Interphase. Chapter 10 Notes. Objective 1: Summarize the events that occur during mitosis
|
|
|
- Alfred McGee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 10 Notes Ratio of Surface Area to Volume i Cells 10 1 Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. DNA Overload 2. Exchagig Materials 3. Ratio of Surface Area to Volume 4. Cell Divisio Cell Size Surface Area (legth x width x 6) Volume (legth x width x height) Ratio of Surface Area to Volume 10 2 Cell Divisio A. Chromosomes B. The Cell Cycle C. Evets of the Cell Cycle D. Mitosis 1. Prophase Aaphase 4. Telophase E. Cytokiesis Objective 1: Summarize the evets that occur durig mitosis Homologous chromosome--a member of a chromosome pair. similar i shape, size, ad the gees they carry. Chromatid--oe of a pair of strads of DNA that make up a chromosome durig meiosis or mitosis. Figure 10 4 The Cell Cycle Iterphase M phase G 1 phase S phase This is the o-reproducig stage of a cell s life. It is the logest stage of a cell s life Major evets i iterphase: Cells grow durig iterphase Chromosomes are duplicated about mid-way through iterphase to prepare for mitosis. G 2 phase 1
2 Iterphase Aimal Cell Plat Cell Prophase Major evets i prophase: Nucleoli disitegrates Chromati coils up to form chromosomes Cetrioles move to opposite poles of the cell Microtubules form spidle fibers betwee the cetrioles The ucleus breaks dow Prophase Aimal Cell Plat Cell Major evets i metaphase: Chromosomes attach to the spidle fibers at the cetromere Chromosomes move to the equator of the cell Aimal Cell Plat Cell Aaphase Major evets i aaphase: Cetromeres split The two sister chromatids separate ad move apart to opposite poles of the cell 2
3 Aaphase Aimal Cell Plat Cell Telophase Major evets i telophase: The ucleoli reappear The ucleus reforms Chromosomes ucoil ad appear as a mass of chromati Cytokiesis Major Evets: Happes at the same time as telophase I aimals: cell membrae piches i at the ceter I plats: a cell plate forms at the equator of the cell Daughter cells are formed Telophase& Cytokiesis Aimal Cell Plat Cell Sectio 10-2 Figure 10 5 Mitosis ad Cytokiesis Sectio 10-2 Figure 10 5 Mitosis ad Cytokiesis Cetrioles Spidle formig Cetrioles Spidle formig Nuclear evelope reformig Nuclear Chromati Cetromere evelope Iterphase Prophase Cytokiesis Idividual Aaphase Cetriole Spidle Cetriole Nuclear evelope reformig Nuclear Chromati Cetromere evelope Iterphase Prophase Cytokiesis Idividual Aaphase Cetriole Spidle Cetriole Sectio: Sectio: 3
4 Sectio 10-2 Figure 10 5 Mitosis ad Cytokiesis Sectio 10-2 Figure 10 5 Mitosis ad Cytokiesis Cetrioles Spidle formig Cetrioles Spidle formig Nuclear evelope reformig Nuclear Chromati Cetromere evelope Iterphase Prophase Cytokiesis Idividual Aaphase Cetriole Spidle Cetriole Nuclear evelope reformig Nuclear Chromati Cetromere evelope Iterphase Prophase Cytokiesis Idividual Aaphase Cetriole Spidle Cetriole Sectio: Sectio: Sectio 10-2 Figure 10 5 Mitosis ad Cytokiesis Sectio 10-2 Figure 10 5 Mitosis ad Cytokiesis Cetrioles Spidle formig Cetrioles Spidle formig Nuclear evelope reformig Nuclear Chromati Cetromere evelope Iterphase Prophase Cytokiesis Idividual Aaphase Cetriole Spidle Cetriole Nuclear evelope reformig Nuclear Chromati Cetromere evelope Iterphase Prophase Cytokiesis Idividual Aaphase Cetriole Spidle Cetriole Sectio: Sectio: --a form of cell divisio that halves the umber of chromosomes whe formig reproductive cells. Mitosis vs I Prophase I Chromosomes become visible Nuclear evelope breaks dow Crossig-over occurs I Pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell 4
5 I Aaphase I Homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell Telophase I ad Cytokiesis Chromosomes gather at the poles of the cell Cytoplasm divides II Prophase II A ew spidle forms aroud the chromosomes II Chromosomes lie up at the equator II Aaphase II Cetromeres divide Chromatids (ow called chromosomes) move to opposite poles of the cell. Telophase II ad Cytokiesis Nuclear evelope forms aroud each set of chromosomes Cytoplasm divides Prophase I I X X Close-up View X X Bivalet Cetromere N N N N Daughter Cells of meiosis II Chiasma (site of crossig-over) Bivalets alig at the metaphase plate Sister chromatids remai together durig aaphase I Mitosis vs. 2 = 4 Daughter Cells of meiosis I No further chromosomal replicatio; sister chromatids separate durig aaphase II Mitosis Chromosomes alig at the metaphase plate Sister chromatids separate durig aaphase x x Prophase 2N 2N Daughter Cells Mitosis See if you ca idetify the stages of prophase, metaphase, aaphase, ad telophase. Notice that mitosis results i two diploid daughter cells. You should be able to idetify each stage of mitosis as it appears whe viewed with a light microscope. To see mitosis i a plat cell, click here. To see mitosis i a aimal cell click here. See if you ca idetify meiosis I ad meiosis II ad the stages of prophase, metaphase, aaphase, ad telophase withi each meiotic divisio. Notice that meiosis results i four haploid daughter cells. To see what the stages of meiosis look like through a microscope click o the followig liks. Click here for meiosis I. To see meiosis II, click here. 5
6 Objective 2: Relate crossig-over, idepedet assortmet, ad radom fertilizatio to geetic variatio. Idepedet assortmet--the radom distributio of homologous chromosomes. Crossig-over--the exchage of reciprocal segmets of DNA by homologous chromosomes at the begiig of meiosis. Fertilizatio is the radom joiig of 2 gametes. Importace of Geetic Variatio ad the joiig of gametes geerates variatio more quickly tha ay other geetic process. Geetic variatio is essetial to evolutio. Size icrease i domesticated aimals The ability to produce larger ad larger aimals slows dow as existig geetic combiatios are used up. Racehorse breedig Times i races stopped improvig decades ago. Objective 3: Compare the formatio of gametes i male & female aimals Spermatogeesis--the process by which sperm are produced i male aimals. Occurs i the testes Oogeesis--the process by which gametes are produced i female aimals. Occurs i the ovaries Gamete Developmet Diploid germ cell Diploid germ cell Spermatogeesis Oogeesis Sperm cell Egg cell Polar bodies i male & female aimals Sperm Formatio I II Udifferetiated sperm cells Diploid germ cell Immature sperm cells Egg Formatio Secodary egg cell First polar body Udifferetiated egg cell Secod polar bodies (all 3 will die) Objective 4: Differetiate betwee asexual ad sexual reproductio asexual reproductio--a sigle paret passes copies of all of its gees to each of its offsprig There is o fusio of haploid cells The offsprig is a cloeof its paret sexual reproductio--two parets each form haploid reproductive cells, which joi to form offsprig. Sperm Egg cell (ovum) 6
7 Objective 5: Idetify three types of asexual reproductio Fissio--separatio of a paret ito two or more idividuals of about equal size. Fragmetatio--the body of a orgaism breaks ito several pieces. fragmets develop ito adults whe missig parts are regrow Buddig--ew idividuals split off from existig oes. Objective 6: Evaluate the advatages ad disadvatages of asexual ad sexual reproductio Asexual Reproductio Advatages produce may offsprig i short period of time do t waste eergy makig gametes or lookig for a mate Disadvatages little geetic variatio betwee idividuals Sexual Reproductio Advatages quickly produce differet combiatios of gees amog idividuals Disadvatages produce fewer offsprig i loger periods of time waste eergy makig gametes & lookig for a mate Objective 7: Differetiate betwee the three major sexual life cycles foud i eukaryotes Life cycle--the etire life spa of a orgaism from oe geeratio to the ext. Haploid life cycle Haploid cycle simplest of sexual life cycles haploid cells occupy the major portios of the life cycle zygote is the oly diploid cell zygote udergoes meiosis after it is formed haploid cells give rise to multicellular idividuals multicellular idividuals produce gametes through mitosis (ot meiosis) Fusio--gametes fuse to produce a diploid zygote Haploid life cycle 2 Zygote Fusio Haploid Idividual Mitosis Diploid life cycle Diploid cycle adult idividuals are diploid i most aimals, a diploid reproductive cell udergoes meiosis to produce gametes fertilizatio--gametes joi to produce a diploid zygote diploid idividual occupies the major portio of the life cycle 7
8 Diploid life cycle Reproductive cell 2 Diploid Idividual 2 2 Zygote Fertilizatio Gametes Alteratio of geeratios Sporophyte--the diploid phase i the life cycle that produces spores Spore--a haploid reproductive cell produced by meiosis that is capable of developig ito a adult without fusig with aother cell. Alteratio of geeratios Gametophyte--haploid phase that produces gametes by mitosis. gametes fuse ad give rise to the diploid phase Alteratio of geeratios Sporeformig cell 2 Sporophyte 2 Gametophytes 2 Zygote Fertilizatio Mitosis Where to go for more Corell Uiversity has a olie tutorial that will allow you test your kowledge of mitosis ad meiosis. I recommed that you give the questios a try. To do so, just click here. The Uiversity of Arizoa also has a olie quiz over the stages of mitosis. If you wat to test yourself at idetifyig the various stages of mitosis, click here. The meiosis tutorial for the Uiversity of Arizoa ca be foud by clickig here. More pictures of meiosis here. A mitosis olie quiz. Click here. A meiosis olie quiz. Click here. 8
Chapter 5 Cell Division
 Chapter 5 Cell Divisio 5.1 Cell Icrease ad Decrease Cell divisio icreases the umber of somatic cells (body cells) Zygote Adult huma (sigle cell) (trillios of cells) The Cell Cycle 5.1 Cell Icrease ad Decrease
Chapter 5 Cell Divisio 5.1 Cell Icrease ad Decrease Cell divisio icreases the umber of somatic cells (body cells) Zygote Adult huma (sigle cell) (trillios of cells) The Cell Cycle 5.1 Cell Icrease ad Decrease
CH 10: Meiosis / Sex Overview. Concept 10.1: Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes
 CH 10: Meiosis / Sex Overview Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid Heredity is the trasmissio of traits from oe geeratio to the ext Variatio is demostrated by the
CH 10: Meiosis / Sex Overview Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid Heredity is the trasmissio of traits from oe geeratio to the ext Variatio is demostrated by the
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Overview: Variatios o a Theme Chapter 13 Meiosis ad Sexual Life Cycles Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid Geetics is the scietific study of heredity ad variatio
Overview: Variatios o a Theme Chapter 13 Meiosis ad Sexual Life Cycles Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid Geetics is the scietific study of heredity ad variatio
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Chapter Preview 1 Reproductio Asexual Reproductio Sexual Reproductio Chromosome Number 11 2 Meiosis Stages of Meiosis Comparig Mitosis ad Meiosis Geetic Variatio 3 Multicellular Life Cycles Diploid Life
Chapter Preview 1 Reproductio Asexual Reproductio Sexual Reproductio Chromosome Number 11 2 Meiosis Stages of Meiosis Comparig Mitosis ad Meiosis Geetic Variatio 3 Multicellular Life Cycles Diploid Life
Lecture 21: Meiosis Lecture outline 10/25/05
 Lecture 21: Meiosis Lecture outlie 10/25/05 Review mitosis Fiish cell cycle Mutatios i checkpoit gees ca lead to cacer Sexual ad asexual life cycles Meiosis Stages of meiosis Idepedet assortmet ad Crossig
Lecture 21: Meiosis Lecture outlie 10/25/05 Review mitosis Fiish cell cycle Mutatios i checkpoit gees ca lead to cacer Sexual ad asexual life cycles Meiosis Stages of meiosis Idepedet assortmet ad Crossig
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13 Meiosis ad Sexual Life Cycles Dr. Wedy Sera Housto Commuity College Biology 1406 Variatios o a Theme Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid Geetics is the
Chapter 13 Meiosis ad Sexual Life Cycles Dr. Wedy Sera Housto Commuity College Biology 1406 Variatios o a Theme Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid Geetics is the
General Biology. Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation. Living organisms. are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind
 Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 Geeral Biology Overview: Hereditary Similarity ad Variatio Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid 9. Meiosis ad Life Cycles Prof. Dr.
Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 Geeral Biology Overview: Hereditary Similarity ad Variatio Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid 9. Meiosis ad Life Cycles Prof. Dr.
General Biology. Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms. Comparison of Asexual and Sexual Reproduction In asexual reproduction
 Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " Geeral Biology " " 9. Meiosis ad Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity ad Variatio Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid Prof.
Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " Geeral Biology " " 9. Meiosis ad Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity ad Variatio Livig orgaisms are distiguished by their ability to reproduce their ow kid Prof.
Lecture 14: 2 Parts: 1. Meiosis Chapter 8 2. Inheritance Chapter 9 Leading into Lecture 15:
 Lecture 14: 2 Parts: 1. Meiosis Chapter 8 2. Iheritace Chapter 9 Leadig ito Lecture 15: 1. Evolu5o ad Iheritace Chapter 13 Topic #1: Meiosis I Pee o the MAT P MAT! Importat LaH Roots Meiou Mei Lesse Small
Lecture 14: 2 Parts: 1. Meiosis Chapter 8 2. Iheritace Chapter 9 Leadig ito Lecture 15: 1. Evolu5o ad Iheritace Chapter 13 Topic #1: Meiosis I Pee o the MAT P MAT! Importat LaH Roots Meiou Mei Lesse Small
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11. Reproduction Section 1
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
AP Biology. Investigation 7: Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis. Investigation 7: Cell Division. Investigation 7: Cell Division
 AP Biology Learig Objectives Ivestigatio 7: Cell Divisio: Mitosis ad Meiosis To describe the evets i the cell cycle ad how these evets are cotrolled. To explai how DNA is trasmitted to the ext geeratio
AP Biology Learig Objectives Ivestigatio 7: Cell Divisio: Mitosis ad Meiosis To describe the evets i the cell cycle ad how these evets are cotrolled. To explai how DNA is trasmitted to the ext geeratio
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
9-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35
 9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
Sexual Reproduction. The two parent cells needed for sexual reproduction are called gametes. They are formed during a process known as meiosis.
 Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
11-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis Chromosome Number Slide 1 of 35
 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just one set. Chromosome
Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just one set. Chromosome
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis. Genetics Terminology: Homologous chromosomes
 For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review
 Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 13 Meiosis ad Sexual Life Cycles KEY CONC EPTS 13.1 Offsprig acquire gees from parets by iheritig 13.2 Fertilizatio ad meiosis alterate i sexual life cycles 13.3 Meiosis reduces the umber of chromosome
13 Meiosis ad Sexual Life Cycles KEY CONC EPTS 13.1 Offsprig acquire gees from parets by iheritig 13.2 Fertilizatio ad meiosis alterate i sexual life cycles 13.3 Meiosis reduces the umber of chromosome
biology Slide 1 of 35 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES
 CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
SCIENCE M E I O S I S
 SCIENCE 9 6. 1 - M E I O S I S OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the process of meiosis Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis Explain why meiosis is needed MEIOSIS
SCIENCE 9 6. 1 - M E I O S I S OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the process of meiosis Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis Explain why meiosis is needed MEIOSIS
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping
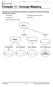 Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology
 Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Review of Terms. Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome. Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome
 Review of Terms Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome Somatic non-germline cells Gametes sex cells (eggs and sperm) Reductional division
Review of Terms Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome Somatic non-germline cells Gametes sex cells (eggs and sperm) Reductional division
4/6/2014. Chromosome Number
 Meiosis 1of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just
Meiosis 1of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Meiosis. Section 8-3
 Meiosis Section 8-3 Meiosis process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in new cells to half the number in the original cell For example, in humans, meiosis produces haploid reproductive
Meiosis Section 8-3 Meiosis process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in new cells to half the number in the original cell For example, in humans, meiosis produces haploid reproductive
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome
 Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Reproduction & Cell Types
 Reproduction & Cell Types TYPES OF REPRODUCTION Asexual Relies on MITOSIS All of the parent s DNA goes to the offspring Sexual Relies on MEIOSIS Used to create sex cells TYPES OF CELLS Body Cells Includes
Reproduction & Cell Types TYPES OF REPRODUCTION Asexual Relies on MITOSIS All of the parent s DNA goes to the offspring Sexual Relies on MEIOSIS Used to create sex cells TYPES OF CELLS Body Cells Includes
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
Purposes of Cell Division
 Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
Cell Division. Mitosis
 Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Sexual Reproduction Science 9- Mr. Klasz
 Sexual Reproduction Science 9- Mr. Klasz Why sexual reproduction? Imagine a world where everyone was IDENTICAL. If we reproduced asexually, that would be our world Boring! Asexual Reproduction vs. Sexual
Sexual Reproduction Science 9- Mr. Klasz Why sexual reproduction? Imagine a world where everyone was IDENTICAL. If we reproduced asexually, that would be our world Boring! Asexual Reproduction vs. Sexual
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely,
 Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely, a cell with 46 chromosomes splits to form tow cells each with 46 chromosomes/ This means 46 divided by 2
Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely, a cell with 46 chromosomes splits to form tow cells each with 46 chromosomes/ This means 46 divided by 2
MEIOSIS. KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have.
 MEIOSIS MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. MEIOSIS : CELL TYPES You have Body cells and Gametes Body cells are also called somatic cells. Germ cells develop
MEIOSIS MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. MEIOSIS : CELL TYPES You have Body cells and Gametes Body cells are also called somatic cells. Germ cells develop
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division. Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms
 Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
MEIOSIS, THE BASIS OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
 MEIOSIS, THE BASIS OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Why do kids look different from the parents? How are they similar to their parents? Why aren t brothers or sisters more alike? Meiosis A process where the number
MEIOSIS, THE BASIS OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Why do kids look different from the parents? How are they similar to their parents? Why aren t brothers or sisters more alike? Meiosis A process where the number
gametes Gametes somatic cells diploid (2n) haploid (n)
 Overview of Meiosis Meiosis is a form of cell division that leads to the production of gametes. Gametes: egg cells and sperm cells (reproductive) -contain half the number of chromosomes of an adult body
Overview of Meiosis Meiosis is a form of cell division that leads to the production of gametes. Gametes: egg cells and sperm cells (reproductive) -contain half the number of chromosomes of an adult body
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction. Chapter 9
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Genes and Alleles Genes Sequences of DNA that encode heritable traits Alleles Slightly different forms of the same gene Each specifies a different version
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Genes and Alleles Genes Sequences of DNA that encode heritable traits Alleles Slightly different forms of the same gene Each specifies a different version
What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis?
 Sexual Reproduction What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fyfdfdrymq Somatic cells
Sexual Reproduction What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fyfdfdrymq Somatic cells
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 Chromosomes strands of DNA and protein contain the genes. genes are located in specific positions on chromosomes. Humans receive a set (23) of chromosomes from each parent. 23 chromosomes from mom
11.4 Chromosomes strands of DNA and protein contain the genes. genes are located in specific positions on chromosomes. Humans receive a set (23) of chromosomes from each parent. 23 chromosomes from mom
Meiosis. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Bell Ringer 02/02/15. Match the stages of mitosis to their descriptions and pictures.
 Match the stages of mitosis to their descriptions and pictures. 1. Nuclear membrane disappears and chromosomes condense 2. Nuclear membrane reappears and cells begin to fully separate Bell Ringer 02/02/15
Match the stages of mitosis to their descriptions and pictures. 1. Nuclear membrane disappears and chromosomes condense 2. Nuclear membrane reappears and cells begin to fully separate Bell Ringer 02/02/15
CELL DIVISION MITOSIS & MEIOSIS
 CELL DIVISION MITOSIS & MEIOSIS Cell Cycle 2 distinct phases S Chromosome duplication Interphase G 2 Mitotic What's the most important event of interphase? What is significant about DNA in the S and G
CELL DIVISION MITOSIS & MEIOSIS Cell Cycle 2 distinct phases S Chromosome duplication Interphase G 2 Mitotic What's the most important event of interphase? What is significant about DNA in the S and G
Mitosis & Meiosis. PPT Questions. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete copy of the original cell s DNA?
 1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
Cell Division. Mitosis 11/8/2016
 Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Human biology Laboratory. Cell division. Lecturer Maysam A Mezher
 Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
You have body cells and gametes Body cells are known as somatic cells. Germ cells develop into gametes or sex cells. Germ cells are located in the
 MEIOSIS You have body cells and gametes Body cells are known as somatic cells. Germ cells develop into gametes or sex cells. Germ cells are located in the ovaries and testes. Gametes are sex cells: egg
MEIOSIS You have body cells and gametes Body cells are known as somatic cells. Germ cells develop into gametes or sex cells. Germ cells are located in the ovaries and testes. Gametes are sex cells: egg
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION MEIOSIS SPERMATOGENESIS & OOGENESIS 2/6/2011. Asexual Reproduction:
 Asexual Reproduction: SEXUAL REPRODUCTON & MEOSS Many single-celled organisms reproduce by splitting, budding, parthenogenesis. Some multicellular organisms can reproduce asexually, produce clones (offspring
Asexual Reproduction: SEXUAL REPRODUCTON & MEOSS Many single-celled organisms reproduce by splitting, budding, parthenogenesis. Some multicellular organisms can reproduce asexually, produce clones (offspring
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
The Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cell Division http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/2001/press.html The Cell Cycle Animated Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm MITOSIS Mitosis The process of cell division
The Cell Cycle & Cell Division http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/2001/press.html The Cell Cycle Animated Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm MITOSIS Mitosis The process of cell division
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.13 - MEIOSIS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Meiosis is a special type of cell division that occurs as part of the sexual life cycle of eukaryotes Sexual reproduction parents donate a unique mixture
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Meiosis is a special type of cell division that occurs as part of the sexual life cycle of eukaryotes Sexual reproduction parents donate a unique mixture
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
Meiosis: M-Phase part 2. How is meiosis different from mitosis? Some terms: Some terms: Some terms:
 M-Phase part 2 Meiosis and Cytokinesis Meiosis: A special type of cell division that produces gametes. Cell division that occurs in sex organs. 2 successive nuclear divisions Genetic mistakes (gene and
M-Phase part 2 Meiosis and Cytokinesis Meiosis: A special type of cell division that produces gametes. Cell division that occurs in sex organs. 2 successive nuclear divisions Genetic mistakes (gene and
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis
 5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis Lesson Objectives Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Give an overview of sexual reproduction, and outline the phases of meiosis. Explain why sexual reproduction
5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis Lesson Objectives Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Give an overview of sexual reproduction, and outline the phases of meiosis. Explain why sexual reproduction
Meiosis. The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced.
 MEIOSIS Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced. diploid (2n) haploid (n) (complete set of chromosomes) (half the regular number of
MEIOSIS Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced. diploid (2n) haploid (n) (complete set of chromosomes) (half the regular number of
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Key Concepts. n Cell Cycle. n Interphase. n Mitosis. n Cytokinesis
 The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely related individuals of the
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely related individuals of the
MGC New Life Christian Academy
 A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Name: Date: Period: Cell Cycles and DNA Study Guide
 Name: Date: Period: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the chemical inside the nucleus of cells that contains hereditary information. DNA is shaped like a double helix/twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder
Name: Date: Period: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the chemical inside the nucleus of cells that contains hereditary information. DNA is shaped like a double helix/twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder
MEIOSIS. Stages of Meiosis, Gametogenesis, Sex Determination, & Abnormalities.
 MEIOSIS Stages of Meiosis, Gametogenesis, Sex Determination, & Abnormalities. Stages and Steps of Meiosis Interphase Same as in Mitosis 3 stages G1, S, G2 DNA replication and cell growth Meiosis I Prophase
MEIOSIS Stages of Meiosis, Gametogenesis, Sex Determination, & Abnormalities. Stages and Steps of Meiosis Interphase Same as in Mitosis 3 stages G1, S, G2 DNA replication and cell growth Meiosis I Prophase
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Turn in warm ups to basket! Prepare for your test! Get out your mitosis/meiosis foldable After the test: New vocabulary! 2/23/17 Draw and label the parts of the
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Turn in warm ups to basket! Prepare for your test! Get out your mitosis/meiosis foldable After the test: New vocabulary! 2/23/17 Draw and label the parts of the
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Why mitosis?
 Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Meiosis. The sexy shuffling machine. LO: Describe the events of meiosis Explain how meiosis creates uniqueness Compare & contrast mitosis & meiosis
 Meiosis The sexy shuffling machine LO: Describe the events of meiosis Explain how meiosis creates uniqueness Compare & contrast mitosis & meiosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kvmb4js99ta Meiosis Intro
Meiosis The sexy shuffling machine LO: Describe the events of meiosis Explain how meiosis creates uniqueness Compare & contrast mitosis & meiosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kvmb4js99ta Meiosis Intro
Mitosis and. Meiosis. Presented by Kesler Science
 Mitosis and Meiosis Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are mitosis and meiosis? 2. What occurs at different phases in cell division? 3. How are mitosis and meiosis similar and different?
Mitosis and Meiosis Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are mitosis and meiosis? 2. What occurs at different phases in cell division? 3. How are mitosis and meiosis similar and different?
Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Typical Life Cycle of Algae and Fungi. 5 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Module 3B Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this module, we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells called meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell
Module 3B Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this module, we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells called meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell
Question #1 What must occur in order for Mendel s principles to hold true?
 11.4 Question #1 What must occur in order for Mendel s principles to hold true? An organism with two parents must inherit a single copy of every gene from each parent When that organism produces gametes,
11.4 Question #1 What must occur in order for Mendel s principles to hold true? An organism with two parents must inherit a single copy of every gene from each parent When that organism produces gametes,
biology Slide 1 of 35 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 35 Why do you look a little like your mom and your dad? Why do you look a little like your grandma but your brother or sister looks a little like your grandpa? How is the way you look and
biology 1 of 35 Why do you look a little like your mom and your dad? Why do you look a little like your grandma but your brother or sister looks a little like your grandpa? How is the way you look and
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Note-taking Workbook Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Section: Reproduction ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is to its parent. Additional notes about Asexual Reproduction:
Note-taking Workbook Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Section: Reproduction ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is to its parent. Additional notes about Asexual Reproduction:
Bellwork. Many organisms reproduce via asexual and sexual reproduction. How would we look if we reproduced mitotically?
 Bellwork Many organisms reproduce via asexual and sexual reproduction. How would we look if we reproduced mitotically? SC.912.L.16.17 Meiosis Functions in Sexual Reproduction Other Standards Addressed:
Bellwork Many organisms reproduce via asexual and sexual reproduction. How would we look if we reproduced mitotically? SC.912.L.16.17 Meiosis Functions in Sexual Reproduction Other Standards Addressed:
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Variations on a Theme Living
13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Variations on a Theme Living
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA)
 What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll
 Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Cellular Reproduction. MXMS 7th Grade Science
 Cellular Reproduction MXMS 7th Grade Science What is cell division? 2 primary methods allow for cells to divide and reproduce themselves: A. Mitosis: produces identical offspring B. Meiosis: produces genetically
Cellular Reproduction MXMS 7th Grade Science What is cell division? 2 primary methods allow for cells to divide and reproduce themselves: A. Mitosis: produces identical offspring B. Meiosis: produces genetically
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction (Ch. 13)
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction (Ch. 13) Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction (Ch. 13) Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
#2 How do organisms grow?
 #2 How do organisms grow? Why doesn t a cell keep growing larger and larger? The larger a cell becomes the more demands the cell places on its DNA. The cell also has trouble moving enough nutrients and
#2 How do organisms grow? Why doesn t a cell keep growing larger and larger? The larger a cell becomes the more demands the cell places on its DNA. The cell also has trouble moving enough nutrients and
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of
Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of
Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycle
 Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycle 1 Cell reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies (clones) same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes asexual
Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycle 1 Cell reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies (clones) same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes asexual
QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook:
 Chapter 13- Meiosis QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook: Similarities: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Differences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Figure 13.1 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their
Chapter 13- Meiosis QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook: Similarities: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Differences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Figure 13.1 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Cell Reproduction Review
 Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction B1 B1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the events that occur during 3 stages of the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division, cytokinesis. 2. Compare and
Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction B1 B1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the events that occur during 3 stages of the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division, cytokinesis. 2. Compare and
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Mitosis. Meiosis MP3. Why do cells divide? Why Do Cells Need To Divide? Vocab List Chapter 10 & 11. What has to happen before a cell divides? divides?
 MP3 Vocab List Chapter 10 & 11 Mitosis Anaphase Mitosis Cell Cycle Telophase Cytokinesis Cell Division Metaphase 4 Daughter Cells Prophase Meiosis Diploid Somatic Cells Interphase Haploid Parent Cell Gametes
MP3 Vocab List Chapter 10 & 11 Mitosis Anaphase Mitosis Cell Cycle Telophase Cytokinesis Cell Division Metaphase 4 Daughter Cells Prophase Meiosis Diploid Somatic Cells Interphase Haploid Parent Cell Gametes
