DEEP-Theory Meeting 30 October 2017 Expected at 4 pm: Elliot Eckholm; Not coming today: Vivian Tang, Graham Vanbenthuysen Prolate galaxies:
|
|
|
- Erin French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEEP-Theory Meeting 30 October 2017 Expected at 4 pm: Elliot Eckholm; Not coming today: Vivian Tang, Graham Vanbenthuysen Prolate galaxies: observation-simulation comparison Haowen Zhang and Vivian Tang: analysis of CANDELS b/a vs. Δa data & mocks; half-stellar-mass radius r_0.5 vs. half-stellar-light radius r_e from simulations. GALFIT analysis of VELA simulations Marc Huertas-Company Deep Learning GALFIT emulator vs. Haowen Zhang running them through GALFIT. Galaxy size vs. local density project Graham Vanbenthuysen, Viraj Pandya, Christoph Lee, Doug Hellinger, Aldo Rodriguez-Puebla, David Koo, Lin Lin We are measuring λ vs. density by various methods in Aldo s mock catalogs from Bolshoi-Planck and MultiDark-Planck, and SDSS galaxy radii vs. density by the same methods. Christoph will show how Rs and Rs(CNFW/7) 0.4 depend on environmental density. Abundance matching is independent of environmental density Radu Dragomir, Aldo, Christoph paper sub. Elongated galaxies aligned with cosmic filaments? Viraj Pandya is working on observations & mocks. Deep Learning for Galaxy Environment project The paper by Nicolas Tejos, Aldo Rodriguez-Puebla, and me is now published in MNRAS. James Kakos, Dominic Pasquale, and Matthew Casali plan to use DL for a project to improve z and local environment for a mixture of spectroscopic and (mostly) photometric redshifts. Deep Learning for Galaxies project Analysis of VELA Gen3 simulations is ongoing by Raymond Simons at JHU, Christoph Lee and Sean Larkin, along with Avishai s student Tomer Nussbaum: finding all satellites. Christoph is also using the DL code that classified CANDELS images to classify VELA mock galaxy images. Halo properties like concentration, accretion history, and spin are mainly determined by environmental density rather than by location within the cosmic web we are finishing the paper led by Tze Goh DM halo mass loss paper being finished Christoph Lee, Doug Hellinger. Related work this summer on halo radial profile by SIP students Shawn Zhang and Peter Wu with Christoph. Simulations of CGM & winds vs. observations Clayton Strawn, Hassen Yesuf Improved Santa Cruz Semi-Analytic Model of galaxy population evolution, including insights from highresolution hydro simulations Viraj Pandya, Christoph Lee, Rachel Somerville, Sandy Faber
2 Comparison between GALFIT measurements of CANDELized VELA images and other things Haowen Zhang Note: first 3 slides are from Oct 23
3 CNN Galfit Emulator (Marc Huertas-Company) vs. Galfit (Haowen Zhang) Applied to VELA Gen3 CANDELized Images
4 CNN Galfit Emulator (Marc Huertas-Company) vs. Galfit (Haowen Zhang) Applied to VELA Gen3 CANDELized Images a b What s causing these large values? What s causing these large values? a a b/a nsersic
5 CNN Galfit Emulator (Marc Huertas-Company) vs. Galfit (Haowen Zhang) Applied to VELA Gen3 CANDELized Images Galfit magnitudes agree with Sunrise magnitudes for bright galaxies (h 24)
6 Cam00 vs. cam02 && Cam01 vs. cam03
7 Cam00 vs. cam02 && Cam01 vs. cam03
8 Comparison between VELA GALFIT and CANDELS
9 Tomassetti mass profile vs. CANDELized light profile: b/a GALFIT GALFIT emulator
10 Tomassetti mass profile vs. CANDELized light profile: b/a
11
12 Comparison between VELA GALFIT and CANDELS
13
14
15
16
17
18 What controls the sizes of galaxies in the NIHAO and VELA simulations? Fangzhou Jiang
19 Sandy: You have already partially made the plot I want to see, as you have plotted r_e vs r_vir, and the latter goes as M-vir^0.33. You have colored by C, which is what I wanted. (Nihou plots) Fangzhou: Right. Note however, r_vir ~ M_vir^0.33 is for a fixed redshift. Take the redshift scaling into account, r_vir ~ a * M_vir^0.33, where a = 1/(1+z) is the expansion factor. So I am not exactly making the plot you asked, but this is not very important. The average c-m_vir-z relation goes as c ~ M_vir^-0.11 / (1+z). I only choose galaxies (snapshots) with M_vir = ^ at z= M_vir = ^ at z=0-0.3 makes r_vir>0kpc. The bins are narrow enough that the variation in c according to the average c-m_vir-z relation is only 20%, so a strong scaling between r_e/r_vir and c, over a large range in c, show that it is not due to the c-m_vir-z relation. With sightly adjusted dynamical range in the color bar, you can see the color trend better. The upper right panel plots r_e / r_vir as a function of c -- you can see the strong scaling with c, which goes roughly as c^-0.6, as we use. NIHAO galaxy size - halo (hydro) size, Size=3D stars, color=concentration Somerville+17 median ± 16,84% re/rvir re/rvir re/rvir re/rvir halo r e =0.017r vir Kravtsov r e =0.14r max gas r e =0r s c r e =0.15r s (c/7.0) re [kpc] re [kpc] re [kpc] re [kpc] c 2 r vir [kpc] 2 r max [kpc] 2 r s [kpc] 2 (c/7.0) 0.4 r s [kpc] 4 log 0.0 RMS= 0 =0.15 log 0.0 RMS= 2 =0. log 0.0 RMS= 0.12 =0.08 log 0.0 RMS= 0.11 = r vir [kpc] r max [kpc] r s [kpc] (c/7.0) 0.4 r s [kpc]
20 11 To further convince you, in 2.FixedConcentrationRedshift (below) I fix c and z in narrow bins of c=6-9 and z=0-0.3, and color the points by halo mass -- you can see again from the upper right-hand panel that r_e/r_vir is almost independent of halo mass. Similarly, "3.FixedConcentrationMass.pdf" shows that r_e/r_vir doesn't depend on z at fixed M_vir and c. To sum up, it is really the concentration parameter that matters, instead of z- or M_vir-dependences that come in via c(m_vir,z) NIHAO galaxy size - halo (hydro) size, Size=3D stars, color=halo mass Somerville+17 median ± 16,84% re/rvir re/rvir re/rvir re/rvir halo gas M vir [M ] r e =0.027r vir Kravtsov 13 r e =0.14r max r e =1r s r e =0r s (c/7.0) re [kpc] re [kpc] re [kpc] re [kpc] 11 2 r vir [kpc] 2 r max [kpc] 2 r s [kpc] 2 (c/7.0) 0.4 r s [kpc] log 0.0 RMS= 0.15 =0.09 log 0.0 RMS= 0.08 =0.14 log 0.0 RMS= 0.13 =0.08 log 0.0 RMS= 0.14 = r vir [kpc] r max [kpc] r s [kpc] (c/7.0) 0.4 r s [kpc]
21 3.FixedConcentrationMass (figures below) shows that r_e/r_vir doesn't depend on z at fixed M_vir and c. To sum up, it is really the concentration parameter that matters, instead of z- or M_vir-dependences that come in via c(m_vir,z) The size-stellar mass plot is a very different story -- First, you probably don't want to color it by c, but by observables (n_sersic, Delta MS, etc). It would be great if you can inform me what you are after so that I can make the plot with appropriate color coding or with appropriate sample selection. I can do this in no time for both VELA and NIHAO, well with the quantities that I have computed... NIHAO galaxy size - halo (hydro) size, Size=3D stars, color=redshift Somerville+17 median ± 16,84% re/rvir re/rvir re/rvir re/rvir halo r e =0.027r vir Kravtsov r e =0.14r max gas r e =0.19r s z r e =0.19r s (c/7.0) re [kpc] re [kpc] re [kpc] re [kpc] z 1 2 r vir [kpc] 2 r max [kpc] 2 r s [kpc] 2 (c/7.0) 0.4 r s [kpc] 0 log 0.0 RMS= 0.08 =0.08 log 0.0 RMS= 0.15 =0.12 log 0.0 RMS= 0.07 =0.09 log 0.0 RMS= 0.08 = r vir [kpc] r max [kpc] r s [kpc] (c/7.0) 0.4 r s [kpc]
22 Re [kpc] ssfr [Gyr 1 ] UDGdiagnostics NIHAO UDGs, surface density-r e, z = M pc Lange+15(GAMA z<0.1) M [M ] [UDG] 1.0 Σ,e [M pc 2 ] I attached two r_e - M* plots for NIHAO 4.UDGdiagnostics (top panel) showing the z=0 size-mass relation and comparing it with the Lange+15 observational result for nearby LTGs (almost all NIHAO galaxies are late types, with n<2.5); 5.EvoTracks showing the average evolution tracks of MW- and dwarf-size galaxies in NIHAO on various parameter spaces, including r_e - M_star (upper left). The main messages with the two r_e - M* plots are: NIHAO produces a lot of ultra diffuse galaxies in the mass range ^7-9; - the evolution of NIHAO galaxies follow the toy-model motivated by observations, i.e, Delta log(r_e) ~ 0.3 Delta log(m_star), at high-z. At low z, the MWs in NIHAO approach the nearby observational relation, the dwarfs in NIHAO shoot up in r_e and easily become ultra diffuse galaxies. re,? [kpc] 5.EvoTracks.pdf Lange+15 (LTG) MW dwarf log r e =0.3 log M? M? [M ] NIHAO size evolution re,gas [kpc] M gas [M ] z M [M ] Kravtsov 13 (z=0) 1.25 B R re,? [kpc] re,gas [kpc] M [M ] 2 r vir [kpc] 2 r vir [kpc]
23 Sandy: Time behavior: Can you plot C and r_e/r_vir for the Nihou and VELA data as a function of time? Use Nihou with and without the baryons. Do halos maintain their C over time, and do galaxies with small r_e stay small, and vice versa? Fangzhou: c as a function of time is the c-m-z relation I referred to earlier. Individual halos will deviate from the average relation, due to detailed accretion histories and baryonic processes. r_e / r_vir evolution can be seen in 6.SpinHistories, bottom left. Why I used r_s c^0.4? Because of the process of finding it out -- I first tried r_e = 0.17 r_s and r_e = 0.1 r_max, both without concentration (r_max is the radius where circular velocity peaks). Then I find that r_s works better, and adding a c-scaling improves it. There are other halo parameters, say, the Einasto shape (alpha) that can help further, but I don't know if it is worth the effort, given that the improvement is going to be marginal. The whole idea of using halo properties alone to pin down galaxy size is going to hit a limit, as the galaxy only sits at the very center of the halo... one can keep shrinking the scatter of r_e vs r_e_predicted(r_vir, c, alpha, halo param x_4, halo param x_5, ) by adding more x_i, but the scatter is going to converge to an intrinsic scatter, I think. halo Mgas re,?/rvir(t) 2 MW dwarf t [Gyr] t [Gyr] SpinHistories NIHAO spin-, size- histories gas Vrot,gas(t) re,gas/rvir(t) t [Gyr] t [Gyr] z t [Gyr] t [Gyr]
24 DM density vs. Density by Counting Galaxies within 4 and 8 Mpc/h Graham Vanbenthuysen
25 Dear Joel I m sorry to say I won't be attending the meeting this afternoon. Just so you know where we're at, I've calculated the nth-nearest densities and am currently working on calibrating those densities for comparison with Christoph's work. I've also color-coded our previous scatter plots by spin parameter, though I don't see any obvious trends from these by initial inspection. Do you think I should split these graphs into bins to see a more pronounced effect? Graham /30/2017
26 Figures by Graham Shown 23 Oct Measuring λb and Rs vs. Density in Spheres of 4 and 8 h -1 Mpc Graham Vanbenthuysen & Viraj Pandya
DEEP-Theory Meeting 14 April 2017 GALFIT and clump analysis of VELA simulations and comparison with observations VivianTang, Yicheng Guo, David Koo
 DEEP-Theory Meeting 14 April 2017 GALFIT and clump analysis of VELA simulations and comparison with observations VivianTang, Yicheng Guo, David Koo Deep Learning for Galaxies project: Analysis of VELA
DEEP-Theory Meeting 14 April 2017 GALFIT and clump analysis of VELA simulations and comparison with observations VivianTang, Yicheng Guo, David Koo Deep Learning for Galaxies project: Analysis of VELA
Identifying Star-Forming Clumps in CANDELS Galaxies
 Properties of Dark Matter Halos: Environment Density, Mass Loss, and Connection to Galaxy Size Deep Learning Applied to Galaxy Evolution: Identifying Star-Forming Clumps in CANDELS Galaxies Christoph Lee
Properties of Dark Matter Halos: Environment Density, Mass Loss, and Connection to Galaxy Size Deep Learning Applied to Galaxy Evolution: Identifying Star-Forming Clumps in CANDELS Galaxies Christoph Lee
Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review)
 Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review) Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Delivered by Fangzhou Jiang Dali, China, November 2018 See also Claude-Andre s talk and Joel s talk
Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review) Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Delivered by Fangzhou Jiang Dali, China, November 2018 See also Claude-Andre s talk and Joel s talk
THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS
 GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
UCSC Cosmology & Galaxy Research Group 2017 Prof. Joel Primack
 UCSC Cosmology & Galaxy Research Group 2017 Prof. Joel Primack UCSC Grad Students: Christoph Lee christoph28@gmail.com 707-338-9543: Galaxy-Halo Connections, LSS, Halo Properties vs. Density, Stripping,
UCSC Cosmology & Galaxy Research Group 2017 Prof. Joel Primack UCSC Grad Students: Christoph Lee christoph28@gmail.com 707-338-9543: Galaxy-Halo Connections, LSS, Halo Properties vs. Density, Stripping,
Identifying and Characterizing Star-Forming Stellar Clumps
 Deep Learning Applied to Galaxy Evolution: Identifying and Characterizing Star-Forming Stellar Clumps Christoph Lee (UCSC) Joel Primack (UCSC), Marc Huertas-Company (Paris Observatory), Yicheng Guo (University
Deep Learning Applied to Galaxy Evolution: Identifying and Characterizing Star-Forming Stellar Clumps Christoph Lee (UCSC) Joel Primack (UCSC), Marc Huertas-Company (Paris Observatory), Yicheng Guo (University
quenching and structural & morphological evolution: physics
 quenching and structural & morphological evolution: physics rachel somerville Rutgers University with thanks to: Ryan Brennan, Viraj Pandya, Ena Choi Guillermo Barro, Stijn Wuyts, Dale Kocevski, Arjen
quenching and structural & morphological evolution: physics rachel somerville Rutgers University with thanks to: Ryan Brennan, Viraj Pandya, Ena Choi Guillermo Barro, Stijn Wuyts, Dale Kocevski, Arjen
Understanding isolated and satellite galaxies through simulations
 Understanding isolated and satellite galaxies through simulations Kenza Arraki! Blue Waters Graduate Fellow! New Mexico State University! Anatoly Klypin! Daniel Ceverino! Sebastian Trujillo-Gomez! Joel
Understanding isolated and satellite galaxies through simulations Kenza Arraki! Blue Waters Graduate Fellow! New Mexico State University! Anatoly Klypin! Daniel Ceverino! Sebastian Trujillo-Gomez! Joel
CDM Controversies. James Bullock (UC Irvine)
 CDM Controversies James Bullock (UC Irvine) Low stellar mass: feedback can t change DM Core Cusp Tollet et al. 2015 Also: Governato+12; Penarrubia+12; Garrison-Kimmel+13, Di Cintio+14 Low stellar mass:
CDM Controversies James Bullock (UC Irvine) Low stellar mass: feedback can t change DM Core Cusp Tollet et al. 2015 Also: Governato+12; Penarrubia+12; Garrison-Kimmel+13, Di Cintio+14 Low stellar mass:
Face recognition for galaxies: Artificial intelligence brings new tools to astronomy
 April 23, 2018 Contact: Tim Stephens (831) 459-4352; stephens@ucsc.edu Face recognition for galaxies: Artificial intelligence brings new tools to astronomy A 'deep learning' algorithm trained on images
April 23, 2018 Contact: Tim Stephens (831) 459-4352; stephens@ucsc.edu Face recognition for galaxies: Artificial intelligence brings new tools to astronomy A 'deep learning' algorithm trained on images
What Can We Learn from Galaxy Clustering 1: Why Galaxy Clustering is Useful for AGN Clustering. Alison Coil UCSD
 What Can We Learn from Galaxy Clustering 1: Why Galaxy Clustering is Useful for AGN Clustering Alison Coil UCSD Talk Outline 1. Brief review of what we know about galaxy clustering from observations 2.
What Can We Learn from Galaxy Clustering 1: Why Galaxy Clustering is Useful for AGN Clustering Alison Coil UCSD Talk Outline 1. Brief review of what we know about galaxy clustering from observations 2.
Characterizing z~2 Galaxies in HYDRO-ART Simulations and Observations
 Characterizing z~2 Galaxies in HYDRO-ART Simulations and Observations Mark Mozena (UCSC) Sandra Faber, Avishai Dekel, Daniel Ceverino, Joel Primack, Kamson Lai, David Koo, David Rosario, Dale Kocevski,
Characterizing z~2 Galaxies in HYDRO-ART Simulations and Observations Mark Mozena (UCSC) Sandra Faber, Avishai Dekel, Daniel Ceverino, Joel Primack, Kamson Lai, David Koo, David Rosario, Dale Kocevski,
Satellite Galaxy Evolution in Groups & Clusters
 Satellite Galaxy Evolution in Groups & Clusters Andrew Wetzel Yale University Jeremy Tinker (NYU) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) Tinker, Wetzel & Conroy 2011, ArXiv 1107.5046 Wetzel, Tinker & Conroy 2011,
Satellite Galaxy Evolution in Groups & Clusters Andrew Wetzel Yale University Jeremy Tinker (NYU) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) Tinker, Wetzel & Conroy 2011, ArXiv 1107.5046 Wetzel, Tinker & Conroy 2011,
Structure of Dark Matter Halos
 Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Elad Zinger Hebrew University Jerusalem Spineto, 12 June Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Yuval Birnboim, Daisuke Nagai & Andrey Kravtsov
 Elad Zinger Hebrew University Jerusalem IGM@50, Spineto, 12 June 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Yuval Birnboim, Daisuke Nagai & Andrey Kravtsov They re still there! Account for most of the accretion.
Elad Zinger Hebrew University Jerusalem IGM@50, Spineto, 12 June 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Yuval Birnboim, Daisuke Nagai & Andrey Kravtsov They re still there! Account for most of the accretion.
Using Hydro-Simulations to Interpret Observed Kinematic Maps of Star-Forming Galaxies
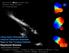 disk from the VELA simulation suite Ceverino, Dekel, Primack, + z = 1.6, young stars Using Hydro-Simulations to Interpret Observed Kinematic Maps of Star-Forming Galaxies Raymond Simons Johns Hopkins University
disk from the VELA simulation suite Ceverino, Dekel, Primack, + z = 1.6, young stars Using Hydro-Simulations to Interpret Observed Kinematic Maps of Star-Forming Galaxies Raymond Simons Johns Hopkins University
QUENCHING AND MORPHOLOGICAL TRANSFORMATIONS. Physics of Groups IAP Mike Hudson, U. Waterloo
 QUENCHING AND MORPHOLOGICAL TRANSFORMATIONS Physics of Groups Conference @ IAP Mike Hudson, U. Waterloo 1 EFFECT OF THE ENVIRONMENT Star-formation quenching via:! Ram-pressure stripping cold gas hot gas
QUENCHING AND MORPHOLOGICAL TRANSFORMATIONS Physics of Groups Conference @ IAP Mike Hudson, U. Waterloo 1 EFFECT OF THE ENVIRONMENT Star-formation quenching via:! Ram-pressure stripping cold gas hot gas
The halo-galaxy connection KITP, May 2017` Assembly bias. Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics
 The halo-galaxy connection KITP, May 2017` Assembly bias Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Halo clustering depends on formation history Gao, Springel & White 2005 The 20% of halos with
The halo-galaxy connection KITP, May 2017` Assembly bias Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Halo clustering depends on formation history Gao, Springel & White 2005 The 20% of halos with
The Mass of the Milky Way from its Satellites. Michael Busha KIPAC/Stanford Collaborators: Phil Marshall, Risa Wechsler
 The Mass of the Milky Way from its Satellites Michael Busha KIPAC/Stanford Collaborators: Phil Marshall, Risa Wechsler Introduction As seen earlier in this conference, the Bolshoi simulation + SHAM does
The Mass of the Milky Way from its Satellites Michael Busha KIPAC/Stanford Collaborators: Phil Marshall, Risa Wechsler Introduction As seen earlier in this conference, the Bolshoi simulation + SHAM does
Galaxy Formation Now and Then
 Galaxy Formation Now and Then Matthias Steinmetz Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam 1 Overview The state of galaxy formation now The state of galaxy formation 10 years ago Extragalactic astronomy in
Galaxy Formation Now and Then Matthias Steinmetz Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam 1 Overview The state of galaxy formation now The state of galaxy formation 10 years ago Extragalactic astronomy in
Nir Mandelker, H.U.J.I.
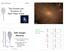
 Compressive vs Solenoidal Turbulence and Non-Linear VDI Nir Mandelker, H.U.J.I. IAU Symposium 319, August 11 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Shigeki Inoue, Daniel Ceverino, Frederic Bournaud, Joel Primack
Compressive vs Solenoidal Turbulence and Non-Linear VDI Nir Mandelker, H.U.J.I. IAU Symposium 319, August 11 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Shigeki Inoue, Daniel Ceverino, Frederic Bournaud, Joel Primack
The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data
 Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
Cosmological Puzzles: Dwarf Galaxies and the Local Group
 Cosmological Puzzles: Dwarf Galaxies and the Local Group Julio F. Navarro Dark-matter-only simulations have highlighted a number of cosmological puzzles Local Group puzzles Missing satellites problem Satellite
Cosmological Puzzles: Dwarf Galaxies and the Local Group Julio F. Navarro Dark-matter-only simulations have highlighted a number of cosmological puzzles Local Group puzzles Missing satellites problem Satellite
pseudo- evolution of halo mass and observable-mass relations Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago
 pseudo- evolution of halo mass and observable-mass relations Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Baseline model for cluster scaling relations Kaiser 1986, 1991 If mass is defined within a spherical
pseudo- evolution of halo mass and observable-mass relations Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Baseline model for cluster scaling relations Kaiser 1986, 1991 If mass is defined within a spherical
Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies
 Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes
 Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes Curtis Struck Iowa State Univ. Work in collab. with B. G. Elmegreen, D. Hunter, H. Salo Lowell Workshop, Oct. 2014 Exponential profiles
Exponential Profile Formation in Simple Models of Scattering Processes Curtis Struck Iowa State Univ. Work in collab. with B. G. Elmegreen, D. Hunter, H. Salo Lowell Workshop, Oct. 2014 Exponential profiles
The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites. Jacqueline Chen
 The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites Jacqueline Chen December 12, 2006 Introduction In the hierarchical assembly of dark matter (DM) halos, progenitor halos merge to form larger systems. Some
The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites Jacqueline Chen December 12, 2006 Introduction In the hierarchical assembly of dark matter (DM) halos, progenitor halos merge to form larger systems. Some
Structure formation in the concordance cosmology
 Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Next Generation (Semi-)Empirical galaxy formation models - Matching individual galaxies
 Next Generation (Semi-)Empirical galaxy formation models - Matching individual galaxies Benjamin Moster (IoA/KICC)! Simon White, Thorsten Naab (MPA), Rachel Somerville (Rutgers), Frank van den Bosch (Yale),
Next Generation (Semi-)Empirical galaxy formation models - Matching individual galaxies Benjamin Moster (IoA/KICC)! Simon White, Thorsten Naab (MPA), Rachel Somerville (Rutgers), Frank van den Bosch (Yale),
DETECTION OF HALO ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE SPLASHBACK RADIUS
 DETECTION OF HALO ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE SPLASHBACK RADIUS Surhud More (Kavli-IPMU) Collaborators: Hironao Miyatake (JPL), Masahiro Takada (Kavli IPMU), David Spergel (Princeton), Rachel Mandelbaum (CMU),
DETECTION OF HALO ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE SPLASHBACK RADIUS Surhud More (Kavli-IPMU) Collaborators: Hironao Miyatake (JPL), Masahiro Takada (Kavli IPMU), David Spergel (Princeton), Rachel Mandelbaum (CMU),
Some useful spherically symmetric profiles used to model galaxies
 Some useful spherically symmetric profiles used to model galaxies de Vaucouleurs R 1/4 law for ellipticals and bulges A good fit to the light profile of many ellipticals and bulges: (constant such that
Some useful spherically symmetric profiles used to model galaxies de Vaucouleurs R 1/4 law for ellipticals and bulges A good fit to the light profile of many ellipticals and bulges: (constant such that
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Jan 2019](/thumbs/88/114537270.jpg) Draft version January 17, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 A mass-dependent slope of the galaxy size mass relation out to z 3: further evidence for a direct relation between median
Draft version January 17, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 A mass-dependent slope of the galaxy size mass relation out to z 3: further evidence for a direct relation between median
A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 05, 2016 Read: Chap 19 04/05/16 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned by next class meeting
A100H Exploring the Universe: Discovering Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 05, 2016 Read: Chap 19 04/05/16 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned by next class meeting
Global Scaling Relations of Spiral Galaxies
 Global Scaling Relations of Spiral Galaxies Aaron A. Dutton Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA), Heidelberg, Germany IAU 311, Galaxy Masses as constraints to Formation Models, Oxford, July 2014 Outline
Global Scaling Relations of Spiral Galaxies Aaron A. Dutton Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA), Heidelberg, Germany IAU 311, Galaxy Masses as constraints to Formation Models, Oxford, July 2014 Outline
high density low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) Springel (2010)
 GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
halo merger histories
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content
 Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
The Stellar Initial Mass Function of Massive Galaxies
 The Stellar Initial Mass Function of Massive Galaxies Aaron A. Dutton Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA), Heidelberg, Germany Quenching and Quiescence, Heidelberg, July 2014 Motivation What is the
The Stellar Initial Mass Function of Massive Galaxies Aaron A. Dutton Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA), Heidelberg, Germany Quenching and Quiescence, Heidelberg, July 2014 Motivation What is the
Origin and Evolution of Disk Galaxy Scaling Relations
 Origin and Evolution of Disk Galaxy Scaling Relations Aaron A. Dutton (CITA National Fellow, University of Victoria) Collaborators: Frank C. van den Bosch (Utah), Avishai Dekel (HU Jerusalem), + DEEP2
Origin and Evolution of Disk Galaxy Scaling Relations Aaron A. Dutton (CITA National Fellow, University of Victoria) Collaborators: Frank C. van den Bosch (Utah), Avishai Dekel (HU Jerusalem), + DEEP2
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative.
 Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation. Carlton Baugh Institute for Computational Cosmology
 A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Carlton Baugh Institute for Computational Cosmology M81 Angel Lopez Sanchez A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Lacey et al. 2015 arxiv:1509.08473
A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Carlton Baugh Institute for Computational Cosmology M81 Angel Lopez Sanchez A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Lacey et al. 2015 arxiv:1509.08473
The Magic Scale of Galaxy Formation: SNe & Hot CGM --> Compaction & BHs
 The Magic Scale of Galaxy Formation: SNe & Hot CGM --> Compaction & BHs Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Silk 75, December 2017 A Characteristic Mass for Galaxy Formation Efficiency
The Magic Scale of Galaxy Formation: SNe & Hot CGM --> Compaction & BHs Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Silk 75, December 2017 A Characteristic Mass for Galaxy Formation Efficiency
Solving. Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics
 Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos
 Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos Mia S. Bovill with Massimo Ricotti University of Maryland The Smallest Galaxies Minihalos DO NOT initiate gas condensation
Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos Mia S. Bovill with Massimo Ricotti University of Maryland The Smallest Galaxies Minihalos DO NOT initiate gas condensation
Structure and substructure in dark matter halos
 Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
The Extragalactic Distance Scale
 One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
Illustris vs Real Universe: Satellite LF, ksz Effect,
 Illustris vs Real Universe: Satellite LF, ksz Effect, Hyunbae Park (KASI), + Many people SFR of High-z Galaxies 2017. 06. 02 (Uleung-Do) Simulation Setup Simulation code : AREPO (moving mesh code) Parameter
Illustris vs Real Universe: Satellite LF, ksz Effect, Hyunbae Park (KASI), + Many people SFR of High-z Galaxies 2017. 06. 02 (Uleung-Do) Simulation Setup Simulation code : AREPO (moving mesh code) Parameter
GALAXIES. Edmund Hodges-Kluck Andrew Ptak
 GALAXIES Edmund Hodges-Kluck Andrew Ptak Galaxy Science with AXIS How does gas get into and out of galaxies? How important is hot accretion for L* or larger galaxies? How does star formation/black hole
GALAXIES Edmund Hodges-Kluck Andrew Ptak Galaxy Science with AXIS How does gas get into and out of galaxies? How important is hot accretion for L* or larger galaxies? How does star formation/black hole
Formation and evolution of CDM halos and their substructure
 Formation and evolution of CDM halos and their substructure 1) cold dark matter and structures on all scales 2) via lactea, z=0 results 3) subhalo evolution Jürg Diemand UC Santa Cruz 4) DM annihilation
Formation and evolution of CDM halos and their substructure 1) cold dark matter and structures on all scales 2) via lactea, z=0 results 3) subhalo evolution Jürg Diemand UC Santa Cruz 4) DM annihilation
halo formation in peaks halo bias if halos are formed without regard to the underlying density, then δn h n h halo bias in simulations
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Bias, the Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Lecture 8 Halo Bias the matter distribution is highly clustered. halos form at the peaks of this distribution 3 2 1 0 halo formation
Physics 463, Spring 07 Bias, the Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Lecture 8 Halo Bias the matter distribution is highly clustered. halos form at the peaks of this distribution 3 2 1 0 halo formation
QSO ABSORPTION LINE STUDIES with the HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE
 QSO ABSORPTION LINE STUDIES with the HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE COLORADO GROUP: JOHN STOCKE, MIKE SHULL, JAMES GREEN, STEVE PENTON, CHARLES DANFORTH, BRIAN KEENEY Results thus far based on: > 300 QSO ABSORBERS
QSO ABSORPTION LINE STUDIES with the HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE COLORADO GROUP: JOHN STOCKE, MIKE SHULL, JAMES GREEN, STEVE PENTON, CHARLES DANFORTH, BRIAN KEENEY Results thus far based on: > 300 QSO ABSORBERS
X- Ray and UV Baryon Accoun1ng
 X- Ray and UV Baryon Accoun1ng Mike Anderson University of Michigan Jess Werk UC Santa Cruz Baryon Budgets of Galaxies Frac%on 24% 24% Stars ISM 24% 24% 4% 0% HVCs Cool CGM Warm CGM Hot Halo A late- type
X- Ray and UV Baryon Accoun1ng Mike Anderson University of Michigan Jess Werk UC Santa Cruz Baryon Budgets of Galaxies Frac%on 24% 24% Stars ISM 24% 24% 4% 0% HVCs Cool CGM Warm CGM Hot Halo A late- type
The Extragalactic Distance Scale
 One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
Observations of galaxy evolution. Pieter van Dokkum
 Observations of galaxy evolution Pieter van Dokkum Overview Broad topic! Split in three conceptually-different parts: ç ç low redshift high redshift 1. Census: what is out there? N (z, L, Mstars, Mdark,
Observations of galaxy evolution Pieter van Dokkum Overview Broad topic! Split in three conceptually-different parts: ç ç low redshift high redshift 1. Census: what is out there? N (z, L, Mstars, Mdark,
Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Outline PART I: The Subhalo Mass Function (van den Bosch, Tormen & Giocoli, 2005) PART II: Statistical Properties of
Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Outline PART I: The Subhalo Mass Function (van den Bosch, Tormen & Giocoli, 2005) PART II: Statistical Properties of
The Distribution of Stellar Mass in Galaxy Clusters since z=1
 The Distribution of Stellar Mass in Galaxy Clusters since z=1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France Adam Muzzin, Henk Hoekstra, Monique Arnaud, Hervé Aussel, Gabriel Pratt, JeanBaptiste Melin, Sean McGee,
The Distribution of Stellar Mass in Galaxy Clusters since z=1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France Adam Muzzin, Henk Hoekstra, Monique Arnaud, Hervé Aussel, Gabriel Pratt, JeanBaptiste Melin, Sean McGee,
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Spin Acquisition, Violent Disks, Compaction and Quenching
 Spin Acquisition, Violent Disks, Compaction and Quenching Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem July 2014 stars 5 kpc Three Provocative Questions concerning high-z massive galaxy formation 1.
Spin Acquisition, Violent Disks, Compaction and Quenching Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem July 2014 stars 5 kpc Three Provocative Questions concerning high-z massive galaxy formation 1.
Violent Disk Instability at z=1-4 Outflows; Clump Evolution; Compact Spheroids
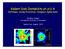 Violent Disk Instability at z=1-4 Outflows; Clump Evolution; Compact Spheroids Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Santa Cruz, August 2013 stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Inflows and Outflows 2. Evolution
Violent Disk Instability at z=1-4 Outflows; Clump Evolution; Compact Spheroids Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Santa Cruz, August 2013 stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Inflows and Outflows 2. Evolution
Are most galaxies in the Universe TSTS:Too shy to shine?
 Are most galaxies in the Universe TSTS:Too shy to shine? R. Giovanelli UAT Workshop @ AO is grand Jan 2015 Some statistical tools with paucity of flashy pix (* ): The HI mass function which tells us the
Are most galaxies in the Universe TSTS:Too shy to shine? R. Giovanelli UAT Workshop @ AO is grand Jan 2015 Some statistical tools with paucity of flashy pix (* ): The HI mass function which tells us the
STAR FORMATION HISTORIES OF GALAXIES FROM Z=0-8
 STAR FORMATION HISTORIES OF GALAXIES FROM Z=0-8 Picture Credit: John Davis Peter Behroozi, Stanford University / KIPAC Risa Wechsler and Charlie Conroy Basic Approach Basic Approach Basic Approach Repeat
STAR FORMATION HISTORIES OF GALAXIES FROM Z=0-8 Picture Credit: John Davis Peter Behroozi, Stanford University / KIPAC Risa Wechsler and Charlie Conroy Basic Approach Basic Approach Basic Approach Repeat
Astronomy 201: Cosmology, Fall Professor Edward Olszewski and Charles Kilpatrick
 Astronomy 201: Cosmology, Fall 2013 Professor Edward Olszewski and Charles Kilpatrick Lab 3, Cluster Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams and the Age of Stars Due October 22, Worth 32 points You may work in groups
Astronomy 201: Cosmology, Fall 2013 Professor Edward Olszewski and Charles Kilpatrick Lab 3, Cluster Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams and the Age of Stars Due October 22, Worth 32 points You may work in groups
Galaxy Ecology. an Environmental Impact Assessment. Frank van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Heidelberg,
Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Heidelberg,
Anthony Aguirre. Physics. Cosmology; inflation; gravity; galaxy formation; Erik Asphaug Earth & Planetary Sciences
 Theoretical Astrophysics Santa Cruz Anthony Aguirre Physics Cosmology; inflation; gravity; galaxy formation; Erik Asphaug Earth & Planetary Sciences Origin and evolution of the solar system; comets and
Theoretical Astrophysics Santa Cruz Anthony Aguirre Physics Cosmology; inflation; gravity; galaxy formation; Erik Asphaug Earth & Planetary Sciences Origin and evolution of the solar system; comets and
The Milky Way. Finding the Center. Milky Way Composite Photo. Finding the Center. Milky Way : A band of and a. Milky Way
 The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8. Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8 Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem Summary to Date We first learned how to construct the Power Spectrum with CDM+baryons. Found CDM agrees with the observed Power Spectrum
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8 Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem Summary to Date We first learned how to construct the Power Spectrum with CDM+baryons. Found CDM agrees with the observed Power Spectrum
The motion of emptiness
 The motion of emptiness Dynamics and evolution of cosmic voids Laura Ceccarelli IATE, Observatorio Astronómico de Córdoba Large scale structure and galaxy flows Quy Nhon, July 2016 Motivations Universe
The motion of emptiness Dynamics and evolution of cosmic voids Laura Ceccarelli IATE, Observatorio Astronómico de Córdoba Large scale structure and galaxy flows Quy Nhon, July 2016 Motivations Universe
ASTRONOMY 460: PROJECT INTRO - GALACTIC ROTATION CURVE
 ASTRONOMY 460: PROJECT INTRO - GALACTIC ROTATION CURVE Snežana Stanimirović, October 6, 2014 1. Introduction This project has two goals: we want to measure the Milky Way (or Galactic) rotation curve by
ASTRONOMY 460: PROJECT INTRO - GALACTIC ROTATION CURVE Snežana Stanimirović, October 6, 2014 1. Introduction This project has two goals: we want to measure the Milky Way (or Galactic) rotation curve by
The sizes of z ~ 6-8 lensed galaxies from the Hubble Frontier Fields data of Abell 2744
 The sizes of z ~ 6-8 lensed galaxies from the Hubble Frontier Fields data of Abell 2744 Kawamata+15, ApJ, 804, 103 Ryota Kawamata The University of Tokyo With: Masafumi Ishigaki, Kazuhiro Shimasaku, Masamune
The sizes of z ~ 6-8 lensed galaxies from the Hubble Frontier Fields data of Abell 2744 Kawamata+15, ApJ, 804, 103 Ryota Kawamata The University of Tokyo With: Masafumi Ishigaki, Kazuhiro Shimasaku, Masamune
Two-halo Galactic Conformity as a Test of Assembly Bias
 Two-halo Galactic Conformity as a Test of Assembly Bias Angela Berti UC San Diego GalFRESCA 2018 1 Galactic Conformity Correlation between star formation rates (SFRs) of central galaxies and their satellites/neighbors
Two-halo Galactic Conformity as a Test of Assembly Bias Angela Berti UC San Diego GalFRESCA 2018 1 Galactic Conformity Correlation between star formation rates (SFRs) of central galaxies and their satellites/neighbors
The Brown Dwarfs of our Milky Way
 The Brown Dwarfs of our Milky Way Benne W. Holwerda (University of Louisville) Isabel van Vledder, Dieuwertje van der Vlucht, Rychard Bouwens, Matthew Kenworthy, Nor Pirzkal Russ Ryan benne.holwerda@gmail.com
The Brown Dwarfs of our Milky Way Benne W. Holwerda (University of Louisville) Isabel van Vledder, Dieuwertje van der Vlucht, Rychard Bouwens, Matthew Kenworthy, Nor Pirzkal Russ Ryan benne.holwerda@gmail.com
GALAXY CLUSTERING. Emmanuel Schaan AST 542 April 10th 2013
 GALAXY CLUSTERING Emmanuel Schaan AST 542 April 10th 2013 INTRODUCTION: SCALES GALAXIES: 10kpc Milky Way: 10kpc, 10 12 Mo GALAXY GROUPS: 100kpc or «poor clusters» Local Group: ~50gal, 3Mpc, 10 13 Mo GALAXY
GALAXY CLUSTERING Emmanuel Schaan AST 542 April 10th 2013 INTRODUCTION: SCALES GALAXIES: 10kpc Milky Way: 10kpc, 10 12 Mo GALAXY GROUPS: 100kpc or «poor clusters» Local Group: ~50gal, 3Mpc, 10 13 Mo GALAXY
Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations and Sunrise Visualizations
 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations and Sunrise Visualizations Joel Primack, UCSC Daniel Ceverino, HU Madrid Avishai Dekel, HU & UCSC Sandra Faber, UCSC Anatoly Klypin, NMSU Patrik Jonsson, Harvard CfA Chris
Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations and Sunrise Visualizations Joel Primack, UCSC Daniel Ceverino, HU Madrid Avishai Dekel, HU & UCSC Sandra Faber, UCSC Anatoly Klypin, NMSU Patrik Jonsson, Harvard CfA Chris
The Structure of the Universe
 Friday January 12, 2018 Panofsky Auditorium The Structure of Universe Joel Primack, UCSC ΛCDM - Double Dark Theory of Cosmology Large Scale Structure of Universe The Galaxy - Halo Connection How Galaxies
Friday January 12, 2018 Panofsky Auditorium The Structure of Universe Joel Primack, UCSC ΛCDM - Double Dark Theory of Cosmology Large Scale Structure of Universe The Galaxy - Halo Connection How Galaxies
Galaxy Ecology. an Environmental Impact Assessment. Frank van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Aspen,
Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Aspen,
The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations
 The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations J. CASADO GÓMEZ (UAM) R. DOMÍNGUEZ-TENREIRO J. OÑORBE (UCA/Irvine) F. MARTINEZ - SERRANO (UMH) A. KNEBE
The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations J. CASADO GÓMEZ (UAM) R. DOMÍNGUEZ-TENREIRO J. OÑORBE (UCA/Irvine) F. MARTINEZ - SERRANO (UMH) A. KNEBE
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology
 The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
The Galaxy Content of Groups and Clusters
 The Galaxy Content of Groups and Clusters results from the SDSS Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zurich) Surhud More (MPIA), Marcello
The Galaxy Content of Groups and Clusters results from the SDSS Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zurich) Surhud More (MPIA), Marcello
Galaxy Cluster Mergers
 Galaxy Cluster Mergers Alexia Schulz Institute for Advanced Study Andrew Wetzel Daniel Holz Mike Warren Talk Overview! Introduction " Why are cluster mergers of interest? " Where will mergers complicate
Galaxy Cluster Mergers Alexia Schulz Institute for Advanced Study Andrew Wetzel Daniel Holz Mike Warren Talk Overview! Introduction " Why are cluster mergers of interest? " Where will mergers complicate
Constraints on dark matter annihilation cross section with the Fornax cluster
 DM Workshop@UT Austin May 7, 2012 Constraints on dark matter annihilation cross section with the Fornax cluster Shin ichiro Ando University of Amsterdam Ando & Nagai, arxiv:1201.0753 [astro-ph.he] Galaxy
DM Workshop@UT Austin May 7, 2012 Constraints on dark matter annihilation cross section with the Fornax cluster Shin ichiro Ando University of Amsterdam Ando & Nagai, arxiv:1201.0753 [astro-ph.he] Galaxy
Homework #7: Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, October points Profs. Rieke
 Homework #7: Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, October 31 30 points Profs. Rieke You are going to work with some famous astronomical data in this homework. The image data
Homework #7: Properties of Galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field Name: Due: Friday, October 31 30 points Profs. Rieke You are going to work with some famous astronomical data in this homework. The image data
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: The Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Frank van den Bosch Yale University, Fall 2018 The Halo Model & Occupation Statistics In this lecture we discuss
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: The Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Frank van den Bosch Yale University, Fall 2018 The Halo Model & Occupation Statistics In this lecture we discuss
The relationship between galaxy and dark matter halo size from z 3 to the present
 Advance Access publication 2017 September 4 doi:10.1093/mnras/stx2040 The relationship between galaxy and dark matter halo size from z 3 to the present Rachel S. Somerville, 1,2 Peter Behroozi, 3 Viraj
Advance Access publication 2017 September 4 doi:10.1093/mnras/stx2040 The relationship between galaxy and dark matter halo size from z 3 to the present Rachel S. Somerville, 1,2 Peter Behroozi, 3 Viraj
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12. The Problems with Satellite Galaxies
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12 The Problems with Satellite Galaxies The Problems with Satellites (1) The Missing Satellites Problem (2) The Too Big to Fail Problem We ll examine potential solutions to each
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12 The Problems with Satellite Galaxies The Problems with Satellites (1) The Missing Satellites Problem (2) The Too Big to Fail Problem We ll examine potential solutions to each
The cosmic distance scale
 The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
Properties of dark matter haloes as a function of local environment density
 Advance Access publication 2016 December 23 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw3348 Properties of dark matter haloes as a function of local environment density Christoph T. Lee, 1 Joel R. Primack, 1 Peter Behroozi,
Advance Access publication 2016 December 23 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw3348 Properties of dark matter haloes as a function of local environment density Christoph T. Lee, 1 Joel R. Primack, 1 Peter Behroozi,
Arvind Borde / AST 10, Week 8: Galaxies I
 Arvind Borde / AST 10, Week 8: Galaxies I It s been known by us, from the dawn of us, that there are stars in the sky. There are also hazy patches called nebulae: objects outside the solar system that
Arvind Borde / AST 10, Week 8: Galaxies I It s been known by us, from the dawn of us, that there are stars in the sky. There are also hazy patches called nebulae: objects outside the solar system that
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy
 Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
Background and Theory
 Homework 4. Cluster HR Diagrams and the Age of Stars NAME: Due: Thursday, October 7, 2010 In Class Astro 201: Cosmology Prof. Bechtold In this assignment, we are going to measure the age of stars in star
Homework 4. Cluster HR Diagrams and the Age of Stars NAME: Due: Thursday, October 7, 2010 In Class Astro 201: Cosmology Prof. Bechtold In this assignment, we are going to measure the age of stars in star
A galaxy is a self-gravitating system composed of an interstellar medium, stars, and dark matter.
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is a Galaxy? It s surprisingly difficult to answer the question what is a galaxy? Many astronomers seem content to say I know one when I see one. But one possible definition
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is a Galaxy? It s surprisingly difficult to answer the question what is a galaxy? Many astronomers seem content to say I know one when I see one. But one possible definition
The Masses of Galaxies from the Galaxy-Halo Connection
 with Charlie Conroy (Princeton) Peter Behroozi (KIPAC/Stanford) R isa Wechsler The Masses of Galaxies from the Galaxy-Halo Connection The Basic Idea Theory: We now have a reasonable accounting for the
with Charlie Conroy (Princeton) Peter Behroozi (KIPAC/Stanford) R isa Wechsler The Masses of Galaxies from the Galaxy-Halo Connection The Basic Idea Theory: We now have a reasonable accounting for the
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
From quasars to dark energy Adventures with the clustering of luminous red galaxies
 From quasars to dark energy Adventures with the clustering of luminous red galaxies Nikhil Padmanabhan 1 1 Lawrence Berkeley Labs 04-15-2008 / OSU CCAPP seminar N. Padmanabhan (LBL) Cosmology with LRGs
From quasars to dark energy Adventures with the clustering of luminous red galaxies Nikhil Padmanabhan 1 1 Lawrence Berkeley Labs 04-15-2008 / OSU CCAPP seminar N. Padmanabhan (LBL) Cosmology with LRGs
