Detection of Earth-like planets
|
|
|
- David Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Planets and life Successful detections of extrasolar giant planets suggests that planetary systems may be fairly common could we detect Earthlike planets? is it likely that such planets would have life? how would we know? Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 1 Detection of Earth-like planets Doppler shift technique will not work Two possible strategies transit detection WASP ground-based (now) CoRoT space-based (now) Kepler (NASA) within 5 years? direct imaging requires space-based interferometer multiple telescopes acting as one Darwin, TPF >10 years One system of Earth-mass planets has been found around a pulsar! not well understood, but clearly not really Earth-like Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 2 1
2 Life on Earth: the fossil record Oldest rocks ~3.8 Gyr old Oldest fossils ~3.5 Gyr bacteria Oldest eukaryotes (nucleated cells) ~2 Gyr coincide with rise of atmospheric oxygen Oldest multicellular organisms ~550 Myr Early hominids ~5 Myr Fossil stromatolites, W. Australia Shark Bay Dickinsonia, Vendian fossil Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 3 Life on Earth: implications Life appears very quickly easy process? but >80% of history of life consists of single-celled organisms becoming multicellular is hard? on the other hand, it evolved several times... and intelligence appears only in last 0.001% of life s timeline intelligence is hard? Main elements used by life are very abundant Organic (carbon-based) compounds form easily in early-earth conditions Route from there to DNA+protein organisms not well understood RNA world first? Liquid water looks essential Arguing from a single example is intrinsically unsafe and there is clear selection bias (we exist!) Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 4 2
3 Life elsewhere: the solar system Venus looks superficially very similar to Earth but runaway greenhouse effect leads to surface temperature of 745 K (472 C) Mars is too small to keep its atmosphere evidence for running water early in its history life might have evolved, but not complex life finding bacterial fossils would be major step: confirm that originating life is easy Europa is heated by tidal forces icy crust probably overlies liquid water ocean Magellan HST Galileo Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 5 Life elsewhere: other stars Criteria for candidate stars: long enough lifetime life unlikely to evolve in 10-millionyear lifetime of 10-solar-mass star star of 1.7 M sun has 2 Gyr main sequence llfetime classes FGKM are OK high heavy element content evidence suggests this is required for planet formation not stars in halo stable star, stable orbits not close binary? not very low mass stars (often unstable flare stars)? Many stars satisfy these criteria I II Stars within 25 pc III IV V WD M K G F A B Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 6 3
4 Habitable zones Liquid water probably essential for life candidate planets must be in appropriate temperature range temperature basically determined by distance from star habitable zone should allow for stellar evolution continuously habitable zone also affected by size of planet problem for low mass stars: tidal locking planets face star extremes of temperature J.F. Kasting et al. Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 7 Planets in habitable zones Some observed extrasolar planets are in habitable zone remember these are (probably gas) giants remember detection method biased in favour of planets near stars certainly no evidence against habitable planets also possibility of rocky satellites of gas giants (Ganymede, Callisto and Titan are Mercury-sized) Extrasolar planets J.F. Kasting et al. Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 8 4
5 Signs of life Oxygen is highly reactive not stable in atmosphere: maintained by plants earliest fossils already photosynthesising oxygen in atmosphere good indicator of life even in early stages spectroscopic detection possible in infra-red to reduce background from star good for 3-atom molecules detect CO 2 (atmosphere), H 2 O (oceans), O 3 (life) Simulated image and spectrum from DARWIN homepage Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 9 Life like us? How probable is evolution of intelligent organisms with technological civilisation? Drake equation (Frank Drake, SETI pioneer) Number of communicating civilisations = rate of formation of suitable stars x fraction of these stars with planets x number of Earth-like planets per system x fraction of such planets which develop life x fraction of life-bearing planets evolving intelligence x fraction of intelligent species developing technology x average lifetime of such a civilisation information obtainable on factors marked last three very difficult to estimate rough guess: assume 10 stars/year and all fractions = 0.1; then number of civilisations = average lifetime/10000 known high?? high? controversial????? Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 10 5
6 Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Drake equation suggests other civilisations may exist only way to confirm this is direct detection obvious method of communication is radio galaxy fairly transparent to appropriate wavelengths travels at speed of light fairly easy to send and detect radio covers a wide wavelength range! need to guess appropriate wavelength SETI@home: Berkeley 21 cm? (hydrogen) programme using Arecibo telescope at 21 cm microwaves? (cosmic background) would we recognise a signal? probably: information-carrying signal very different from natural sources would we be able to decode it? much more problematic Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 11 What if. Conversations with alien intelligence requires patience! disc of Milky Way is ~40000 light years in radius optimistically suppose 1000 civilisations nearest one, on average, 2000 light years away wait 4000 years for answer: not very practical so, don t converse, just send Encyclopaedia Britannica and assume they will too advantage: will also take 4000 years for their invasion fleet to get here.. They re not there because they re not here? unmanned (unaliened?) probes could in principle colonise Galaxy fact that this has not happened suggests no advanced civilisations? advanced civilisations are all eco-warriors, robot probes environmentally unfriendly? Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 12 6
7 Conclusions Evidence from history of life on Earth is that origin of life may be easy evidence of past existence of life on Mars would be strong confirmation of this Basic criteria for stars suitable for life are not too difficult to satisfy detection of Earth-like planets around nearby stars possible on year timescale spectroscopy could provide evidence for life on these planets Other technological civilisations might exist probability depends on hard-to-estimate factors radio searches so far found nothing, but you never know even if they do exist, United Federation of Planets probably precluded by large distances (at least on basis of current physics) Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 13 7
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe. Earliest Life Forms. When did life arise on Earth? Fossils in Sedimentary Rock. Fossils in Sedimentary Rock
 Chapter 24 Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of life? When did life arise on Earth? Earliest
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of life? When did life arise on Earth? Earliest
Extrasolar Planets What are the odds?
 Honors 228: Astrobiology using Bennett and Shostak Chapter 12 overview Spring 2007 Dr. H. Geller What s talked about The Drake Equation (12.1) The Question of Intelligence (12.2) Searching for Intelligence
Honors 228: Astrobiology using Bennett and Shostak Chapter 12 overview Spring 2007 Dr. H. Geller What s talked about The Drake Equation (12.1) The Question of Intelligence (12.2) Searching for Intelligence
Searching for Life: Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds. Life in the Universe. Earliest Fossils. Laboratory Experiments.
 Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
Young Solar-like Systems
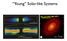 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Astrobiology: The Semester in Review
 A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
Simon P. Balm Astro 5 Test #3 Sample Questions
 Simon P. Balm Astro 5 Test #3 Sample Questions 1. What do we mean by the general habitability of a planet? A. the suitability for Life on it surface B. the suitability for Life beneath its surface C. its
Simon P. Balm Astro 5 Test #3 Sample Questions 1. What do we mean by the general habitability of a planet? A. the suitability for Life on it surface B. the suitability for Life beneath its surface C. its
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 28. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
NSCI EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION. Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
Habitability Outside the Solar System. A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller
 Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Chapter 24: Life in the Universe
 Chapter 24 Lecture Chapter 24: Life in the Universe Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning: When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of
Chapter 24 Lecture Chapter 24: Life in the Universe Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning: When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of
Habitable Planets: 2 Estimating f s "
 Habitable Planets: 2 Estimating f s " Stellar Requirements (f s )" We assume that our planet needs to orbit a star" Leaves out planets around brown dwarfs" Leaves out nomad planets (may be many)" About
Habitable Planets: 2 Estimating f s " Stellar Requirements (f s )" We assume that our planet needs to orbit a star" Leaves out planets around brown dwarfs" Leaves out nomad planets (may be many)" About
N = R * f p n e f l f i f c L
 Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 106 B6 Eng Hall This Class (Lecture 10): Nature of Life Next Class: Nucleic Acids Some Oral Presentation on Feb 16 th and 18 th! Mike Somers Chris Kramer Sarah Goldrich
Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 106 B6 Eng Hall This Class (Lecture 10): Nature of Life Next Class: Nucleic Acids Some Oral Presentation on Feb 16 th and 18 th! Mike Somers Chris Kramer Sarah Goldrich
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Life in the Universe
 Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
12/5/ Life on Earth. Chapter 19: Life in the Universe. When did life arise on Earth? Earliest Life Forms. Important Stuff (Section 001)
 Important Stuff (Section 001) The Final Exam is Thursday, December 22, 8:00 10:00 am The Final Exam will be given in: Willey 175 Don t come to Anderson 210. No one will be there. No one. Bring 2 pencils
Important Stuff (Section 001) The Final Exam is Thursday, December 22, 8:00 10:00 am The Final Exam will be given in: Willey 175 Don t come to Anderson 210. No one will be there. No one. Bring 2 pencils
Physics can only take us so far!
 Physics can only take us so far! The usual approach of science of constructing a mathematical model cannot answer the questions of why there should be a universe for the model to describe. Why does the
Physics can only take us so far! The usual approach of science of constructing a mathematical model cannot answer the questions of why there should be a universe for the model to describe. Why does the
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
Measuring Distances to Galaxies. Galaxies in Motion. Hubble s Law. Galaxy Redshifts. Type Ia Supernovae. Supernovae are Good Standard Candles
 Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere
 Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere Where is everybody? Fermi s paradox (1950 lunch conversation) Assume 3 levels of extraterrestrial civilizations ETC1, like ours (energy resources of a planet) ETC2,
Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere Where is everybody? Fermi s paradox (1950 lunch conversation) Assume 3 levels of extraterrestrial civilizations ETC1, like ours (energy resources of a planet) ETC2,
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence
 Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
n p = n e for stars like Sun f s = fraction of stars with suitable properties
 Habitable Planets n e Number of planets, per planetary system that are suitable for life n e = n p x f s planetary stellar n p = n e for stars like Sun f s = fraction of stars with suitable properties
Habitable Planets n e Number of planets, per planetary system that are suitable for life n e = n p x f s planetary stellar n p = n e for stars like Sun f s = fraction of stars with suitable properties
Our Planetary System. Chapter 7
 Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
II Planet Finding.
 II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
Planets & Life. Planets & Life PHYS 214. Please start all class related s with 214: 214: Dept of Physics (308A)
 Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s lecture Assignment 1 marked will hand
Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s lecture Assignment 1 marked will hand
Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion
 Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder
Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Kira Bonk ascension.html
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Planet discovery accounced Feb. 3
 Announcements The third homework is due Monday, Feb. 9. The first exam is Wednesday, Feb. 11. Monday, Feb. 9, will be a review, please e-mail questions. If you need help to go an Astronomy tutorial; the
Announcements The third homework is due Monday, Feb. 9. The first exam is Wednesday, Feb. 11. Monday, Feb. 9, will be a review, please e-mail questions. If you need help to go an Astronomy tutorial; the
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Presentations. Outline. ! Nicholas Langhammer esp_sociopol_washingtondc01.
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 13): What is n p? Anna Dorn Praneet Sahgal HW 2 Nicholas Langhammer http://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/sociopolitica/ esp_sociopol_washingtondc01.htm Next Class: Life on
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 13): What is n p? Anna Dorn Praneet Sahgal HW 2 Nicholas Langhammer http://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/sociopolitica/ esp_sociopol_washingtondc01.htm Next Class: Life on
The Search of Life In The Solar System
 The Search of Life In The Solar System 1 BY: Yasir M. O. ABBAS October 2017 Exploring New Worlds In Space 2 3 Evidences Is there an evidence for life out of the Earth??? Is there evidence that there isn
The Search of Life In The Solar System 1 BY: Yasir M. O. ABBAS October 2017 Exploring New Worlds In Space 2 3 Evidences Is there an evidence for life out of the Earth??? Is there evidence that there isn
The Physical Basis of Life
 Origins of Life Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 19 Learning Outcomes: The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry.
Origins of Life Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 19 Learning Outcomes: The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry.
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets
 Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology
 Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI)
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) Our goals for learning What is the Drake equation? How many habitable planets have life? How many civilizations are out there? How does SETI work? Can
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) Our goals for learning What is the Drake equation? How many habitable planets have life? How many civilizations are out there? How does SETI work? Can
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets
 Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets star--about 10 11 in our galaxy. Average separation is a few light years. (Compare with size of Galaxy: about 100,000 light years) planet--indirect
Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets star--about 10 11 in our galaxy. Average separation is a few light years. (Compare with size of Galaxy: about 100,000 light years) planet--indirect
Today s Class. Last Class. Earliest Life Forms. Today s Class: Search for Life. When did life arise on Earth?
 Today s Class: Search for Life Exam #3 on Friday, April 26: Covers all the reading March 23 rd (Earth) through April 23 rd (Exoplanets). Includes homework assignments 7, 8, 9. Includes Space in the News
Today s Class: Search for Life Exam #3 on Friday, April 26: Covers all the reading March 23 rd (Earth) through April 23 rd (Exoplanets). Includes homework assignments 7, 8, 9. Includes Space in the News
Intelligent Life in the Universe
 Intelligent Life in the Universe Lecture 33 APoD: Easter Island Eclipse In-Class Question 1) Do you think life exists elsewhere in the Universe? a) Yes b) No c) Don t know d) Don t care 2 33-1 Lecture
Intelligent Life in the Universe Lecture 33 APoD: Easter Island Eclipse In-Class Question 1) Do you think life exists elsewhere in the Universe? a) Yes b) No c) Don t know d) Don t care 2 33-1 Lecture
In-Class Question 1) Do you think that there are planets outside the solar which would be habitable for human life?
 The Habitability of Worlds Lecture 31 NASA: The Visible Earth In-Class Question 1) Do you think that there are planets outside the solar which would be habitable for human life? a) 1 (yes, definitely)
The Habitability of Worlds Lecture 31 NASA: The Visible Earth In-Class Question 1) Do you think that there are planets outside the solar which would be habitable for human life? a) 1 (yes, definitely)
The evolution of a Solar-like system. Young Solar-like Systems. Searching for Extrasolar Planets: Motivation
 Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Other migration processes. New transiting hot Jupiters from last week. First success from CoRoT. Kozai mechanism
 Other migration processes Previous lecture: Migration through planet-disk interactions Type I: low-mass planet (does not clear a gap in disk) Type II: high-mass panet (has cleared gap) Type III: runaway
Other migration processes Previous lecture: Migration through planet-disk interactions Type I: low-mass planet (does not clear a gap in disk) Type II: high-mass panet (has cleared gap) Type III: runaway
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site:
 ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 37: Life in the Universe [4/18/07] Announcements Habitability of
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 37: Life in the Universe [4/18/07] Announcements Habitability of
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder. AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life
 Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life The Drake Equation: N = N * f pl n hab f L f C f T L/T Stars? Planets? Habitable Origin Complex Intelligence, Lifetime planets?
Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life The Drake Equation: N = N * f pl n hab f L f C f T L/T Stars? Planets? Habitable Origin Complex Intelligence, Lifetime planets?
Cosmology Overview (so far): Cosmology Overview (so far): The Age of the Universe. The Big Bang. The Age of the Universe
 Cosmology Overview (so far): The Universe: Everything Observable Universe: Everything we can The Universe has no special locations No If no, then no Cosmology Overview (so far): Oblers s Paradox: The sky
Cosmology Overview (so far): The Universe: Everything Observable Universe: Everything we can The Universe has no special locations No If no, then no Cosmology Overview (so far): Oblers s Paradox: The sky
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Review. Semester Recap. Nature of Light. Wavelength. Red/Blue Light 4/30/18
 https://www.theverge.com/2018/ 3/10/17104188/melodysheeptime-lapse-universe-earthformation-watch Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Review Semester Recap ³Light and Radiation ³The Sun ³Measuring
https://www.theverge.com/2018/ 3/10/17104188/melodysheeptime-lapse-universe-earthformation-watch Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Review Semester Recap ³Light and Radiation ³The Sun ³Measuring
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 8. The scale of time and nature of worlds (Page
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 8. The scale of time and nature of worlds (Page
Honors 228 Astrobiology w/ Dr. H. Geller Meeting #2 - Physical Origins. Presented 21 January 2010
 Honors 228 Astrobiology w/ Dr. H. Geller Meeting #2 - Physical Origins Presented 21 January 2010 The Phase Diagram What is the name of the phase change from liquid to gas? A Vaporization B Condensation
Honors 228 Astrobiology w/ Dr. H. Geller Meeting #2 - Physical Origins Presented 21 January 2010 The Phase Diagram What is the name of the phase change from liquid to gas? A Vaporization B Condensation
About the Midterm. Same rules. About the same length/structure Objects in the Solar System through Stars & Galaxy Classification. Use your index card!
 ABOUT THE MIDTERM About the Midterm Same rules Use your index card! About the same length/structure Objects in the Solar System through Stars & Galaxy Classification roughly 33% Solar System topics & 67%
ABOUT THE MIDTERM About the Midterm Same rules Use your index card! About the same length/structure Objects in the Solar System through Stars & Galaxy Classification roughly 33% Solar System topics & 67%
Life Carbon+Water based?
 Life in the Universe 1 example of Life - Carbon-water based (on Earth) 1 example of intelligence able to communicate with other intelligent life for about 75 years (us humans) Intelligence = able to use
Life in the Universe 1 example of Life - Carbon-water based (on Earth) 1 example of intelligence able to communicate with other intelligent life for about 75 years (us humans) Intelligence = able to use
Planets Everywhere. Dave Stevenson Caltech. Insight Cruises, January 21, 2018
 Planets Everywhere Dave Stevenson Caltech Insight Cruises, January 21, 2018 Galileo s notebook (1610) Detecting Planets by the Transit Method Conclusion (So Far) Planets are common Most
Planets Everywhere Dave Stevenson Caltech Insight Cruises, January 21, 2018 Galileo s notebook (1610) Detecting Planets by the Transit Method Conclusion (So Far) Planets are common Most
Lecture 23: Jupiter. Solar System. Jupiter s Orbit. The semi-major axis of Jupiter s orbit is a = 5.2 AU
 Lecture 23: Jupiter Solar System Jupiter s Orbit The semi-major axis of Jupiter s orbit is a = 5.2 AU Jupiter Sun a Kepler s third law relates the semi-major axis to the orbital period 1 Jupiter s Orbit
Lecture 23: Jupiter Solar System Jupiter s Orbit The semi-major axis of Jupiter s orbit is a = 5.2 AU Jupiter Sun a Kepler s third law relates the semi-major axis to the orbital period 1 Jupiter s Orbit
Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)
![Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)](/thumbs/77/76655554.jpg) Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Chapter 24 Lif i e n the Universe
 Chapter 24 Life in the Universe ASTROBIOLOGY A FIELD OF SERIOUS STUDY NASA ASTROBIOLGY Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe ASTROBIOLOGY A FIELD OF SERIOUS STUDY NASA ASTROBIOLGY Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 16 4 Moons SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.d, 8.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How did Earth s moon
CHAPTER 16 4 Moons SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.d, 8.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How did Earth s moon
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section XII
 ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section XII Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section XII Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
PLANETARY SYSTEM: FROM GALILEO TO EXOPLANETS
 PLANETARY SYSTEM: FROM GALILEO TO EXOPLANETS Rosa M. Ros Technical University of Catalonia, Barcelona (Spain) Abstract When in 1610 Galileo Galilei looked at Jupiter with the use of his telescope, he saw
PLANETARY SYSTEM: FROM GALILEO TO EXOPLANETS Rosa M. Ros Technical University of Catalonia, Barcelona (Spain) Abstract When in 1610 Galileo Galilei looked at Jupiter with the use of his telescope, he saw
Light. Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation. Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays
 Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
Class Announcements. Solar System. Objectives for today. Will you read Chap 32 before Wed. class? Chap 32 Beyond the Earth
 Class Announcements Please fill out an evaluation for this class. If you release your name I ll I give you quiz credit. Will you read Chap 32 before Wed. class? a) Yes b) No Chap 32 Beyond the Earth Objectives
Class Announcements Please fill out an evaluation for this class. If you release your name I ll I give you quiz credit. Will you read Chap 32 before Wed. class? a) Yes b) No Chap 32 Beyond the Earth Objectives
Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry. Exoplanets
 Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry Exoplanets Outline What is an exoplanet? Why are they interesting? How can we find them? Exolife?? The future... Jon Thaler Exoplanets 2 What is an Exoplanet? Most
Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry Exoplanets Outline What is an exoplanet? Why are they interesting? How can we find them? Exolife?? The future... Jon Thaler Exoplanets 2 What is an Exoplanet? Most
telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us?
 The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
Astronomy 141 Life in the Universe Professor Gaudi Homework #4 Solutions
 Astronomy 141 Life in the Universe Autumn Quarter 008 Prof Gaudi Homework #4 Solutions These questions concern the concept of targets for searches for extrasolar planets specifically (a) the number of
Astronomy 141 Life in the Universe Autumn Quarter 008 Prof Gaudi Homework #4 Solutions These questions concern the concept of targets for searches for extrasolar planets specifically (a) the number of
Planets are plentiful
 Extra-Solar Planets Planets are plentiful The first planet orbiting another Sun-like star was discovered in 1995. We now know of 209 (Feb 07). Including several stars with more than one planet - true planetary
Extra-Solar Planets Planets are plentiful The first planet orbiting another Sun-like star was discovered in 1995. We now know of 209 (Feb 07). Including several stars with more than one planet - true planetary
[26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17)
![[26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17) [26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17)](/thumbs/79/79849652.jpg) 1 [26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17) Upcoming Items Homework #12 due next class. Read chapters 24.4-24.5 for Thursday Have you done the course evaluation yet? If not, please do so! FINAL EXAM on Wednesday,
1 [26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17) Upcoming Items Homework #12 due next class. Read chapters 24.4-24.5 for Thursday Have you done the course evaluation yet? If not, please do so! FINAL EXAM on Wednesday,
The Solar System consists of
 The Universe The Milky Way Galaxy, one of billions of other galaxies in the universe, contains about 400 billion stars and countless other objects. Why is it called the Milky Way? Welcome to your Solar
The Universe The Milky Way Galaxy, one of billions of other galaxies in the universe, contains about 400 billion stars and countless other objects. Why is it called the Milky Way? Welcome to your Solar
Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Akos Kereszturi Editorial Board member
 Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Akos Kereszturi Editorial Board member Research Center for Astronomy and Earth Sciences Hungarian Academy of Sciences Hungary Biography Dr. Akos Kereszturi Akos
Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Akos Kereszturi Editorial Board member Research Center for Astronomy and Earth Sciences Hungarian Academy of Sciences Hungary Biography Dr. Akos Kereszturi Akos
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Alex Bara
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 10): Origin of the Moon Ilana Strauss Next Class: Our Planet Scott Huber Thomas Hymel HW 2! Alex Bara http://userpages.bright.net/~phobia/main.htm! Margaret Sharp http://hubpages.com/hub/proof-that-ufos-exist---
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 10): Origin of the Moon Ilana Strauss Next Class: Our Planet Scott Huber Thomas Hymel HW 2! Alex Bara http://userpages.bright.net/~phobia/main.htm! Margaret Sharp http://hubpages.com/hub/proof-that-ufos-exist---
1 of 5 4/21/2015 6:40 PM
 1 of 5 4/21/2015 6:40 PM 1. Which of the following lists the outer planets in order of increasing mass?,,,,,,,,,,,, 2. The surface structure of 's largest satellite, Titan, is completely unknown because
1 of 5 4/21/2015 6:40 PM 1. Which of the following lists the outer planets in order of increasing mass?,,,,,,,,,,,, 2. The surface structure of 's largest satellite, Titan, is completely unknown because
Life in the Universe: More E. Coli than E.T.
 Life in the Universe: More E. Coli than E.T. Dr Euan D. Bennet University of Glasgow Euan.Bennet@glasgow.ac.uk What do aliens look like? What do aliens look like? UNLIKELY* * But not impossible! MORE LIKELY**
Life in the Universe: More E. Coli than E.T. Dr Euan D. Bennet University of Glasgow Euan.Bennet@glasgow.ac.uk What do aliens look like? What do aliens look like? UNLIKELY* * But not impossible! MORE LIKELY**
A Recipe for Life on Earth... and elsewhere?
 A Recipe for Life on Earth... and elsewhere? We know that life evolved on Earth. But did it also form on other planets, either in our Solar System or elsewhere? At the moment, we just don't know. But we
A Recipe for Life on Earth... and elsewhere? We know that life evolved on Earth. But did it also form on other planets, either in our Solar System or elsewhere? At the moment, we just don't know. But we
General Considerations! Habitable Planets! Key Requirement: a Liquid! Water Phase Diagram! 2/3/11!
 General Considerations! Habitable Planets! Number of planets, per planetary system, suitable for life (n e )! Useful to break into 2 factors! n e = n p x f s! n p = n e for stars like Sun! f s is fraction
General Considerations! Habitable Planets! Number of planets, per planetary system, suitable for life (n e )! Useful to break into 2 factors! n e = n p x f s! n p = n e for stars like Sun! f s is fraction
Extrasolar Planets. Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects
 Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
UNIT 3: Chapter 8: The Solar System (pages )
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
Big Questions About the Existence of Earth-like Planets. James Kasting Department of Geosciences Penn State University
 Big Questions About the Existence of Earth-like Planets James Kasting Department of Geosciences Penn State University Talk outline Introduction: What are the basic planetary requirements for life, and
Big Questions About the Existence of Earth-like Planets James Kasting Department of Geosciences Penn State University Talk outline Introduction: What are the basic planetary requirements for life, and
Overview of Solar System
 Overview of Solar System The solar system is a disk Rotation of sun, orbits of planets all in same direction. Most planets rotate in this same sense. (Venus, Uranus, Pluto are exceptions). Angular momentum
Overview of Solar System The solar system is a disk Rotation of sun, orbits of planets all in same direction. Most planets rotate in this same sense. (Venus, Uranus, Pluto are exceptions). Angular momentum
Planets and Brown Dwarfs
 Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Electromagnetic Radiation.
 Electromagnetic Radiation http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html CLASSICALLY -- ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION Classically, an electromagnetic wave can be viewed as a self-sustaining wave of electric and magnetic
Electromagnetic Radiation http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html CLASSICALLY -- ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION Classically, an electromagnetic wave can be viewed as a self-sustaining wave of electric and magnetic
Life in the Universe. Key Concepts: Lecture 35: Admin. 11/21/17. All Formulae (for final):
 Admin. 11/21/17 Key Concepts: Lecture 35: 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period
Admin. 11/21/17 Key Concepts: Lecture 35: 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period
1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day. 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space
 Vocabulary: Match the vocabulary terms on the left with the definitions on the right 1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space 3. Orbital Period
Vocabulary: Match the vocabulary terms on the left with the definitions on the right 1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space 3. Orbital Period
The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals. Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV
 The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV Associated Universities, Inc; April/2016 2 Preliminary thoughts a. How certain are you that other
The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV Associated Universities, Inc; April/2016 2 Preliminary thoughts a. How certain are you that other
Terrestrial World Atmospheres
 1 Terrestrial World Atmospheres Some terrestrial worlds have atmospheres. Others don't. Venus and Mars have thick/thin atmospheres respectively made mostly of Carbon Dioxide. Earth is the oddball with
1 Terrestrial World Atmospheres Some terrestrial worlds have atmospheres. Others don't. Venus and Mars have thick/thin atmospheres respectively made mostly of Carbon Dioxide. Earth is the oddball with
Lecture 44: The Future of Life in the Solar System
 Lecture 44 The Future of Life in the Solar System Astronomy 141 Autumn 2009 This lecture is about the future of life in the Solar System. The Sun today is a steadily shining, middle-aged Main Sequence
Lecture 44 The Future of Life in the Solar System Astronomy 141 Autumn 2009 This lecture is about the future of life in the Solar System. The Sun today is a steadily shining, middle-aged Main Sequence
8. Solar System Origins
 8. Solar System Origins Chemical composition of the galaxy The solar nebula Planetary accretion Extrasolar planets Our Galaxy s Chemical Composition es Big Bang produced hydrogen & helium Stellar processes
8. Solar System Origins Chemical composition of the galaxy The solar nebula Planetary accretion Extrasolar planets Our Galaxy s Chemical Composition es Big Bang produced hydrogen & helium Stellar processes
The Jamie Drake Equation
 The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Life in the Universe
 Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
Planets in other Star Systems
 Planets in other Star Systems test out how planets are formed with more examples first extrasolar planet observed in 1995. In Jan 2000, 28 observed and now >3700 confirmed (10/2017). Many systems with
Planets in other Star Systems test out how planets are formed with more examples first extrasolar planet observed in 1995. In Jan 2000, 28 observed and now >3700 confirmed (10/2017). Many systems with
Finding habitable earths around white dwarfs with a robotic telescope transit survey
 Finding habitable earths around white dwarfs with a robotic telescope transit survey Eric Agol Associate Professor Department of Astronomy University of Washington (UW) Feb 16, 2011 1 Evolution of a Sun-Like
Finding habitable earths around white dwarfs with a robotic telescope transit survey Eric Agol Associate Professor Department of Astronomy University of Washington (UW) Feb 16, 2011 1 Evolution of a Sun-Like
CHAPTER 6. The Solar System
 CHAPTER 6 The Solar System 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System The Greeks knew about 5 planets other than Earth They also knew about two other objects that were not planets or stars: meteors and comets
CHAPTER 6 The Solar System 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System The Greeks knew about 5 planets other than Earth They also knew about two other objects that were not planets or stars: meteors and comets
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Requirements for Life. What is Life? Definition of Life. One of the biggest questions in astronomy is whether life exists elsewhere in the universe
 Requirements for Life One of the biggest questions in astronomy is whether life exists elsewhere in the universe Before we discuss the possibility of life elsewhere, we must have a better understanding
Requirements for Life One of the biggest questions in astronomy is whether life exists elsewhere in the universe Before we discuss the possibility of life elsewhere, we must have a better understanding
Helmut Lammer Austrian Academy of Sciences, Space Research Institute Schmiedlstr. 6, A-8042 Graz, Austria (
 The search of habitable Earth-like exoplanets Helmut Lammer Austrian Academy of Sciences, Space Research Institute Schmiedlstr. 6, A-8042 Graz, Austria (email: helmut.lammer@oeaw.ac.at) Graz in Space 2008
The search of habitable Earth-like exoplanets Helmut Lammer Austrian Academy of Sciences, Space Research Institute Schmiedlstr. 6, A-8042 Graz, Austria (email: helmut.lammer@oeaw.ac.at) Graz in Space 2008
The Search for Extra-terrestrial. Is there anybody out there?
 The Search for Extra-terrestrial Intelligence! Is there anybody out there? Summary: we will investigate (a) the Drake Equation and (b) the factors that determine how many, if any, other civilizations
The Search for Extra-terrestrial Intelligence! Is there anybody out there? Summary: we will investigate (a) the Drake Equation and (b) the factors that determine how many, if any, other civilizations
Life in the Universe (1)
 Conditions for the emergence of life and habitability Life in the Universe (1) We call biogenic conditions the set of physico-chemical requirements that must be fulfilled for abiogenesis to take place
Conditions for the emergence of life and habitability Life in the Universe (1) We call biogenic conditions the set of physico-chemical requirements that must be fulfilled for abiogenesis to take place
Life in the Solar System
 Life in the Solar System Basic Requirements for Life 1. Chemical elements to make biological molecules. On Earth these are mostly C, H, O and N 2. Source of energy for metabolism. This can come from a
Life in the Solar System Basic Requirements for Life 1. Chemical elements to make biological molecules. On Earth these are mostly C, H, O and N 2. Source of energy for metabolism. This can come from a
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Build Your Own Planet Lesson 5: Final Planet Details
 Build Your Own Planet Lesson 5: Final Planet Details You have been traveling through space for many years at close to the speed of light. For most of those years you and your crewmates have been in a very
Build Your Own Planet Lesson 5: Final Planet Details You have been traveling through space for many years at close to the speed of light. For most of those years you and your crewmates have been in a very
Chapter 7 Our Planetary System
 Chapter 7 Our Planetary System What does the solar system look like? Earth, as viewed by the Voyager spacecraft Eight major planets with nearly circular orbits Pluto is smaller than the major planets and
Chapter 7 Our Planetary System What does the solar system look like? Earth, as viewed by the Voyager spacecraft Eight major planets with nearly circular orbits Pluto is smaller than the major planets and
