Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Life in the Universe
|
|
|
- Julianna Hancock
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Life in the Universe
2 Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s history here on Earth When we do, we can get an idea how likely life as we know it is We should keep in mind that life as we know it may not be the only kind possible But it is the kind that we will be best able to recognize, if it does exist
3
4 When did life arise on Earth? What do these events tell us about the possibility that life exists elsewhere in the universe?
5 When did life arise on Earth? The first evidence of life appears ~150 million years after it became possible It is not fossil evidence, but trace chemical evidence The evidence is in the ratio of carbon-12 to carbon-13
6 Carbon isotope evidence for life In >3.8-billion-year-old rocks like these in Greenland there is a higher than normal ratio of 12 C: 13 C Living things incorporate 12 C more easily than 13 C So the higher ratio is taken as indirect evidence for life
7 When did life arise on Earth? The oldest fossils of living things date to ~3.5 billion years ago.
8 Earliest Fossils The oldest fossils of living things date to ~3.5 billion years ago. Fossil stromatolite in 3.5-billionyear-old rock
9 Earliest Fossils The oldest fossils of living things date to ~3.5 billion years ago. Fossil stromatolite in 3.5-billionyear-old rock This is a living stromatolite Stromatolites are layered structures formed by colonies of bacteria They still exist today, typically in extreme environments like hypersalty lakes and lagoons
10 Earliest Fossils The oldest fossils of living things date to ~3.5 billion years ago. Fossil stromatolite in 3.5-billionyear-old rock This is a living stromatolite Stromatolites are layered structures formed by colonies of bacteria They still exist today, typically in extreme environments like hypersalty lakes and lagoons Here are some in a lagoon in Australia
11 When did life arise on Earth? So fossil evidence shows that life certainly existed on Earth by 500 million years after conditions would permit it to survive And chemical evidence suggests it probably existed much earlier But how did it come to be? We don t know
12 How did life arise on Earth? We do know that all life as we know it has an inside and an outside These are separated by a lipid membrane (along with a cell wall in plants) Vesicles made of lipids are easy to make in the laboratory
13 How did life arise on Earth? Life as we know it also has a nucleic acid genome containing instructions for building the organism And we know that all of that was accomplished here on Earth surprisingly quickly So we believe that given similar conditions elsewhere, life will also arise
14 Necessities for Life As We Know It Nutrient source Energy (starlight, chemicals, heat) Liquid water (hardest to come by) And can only exist if planet is in habitable zone
15 Are habitable planets likely?
16 Habitable Planets Definition: A habitable world contains the basic necessities for life as we know it, including liquid water. It does not necessarily have life. There still needs to be sufficient time for life to evolve And certain other requirements as well
17 Constraints on star systems: 1. Old enough to allow time for origin and evolution (rules out high-mass stars 1%) 2. Need to have stable orbits (might rule out binary/multiple star systems 50%) 3. Size of habitable zone: region in which a planet of the right size could have liquid water on its surface Even so billions of stars in the Milky Way seem at least to offer the possibility of habitable worlds.
18 Finding them will be hard Looking for an Earth-like planet around a nearby star is like standing on the East Coast of the United States and looking for a pinhead on the West Coast with a VERY bright grapefruit nearby. But new technologies should soon show the way.
19 The Kepler Space Telescope is monitoring 156,000 stars for transit events for 4 years.
20
21
22
23
24
25 Planned orbiting interferometers will obtain spectra and crude images of Earth-size planets.
26 Spectral Signatures of Life Venus Earth oxygen/ozone Mars
27 Are Earth-like planets rare or common?
28 Elements and Habitability Some scientists argue that proportions of heavy elements need to be just right for the formation of habitable planets. If so, then Earth-like planets are restricted to a galactic habitable zone.
29 Impacts and Habitability Some scientists argue that Jupiter-like planets are necessary to reduce the rate of impacts. If so, then Earth-like planets are restricted to star systems with Jupiterlike planets.
30 Climate and Habitability Some scientists argue that plate tectonics and/or a large moon are necessary to keep the climate of an Earth-like planet stable enough for life.
31 Jovian Moons An intriguing possibility is that life as we know it could exist on jovian moons If, that is, those moons are in the HZ of their star Of the 542 confirmed exoplanets, 124 of them are in the HZ Only 2 of those are near Earthsize, and they are close with highly elliptical orbits A number of the jovian planets are in more Earth-like orbits Good for jovian moon life
32 The Bottom Line We don t yet know how important or negligible these concerns are. The general feeling among most scientists is that microbial life is likely to be common But how common intelligent, technological life like us humans is, is unknown
33 How many civilizations are out there?
34 The Drake Equation Number of civilizations with whom we could potentially communicate = N HP f life f civ f now N HP = total number of habitable planets in galaxy f life = fraction of habitable planets with life f civ = fraction of life-bearing planets with civilization at some time f now = fraction of civilizations around now
35 We do not know the following values for the Drake equation: N HP : probably billions f life :??? Hard to say (near 0 or near 1) f civ :??? It took 4 billion years on Earth f now :??? Can civilizations survive long-term?
36 Are we off-the-chart smart? Humans have comparatively large brains. Does that mean our level of intelligence is improbably high?
37 How does SETI work?
38 SETI experiments look for deliberate signals from E.T.
39 We ve even sent a few signals ourselves Earth to globular cluster M13: Hoping we ll hear back in about 42,000 years!
40 Your computer can help! Home: a screensaver with a purpose
41 Where are the aliens?
42 Fermi s Paradox Plausible arguments suggest that civilizations should be common. For example, even if only 1 in 1 million stars gets a civilization at some time 100,000 civilizations! So why haven t we detected them?
43 Possible solutions to the paradox 1. We are alone: life/civilizations much rarer than we might have guessed Our own planet/civilization looks all the more precious
44 Possible solutions to the paradox 2. Civilizations are common, but interstellar travel is not, perhaps because: interstellar travel is more difficult than we think. the desire to explore is rare. civilizations destroy themselves before achieving interstellar travel. These are all possibilities, but they are not very appealing.
45 Possible solutions to the paradox 3. There IS a galactic civilization and someday we ll meet them.
46 Exocivilizations If there are other civilizations as advanced as ours. What would they be like? What would the people look like? How would they think? Presumably they would have similar science to ours What would their art be like? What would their philosophy be like? What would their religion be like?
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Life in the Universe
 Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
29-Jul-13. Life in the Universe. Life in the Universe
 Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we knowlife exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s history
Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we knowlife exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s history
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe. Earliest Life Forms. When did life arise on Earth? Fossils in Sedimentary Rock. Fossils in Sedimentary Rock
 Chapter 24 Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of life? When did life arise on Earth? Earliest
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of life? When did life arise on Earth? Earliest
Chapter 24: Life in the Universe
 Chapter 24 Lecture Chapter 24: Life in the Universe Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning: When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of
Chapter 24 Lecture Chapter 24: Life in the Universe Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning: When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of
12/5/ Life on Earth. Chapter 19: Life in the Universe. When did life arise on Earth? Earliest Life Forms. Important Stuff (Section 001)
 Important Stuff (Section 001) The Final Exam is Thursday, December 22, 8:00 10:00 am The Final Exam will be given in: Willey 175 Don t come to Anderson 210. No one will be there. No one. Bring 2 pencils
Important Stuff (Section 001) The Final Exam is Thursday, December 22, 8:00 10:00 am The Final Exam will be given in: Willey 175 Don t come to Anderson 210. No one will be there. No one. Bring 2 pencils
Searching for Life: Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds. Life in the Universe. Earliest Fossils. Laboratory Experiments.
 Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
What I know today about the Final
 What I know today about the Final Tuesday, December 10, 8 11 am, same place Around 90 mul9ple choice ques9ons Closed book and closed note No smartphones allowed Calculators of any kind are permiced, but
What I know today about the Final Tuesday, December 10, 8 11 am, same place Around 90 mul9ple choice ques9ons Closed book and closed note No smartphones allowed Calculators of any kind are permiced, but
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI)
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) Our goals for learning What is the Drake equation? How many habitable planets have life? How many civilizations are out there? How does SETI work? Can
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) Our goals for learning What is the Drake equation? How many habitable planets have life? How many civilizations are out there? How does SETI work? Can
Please fill in course evaluation. Deadline * Today *
 Admin Please fill in course evaluation. Deadline * Today * http://www.udel.edu/course-evals Final Exam: Saturday 7 Feb. 3.30 PM. SHL 100 Example-problems and MC questions for parts covered after mid term
Admin Please fill in course evaluation. Deadline * Today * http://www.udel.edu/course-evals Final Exam: Saturday 7 Feb. 3.30 PM. SHL 100 Example-problems and MC questions for parts covered after mid term
The Search for Extra-terrestrial. Is there anybody out there?
 The Search for Extra-terrestrial Intelligence! Is there anybody out there? Summary: we will investigate (a) the Drake Equation and (b) the factors that determine how many, if any, other civilizations
The Search for Extra-terrestrial Intelligence! Is there anybody out there? Summary: we will investigate (a) the Drake Equation and (b) the factors that determine how many, if any, other civilizations
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site:
 ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 37: Life in the Universe [4/18/07] Announcements Habitability of
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 37: Life in the Universe [4/18/07] Announcements Habitability of
Measuring Distances to Galaxies. Galaxies in Motion. Hubble s Law. Galaxy Redshifts. Type Ia Supernovae. Supernovae are Good Standard Candles
 Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
[26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17)
![[26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17) [26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17)](/thumbs/79/79849652.jpg) 1 [26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17) Upcoming Items Homework #12 due next class. Read chapters 24.4-24.5 for Thursday Have you done the course evaluation yet? If not, please do so! FINAL EXAM on Wednesday,
1 [26] Life in the Universe 1 (12/5/17) Upcoming Items Homework #12 due next class. Read chapters 24.4-24.5 for Thursday Have you done the course evaluation yet? If not, please do so! FINAL EXAM on Wednesday,
Today s Class. Last Class. Earliest Life Forms. Today s Class: Search for Life. When did life arise on Earth?
 Today s Class: Search for Life Exam #3 on Friday, April 26: Covers all the reading March 23 rd (Earth) through April 23 rd (Exoplanets). Includes homework assignments 7, 8, 9. Includes Space in the News
Today s Class: Search for Life Exam #3 on Friday, April 26: Covers all the reading March 23 rd (Earth) through April 23 rd (Exoplanets). Includes homework assignments 7, 8, 9. Includes Space in the News
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
Cosmology Overview (so far): Cosmology Overview (so far): The Age of the Universe. The Big Bang. The Age of the Universe
 Cosmology Overview (so far): The Universe: Everything Observable Universe: Everything we can The Universe has no special locations No If no, then no Cosmology Overview (so far): Oblers s Paradox: The sky
Cosmology Overview (so far): The Universe: Everything Observable Universe: Everything we can The Universe has no special locations No If no, then no Cosmology Overview (so far): Oblers s Paradox: The sky
Chapter 24 Lif i e n the Universe
 Chapter 24 Life in the Universe ASTROBIOLOGY A FIELD OF SERIOUS STUDY NASA ASTROBIOLGY Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe ASTROBIOLOGY A FIELD OF SERIOUS STUDY NASA ASTROBIOLGY Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities
Astrobiology: The Semester in Review
 A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets
 Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets star--about 10 11 in our galaxy. Average separation is a few light years. (Compare with size of Galaxy: about 100,000 light years) planet--indirect
Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets star--about 10 11 in our galaxy. Average separation is a few light years. (Compare with size of Galaxy: about 100,000 light years) planet--indirect
The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals. Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV
 The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV Associated Universities, Inc; April/2016 2 Preliminary thoughts a. How certain are you that other
The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV Associated Universities, Inc; April/2016 2 Preliminary thoughts a. How certain are you that other
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 28. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
NSCI EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION. Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
Physics can only take us so far!
 Physics can only take us so far! The usual approach of science of constructing a mathematical model cannot answer the questions of why there should be a universe for the model to describe. Why does the
Physics can only take us so far! The usual approach of science of constructing a mathematical model cannot answer the questions of why there should be a universe for the model to describe. Why does the
Detection of Earth-like planets
 Planets and life Successful detections of extrasolar giant planets suggests that planetary systems may be fairly common could we detect Earthlike planets? is it likely that such planets would have life?
Planets and life Successful detections of extrasolar giant planets suggests that planetary systems may be fairly common could we detect Earthlike planets? is it likely that such planets would have life?
Primary KS1 1 VotesForSchools2018
 Primary KS1 1 Do aliens exist? This photo of Earth was taken by an astronaut on the moon! Would you like to stand on the moon? What is an alien? You probably drew some kind of big eyed, blue-skinned,
Primary KS1 1 Do aliens exist? This photo of Earth was taken by an astronaut on the moon! Would you like to stand on the moon? What is an alien? You probably drew some kind of big eyed, blue-skinned,
Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion
 Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder
Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
Young Solar-like Systems
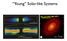 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
So powerful is the illusion of design, it took humanity until the mid-19th century to realise that it is an illusion.
 24. Life Beyond Earth: Prospects for Microbes, Civilizations, and Interstellar Travel We, this people, on a small and lonely planet Traveling through casual space Past aloof stars, across the way of indifferent
24. Life Beyond Earth: Prospects for Microbes, Civilizations, and Interstellar Travel We, this people, on a small and lonely planet Traveling through casual space Past aloof stars, across the way of indifferent
Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Akos Kereszturi Editorial Board member
 Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Akos Kereszturi Editorial Board member Research Center for Astronomy and Earth Sciences Hungarian Academy of Sciences Hungary Biography Dr. Akos Kereszturi Akos
Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Akos Kereszturi Editorial Board member Research Center for Astronomy and Earth Sciences Hungarian Academy of Sciences Hungary Biography Dr. Akos Kereszturi Akos
A Cosmic Perspective. Scott Fisher, Ph.D. - Director of Undergraduate Studies - UO Department of Physics
 A Cosmic Perspective Scott Fisher, Ph.D. - Director of Undergraduate Studies - UO Department of Physics Presentation Overview Let s talk about 3 (or 4) important and relevant topics: Me You and your place
A Cosmic Perspective Scott Fisher, Ph.D. - Director of Undergraduate Studies - UO Department of Physics Presentation Overview Let s talk about 3 (or 4) important and relevant topics: Me You and your place
Ultimate Events. Galaxy clustering in ever deeper surveys. Models of universe and its fates
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Ultimate Events Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 30 Thur 28 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Allen Telescope Array Review current big
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Ultimate Events Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 30 Thur 28 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Allen Telescope Array Review current big
Extrasolar Planets. Today. Dwarf Planets. Extrasolar Planets. Next week. Review Tuesday. Exam Thursday. also, Homework 6 Due
 Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Life on a New Planet
 Life on a New Planet Your Assignment: A national magazine is sponsoring a short story contest. Your teacher has assigned your class the task of entering this contest. The first, second, and third place
Life on a New Planet Your Assignment: A national magazine is sponsoring a short story contest. Your teacher has assigned your class the task of entering this contest. The first, second, and third place
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway?
 Welcome to Class 1: Drake EquaCon, SETI & Fermi Paradox Is it crazy to search for intelligent life? Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway? What would you like to spend most of our last class on? 1. Early SETI,
Welcome to Class 1: Drake EquaCon, SETI & Fermi Paradox Is it crazy to search for intelligent life? Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway? What would you like to spend most of our last class on? 1. Early SETI,
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)
 Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
What makes a planet habitable?
 What makes a planet habitable? By NASA.gov, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.26.17 Word Count 862 Level 1040L TOP: This artist's concept depicts Kepler-186f, the first proven Earth-sized planet to orbit
What makes a planet habitable? By NASA.gov, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.26.17 Word Count 862 Level 1040L TOP: This artist's concept depicts Kepler-186f, the first proven Earth-sized planet to orbit
Extrasolar Planets What are the odds?
 Honors 228: Astrobiology using Bennett and Shostak Chapter 12 overview Spring 2007 Dr. H. Geller What s talked about The Drake Equation (12.1) The Question of Intelligence (12.2) Searching for Intelligence
Honors 228: Astrobiology using Bennett and Shostak Chapter 12 overview Spring 2007 Dr. H. Geller What s talked about The Drake Equation (12.1) The Question of Intelligence (12.2) Searching for Intelligence
Intelligent Life in the Universe
 Intelligent Life in the Universe Lecture 33 APoD: Easter Island Eclipse In-Class Question 1) Do you think life exists elsewhere in the Universe? a) Yes b) No c) Don t know d) Don t care 2 33-1 Lecture
Intelligent Life in the Universe Lecture 33 APoD: Easter Island Eclipse In-Class Question 1) Do you think life exists elsewhere in the Universe? a) Yes b) No c) Don t know d) Don t care 2 33-1 Lecture
7 Good Reasons Why There Might Be Life On Other Planets Reason #1: Extremophiles on Earth
 Reason #1: Extremophiles on Earth One of the big questions is whether life could evolve and survive on a world radically different than Earth. The answer appears to be yes, if you consider that even Earth
Reason #1: Extremophiles on Earth One of the big questions is whether life could evolve and survive on a world radically different than Earth. The answer appears to be yes, if you consider that even Earth
The Jamie Drake Equation
 The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc. Indirect searches
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc. Indirect searches
Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book At the bottom of page 4 is an example of a transit graph. A transit graph shows changes in the brightness of a star s light as a planet crosses in front of the star as seen from Earth. Suppose
FOCUS Book At the bottom of page 4 is an example of a transit graph. A transit graph shows changes in the brightness of a star s light as a planet crosses in front of the star as seen from Earth. Suppose
Other migration processes. New transiting hot Jupiters from last week. First success from CoRoT. Kozai mechanism
 Other migration processes Previous lecture: Migration through planet-disk interactions Type I: low-mass planet (does not clear a gap in disk) Type II: high-mass panet (has cleared gap) Type III: runaway
Other migration processes Previous lecture: Migration through planet-disk interactions Type I: low-mass planet (does not clear a gap in disk) Type II: high-mass panet (has cleared gap) Type III: runaway
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence
 Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
Honors 228 Astrobiology w/ Dr. H. Geller Meeting #2 - Physical Origins. Presented 21 January 2010
 Honors 228 Astrobiology w/ Dr. H. Geller Meeting #2 - Physical Origins Presented 21 January 2010 The Phase Diagram What is the name of the phase change from liquid to gas? A Vaporization B Condensation
Honors 228 Astrobiology w/ Dr. H. Geller Meeting #2 - Physical Origins Presented 21 January 2010 The Phase Diagram What is the name of the phase change from liquid to gas? A Vaporization B Condensation
LESSON TITLE Earth 2.0. Guiding Question: Why should we continue to explore? Ignite Curiosity
 SUBJECTS Science Language Arts COMPUTATIONAL THINKING PRACTICE Find Patterns COMPUTATIONAL THINKING STRATEGIES Developing and Using Abstractions MATERIALS Conditions of Life on Earth student capture sheet
SUBJECTS Science Language Arts COMPUTATIONAL THINKING PRACTICE Find Patterns COMPUTATIONAL THINKING STRATEGIES Developing and Using Abstractions MATERIALS Conditions of Life on Earth student capture sheet
Life in the Universe. Key Concepts: Lecture 35: Admin. 11/21/17. All Formulae (for final):
 Admin. 11/21/17 Key Concepts: Lecture 35: 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period
Admin. 11/21/17 Key Concepts: Lecture 35: 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period
3 Astronomers first made measurements of distant galaxies using telescopes on the Earth.
 3 Astronomers first made measurements of distant galaxies using telescopes on the Earth. 7 Accurate measurements of the distances were very difficult to make. Describe how astronomers measure distances
3 Astronomers first made measurements of distant galaxies using telescopes on the Earth. 7 Accurate measurements of the distances were very difficult to make. Describe how astronomers measure distances
Sample Test. 5. Which of the surfaces is the youngest? A) 1A B) 1B C) 1C D) 1D E) There is no way to tell.
 Sample Test 1. The yellow arrows in image 1B are pointing to a form of A) liquid erosion. B) plate tectonics. C) tidally cracked surface. D) wind erosion (sand dunes). E) All of the above. 2. If an object
Sample Test 1. The yellow arrows in image 1B are pointing to a form of A) liquid erosion. B) plate tectonics. C) tidally cracked surface. D) wind erosion (sand dunes). E) All of the above. 2. If an object
Lecture 16: Life in the Universe
 Lecture 16: Life in the Universe Please remind me to take a break at 12:45 pm! Claire Max May 29, 2014 Astro 18: Planets and Planetary Systems UC Santa Cruz Page 1 Schedule for project presentations next
Lecture 16: Life in the Universe Please remind me to take a break at 12:45 pm! Claire Max May 29, 2014 Astro 18: Planets and Planetary Systems UC Santa Cruz Page 1 Schedule for project presentations next
N = R * f p n e f l f i f c L
 Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 106 B6 Eng Hall This Class (Lecture 10): Nature of Life Next Class: Nucleic Acids Some Oral Presentation on Feb 16 th and 18 th! Mike Somers Chris Kramer Sarah Goldrich
Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 106 B6 Eng Hall This Class (Lecture 10): Nature of Life Next Class: Nucleic Acids Some Oral Presentation on Feb 16 th and 18 th! Mike Somers Chris Kramer Sarah Goldrich
Today. Clicker Questions. Announcements:
 Today Announcements: HW#9 is due April 2 at 8:00 am. Submission for the Spring Break Story contest are due April 2 at 8:00 am. Life in the Universe Are we alone? Clicker Questions Do you believe the Earth
Today Announcements: HW#9 is due April 2 at 8:00 am. Submission for the Spring Break Story contest are due April 2 at 8:00 am. Life in the Universe Are we alone? Clicker Questions Do you believe the Earth
The Physical Basis of Life
 Origins of Life Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 19 Learning Outcomes: The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry.
Origins of Life Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 19 Learning Outcomes: The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry.
TABLE OF CONTENTS. click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? Neptune (Pluto) The Sun. Asteroids. Mercury.
 The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
Simon P. Balm Astro 5 Test #3 Sample Questions
 Simon P. Balm Astro 5 Test #3 Sample Questions 1. What do we mean by the general habitability of a planet? A. the suitability for Life on it surface B. the suitability for Life beneath its surface C. its
Simon P. Balm Astro 5 Test #3 Sample Questions 1. What do we mean by the general habitability of a planet? A. the suitability for Life on it surface B. the suitability for Life beneath its surface C. its
Build Your Own Planet Lesson 5: Final Planet Details
 Build Your Own Planet Lesson 5: Final Planet Details You have been traveling through space for many years at close to the speed of light. For most of those years you and your crewmates have been in a very
Build Your Own Planet Lesson 5: Final Planet Details You have been traveling through space for many years at close to the speed of light. For most of those years you and your crewmates have been in a very
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Questions Sometimes Asked About the Theory of Evolution
 Chapter 9: Evidence for Plant and Animal Evolution Questions Sometimes Asked About the Theory of Evolution Many questions about evolution arise in Christian circles. We ll discuss just a few that we frequently
Chapter 9: Evidence for Plant and Animal Evolution Questions Sometimes Asked About the Theory of Evolution Many questions about evolution arise in Christian circles. We ll discuss just a few that we frequently
The evolution of a Solar-like system. Young Solar-like Systems. Searching for Extrasolar Planets: Motivation
 Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Sun Building Activity 2 The Signature of the Stars
 Sun Building The Signature of the Stars Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours
Sun Building The Signature of the Stars Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours
Life on Other Worlds: The Drake Equation Author: Meagan Morscher GK-12 Reach for the Stars Fellow, Northwestern University
 Life on Other Worlds: The Drake Equation Author: Meagan Morscher GK-12 Reach for the Stars Fellow, Northwestern University Time 2-3 class periods (will vary depending on grade level and experience with
Life on Other Worlds: The Drake Equation Author: Meagan Morscher GK-12 Reach for the Stars Fellow, Northwestern University Time 2-3 class periods (will vary depending on grade level and experience with
Questions that science may help to answer. This module offers opportunities to develop mathematics skills. For example:
 3.3.1 Module P1: The Earth in the Universe Overview Scienti c discoveries in the solar system and beyond continue to inspire popular culture and affect our understanding of our place in the Universe. In
3.3.1 Module P1: The Earth in the Universe Overview Scienti c discoveries in the solar system and beyond continue to inspire popular culture and affect our understanding of our place in the Universe. In
Which letter on the timeline best represents the time when scientists estimate that the Big Bang occurred? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. The red shift of light from most galaxies is evidence that A) most galaxies are moving away from Earth B) a majority of stars in most galaxies are red giants C) the light slows down as it nears Earth
1. The red shift of light from most galaxies is evidence that A) most galaxies are moving away from Earth B) a majority of stars in most galaxies are red giants C) the light slows down as it nears Earth
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
Are We Alone in the Universe? An Introduction to Astrobiology. Dr. Henry Throop Planetary Science Institute Tucson, Arizona, USA
 Are We Alone in the Universe? An Introduction to Astrobiology Dr. Henry Throop Planetary Science Institute Tucson, Arizona, USA SciFest Africa, March 2013 The biggest question facing astronomers today...
Are We Alone in the Universe? An Introduction to Astrobiology Dr. Henry Throop Planetary Science Institute Tucson, Arizona, USA SciFest Africa, March 2013 The biggest question facing astronomers today...
Star. Planet. Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe?
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Questions for Dr. Harold Geller
 Questions for Dr. Harold Geller Questions from Ms. Bullock Would you be able to give a brief introduction about yourself, and what has led you to your career and research. I am Dr. Harold A. Geller. I
Questions for Dr. Harold Geller Questions from Ms. Bullock Would you be able to give a brief introduction about yourself, and what has led you to your career and research. I am Dr. Harold A. Geller. I
What is Earth Science?
 What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
Start with known facts and reasonable guesses. More on order of magnitude Astronomy How many piano tuners are there in Boulder County?
 ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Rosalba Perna TA: Cameron Clarke http://amalfi.astrosunysb.edu/rosalba/ast101/ast101.html MAKE SURE TO GO OVER THE SYLLABUS (if you haven t already
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Rosalba Perna TA: Cameron Clarke http://amalfi.astrosunysb.edu/rosalba/ast101/ast101.html MAKE SURE TO GO OVER THE SYLLABUS (if you haven t already
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe First Hour Exam October 6, 2010 Form A
 29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe First Hour Exam October 6, 2010 Form A There are 32 questions. Read through each question and all the answers before choosing. Budget your time. No whining. Walk
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe First Hour Exam October 6, 2010 Form A There are 32 questions. Read through each question and all the answers before choosing. Budget your time. No whining. Walk
Earth-like planet discovered deep in space
 Earth-like planet discovered deep in space By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.24.14 Word Count 905 An artist's concept depicts Kepler-186f, the first validated Earth-size planet to orbit
Earth-like planet discovered deep in space By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.24.14 Word Count 905 An artist's concept depicts Kepler-186f, the first validated Earth-size planet to orbit
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes
 Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
ISP205-2 Visions of the Universe
 ISP205-2 Visions of the Universe The big questions Course details Example of how scientific discoveries are made Brief tour of the universe Reading for next class The Big Questions 1. Laws of physics.
ISP205-2 Visions of the Universe The big questions Course details Example of how scientific discoveries are made Brief tour of the universe Reading for next class The Big Questions 1. Laws of physics.
-- Lewis Carroll, Alice in Wonderland
 Where Are They? There s no use trying, she said: one can t believe impossible things. I daresay you haven t had much practice, said the Queen. When I was your age, I always did it for half-anhour a day.
Where Are They? There s no use trying, she said: one can t believe impossible things. I daresay you haven t had much practice, said the Queen. When I was your age, I always did it for half-anhour a day.
Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers
 Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers Prof. Pradhan April 24, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. 2. What number is the metric system based around? What
Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers Prof. Pradhan April 24, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. 2. What number is the metric system based around? What
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Galaxies and the Universe
 Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
NOTES 1. Fossils. The BIG Idea Rocks, fossils, and other types of natural evidence tell Earth s story.
 Name Period Date UNIT 6 NOTES 1 Fossils Objectives Identify and describe the types of fossils. Define fossils Explain fossil formation Explain how different kinds of fossils show traces of life from Earth
Name Period Date UNIT 6 NOTES 1 Fossils Objectives Identify and describe the types of fossils. Define fossils Explain fossil formation Explain how different kinds of fossils show traces of life from Earth
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
What is a black hole s event horizon? What is a black hole s Schwarzschild radius? What is a black hole s singularity? How do they change with mass?
 What is a black hole s event horizon? What is a black hole s Schwarzschild radius? What is a black hole s singularity? How do they change with mass? A probe/human falls into a black hole. Describe what
What is a black hole s event horizon? What is a black hole s Schwarzschild radius? What is a black hole s singularity? How do they change with mass? A probe/human falls into a black hole. Describe what
What makes a planet habitable?
 What makes a planet habitable? By NASA.gov on 01.26.17 Word Count 977 TOP: This artist's concept depicts Kepler-186f, the first proven Earth-sized planet to orbit a distant star in the habitable zone,
What makes a planet habitable? By NASA.gov on 01.26.17 Word Count 977 TOP: This artist's concept depicts Kepler-186f, the first proven Earth-sized planet to orbit a distant star in the habitable zone,
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology
 Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
WHERE ARE THEY? The Fermi Paradox
 WHERE ARE THEY? The Fermi Paradox Milan S. Dimitrijević Astronomical Observatory, Volgina 7, 11160 Belgrade, Serbia ENRICO FERMI FERMI PARADOX Or GREAT SILENCE (Brin 1983) Or ASTROSOCIOLOGICAL PARADOX
WHERE ARE THEY? The Fermi Paradox Milan S. Dimitrijević Astronomical Observatory, Volgina 7, 11160 Belgrade, Serbia ENRICO FERMI FERMI PARADOX Or GREAT SILENCE (Brin 1983) Or ASTROSOCIOLOGICAL PARADOX
Across the Universe. By Gabrielle Sierra
 Across the Universe By Gabrielle Sierra Our universe is an amazing place. Since prehistoric days, inquisitive minds have been wondering about the celestial objects that surround our planet, and today scientists
Across the Universe By Gabrielle Sierra Our universe is an amazing place. Since prehistoric days, inquisitive minds have been wondering about the celestial objects that surround our planet, and today scientists
Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND
 Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Finding Other Earths. Jason H. Steffen. Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009
 Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Kepler, a Planet Hunting Mission
 Kepler, a Planet Hunting Mission Riley Duren Kepler Chief Engineer Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology with thanks to Jim Fanson (Kepler Project Manager) for slide contributions
Kepler, a Planet Hunting Mission Riley Duren Kepler Chief Engineer Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology with thanks to Jim Fanson (Kepler Project Manager) for slide contributions
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 1
 Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE (Right answers are reported in red) 1.. A solar system contains a. primarily planets. b. large amounts of gas and dust
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE (Right answers are reported in red) 1.. A solar system contains a. primarily planets. b. large amounts of gas and dust
Lecture #26: Plan. Cosmology: Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe. The Great Unanswered Questions (cont d)
 Lecture #26: Plan Cosmology: The Great Unanswered Questions (cont d) Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe Reminders Course evaluations: CourseEvalUM.umd.edu Review session: Monday, December 11,
Lecture #26: Plan Cosmology: The Great Unanswered Questions (cont d) Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe Reminders Course evaluations: CourseEvalUM.umd.edu Review session: Monday, December 11,
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Kira Bonk ascension.html
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Killer Skies. HW 11 due tonight Exam 3, Dec 11 Last time: End of the Universe Today: Aliens. Music: Pets Porno For Pyros
 Killer Skies HW 11 due tonight Exam 3, Dec 11 Last time: End of the Universe Today: Aliens Music: Pets Porno For Pyros 2 Hour Exam 3 Hour Exam 3 Wed, Dec 11th, in class information on course website 40
Killer Skies HW 11 due tonight Exam 3, Dec 11 Last time: End of the Universe Today: Aliens Music: Pets Porno For Pyros 2 Hour Exam 3 Hour Exam 3 Wed, Dec 11th, in class information on course website 40
Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere
 Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere Where is everybody? Fermi s paradox (1950 lunch conversation) Assume 3 levels of extraterrestrial civilizations ETC1, like ours (energy resources of a planet) ETC2,
Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere Where is everybody? Fermi s paradox (1950 lunch conversation) Assume 3 levels of extraterrestrial civilizations ETC1, like ours (energy resources of a planet) ETC2,
- Both reactions sacrifice. - This in a nuclear reaction is called the. and is the energy in the reaction
 Unit 2: Origins I. Time Begins a. The b. The universe begins as the size of a single atom c. The universe began as a i. All matter and space were created from a single point of pure energy in an instant
Unit 2: Origins I. Time Begins a. The b. The universe begins as the size of a single atom c. The universe began as a i. All matter and space were created from a single point of pure energy in an instant
Announcements. Distances in the Solar System. The Main Point. Lecture #10: Solar System Survey II
 Lecture #10: Solar System Survey II Distances and a Solar System Scale Model Overview of Planetary Atmospheres Terrestrial Planet Atmospheres Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Overview of Solar System Formation
Lecture #10: Solar System Survey II Distances and a Solar System Scale Model Overview of Planetary Atmospheres Terrestrial Planet Atmospheres Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Overview of Solar System Formation
The following data for the Sun and the four inner planets of the Solar System have been observed. Diameter (kilometers)
 The following data for the Sun and the four inner planets of the Solar System have been observed. Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Diameter (kilometers) Sun 1,400,000 Mercury 58 4,900 Venus
The following data for the Sun and the four inner planets of the Solar System have been observed. Mean Distance from the Sun (million kilometers) Diameter (kilometers) Sun 1,400,000 Mercury 58 4,900 Venus
