The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI)
|
|
|
- Ira Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) Our goals for learning What is the Drake equation? How many habitable planets have life? How many civilizations are out there? How does SETI work? Can SETI be justified rationally?
2 How many civilizations are out there? The Drake Equation Number of civilizations with whom we could potentially communicate = N HP f life f civ f now N HP = total # of habitable planets in galaxy f life = fraction of habitable planets with life f civ = fraction of life-bearing planets with civilizations at some time f now = fraction of civilizations around now.
3 Our activity Number of Sophomore, sociology students in the library on a weekday night with short hair using a laptop Min = 1 Max = 625 Average = 65 Most around 50 Good deal of uncertainty, even on this simple problem
4 How many Habitable Planets in Milky Way? N HP f life f civ f now Best estimates come from Kepler observations:
5 Kepler observes only a small fraction of the sky Kepler Field of View
6 Kepler Mission is becoming more sensitive to smaller planets BLUE = 1 st yr data RED = 2 nd yr data YELLOW = 3 rd yr data Notice smaller planets with longer periods being discovered in 3 rd yr data
7 How many Habitable Planets in Milky Way? N HP f life f civ f now Initial extrapolations from Kepler observations: N stars in the Galaxy with planets ~ 50 billion
8 What fraction of our Solar System in Habitable Zone? Solar System Habitable Zone from AU Orbit of Neptune (farthest planet) is ~ 30 AU Area of H.Z. p ( ) Fraction of H.Z. = = ~ 0.01 Area of Sol. Sys. p 30 2
9 How many Habitable Planets in Milky Way? N HP f life f civ f now Initial extrapolations from Kepler observations: N stars in the Galaxy with planets ~ 50 billion But only ~ 1:100 of those stars has a planet in a Habitable Zone N HP ~ 500 million
10 How many Habitable Planets have life? N HP f life f civ f now To date, we only know of 1 example: Most Pessimistic Estimate: f life ~ 1 / 500 million
11 Solid surface with atmosphere conducive to life 40% of Kepler-discovered planets are Super-Earths or smaller
12 However - Moon of Gas Giants Could be Habitable
13 Development of life happened in few 100 million years
14 Earth was heavily bombarded with rocks/comets Possible sterilization of biogensis
15 Age dating craters on Moon are direct evidence of this
16 Indeed the Moon was formed by a large impact
17 And the Moon coalesced from the debris
18 Impacts may have sterilized early Earth shortening time for biogenesis
19 Is Biogensis Common?? If yes, then optimistic estimate: f life ~ 0.5-1
20 Water is common in all Star-Forming Regions
21 Need enough time for SUPERGIANTS Biogensis GIANTS High mass limit of 2 times solar mass for lifetime to be at least 1 billion years for development of complex life. WHITE DWARFS Low mass limit of 30% of solar mass to have a habitable zone spanning region of the terrestrial planets.
22 Red dwarfs are most numerous stars in Milky Way (~90%) But they have the smallest Habitable Zones The less massive the star is, the smaller the habitable zone.
23 Tidal locking can occur with strong interaction (being close) Same side of Moon always faces Earth
24 Tidal locking should occur for planets close to stars Planets in H.Z. around red dwarfs may have same face always facing the star = potentially bad for life
25 Stellar Flares can be detrimental to life Fast rotating large planets can have strong, protective magnetic field Red dwarf are more active than solar-type stars
26 Gas Speed (km/s) More evidence size matters : retaining an atmosphere Retains hydrogen Retains water Below this line, H 2 can escape planet gravity Below this line, H 2 O can escape planet gravity Temperature (K)
27 Our Solar System may hold the answer Life on Europa? Was there ever life on Mars?
28 How many Habitable Planets have life? N HP f life f civ f now Bottom line is that we don t know and the answer could be anywhere between ~ 0 and 1 Most Pessimistic Estimate: f life ~ 1 / 500 million Is Biogensis Common?? If yes, then Optimistic Estimate: f life ~ 0.5-1
29 How many planets with life develop intelligence? N HP f life f civ f now To date, we only know of 1 example and it took 4.5 billion years:
30 It took almost 4 billion years before Cambrian Explosion
31 How many planets with life develop intelligence? N HP f life f civ f now To date, we only know of 1 example and it took 4.5 billion years:
32 Earth s Moon has stabilized tilt of orbital axis
33 Mars has no moon to stabilize its rotation axis Climatic variability how does this affect life?
34 Earth has plate tectonics which cycles Carbon Plate tectonics favor larger planets?
35 Was Earth lucky? Water from comets? Jupiter protecting us from sterilizing events Large moon, stable rotation Magnetic field Plate tectonics
36 How many planets have intelligent life now? N HP f life f civ f now Major extinction events have occurred in the past
37 f now = L civ /L planet How many planets have intelligent life now? N HP f life f civ f now Ends of civilizations may be self-inflicted
38 We do not know the values for the Drake Equation N HP : ~ 500 million (estimates will improve next few yrs) f life :??? Hard to say (near 0 or near 1) f civ :??? It took 4.5 billion years on Earth f now :??? Can civilizations survive long-term?
39 Optimistic case N HP : ~ 500 million f life : 0.5 f civ : 0.1 f now : L civ = 1 million years, L planet = 10 billion years f now = 10-4 N civ = 2500 Note: this is highly dependent on L civ
40 Pessimistic case N HP : ~ 500 million f life : 1 in a million f civ : 1 in a million f now : L civ = years, L planet = 10 billion years f now = 10-6 N civ = 5*10-10 However, with galaxies life in the Universe is not out of the question
41 A Series of Diminishing Factors
42 So why is this a useful equation? Frank Drake
43 How many planets have communicating civilizations? N HP f life f civ f communicate Humans have had radio communication for only ~ 100 years
44 We ve even sent a few deliberate signals ourselves Earth to globular cluster M13: Hoping we ll hear back in about 42,000 years!
45 How does SETI work? Looking for deliberate signals from E.T.
46 Best Frequency to search is in Radio lowest noise
47 Your computer can help! Home: a screensaver with a purpose, looking for signals in radio data (mostly just noise).
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Life in the Universe
 Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe. Earliest Life Forms. When did life arise on Earth? Fossils in Sedimentary Rock. Fossils in Sedimentary Rock
 Chapter 24 Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of life? When did life arise on Earth? Earliest
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of life? When did life arise on Earth? Earliest
Searching for Life: Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds. Life in the Universe. Earliest Fossils. Laboratory Experiments.
 Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
12/5/ Life on Earth. Chapter 19: Life in the Universe. When did life arise on Earth? Earliest Life Forms. Important Stuff (Section 001)
 Important Stuff (Section 001) The Final Exam is Thursday, December 22, 8:00 10:00 am The Final Exam will be given in: Willey 175 Don t come to Anderson 210. No one will be there. No one. Bring 2 pencils
Important Stuff (Section 001) The Final Exam is Thursday, December 22, 8:00 10:00 am The Final Exam will be given in: Willey 175 Don t come to Anderson 210. No one will be there. No one. Bring 2 pencils
Habitable Planets: 2 Estimating f s "
 Habitable Planets: 2 Estimating f s " Stellar Requirements (f s )" We assume that our planet needs to orbit a star" Leaves out planets around brown dwarfs" Leaves out nomad planets (may be many)" About
Habitable Planets: 2 Estimating f s " Stellar Requirements (f s )" We assume that our planet needs to orbit a star" Leaves out planets around brown dwarfs" Leaves out nomad planets (may be many)" About
NSCI EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION. Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
Chapter 24: Life in the Universe
 Chapter 24 Lecture Chapter 24: Life in the Universe Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning: When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of
Chapter 24 Lecture Chapter 24: Life in the Universe Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning: When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of
The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals. Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV
 The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV Associated Universities, Inc; April/2016 2 Preliminary thoughts a. How certain are you that other
The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV Associated Universities, Inc; April/2016 2 Preliminary thoughts a. How certain are you that other
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site:
 ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 37: Life in the Universe [4/18/07] Announcements Habitability of
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 37: Life in the Universe [4/18/07] Announcements Habitability of
Young Solar-like Systems
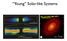 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 28. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes
 Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
Earth in the Universe Unit Notes The Universe - everything everywhere, 15-20 billion years old Inside the universe there are billions of Galaxies Inside each Galaxy there are billions of Solar Systems
Cosmology Overview (so far): Cosmology Overview (so far): The Age of the Universe. The Big Bang. The Age of the Universe
 Cosmology Overview (so far): The Universe: Everything Observable Universe: Everything we can The Universe has no special locations No If no, then no Cosmology Overview (so far): Oblers s Paradox: The sky
Cosmology Overview (so far): The Universe: Everything Observable Universe: Everything we can The Universe has no special locations No If no, then no Cosmology Overview (so far): Oblers s Paradox: The sky
1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day. 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space
 Vocabulary: Match the vocabulary terms on the left with the definitions on the right 1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space 3. Orbital Period
Vocabulary: Match the vocabulary terms on the left with the definitions on the right 1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space 3. Orbital Period
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Kira Bonk ascension.html
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)
 Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Intelligent Life in the Universe
 Intelligent Life in the Universe Lecture 33 APoD: Easter Island Eclipse In-Class Question 1) Do you think life exists elsewhere in the Universe? a) Yes b) No c) Don t know d) Don t care 2 33-1 Lecture
Intelligent Life in the Universe Lecture 33 APoD: Easter Island Eclipse In-Class Question 1) Do you think life exists elsewhere in the Universe? a) Yes b) No c) Don t know d) Don t care 2 33-1 Lecture
n p = n e for stars like Sun f s = fraction of stars with suitable properties
 Habitable Planets n e Number of planets, per planetary system that are suitable for life n e = n p x f s planetary stellar n p = n e for stars like Sun f s = fraction of stars with suitable properties
Habitable Planets n e Number of planets, per planetary system that are suitable for life n e = n p x f s planetary stellar n p = n e for stars like Sun f s = fraction of stars with suitable properties
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
CHAPTER 11. We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration
 CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Alex Bara
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 10): Origin of the Moon Ilana Strauss Next Class: Our Planet Scott Huber Thomas Hymel HW 2! Alex Bara http://userpages.bright.net/~phobia/main.htm! Margaret Sharp http://hubpages.com/hub/proof-that-ufos-exist---
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 10): Origin of the Moon Ilana Strauss Next Class: Our Planet Scott Huber Thomas Hymel HW 2! Alex Bara http://userpages.bright.net/~phobia/main.htm! Margaret Sharp http://hubpages.com/hub/proof-that-ufos-exist---
The Physical Basis of Life
 Origins of Life Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 19 Learning Outcomes: The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry.
Origins of Life Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 19 Learning Outcomes: The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry.
Measuring Distances to Galaxies. Galaxies in Motion. Hubble s Law. Galaxy Redshifts. Type Ia Supernovae. Supernovae are Good Standard Candles
 Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Presentations. Outline. ! Nicholas Langhammer esp_sociopol_washingtondc01.
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 13): What is n p? Anna Dorn Praneet Sahgal HW 2 Nicholas Langhammer http://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/sociopolitica/ esp_sociopol_washingtondc01.htm Next Class: Life on
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 13): What is n p? Anna Dorn Praneet Sahgal HW 2 Nicholas Langhammer http://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/sociopolitica/ esp_sociopol_washingtondc01.htm Next Class: Life on
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
The Physics of Exoplanets
 The Physics of Exoplanets Heike Rauer Institut für Planetenforschung, DLR, Berlin-Adlershof, Zentrum für Astronomie und Astrophysik, TU Berlin Formation in protoplanetary disk, migration Loss of primary,
The Physics of Exoplanets Heike Rauer Institut für Planetenforschung, DLR, Berlin-Adlershof, Zentrum für Astronomie und Astrophysik, TU Berlin Formation in protoplanetary disk, migration Loss of primary,
The evolution of a Solar-like system. Young Solar-like Systems. Searching for Extrasolar Planets: Motivation
 Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
General Considerations! Habitable Planets! Key Requirement: a Liquid! Water Phase Diagram! 2/3/11!
 General Considerations! Habitable Planets! Number of planets, per planetary system, suitable for life (n e )! Useful to break into 2 factors! n e = n p x f s! n p = n e for stars like Sun! f s is fraction
General Considerations! Habitable Planets! Number of planets, per planetary system, suitable for life (n e )! Useful to break into 2 factors! n e = n p x f s! n p = n e for stars like Sun! f s is fraction
The Moon & Mercury: Dead Worlds
 The Moon & Mercury: Dead Worlds There are many similarities between the Moon and Mercury, and some major differences we ll concentrate mostly on the Moon. Appearance of the Moon from the Earth We ve already
The Moon & Mercury: Dead Worlds There are many similarities between the Moon and Mercury, and some major differences we ll concentrate mostly on the Moon. Appearance of the Moon from the Earth We ve already
Celestial Objects. Background Questions. 1. What was invented in the 17 th century? How did this help the study of our universe? 2. What is a probe?
 Background Questions Celestial Objects 1. What was invented in the 17 th century? How did this help the study of our universe? 2. What is a probe? 3. Describe the Galileo probe mission. 4. What are scientists
Background Questions Celestial Objects 1. What was invented in the 17 th century? How did this help the study of our universe? 2. What is a probe? 3. Describe the Galileo probe mission. 4. What are scientists
Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets
 Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets star--about 10 11 in our galaxy. Average separation is a few light years. (Compare with size of Galaxy: about 100,000 light years) planet--indirect
Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets star--about 10 11 in our galaxy. Average separation is a few light years. (Compare with size of Galaxy: about 100,000 light years) planet--indirect
Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway?
 Welcome to Class 1: Drake EquaCon, SETI & Fermi Paradox Is it crazy to search for intelligent life? Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway? What would you like to spend most of our last class on? 1. Early SETI,
Welcome to Class 1: Drake EquaCon, SETI & Fermi Paradox Is it crazy to search for intelligent life? Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway? What would you like to spend most of our last class on? 1. Early SETI,
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence
 Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
The Physical Basis of Life. The Origin of Life on Earth. Information Storage and Duplication
 The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry. Carbon-based DNA and RNA molecule strands are the basic carriers of
The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry. Carbon-based DNA and RNA molecule strands are the basic carriers of
Star. Planet. Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe?
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Our Solar System and Its Place in the Universe
 Our Solar System and Its Place in the Universe The Formation of the Solar System Our Solar System includes: Planets Dwarf Planets Moons Small Solar System bodies Sun Outer portion created Planets and their
Our Solar System and Its Place in the Universe The Formation of the Solar System Our Solar System includes: Planets Dwarf Planets Moons Small Solar System bodies Sun Outer portion created Planets and their
Test 4 Final Review. 5/2/2018 Lecture 25
 Test 4 Final Review 5/2/2018 Lecture 25 Apparent daily motion of celestial objects is due to earth s rotation Seasons are created due to the title of the Earth relative to the Sun Phases of the moon due
Test 4 Final Review 5/2/2018 Lecture 25 Apparent daily motion of celestial objects is due to earth s rotation Seasons are created due to the title of the Earth relative to the Sun Phases of the moon due
Solar System Unit Tracking Sheet
 Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science Solar System Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target The Solar System is 4.6 billion years old Question Example How is the age of the solar system estimated by scientists?
Name Period Mrs. Coates Earth Science Solar System Unit Tracking Sheet Learning Target The Solar System is 4.6 billion years old Question Example How is the age of the solar system estimated by scientists?
The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Natures, Orbits, and Impacts. Chapter 12 Review Clickers
 Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Natures, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroids a) are rocky and small typically the size of a grain of rice or
Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Natures, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroids a) are rocky and small typically the size of a grain of rice or
Asteroids, Comets and NEOs. (Answers) Solar System Impacts. Author: Sarah Roberts
 Asteroids, Comets and NEOs (Answers) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Impact craters on the Earth 1. Using the data given below for real impact craters on the Earth, investigate the effect
Asteroids, Comets and NEOs (Answers) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Impact craters on the Earth 1. Using the data given below for real impact craters on the Earth, investigate the effect
Solar System Research Teacher Notes The Sun
 The Sun G-type main sequence star (G2V), also known as a yellow dwarf Mass = 1.99 x 10 30 kg or 333,000 Earths. Volume = 1.41 x 10 18 km 3 or 1,300,000 Earths. Density (average) = 1.41 g/cm 3 or 0.255
The Sun G-type main sequence star (G2V), also known as a yellow dwarf Mass = 1.99 x 10 30 kg or 333,000 Earths. Volume = 1.41 x 10 18 km 3 or 1,300,000 Earths. Density (average) = 1.41 g/cm 3 or 0.255
Introduction to the Universe. What makes up the Universe?
 Introduction to the Universe What makes up the Universe? Objects in the Universe Astrophysics is the science that tries to make sense of the universe by - describing the Universe (Astronomy) - understanding
Introduction to the Universe What makes up the Universe? Objects in the Universe Astrophysics is the science that tries to make sense of the universe by - describing the Universe (Astronomy) - understanding
Space Science Jeopardy!
 Space Science Jeopardy! Structure of the Universe Stars & HR Diagram Seasons, Tides, Phases, Eclipses Astronomical Bodies The Sun & Gravity 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50
Space Science Jeopardy! Structure of the Universe Stars & HR Diagram Seasons, Tides, Phases, Eclipses Astronomical Bodies The Sun & Gravity 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50
Physics can only take us so far!
 Physics can only take us so far! The usual approach of science of constructing a mathematical model cannot answer the questions of why there should be a universe for the model to describe. Why does the
Physics can only take us so far! The usual approach of science of constructing a mathematical model cannot answer the questions of why there should be a universe for the model to describe. Why does the
JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS. To begin lets start with an outline of the solar system.
 JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS To begin lets start with an outline of the solar system. JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS What are Jovian and Terrestrial planets? Terrestrial planets are Earth like planets,
JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS To begin lets start with an outline of the solar system. JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS What are Jovian and Terrestrial planets? Terrestrial planets are Earth like planets,
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name
 ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
CVtpf 2-1. Section 1 Review. 3. Describe How did the process of outgassing help shape Earth's atmosphere?
 ----------------------------- ---------- ------ Section 1 Review CVtpf 2-1 -- SECTION VOCABULARY planet a celestial body that orbits the sun, is round because of its own gravity, and has cleared the neighborhood
----------------------------- ---------- ------ Section 1 Review CVtpf 2-1 -- SECTION VOCABULARY planet a celestial body that orbits the sun, is round because of its own gravity, and has cleared the neighborhood
Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)
![Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)](/thumbs/77/76655554.jpg) Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
What I know today about the Final
 What I know today about the Final Tuesday, December 10, 8 11 am, same place Around 90 mul9ple choice ques9ons Closed book and closed note No smartphones allowed Calculators of any kind are permiced, but
What I know today about the Final Tuesday, December 10, 8 11 am, same place Around 90 mul9ple choice ques9ons Closed book and closed note No smartphones allowed Calculators of any kind are permiced, but
The Modern Origins Story: From the Big Bang to Habitable Planets
 The Modern Origins Story: From the Big Bang to Habitable Planets Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) The Solar System Age 4.5Gyrs 8 (9? 10? 12?) planets orbiting the sun all in roughly the same plane Lots of
The Modern Origins Story: From the Big Bang to Habitable Planets Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) The Solar System Age 4.5Gyrs 8 (9? 10? 12?) planets orbiting the sun all in roughly the same plane Lots of
Sample Test. 5. Which of the surfaces is the youngest? A) 1A B) 1B C) 1C D) 1D E) There is no way to tell.
 Sample Test 1. The yellow arrows in image 1B are pointing to a form of A) liquid erosion. B) plate tectonics. C) tidally cracked surface. D) wind erosion (sand dunes). E) All of the above. 2. If an object
Sample Test 1. The yellow arrows in image 1B are pointing to a form of A) liquid erosion. B) plate tectonics. C) tidally cracked surface. D) wind erosion (sand dunes). E) All of the above. 2. If an object
4 Decoding the Arecibo Message
 4 Decoding the Arecibo Message In 1974, the Arecebo radio telescope was used to send a message into space. The message was directed at the globular cluster M13, which is an assembly of hundreds of thousands
4 Decoding the Arecibo Message In 1974, the Arecebo radio telescope was used to send a message into space. The message was directed at the globular cluster M13, which is an assembly of hundreds of thousands
Galaxies and Stars. 3. Base your answer to the following question on The reaction below represents an energy-producing process.
 Galaxies and Stars 1. To an observer on Earth, the Sun appears brighter than the star Rigel because the Sun is A) hotter than Rigel B) more luminous than Rigel C) closer than Rigel D) larger than Rigel
Galaxies and Stars 1. To an observer on Earth, the Sun appears brighter than the star Rigel because the Sun is A) hotter than Rigel B) more luminous than Rigel C) closer than Rigel D) larger than Rigel
I always wanted to be somebody, but I should have been more specific. Lilly Tomlin Reading has been updated. (All of Chaps. 9& 10) Friday, first sit
 I always wanted to be somebody, but I should have been more specific. Lilly Tomlin Reading has been updated. (All of Chaps. 9& 10) Friday, first sit for passing back HW, then with chart. Water on the Moon?
I always wanted to be somebody, but I should have been more specific. Lilly Tomlin Reading has been updated. (All of Chaps. 9& 10) Friday, first sit for passing back HW, then with chart. Water on the Moon?
21/11/ /11/2017 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8
 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 8. The scale of time and nature of worlds (Page
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 8. The scale of time and nature of worlds (Page
What is Earth Science?
 What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
LESSON topic: formation of the solar system Solar system formation Star formation Models of the solar system Planets in our solar system
 Unit 2 Lesson 1 LESSON topic: formation of the solar system - Solar system formation - Star formation - Models of the solar system - Planets in our solar system Big bang theory Origin of the universe According
Unit 2 Lesson 1 LESSON topic: formation of the solar system - Solar system formation - Star formation - Models of the solar system - Planets in our solar system Big bang theory Origin of the universe According
Overview of Solar System
 Overview of Solar System The solar system is a disk Rotation of sun, orbits of planets all in same direction. Most planets rotate in this same sense. (Venus, Uranus, Pluto are exceptions). Angular momentum
Overview of Solar System The solar system is a disk Rotation of sun, orbits of planets all in same direction. Most planets rotate in this same sense. (Venus, Uranus, Pluto are exceptions). Angular momentum
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
TABLE OF CONTENTS. click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? Neptune (Pluto) The Sun. Asteroids. Mercury.
 The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe
 Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Learning Objectives. they differ in density (composition, core), atmosphere, surface age, size, geological activity, magnetic field?
 Mercury and Venus Learning Objectives! Contrast the Earth, the Moon, Venus and Mercury. Do they differ in density (composition, core), atmosphere, surface age, size, geological activity, magnetic field?!
Mercury and Venus Learning Objectives! Contrast the Earth, the Moon, Venus and Mercury. Do they differ in density (composition, core), atmosphere, surface age, size, geological activity, magnetic field?!
Habitability Outside the Solar System. A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller
 Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion
 Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder
Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Cosmology Vocabulary
 Cosmology Vocabulary Vocabulary Words Terrestrial Planets The Sun Gravity Galaxy Lightyear Axis Comets Kuiper Belt Oort Cloud Meteors AU Nebula Solar System Cosmology Universe Coalescence Jovian Planets
Cosmology Vocabulary Vocabulary Words Terrestrial Planets The Sun Gravity Galaxy Lightyear Axis Comets Kuiper Belt Oort Cloud Meteors AU Nebula Solar System Cosmology Universe Coalescence Jovian Planets
Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Akos Kereszturi Editorial Board member
 Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Akos Kereszturi Editorial Board member Research Center for Astronomy and Earth Sciences Hungarian Academy of Sciences Hungary Biography Dr. Akos Kereszturi Akos
Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Akos Kereszturi Editorial Board member Research Center for Astronomy and Earth Sciences Hungarian Academy of Sciences Hungary Biography Dr. Akos Kereszturi Akos
Introduction to the Universe
 What makes up the Universe? Introduction to the Universe Book page 642-644 Objects in the Universe Astrophysics is the science that tries to make sense of the universe by - describing the Universe (Astronomy)
What makes up the Universe? Introduction to the Universe Book page 642-644 Objects in the Universe Astrophysics is the science that tries to make sense of the universe by - describing the Universe (Astronomy)
2. Very generally, describe how the Milky Way Galaxy formed. (Words or labeled picture)
 Potter Name: Date: Hour: Score: /11 Learning Check 2.1 LT 2.1 Galaxy Formation: I am able to describe the formation of the Milky Way Galaxy and our solar system and model earth s position in each. 1. Label
Potter Name: Date: Hour: Score: /11 Learning Check 2.1 LT 2.1 Galaxy Formation: I am able to describe the formation of the Milky Way Galaxy and our solar system and model earth s position in each. 1. Label
Universe Celestial Object Galaxy Solar System
 ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
Earth Space Systems. Semester 1 Exam. Astronomy Vocabulary
 Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
UNIT 3: Chapter 8: The Solar System (pages )
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
Lesson 1 The Structure of the Solar System
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
LESSON 1. Solar System
 Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Solar system Stars and Galaxies
 5/18/16 Solar system Stars and Solar system, stars and galaxies The life cycle of stars inner planets/outer planets nebular theory novae and supernovae gravita>onal contrac>on white dwarf and black holes
5/18/16 Solar system Stars and Solar system, stars and galaxies The life cycle of stars inner planets/outer planets nebular theory novae and supernovae gravita>onal contrac>on white dwarf and black holes
ASTRONOMY. Eric Chaisson. Steve McMillan. A Beginner's Guide to the Universe FOURTH EDITION. Tufts University. Drexel University
 ASTRONOMY A Beginner's Guide to the Universe FOURTH EDITION Eric Chaisson Tufts University Steve McMillan Drexel University PEARSON Prentice Hall Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey
ASTRONOMY A Beginner's Guide to the Universe FOURTH EDITION Eric Chaisson Tufts University Steve McMillan Drexel University PEARSON Prentice Hall Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates.
 1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
What is the solar system?
 Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner Teaching Packs - Space - Page 1 In this section, you will learn about... 1. About the objects in the Solar System. 2. How the Solar System formed. 3. About the Asteroid Belt, Kuiper
By Helen and Mark Warner Teaching Packs - Space - Page 1 In this section, you will learn about... 1. About the objects in the Solar System. 2. How the Solar System formed. 3. About the Asteroid Belt, Kuiper
The Search for Extra-terrestrial. Is there anybody out there?
 The Search for Extra-terrestrial Intelligence! Is there anybody out there? Summary: we will investigate (a) the Drake Equation and (b) the factors that determine how many, if any, other civilizations
The Search for Extra-terrestrial Intelligence! Is there anybody out there? Summary: we will investigate (a) the Drake Equation and (b) the factors that determine how many, if any, other civilizations
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology
 Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
Directions: For numbers 1-30 please choose the letter that best fits the description.
 Directions: For numbers 1-30 please choose the letter that best fits the description. 1. The main force responsible for the formation of the universe is: a. Gravity b. Frictional force c. Magnetic force
Directions: For numbers 1-30 please choose the letter that best fits the description. 1. The main force responsible for the formation of the universe is: a. Gravity b. Frictional force c. Magnetic force
Primary KS1 1 VotesForSchools2018
 Primary KS1 1 Do aliens exist? This photo of Earth was taken by an astronaut on the moon! Would you like to stand on the moon? What is an alien? You probably drew some kind of big eyed, blue-skinned,
Primary KS1 1 Do aliens exist? This photo of Earth was taken by an astronaut on the moon! Would you like to stand on the moon? What is an alien? You probably drew some kind of big eyed, blue-skinned,
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley Comparative Planetology Studying the similarities among and differences between the planets
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley Comparative Planetology Studying the similarities among and differences between the planets
þ Tiered questions that probe lower and higher-order thinking þ Differentiated for upper elementary and intermediate students þ Addresses NGSS and
 þ Tiered questions that probe lower and higher-order thinking þ Differentiated for upper elementary and intermediate students þ Addresses NGSS and many state science standard concepts By Stephanie Elkowitz
þ Tiered questions that probe lower and higher-order thinking þ Differentiated for upper elementary and intermediate students þ Addresses NGSS and many state science standard concepts By Stephanie Elkowitz
Ultimate Events. Galaxy clustering in ever deeper surveys. Models of universe and its fates
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Ultimate Events Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 30 Thur 28 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Allen Telescope Array Review current big
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Ultimate Events Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 30 Thur 28 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Allen Telescope Array Review current big
Which of the following statements best describes the general pattern of composition among the four jovian
 Part A Which of the following statements best describes the general pattern of composition among the four jovian planets? Hint A.1 Major categories of ingredients in planetary composition The following
Part A Which of the following statements best describes the general pattern of composition among the four jovian planets? Hint A.1 Major categories of ingredients in planetary composition The following
The Solar System. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left.
 The Solar System Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The fact that each planet s orbit is an ellipse was discovered by a. Copernicus.
The Solar System Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The fact that each planet s orbit is an ellipse was discovered by a. Copernicus.
Space Notes 2. Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8
 Space Notes 2 Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8 Sun Average Size Star Sun 101 Sun s Mass almost 100 times the mass of all the planets combined. Most of the mass is hydrogen gas Thermonuclear Reaction Thermonuclear
Space Notes 2 Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8 Sun Average Size Star Sun 101 Sun s Mass almost 100 times the mass of all the planets combined. Most of the mass is hydrogen gas Thermonuclear Reaction Thermonuclear
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements
 Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Fusion in first few minutes after Big Bang form lightest elements Stars build the rest of the elements up to Iron (Fe) through fusion The rest of the elements beyond Iron (Fe) are produced in the dying
Solar System Test Review
 Solar System Test Review There are several planets in the solar system. What do all of these planets have in common? A.They all orbit the Sun. B. They are all close to the Moon. C.They are all called Earth.
Solar System Test Review There are several planets in the solar system. What do all of these planets have in common? A.They all orbit the Sun. B. They are all close to the Moon. C.They are all called Earth.
Apparent Motion. How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky?
 Apparent Motion How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky? 1 Apparent Motions Geocentric Universe - idea that Earth was at the center of the solar system Stars all rotate around the Earth
Apparent Motion How do celestial objects appear to move across the sky? 1 Apparent Motions Geocentric Universe - idea that Earth was at the center of the solar system Stars all rotate around the Earth
FCAT Review Space Science
 FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
Astronomy: Exploring the Universe
 Course Syllabus Astronomy: Exploring the Universe Course Description Why do stars twinkle? Is it possible to fall into a black hole? Will the sun ever stop shining? Since the first glimpse of the night
Course Syllabus Astronomy: Exploring the Universe Course Description Why do stars twinkle? Is it possible to fall into a black hole? Will the sun ever stop shining? Since the first glimpse of the night
Our Planetary System. Chapter 7
 Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Detection of Earth-like planets
 Planets and life Successful detections of extrasolar giant planets suggests that planetary systems may be fairly common could we detect Earthlike planets? is it likely that such planets would have life?
Planets and life Successful detections of extrasolar giant planets suggests that planetary systems may be fairly common could we detect Earthlike planets? is it likely that such planets would have life?
