Name: Period: Date: Evolutionary Relationships HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10 Introduction Common Descent common descent Comparative Anatomy
|
|
|
- Darren Tyler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
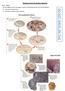
1 Name: Period: Date: Evolutionary Relationships HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10 MS-LS4-1, MS-LS4-2, MS-LS4-3 Introduction Common Descent Universal common descent was first proposed by Charles Darwin in On the Origin of Species in It is the theory that all living things on Earth evolved over many generations from a single common ancestor and is universally accepted throughout the scientific community. In fact, evidence suggests that the Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA), or most recent organisms from which all living organisms on Earth have evolved from, is a single cell that lived 3.5 to 3.8 billion years ago. Since Charles Darwin proposed his theory of evolution, scientists have found a great deal of evidence that supports his claim. Similar body structures, patterns of early development, molecular structure, and fossils all provide evidence that organisms have changed over time. 5/figure% jpg Comparative Anatomy The theory of evolution predicts that organisms that are closely related will display similarities. In fact, early evolutionary relationship theories were solely based upon observations of similarities between organisms. The comparison of the body structures of different organisms is called comparative anatomy. Fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals for example all have an internal skeleton with a backbone. All of these animals probably inherited this trait from an earlier ancestor, leading scientists to classify all five groups as vertebrates. The image to the left shows the similarities in skeletal arrangement of the limbs of a few different animals. These similar structures are known as homologous structures and provide evidence that these organisms all evolved from a common ancestor. Genetic Similarities The structure of an organisms genetic material also provides evidence for evolution. An individual s physical traits, or phenotype, are a direct result of its genetic makeup, or genotype. By comparing the genes or DNA, RNA, amino acid sequence, and cellular structure, scientists can infer evolutionary Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab
2 relationships. If two organisms have molecular structures that are similar, it makes sense that they are closely related. On the other hand, if two organisms have molecular structures that are very different, they must have diverged evolutionary a much longer time ago. 350 SPECIES % Identical DNA SPECIES % Identical DNA Humans 99.9 Chicken 65 Chimpanzee 93 Fruit Fly 47 Mouse 88 Honey Bee 44 Cow 85 Round Worm 38 Dog 84 Wine Grape 24 Zebra Fish 73 Baker s Yeast 18 Embryology Embryology is the study of the formation and development of an embryo and fetus. Scientists can make inferences about evolutionary relationships by comparing how different species develop before birth. For example, nearly all vertebrates have similar stages of embryo development and are difficult to differentiate until much later in their growth process. The image to the right illustrates how all vertebrate embryos, including humans start with a tail and gill slits. The Fossil Record Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals, plants, and other organisms from the remote past. The formation of any fossil is actually a rare event and requires the right circumstances. Mold fossils form when part of an organism forms an imprint on sediment and hardens to become rock. Cast fossils form when minerals fill in the hollows of an animal track, shell, or other parts of an organism. Petrified wood forms when minerals replace the organic material in trees and fossil fuels form from the remains of dead plants and animals. In really rare circumstances, like when a bug gets trapped in tree sap or an animal gets frozen in ice or gets stuck in a tar pit, whole body fossils are preserved. Biology%20by%20Raven%20-%20416.jpg By looking closely at fossils, scientists can discover when and where certain organisms lived along the geological time scale. Scientists are able to compare the location of fossils within certain rock strata, or layers of sediment to gain an idea of how old these organisms are. The accuracy of dating fossils has dramatically improved with the advancements in radioactive dating techniques, which is based on the comparison between the abundance of naturally occurring radioactive isotopes and decay products. When looking at the whole fossil record, scientists can deduce evolutionary relationships between organisms to gain a better understanding of how each fits in the entire history of Earth. Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
3 Evolution and Medicine Medical science is continually changing. Not only are new medications and treatments being developed, but the organisms that cause certain diseases are changing as well. Understanding evolution can make a big difference in how scientists and doctors are able to treat certain diseases. Scientists can gather clues in the fossil record, compare anatomical structures, and even pinpoint certain genetic strands and the production of key proteins in other species to understand how and why certain organism adapt and thrive. These clues not only give insight on how people get sick, but also shed light on why people get sick. Incorporating principles of evolution into medicine has already proven to be beneficial in developing strategies for minimizing antibiotic resistance and improving vaccine strategies against some of the most infectious virus strains. Evolutionary principles have also directed research in genetic engineering and the possibilities of gene therapy. By manipulating DNA, scientists are already able to genetically modify organisms to produce key enzymes and antibodies for medical treatment. Future advancements in gene therapy may allow doctors to treat disorders by inserting specific genes into a patient s cells instead of using drugs or surgery. The image below outlines the basic principles of gene therapy. Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab
4 Review Questions 1. What is the idea of common descent? 2. What does LUCA stand for? 3. What is a vertebrate? Provide examples. 4. What are homologous structures? Provide examples. 5. How similar is your genetic makeup to any one of your classmates? 6. Which animal has the most genetic similarities as humans? What does this infer about the evolutionary relationship between humans and this animal? 7. Define embryology. 8. How are fossils formed? 9. How do scientists determine how old a fossil is? 10. Understanding the principles of evolution not only give insight on how people get sick, but also shed light on people get sick. 11. How can gene therapy be used to treat certain disorders? 352 Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
5 Name: Period: Date: Hominid Skull Comparisons HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10a Introduction Hominid, or Homidae, refers to the family of primates that includes humans and their closest relatives: chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans. The image to the right illustrates the lineage from which modern day humans, sapiens, have evolved. Fossil records indicate that humans branched away from their closest living relative, the chimpanzee, about 6 million years ago. In that time frame, the image also indicates that the evolution from ancient primates to modern day humans was not linear. Most scientists currently recognize some 15 to 20 different species of early humans, but do not all agree on how each species was related or which ones simply died out. It is in consensus however, that the three most recent species of hominids ( heidelbergensis, neanderthalensis, and sapiens) all evolved from an earlier species called erectus. Hominid species changed over periods of hundreds of thousands of years, adapting to new environmental conditions. In order to understand human evolution, scientists analyzed fossils they discovered, and categorized them based on similarities and differences. They were able to find trends among species and better understand how they came to be. In this activity you and your partners will examine images of fossils to find similarities and differences between different members of the hominid family. Materials e_f/belk_8_16_humevo_tree_72.jpg Hominid Skull Information sheet Hominid Skull Comparisons record sheet Directions Task Obtain the 7 Hominid Skull Information sheets from your teacher. Read the information provided and examine the images of each skull very carefully. As you read the information and examine each picture provided for each hominid, complete the Hominid Skull Comparison record sheet. Image Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab
6 Analysis & Interpretation Summarize your findings in the table below. For each trait, characterize the condition in Modern Human and Modern Chimpanzee. For each of the other species, indicate whether each trait is more ape-like (A) or more human-like (H). Add up all the A s and H s in each column and place their respective totals in the spaces below. Skull Trait Sapiens (Modern Human) P. troglodytes (Modern Chimpanzee) Au. boisei Au. Africanus erectus neanderthalensis sapiens (Cromagnon) Cranium Size 1215ml (m) 1375 ml (f) ml A A A/H? H H Forehead Shape Vertical Flat A A H H H Foramen Magnum Position Browridge Nasal Bone Chin Shape Dental Arcade Shape Incisor Angle Canine Diastema Canine Protrusion Total Ape- Like Traits Total Human- Like Traits 354 Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
7 Analysis Questions 1. List the species that you examined in order from oldest to youngest. 2. What overall trends did you notice amongst the skull traits as the hominid species progressed through time? 3. What features did all hominid skulls have in common? 4. Which features were most useful for distinguishing between species? 5. What is a hominid? 6. How long ago does the fossil record suggest humans diverged from apes on the evolutionary tree? 7. Why do you think it is difficult for all scientists to agree on an exact number of early human species? Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab
8 356 Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
9 Name: Period: Date: Hominid Skull Comparisons HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10a Sapiens (Modern Human) P. troglodytes (Modern Chimpanzee) Au. boisei Au. africanus erectus neanderthalensis sapiens (Cromagnon) Cranium Size What is the average volume of the brain cavity? Forehead Shape Does the forehead (frontal bone) look more vertical or flatter? Foramen Magnum Position The foramen magnum is the large opening in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord connects with the brain. Is the foramen magnum oriented toward the rear or towards the middle of the base of the skull? Browridge Is a supraorbital browridge (bony ridge above the eye sockets) present? If present, is the browridge divided in the middle or continuous? Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab
10 Sapiens (Modern Human) P. troglodytes (Modern Chimpanzee) Au. boisei Au. africanus erectus neanderthalensis sapiens (Cromagnon) Nasal Bones Are the nasal bones raised or arched? Chin Shape Does the front of the lower mandible angle forward or backward? Dental Arcade Shape Do the teeth rows diverge toward the back (form a parabola shape) or more straight-sided and parallel to one another (rectangular shape)? Incisor Angle When viewed from the side, are the incisors (front row of teeth) angled out or are they vertical? Canine Diastema Is a diastema, or space or gap, present between the canine and the incisors? Canine Protrusion Does the canine project above the chewing surfaces of the other teeth? 358 Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
11 Name: Period: Date: logous Structures HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10b Introduction Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of humans, animals, and other living organisms. Since the beginning of existence, the human anatomy has been studied and compared to the structures of other organisms to form one of the basic essential sciences of medicine. Even though there is great diversity in species on Earth, there are still many similarities between their anatomical structures. These similarities provide evidence that life on Earth has a common ancient ancestor that all species have evolved from over time. logous structures, in particular, are parts of the body that are similar in structure to the comparative parts of other species. The more closely organisms are related, the more similar the homologous structures are, even if their functions are different. Most examples of homologous structures revolve around the limbs of the species being compared. Mammals in particular have similar limb structures. The flipper of a whale, the wing of a bat, and leg of a cat are all very similar to the human arm. All species have a large upper arm bone (humerus) and the lower part of the limb is made of two bones (radius and ulna). Each species also has a collection of smaller bones in the wrist (carpals) that lead into the longer fingers (phalanges). Even though the bone structures in these limbs of the mammals are very similar, the function of the limb itself is very different as bats use their limbs for flying, cats for walking, whales for swimming, and humans for everything they do with their arms. These functions evolved through the process of natural selection as common ancestors experienced changes in their respective environements. Originally, how species looked were the determining factor for classifying organisms. Sceintists would look at analagous structures, or body parts that look the same and are used for similar functions. The wings of insects, birds, bats, and pterodactyls are examples of analagous structures. But just because the functions are very similar does not mean the species are more closely related. DNA research reaffirms the evolutionary relatedness of species with homologous structures. Bats for example, are more closely related to humans than they are to birds or insects. In this activity you and your partners will recreate the bone structures of the limbs of 4 mammals to identify similarities in hoomologous structures. Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab
12 Materials logous Structures sheet Scissors Tape or glue Directions 1 Task Obtain the logous Structures sheet from your teacher. The logous Structures sheet includes the main bones of the limbs for 4 mammals: cat, whale, human, and bat. The bones will be color coordinated. 2 Using a pair of scissors, cut out each of the bones. 3 Determine which bones belong to each of the 4 animals and reconstruct the anatomical structure of the each limb. 4 Tape or glue each of the bones onto the limb outline of each of the animals. For each limb, label the different types of bones: 5 Humerus Radius Ulna Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Analysis Questions 1. What is the difference between homologous structures and analogous structures? Provide examples of each. 2. Which provides stronger evidence that two species are more closely related, homologous structures or analogous structures? 3. Of the four animals in this activity (human, cat, whale, bat), which would you argue are the most closely related on the evolutionary tree? Justify your answer. 4. What causes the function of homologous structures to be different even though their structures are very similar? 368 Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
13 Name: Period: Date: logous Structures HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10b BAT CAT WHALE HUMAN Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab
14 370 Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
15 Name: Period: Date: Embryology HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10c Introduction In his book, On the Origin of Species, Charles Darwin offered several pieces of evidence that supported his theory of evolution. One of the things Darwin discussed was the striking similarity amongst the embryos, or unborn offspring, of complex animals such as humans, chickens, frogs, reptiles, and fish. When comparing the embryos of different species, similarities can be seen in the early stages of development. Fish and human embryos, for example, both have gill slits, a two-chambered heart, and a tail with muscles to move it. Later on, as the embryos grow and develop, they become less and less similar. The gill slits and tail of a fish eventually develop into important structures necessary for survival in aquatic environments while the gill slits and tail of the human embryo simply disappear. Darwin wrote that this uniformity observed in embryo development is evidence for evolution. Humans, along with many other organisms, pass through a number of embryonic stages of development that was inherited from common ancestors that started out the same, gradually evolved different traits, but had the same basic mechanisms of early development. The farther into development that two different species maintain similarities, the more closely related they are evolutionarily. In this activity you and your partners will complete the PBS NOVA activity, Timing Is Everything, in which you will be tasked with putting the developmental stages of a few different animals in the correct order. Materials Timing Is Everything student handout Scissors Tape or glue Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab
16 Directions 1 Task Obtain the Timing Is Everything student handout sheet from your teacher. 2 Using a pair of scissors, cut out the squares with illustrations of embryos. 3 Correctly match the embryos of the fish, chick, pig, calf, and human. Place them in order from earliest to latest stages of development. Tape or glue each illustration in the table below. Fish Chick Pig Calf Human 4 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
17 Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab Analysis Questions 1. What similarities do the embryos have during development? 2. What differences do the embryos have during development? 3. What trends, if any, do you see as the embryos develop from Stage 1 to Stage 3? 4. Which 2 out of the 5 animals in this activity are the most closely related on the evolutionary tree? Justify your answer.
18 374 Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
19 Name: Period: Date: Evolutionary Relationships HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10 MS-LS4-1, MS-LS4-2, MS-LS4-3 Connections & Applications Your instructor may assign or allow you to choose any of the following activities. As per NGSS/CCSS, these extensions allow students to explore outside activities recommended by the standards. 1. The influenza virus is one of most well-known pathogens and is found in many different mammals besides humans. Every year, the influenza virus infects millions around the world, costing the health care industry billions of dollars and claims thousands of lives. One of the main reasons why the virus has always been such threat to human welfare is because of its rapid rate of mutation. Conduct a research project to gain a better understanding of the influenza virus. Create a research paper, multimedia presentation, or visual display to summarize your findings. Be sure to include, but do not limit your research on, the following information: History of the flu, including major epidemics Annual statistics Mechanisms for mutation Different strains of the flu How is the flu vaccine formulated? Why does the effectiveness of the flu vaccine change year to year? ws/img/flu_virus.jpg 2. When scientists discover a fossil skull, they compare it to skulls that have already been identified as particular early human species. Access and complete the Mystery Skull Interactive Simulation on the Smithsonian, National Museum of Natural History s website. Identify the 4 mystery skulls and provide a brief description of the clues that led you to your findings. Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab
20 3. Watch one of the following TED Talks Will Our Kids Be a Different Species?, Juan Enriquez (Futurist) What Veterinarians Know That Physicians Don t, Barbara Natterson-Horowitz (Cardiologist) on_t DNA Clues to Our Inner Neanderthal, Svante Pääbo (Geneticist) Digging Up Dinosaurs, Paul Sereno (Paleontologist) Write a one to two paragraph response to the article. Be sure to: Summarize the main points the author is trying to make in the article Share your thoughts about the article. o Do you agree/disagree with statements made in the article? o Have you experienced real life examples that relate to the ideas discussed in this article? o How does this article relate to other things you have read or learned about? o What would you like to know more about after reading this article? How does the presentation relate to evolution? 378 Evolutionary Relationships, HASPI MS Medical Life Science Lab 10
EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION
 NAME Block EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION Background Much evidence has been found to indicate that living things have evolved or changed gradually during their natural history. Scientists have studied fossils,
NAME Block EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION Background Much evidence has been found to indicate that living things have evolved or changed gradually during their natural history. Scientists have studied fossils,
Final Revision G8 Biology ( ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Final Revision G8 Biology ( 2017-2018 ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A species is a group of similar organisms that A can mate with each
Final Revision G8 Biology ( 2017-2018 ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A species is a group of similar organisms that A can mate with each
Evidence for Evolution Notes:
 Evidence for Evolution Notes: Evidence that supports the theory of evolution is usually grouped into four main areas, such as 1. Biochemical DNA analysis 2. Comparative anatomy morphology, homologous structures,
Evidence for Evolution Notes: Evidence that supports the theory of evolution is usually grouped into four main areas, such as 1. Biochemical DNA analysis 2. Comparative anatomy morphology, homologous structures,
Chapter 7- Changes Over Time. Section 2 Evidence of Evolution
 Chapter 7- Changes Over Time Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Pg 31 Topic: Evidence of Evolution (7.2) EQ: How do varying pieces of evidence support the theory of evolution and changes in Earth s history?
Chapter 7- Changes Over Time Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Pg 31 Topic: Evidence of Evolution (7.2) EQ: How do varying pieces of evidence support the theory of evolution and changes in Earth s history?
Doc #1 Evidence of Evolution Name: Period:
 Doc #1 Evidence of Evolution Name: Period: Convergent Evolution What does it mean to converge? What is the same about the animals under convergent evolution? Divergent Evolution What does it mean to diverge?
Doc #1 Evidence of Evolution Name: Period: Convergent Evolution What does it mean to converge? What is the same about the animals under convergent evolution? Divergent Evolution What does it mean to diverge?
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 10 1 Change Over Time SECTION The Evolution of Living Things 7.3.c, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 10 1 Change Over Time SECTION The Evolution of Living Things 7.3.c, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
b. In Table 1 (question #2 on the Answer Sheet describe the function of each set of bones and answer the question.)
 Biology EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION INTRODUCTION: Evidence has been found to indicate that living things have changed gradually during their natural history. The study of fossils as well as embryology, biochemistry,
Biology EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION INTRODUCTION: Evidence has been found to indicate that living things have changed gradually during their natural history. The study of fossils as well as embryology, biochemistry,
The Environment and Change Over Time
 The Environment and Change Over Time Biological Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column
The Environment and Change Over Time Biological Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column
Evidence of Common Ancestry Stations
 Stations Scientists have long wondered where organisms came from and how they evolved. One of the main sources of evidence for the evolution of organisms comes from the fossil record. Thousands of layers
Stations Scientists have long wondered where organisms came from and how they evolved. One of the main sources of evidence for the evolution of organisms comes from the fossil record. Thousands of layers
Station 1: Evidence from Current Examples
 Station 1: Evidence from Current Examples Go to the website below: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/educators/lessons/lesson6/act1.html Watch the video segment called Why does evolution matter now? After
Station 1: Evidence from Current Examples Go to the website below: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/educators/lessons/lesson6/act1.html Watch the video segment called Why does evolution matter now? After
Evidence of Evolution
 Evidence of Evolution There is a gigantic body of evidence supporting evolution. Six major areas of study contribute to that body of evidence: 1. The Fossil Record 2. Comparative Anatomy 3. Comparative
Evidence of Evolution There is a gigantic body of evidence supporting evolution. Six major areas of study contribute to that body of evidence: 1. The Fossil Record 2. Comparative Anatomy 3. Comparative
Homework. Directed Reading Chapter 5 Section 1 #1-17
 Homework Directed Reading Chapter 5 Section 1 #1-17 Create a Species Project Learning Targets I can explain how comparing organisms can provide evidence that they have common ancestors. What is the evidence
Homework Directed Reading Chapter 5 Section 1 #1-17 Create a Species Project Learning Targets I can explain how comparing organisms can provide evidence that they have common ancestors. What is the evidence
Evidence of Evolution (PAP)
 Name: Date: Period: Background Evidence of Evolution (PAP) When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide
Name: Date: Period: Background Evidence of Evolution (PAP) When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide
Origin of an idea about origins
 Origin of an idea about origins Biological evolution is the process of change during the course of time because of the alteration of the genotype and the transfer of these altered genes to the next generation.
Origin of an idea about origins Biological evolution is the process of change during the course of time because of the alteration of the genotype and the transfer of these altered genes to the next generation.
EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION. An Overview
 EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION An Overview 13.4 The study of fossils provides strong evidence for evolution The fossil record shows that organisms have evolved in a historical sequence The oldest known fossils
EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION An Overview 13.4 The study of fossils provides strong evidence for evolution The fossil record shows that organisms have evolved in a historical sequence The oldest known fossils
Biodiversity. The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life
 Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
LAB. ANATOMICAL EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION
 Period Date LAB. ANATOMICAL EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION In our studies of the anatomy and development of animals we have discovered that many living creatures that look quite different on the surface have similarities
Period Date LAB. ANATOMICAL EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION In our studies of the anatomy and development of animals we have discovered that many living creatures that look quite different on the surface have similarities
Darwin s Conclusions. The Theory of Evolution
 The Theory of Evolution More Evidence for Evolution Notes Pt. 3 Darwin s Conclusions 1. Many traits are heritable 2. Mutations result in variation populations have individuals with many different traits
The Theory of Evolution More Evidence for Evolution Notes Pt. 3 Darwin s Conclusions 1. Many traits are heritable 2. Mutations result in variation populations have individuals with many different traits
Biodiversity. The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life
 Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
(http://www.cliffsnotes.com/study_guide/evidence-for-evolution.topicarticleid-8741,articleid-8636.html)
 Teacher Wrap-up Background Information Darwin noted the striking similarity among embryos of complex animals such as humans, chickens, frogs, reptiles, and fish. He wrote that the uniformity is evidence
Teacher Wrap-up Background Information Darwin noted the striking similarity among embryos of complex animals such as humans, chickens, frogs, reptiles, and fish. He wrote that the uniformity is evidence
Outline. Evolution: Speciation and More Evidence. Key Concepts: Evolution is a FACT. 1. Key concepts 2. Speciation 3. More evidence 4.
 Evolution: Speciation and More Evidence Evolution is a FACT 1. Key concepts 2. Speciation 3. More evidence 4. Conclusions Outline Key Concepts: A species consist of one or more populations of individuals
Evolution: Speciation and More Evidence Evolution is a FACT 1. Key concepts 2. Speciation 3. More evidence 4. Conclusions Outline Key Concepts: A species consist of one or more populations of individuals
Evidence of Evolution
 Lesson 3 Evidence of Evolution ESSENTIAL QUESTION What evidence supports the theory of evolution? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the evidence that supports the theory of evolution
Lesson 3 Evidence of Evolution ESSENTIAL QUESTION What evidence supports the theory of evolution? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the evidence that supports the theory of evolution
Piecing It Together. 1) The envelope contains puzzle pieces for 5 vertebrate embryos in 3 different stages of
 Piecing It Together 1) The envelope contains puzzle pieces for 5 vertebrate embryos in 3 different stages of development. Lay out the pieces so that you have matched up each animal name card with its 3
Piecing It Together 1) The envelope contains puzzle pieces for 5 vertebrate embryos in 3 different stages of development. Lay out the pieces so that you have matched up each animal name card with its 3
Station 1 Fossil Record
 The very first horses evolved on the North American continent over 55 million years ago. The horse fossil record is very rich in transitional species. This is a series of skulls and front leg fossils of
The very first horses evolved on the North American continent over 55 million years ago. The horse fossil record is very rich in transitional species. This is a series of skulls and front leg fossils of
Topics. Antibiotic resistance, changing environment LITERACY MATHEMATICS. Traits, variation, population MATHEMATICS
 UNIT OVERVIEW EVOLUTION Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit. Note that the total teaching time is listed as 9 34 periods of approximately 45 50 minutes (approximately 6-7 weeks). 1.
UNIT OVERVIEW EVOLUTION Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit. Note that the total teaching time is listed as 9 34 periods of approximately 45 50 minutes (approximately 6-7 weeks). 1.
Evidences of Evolution
 Evidences of Evolution Darwin stated that all organisms descend from a common ancestor Darwin based his theory of Natural Selection on observations of: Traits, geographical distribution, selective breeding,
Evidences of Evolution Darwin stated that all organisms descend from a common ancestor Darwin based his theory of Natural Selection on observations of: Traits, geographical distribution, selective breeding,
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS. Evidence from Evolution Activity. The Fossilization Process. Types of Fossils
 Evidence from Evolution Activity Part 1 - Fossils Use the diagrams on the next page to answer the following questions IN YOUR NOTEBOOK. 1. Describe how fossils form. 2. Describe the different types of
Evidence from Evolution Activity Part 1 - Fossils Use the diagrams on the next page to answer the following questions IN YOUR NOTEBOOK. 1. Describe how fossils form. 2. Describe the different types of
Evolution. Darwin s Voyage
 Evolution Darwin s Voyage Charles Darwin Explorer on an observation trip to the Galapagos Islands. He set sail on the HMS Beagle in 1858 from England on a 5 year trip. He was a naturalist (a person who
Evolution Darwin s Voyage Charles Darwin Explorer on an observation trip to the Galapagos Islands. He set sail on the HMS Beagle in 1858 from England on a 5 year trip. He was a naturalist (a person who
Change over Time. Differences Between Organisms. 298 Chapter 10 The Evolution of Living Things
 1 What You Will Learn The fossil record provides evidence that species have changed over time. Fossils support the hypothesis that modern whales evolved from land mammals. Comparing the anatomy and DNA
1 What You Will Learn The fossil record provides evidence that species have changed over time. Fossils support the hypothesis that modern whales evolved from land mammals. Comparing the anatomy and DNA
Theory a well supported testable explanation of phenomenon occurring in the natural world.
 Evolution Theory of Evolution Theory a well supported testable explanation of phenomenon occurring in the natural world. Evolution the process by which modern organisms changed over time from ancient common
Evolution Theory of Evolution Theory a well supported testable explanation of phenomenon occurring in the natural world. Evolution the process by which modern organisms changed over time from ancient common
Evidence of Evolution Background
 Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as
Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as
Vestigial Structures. Structure Possible Function(s) Why it is considered vestigial Appendix
 Vestigial Structures A vestigial structure is a structure or organ that through the course of evolution has either diminished in size or usefulness. It is believed that the human appendix, wisdom teeth
Vestigial Structures A vestigial structure is a structure or organ that through the course of evolution has either diminished in size or usefulness. It is believed that the human appendix, wisdom teeth
Stnd: 8 e C-Notes: Evidence of Evolution
 Stnd: 8 e C-Notes: Evidence of Evolution 3/10/2014 Objective: SWBAT analyze different types of evidence of evolution with regard to diversity of different organisms. What evidence supports evolution? 1.
Stnd: 8 e C-Notes: Evidence of Evolution 3/10/2014 Objective: SWBAT analyze different types of evidence of evolution with regard to diversity of different organisms. What evidence supports evolution? 1.
Evolution Evidence of Change
 6 Evolution Evidence of Change lesson 1 Fossils and Evolution Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.e. Students know fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. Also
6 Evolution Evidence of Change lesson 1 Fossils and Evolution Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.e. Students know fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. Also
Evolution Common Assessment 1
 Evolution Common Assessment 1 1. The field of biology that includes the study of the origin of new species through time is known as 5. A. biochemistry B. evolution C. ecology D. embryology 2. Evidence
Evolution Common Assessment 1 1. The field of biology that includes the study of the origin of new species through time is known as 5. A. biochemistry B. evolution C. ecology D. embryology 2. Evidence
Evidence of Evolution. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution
 Lesson Overview Lesson Overview 16.4 THINK ABOUT IT Scientists in some fields, including geology, physics, paleontology, chemistry, and embryology, did not have the technology or understanding to test
Lesson Overview Lesson Overview 16.4 THINK ABOUT IT Scientists in some fields, including geology, physics, paleontology, chemistry, and embryology, did not have the technology or understanding to test
Evidence for the Theory of Evolution (Adapted from: Prentice Hall Laboratory Manual)
 Evidence for the Theory of Evolution (Adapted from: Prentice Hall Laboratory Manual) NGSSS: SC.912.L.15.1 Explain the scientific theory of evolution is supported by the fossil record, comparative anatomy,
Evidence for the Theory of Evolution (Adapted from: Prentice Hall Laboratory Manual) NGSSS: SC.912.L.15.1 Explain the scientific theory of evolution is supported by the fossil record, comparative anatomy,
Evidence for Evolution
 Evidence for Evolution Evolution Biological evolution is descent with modification. It is important to remember that: Humans did not evolve from chimpanzees. Humans and chimpanzees are evolutionary cousins
Evidence for Evolution Evolution Biological evolution is descent with modification. It is important to remember that: Humans did not evolve from chimpanzees. Humans and chimpanzees are evolutionary cousins
EVOLUTION. It s a Family Affair
 EVOLUTION It s a Family Affair TODAY S LESSON Diversity and Evolution of Living Organisms I. The scientific theory of evolution is the organizing principle of life science. II. The scientific theory of
EVOLUTION It s a Family Affair TODAY S LESSON Diversity and Evolution of Living Organisms I. The scientific theory of evolution is the organizing principle of life science. II. The scientific theory of
Science in Motion Ursinus College
 Science in Motion Ursinus College NAME EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION LAB INTRODUCTION: Evolution is not just a historical process; it is occurring at this moment. Populations constantly adapt in response to changes
Science in Motion Ursinus College NAME EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION LAB INTRODUCTION: Evolution is not just a historical process; it is occurring at this moment. Populations constantly adapt in response to changes
Darwin's Theory. Use Target Reading Skills. Darwin's Observations. Changes Over Time Guided Reading and Study
 Darwin's Theory This section discusses Charles Darwin and his theories ofevolution, which are based on what he saw during his trip around the world. Use Target Reading Skills In the graphic organizer,
Darwin's Theory This section discusses Charles Darwin and his theories ofevolution, which are based on what he saw during his trip around the world. Use Target Reading Skills In the graphic organizer,
Evolutionary Evidence of Evolution
 Evolutionary Evidence of Evolution Evolution - the process in which relative changes in the genetic makeup (characteristics) of a species occurs over time Sometimes changes in populations are environmental
Evolutionary Evidence of Evolution Evolution - the process in which relative changes in the genetic makeup (characteristics) of a species occurs over time Sometimes changes in populations are environmental
Section 1 Darwin s theory
 Evolution Section 1 Darwin s theory EVOLUTION The gradual change in a species over time. 2 types EVOLUTION Microevolution: change within a species. Macroevolution: change of a species into a new species.
Evolution Section 1 Darwin s theory EVOLUTION The gradual change in a species over time. 2 types EVOLUTION Microevolution: change within a species. Macroevolution: change of a species into a new species.
16.4 Evidence of Evolution
 16.4 Evidence of Evolution Lesson Objectives Explain how geologic distribution of species relates to their evolutionary history. Explain how fossils and the fossil record document the descent of modern
16.4 Evidence of Evolution Lesson Objectives Explain how geologic distribution of species relates to their evolutionary history. Explain how fossils and the fossil record document the descent of modern
Evidence for Evolution
 Evidence for Evolution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Paleontology Comparative Anatomy Embryology Comparative Biochemistry Geographical Distribution How old is everything? The History of Earth as a Clock Station 1: Paleontology
Evidence for Evolution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Paleontology Comparative Anatomy Embryology Comparative Biochemistry Geographical Distribution How old is everything? The History of Earth as a Clock Station 1: Paleontology
Theory of Evolution. Data Driven Process Supported by Evidence
 Theory of Evolution Data Driven Process Supported by Evidence TEKS (7) The student knows evolutionary theory is a scientific explanation for the unity and diversity of life. The student is expected to:
Theory of Evolution Data Driven Process Supported by Evidence TEKS (7) The student knows evolutionary theory is a scientific explanation for the unity and diversity of life. The student is expected to:
Biology. Evolution: History & Process
 Biology Evolution: History & Process Terms: A species is a group of organisms, or population, that can be interbreed & produce fertile offspring. Variations are the differences found within species. Ex:
Biology Evolution: History & Process Terms: A species is a group of organisms, or population, that can be interbreed & produce fertile offspring. Variations are the differences found within species. Ex:
The Living Environment Unit 4 History of Biologic Diversity Unit 15 Evolution: (15.2) Evidence of Evolution-class key. Name: Class key.
 Name: Class key Period: Topic 15.2 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Topic: Evidence for Evolution Objective: What scientific evidence supports evolution theory? Evidence supporting evolution
Name: Class key Period: Topic 15.2 assignments Pages/Sections Date Assigned Date Due Topic: Evidence for Evolution Objective: What scientific evidence supports evolution theory? Evidence supporting evolution
At the present time, scientists generally accept the theory of (1) ( 進化 ), which suggests that life on earth started from a (2) ( 共同祖先 ).
 Class: Name: ( ) Date: 29 Evolution I 29.1 The origin of life (Book 4, p. 29-3) Scientists generally believe that the first organisms were formed by joining (1) molecules together. The organic molecules
Class: Name: ( ) Date: 29 Evolution I 29.1 The origin of life (Book 4, p. 29-3) Scientists generally believe that the first organisms were formed by joining (1) molecules together. The organic molecules
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Regents Biology
 Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Objective: Determine the different types of evidence for proving evolution Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Comparative Anatomy
Evidence for Evolution by Natural Selection Objective: Determine the different types of evidence for proving evolution Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record shows change over time Comparative Anatomy
1. The Fossil Record 2. Biogeography 3. Comparative Anatomy 4. Comparative Embryology 5. Molecular Biology
 What Darwin Observed. copy 1. The Fossil Record 2. Biogeography 3. Comparative Anatomy 4. Comparative Embryology 5. Molecular Biology Activity in groups copy Provides a chronological record of organisms
What Darwin Observed. copy 1. The Fossil Record 2. Biogeography 3. Comparative Anatomy 4. Comparative Embryology 5. Molecular Biology Activity in groups copy Provides a chronological record of organisms
Lesson Topic Learning Goals
 Unit 2: Evolution Part B Lesson Topic Learning Goals 1 Lab Mechanisms of Evolution Cumulative Selection - Be able to describe evolutionary mechanisms such as genetic variations and key factors that lead
Unit 2: Evolution Part B Lesson Topic Learning Goals 1 Lab Mechanisms of Evolution Cumulative Selection - Be able to describe evolutionary mechanisms such as genetic variations and key factors that lead
MS-LS4-1 Biological Evolution: Unity and Diversity
 MS-LS4-1 Biological Evolution: Unity and Diversity MS-LS4-1. Analyze and interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity, extinction, and change of life forms throughout
MS-LS4-1 Biological Evolution: Unity and Diversity MS-LS4-1. Analyze and interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity, extinction, and change of life forms throughout
What is Evolution? Evolution Unit Vocabulary. Answer: Evidence of Evolution. What is a Gene Pool? Change over time.
 What is Evolution? Evolution Unit Vocabulary Practice Quiz Change over time. Evidence of Evolution The gradual development of something, especially from simple to more complex. Can be big or very small
What is Evolution? Evolution Unit Vocabulary Practice Quiz Change over time. Evidence of Evolution The gradual development of something, especially from simple to more complex. Can be big or very small
Evidence of Evolution
 NAME PER DATE Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much
NAME PER DATE Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much
Evolution & Natural Selection
 Evolution & Natural Selection Human Origins & Adaptations Charles Darwin Darwin did not discover evolution Darwin explain how natural selection decided which genes would be selected and passed on to the
Evolution & Natural Selection Human Origins & Adaptations Charles Darwin Darwin did not discover evolution Darwin explain how natural selection decided which genes would be selected and passed on to the
Where Do Bat Wings Come From?
 Where o at Wings ome From? 1 ats are the only mammals that have evolved the power of flight. They can avoid obstacles and slip through tight spaces. Many species are nocturnal and use echolocation to guide
Where o at Wings ome From? 1 ats are the only mammals that have evolved the power of flight. They can avoid obstacles and slip through tight spaces. Many species are nocturnal and use echolocation to guide
EVOLUTION: EVIDENCE AND THEORY
 Name Class Date CHAPTER 15 TEST EVOLUTION: EVIDENCE AND THEORY MATCHING Write the correct letter in the blank before each numbered term. 1. natural selection 2. fitness 3. acquired trait 4. biogeography
Name Class Date CHAPTER 15 TEST EVOLUTION: EVIDENCE AND THEORY MATCHING Write the correct letter in the blank before each numbered term. 1. natural selection 2. fitness 3. acquired trait 4. biogeography
15.3 Darwin Presents his Case. Biology Mr. Hines
 15.3 Darwin Presents his Case Biology Mr. Hines Darwin returned to England with a wealth of new data. He brought many specimens from the Galapagos to further his studies and to present his data to others.
15.3 Darwin Presents his Case Biology Mr. Hines Darwin returned to England with a wealth of new data. He brought many specimens from the Galapagos to further his studies and to present his data to others.
Chapter 22 Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life
 Chapter 22 Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life 1. Evolution by Natural Selection 2. Evidence for the Evolutionary Process 1. Evolution by Natural Selection Chapter Reading pp. 462-470 1809
Chapter 22 Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life 1. Evolution by Natural Selection 2. Evidence for the Evolutionary Process 1. Evolution by Natural Selection Chapter Reading pp. 462-470 1809
of EVOLUTION???????????? states that existing forms of life on earth have arisen from earlier forms over long periods of time.
 Evolution The WHAT theory IS of EVOLUTION???????????? states that existing forms of life on earth have arisen from earlier forms over long periods of time. Some of the strongest evidence to support evolution
Evolution The WHAT theory IS of EVOLUTION???????????? states that existing forms of life on earth have arisen from earlier forms over long periods of time. Some of the strongest evidence to support evolution
Processing Activities
 Processing Activities Which animals would your group together based on their similarities? horse, rabbit, zebra, squirrel, donkey, deer, chipmunk, and mouse. Describe below how you would group them. 1
Processing Activities Which animals would your group together based on their similarities? horse, rabbit, zebra, squirrel, donkey, deer, chipmunk, and mouse. Describe below how you would group them. 1
Lecture Title ( Fossils ) & Date. Main Ideas/Lecture Topics/Questions. Big Ideas or Chunking the Lecture
 Lecture Title ( Fossils ) & Date Main Ideas/Lecture Topics/Questions Big Ideas or Chunking the Lecture Fossil Trilobites Point of View #1 Natural selection provides a scientific explanation for the fossil
Lecture Title ( Fossils ) & Date Main Ideas/Lecture Topics/Questions Big Ideas or Chunking the Lecture Fossil Trilobites Point of View #1 Natural selection provides a scientific explanation for the fossil
UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution. I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution
 UNIT IV Chapter 10 Principles of Evolution UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution 1. Evolution- process
UNIT IV Chapter 10 Principles of Evolution UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution 1. Evolution- process
Name Date Period Evolution and the History of Life, MLK 2005
 Evolution and the History of Life, MLK 2005 Chapter 8.1 Change Over Time Differences Among Organisms Do Species Change Over Time Evidence of Evolution: The Fossil Record Fossils Reading the Fossil Record
Evolution and the History of Life, MLK 2005 Chapter 8.1 Change Over Time Differences Among Organisms Do Species Change Over Time Evidence of Evolution: The Fossil Record Fossils Reading the Fossil Record
Evolution Unit: What is Evolution?
 Evolution Unit: What is Evolution? What is The Theory of Evolution? Evolution is, a change (in the genetic composition) of a population over time. on a larger scale, the entire biological history, from
Evolution Unit: What is Evolution? What is The Theory of Evolution? Evolution is, a change (in the genetic composition) of a population over time. on a larger scale, the entire biological history, from
Evidence of Evolution by Natural Selection. Dodo bird
 Evidence of Evolution by Natural Selection Dodo bird 2007-2008 Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record transition species Anatomical record homologous & vestigial structures embryology & development
Evidence of Evolution by Natural Selection Dodo bird 2007-2008 Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record transition species Anatomical record homologous & vestigial structures embryology & development
6 HOW DID OUR ANCESTORS EVOLVE?
 6 HOW DID OUR ANCESTORS EVOLVE? David Christian introduces the science of taxonomy and explains some of the important methods used to identify and classify different species and several key human ancestors.
6 HOW DID OUR ANCESTORS EVOLVE? David Christian introduces the science of taxonomy and explains some of the important methods used to identify and classify different species and several key human ancestors.
Evidences of Evolution (Clues)
 Evidences of Evolution (Clues) Darwin stated that all organisms descended from a common ancestor Darwin based his theory of Natural Selection on observations of: Traits, geographical distribution, selective
Evidences of Evolution (Clues) Darwin stated that all organisms descended from a common ancestor Darwin based his theory of Natural Selection on observations of: Traits, geographical distribution, selective
THE EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
 Unit 37 THE EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the meaning of the term evolution. 2. Learn about fossil evidence including how fossils are formed. 3. Learn how comparative anatomy
Unit 37 THE EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the meaning of the term evolution. 2. Learn about fossil evidence including how fossils are formed. 3. Learn how comparative anatomy
MS-LS3-1 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits
 MS-LS3-1 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits MS-LS3-1. Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes (mutations) located on chromosomes may affect proteins and may result
MS-LS3-1 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits MS-LS3-1. Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes (mutations) located on chromosomes may affect proteins and may result
NGSS UNIT OVERVIEW EVOLUTION
 UNIT SPECIFIC RESOURCES TEACHER RESOURCES IV NGSS UNIT OVERVIEW EVOLUTION Performance Expectation MS-LS4-1: Analyze interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity,
UNIT SPECIFIC RESOURCES TEACHER RESOURCES IV NGSS UNIT OVERVIEW EVOLUTION Performance Expectation MS-LS4-1: Analyze interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity,
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION. Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology
 SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
MAIN IDEA: Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution. In a phrase, tell what each scientist did to help develop evolutionary theory.
 SECTION 10.1 KEY CONCEPT EARLY IDEAS ABOUT EVOLUTION Study Guide There were theories of biological and geologic change before Darwin. VOCABULARY evolution fossil gradualism species catastrophism uniformitarianism
SECTION 10.1 KEY CONCEPT EARLY IDEAS ABOUT EVOLUTION Study Guide There were theories of biological and geologic change before Darwin. VOCABULARY evolution fossil gradualism species catastrophism uniformitarianism
The Theory of Evolution Chapter 6
 The Theory of Evolution Chapter 6 Change over time. What is evolution? What Do You See? Two faces.. or one? A lady at her dressing table... or a skull? (try blinking.. or moving away from the screen) A
The Theory of Evolution Chapter 6 Change over time. What is evolution? What Do You See? Two faces.. or one? A lady at her dressing table... or a skull? (try blinking.. or moving away from the screen) A
Evolution: change in the hereditary
 Mechanisms of Evolution Evolution: change in the hereditary features of species over time. Species: a group of organisms that successfully reproduce among themselves. There are two kinds of evolution:
Mechanisms of Evolution Evolution: change in the hereditary features of species over time. Species: a group of organisms that successfully reproduce among themselves. There are two kinds of evolution:
I Can Statement Conversation/Assignment
 I Can Statement Conversation/Assignment B- 5.5 Exemplify scientific evidence in the fields of anatomy, embryology, biochemistry, and paleontology that underlies the theory of biological evolution B- 5.6
I Can Statement Conversation/Assignment B- 5.5 Exemplify scientific evidence in the fields of anatomy, embryology, biochemistry, and paleontology that underlies the theory of biological evolution B- 5.6
Sources of Evidence of Evolution
 Sources of Evidence of Evolution In The Origin of Species, Darwin assembled a group of facts that had previously seemed unrelated. Darwin s ideas were developed, for the most part, by his observations
Sources of Evidence of Evolution In The Origin of Species, Darwin assembled a group of facts that had previously seemed unrelated. Darwin s ideas were developed, for the most part, by his observations
Evolution and Taxonomy Laboratory
 Evolution and Taxonomy Laboratory 1 Introduction Evolution refers to the process by which forms of life have changed through time by what is described as descent with modification. Evolution explains the
Evolution and Taxonomy Laboratory 1 Introduction Evolution refers to the process by which forms of life have changed through time by what is described as descent with modification. Evolution explains the
Chapter 15 Theory of Evolution
 Chapter 15 Theory of Evolution 15-1 History of Evolutionary Thought Evolution- the development of new species form pre-existing species. -change over time. In the 1800 s scientists began to present evidence
Chapter 15 Theory of Evolution 15-1 History of Evolutionary Thought Evolution- the development of new species form pre-existing species. -change over time. In the 1800 s scientists began to present evidence
Phylogenetic Trees. How do the changes in gene sequences allow us to reconstruct the evolutionary relationships between related species?
 Why? Phylogenetic Trees How do the changes in gene sequences allow us to reconstruct the evolutionary relationships between related species? The saying Don t judge a book by its cover. could be applied
Why? Phylogenetic Trees How do the changes in gene sequences allow us to reconstruct the evolutionary relationships between related species? The saying Don t judge a book by its cover. could be applied
Evidence of EVOLUTION
 Evidence of EVOLUTION Evolution: Genetic change in a population through time Charles Darwin On his journey around the world, Darwin found evidence of GRADUAL CHANGE (evolution) He cited evidences he found
Evidence of EVOLUTION Evolution: Genetic change in a population through time Charles Darwin On his journey around the world, Darwin found evidence of GRADUAL CHANGE (evolution) He cited evidences he found
Evidences of Evolution. Read Section 8.2 on pp of your textbook
 Evidences of Evolution Read Section 8.2 on pp. 332 338 of your textbook There are 5 key evidences for evolution: 1. Fossil record 2. Biogeography 3. Anatomical evidence (homologous structures, vestigial
Evidences of Evolution Read Section 8.2 on pp. 332 338 of your textbook There are 5 key evidences for evolution: 1. Fossil record 2. Biogeography 3. Anatomical evidence (homologous structures, vestigial
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Theory of Evolution - (BIO.B ) Theory Of Evolution, (BIO.B ) Scientific Terms
 Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Theory of Evolution - (BIO.B.3.2.1 ) Theory Of Evolution, (BIO.B.3.3.1 ) Scientific Terms Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George Date: Score: 1) Evidence for evolution
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Theory of Evolution - (BIO.B.3.2.1 ) Theory Of Evolution, (BIO.B.3.3.1 ) Scientific Terms Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George Date: Score: 1) Evidence for evolution
Evolution. Changes over Time
 Evolution Changes over Time TEKS Students will analyze and evaluate B. 7 C how natural selection produces change in populations, not individuals B. 7 E/F effects of genetic mechanisms and their relationship
Evolution Changes over Time TEKS Students will analyze and evaluate B. 7 C how natural selection produces change in populations, not individuals B. 7 E/F effects of genetic mechanisms and their relationship
Biology 20 Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Evidence for Evolution. Today s species that exist have evolved from ancestral ones.
 Biology 20 Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Evidence for Evolution Today s species that exist have evolved from ancestral ones. This theory of evolution is supported by many different types of evidence collected by
Biology 20 Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Evidence for Evolution Today s species that exist have evolved from ancestral ones. This theory of evolution is supported by many different types of evidence collected by
2/17/17. B. Four scientists important in development of evolution theory
 UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution 1. Evolution- process of biological change by which descendants
UNIT 4: EVOLUTION Chapter 10: Principles of Evolution I. Early Ideas about Evolution (10.1) A. Early scientists proposed ideas about evolution 1. Evolution- process of biological change by which descendants
Since Darwin s work, every scientific test has supported Darwin s basic ideas about evolution
 Guided Reading Answers Since Darwin s work, every scientific test has supported Darwin s basic ideas about evolution Biogeography Biogeography is the study of where organisms live now, and where they and
Guided Reading Answers Since Darwin s work, every scientific test has supported Darwin s basic ideas about evolution Biogeography Biogeography is the study of where organisms live now, and where they and
NGSS Example Bundles. 1 of 15
 Middle School Topics Model Course III Bundle 3 Mechanisms of Diversity This is the third bundle of the Middle School Topics Model Course III. Each bundle has connections to the other bundles in the course,
Middle School Topics Model Course III Bundle 3 Mechanisms of Diversity This is the third bundle of the Middle School Topics Model Course III. Each bundle has connections to the other bundles in the course,
Hard Parts of Organisms: Bones Shells Hard Parts of Insects Woody Material (trunks) Fossils provide evidence of how life has changed over time.
 PLEASE, PICK UP OUTLINE FROM THE FRONT TABLE! *recommend adding the extra stuff to the notes Fossus - means to dig up Fossils are preserved remains or traces of living things. Most fossils form when living
PLEASE, PICK UP OUTLINE FROM THE FRONT TABLE! *recommend adding the extra stuff to the notes Fossus - means to dig up Fossils are preserved remains or traces of living things. Most fossils form when living
CHANGE OVER TIME. Ms. Feierabend
 CHANGE OVER TIME Ms. Feierabend OBJECTIVES Demonstrate the theory of natural selection through historical & modern-day examples. Recognize that variation exists in every population & describe how a variation
CHANGE OVER TIME Ms. Feierabend OBJECTIVES Demonstrate the theory of natural selection through historical & modern-day examples. Recognize that variation exists in every population & describe how a variation
Mechanisms of Evolution Darwinian Evolution
 Mechanisms of Evolution Darwinian Evolution Descent with modification by means of natural selection All life has descended from a common ancestor The mechanism of modification is natural selection Concept
Mechanisms of Evolution Darwinian Evolution Descent with modification by means of natural selection All life has descended from a common ancestor The mechanism of modification is natural selection Concept
Evolutionary change. Evolution and Diversity. Two British naturalists, one revolutionary idea. Darwin observed organisms in many environments
 Evolutionary change Evolution and Diversity Ch 13 How populations evolve Organisms change over time In baby steps Species (including humans) are descended from other species Two British naturalists, one
Evolutionary change Evolution and Diversity Ch 13 How populations evolve Organisms change over time In baby steps Species (including humans) are descended from other species Two British naturalists, one
The History of Life on Earth
 CHAPTER 9 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET The History of Life on Earth By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary
CHAPTER 9 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET The History of Life on Earth By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary
Evolution = descent with modification
 Chapter 21: Evidence for Evolution I. Evolution & Darwin II. Artificial Selection III. Fossil Record IV. Comparative Anatomy V. Embryology VI. Genetic Analysis VII. Biogeographical Evidence VIII. Conclusions
Chapter 21: Evidence for Evolution I. Evolution & Darwin II. Artificial Selection III. Fossil Record IV. Comparative Anatomy V. Embryology VI. Genetic Analysis VII. Biogeographical Evidence VIII. Conclusions
Evolution. 1. The figure below shows the classification of several types of prairie dogs.
 Name: Date: 1. The figure below shows the classification of several types of prairie dogs. 3. Which statement describes the best evidence that two species share a recent common ancestor? A. The species
Name: Date: 1. The figure below shows the classification of several types of prairie dogs. 3. Which statement describes the best evidence that two species share a recent common ancestor? A. The species
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS. Chapter 18
 CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS Chapter 18 How many species are there? About 1.8 million species have been given scientific names Nearly 2/3 of which are insects 99% of all known animal species are smaller
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS Chapter 18 How many species are there? About 1.8 million species have been given scientific names Nearly 2/3 of which are insects 99% of all known animal species are smaller
Review sheet for the material covered by exam III
 Review sheet for the material covered by exam III WARNING: Like last time, I have tried to be complete, but I may have missed something. You are responsible for all the material discussed in class. This
Review sheet for the material covered by exam III WARNING: Like last time, I have tried to be complete, but I may have missed something. You are responsible for all the material discussed in class. This
Dichotomous Key for Genus Problematica
 Evolution Summative Assessment DO NOT WRITE ON TEST 1. Industrial melanism describes the change in moth color from pale to dark after pollution from factories resulting in coating tree trunks with a layer
Evolution Summative Assessment DO NOT WRITE ON TEST 1. Industrial melanism describes the change in moth color from pale to dark after pollution from factories resulting in coating tree trunks with a layer
Chapter 10 Study Guide SECTION 1: Early Ideas about Evolution
 NAME Chapter 10 Study Guide SECTION 1: Early Ideas about Evolution BIOLOGY PREAP/GT Match each scientist with the statement that best reflects his ideas about evolutionary theory. 1. Linnaeus a. Species
NAME Chapter 10 Study Guide SECTION 1: Early Ideas about Evolution BIOLOGY PREAP/GT Match each scientist with the statement that best reflects his ideas about evolutionary theory. 1. Linnaeus a. Species
