CLASS: RHODOPHYCEAE SUB-CLASS: BANGIOPHYCIDEAE FLORIDEOPHYCIDEAE
|
|
|
- Barrie Powers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 CLASS: RHODOPHYCEAE SUB-CLASS: BANGIOPHYCIDEAE FLORIDEOPHYCIDEAE CHLOROPHYLL A, D PHYCOCYANIN AND PHYCOERYTHRIN α & β CAROTENES FLORIDEAN STARCH CELLULOSIC CELL WALL XYLAN IN BANGIOPHYCIDAE SOME WITH POLYSACCHARIDE FEW CALCIFIED FLAGELLA ABSENT SEXUAL REPRODUCTION PLASTID ENVELOPE 2 LAYERED INVOLVES POST-FERTILIZATION CER- ABSENT DEVELOPMENT THYLAKOIDS UNSTACKED SOMATIC AND SPORIC ISO OR HETEROMORPHIC (AS IN PALMARIALES)
3 SUB-CLASS BANGIOPHYCIDEAE Thalli are always of simple construction. Cell division is intercalary and cells are uninucleate often with single plastid which has a pyrenoid. Pit connections are seen only in some genera. Reproductive structures such as gametangia are not well differentiated. Complex post fertilization development is absent. Asexual reproduction takes place by the formation of monospores. Life-cycle of some genera involves a filamentous stage. This sub class includes four orders. Viz., Porphyridiales, Bangiales, Compsopogonales and Rhodochaetales.
4 SUB-CLASS BANGIOPHYCIDEAE Bangiales: Plant body is filamentous or parenchymatous. Filamentous thalli have a basal disc, whereas the parenchymatous thalli have secondary development of a basal attaching structure formed by descending rhizoids. Cells are with single, axile, stellate plastids with a pyrenoid. Cells are with single, axile, stellate plastids with a pyrenoid. Some have filamentous phases in their life histories. Asexual reproduction is effected by monospores. Male gametes or spermatia are produced in packets up to 128 per mother cell. Female gametes are undifferentiated or slightly differentiated vegetative cells.
5 SUB-CLASS FLORIDIOPHYCIDEAE Thalli filamentous, parenchymatous aggregations of filaments of either discoid or crustose or erect, and frondose. Erect fronds are of varied morphology of uniaxial or multiaxial construction. Growth is apical and only in a few it is intercalary. Cells are uninucleate or multinucleate with one or more plastids. Pyrenoids present only in the members of Nemalionales.
6 SUB-CLASS FLORIDIOPHYCIDEAE Gametangia are well differentiated. Male gametes are non-motile, produced singly from isolated or clustered spermatangia. Female gametes are formed within a carpogonium produced by a transformation of the apical cell of a short filament carpogonial branch. Post fertilization development consists of a one to many celled tissue which remains attached to the gametangial thallus. The tissue formed during the post fertilization development is called as the carposporophyte. The latter gives rise to carposporangia by transformation of the apical cells and occasionally also intercalary cells. The carposporangia may liberate a single spore carpospore or four spores-carpotetraspores. The carposporophyte may consist of a few filaments or surrounded by a massive flask shaped tissue with an apical opening and called as a cystocarp.
7 SUB-CLASS FLORIDIOPHYCIDEAE Asexual reproduction occurs through spores formed singly (in monosporangia), in pairs (in bisporangia), in fours (in tetrasporangia) or in large numbers (in parasporangia and polysporangia).
8 SUB-CLASS FLORIDIOPHYCIDEAE Life histories involve three phases, male and female gametophytes, carposporophyte and tetrasporophyte. Gametophytes and sporophytes are morphologically similar or dissimilar. This subclass includes six orders. Viz., Nemalionales, Cryptonemiales, Gigartinales, Rhodymeniales, Palmariales and Ceramiales. ORDERS ARE DISTINGUISHED BASED ON THE PRESENCE OR ABSENCE,ORIGIN, POSITION AND TIME OF PRODUCTION OF AUXILIARY CELL.
9 UNICELLULAR COCCOID THALLUS UNICELLULAR UNINUCLEATED SPHERICAL SINGLE, STELLATE PLASTID CENTRAL PYRENOID
10 UNICELLULAR COCCOID THALLUS
11 PLASTID THYLAKOIDS FREE WITHIN THE PLASTID
12 FILAMENTOUS THALLUS-BRANCHED FILAMENTS UNIAXIAL FILAMENT: SIMPLE BRANCHED-AUDOUINELLA
13 FILAMENTOUS THALLUS-BRANCHED FILAMENTS UNIAXIAL FILAMENT: BRANCHED-BATRACHOSPERMUM
14 FILAMENTOUS THALLUS-BRANCHED FILAMENTS UNIAXIAL FILAMENT: (HETEROTRICHOUS) BRANCHED-BATRACHOSPERMUM, ACHROCHAETIUM, ANTITHAMNION, CALLITHAMNION (NO CORTICATION}
15 SEVERAL LAYERS OF CORTICATING FILAMENTS FORMING CORTICATION
16 UNIAXIALLY CONSTRUCTED FOLIOSE THALLI: PLATYSIPHONIA NITOPHYLLUM (BOTH OF DELESSERIACEAE)
17 UNIAXIALLY CONSTRUCTED FOLIOSE THALLI: PLATYSIPHONIA (DELESSERIACEAE)
18 UNIAXIALLY CONSTRUCTED FOLIOSE THALLI: NITOPHYLLUM (DELESSERIACEAE)
19 CENTROCERAS SIMPLE HETERO- TRICHOUS BRANCHED FILAMENT PARTIALLY CORTICATED BY DETERMINATE BRANCHES AS IN CERAMIUM OR FULLY CORTICATED AS IN CENTROCERAS
20
21 FILAMENTOUS THALLUS- BRANCHED FILAMENTS SIMPLE MULTIAXIAL THALLUS: LIAGORA
22 FILAMENTOUS THALLUS- BRANCHED FILAMENTS SIMPLE MULTIAXIAL THALLUS: LIAGORA GALAXURA
23 SPECIALIZED MULTIAXIAL THALLI: heavily calcified articulated corallines (Cryptonemiales) such as Jania, Amphiroa and Arthrocladia AMPHIROA ACEPS
24 Highly complex multi axial types include terete, fleshy or foliose species of dense construction. In these types the apical cells can be distinguished only during their young stages. Terete forms include species of Gracilaria (where thallus is further specialized with cortex and medulla), while large foliose forms include Gigartina (which may reach 1 m in length). In Rhodymeniales, growth occurs characteristically, in which the hollow, tubular thalli are chambered. The chambers are separated by transverse medullary hyphae (diapharum) eg. Champia and Gastroclonium. Parenchymatous construction is seen in Porphyra
25 MULTIAXIAL, TUBULAR AND SEGMENTED THALLUS OF CHAMPIA AND NON-SEGMENTED THALLUS OF GRATELOUPIA WITH CORTEX AND MEDULLA. MEDULLA WITH STELLATE CELLS
26 CHAMPIA PARVULA GRATEOUPIA LITHOPHILA
27 UNIAXIALLY CONSTRUCTED COMPLEX THALLI HYPNEA VALENTIAE
28 SPECIALIZED MULTIAXIAL THALLUS
29 UNIAXIAL THALLUS OF HYPNEA AND MULTIAXIAL THALLUS OF GRACILARIA
30 CRUSTOSE THALLUS
31 FOLIOSE PARENCHYMATOUS THALLUS
32
0.9 bya = first multicellular algae!
 8/12/14 Photosynthetic organisms on earth 3.45 bya = Cyanobacteria appear and introduce photosynthesis 1.5 bya = first Eukaryotes appeared (nuclear envelope and ER thought to come from invagination of
8/12/14 Photosynthetic organisms on earth 3.45 bya = Cyanobacteria appear and introduce photosynthesis 1.5 bya = first Eukaryotes appeared (nuclear envelope and ER thought to come from invagination of
The Rhodophytes Class Rhodymeniophycedae Order Ceramiales
 The Rhodophytes Red algae are red because of the presence of the pigment phycoerythrin. This pigment reflects red light and absorbs blue light. Because blue light penetrates water to a greater depth than
The Rhodophytes Red algae are red because of the presence of the pigment phycoerythrin. This pigment reflects red light and absorbs blue light. Because blue light penetrates water to a greater depth than
Dr.Ayad M.J. Lecture 8 Algae Rhodophyta
 Rhodophyta 1-2 General characteristics phylum (division) of the kingdom Protista consisting of the photosynthetic organisms commonly known as red algae. Most of the world's seaweeds belong to this group.
Rhodophyta 1-2 General characteristics phylum (division) of the kingdom Protista consisting of the photosynthetic organisms commonly known as red algae. Most of the world's seaweeds belong to this group.
Plantae. Division: Rhodophyta. Glaucophytes Rhodophyta Chlorophytes Charophytes Land Plants
 Division: Rhodophyta DOMAIN Groups (Kingdom) 1.Bacteria- cyanobacteria (blue green algae) 2.Archae 3.Eukaryotes 1. Alveolates- dinoflagellates 2. Stramenopiles- diatoms, Ochrophyta 3. Rhizaria- unicellular
Division: Rhodophyta DOMAIN Groups (Kingdom) 1.Bacteria- cyanobacteria (blue green algae) 2.Archae 3.Eukaryotes 1. Alveolates- dinoflagellates 2. Stramenopiles- diatoms, Ochrophyta 3. Rhizaria- unicellular
Glaucophyta. Glaucophyta
 Glaucophyta The Glaucophyta include those algae that have endosymbiotic cyanobacteria in the cytoplasm instead of chloroplasts. Because of the nature of their symbiotic association, they are thought to
Glaucophyta The Glaucophyta include those algae that have endosymbiotic cyanobacteria in the cytoplasm instead of chloroplasts. Because of the nature of their symbiotic association, they are thought to
Frequently asked questions (FAQs).
 Frequently asked questions (FAQs). Q.1. What is The term algae (singular: alga), has been derived from a Latin word algere, meaning seaweeds. Algae include a diverse group of mostly autotrophic, eukaryotic
Frequently asked questions (FAQs). Q.1. What is The term algae (singular: alga), has been derived from a Latin word algere, meaning seaweeds. Algae include a diverse group of mostly autotrophic, eukaryotic
Division: Rhodophyta. Division: Rhodophyta species Class: Florideophycidae-6199 species
 Division: Rhodophyta Division: Rhodophyta- 6504 species Class: Florideophycidae-6199 species - advanced reds - always multicellular: filaments or psuedoparenchymat ous -marine, freshwater -almost always
Division: Rhodophyta Division: Rhodophyta- 6504 species Class: Florideophycidae-6199 species - advanced reds - always multicellular: filaments or psuedoparenchymat ous -marine, freshwater -almost always
Algal Morphology. Unicells- solitary cells can be motile or non motile ex. Chlamydomonas
 Algal Morphology I. Internal thallus morphologies II. External thallus morphologies III.Algal Growth Unicells- solitary cells can be motile or non motile ex. Chlamydomonas Colony- an assemblage of individual
Algal Morphology I. Internal thallus morphologies II. External thallus morphologies III.Algal Growth Unicells- solitary cells can be motile or non motile ex. Chlamydomonas Colony- an assemblage of individual
ALGAE (L. Seaweed) HABITAT:
 ALGAE (L. Seaweed) SALIENT FEATURES: 1. Algae are autotrophic organisms and they have chlorophyll. 2. They are O2 producing photosynthetic organisms. 3. In algae the plant body shows no differentiation
ALGAE (L. Seaweed) SALIENT FEATURES: 1. Algae are autotrophic organisms and they have chlorophyll. 2. They are O2 producing photosynthetic organisms. 3. In algae the plant body shows no differentiation
Major groups of algae
 Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
GREEN ALGAE DIVISION CHLOROPHYTA
 GREEN ALGAE DIVISION CHLOROPHYTA Introduction Of the approximately 16,000 species of green algae, 90% are restricted to the freshwater environment: damp soil, rivers, lakes, ponds, puddles, tree bark,
GREEN ALGAE DIVISION CHLOROPHYTA Introduction Of the approximately 16,000 species of green algae, 90% are restricted to the freshwater environment: damp soil, rivers, lakes, ponds, puddles, tree bark,
Introduction to Bryophyta
 Introduction to Bryophyta Botany Department, Brahmanand PG College, Bryophyta (Greek Bryon = Moss, phyton = plants) is a group of simplest and primitive plants of the class Embryophyta. The group is represented
Introduction to Bryophyta Botany Department, Brahmanand PG College, Bryophyta (Greek Bryon = Moss, phyton = plants) is a group of simplest and primitive plants of the class Embryophyta. The group is represented
MODEL ANSWER SEMESTER - V
 Q1. Multiple choice/one sentence/fill in the blanks i. a) Gelidium ii. a) Blue green algae iii. c) Glycogen iv. d) Cell wall is chitinous and chlorophyll is absent v. d) all of these vi. b) perithecium
Q1. Multiple choice/one sentence/fill in the blanks i. a) Gelidium ii. a) Blue green algae iii. c) Glycogen iv. d) Cell wall is chitinous and chlorophyll is absent v. d) all of these vi. b) perithecium
Nonvascular Plants. Believed to have evolved from green-algae. Major adaptations in going from water to land. Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids
 Nonvascular Plants Believed to have evolved from green-algae Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids Store starch within chloroplasts Cell wall made up mostly of cellulose Major adaptations in going from water
Nonvascular Plants Believed to have evolved from green-algae Chlorophylls a & b and cartenoids Store starch within chloroplasts Cell wall made up mostly of cellulose Major adaptations in going from water
-plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem. -spores with tough walls. -life history of alternation of generations
 Chapter 21-Seedless Plants Major modern plant groups All groups of land-adapted plants have a common set of characteristics: -plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem -spores with
Chapter 21-Seedless Plants Major modern plant groups All groups of land-adapted plants have a common set of characteristics: -plant bodies composed of tissues produced by an apical meristem -spores with
Plant Evolution & Diversity
 Plant Evolution & Diversity Ancestors of plants were probably charophytes (green algae) Chlorophyll a and b, beta carotene Similar thylakoid arrangements Identical cell walls Starch as a storage carbohydrate
Plant Evolution & Diversity Ancestors of plants were probably charophytes (green algae) Chlorophyll a and b, beta carotene Similar thylakoid arrangements Identical cell walls Starch as a storage carbohydrate
Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Algae Eukaryotic Algae
 Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Algae Eukaryotic Algae I. General Characteristics II. Reproduction and Life History Patterns III. Photosynthetic Pigments IV. Chloroplast types V. Major Polysaccharide Reserves
Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Algae Eukaryotic Algae I. General Characteristics II. Reproduction and Life History Patterns III. Photosynthetic Pigments IV. Chloroplast types V. Major Polysaccharide Reserves
Plantae. Rhodophyta Chlorophytes Charophytes Land Plants. II. Algal taxonomy. Division: Chlorophyta (green algae)
 Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Distinguishing Classes III. Morphology IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Distinguishing Classes III. Morphology IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
B.Sc. PLANT BIOLOGY & PLANT BIOTECHNOLGY. ALGOLOGY AND MYCOLOGY B. Sc. va (Candidates admitted from the academic year )
 B.Sc. PLANT BIOLOGY & PLANT BIOTECHNOLGY ALGOLOGY AND MYCOLOGY Paper 1a ALGOLOGY AND MYCOLOGY Algology CORE THEORY UNIT I Introduction to Algae: Definition; Distribution of algae: Freshwater algae, Brackish
B.Sc. PLANT BIOLOGY & PLANT BIOTECHNOLGY ALGOLOGY AND MYCOLOGY Paper 1a ALGOLOGY AND MYCOLOGY Algology CORE THEORY UNIT I Introduction to Algae: Definition; Distribution of algae: Freshwater algae, Brackish
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants
 Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
Division: Chlorophyta! The mean Greens!
 8/12/14 Division: Chlorophyta The mean Greens I. Taxonomy II. Unifying Characteristics III. Distinguishing Classes IV. Classes in Detail Easiest division of Chlorophyta from other algae: - usually bright
8/12/14 Division: Chlorophyta The mean Greens I. Taxonomy II. Unifying Characteristics III. Distinguishing Classes IV. Classes in Detail Easiest division of Chlorophyta from other algae: - usually bright
Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes. Fungi. Chemoheterotrophic. Have cell walls typically composed of chitin. Do not perform photosynthesis
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes. Fungi. Chemoheterotrophic. Have cell walls typically composed of chitin. Do not perform photosynthesis
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-03 PLANT KINGDOM
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-03 PLANT KINGDOM Eukaryotic, multicellular, chlorophyll containing and having cell wall, are grouped the kingdom Plantae, popularly known as plant kingdom.
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-03 PLANT KINGDOM Eukaryotic, multicellular, chlorophyll containing and having cell wall, are grouped the kingdom Plantae, popularly known as plant kingdom.
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Biology. Slide 1of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Chlamydomonas. Organelle?
 Chlamydomonas Organelle? Structure? Organelle? Unicellular thalli typically spherical to subspherical. Eyespot prominent in many species, at cell anterior embedded in chloroplast. Nucleus single and typically
Chlamydomonas Organelle? Structure? Organelle? Unicellular thalli typically spherical to subspherical. Eyespot prominent in many species, at cell anterior embedded in chloroplast. Nucleus single and typically
Biology. Slide 1 of 34. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 34 2 of 34 What are the similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi? 3 of 34 Funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb nutrients from dead or decaying organic
Biology 1 of 34 2 of 34 What are the similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi? 3 of 34 Funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb nutrients from dead or decaying organic
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.29 - PROTISTS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
!! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
Title. Author(s)MASUDA, Michio. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information. bulletin. 12(3)_P
 Title Further observations on the life history of Gymnogon Author(s)MASUDA, Michio CitationJournal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido Universi Issue Date 1981 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/26383
Title Further observations on the life history of Gymnogon Author(s)MASUDA, Michio CitationJournal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido Universi Issue Date 1981 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/26383
Multicellular Algae. Multicellular Algae 2/11/2015. Chapter 7 Multicellular Primary Producers
 Chapter 7 Multicellular Primary Producers Karleskint Turner Small Multicellular Algae Most primary production in marine ecosystems takes place by phytoplankton but seaweed and flowering plants contribute
Chapter 7 Multicellular Primary Producers Karleskint Turner Small Multicellular Algae Most primary production in marine ecosystems takes place by phytoplankton but seaweed and flowering plants contribute
Bryophytes: Liverworts, Hornworts and Mosses.
 Bryophytes: Liverworts, Hornworts and Mosses. Bryophytes Plant scien+sts recognize two kinds of land plants Bryophytes, or nonvascular plants Tracheophytes, or vascular plants. Distribu+on tropical rainforests,
Bryophytes: Liverworts, Hornworts and Mosses. Bryophytes Plant scien+sts recognize two kinds of land plants Bryophytes, or nonvascular plants Tracheophytes, or vascular plants. Distribu+on tropical rainforests,
Molecular Systematics of Red Algae.
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses Graduate School 1996 Molecular Systematics of Red Algae. Jeffrey Craig Bailey Louisiana State University and Agricultural
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses Graduate School 1996 Molecular Systematics of Red Algae. Jeffrey Craig Bailey Louisiana State University and Agricultural
What is a Plant? Plant Life Cycle. What did they evolve from? Original Habitat 1/15/2018. Plant Life Cycle Alternation of Generations
 What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
New record of Dumontia contorta and D. alaskana (Dumontiaceae, Gigartinales) in Korea
 Kang et al. Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences (2018) 21:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41240-018-0106-z RESEARCH ARTICLE New record of Dumontia contorta and D. alaskana (Dumontiaceae, Gigartinales) in Korea
Kang et al. Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences (2018) 21:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41240-018-0106-z RESEARCH ARTICLE New record of Dumontia contorta and D. alaskana (Dumontiaceae, Gigartinales) in Korea
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Downloaded from
 3. Plant Kingdom POINTS TO REMEMBER : CLASSIFICATION : Artificial System of Classification : Used superficial morphological characters. Based on a few characteristics like habit, colors, number and shape
3. Plant Kingdom POINTS TO REMEMBER : CLASSIFICATION : Artificial System of Classification : Used superficial morphological characters. Based on a few characteristics like habit, colors, number and shape
Curriculum for Plant Biology 18 Kingdom Protoctista. Prerequisite Skills. Framework Standard(s) Biology. Skills
 Plant Biology 18 Kingdom Protoctista I. Introduction A. Oceanic Beginnings of Life B. Transition to Land and Origin of Lignin 1. coleochaete a. freshwater alga b. ancestor of today s land plants II. Features
Plant Biology 18 Kingdom Protoctista I. Introduction A. Oceanic Beginnings of Life B. Transition to Land and Origin of Lignin 1. coleochaete a. freshwater alga b. ancestor of today s land plants II. Features
CHAPTER 3 : PLANT KINGDOM. K C Meena PGT Biology KVS
 CHAPTER 3 : PLANT KINGDOM K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Classification System Artificial classification oldest classification and it is based on few vegetative and sexual characters. Natural classification
CHAPTER 3 : PLANT KINGDOM K C Meena PGT Biology KVS Classification System Artificial classification oldest classification and it is based on few vegetative and sexual characters. Natural classification
Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land
 Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
SYNOPSIS OF BIOLOGICAL DATA ON THE SEAWEED GENE Gelidium aid Pterocladia (RHODOPHYTA)
 ries Synopsis No. 145 FIR/S145 SAST - Gelidinm - 7,85(O1),002 Pterocladia - 7,85(O1),003 SYNOPSIS OF BIOLOGICAL DATA ON THE SEAWEED GENE Gelidium aid Pterocladia (RHODOPHYTA) A FO FOOD AND AGRICULTURE
ries Synopsis No. 145 FIR/S145 SAST - Gelidinm - 7,85(O1),002 Pterocladia - 7,85(O1),003 SYNOPSIS OF BIOLOGICAL DATA ON THE SEAWEED GENE Gelidium aid Pterocladia (RHODOPHYTA) A FO FOOD AND AGRICULTURE
Vegetative and reproductive morphology of Kallymenia patens (Kallymeniaceae, Rhodophyta) in the Mediterranean Sea
 Botanica Marina 49 (2006): 310 314 2006 by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/BOT.2006.038 Vegetative and reproductive morphology of Kallymenia patens (Kallymeniaceae, Rhodophyta) in the Mediterranean
Botanica Marina 49 (2006): 310 314 2006 by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/BOT.2006.038 Vegetative and reproductive morphology of Kallymenia patens (Kallymeniaceae, Rhodophyta) in the Mediterranean
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta
 Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
ALGAE. Biol 165: Diversity of Life :24 PM
 Biol 165: Diversity of Life 2013-04-21 9:24 PM ALGAE Introduction Eukaryotic Algae are members of the Kingdom Protoctista Cyanobacteria is a Prokaryotic bacterial Algae, and part of the Domain Bacteria,
Biol 165: Diversity of Life 2013-04-21 9:24 PM ALGAE Introduction Eukaryotic Algae are members of the Kingdom Protoctista Cyanobacteria is a Prokaryotic bacterial Algae, and part of the Domain Bacteria,
Algal Physiology. I. Photosynthesis in algae II. Characteristics to distinguish algal divisions. I. Photosynthesis
 Algal Physiology I. Photosynthesis in algae II. Characteristics to distinguish algal divisions 1 I. Photosynthesis 2 1 PSU : Photosynthetic Unit = Antennae + rxn center Light reactions: solar energy is
Algal Physiology I. Photosynthesis in algae II. Characteristics to distinguish algal divisions 1 I. Photosynthesis 2 1 PSU : Photosynthetic Unit = Antennae + rxn center Light reactions: solar energy is
I. Photosynthesis. Algal Physiology. I. Photosynthesis in algae II. Characteristics to distinguish algal divisions
 Algal Physiology I. Photosynthesis I. Photosynthesis in algae II. Characteristics to distinguish algal divisions 1 2 PSU : Photosynthetic Unit = Antennae + rxn center Light reactions: solar energy is harvested
Algal Physiology I. Photosynthesis I. Photosynthesis in algae II. Characteristics to distinguish algal divisions 1 2 PSU : Photosynthetic Unit = Antennae + rxn center Light reactions: solar energy is harvested
3/22/2011. Review. Review. Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell
 Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
Plantae. Rhodophyta Chlorophytes Charophytes Land Plants. II. Algal taxonomy. Division: Chlorophyta (green algae)
 Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Morphology III. Distinguishing Classes IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Morphology III. Distinguishing Classes IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
CHAPTER 4. Studies on the sexual reproduction of Kappaphycus alvarezii at Kurusadai Island in the Gulf of Mannar
 CHAPTER 4 Studies on the sexual reproduction of Kappaphycus alvarezii at Kurusadai Island in the Gulf of Mannar 4.1 Introduction Local range expansion of invasive species after their establishment in introduced
CHAPTER 4 Studies on the sexual reproduction of Kappaphycus alvarezii at Kurusadai Island in the Gulf of Mannar 4.1 Introduction Local range expansion of invasive species after their establishment in introduced
Life history and morphology of Chondrus nipponicus (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) from Japan
 British Phycological Journal ISSN: 0007-1617 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tejp19 Life history and morphology of Chondrus nipponicus (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) from
British Phycological Journal ISSN: 0007-1617 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tejp19 Life history and morphology of Chondrus nipponicus (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) from
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants. Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR
 Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Chapter 20 Nonvascular Plants: Mosses, Liverworts, and Hornworts
 Chapter 20 Nonvascular Plants: Mosses, Liverworts, and Hornworts Major plant groups Topics Bryophyte adaptations synapomorphies Alternation of generation in Bryophytes Phylum Hepaticophyta Phylum Bryophyta
Chapter 20 Nonvascular Plants: Mosses, Liverworts, and Hornworts Major plant groups Topics Bryophyte adaptations synapomorphies Alternation of generation in Bryophytes Phylum Hepaticophyta Phylum Bryophyta
Division Ochrophyta (Chromophyta)
 Division Ochrophyta (Chromophyta) I. General characteristic of the Ochrophyta II. Class Pheophyceae III. Class Bacillariophyceae Division Ochrophyta General Characteristics: na cos from ocher color chl
Division Ochrophyta (Chromophyta) I. General characteristic of the Ochrophyta II. Class Pheophyceae III. Class Bacillariophyceae Division Ochrophyta General Characteristics: na cos from ocher color chl
Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely,
 Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely, a cell with 46 chromosomes splits to form tow cells each with 46 chromosomes/ This means 46 divided by 2
Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely, a cell with 46 chromosomes splits to form tow cells each with 46 chromosomes/ This means 46 divided by 2
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping
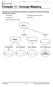 Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Transition to Land & Life Cycles. Background. Plants from Algae 8/28/2011. What does it mean to be a plant? Lecture 1
 Transition to Land & Life Cycles What does it mean to be a plant? Lecture 1 Background Descendants of charophytan green algae Photosynthesis Modular growth (mitosis & apices) Sexual Reproduction in Eukaryotes
Transition to Land & Life Cycles What does it mean to be a plant? Lecture 1 Background Descendants of charophytan green algae Photosynthesis Modular growth (mitosis & apices) Sexual Reproduction in Eukaryotes
Protist Classification the Saga Continues
 Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Lecture-1- Introduction to Algae
 Lecture-1- Introduction to 1-General Characteristics 1-Size Criterion: picoplankton ( 20 mm) 2- Most reproduce asexually 3- Both heterotrophic and autotrophic
Lecture-1- Introduction to 1-General Characteristics 1-Size Criterion: picoplankton ( 20 mm) 2- Most reproduce asexually 3- Both heterotrophic and autotrophic
CHAPTERS 16 & 17: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 2012 PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES. Fig Lived alone on Earth for over 1 billion years
 CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land
 Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
Biology. Slide 1of 34. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists 2of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists Similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi Like fungi, g, funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb
Biology 1of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists 2of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists Similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi Like fungi, g, funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Downloaded from
 A.I.P.M.T. Foundation - XI Biology MCQs Time: 30 min MCQ#8 Full Marks: 40 Choose the most appropriate answer. 1. They are non-vascular plants: 1. Hosrsetails 2. Conifers 3. Club mosses 4. Liverworts 2.
A.I.P.M.T. Foundation - XI Biology MCQs Time: 30 min MCQ#8 Full Marks: 40 Choose the most appropriate answer. 1. They are non-vascular plants: 1. Hosrsetails 2. Conifers 3. Club mosses 4. Liverworts 2.
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11. Reproduction Section 1
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
Early-bird Special The following terms refer to alternation of generation:
 Early-bird Special The following terms refer to alternation of generation: Homosporous ( one type of spore. a single type of spore produces a single type of gametophyte which produces both male and female
Early-bird Special The following terms refer to alternation of generation: Homosporous ( one type of spore. a single type of spore produces a single type of gametophyte which produces both male and female
Plants. and their classi.ication
 + Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
+ Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring Protist Phylogeny. Meet the algae. Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis. Endosymbiosis. Secondary Endosymbiosis
 Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014
 Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Polyphyletic group: multiple genealogies Prokaryotic algae (cyanobacteria) and Eukaryotic algae (protistans; not true plants) Autotrophy Body form:
 Algae Seaweeds Polyphyletic group: multiple genealogies Prokaryotic algae (cyanobacteria) and Eukaryotic algae (protistans; not true plants) Autotrophy Body form: unicellular, filamentous, and multicellular
Algae Seaweeds Polyphyletic group: multiple genealogies Prokaryotic algae (cyanobacteria) and Eukaryotic algae (protistans; not true plants) Autotrophy Body form: unicellular, filamentous, and multicellular
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13)
 Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
Diversity of freshwater algae from Tamil Nadu
 Seaweed Res. Utiln., 38(2) : 1-7, 2016 Diversity of freshwater algae from Tamil Nadu K. SIVAKUMAR Department of Botany, Annamalai University, nnamalainagar - 608 002, Tamil Nadu E-mail : kshivam69@gmail.com
Seaweed Res. Utiln., 38(2) : 1-7, 2016 Diversity of freshwater algae from Tamil Nadu K. SIVAKUMAR Department of Botany, Annamalai University, nnamalainagar - 608 002, Tamil Nadu E-mail : kshivam69@gmail.com
Unit 2B- The Plants. Plants can be classified according to the presence or absence of vascular tissue.
 Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Plants Alive What are the characteristics of plants? All plants are multicellular, which means their bodies are made up of more than one cell. Plants are eukaryotes, which means
Introduction to Plants Plants Alive What are the characteristics of plants? All plants are multicellular, which means their bodies are made up of more than one cell. Plants are eukaryotes, which means
more than 380,000 species, of which more than two-thirds
 The plant world contains more than 380,000 species, of which more than two-thirds are green plants. From the most complex flowering plants to single-cell sea algae, plants present a surprising diversity
The plant world contains more than 380,000 species, of which more than two-thirds are green plants. From the most complex flowering plants to single-cell sea algae, plants present a surprising diversity
Topic 22. Introduction to Vascular Plants: The Lycophytes
 Topic 22. Introduction to Vascular Plants: The Lycophytes Introduction to Vascular Plants Other than liverworts, hornworts, and mosses, all plants have vascular tissues. As discussed earlier, the mosses
Topic 22. Introduction to Vascular Plants: The Lycophytes Introduction to Vascular Plants Other than liverworts, hornworts, and mosses, all plants have vascular tissues. As discussed earlier, the mosses
Phylum Mucoromycota Subphylum Mucoromycotina
 Phylum Mucoromycota Subphylum Mucoromycotina Mucorales part 1 Terrestrial fungi Fig. 1 RAxML phylogenetic tree of Kingdom Fungi based on the concatenated alignment of 192 conserved orthologous proteins.
Phylum Mucoromycota Subphylum Mucoromycotina Mucorales part 1 Terrestrial fungi Fig. 1 RAxML phylogenetic tree of Kingdom Fungi based on the concatenated alignment of 192 conserved orthologous proteins.
Pteridophytes: Pteridophytes are vascular cryptogams. They are the earliest know vascular plants which originated in the Silurian period of
 Pteridophytes: Pteridophytes are vascular cryptogams. They are the earliest know vascular plants which originated in the Silurian period of Palaeozoic era. They are the successful colonizers on land habit.
Pteridophytes: Pteridophytes are vascular cryptogams. They are the earliest know vascular plants which originated in the Silurian period of Palaeozoic era. They are the successful colonizers on land habit.
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
THE GROWTH AND FRUITING OF GRACILARIA VERRUCOSA (HUDSON) PAPENFUSS
 J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. (1959), 38, 47-56 Printed in Great Britain 47 THE GROWTH AND FRUITING OF GRACILARIA VERRUCOSA (HUDSON) PAPENFUSS Marine By W. EIFION JONES Biology Station, Menai Bridge, Anglesey
J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. (1959), 38, 47-56 Printed in Great Britain 47 THE GROWTH AND FRUITING OF GRACILARIA VERRUCOSA (HUDSON) PAPENFUSS Marine By W. EIFION JONES Biology Station, Menai Bridge, Anglesey
Department of Botany, University of Dhaka, Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh. Key words: Seaweeds, Marine algae, Kallymenia spp., St. Martin's Is.
 Bangladesh J. Bot. 37(2): 173-178, 2008 (December) MARINE ALGAE OF THE ST. MARTIN S ISLAND, BANGLADESH. VI. NEW RECORDS OF SPECIES OF THE GENUS KALLYMENIA J. AG. (RHODOPHYTA) ABDUL AZIZ, A.K.M. NURUL ISLAM
Bangladesh J. Bot. 37(2): 173-178, 2008 (December) MARINE ALGAE OF THE ST. MARTIN S ISLAND, BANGLADESH. VI. NEW RECORDS OF SPECIES OF THE GENUS KALLYMENIA J. AG. (RHODOPHYTA) ABDUL AZIZ, A.K.M. NURUL ISLAM
of the marine red algal class
 Systematics & phylogenomics of the marine red algal class Florideophyceae from west Pacific Ocean Showe-Mei Lin 1*, Li-Chia Liu 1, Chien-Ming Chen 2 Tsang-Huang Shih 2 & Tun-Wen Pai 2 1 Institute of Marine
Systematics & phylogenomics of the marine red algal class Florideophyceae from west Pacific Ocean Showe-Mei Lin 1*, Li-Chia Liu 1, Chien-Ming Chen 2 Tsang-Huang Shih 2 & Tun-Wen Pai 2 1 Institute of Marine
BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS 12 FEBRUARY 2014
 BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS 12 FEBRUARY 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at how plants are classified Define Alternation of generations Summarise the main characteristics of four groupings of
BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS 12 FEBRUARY 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at how plants are classified Define Alternation of generations Summarise the main characteristics of four groupings of
I. Photosynthesis. Algal Physiology. I. Photosynthesis in algae II. Characteristics to distinguish algal divisions
 Algal hysiology I. hotosynthesis I. hotosynthesis in algae II. Characteristics to distinguish algal divisions 1 2 SU : hotosynthetic Unit = Antennae rxn center Light reactions: solar energy is harvested
Algal hysiology I. hotosynthesis I. hotosynthesis in algae II. Characteristics to distinguish algal divisions 1 2 SU : hotosynthetic Unit = Antennae rxn center Light reactions: solar energy is harvested
Topic 10 Algae. Chap. 17 (pp ) Chap. 18 (Protista; pp )
 Topic 10 Algae Chap. 17 (pp. 305 309) Chap. 18 (Protista; pp. 319 341) I. What is an alga? A. Any photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae 3. Brown algae & Diatoms 4. Dinoflagellates
Topic 10 Algae Chap. 17 (pp. 305 309) Chap. 18 (Protista; pp. 319 341) I. What is an alga? A. Any photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae 3. Brown algae & Diatoms 4. Dinoflagellates
Class XI Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Biology
 Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions are based on the following factors:
Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions are based on the following factors:
Eukaryotes Most are saprobes (live on dead organisms) Grow best in warm, moist environments Mycology is the study of fungi
 KINGDOM FUNGI 1 Characteristics 2 THE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Eukaryotes Most are saprobes (live on dead organisms) Grow best in warm, moist environments Mycology is the study of fungi 3 THE CHARACTERISTICS
KINGDOM FUNGI 1 Characteristics 2 THE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Eukaryotes Most are saprobes (live on dead organisms) Grow best in warm, moist environments Mycology is the study of fungi 3 THE CHARACTERISTICS
The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to Plants and the Mosses
 The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to Plants and the Mosses Mosses Phylum Bryophyta - ~12,000 species Liverworts - Phylum Hepaticophyta - ~8,500 species Hornworts - Phylum Anthocerophyta
The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to Plants and the Mosses Mosses Phylum Bryophyta - ~12,000 species Liverworts - Phylum Hepaticophyta - ~8,500 species Hornworts - Phylum Anthocerophyta
Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
 Class XI Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Biology Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions
Class XI Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom Biology Question 1: What is the basis of classification of algae? Algae are classified into three main classes Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Chlorophyta. I. Diversity of Form Among the Chlorophyta--A First Gauntlet!
 ` Chlorophyta Name I. Diversity of Form Among the Chlorophyta--A First Gauntlet! Work as part of the class team to set up all prepared slides and wet-mount(s) at ten microscopes. When all are ready, the
` Chlorophyta Name I. Diversity of Form Among the Chlorophyta--A First Gauntlet! Work as part of the class team to set up all prepared slides and wet-mount(s) at ten microscopes. When all are ready, the
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
Topic 20. Protista II: The Stramenopiles
 Topic 20. Protista II: The Stramenopiles The Stramenopiles (heterokonts) are a phylogenetic group within the kingdom, Protista. These organisms were derived from an ancestor with two dissimilar flagella,
Topic 20. Protista II: The Stramenopiles The Stramenopiles (heterokonts) are a phylogenetic group within the kingdom, Protista. These organisms were derived from an ancestor with two dissimilar flagella,
10.2 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 10.2 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis There are thousands of different species of organisms. Each species produces more of its own. A species of bacteria splits to make two identical bacteria. A eucalyptus
10.2 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis There are thousands of different species of organisms. Each species produces more of its own. A species of bacteria splits to make two identical bacteria. A eucalyptus
Biology 2015 Evolution and Diversity
 Biology 2015 Evolution and Diversity Lab 3: Protista, part II Algae The term "algae" refers to eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms that are mostly aquatic and lack the characters that are found in plants.
Biology 2015 Evolution and Diversity Lab 3: Protista, part II Algae The term "algae" refers to eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms that are mostly aquatic and lack the characters that are found in plants.
Introduction to the Plant Kingdom - 1
 Introduction to the Plant Kingdom - 1 The Plant Kingdom comprises a large and varied group of organisms that have the following characteristics in common. All plants are: Eukaryotic Photosynthetic Multicellular
Introduction to the Plant Kingdom - 1 The Plant Kingdom comprises a large and varied group of organisms that have the following characteristics in common. All plants are: Eukaryotic Photosynthetic Multicellular
Have cell walls made of chitin (same material is found in the skeletons of arthropods)
 Fungi are multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs that do not ingest their food but rather absorb it through their cell walls and cell membranes after breaking it down with powerful digestive enzymes. Fungi
Fungi are multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs that do not ingest their food but rather absorb it through their cell walls and cell membranes after breaking it down with powerful digestive enzymes. Fungi
ISSN: (Print) (Online) Journal homepage:
 European Journal of Phycology ISSN: 0967-0262 (Print) 1469-4433 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tejp20 Life history, morphology and crossability of Chondrus ocellatus forma ocellatus
European Journal of Phycology ISSN: 0967-0262 (Print) 1469-4433 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tejp20 Life history, morphology and crossability of Chondrus ocellatus forma ocellatus
Topic 14. Algae. Raven Chap. 12 regarding Cyanobacteria (pp ), Chap 15 regarding algae (pp )
 Topic 14 Algae Raven Chap. 12 regarding Cyanobacteria (pp. 263 266), Chap 15 regarding algae (pp. 317 358) I. What is an alga? A. Any* photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae
Topic 14 Algae Raven Chap. 12 regarding Cyanobacteria (pp. 263 266), Chap 15 regarding algae (pp. 317 358) I. What is an alga? A. Any* photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae
Topic 23. The Ferns and Their Relatives
 Topic 23. The Ferns and Their Relatives Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Plantae Ferns Leptosporangiate Ferns Psilophytes Genus: Psilotum Horsetails Genus: Equisetum In this treatment we lump the Psilophytes and
Topic 23. The Ferns and Their Relatives Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Plantae Ferns Leptosporangiate Ferns Psilophytes Genus: Psilotum Horsetails Genus: Equisetum In this treatment we lump the Psilophytes and
