Cell Growth And Division Answers Study Guide
|
|
|
- Coleen Stafford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION ANSWERS STUDY GUIDE PDF - Are you looking for cell growth and division answers study guide Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time cell growth and division answers study guide PDF is available at our online library. With our complete resources, you could find cell growth and division answers study guide PDF or just found any kind of Books for your readings everyday. We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cell growth and division answers study guide. To get started finding cell growth and division answers study guide, you are right to find our website which has a comprehensive collection of manuals listed. Our library is the biggest of these that have literally hundreds of thousands of different products represented. You will also see that there are specific sites catered to different product types or categories, brands or niches related with cell growth and division answers study guide. So depending on what exactly you are searching, you will be able to choose ebooks to suit your own need Need to access completely for Ebook PDF cell growth and division answers study guide You could find and download any of books you like and save it into your disk without any problem at all. We also provide a lot of books, user manual, or guidebook that related to cell growth and division answers study guide PDF, such as ; - Weebly the cell cycle the cell cycle is the series of events in the growth and division of a cell. in the prokaryotic cell cycle, the cell grows, duplicates its dna, and divides by pinching in the cell membrane. Chapter 5: Cell Growth And Division - Cdn.compknowhow.com cell growth and division. 2 background info formation of new cells ~2 trillion cells formed/day in human body ~25 million cells/second cell division = cell reproduction dna must be copied before a cell divides. 3 types of cell division prokaryotic eukaryotic gamete formation. 4 1 / 7
2 Chapter 5 Cell Growth And Division - Weebly chapter5 cell growth and division key concepts 5.1 the cell cycle cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.2 mitosis and cytokinesis cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. 5.3 regulation of the cell cycle cell cycle regulation is necessary for healthy growth. 5.4 asexual reproduction Cell Growth And Division - Northallegheny.org limits to cell growth exchanging materials materials enter and exit a cell through the cell membrane. surface area the total area of the cell membrane the rate at which materials can be exchanged depends on the surface area. the rate at which materials are used up and waste is produced depends on the cell s volume. lesson overview cell growth, division, and reproduction question #1 why is a cell s growth limited? dna as a cell increases in size, its dna does not the need for materials to be built is too great for the ability of the dna to Chapter 10 Cell Growth And Division, Se - District 196 chapter 10, cell growth and division (continued) reading skill practice you may sometimes forget the meanings of the vocabulary terms that were introduced earlier in the textbook. when this happens, you can check the meanings of the terms in the glossary, which you can find at the end of the book just before the index. cell growth and division occur in a regular cycle. this cycle is 2, and m. the m phase of the cell cycle is called es required for cell. mitosis... cell division uncontrolled cell growth e cell differentiation lesson objectives describe the process of differentiation. Chapter 10 The Cell Cycle, Mitosis, And Meiosis Practice Test chapter 10 the cell cycle, mitosis, and meiosis practice test 1. a cell s size is limited because as it grows... b. cell division. c. replication. d. transcription. 8. what are the four phases of the cell cycle?... its growth would be through cell division via mitosis. use figure 10.3 to answer questions figure 10.3 is an The Process Of Cell Division Worksheet Answer Key 10.2 the process of cell division worksheet answer key division concept map answers, biology workbook answers cell. honors biology cell division worksheet *#53 ch 10.2 mitosis 3rd/4thwatched wolf video (predator/prey) and answered division, and the process of differentiation. student. 10.1: cell growth, division, and Mitosis And Meiosis Webquest - Anglophone South School what is the role of the nucleus in cell division? the role of the nucleus is to be the control center of the cell and it contains chromosomes made up of long strands of molecules called dna. 3. what is the role of the centrioles in cell division? the role of the centrioles in cell division is they duplicate and they help to anchor the spindle... 2 / 7
3 Hapter 10 - National Council Of Educational Research And... cycles of growth and division allow a single cell to form a structure consisting of millions of cells cell cycle cell division is a very important process in all living organisms. during the division of a cell, dna replication and cell growth also take place. all these processes, i.e., cell division, dna replication, and cell growth, hence, Cell Growth And Reproduction - Colonial School District cell growth and reproduction module b, anchor 1 cell growth, division, and reproduction: 1. what are the reasons why cells divide? how does division address these issues? materials exchange as cells grown, their volume increases faster than their surface area. this prevents them from effectively exchanging materials with their environments. Biology - Annenberg Learner molecular to global perspectives rediscovering biology we now understand a lot about cancer. we know that it results from a series of genetic changes having to do with cell division and growth control and genetic Cell Division Worksheet - Lancaster City School District cell division worksheet 1. on figure 12.1 below identify the sister chromatids by drawing a line to the sister... dna duplication, cytokinesis, cell growth. 4 circle the term that includes all the others in the list. 1. gene, dna synthesis, mitosis, cytokinesis, cell cycle 2. s subphase, cytokinesis, interphase, mitosis, cell cycle 3. cell... Cell Growth, Division, Lesson 10.1 Getting... cell growth and division 275 lesson 10.1 teach build math skills some students may have limited experience with ratios. explain that a ratio is a comparison. in this case, it compares the amount of surface area a cell has to its volume. a ratio can be expressed as a Chapter 10 Cell Growth And Division cell division in eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. the first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. the second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. most eukaryotic cells go through a regular cycle of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis. mitosis - Weebly the cell cycle the cell cycle is the series of events in the growth and division of a cell. in the prokaryotic cell cycle, the cell grows, duplicates its dna, and divides by pinching in the cell membrane Cell Division - Parkway Schools 2 copyright pearson prentice hall end show 10-2 cell division slide 7 of 38 the cell cycle what are the main events of the cell cycle? copyright pearson prentice hall Study Guide- Unit 4: Cell Growth And Division (chapter 10) study guide- unit 4: cell growth and division (chapter 10) answer the following questions using your lecture notes, textbook, and other study charts. remember, this is a study guide and the 3 / 7
4 test is not limited to just the information here. a) in your textbook, turn to pages and answer the selected question by putting the answers in the Biology Chapter 10 Cell Growth And Division Worksheet Answers growth and division growth, development, and in chapter 10, they will explore cell size, cell division, and the process of differentiation. student resources study workbooks a and b, 10.1 Cell Biology - Nicholls State University cell biology a cell is chemical system that is able to maintain its structure and reproduce. cells are the fundamental unit of life.... vesicles that form through growth and division within the cytoplasm glyoxisomes are found in plants - contain enzymes that convert fats into carbohydrates peroxisomes - used for Section 10 2 Cell Division - Hanover Area School District during cell division. 2. when chromosomes become visible at the beginning of cell division, what does each chromosome consist of?each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids. 3. each pair of chromatids is attached at an area called the. the cell cycle(page 245) 4. the period of growth in between cell divisions is called. 5. Lab 4. Normal And Abnormal Cell Division: Which Of These... normal and abnormal cell division: which of these patients could have cancer? introduction hundreds of genes control the process of cell division in normal cells. normal cell growth requires a balance between the activity of those genes that promote cell division and those that suppress it. Cell Growth And Division - Ihsmoberlybiology.weebly.com chromosomes in cell division: chromosomes must be duplicated, and separated properly, to make 2 identical daughter cells 5. describe the main events of the cell cycle: the cell grows and prepares to divide, before splitting into two identical diploid daughter cells cell growth and division Cell Growth & Division Review - Poudre School District cell growth & division review name 1. the period of time between one cell division and the next is called the. cell cycle. 2. cell division is called. mitosis. 3. uncontrolled cell division is called. cancer. 4. examples of cells that rarely divide are. skeletal muscle. cells and. nerve. cells. 5. Cell Growth, Cell Reproduction And Mitosis cell growth and division vocabulary anaphase twin copies of the chromosomes get separated and move to the opposite sides of the cell. cell division- the method of one cell dividing into two cells.mitosis, meosis cell plate the site of growth of a new cell wall between the two new daughter cells in the mitosis of plant cells. centromere site of attachment for sister chromosomes. 5 Cell Growth And Division - Weebly the cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, dna duplication*, and cell division* that occurs in 4 / 7
5 eukaryotic cells. recall that your cells are eukaryotic cells, and they have a nucleus. there are four main stages of the cell cycle: gap 1 normal growth synthesis dna is copied gap 2 more growth mitosis nuclear division Cell Growth And Division Questions And Lab Integrated... cell growth and division questions and lab integrated science 2 name: per: read pages in the is book and answer the following questions. 1. there are two main reasons cells divide rather than continuing to grow indefinitely. Chapter 10 Cell Growth And Division.notebook chapter 10 cell growth and division.notebook 4 february 09, 2017 mar 10:03 pm section 10 regulating the cell cycle key concepts how is the cell cycle regulated? how are cancer cells different from other cells? controls on cell division cells will grow until a signal is given. Section 10 3 Regulating The Cell Cycle section 10 3 regulating the cell cycle(pages ) this section describes how the cell cycle is regulated. it also explains how... the rate of cell division slows down, controls on growth are restored, and everything returns to normal. cell cycle regulators(page 251) 3. The Cell Cycle: A Series Of Modeling Activities the cell cycle: a series of modeling activities cancer education project university of rochester. premise: students learn best when exposed to a variety of activities.... growth signal that stimulates cell division. growth signal. turn your wheel to g 1 phase zto simulate growth of your cell, please add beans to your small bag Cell Growth - Mrs Holland's Webpage - Home cancer is uncontrolled cell growth and division. there is no one cure or treatment because there is no single cause. your own cells lose the ability to control when/how often they divide. cyclins= proteins that control the progression of cells through the cell cycle. if these cyclins stop working, there is a greater chance of Chapter 10 Cell Growth And Division Summary chapter 10 cell growth and division the larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its dna the molecule that contains information that controls cell functions. as a cell increases in size, it usu-ally does not make copies of dna. if a cell were to grow without limit, an information crisis would occur. in addition, as a cell 5.3 Regulation Of The Cell Cycle - Murrieta Valley Unified... growth factors are proteins that stimulate cell division. most mammal cells form a single layer in a culture dish and stop dividing once they touch other cells. 5.3 regulation of the cell cycle two of the most important internal factors are kinases and cyclins. Esson 10.1 Getting Started Cell Growth, Division, And... cell growth, division, and reproduction key questions what are some of the difficulties a cell faces as it increases in size? how do asexual and sexual reproduction compare? vocabulary cell division asexual reproduction sexual reproduction taking notes outline as you read, create 5 / 7
6 an outline about cell growth, divi-sion, and reproduction. as you Chapter 5 Power Notes Answer Key - Weebly cell size is limited if cells were too small, they could not contain all the organelles and molecules necessary for life. if cells were too large, they could not move enough materials across the membrane surface. to maintain a suitable size, cell growth and division must be coordinated. the smallest cube should be circled. section 5.2 Big Genetics And Information Transfer 3 - College Board cell division: mitosis and meiosis... page s83, figure 1). in the first growth phase (g 1), the cell grows and prepares to duplicate its dna. in the synthesis phase (s), the chromosomes are replicated. in the second growth phase (g 2... cell division is tightly controlled by complexes made of several specific proteins. - Stone Science 10.1 cell growth, division, and... explain the problems that growth causes for cells. compare asexual and sexual reproduction. lesson summary limits to cell size there are two main reasons why cells divide:... for single-celled organisms, cell division is a form of reproduction cell growth, division, and reproduction lesson objectives explain the problems that growth causes for cells. compare asexual and sexual reproduction.... for single-celled organisms, cell division is a form of reproduction. 8. most multicellular organisms reproduce by reproduction. 9. a cell divides into two new daughter cells cell division reproduction involving only one parent organism division, divides, and daughter all begin with d. a cell divides into daughter cells. sexual reproduction reproduction in which cells from two different parents join to form a new organism b Cell Division - Quia 1. first growth (g 1) phase: cell grows rapidly and carries out its routine functions 2. synthesis (s) phase: cell s dna is copied (replicated). (once in s phase, a cell often completes the rest of cycle) 3. second growth (g 2) phase: organelles and molecules required for cell division are produced; nucleus prepares to divide 4. Cell Growth & Division - West Linn the eukaryotic cell cycle during the cell cycle, the cell grows, prepares for division, and divides into 2 daughter cells, each of which begins the cycle again. phases: g1: cell growth s: dna replication interphase g2: preparation for mitosis m: mitosis (division of the cell nucleus) & cytokinesis Cell Division Mitosis And The Cell Cycle external regulatory proteins direct the cell to speed up or slow down the cycle ex. growth factors stimulate the division of the cell (embryonic development and wound healing) how do 6 / 7
7 cells know when to divide? Cell Cycle, Mitosis And Meiosis - Bemidji State University regujation of the cell cycle. how cell division (and thus tissue growth) is controlled is very complex. the following. terms are some of the features that are important in regulation, and places where errors can. lead to cancer. cancer is a disease where regulation of the cell cycle goes awry and normal. cell growth and behavior is lost. Cell Division Worksheet Answer Key - Sintich Science cell division worksheet answer key cell cycle (mitosis) reinforcement worksheet 1. e 2. c 3. c choose between: reproduction, repair, growth, development 2. g1, s, g2 3. dna replication (dna gets copied) 4. nucleus 5. 2 diploid cells that are identical to the parent cell 6. metaphase 7. cytokinesis 8. prophase 9. telophase Chapter 10 Homework Answers (p. 257) D C B C growth of a cell. 15. well before cell division, each chromosome is duplicated. at the beginning of cell division, each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids. 16. together, interphase and cell division make up the cell cycle. 17. during interphase, a cell increases in size, synthesizes new proteins and organelles, duplicates its Cell Growth And Size Control: Controlling The Cell Cycle cell growth and size control: controlling the cell cycle peter takizawa... irreversible commitment to cell division.!" #!$ %&'()&) start the decision to enter the cell cycle is made at start in g1. after start, cell committed to cell division because the cell will commence chromosome replication... cells division and mutations in prb can... Understanding The Mechanical Link Between Oriented Cell... model of granule cell progenitor clones where cell growth and division algorithms are motivated by experimental results from the literature. we introduce a strategy for post-processing the cellular-scale agent-based model results such that they feed into the second tissue-scale model which treats the cerebellum as a continuum. 7 / 7
Cell Growth And Division Answers Study Guide
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION ANSWERS STUDY GUIDE PDF - Are you looking for cell growth and division answers study guide Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time cell growth and division answers study
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION ANSWERS STUDY GUIDE PDF - Are you looking for cell growth and division answers study guide Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time cell growth and division answers study
Cell Growth Division And Reproduction Answers
 CELL GROWTH DIVISION AND REPRODUCTION ANSWERS PDF - Are you looking for cell growth division and reproduction answers Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time cell growth division and reproduction
CELL GROWTH DIVISION AND REPRODUCTION ANSWERS PDF - Are you looking for cell growth division and reproduction answers Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time cell growth division and reproduction
Cell Reproduction Mitosis And Meiosis Webquest Answers
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cell reproduction mitosis
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cell reproduction mitosis
Chapter 10 Cell Growth And Division Answer Key
 CHAPTER 10 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION ANSWER KEY PDF - Are you looking for chapter 10 cell growth and division answer key Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time chapter 10 cell growth and division
CHAPTER 10 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION ANSWER KEY PDF - Are you looking for chapter 10 cell growth and division answer key Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time chapter 10 cell growth and division
Chapter 10 Cell Growth And Division Vocabulary Review Page 112 Answers
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth And Division Vocabulary Review Page 112 Answers CHAPTER 10 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION VOCABULARY REVIEW PAGE 112 ANSWERS PDF - Are you looking for chapter 10 cell growth and division
Chapter 10 Cell Growth And Division Vocabulary Review Page 112 Answers CHAPTER 10 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION VOCABULARY REVIEW PAGE 112 ANSWERS PDF - Are you looking for chapter 10 cell growth and division
Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division Growth, Development, and Reproduction Q: How does a cell produce a new cell? 10.1 Why do cells divide? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Cells divide to produce more cells. WHAT I LEARNED
Cell Growth and Division Growth, Development, and Reproduction Q: How does a cell produce a new cell? 10.1 Why do cells divide? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Cells divide to produce more cells. WHAT I LEARNED
Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There
Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There
10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There are two
10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There are two
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
10.2 The Process of Cell Division
 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Lesson Objectives Describe the role of chromosomes in cell division. Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four phases of mitosis. Describe
10.2 The Process of Cell Division Lesson Objectives Describe the role of chromosomes in cell division. Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four phases of mitosis. Describe
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis No matter the type of cell, all cells come from preexisting cells through the process of cell division. The cell may be the
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis No matter the type of cell, all cells come from preexisting cells through the process of cell division. The cell may be the
Cellular Reproduction
 Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
The Process of Cell Division. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
2 The Cell Cycle. TAKE A LOOK 2. Complete Prokaryotic cells divide by.
 CHAPTER 5 2 The Cell Cycle SECTION The Cell in Action BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are new cells made? What is mitosis? What happens when
CHAPTER 5 2 The Cell Cycle SECTION The Cell in Action BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are new cells made? What is mitosis? What happens when
Cell Reproduction Review
 Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 25: Mitosis
 Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 25: Mitosis Objective: Students will be able to explain the phases of Mitosis. Date Essential Questions: 1. What are the phases of the eukaryotic cell
Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 25: Mitosis Objective: Students will be able to explain the phases of Mitosis. Date Essential Questions: 1. What are the phases of the eukaryotic cell
Topic 6 Cell Cycle and Mitosis. Day 1
 Topic 6 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Day 1 Bell Ringer (5 minutes) *pick up worksheet by the door* Get out your homework and answer these questions on the back page: What do I need to do to pass my real EOC?
Topic 6 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Day 1 Bell Ringer (5 minutes) *pick up worksheet by the door* Get out your homework and answer these questions on the back page: What do I need to do to pass my real EOC?
Answer Key. Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle: (1) Gap1 (G 1): cells grow, carry out normal functions, and copy their organelles. (2) Synthesis (S): cells replicate DNA. (3)
Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle: (1) Gap1 (G 1): cells grow, carry out normal functions, and copy their organelles. (2) Synthesis (S): cells replicate DNA. (3)
Biology: Life on Earth
 Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
Section 1 Reinforcement Cell Structure Answer Key
 SECTION 1 REINFORCEMENT CELL STRUCTURE ANSWER KEY PDF - Are you looking for section 1 reinforcement cell structure answer key Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time section 1 reinforcement cell
SECTION 1 REINFORCEMENT CELL STRUCTURE ANSWER KEY PDF - Are you looking for section 1 reinforcement cell structure answer key Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time section 1 reinforcement cell
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES
 CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
Stages Of Meiosis Answer Key By Instructional Fair Inc Biology If8765
 Stages Of Meiosis Answer Key By Instructional Fair Inc Biology If8765 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on
Stages Of Meiosis Answer Key By Instructional Fair Inc Biology If8765 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on
Cell Division Review And Reinforce Answers
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cell division review
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cell division review
5.1. Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. G 1. Cell Growth and Division CHAPTER 5 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT
 SECTION 5.1 THE CELL CYCLE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. VOCABULARY cell cycle mitosis cytokinesis The cell cycle has four main stages.
SECTION 5.1 THE CELL CYCLE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. VOCABULARY cell cycle mitosis cytokinesis The cell cycle has four main stages.
The Importance of Cell Division Cell division
 Cell Division The Importance of Cell Division Cell division allows organisms to carry out three necessary functions: REPRODUCE GROW REPAIR DAMAGE FERTILIZATION: You started life as a single cell, but today
Cell Division The Importance of Cell Division Cell division allows organisms to carry out three necessary functions: REPRODUCE GROW REPAIR DAMAGE FERTILIZATION: You started life as a single cell, but today
Cellular Growth & Reproduction. Biology 1B Ms. Morris
 Cellular Growth & Reproduction Biology 1B Ms. Morris Friday, February 7, 2014 Warm Up: Look around at the other people in the classroom. What types of variation (differences) do you see? What similarities
Cellular Growth & Reproduction Biology 1B Ms. Morris Friday, February 7, 2014 Warm Up: Look around at the other people in the classroom. What types of variation (differences) do you see? What similarities
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review
 Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction B1 B1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the events that occur during 3 stages of the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division, cytokinesis. 2. Compare and
Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction B1 B1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the events that occur during 3 stages of the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division, cytokinesis. 2. Compare and
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Chapter 10 2 Cell Division
 CHAPTER 10 2 CELL DIVISION PDF - Are you looking for chapter 10 2 cell division Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time chapter 10 2 cell division PDF is available at our online library. With our
CHAPTER 10 2 CELL DIVISION PDF - Are you looking for chapter 10 2 cell division Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time chapter 10 2 cell division PDF is available at our online library. With our
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
5.1 Cell Division and the Cell Cycle
 5.1 Cell Division and the Cell Cycle Lesson Objectives Contrast cell division in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how the cell cycle is controlled.
5.1 Cell Division and the Cell Cycle Lesson Objectives Contrast cell division in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how the cell cycle is controlled.
Why do we have to cut our hair, nails, and lawn all the time?
 Chapter 5 Cell Reproduction Mitosis Think about this Why do we have to cut our hair, nails, and lawn all the time? EQ: Why is cell division necessary for the growth & development of living organisms? Section
Chapter 5 Cell Reproduction Mitosis Think about this Why do we have to cut our hair, nails, and lawn all the time? EQ: Why is cell division necessary for the growth & development of living organisms? Section
Name: Date: Hour: Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis. Monomer Polymer Example Drawing Function in a cell DNA
 Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Cell Division. Genetic info must be copied. Each cell gets a complete copy of that info. It occurs in two main stages:
 10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS. Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent.
 THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction. What is Cellular Reproduction?
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Cellular Reproduction. MXMS 7th Grade Science
 Cellular Reproduction MXMS 7th Grade Science What is cell division? 2 primary methods allow for cells to divide and reproduce themselves: A. Mitosis: produces identical offspring B. Meiosis: produces genetically
Cellular Reproduction MXMS 7th Grade Science What is cell division? 2 primary methods allow for cells to divide and reproduce themselves: A. Mitosis: produces identical offspring B. Meiosis: produces genetically
Name 8 Cell Cycle and Meiosis Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of the replicated chromosome. The stages of mitosis.
 Name 8 Cell Cycle and Meiosis Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of the replicated chromosome. The stages of mitosis. The role of kinases and cyclin in the regulation of the cell cycle.
Name 8 Cell Cycle and Meiosis Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of the replicated chromosome. The stages of mitosis. The role of kinases and cyclin in the regulation of the cell cycle.
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis
 Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
MGC New Life Christian Academy
 A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
Key Concepts. n Cell Cycle. n Interphase. n Mitosis. n Cytokinesis
 The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Growth and Division. SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6.
 Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6. G 1 7. G 0 8. c 9. faster; too large 10. volume 11. a and b 12. repeating pattern or repetition
Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6. G 1 7. G 0 8. c 9. faster; too large 10. volume 11. a and b 12. repeating pattern or repetition
The Cellular Basis of Inheritance
 CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
Reading Assignments. A. Systems of Cell Division. Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Mitosis. Meiosis MP3. Why do cells divide? Why Do Cells Need To Divide? Vocab List Chapter 10 & 11. What has to happen before a cell divides? divides?
 MP3 Vocab List Chapter 10 & 11 Mitosis Anaphase Mitosis Cell Cycle Telophase Cytokinesis Cell Division Metaphase 4 Daughter Cells Prophase Meiosis Diploid Somatic Cells Interphase Haploid Parent Cell Gametes
MP3 Vocab List Chapter 10 & 11 Mitosis Anaphase Mitosis Cell Cycle Telophase Cytokinesis Cell Division Metaphase 4 Daughter Cells Prophase Meiosis Diploid Somatic Cells Interphase Haploid Parent Cell Gametes
Cells & Cell Division
 Cells & Cell Division An informative presentation by your wacky science teacher! LG4: Explain basic principles of HEREDITY, including CELL DIVISION (MITOSIS & MEIOSIS). A Question.. What do you, an ant,
Cells & Cell Division An informative presentation by your wacky science teacher! LG4: Explain basic principles of HEREDITY, including CELL DIVISION (MITOSIS & MEIOSIS). A Question.. What do you, an ant,
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION PART I: MEIOSIS
 MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction division. It is this first division that reduces the chromosome number
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction division. It is this first division that reduces the chromosome number
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
CHAPTER 12 - THE CELL CYCLE (pgs )
 CHAPTER 12 - THE CELL CYCLE (pgs. 228-245) CHAPTER SEVEN TARGETS I. Describe the importance of mitosis in single-celled and multi-cellular organisms. II. Explain the organization of DNA molecules and their
CHAPTER 12 - THE CELL CYCLE (pgs. 228-245) CHAPTER SEVEN TARGETS I. Describe the importance of mitosis in single-celled and multi-cellular organisms. II. Explain the organization of DNA molecules and their
11-4 Meiosis Chromosome Number Slide 1 of 35
 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just one set. Chromosome
Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just one set. Chromosome
biology Slide 1 of 35 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. 3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life.
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. 3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life.
The Cell Cycles Mitosis and Meiosis. Essential question: How do cells reproduce and why?
 The Cell Cycles Mitosis and Meiosis Essential question: How do cells reproduce and why? Objectives Section 10.1 Explain why cells divide in terms of growth and cell size Review - Types of Cell Division
The Cell Cycles Mitosis and Meiosis Essential question: How do cells reproduce and why? Objectives Section 10.1 Explain why cells divide in terms of growth and cell size Review - Types of Cell Division
GENERAL SAFETY: Follow your teacher s directions. Do not work in the laboratory without your teacher s supervision.
 Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
CH 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 CH 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles AP Biology 2005-2006 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA
CH 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles AP Biology 2005-2006 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Meiosis produces haploid gametes.
 Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis?
 Sexual Reproduction What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fyfdfdrymq Somatic cells
Sexual Reproduction What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fyfdfdrymq Somatic cells
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
2. is the period of growth and development for a cell. 3. During interphase, most cells go through three stages rapid growth and
 Chapter 5 Lesson 1- General Lesson Outline Directions: Use the words below to fill in the outline of the text from lesson one. If the word is used more than once, it is followed by the number of times
Chapter 5 Lesson 1- General Lesson Outline Directions: Use the words below to fill in the outline of the text from lesson one. If the word is used more than once, it is followed by the number of times
Cell Division. Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 2/9/2016. Dr. Saud Alamri
 Cell Division Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 1 Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually by a type of cell division called binary fission 2 Prokaryotic chromosome Division into two daughter cells Plasma
Cell Division Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 1 Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually by a type of cell division called binary fission 2 Prokaryotic chromosome Division into two daughter cells Plasma
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA)
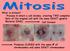 What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cell Division http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/2001/press.html The Cell Cycle Animated Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm MITOSIS Mitosis The process of cell division
The Cell Cycle & Cell Division http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/2001/press.html The Cell Cycle Animated Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm MITOSIS Mitosis The process of cell division
cycle & cell the division
 the cycle & celldivision the cell cycle Most cells in an organism go through a cycle of growth, development, and division called the cell cycle. The cell cycle makes it possible for organisms to grow and
the cycle & celldivision the cell cycle Most cells in an organism go through a cycle of growth, development, and division called the cell cycle. The cell cycle makes it possible for organisms to grow and
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Why are cells small? As cells get bigger they don t work as well WHY? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient in moving nutrients/waste across its
The Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Why are cells small? As cells get bigger they don t work as well WHY? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient in moving nutrients/waste across its
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
11-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
9-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35
 9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test
 Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Mitosis and. Meiosis. Presented by Kesler Science
 Mitosis and Meiosis Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are mitosis and meiosis? 2. What occurs at different phases in cell division? 3. How are mitosis and meiosis similar and different?
Mitosis and Meiosis Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are mitosis and meiosis? 2. What occurs at different phases in cell division? 3. How are mitosis and meiosis similar and different?
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR
 Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR meiosis plus fertilization Objective: You will be able
Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR meiosis plus fertilization Objective: You will be able
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
CELL CYCLE. How Cells Divide
 CELL CYCLE How Cells Divide Catalyst: Describe what happened after the last time you scraped or cut yourself? How did your wound heal itself? Cell Cycle Notes 12/2/16 Reflection: 26L 26R Cell cycle
CELL CYCLE How Cells Divide Catalyst: Describe what happened after the last time you scraped or cut yourself? How did your wound heal itself? Cell Cycle Notes 12/2/16 Reflection: 26L 26R Cell cycle
Cell Division and Reproduction
 Cell Division and Reproduction What do you think this picture shows? If you guessed that it s a picture of two cells, you are right. In fact, the picture shows human cancer cells, and they are nearing
Cell Division and Reproduction What do you think this picture shows? If you guessed that it s a picture of two cells, you are right. In fact, the picture shows human cancer cells, and they are nearing
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
10.1 Growth and Cell Reproduction
 10.1 Growth and Cell Reproduction Growth is a characteristic of all living things. You started out as a single cell. That cell quickly divided into two cells. Two cells became four and four became eight.
10.1 Growth and Cell Reproduction Growth is a characteristic of all living things. You started out as a single cell. That cell quickly divided into two cells. Two cells became four and four became eight.
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS STUDY GUIDE CREATED BY : Alistaire Rauch (Mr. Galego s Class) Definition of Mitosis and Meiosis (Basic):
 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS STUDY GUIDE CREATED BY : Alistaire Rauch (Mr. Galego s Class) Definition of Mitosis and Meiosis (Basic): Mitosis and Meiosis are basically cycles of cells but they are different in
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS STUDY GUIDE CREATED BY : Alistaire Rauch (Mr. Galego s Class) Definition of Mitosis and Meiosis (Basic): Mitosis and Meiosis are basically cycles of cells but they are different in
Biology Notes 2. Mitosis vs Meiosis
 Biology Notes 2 Mitosis vs Meiosis Diagram Booklet Cell Cycle (bottom corner draw cell in interphase) Mitosis Meiosis l Meiosis ll Cell Cycle Interphase Cell spends the majority of its life in this phase
Biology Notes 2 Mitosis vs Meiosis Diagram Booklet Cell Cycle (bottom corner draw cell in interphase) Mitosis Meiosis l Meiosis ll Cell Cycle Interphase Cell spends the majority of its life in this phase
Reproduction of Organisms
 Reproduction of Organisms Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Reproduction of Organisms Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
#2 How do organisms grow?
 #2 How do organisms grow? Why doesn t a cell keep growing larger and larger? The larger a cell becomes the more demands the cell places on its DNA. The cell also has trouble moving enough nutrients and
#2 How do organisms grow? Why doesn t a cell keep growing larger and larger? The larger a cell becomes the more demands the cell places on its DNA. The cell also has trouble moving enough nutrients and
Reproduction & Development. 1 parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells All offspring have exact same DNA as parent
 Living Environment Dr. Golub Reproduction & Development Asexual reproduction 1 parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells All offspring have exact same DNA as parent Sexual Reproduction Requires 2 parents
Living Environment Dr. Golub Reproduction & Development Asexual reproduction 1 parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells All offspring have exact same DNA as parent Sexual Reproduction Requires 2 parents
CELL CYCLE UNIT GUIDE- Due January 19, 2016
 CELL CYCLE UNIT GUIDE- Due January 19, 2016 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday January 4- No School 5-Cell Cycle/Mitosis 6-Cell Cycle/ Mitosis 7-Mitosis 8-Meiosis Reading Check Quiz #1 sections 5.1-5.5
CELL CYCLE UNIT GUIDE- Due January 19, 2016 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday January 4- No School 5-Cell Cycle/Mitosis 6-Cell Cycle/ Mitosis 7-Mitosis 8-Meiosis Reading Check Quiz #1 sections 5.1-5.5
LS_C2-quizzes, Version: 1 1
 Name: Select the term that best completes the statement. A. cell division B. chromosomes C. cells D. divides E. centromere F. DNA G. chromatids H. nucleus Date: 1. is the chemical code that contains information
Name: Select the term that best completes the statement. A. cell division B. chromosomes C. cells D. divides E. centromere F. DNA G. chromatids H. nucleus Date: 1. is the chemical code that contains information
CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS NOTES
 CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS NOTES DNA - Genetic information is stored in the DNA strand in the form of genes. DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid Genes located on the DNA strand 2 Types of DNA
CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS NOTES DNA - Genetic information is stored in the DNA strand in the form of genes. DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid Genes located on the DNA strand 2 Types of DNA
Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction. That cell divided and becomes two, two become four, four become eight, and so on.
 4.1 Cell Division and Mitosis Many organisms start as one cell. Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction That cell divided and becomes two, two become four, four become eight, and so on. Many-celled organisms,
4.1 Cell Division and Mitosis Many organisms start as one cell. Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction That cell divided and becomes two, two become four, four become eight, and so on. Many-celled organisms,
Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring
 In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology
 Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Why mitosis?
 Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
ACCELERATE ITS BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES WHICH WERE SLOWED DOWN BY MITOSIS. THE LENGTH OF THE G1 PHASE CREATES THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FAST DIVIDING
 CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome
 Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
