INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing Association
|
|
|
- Agatha McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing Association Research article ISSN Haematology and Haemochemistry of Silkworm, Bombyx Mori L. Infected with Bacillus Thurungenses Anandakumar, M. D 1, Ann Sandhya Michael 2 1- Department of Biochemistry, Adarsh Institute of research & postgraduate studies, SRN Adarsh college, Chamarajpet, Bangalore , India. 2- Department of Life Sciences, Bangalore University, Jnanabharathi, Bangalore , India anupol2004@yahoo.co.in doi: /ijes ABSTRACT Total haemocyte count, differential haemocyte count, changes in nucleus/nucleolar ratios of various haemocytes, as well as haemolymph protein and reducing sugar of fifth instar larvae of Bombyx mori L. inoculated with flacherie were studied. The inoculated worms received spores/ml on the third day of fifth instar. The infected larvae showed 15.3% decrease in total haemocyte count (THC) when compared to healthy worms. Prohaemocytes and granular haemocytes, which form the bulk of the total population, were not influenced by Bacillus thurungienses, where as significant increase was observed in differential haemocyte count (DHC) of plasmocytes alone. Bacterial infection also influenced nucleus/nucleolar (N/Nu) ratio of plasmocytes and oenocytoids indicating their role in larval immunity process. Plasma protein and reducing sugars were marginally reduced on infection. The above results were discussed in the light of pathophysiology of silkworm on bacterial infection. Key words: Silkworm, haemocytes, flacherie, Bacillus thurungienses, plasma. 1. Introduction Flacherie is the most common disease that inflicts the maximum damage to Sericulture. Due to their variations in the symptoms it is often called by different names like flacherie, sotto disease, shrinking disease, softening disease, fecal disease etc. When the larvae affected with flacherie, the nature of haemolymph and digestive fluid also changes and as a result the cells of the gut wall gets affected. Since haemolymph is a circulatory fluid, with several functions, such as storage and transportation of nutrients and also plays an important role in excretion, defense, moulting and metamorphosis (Mullins, 1985). Nucleated haemocytes number varies with the insects; these haemocytes are classified as prohaemocytes, plasmocytes, granular haemocytes, oenocytes or oenocytoid and spherule cells (Arnold & Hinks, 1976). Major function of haemocytes includes phagocytosis of small particles, encapsulation of large foreign materials, haemolymph coagulation and storage and distribution of nutritive materials. Despite several studies made on bacterial disease of silkworm, information regarding the exact biochemical and physiological changes occurring inside the body of silkworm throughout the progress of disease is scanty. Here we present investigate on this disease with a view to find out the changes in haemotology and haemochemistry of silkworm, Bombyx mori infected with Bacillus. Received on September 2011 Published on November
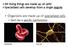
2 2. Materials and Methods The disease free layings of silkworm hybrid PM X NB 4 D 2 were procured from private agency Sri Gurukrupa grainage, Ramanagaram, Bangalore. The silkworm hybrid was reared in environmental chamber at Silkworm physiology research laboratory, Dept of studies in Sericulture, Bangalore University, Bangalore, under the standard rearing conditions at temperature 26 1 C with 75 5% relative humidity and photoperiod of 16 L: 8D as per the recommended rearing practice (Raja Ram, 2000). During inoculation time silkworm larvae were divided in to two batches one batch for inoculation and one for normal/with out any treatment. The Bacillus spores were obtained from the KSSR & DI, Thalaghattapura, Bangalore. Bacillus infection was made orally to the silkworm larvae on 3 rd day of fifth instar for multiplication and the supplement had spores/ml. After 48 hours of inoculation the haemolymph smear was made according to Shapiro (1979). The commonly used parameters to describe the blood profile of an insect are total haemocyte count (THC) and differential haemocyte count (DHC). Total haemocyte count was made according to Tauber and Yeager (1934). DHC count was carried out according to the method of Yeager (1945). Nucleus/nucleorlar (N/NU) ratios were also calculated for each type of cells. For biochemical analysis few larvae were collected in normal and Bacillus treated batches. The larvae were kept in refrigerator at 4-5 o C for 5-10 minutes to facilitate the free running of heamolymph. The caudal horn of larvae was punctured and the heamolymph was collected in cleaned, sterilized and pre-cooled vials. A pinch of phenylthiourea is added to prevent the oxidation of heamolymph. The vials were preserved in the refrigerator as stock and used for estimation of haemolymph protein and reducing sugar by following the standard procedures (Lowry et al., 1951 and Burton 1956). The collected data were subjected to statistical analysis of t-test (Khan and Khanum 1994) 3. Results The THC count (number per mm3) decreased significantly (P>0.010, t = , df 4, n 3) when larvae were fed orally with Bacillus. Bacterial infected silkworms showed 15.3% decrease in the number of blood cells compared to healthy worms (Figure 1). The prohaemocytes and granular haemocytes formed the bulk of the haemocytes in the present study and their population not influenced by Bacillus infection. finding in the present study is the change in the number of plasmocytes on treatment with pathogen. Infection due to Bacillus significantly increased the plasmocytes population by 40%. However, there is no much variation in oenocyte and spherule cells population on infection in haemolymph of silkworm (Table-1). Table-2 Reveals the N/NU ratio in different haemocytes of silkworm and also the changes brought out by infection with bacillus. Prohaemocytes did not show any change in N/NU on treatment, whereas notable decrease was observed in rest of the haemocytes on infection. Plasmocytes showed significantly (P>0.100) increased ratio in healthy larval batch, indicating their significant role in protein synthesis and on bacteria infection the ratio was brought down by 20%. However, significantly (P>0.100) decreased in oenocytes N/NU ratio on infection was observed when compared with other cell types. The Bacillus inoculation induced a significant (P>0.010, t , df 4, n 3) decrease in the protein content of haemolymph, and similar decrease was observed in reducing sugars. The protein contents in the healthy worms were found to be 47.9 mg/ml, which decreased to 41.7 mg/ml of haemolymph in inoculated worms. Reducing sugar was also significantly (P>0.050, t 464
3 2.2404, df 4, n 3) decreased in inoculated worms and the amount was found to be 3.0mg/ml where as in normal worms 3.26mg/ml (figure 2). 4. Discussion Flacherie, a bacterial disease infects the silkworm through injury or wounds and multiplies in the haemolymph, disrupting the normal physiological function. Haemolymph being a circulatory fluid performs several functions (Mullins, 1985) and haemolymph consists of nucleated haemocytes, which are classified into granular haemocytes, spherule cells, oenocytoids, prohaemocytes and plasmocytes (Arnold & Hinks, 1975). The most prominent haemocytes in Bombyx mori are prohaemocytes, granular haemocytes, plasmocytes, oenocytoids and spherule cells (Akai, 1976). Hence it is of interest to know the role of haemocytes and their participation in immune response. From the present experimental result, it was found that the total cell count decreased significantly when treated with Bacillus. About 15.3% of the total haemocytes were decreased when compared to normal worms. Further, the decrease in total count infected with Bacillus was due to the depletion of prohaemocytes, which accounts for most of the lowered total counts compared to normal. The DHC further helps in the investigation of cellular defense mechanisms and to know the participation of a particular type of blood cell in such function. Peake (1979) found that there was an increase in the proportion of phagocytic haemocytes in Calliphora with age. An increase with the granular haemocytes percentage was found in Bombyx mori larvae between first and fifth instar (Wago & Ishikawa, 1979). Increased numbers of phagocytic blood cells were recorded by Crossely (1968) in a study on muscle autolyses and regeneration in the larvae of Calliphora. The increase in the proportion of plasmocytes and its morphological modification was similar to lamellocyte at the end of larval development in Drosophilla (Rizki, 1957). Those findings infer that some of the haemocytes appear in the haemolymph in greater numbers at certain times and at certain physiological state. Whitter (1964) also mentioned that changes in haemocytes are likely under hormonal control. The DHC of Bacillus infected larvae of Bombyx mori in the present study showed changes in haemocytes, with a significant increase in plasmocytes and granular haemocytes. There was no significant change in proportion of oenocytes and spherule cells. Increased population of granular haemocytes and plasmocytes can be related as defense mechanisms in B.mori, since both the types of haemocytes functions as phagocytes. Haemocytes are found to undergo mitosis in insects (Wigglesworth, 1993) on the basis of studies on morphological radio isotopic and ultra-structural features. It is almost universally accepted that prohaemocytes are stem cells and divide to produce plasmocytes (Gupta & Sutherland, 1966; Lea, 1986). But it is believed that plasmocytes gives rise to granular haemocytes from which all other types developed (Gupta 1979). The formations of granular haemocytes from plasmocytes in lepidoplerans are also reported (Lai-fook, 1973; Beemam et al., 1983). Bacillus infected silkworm larvae showed that the N/NU ratio was decreased compared to healthy worms. The decreased N/NU ratio indicates decreased protein synthesis in the haemocytes on infection. In view of the above reports and the results of the experiment, it shows that the prohaemocytes undergo division in order to increase the number of granular haemocytes and plasmocytes, which take part in cellular defense mechanism. Thus, in the 465
4 inoculated larvae, we find the decreased proportion of prohaemocytes with the increased proportion of granular haemocytes and plasmocytes. In the present work the amount of protein content was found to decrease in the inoculated worms, when compared to healthy worms. Reducing sugar in the haemolymph of silkworm, Bombyx mori infected with Bacillus was also low. Perhaps, the silkworms were not able to feed at normal rate when infected by Bacillus and there could be a change in digestion and absorption of nutrient in silkworm on bacterial infection. Table 1: Effect of Bacillus Thurungiensis on different haemocyte count (%) in silkworm, Bombyx mori L. larva Different Haemocytes Prohaemocytes Granular haemocytes Plasmocytes Oenocytes Spherule cells Normal larva Inoculated larva Standard deviation t-value degrees of freedom (df) No of Replications (n) Prabability (P) Remarks Highly Table 2: Changes in Nucleus/nucleolar ratio of different haemocyte population (%) in silkworm, Bombyx mori L. inoculated with Bacillus Thurungienses. Different Haemocytes Granular Prohaemocytes haemocytes Pasmocytes Oenocytes Spherule cells Normal larva Inoculated larva Standard deviation t-value degrees of freedom (df) No of Replications (n) Prabability (P) Remarks 466
5 biochemical constituents (mg/ml) No. of haemocytes/mm3 Haematology and Haemochemistry of Silkworm, Bombyx Mori L. Infected with Bacillus Thurungenses 640 Effect of Bacillusthurungienses on total heamocyte count in silkworm Bombyx mori, L healthy infected fig-1 Fig-2 Changes in heamolymph biochemical constituents (protein and reducing sugar) in silkworm Bombyx mori, L. infected with Bacillus thurungienses protein reducing sugar healthy inoculated Figure 2: Changes in heamolymph biochemical constituents (protein and reducing sugar) in silkworm Bombyx mori, L. infected with Bacillus thurungienses 5. References 1. Akai. H., Sato, S (1976), Surface ultrastructure of the larval haemocytes of the silkworm, Bombyx mori L. International Journal of Insect Morphology and Embryology, 5(1), pp Arnold. J. W., Hinks, C. F (1976), Haemopoiesis in Lepidoptera I. The multiplication of circulating haemocytes. Cannadian Journal of Zoology, 54, pp
6 3. S. C. Beeman (1983), Structural characterization of the haemocytes of Plodia interpunctella. Journal of Morphology, 175, pp K. Burton (1956), A study of the condition and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry Journal, 62, pp A. C. Crossley (1968), The fine structure and mechanism of breakdown of larval intersegmental muscles in the blowfly, Calliphora erythrocephala. Journal of Insect Physiology, 14, pp Gupta, A. P., Sutherland, D. J (1966), In vitro transformation of the insect plasmocytes in some insects. Journal of Insect Physiology, 12, pp A. P. Gupta (1979), Haemocyte types: their structures, synonymies, interrelationships and taxonomic significance. In insect Haemocytes (Ed. A.P.Gupta), pp Irfan. A, Khan, Atiya Khanum (1994), Fundamentals of Bio-statistics, Ukaaz publications, Hydrabad, India, pp J. Lai-fook (1973), The structure of haemocytes of Calopodes ethlius (Lepidoptera). Journal of Morphology, 139, pp M. S. Lea (1986), A sericesthis iridescent virus infection of the haemocytes of the wax moth, Galleria mellanella effects on total and differential counts and haemocytogeny. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 48, pp O. H. Lowry (1951), Protein measurement with folin-phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, pp D. E. Mullins (1985), Chemistry and physiology of the haemolymph. In Comp. Insect. Physiol.Biochem. Pharm. Vol. 3.(Ed.,by Kerkut GA, Gilbert LF) Pergamon Press, Newyork, pp P. W. Peake (1979), Isolation and characterization of the haemocytes of Caliphora vicina on density gradients of Ficoll. Journal of Insect Physiology, 25, pp T. M. Rizki (1957), Alterations in the haemocyte population of Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Morphology, 100, pp Raja Ram (2000), Appropriate silkworm rearing technology. In:Hari Om Agrawal, Seth MK, editors.sericulture in India,pp: :Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh press, Dehradun, India. 14. M. Shapiro (1979), Changes in haemocyte populations. In Insect Haemocyte (Ed. Gupta AP) Cambridge University Press. Cambridge, pp Tauber. O. E., Yeager. J. F (1935), On total haemolymph (Blood) counts of insects-i Orthoptera, Odonata, Hemiptera and Homoptera. Annual Entamological Science of America, 28, pp
7 16. Wago, H., Ishikawa, Y (1979), Haemocytic reactions to foreign cells in the silkworms, Bombyx mori during post-embryonic development. Applied Entamological Zoology, 14, pp J. M. Whitter (1964), Haemocytes and metamorphosing tissues in Sarcophagar bullata, Drosophila melanogaster, and other Chyclorrhaphous dipter. Journal of Insect Physiology, 10, pp V. B. Wigglesworth (1993), The physiology of the cuticle and of ecdysis in Rhodinus prolixus Triatonidae (Hemiptera) with special reference to the function of the oenocytes and of the dermal glands. QJI micross. Sci., 76, pp J. F. Yeager (1935), The blood picture of the Southern army worm (prodenia eridania). Journal of agriculture Research, 71, pp
J. A. Chavan, G. P. Bhawane. International Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences (IJEAS) ISSN: , Volume-4, Issue-7, July 2017
 Efficacy of Beauveria bassiana infection and subsequent oral treatment of ehtanolic plant extract on total haemocyte count and differential haemocyte count on 3rd day of fifth instar larvae of and Bombyx
Efficacy of Beauveria bassiana infection and subsequent oral treatment of ehtanolic plant extract on total haemocyte count and differential haemocyte count on 3rd day of fifth instar larvae of and Bombyx
Available online at
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Bardoloi et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 4 (5): 144-152 (2016) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2368 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Bardoloi et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 4 (5): 144-152 (2016) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2368 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Highlights from Pesticides Lecture
 Highlights from Pesticides Lecture Prior to World War II pesticides were, while post-ww II they were. What is meant by the biomagnification of pesticides and what are its consequences? Differentiate between
Highlights from Pesticides Lecture Prior to World War II pesticides were, while post-ww II they were. What is meant by the biomagnification of pesticides and what are its consequences? Differentiate between
Essawy M. M., Saad I. A. I.
 2014; 2 (6): 270-277 ISSN 2320-7078 JEZS 2014; 2 (6): 270-277 2014 JEZS Received: 27-10-2014 Accepted: 02-12-2014 Essawy M. M. Economic entomology Department, Faculty of Agricultural, Kafr El- Sheikh University,
2014; 2 (6): 270-277 ISSN 2320-7078 JEZS 2014; 2 (6): 270-277 2014 JEZS Received: 27-10-2014 Accepted: 02-12-2014 Essawy M. M. Economic entomology Department, Faculty of Agricultural, Kafr El- Sheikh University,
Quantitative profile Analysis of Mulberry Silkworm Bombyx mori. L (CSR 2 XCSR 4 )
 International Letters of Natural Sciences Online: 2015-02-17 ISSN: 2300-9675, Vol. 34, pp 34-41 doi:10.18052/www.scipress.com/ilns.34.34 2015 SciPress Ltd., Switzerland Quantitative profile Analysis of
International Letters of Natural Sciences Online: 2015-02-17 ISSN: 2300-9675, Vol. 34, pp 34-41 doi:10.18052/www.scipress.com/ilns.34.34 2015 SciPress Ltd., Switzerland Quantitative profile Analysis of
STUDIES ON BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES DURING LARVA TO PUPA TRANSFORMATION IN ANTHEREAEMYLITTADRURY (DABA TV)
 STUDIES ON BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES DURING LARVA TO PUPA TRANSFORMATION IN ANTHEREAEMYLITTADRURY (DABA TV) Lakshmi Marepally Post - Doctoral Fellow-UGC, Department of Zoology, Kakatiya University, Warangal,
STUDIES ON BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES DURING LARVA TO PUPA TRANSFORMATION IN ANTHEREAEMYLITTADRURY (DABA TV) Lakshmi Marepally Post - Doctoral Fellow-UGC, Department of Zoology, Kakatiya University, Warangal,
Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard. Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard
 Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic diseases Cultural disease control Disease avoidance
Unit D: Controlling Pests and Diseases in the Orchard Lesson 5: Identify and Control Diseases in the Orchard 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic diseases Cultural disease control Disease avoidance
BIOLOGY Grades Summer Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d. General Description:
 Summer 2015 Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d General Description: BIOLOGY Grades 9-12 Summer session biology will be an intense, fast paced course. Students will gain an understanding
Summer 2015 Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d General Description: BIOLOGY Grades 9-12 Summer session biology will be an intense, fast paced course. Students will gain an understanding
Program Specific Outcomes: PSO of B. Sc., Zoology
 Program Specific Outcomes: PSO of B. Sc., Zoology Demonstrated a broad understood of animal diversity, including knowledge of the scientific classification and evolutionary relationships of major groups
Program Specific Outcomes: PSO of B. Sc., Zoology Demonstrated a broad understood of animal diversity, including knowledge of the scientific classification and evolutionary relationships of major groups
YEAGER (1945) found many different kinds of blood-cells in the southern
 A Phase Contrast Study of the Blood-cells in Prodenia Larvae (Order Lepidoptera) By JACK COLVARD JONES (From the Department of Entomology, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland, U.S.A.) SUMMARY
A Phase Contrast Study of the Blood-cells in Prodenia Larvae (Order Lepidoptera) By JACK COLVARD JONES (From the Department of Entomology, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland, U.S.A.) SUMMARY
Prereq: Concurrent 3 CH
 0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
Unit G: Pest Management. Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases
 Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic disease Cultural disease control Disease avoidance Disease resistance Disease tolerance Fungi Infectious
Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 2: Managing Crop Diseases 1 Terms Abiotic disease Bacteria Biotic disease Cultural disease control Disease avoidance Disease resistance Disease tolerance Fungi Infectious
STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF THE DIAPAUSE HORMONE IN THE SILKWORM, BOMBYX MORI L.
 J. Exp. Biol. (1965), 43, 271-277 Printed in Great Britain STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF THE DIAPAUSE HORMONE IN THE SILKWORM, BOMBYX MORI L. VI. THE TARGET ORGAN OF THE DIAPAUSE HORMONE BY KINSAKU
J. Exp. Biol. (1965), 43, 271-277 Printed in Great Britain STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF THE DIAPAUSE HORMONE IN THE SILKWORM, BOMBYX MORI L. VI. THE TARGET ORGAN OF THE DIAPAUSE HORMONE BY KINSAKU
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Introduction to Biology with Lab
 Introduction to Biology with Lab Course Text/Materials Mader, Sylvia S. Inquiry into Life, 12th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008, ISBN: 9780073309330 [find and buy the text: Straighterline.com/textbooks] Custom
Introduction to Biology with Lab Course Text/Materials Mader, Sylvia S. Inquiry into Life, 12th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008, ISBN: 9780073309330 [find and buy the text: Straighterline.com/textbooks] Custom
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Microorganisms Answer Key
 Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Physiological Studies on the House Fly Musca Domestica Vicina Muscidae, Diptera
 JKAU: Sci., Vol. 22 No. 2, pp: 27-38 (2010 A.D./1431 A.H.) Doi: 10.4197 / Sci. 22-2.3 Physiological Studies on the House Fly Musca Domestica Vicina Muscidae, Diptera Najla a Y.A. Abozenadah Biology Department,
JKAU: Sci., Vol. 22 No. 2, pp: 27-38 (2010 A.D./1431 A.H.) Doi: 10.4197 / Sci. 22-2.3 Physiological Studies on the House Fly Musca Domestica Vicina Muscidae, Diptera Najla a Y.A. Abozenadah Biology Department,
ELECTROPHORETIC PROTEIN PATTERNS DURING LARVAL DEVELOPMENT OF CHILO PARTELLUS ( SWINHOE)
 Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 12(2) 3163-3168 (2012) ISSN: 0974-0910 (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) Original Article ELECTROPHORETIC PROTEIN PATTERNS DURING LARVAL DEVELOPMENT OF
Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 12(2) 3163-3168 (2012) ISSN: 0974-0910 (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) Original Article ELECTROPHORETIC PROTEIN PATTERNS DURING LARVAL DEVELOPMENT OF
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau
 Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
7th Grade Life Science Grade Remediation Packet
 7th Grade Life Science Grade Remediation Packet Purpose of this packet If you have received this packet it is because you are currently or in jeopardy of failing this class. This is not a punishment, but
7th Grade Life Science Grade Remediation Packet Purpose of this packet If you have received this packet it is because you are currently or in jeopardy of failing this class. This is not a punishment, but
CELL BIOLOGY. Which of the following cell structures does not have membranes? A. Ribosomes B. Mitochondria C. Chloroplasts D.
 1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
Biology B. There are no objectives for this lesson.
 Biology B Course Summary This is the second of two courses that comprise Biology. This course is designed to prepare the student to confidently enter and complete college-level biology courses. The Glencoe
Biology B Course Summary This is the second of two courses that comprise Biology. This course is designed to prepare the student to confidently enter and complete college-level biology courses. The Glencoe
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Human Anatomy and Physiology: Blood, Guts, Senses and Defenses
 Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Human Anatomy and Physiology: Blood, Guts, Senses and Defenses BOE Approved 5/8/2018 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology Blood, Guts, Senses and Defenses: Description
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Human Anatomy and Physiology: Blood, Guts, Senses and Defenses BOE Approved 5/8/2018 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology Blood, Guts, Senses and Defenses: Description
Studies on Biochemical Changes in Bombyx mori L. Races at Different Developmental Stages
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 10 (2015) pp. 101-109 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Studies on Biochemical Changes in Bombyx mori L. Races at Different Developmental Stages Rohith L Shankar
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 10 (2015) pp. 101-109 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Studies on Biochemical Changes in Bombyx mori L. Races at Different Developmental Stages Rohith L Shankar
Side-by-Side Comparison of the Texas Educational Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and Louisiana Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) SCIENCE: Biology
 Side-by-Side Comparison of the Texas Educational Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and Louisiana Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) SCIENCE: Biology TEKS Comments Louisiana GLE (Bio.1) Scientific Processes. The
Side-by-Side Comparison of the Texas Educational Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) and Louisiana Grade Level Expectations (GLEs) SCIENCE: Biology TEKS Comments Louisiana GLE (Bio.1) Scientific Processes. The
Physiological Bases of Using Insect Hormone Analogs for. Use of tebufenozide against the spruce budworm, Pest Management. Choristoneura fumiferana
 Physiological Bases of Using Insect Hormone Analogs for Pest Management Use of tebufenozide against the spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana Arthur Retnakaran, Daniel Doucet, Basil M. Arif, Great Lakes
Physiological Bases of Using Insect Hormone Analogs for Pest Management Use of tebufenozide against the spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana Arthur Retnakaran, Daniel Doucet, Basil M. Arif, Great Lakes
Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce and to maintain dynamic homeostasis.
 Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. Enduring understanding 2.B: Growth, reproduction and dynamic
Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. Enduring understanding 2.B: Growth, reproduction and dynamic
d. Abscisic Acid (ABA) e. Ethylene
 AP Bio Plant Unit Review Guide and FRQs Plant Diversity Ch 23 1. List characteristics that distinguish plants from other organisms in other kingdoms. 2. Distinguish between sporophyte or gametophyte, which
AP Bio Plant Unit Review Guide and FRQs Plant Diversity Ch 23 1. List characteristics that distinguish plants from other organisms in other kingdoms. 2. Distinguish between sporophyte or gametophyte, which
Distance Learning course Plant pathology and entomology Covered topics
 Distance Learning course Plant pathology and entomology Covered topics The distance learning course Plant pathology and entomology consist of four online modules that treat with the main groups of plant
Distance Learning course Plant pathology and entomology Covered topics The distance learning course Plant pathology and entomology consist of four online modules that treat with the main groups of plant
California Biology Handbook... CA1
 California Biology Handbook........................... CA1 The California Biology Handbook includes correlations of the Biology/Life Science standards to the content in Biology: The Dynamics of Life. Also
California Biology Handbook........................... CA1 The California Biology Handbook includes correlations of the Biology/Life Science standards to the content in Biology: The Dynamics of Life. Also
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Basic Biological Principles
 Basic Biological Principles Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Moth Life Cycle larva egg pupa Adult 1. Which characteristic of life is best shown by this diagram? A. DNA is the genetic code in
Basic Biological Principles Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Moth Life Cycle larva egg pupa Adult 1. Which characteristic of life is best shown by this diagram? A. DNA is the genetic code in
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE. Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE)
 Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE) A. Nature of scientific knowledge, inquiry, and historical perspectives 1. Scientific methods...1 2. Processes involved in
Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE) A. Nature of scientific knowledge, inquiry, and historical perspectives 1. Scientific methods...1 2. Processes involved in
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum. Draft Units
 Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Draft Units Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses: Description
Fairfield Public Schools Science Curriculum Draft Units Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Blood, Guts, Senses, and Defenses: Description
DURATION OF PUPAL DIAPAUSE IN THE TOBACCO HORNWORM IS DETERMINED BY NUMBER OF SHORT DAYS RECEIVED BY THE LARVA
 jf. exp. Biol. (1981), 91, 331-337 With 3 figures ^^ttted in Great Britain DURATION OF PUPAL DIAPAUSE IN THE TOBACCO HORNWORM IS DETERMINED BY NUMBER OF SHORT DAYS RECEIVED BY THE LARVA BY DAVID L. DENLINGER
jf. exp. Biol. (1981), 91, 331-337 With 3 figures ^^ttted in Great Britain DURATION OF PUPAL DIAPAUSE IN THE TOBACCO HORNWORM IS DETERMINED BY NUMBER OF SHORT DAYS RECEIVED BY THE LARVA BY DAVID L. DENLINGER
Cells: 2 Star. 7. The diagram below represents a cell.
 ells: 2 Star 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a cell and its changes as a result of two laboratory procedures,
ells: 2 Star 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a cell and its changes as a result of two laboratory procedures,
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(7):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 2512-2524 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.356
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 2512-2524 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.356
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Advanced Anatomy and Physiology
 Lakeshore Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Alternate Title Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 90 Adv Anatomy & Physiology Advanced
Lakeshore Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Alternate Title Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 90 Adv Anatomy & Physiology Advanced
Course Syllabus. Department: Science and Technology. Date: February 3, I. Course Prefix and Number: BIO 122. Course Name: General Biology II
 Department: Science and Technology Date: February 3, 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: BIO 122 Course Name: General Biology II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 4 Credit hours and 5 Contact
Department: Science and Technology Date: February 3, 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: BIO 122 Course Name: General Biology II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 4 Credit hours and 5 Contact
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY, lecture and lab
 LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF THE DIAPAUSE HORMONE IN THE SILKWORM, BOMBYX MORI L.
 Biol. (1963), 40, 517-52 517 text-figures Printed in Great Britain STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF THE DIAPAUSE HORMONE IN THE SILKWORM, BOMBYX MORI L. I. THE ACTION OF DIAPAUSE HORMONE INJECTED INTO
Biol. (1963), 40, 517-52 517 text-figures Printed in Great Britain STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF THE DIAPAUSE HORMONE IN THE SILKWORM, BOMBYX MORI L. I. THE ACTION OF DIAPAUSE HORMONE INJECTED INTO
Broken Arrow Public Schools Physiology Objectives
 1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
Life Science FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES
 FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *3467159578* BILGY 9700/23 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions ctober/november 2018 1 hour 15 minutes
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *3467159578* BILGY 9700/23 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions ctober/november 2018 1 hour 15 minutes
Jordan University of Science & Technology. Faculty of Arts and Sciences. Department of Applied Biological Sciences
 Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Arts and Sciences Department of Applied Biological Sciences Course Title Title & Instructor General Biology Course Number BIO 104 Instructor Office
Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Arts and Sciences Department of Applied Biological Sciences Course Title Title & Instructor General Biology Course Number BIO 104 Instructor Office
Nerve cells have many branches that help them send signals throughout the body.
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
Assessment Schedule 2016 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to micro-organisms (90927)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90927) 2016 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2016 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to micro-organisms (90927) Evidence Statement Question One No response
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90927) 2016 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2016 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to micro-organisms (90927) Evidence Statement Question One No response
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Cells, Tissues, and Membranes
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
Which row in the chart correctly identifies the functions of structures A, B, and C? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment
 Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Introduction to Biology Web Course Informational and Test Schedule
 Introduction to Biology Web Course Informational and Test Schedule Spring 2011 Inquiry into Life by Sylvia Mader Introduction to Biological Science (BIO1100AAW1 & 2) Three Hours Credit Nancy Petersen Brian
Introduction to Biology Web Course Informational and Test Schedule Spring 2011 Inquiry into Life by Sylvia Mader Introduction to Biological Science (BIO1100AAW1 & 2) Three Hours Credit Nancy Petersen Brian
1. Which of these organelles are found only in plant cells? a) cell membranes c) mitochondria b) chloroplast d) ribosome
 BIOLOGY UNIT REVIEW SNC 2D PART A: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING 1. Which of these organelles are found only in plant cells? a) cell membranes c) mitochondria b) chloroplast d) ribosome 2. The replicated
BIOLOGY UNIT REVIEW SNC 2D PART A: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING 1. Which of these organelles are found only in plant cells? a) cell membranes c) mitochondria b) chloroplast d) ribosome 2. The replicated
Do NOT write on this test. Thank you!
 Organization and Development of Living Organisms (SC.6.L.14.1,2,3,4 and 5) 1. The diagram below represents a plant cell. Letter X represents a structure in the cell. Which structure is represented by X?
Organization and Development of Living Organisms (SC.6.L.14.1,2,3,4 and 5) 1. The diagram below represents a plant cell. Letter X represents a structure in the cell. Which structure is represented by X?
Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals. Image from:
 Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Zoology Definition: the scientific study of the behavior, structure, physiology, classification, and distribution
Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Zoology Definition: the scientific study of the behavior, structure, physiology, classification, and distribution
ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY
 ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY Description Advanced Placement Biology is designed to be the equivalent of a two-semester college introductory course for Biology majors. The course meets seven periods per week
ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY Description Advanced Placement Biology is designed to be the equivalent of a two-semester college introductory course for Biology majors. The course meets seven periods per week
Insect Structure Function & Physiology
 Insect Structure Function & Physiology BIOL3238 Ametaboly Primitive developmental pattern. The only major change from instar to instar is increased size. Multiple adult moults. Found in the orders Zygentoma
Insect Structure Function & Physiology BIOL3238 Ametaboly Primitive developmental pattern. The only major change from instar to instar is increased size. Multiple adult moults. Found in the orders Zygentoma
4) The diagram below represents the organization of genetic information within a cell nucleus.
 Name: 3987-1 - Page 1 1) Every single-celled organism is able to survive because it carries out A) sexual reproduction B) heterotrophic nutrition C) autotrophic nutrition D) metabolic activities 2) Which
Name: 3987-1 - Page 1 1) Every single-celled organism is able to survive because it carries out A) sexual reproduction B) heterotrophic nutrition C) autotrophic nutrition D) metabolic activities 2) Which
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport
 Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC
 BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
No. 9] Hormonal Control of Butterfly Seasonal Forms 1083
![No. 9] Hormonal Control of Butterfly Seasonal Forms 1083 No. 9] Hormonal Control of Butterfly Seasonal Forms 1083](/thumbs/82/85102142.jpg) 1082 [Vol. 42, 235. Hormonal Control o f the Development o f Seasonal Forms in the Butterfly, Polygonia c aureum L By Soichi FUKUDA and Katsuhiko ENDO Biological Institute, Faculty of Science, Nagoya University
1082 [Vol. 42, 235. Hormonal Control o f the Development o f Seasonal Forms in the Butterfly, Polygonia c aureum L By Soichi FUKUDA and Katsuhiko ENDO Biological Institute, Faculty of Science, Nagoya University
Acid Phosphatase Activity Changes Under Magnetic Exposure of Eggs in Bombyx mori: A Multivoltine Mulberry Silkworm
 World Journal of Zoology 8 (4): 407-414, 2013 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2013.8.4.81141 Acid Phosphatase Activity Changes Under Magnetic Exposure of Eggs in Bombyx mori:
World Journal of Zoology 8 (4): 407-414, 2013 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2013.8.4.81141 Acid Phosphatase Activity Changes Under Magnetic Exposure of Eggs in Bombyx mori:
Highland Park Science Curriculum
 08/08/20115:20 PM 1 Biology I Semester I Unit IV Highland Park Science Curriculum Components Biology I Biology I Pre AP Extensions Biology I Pre AP TAG Extensions Unit Overview Cells and Cellular Mechanisms
08/08/20115:20 PM 1 Biology I Semester I Unit IV Highland Park Science Curriculum Components Biology I Biology I Pre AP Extensions Biology I Pre AP TAG Extensions Unit Overview Cells and Cellular Mechanisms
Chapter Chemical Uniqueness 1/23/2009. The Uses of Principles. Zoology: the Study of Animal Life. Fig. 1.1
 Fig. 1.1 Chapter 1 Life: Biological Principles and the Science of Zoology BIO 2402 General Zoology Copyright The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Uses of
Fig. 1.1 Chapter 1 Life: Biological Principles and the Science of Zoology BIO 2402 General Zoology Copyright The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Uses of
Plants are sessile. 10d-17/giraffe-grazing.jpg
 Plants are sessile www.mccullagh.org/db9/ 10d-17/giraffe-grazing.jpg Plants have distinct requirements because of their sessile nature Organism-level requirements Must adjust to environment at given location
Plants are sessile www.mccullagh.org/db9/ 10d-17/giraffe-grazing.jpg Plants have distinct requirements because of their sessile nature Organism-level requirements Must adjust to environment at given location
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport
 Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Chemistry. Animal Health Technology Student Development Program
 Chemistry Animal Health Technology Student Development Program Chemistry Chemistry is a fundamental component in all of us. Chemical reactions are happening in our bodies constantly. In the Animal Health
Chemistry Animal Health Technology Student Development Program Chemistry Chemistry is a fundamental component in all of us. Chemical reactions are happening in our bodies constantly. In the Animal Health
Seminar 2 : Good Bugs
 Seminar 2 : Good Bugs Part 2 Viruses What is a virus? Microscopic particles that infect other organisms and can only replicate within a host cell Contain either contain DNA or RNA surrounded by a protective
Seminar 2 : Good Bugs Part 2 Viruses What is a virus? Microscopic particles that infect other organisms and can only replicate within a host cell Contain either contain DNA or RNA surrounded by a protective
Unit 2 Benchmark Review. Disease Review:
 Match the term with the definition: Unit 2 Benchmark Review Disease Review: 1. Caused by tiny organisms called pathogens B 2. This is responsible for distinguishing between the different kinds of pathogens
Match the term with the definition: Unit 2 Benchmark Review Disease Review: 1. Caused by tiny organisms called pathogens B 2. This is responsible for distinguishing between the different kinds of pathogens
Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1
 Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
NEET A Detailed Analysis by Resonance
 NEET 2017 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2017 was conducted as per the schedule (7 th May 2017). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national
NEET 2017 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2017 was conducted as per the schedule (7 th May 2017). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials
 Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
Classification: Evolution:
 Review for Final Exam Suggestions All material covered in the course is testable. The following are suggested topics to cover, but is not meant to be an exhaustive list. Topics that are not listed but
Review for Final Exam Suggestions All material covered in the course is testable. The following are suggested topics to cover, but is not meant to be an exhaustive list. Topics that are not listed but
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Kingdom Animalia. Zoology the study of animals
 Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Why Calcium is So Important
 Why Calcium is So Important Calcium - A Transportation Problem By Dr. Lynette Morgan As hydroponic growers we like to think that by supplying our plants with all the nutrients they need in the right ratios,
Why Calcium is So Important Calcium - A Transportation Problem By Dr. Lynette Morgan As hydroponic growers we like to think that by supplying our plants with all the nutrients they need in the right ratios,
Mr. Jensen/Period: 1. The diagram below illustrates the distribution of fossils in undisturbed layers of silt at the bottom of the ocean.
 Name: 1. The diagram below illustrates the distribution of fossils in undisturbed layers of silt at the bottom of the ocean. Date: /Page#: Mr. Jensen/Period: 3. In the diagram below of undisturbed sedimentary
Name: 1. The diagram below illustrates the distribution of fossils in undisturbed layers of silt at the bottom of the ocean. Date: /Page#: Mr. Jensen/Period: 3. In the diagram below of undisturbed sedimentary
Anatomy & Physiology Standards and Benchmarks
 Anatomy & Standards and Standard 1: Understands and applies principles of scientific inquiry Power : Identifies questions and concepts that guide science investigations Uses technology and mathematics
Anatomy & Standards and Standard 1: Understands and applies principles of scientific inquiry Power : Identifies questions and concepts that guide science investigations Uses technology and mathematics
Cell Biology. AQA Biology topic 1
 Cell Biology AQA Biology topic 1 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
Cell Biology AQA Biology topic 1 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
Answers to Practice Items
 nswers to Practice Items Question 1 TEKS 4 This is a picture of a bacteria cell. This is a picture of a plant cell. This is the correct answer. This picture is representative of a virus. This is a picture
nswers to Practice Items Question 1 TEKS 4 This is a picture of a bacteria cell. This is a picture of a plant cell. This is the correct answer. This picture is representative of a virus. This is a picture
Acta Biologica Indica 2014, 3(2):
 The ecdysone mimic, methoxyfenozide, alters the level of major haemolymph proteins in the larvae of Spodoptera mauritia Boisd. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) C. Resmitha 1, R.M. Reshma 1, Bindu Punathumparambath
The ecdysone mimic, methoxyfenozide, alters the level of major haemolymph proteins in the larvae of Spodoptera mauritia Boisd. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) C. Resmitha 1, R.M. Reshma 1, Bindu Punathumparambath
Chapter 3: Cells. Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College
 Chapter 3: Cells Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Be able to describe: what a cell is & two main classes of cells. structure & functions of cell membranes. how
Chapter 3: Cells Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Be able to describe: what a cell is & two main classes of cells. structure & functions of cell membranes. how
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
STUDIES ON INSECT METAMORPHOSIS.
 STUDIES ON INSECT METAMORPHOSIS. IV. EFFECT OF CARBON DIOXIDE.* BY HEM SINGH-PRUTHI, Ph.D. {From the Zoological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE problem of how the apparently healthy organs of the larva of
STUDIES ON INSECT METAMORPHOSIS. IV. EFFECT OF CARBON DIOXIDE.* BY HEM SINGH-PRUTHI, Ph.D. {From the Zoological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE problem of how the apparently healthy organs of the larva of
Organisms are made up of specialized cells.
 All living things are made up of cells! Specialized cells develop from a single zygote Organisms are made up of specialized cells. Each has a specific job/function red blood cell nerve cell Zygotes (fertilized
All living things are made up of cells! Specialized cells develop from a single zygote Organisms are made up of specialized cells. Each has a specific job/function red blood cell nerve cell Zygotes (fertilized
Course Description: Anatomy & Physiology 10 th 12 th grades. Grade
 Anatomy & Physiology 10 th 12 th grades Essential principles of human anatomy and physiology are presented. Students will develop an appreciation for God s greatest creation the human body. Hole s Essentials
Anatomy & Physiology 10 th 12 th grades Essential principles of human anatomy and physiology are presented. Students will develop an appreciation for God s greatest creation the human body. Hole s Essentials
TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY
 Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
SWAMI RAMANAND TEERTH MARATHWADA UNIVERSITY, NANDED PET (Ph.D. ENTRANCE TEST) ( June 2013 ) SYLLABUS SUBJECT: BOTANY
 CURRICULUM DESIGNING COMMITTEE 1. Dr.Bodke S.S. Chairman Yeshwant Mahavidyalaya, Nanded 2. Dr. Kadam A.S. Member D.S.M. Mahavidyalaya, Jintur 3. Dr. Mandge S.V. Member Shri. SGM College, Loha 4. Dr. Gawai
CURRICULUM DESIGNING COMMITTEE 1. Dr.Bodke S.S. Chairman Yeshwant Mahavidyalaya, Nanded 2. Dr. Kadam A.S. Member D.S.M. Mahavidyalaya, Jintur 3. Dr. Mandge S.V. Member Shri. SGM College, Loha 4. Dr. Gawai
What is the structure of DNA?
 NAME Biology Final Review Sem. II Genetics 1. Define: a. allele b. phenotype c. genotype d. recessive e. dominant f. heterozygous g. homozygous h. autosomes i. sex chromosomes j. Punnett square k. pedigree
NAME Biology Final Review Sem. II Genetics 1. Define: a. allele b. phenotype c. genotype d. recessive e. dominant f. heterozygous g. homozygous h. autosomes i. sex chromosomes j. Punnett square k. pedigree
Principles of Experimental Embryology
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Principles of Experimental Embryology September 19, 2006 Major Research Questions How do forces outside the embryo affect its development? (Environmental Developmental
CONTENTS. Physics Chemistry Motion Work, Energy and Power Gravitation Properties of Fluid 22-23
 CONTENTS Physics...5-58 1. Motion 7-13 2. Work, Energy and Power 14-16 3. Gravitation 17-21 4. Properties of Fluid 22-23 5. Heat 24-27 6. Wave 28-30 7. Sound 31-35 8. Light 36-46 9. Electricity and Magnetism
CONTENTS Physics...5-58 1. Motion 7-13 2. Work, Energy and Power 14-16 3. Gravitation 17-21 4. Properties of Fluid 22-23 5. Heat 24-27 6. Wave 28-30 7. Sound 31-35 8. Light 36-46 9. Electricity and Magnetism
JEFFERSON COLLEGE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
Subject: PAP Biology Calendar : 1 st 9 Weeks Timeframe:2 Weeks Level/Grade: 9th
 Subject: PAP Biology Calendar : 1 st 9 Weeks Timeframe:2 Weeks Level/Grade: 9th Reference and Safety Safety, Scientific Method, Graphing, Lab Equipment, Characteristics of Life Activity Type:, Labs, Materials:
Subject: PAP Biology Calendar : 1 st 9 Weeks Timeframe:2 Weeks Level/Grade: 9th Reference and Safety Safety, Scientific Method, Graphing, Lab Equipment, Characteristics of Life Activity Type:, Labs, Materials:
Science TAKS Objectives for Grades 10 and 11
 Science TAKS Objectives for s and Objective 1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of science. Bio (1) and IPC (1) The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, conducts field
Science TAKS Objectives for s and Objective 1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of science. Bio (1) and IPC (1) The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, conducts field
Plant Stimuli pp Topic 3: Plant Behaviour Ch. 39. Plant Behavioural Responses. Plant Hormones. Plant Hormones pp
 Topic 3: Plant Behaviour Ch. 39 Plants exist in environments that are constantly changing. Like animals, plants must be able to detect and react to stimuli in the environment. Unlike animals, plants can
Topic 3: Plant Behaviour Ch. 39 Plants exist in environments that are constantly changing. Like animals, plants must be able to detect and react to stimuli in the environment. Unlike animals, plants can
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE FOUNDATIONS OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY
 Table of Contents SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 FOUNDATIONS OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY UNDERSTAND THE RELATIONSHIPS AND COMMON THEMES THAT CONNECT MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE, AND TECHNOLOGY... 0H1 Skill 1.1 Skill 1.2
Table of Contents SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 FOUNDATIONS OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY UNDERSTAND THE RELATIONSHIPS AND COMMON THEMES THAT CONNECT MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE, AND TECHNOLOGY... 0H1 Skill 1.1 Skill 1.2
