A Recipe for Life on Earth... and elsewhere?
|
|
|
- Sophia Jessica Harper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Recipe for Life on Earth... and elsewhere? We know that life evolved on Earth. But did it also form on other planets, either in our Solar System or elsewhere? At the moment, we just don't know. But we don't have to let that ignorance stop us from speculating on some of the factors involved in the formation of life. In the following discussion, I consider "life" to mean only life as we know it. There could very well be alien beings made of magnetic field loops or ionized hydrogen, but we couldn't really engage in any quantitative discussions about them. Step 1: Find a planet In recent years, astronomers have started to find quite a few planets around other stars, using several different techniques. The radial-velocity technique has been the most successful in the past few years. What fraction of the stars examined (*) by planet hunters turn out to have planets (**)?
2 Read more about this study So you might conclude that between one-tenth and one-fifth of all stars might have planets... The fine print: All the stars chosen for this study are similar to the Sun. None of the detected planets is similar to the Earth; they are all hundreds of times more massive. Actually, there is one case in which we have detected planets with masses similar to the Earth orbiting around some other star. About a decade ago, as radio astronomer Alexander Wolszczan studied a pulsar, he noticed a peculiar periodic shift in the arrival times of its pulses.
3 A planetary system around the millisecond pulsar PSR Nature 355, 145 (1992) He was able to make VERY accurate measurements of the pulse times, deriving the motion of the pulsar from the tiny deviations from the average interval between pulses. These measurements were MUCH more precise than one could do with ordinary spectrographs and ordinary stars. Note the units of time on the graph below.
4 Step 1A: Find a GOOD planet Planets of roughly Earth mass! Hooray! Or so one might think at first. But look closely at the system:
5 These planets are very close to a pulsar... Q: What sort of star was originally at the center of this system, before it turned into a pulsar? Q: How did it turn into a pulsar? Hmmm. Maybe these aren't the best planets for life. Can we do any better? Let's take a second look at what we know about planets orbiting other stars. Most are detected by their gravitational influence on their host star:
6 That means that all we really know is 1. mass of the planet 2. period of its orbit 3. radius of the orbit, which we can derive from the first two We find that almost all these planets have masses much, much larger than the Earth. Is that important? Yes, we think so. Take a look at the planets in our own solar system. They break up into three groups:
7 the terrestrial planets are small, dense, rocky the gas giants are large and covered with very thick atmospheres snowballs like Pluto occupy the icy depths of the solar system The only ones which we humans could easily inhabit are the terrestrial planets because they have solid surfaces and surface gravities which wouldn't break our spindly little legs. Check out Elvis' weight on other planets So, we know the MASS of planets around other stars --- but do we know anything about their SIZES? It turns out that in just a very few cases, we do. The transit
8 technique tells us how large a planet is, relative to its star. Since we have a decent guess at the size of most stars, we can figure out the size of the planet. The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia currently (as of Nov 10, 2004) lists 6 planets with measured sizes: name mass (Jupiters) radius (Jupiters) OGLE-TR-56 b OGLE-TR-113 b OGLE-TR-132 b TrES HD b OGLE-TR-111 b So all these planets have roughly the mass of Jupiter, and roughly the size of Jupiter. That combination yields a surface gravity of about 2.5 times the Earth's: in other words, if you were standing on one of these planets (or on an airship floating in the atmosphere of one), you would weigh about 2.5 times what you weigh here on Earth. That's not good news for us humans, but it probably wouldn't bother some creature which had evolved there. Step 2: Set oven to a temperature of about 300 Kelvin Here on Earth, liquid water is necessary for life to thrive. Therefore, if we are looking for Earth-like organisms, we need to discard any planets which are too hot or too cold for liquid water. The temperature of a planet depends largely on two factors: the luminosity of its star the radius of its orbit
9 In real life, there are complications -- the effects of albedo, radiation transfer through the atmosphere, internal generation of energy -- but to a very rough approximation, we can calculate the temperature of a planet in the following way: [ L ] 1/4 Temp of planet = [ ] [ 16 * pi * s * R^2 ] where L = luminosity of the star (Watts) s = Stefan-Boltzmann constant = 5.67 x 10^(-8) R = radius of planet's orbit (meters) Does this really work? If we plug in the values for the Sun and the Earth's orbit, we find a temperature of 278 Kelvin = 5 degrees C = 41 degrees F. That's roughly right. Earth's actual temperature is a bit warmer because our atmosphere traps some of the heat which would be radiated away into space. Okay, so what about all those other planets discovered around other stars? Recall that a lot of them are pretty close to their stars...
10
11 That means that they will be pretty hot. Consider, for example, the very first planet to be discovered by radial-velocity measurements back in 1995, the one which orbits star 51 Peg: According to the California & Carnegie Planet Search, this system has stellar luminosity L = 4.7 x 10^(26) Watts planet's orbital radius R = 0.05 AU Q: Estimate the temperature of the planet circling 51 Peg.
12 Step 3: Gather the right ingredients What are the ingredients needed to make a human? lots of water = hydrogen + oxygen carbon plus a bit of calcium sodium chlorine iron phosphorus and other things... Here, for example, is the list of ingredients in one particular multivitamin pill.
13 Fortunately, most of these are pretty common, as elements go in the universe: Element Symbol Atomic Number Number of Atoms per million of hydrogen Hydrogen H 1 1,000,000 Helium He 2 68,000
14 Carbon C Nitrogen N 7 87 Oxygen O Neon Ne Sodium Na 11 2 Magnesium Mg Aluminum Al 13 3 Silicon Si Sulfur S Calcium Ca 20 2 Iron Fe Nickel Ni Step 4: Stir gently Of course, it's not just the amount of each element which is important; it must also have the appropriate chemical form. Our bodies contain complicated organic molecules, consisting of tens or hundreds or thousands of atoms all joined together in very particular ways. That isn't very likely... or is it? In 1953, Stanley Miller and Harold Urey, at the University of Chicago, performed a simple experiment to see what would happen to simple chemicals in the atmosphere of the early Earth. They combined in a beaker gases which they believed to make up the bulk of the young Earth's atmosphere methane (C-H4) ammonia (C-N3) hydrogen (H2) water (H2-O) and cycled the materials repeatedly through an electric spark. After one week, a significant fraction of the carbon had turned into organic compounds; several percent had created amino acids. More recent research indicates that the early atmosphere of the Earth may not have contained exactly this combination of gases. However, the Earth is a heck of a lot bigger than a beaker, and it also cooked its ingredients for a lot longer than a single
15 week. It does seem likely that simple molecules do turn into more complicated ones if given enough time and a bit of energy. The real proof is in the pudding: when astronomers look carefully, they find complex molecules in several forms out in space. Radio astronomers have detected emission lines coming from giant clouds of interstellar gas, due to molecules such as vinyl alcohol glycoaldehyde Geologists have identified many amino acids in a certain type of meteorite:... The amino acids of the Murchison meteorite (CM2) have been extensively analyzed and 52 amino acids have been positively identified. Thirty three of these amino acids are unknown in natural materials other than carbonaceous chondrites. Thus the Murchison meteorite has recently been the major source of new naturally-occurring amino acids.... Step 5: Allow to bake for... Okay, so you find a planet which is
16 at the proper distance from its star big enough to hold an atmosphere stocked with all the necessary chemical ingredients How long will it take for this "soup" to give rise to some sort of life? Let's look at the example of the Earth. The planet formed roughly 4.6 billion years ago. Although the fossil record isn't a perfect record, and grows more and more fragmentary the further back one looks, we have some notion of the evolution of life on the planet. Suppose that we compress the entire history of the Earth into a single calendar year... Calendar history of the Earth So, on the Earth, it took over one billion years for life to form and reach the point that it left recognizable fossils. There was then a very long period when, as far as we can tell, not much happened: the only living things were simple single-celled organisms, similar to bacteria. Roughly another THREE BILLION YEARS passed before we detect the remains of creatures as complex as a jellyfish. That's a long time with -- from our anthropocentric point of view -- not much to show for it. It's so long a time, in fact, that it exceeds the lifetime of many stars. Remember that massive stars run through their fuel rapidly: to a rough approximation, -2.5 lifetime ( mass ) = ( ) solar lifetime ( solar mass ) Q: The Sun will fuse hydrogen for about 10 billion years. How long will a star of 1.5 solar masses last? A star of 2 solar masses? A star of 3 solar masses?
17 This adds another requirement to the recipe for (complex) life to evolve: it must exist on a planet orbiting a relatively low-mass star. Fortunately, most stars in our Milky Way Galaxy are less massive than the Sun, so this may not disqualify too many systems. Step 6: Let sit for several eons Gee, there are a lot of factors which go into the formation of life. And we haven't even started to worry about additional factors which are important for confirming our guesses. Since we can't (yet) go off and have a look at planets around other stars, the only ways we could detect life on other planets are a. to meet aliens who have travelled here to Earth (yeah, right...) b. to overhear radio transmissions from other civilizations The second option is worth trying... but it places some additional constraints on our calculations: the life must evolve to reach some intelligent stage the civilization must create radio transmissions the transmissions must continue for a long time In the nineteen-sixties, radio astronomer Frank Drake tried to combine all the factors into a single equation which would calculate the number of alien civilizations in our galaxy with which we could communicate. Here's the version of his famous Drake Equation you can find in your textbook (there are many variations): N = N* fp nlz fl fi fs where N* = number of stars in the Milky Way Galaxy fp = fraction of stars with planets nlz = number of planets per star which lie in the "life zone" for a long time
18 fl = fraction of suitable planets upon which life evolves fi = fraction of life which become intelligent fs = fraction of star's life for which intelligent life continues N = number of communicative civilizations in our galaxy We have some reasonable order-of-magnitude estimates for the first three parameters in this equation, but nothing better than wild-eyed guesses for the final three values. That means, unfortunately, that what you get out of this equation is really what you choose to put into it... Step right up and plug in your own guesses in the Interactive Drake Equation Another interactive Drake calculator Source:
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Kira Bonk ascension.html
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Outline: Cosmological Origins. The true basics of life The age of Earth and the Universe The origin of the heavy elements Molecules in space
 Outline: Cosmological Origins The true basics of life The age of Earth and the Universe The origin of the heavy elements Molecules in space Reminder: HW #1 due in one week Homework is on class webpage
Outline: Cosmological Origins The true basics of life The age of Earth and the Universe The origin of the heavy elements Molecules in space Reminder: HW #1 due in one week Homework is on class webpage
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Young Solar-like Systems
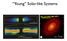 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Late stages of stellar evolution for high-mass stars
 Late stages of stellar evolution for high-mass stars Low-mass stars lead a relatively peaceful life in their old age: although some may gently blow off their outer envelopes to form beautiful planetary
Late stages of stellar evolution for high-mass stars Low-mass stars lead a relatively peaceful life in their old age: although some may gently blow off their outer envelopes to form beautiful planetary
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam]
![Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam] Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam]](/thumbs/85/91935248.jpg) Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam] Although we can be certain that other stars are as complex as the Sun, we will try to
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam] Although we can be certain that other stars are as complex as the Sun, we will try to
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM?
 4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Mystery Object #1. Mystery Object #2
 Mystery Object #1 Diameter (km) 12,756 Revolution Period (Earth days) 150 million km 24 hours/ 1 Earth day 365 days Nitrogen and Oxygen A terrestrial body including iron, oxygen, silicon, magnesium, sulfur,
Mystery Object #1 Diameter (km) 12,756 Revolution Period (Earth days) 150 million km 24 hours/ 1 Earth day 365 days Nitrogen and Oxygen A terrestrial body including iron, oxygen, silicon, magnesium, sulfur,
Astro 21 first lecture. stars are born but also helps us study how. Density increases in the center of the star. The core does change from hydrogen to
 Astro 21 first lecture The H-R H R Diagram helps us study how stars are born but also helps us study how they die. Stars spend most of their lives as main sequence stars. The core does change from hydrogen
Astro 21 first lecture The H-R H R Diagram helps us study how stars are born but also helps us study how they die. Stars spend most of their lives as main sequence stars. The core does change from hydrogen
Chapter 11 Review. 1) Light from distant stars that must pass through dust arrives bluer than when it left its star. 1)
 Chapter 11 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Light from distant stars that must pass through dust arrives bluer than when it left its star. 1)
Chapter 11 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Light from distant stars that must pass through dust arrives bluer than when it left its star. 1)
NSCI EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION. Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
V. Stars.
 V. Stars http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 0. The local HR diagram We saw that locally we can make an HR diagram of absolute luminosity against temperature. We find a main sequence, giants and
V. Stars http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 0. The local HR diagram We saw that locally we can make an HR diagram of absolute luminosity against temperature. We find a main sequence, giants and
Review: HR Diagram. Label A, B, C respectively
 Stellar Evolution Review: HR Diagram Label A, B, C respectively A C B a) A: White dwarfs, B: Giants, C: Main sequence b) A: Main sequence, B: Giants, C: White dwarfs c) A: Main sequence, B: White Dwarfs,
Stellar Evolution Review: HR Diagram Label A, B, C respectively A C B a) A: White dwarfs, B: Giants, C: Main sequence b) A: Main sequence, B: Giants, C: White dwarfs c) A: Main sequence, B: White Dwarfs,
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System. Chapter Eight
 Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 07 Oct. 15, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 07 Oct. 15, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Stellar Evolution Notes
 Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
26. Introduction to the Solar System page 1
 26. Introduction to the Solar System page 1 A. To get a sense of scale: Here is a "scale model for the Solar System" illustrating the relative sizes of, and distances between, the planets and the Sun.
26. Introduction to the Solar System page 1 A. To get a sense of scale: Here is a "scale model for the Solar System" illustrating the relative sizes of, and distances between, the planets and the Sun.
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 28. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence
 Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
Online Quiz Chapter 16 Due Wednesday at 11:59PM. Online Quiz Chapter 7 Due Wednesday at 11:59PM. Online Quiz Chapter 8 Due Wednesday at 11:59PM
 Reminders I 1 Online Quiz Chapter 16 Due Wednesday at 11:59PM 2 Online Quiz Chapter 7 Due Wednesday at 11:59PM 3 Online Quiz Chapter 8 Due Wednesday at 11:59PM 4 Online Quiz Chapter 18 Due Friday at 11:59PM
Reminders I 1 Online Quiz Chapter 16 Due Wednesday at 11:59PM 2 Online Quiz Chapter 7 Due Wednesday at 11:59PM 3 Online Quiz Chapter 8 Due Wednesday at 11:59PM 4 Online Quiz Chapter 18 Due Friday at 11:59PM
Logistics. Test 3 will be 4/24 MRS 2 due Thursday 4/17
 Stellar Evolution Logistics Test 3 will be 4/24 MRS 2 due Thursday 4/17 GTA Award The Graduate Teaching Assistant Excellence Award is an internal initiative which is intended to promote, recognize, and
Stellar Evolution Logistics Test 3 will be 4/24 MRS 2 due Thursday 4/17 GTA Award The Graduate Teaching Assistant Excellence Award is an internal initiative which is intended to promote, recognize, and
Low mass stars. Sequence Star Giant. Red. Planetary Nebula. White Dwarf. Interstellar Cloud. White Dwarf. Interstellar Cloud. Planetary Nebula.
 Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud
Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology
 Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Alex Bara
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 10): Origin of the Moon Ilana Strauss Next Class: Our Planet Scott Huber Thomas Hymel HW 2! Alex Bara http://userpages.bright.net/~phobia/main.htm! Margaret Sharp http://hubpages.com/hub/proof-that-ufos-exist---
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 10): Origin of the Moon Ilana Strauss Next Class: Our Planet Scott Huber Thomas Hymel HW 2! Alex Bara http://userpages.bright.net/~phobia/main.htm! Margaret Sharp http://hubpages.com/hub/proof-that-ufos-exist---
AST Section 2: Test 2
 AST1002 - Section 2: Test 2 Date: 11/05/2009 Name: Equations: E = m c 2 Question 1: The Sun is a stable star because 1. gravity balances forces from pressure. (!) Miniquiz 7, Q3 2. the rate of fusion equals
AST1002 - Section 2: Test 2 Date: 11/05/2009 Name: Equations: E = m c 2 Question 1: The Sun is a stable star because 1. gravity balances forces from pressure. (!) Miniquiz 7, Q3 2. the rate of fusion equals
N = R *! f p! n e! f l! f i! f c! L
 Astronomy 330 Drake Equation The class s first estimate is Frank Drake This class (Lecture 6): Stars Next Class: Star Formation Music: We are all made of Stars Moby Feb 5, 2009 Astronomy 330 N = R *! f
Astronomy 330 Drake Equation The class s first estimate is Frank Drake This class (Lecture 6): Stars Next Class: Star Formation Music: We are all made of Stars Moby Feb 5, 2009 Astronomy 330 N = R *! f
Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti
 Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
Exam # 3 Tue 12/06/2011 Astronomy 100/190Y Exploring the Universe Fall 11 Instructor: Daniela Calzetti INSTRUCTIONS: Please, use the `bubble sheet and a pencil # 2 to answer the exam questions, by marking
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
7 Good Reasons Why There Might Be Life On Other Planets Reason #1: Extremophiles on Earth
 Reason #1: Extremophiles on Earth One of the big questions is whether life could evolve and survive on a world radically different than Earth. The answer appears to be yes, if you consider that even Earth
Reason #1: Extremophiles on Earth One of the big questions is whether life could evolve and survive on a world radically different than Earth. The answer appears to be yes, if you consider that even Earth
Astronomy 122 Midterm
 Astronomy 122 Midterm This Class (Lecture 15): Stellar Evolution: The Main Sequence Next Class: Stellar Evolution: Post-Main Sequence Midterm on Thursday! Last week for Nightlabs 1 hour exam in this classroom
Astronomy 122 Midterm This Class (Lecture 15): Stellar Evolution: The Main Sequence Next Class: Stellar Evolution: Post-Main Sequence Midterm on Thursday! Last week for Nightlabs 1 hour exam in this classroom
Possible Extra Credit Option
 Possible Extra Credit Option Attend an advanced seminar on Astrophysics or Astronomy held by the Physics and Astronomy department. There are seminars held every 2:00 pm, Thursday, Room 190, Physics & Astronomy
Possible Extra Credit Option Attend an advanced seminar on Astrophysics or Astronomy held by the Physics and Astronomy department. There are seminars held every 2:00 pm, Thursday, Room 190, Physics & Astronomy
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System. Chapter Eight
 Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 06 Oct. 09, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 06 Oct. 09, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4)
 Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
Stars IV Stellar Evolution
 Stars IV Stellar Evolution Attendance Quiz Are you here today? Here! (a) yes (b) no (c) my views are evolving on the subject Today s Topics Stellar Evolution An alien visits Earth for a day A star s mass
Stars IV Stellar Evolution Attendance Quiz Are you here today? Here! (a) yes (b) no (c) my views are evolving on the subject Today s Topics Stellar Evolution An alien visits Earth for a day A star s mass
Chapter 8 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Formation of the Solar System
 Chapter 8 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Formation of the Solar System Formation of the Solar System 8.1 The Search for Origins Our goals for learning: Develop a theory of solar system
Chapter 8 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Formation of the Solar System Formation of the Solar System 8.1 The Search for Origins Our goals for learning: Develop a theory of solar system
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
Abundance of Elements. Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System
 Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
What is the solar system?
 Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Recall what you know about the Big Bang.
 What is this? Recall what you know about the Big Bang. Most of the normal matter in the universe is made of what elements? Where do we find most of this normal matter? Interstellar medium (ISM) The universe
What is this? Recall what you know about the Big Bang. Most of the normal matter in the universe is made of what elements? Where do we find most of this normal matter? Interstellar medium (ISM) The universe
Astronomy December, 2016 Introduction to Astronomy: The Solar System. Final exam. Practice questions for Unit V. Name (written legibly):
 Astronomy 101 12 December, 2016 Introduction to Astronomy: The Solar System Final exam Practice questions for Unit V Name (written legibly): Honor Pledge: On my honor, I have neither given nor received
Astronomy 101 12 December, 2016 Introduction to Astronomy: The Solar System Final exam Practice questions for Unit V Name (written legibly): Honor Pledge: On my honor, I have neither given nor received
Solar System Unit Tracking Sheet
 Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science Solar System Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target The Solar System is 4.6 billion years old Question Example How is the age of the solar system estimated by scientists?
Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science Solar System Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target The Solar System is 4.6 billion years old Question Example How is the age of the solar system estimated by scientists?
Question 1 (1 point) Question 2 (1 point) Question 3 (1 point)
 Question 1 (1 point) If the Earth accreted relatively slowly, the heat obtained from the gravitational potential energy would have had time to escape during its accretion. We know that the Earth was already
Question 1 (1 point) If the Earth accreted relatively slowly, the heat obtained from the gravitational potential energy would have had time to escape during its accretion. We know that the Earth was already
Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death
 Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death Stars have lives: born, evolve, die Mass determines stellar evolution: Really Low Mass (0.08 to 0.4 M sun ) Low Mass: (0.4 to 4 M sun ) Long lives High Mass (4
Ch. 16 & 17: Stellar Evolution and Death Stars have lives: born, evolve, die Mass determines stellar evolution: Really Low Mass (0.08 to 0.4 M sun ) Low Mass: (0.4 to 4 M sun ) Long lives High Mass (4
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture
 (Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
Star Formation A cloud of gas and dust, called a nebula, begins spinning & heating up. Eventually, it gets hot enough for fusion to take place, and a
 Stars Star- large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of energy and shines Sun- our closest star Star Formation A cloud of gas and dust, called a nebula, begins spinning
Stars Star- large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of energy and shines Sun- our closest star Star Formation A cloud of gas and dust, called a nebula, begins spinning
The History of the Solar System. From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies
 The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe
 Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Evolution of High Mass Stars
 Luminosity (L sun ) Evolution of High Mass Stars High Mass Stars O & B Stars (M > 4 M sun ): Burn Hot Live Fast Die Young Main Sequence Phase: Burn H to He in core Build up a He core, like low-mass stars
Luminosity (L sun ) Evolution of High Mass Stars High Mass Stars O & B Stars (M > 4 M sun ): Burn Hot Live Fast Die Young Main Sequence Phase: Burn H to He in core Build up a He core, like low-mass stars
Astronomy 104: Second Exam
 Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
Chapter 11 Review Clickers. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Jovian Planet Systems Pearson Education, Inc.
 Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Jovian Planet Systems If Jupiter was the size of a basketball, Earth would be the size of a(n) a) bacterium. b) grain of rice. c) marble. d) orange.
Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Jovian Planet Systems If Jupiter was the size of a basketball, Earth would be the size of a(n) a) bacterium. b) grain of rice. c) marble. d) orange.
Astronomy 330. Presentations. Outline
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 7): Why does the Sun Shine? Presentations! The presentation schedule has been decided by random selection.! It is posted in the schedule section of the webpage.! Make
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 7): Why does the Sun Shine? Presentations! The presentation schedule has been decided by random selection.! It is posted in the schedule section of the webpage.! Make
The Universe and Galaxies
 The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
N = R * f p n e f l f i f c L
 Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 106 B6 Eng Hall This Class (Lecture 10): Nature of Life Next Class: Nucleic Acids Some Oral Presentation on Feb 16 th and 18 th! Mike Somers Chris Kramer Sarah Goldrich
Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 106 B6 Eng Hall This Class (Lecture 10): Nature of Life Next Class: Nucleic Acids Some Oral Presentation on Feb 16 th and 18 th! Mike Somers Chris Kramer Sarah Goldrich
Daily Science 03/30/2017
 Daily Science 03/30/2017 The atmospheres of different planets contain different gases. Which planet is most likely Earth? a. planet 1 b. planet 2 c. planet 3 d. planet 4 KeslerScience.com Can you name
Daily Science 03/30/2017 The atmospheres of different planets contain different gases. Which planet is most likely Earth? a. planet 1 b. planet 2 c. planet 3 d. planet 4 KeslerScience.com Can you name
THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM
 THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM An IR view of dust clouds In particular, light from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH s) Little bit of carbon out there, forms hydrocarbons like car exhaust Associated with
THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM An IR view of dust clouds In particular, light from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH s) Little bit of carbon out there, forms hydrocarbons like car exhaust Associated with
Life in the Universe. Key Concepts: Lecture 35: Admin. 11/21/17. All Formulae (for final):
 Admin. 11/21/17 Key Concepts: Lecture 35: 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period
Admin. 11/21/17 Key Concepts: Lecture 35: 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period
Physics HW Set 3 Spring 2015
 1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09. Astronomy 101
 High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
Overview of the Solar System. Solar system contents one star, several planets, lots of debris.
 Overview of the Solar System Solar system contents one star, several planets, lots of debris. Most of it is the Sun! 99.8% of the mass of the Solar System resides in the Sun. A hot ball of mostly hydrogen
Overview of the Solar System Solar system contents one star, several planets, lots of debris. Most of it is the Sun! 99.8% of the mass of the Solar System resides in the Sun. A hot ball of mostly hydrogen
Star. Planet. Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe?
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Atomic Structure Chapter 4 Mr. Hines
 Atomic Structure Chapter 4 Mr. Hines Part A Standard model of the atom Learning Targets and I can statements 1 List, label, and describe the parts of an atom. 2 Identify the atomic number and the atomic
Atomic Structure Chapter 4 Mr. Hines Part A Standard model of the atom Learning Targets and I can statements 1 List, label, and describe the parts of an atom. 2 Identify the atomic number and the atomic
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
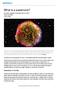 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
LESSON 1. Solar System
 Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
IX. Dwarf Planets A. A planet is defined to be an object that is large enough to coalesce into a sphere and to have cleared its orbit of other
 7/1 VII. VIII. Uranus A. Gas Giant 1. Rings but not visible 2. HUGE axial tilt 97! 3. Mostly hydrogen and helium 4. Medium rotation rate 5. Cold 55 K at the cloud tops B. Physical characteristics 1. Mass:
7/1 VII. VIII. Uranus A. Gas Giant 1. Rings but not visible 2. HUGE axial tilt 97! 3. Mostly hydrogen and helium 4. Medium rotation rate 5. Cold 55 K at the cloud tops B. Physical characteristics 1. Mass:
1 A Solar System Is Born
 CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Topics we will explore: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Topics we will explore: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Galaxies and the Universe. Our Galaxy - The Milky Way The Interstellar Medium
 Galaxies and the Universe Our Galaxy - The Milky Way The Interstellar Medium Our view of the Milky Way The Radio Sky COBE Image of our Galaxy The Milky Way Galaxy - The Galaxy By Visual Observation
Galaxies and the Universe Our Galaxy - The Milky Way The Interstellar Medium Our view of the Milky Way The Radio Sky COBE Image of our Galaxy The Milky Way Galaxy - The Galaxy By Visual Observation
Clicker Question: Clicker Question: What is the expected lifetime for a G2 star (one just like our Sun)?
 How Long do Stars Live (as Main Sequence Stars)? A star on Main Sequence has fusion of H to He in its core. How fast depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass
How Long do Stars Live (as Main Sequence Stars)? A star on Main Sequence has fusion of H to He in its core. How fast depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass
Ultimate Events. Galaxy clustering in ever deeper surveys. Models of universe and its fates
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Ultimate Events Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 30 Thur 28 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Allen Telescope Array Review current big
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Ultimate Events Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 30 Thur 28 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Allen Telescope Array Review current big
Atomic Structure Chapter 4 Mr. Hines
 Atomic Structure Chapter 4 Mr. Hines Part A Standard model of the atom Learning Targets and I can statements 1 List, label, and describe the parts of an atom. 2 Identify the atomic number and the atomic
Atomic Structure Chapter 4 Mr. Hines Part A Standard model of the atom Learning Targets and I can statements 1 List, label, and describe the parts of an atom. 2 Identify the atomic number and the atomic
Low-mass Stellar Evolution
 Low-mass Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars The Structure of the Sun Let s review: The Sun is held together by? The inward force is balanced by? Thinking about
Low-mass Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars The Structure of the Sun Let s review: The Sun is held together by? The inward force is balanced by? Thinking about
1 The Life Cycle of a Star
 CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
The evolution of a Solar-like system. Young Solar-like Systems. Searching for Extrasolar Planets: Motivation
 Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Birth & Death of Stars
 Birth & Death of Stars Objectives How are stars formed How do they die How do we measure this The Interstellar Medium (ISM) Vast clouds of gas & dust lie between stars Diffuse hydrogen clouds: dozens of
Birth & Death of Stars Objectives How are stars formed How do they die How do we measure this The Interstellar Medium (ISM) Vast clouds of gas & dust lie between stars Diffuse hydrogen clouds: dozens of
Astronomy. physics.wm.edu/~hancock/171/ A. Dayle Hancock. Small 239. Office hours: MTWR 10-11am
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Astrobiology. Joseph Spitale
 Astrobiology Joseph Spitale 1 What is Astrobiology? Science that studies the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe - Combines many sciences: Biology, Chemistry, Planetary
Astrobiology Joseph Spitale 1 What is Astrobiology? Science that studies the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe - Combines many sciences: Biology, Chemistry, Planetary
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4
 Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)
 Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Selected Questions from Minute Papers. Outline - March 2, Stellar Properties. Stellar Properties Recap. Stellar properties recap
 Black Holes: Selected Questions from Minute Papers Will all the material in the Milky Way eventually be sucked into the BH at the center? Does the star that gives up mass to a BH eventually get pulled
Black Holes: Selected Questions from Minute Papers Will all the material in the Milky Way eventually be sucked into the BH at the center? Does the star that gives up mass to a BH eventually get pulled
Pluto. Touring our Solar System. September 08, The Solar System.notebook. Solar System includes: Sun 8 planets Asteroids Comets Meteoroids
 Touring our Solar System Solar System includes: Sun 8 planets Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Jan 4 5:48 PM Jan 4 5:50 PM A planet's orbit lies in an inclined orbital plane Planes of seven planets lie within
Touring our Solar System Solar System includes: Sun 8 planets Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Jan 4 5:48 PM Jan 4 5:50 PM A planet's orbit lies in an inclined orbital plane Planes of seven planets lie within
The Big Bang Theory (page 854)
 Name Class Date Space Homework Packet Homework #1 Hubble s Law (pages 852 853) 1. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? 2. The shift in the light of a galaxy toward the red wavelengths is called
Name Class Date Space Homework Packet Homework #1 Hubble s Law (pages 852 853) 1. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? 2. The shift in the light of a galaxy toward the red wavelengths is called
Astronomy 101 Lab: Spectra
 Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Spectra You will access your textbook in this lab. Pre-Lab Assignment: In class, we've talked about different kinds of spectra and what kind of object produces each kind of spectrum.
Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Spectra You will access your textbook in this lab. Pre-Lab Assignment: In class, we've talked about different kinds of spectra and what kind of object produces each kind of spectrum.
Radioactive Dating. U238>Pb206. Halflife: Oldest earth rocks. Meteors and Moon rocks. 4.5 billion years billion years
 U238>Pb206 Halflife: 4.5 billion years Oldest earth rocks 3.96 billion years Meteors and Moon rocks 4.6 billion years This is the time they solidified The solar system is older than this. Radioactive Dating
U238>Pb206 Halflife: 4.5 billion years Oldest earth rocks 3.96 billion years Meteors and Moon rocks 4.6 billion years This is the time they solidified The solar system is older than this. Radioactive Dating
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes
 Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
TABLE OF CONTENTS. click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? Neptune (Pluto) The Sun. Asteroids. Mercury.
 The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
The Jamie Drake Equation
 The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
ASTR 380. The Universe: the context for Life
 ASTR 380 The Universe: the context for Life Simple facts: The Universe is vast. The Universe is old. The elements for life are wide-spread. Our physical laws appear universal The Universe is mostly empty!
ASTR 380 The Universe: the context for Life Simple facts: The Universe is vast. The Universe is old. The elements for life are wide-spread. Our physical laws appear universal The Universe is mostly empty!
Life and Death of a Star. Chapters 20 and 21
 Life and Death of a Star Chapters 20 and 21 90 % of a stars life Most stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. A star like the Sun, for example, after spending a few tens of millions of years
Life and Death of a Star Chapters 20 and 21 90 % of a stars life Most stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. A star like the Sun, for example, after spending a few tens of millions of years
the nature of the universe, galaxies, and stars can be determined by observations over time by using telescopes
 the nature of the universe, galaxies, and stars can be determined by observations over time by using telescopes The spectral lines of stars tell us their approximate composition Remember last year in Physics?
the nature of the universe, galaxies, and stars can be determined by observations over time by using telescopes The spectral lines of stars tell us their approximate composition Remember last year in Physics?
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates.
 1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Mar 22, INSTRUCTIONS: First ll in your name and social security number (both by printing
 ASTRONOMY 0089: EXAM 2 Class Meets M,W,F, 1:00 PM Mar 22, 1996 INSTRUCTIONS: First ll in your name and social security number (both by printing and by darkening the correct circles). Sign your answer sheet
ASTRONOMY 0089: EXAM 2 Class Meets M,W,F, 1:00 PM Mar 22, 1996 INSTRUCTIONS: First ll in your name and social security number (both by printing and by darkening the correct circles). Sign your answer sheet
Exploring Our Solar System
 Exploring Our Solar System Our Solar System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Exploring Our Solar System Our Solar System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Stellar Composition. How do we determine what a star is made of?
 Stars Essential Questions What are stars? What is the apparent visual magnitude of a star? How do we locate stars? How are star classified? How has the telescope changed our understanding of stars? What
Stars Essential Questions What are stars? What is the apparent visual magnitude of a star? How do we locate stars? How are star classified? How has the telescope changed our understanding of stars? What
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Origin of the Solar System
 Origin of the Solar System and Solar System Debris 1 Debris comets meteoroids asteroids gas dust 2 Asteroids irregular, rocky hunks small in mass and size Ceres - largest, 1000 km in diameter (1/3 Moon)
Origin of the Solar System and Solar System Debris 1 Debris comets meteoroids asteroids gas dust 2 Asteroids irregular, rocky hunks small in mass and size Ceres - largest, 1000 km in diameter (1/3 Moon)
Today. Solar System Formation. a few more bits and pieces. Homework due
 Today Solar System Formation a few more bits and pieces Homework due Pluto Charon 3000 km Asteroids small irregular rocky bodies Comets icy bodies Formation of the Solar System How did these things come
Today Solar System Formation a few more bits and pieces Homework due Pluto Charon 3000 km Asteroids small irregular rocky bodies Comets icy bodies Formation of the Solar System How did these things come
