photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae
Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response
 Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response generally reproduce sexually, though many can also reproduce asexually. Some have lost ability to reproduce sexually. All plant lifecycles involve alternation
Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response generally reproduce sexually, though many can also reproduce asexually. Some have lost ability to reproduce sexually. All plant lifecycles involve alternation
Ocean Zones How are the intertidal, neritic, and oceanic zones different?
 Ocean Zones How are the intertidal, neritic, and oceanic zones different? How deep does sunlight travel into the ocean and how does that affect plants and animals? What technology is used to explore the
Ocean Zones How are the intertidal, neritic, and oceanic zones different? How deep does sunlight travel into the ocean and how does that affect plants and animals? What technology is used to explore the
CLIMATE CHANGE EFFECTS ON SEAGRASSES, MACROALGAE AND THEIR ECOSYSTEMS: ELEVATED DIC, TEMPERATURE, OA AND THEIR INTERACTIONS
 CLIMATE CHANGE EFFECTS ON SEAGRASSES, MACROALGAE AND THEIR ECOSYSTEMS: ELEVATED DIC, TEMPERATURE, OA AND THEIR INTERACTIONS Marguerite S. Koch, George E. Bowes, Cliff Ross, XingHai Zhang Josh Filina, Kate
CLIMATE CHANGE EFFECTS ON SEAGRASSES, MACROALGAE AND THEIR ECOSYSTEMS: ELEVATED DIC, TEMPERATURE, OA AND THEIR INTERACTIONS Marguerite S. Koch, George E. Bowes, Cliff Ross, XingHai Zhang Josh Filina, Kate
ReefBudget: Introduction and Underpinning Concepts
 ReefBudget: Introduction and Underpinning Concepts Funded by: The Leverhulme Trust (International Research Network Programme) Project Contributors: Chris Perry (University of Exeter, UK) Gary Murphy (Manchester
ReefBudget: Introduction and Underpinning Concepts Funded by: The Leverhulme Trust (International Research Network Programme) Project Contributors: Chris Perry (University of Exeter, UK) Gary Murphy (Manchester
Chapter 4 Warm Ups MRS. HILLIARD
 Chapter 4 Warm Ups MRS. HILLIARD Work on all missing assignments and Test Remediation Topics Chapter 4 Vocabulary 1. Ecosystem- a community of organisms and their abiotic environment. 2. Biotic factor-
Chapter 4 Warm Ups MRS. HILLIARD Work on all missing assignments and Test Remediation Topics Chapter 4 Vocabulary 1. Ecosystem- a community of organisms and their abiotic environment. 2. Biotic factor-
Division: Heterokontophyta Or (Ochrophyta, Chromophyta, Phaeophyta) Midterm in one week (Monday, April 28)
 University of California, Santa Cruz ALGAE OF Chlorophyta, Cladophorales Name Acrosiphonia coalita (Ruprect) R.F. Scagel, D.J. Garbary, L.Golden & M.J.Hawkes Location Davenport Landing, Santa Cruz, California
University of California, Santa Cruz ALGAE OF Chlorophyta, Cladophorales Name Acrosiphonia coalita (Ruprect) R.F. Scagel, D.J. Garbary, L.Golden & M.J.Hawkes Location Davenport Landing, Santa Cruz, California
Plant Growth & Reproduction
 Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) 4/24/2014 Plant Growth & Reproduction BI 103 Plant-Animal Systems Turn in Homework #1 Lab Wed! (schedule change) 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 no wind
Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) 4/24/2014 Plant Growth & Reproduction BI 103 Plant-Animal Systems Turn in Homework #1 Lab Wed! (schedule change) 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 no wind
Chapter 7 Benthic deep-sea carbonates: reefs and seeps
 Chapter 7 Benthic deep-sea carbonates: reefs and seeps Carbonates are formed across most latitudes and they are not restricted to shallow water but are also found in all but the deepest abyssal and hadal
Chapter 7 Benthic deep-sea carbonates: reefs and seeps Carbonates are formed across most latitudes and they are not restricted to shallow water but are also found in all but the deepest abyssal and hadal
Primary Productivity. Global Net PP. Chapter 5- The Microbial World. Fill in the blank. Bacteria Unicellular algae Protists The Microbial Loop
 Chapter 5- The Microbial World Bacteria Unicellular algae Protists The Microbial Loop Megaplankton Macroplankton Mesoplankton Microplankton Nanoplankton Picoplankton Fill in the blank A. Femtoplankton
Chapter 5- The Microbial World Bacteria Unicellular algae Protists The Microbial Loop Megaplankton Macroplankton Mesoplankton Microplankton Nanoplankton Picoplankton Fill in the blank A. Femtoplankton
Chapter 14. Coral Reefs
 Chapter 14 Coral Reefs What is a coral reef? - Coral reefs are massive complex structures made of limestone (CaCO3) deposited by living organisms - Most established coral reefs are between 5,000 and 10,000
Chapter 14 Coral Reefs What is a coral reef? - Coral reefs are massive complex structures made of limestone (CaCO3) deposited by living organisms - Most established coral reefs are between 5,000 and 10,000
Curriculum for Plant Biology 18 Kingdom Protoctista. Prerequisite Skills. Framework Standard(s) Biology. Skills
 Plant Biology 18 Kingdom Protoctista I. Introduction A. Oceanic Beginnings of Life B. Transition to Land and Origin of Lignin 1. coleochaete a. freshwater alga b. ancestor of today s land plants II. Features
Plant Biology 18 Kingdom Protoctista I. Introduction A. Oceanic Beginnings of Life B. Transition to Land and Origin of Lignin 1. coleochaete a. freshwater alga b. ancestor of today s land plants II. Features
4. An object vibrating faster will have a higher frequency and a higher: 5. Sound is a wave.
 Name : Put a check in the box each time you answer the question correctly Science Review checklist Part Two Cover the right column with a piece of paper or your hand. Answer the question and check your
Name : Put a check in the box each time you answer the question correctly Science Review checklist Part Two Cover the right column with a piece of paper or your hand. Answer the question and check your
