(x! 4) (x! 4)10 + C + C. 2 e2x dx = 1 2 (1 + e 2x ) 3 2e 2x dx. # 8 '(4)(1 + e 2x ) 3 e 2x (2) = e 2x (1 + e 2x ) 3 & dx = 1
|
|
|
- Laureen Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 33. x(x - 4) 9 Let u = x - 4, then du = and x = u + 4. x(x - 4) 9 = (u + 4)u 9 du = (u 0 + 4u 9 )du = u + 4u0 0 = (x! 4) (x! 4)0 (x " 4) (x " 4)0 ( '( = ()(x - 4)0 () (0)(x - 4)9 () = (x - 4) 9 [(x - 4) + 4] = x(x - 4) Let u = + e 2x, then du = 2e 2x. e 2x ( + e 2x ) 3 = ( + e 2x ) e2x = 2 ( + e 2x ) 3 2e 2x = 2 u3 du = 2 u 4 4 = 8 ( + e2x ) 4 " 8 ( + e2x ) 4 ' = " 8 '(4)( + e 2x ) 3 e 2x (2) = e 2x ( + e 2x ) Let u = 4 + 2x + x 2, then du = (2 + 2x) = 2( + x). + x 4 + 2x + x 2 = + x 4 + 2x + x 2 2( + x) = + x x + x 2 2(2 + x) = 2 u du = 2 ln u = 2 ln 4 + 2x + x2 " 2 ln4 + 2x + x2 ' = " 2 ' 4 + 2x + x 2 (2 + 2x) = + x 4 + 2x + x Let u = x 4 + 2x 2 +, then du = (4x 3 + 4x) = 4(x 3 + x). x 3 + x (x 4 + 2x 2 + ) 4 = (x 4 + 2x 2 + ) (x3 + x) = 4 (x 4 + 2x 2 + ) -4 4(x 3 + x) = 4 u -4 du = 4 u!3!3 =!u!3 2 = "(x4 + 2x 2 + ) "3 2 " 2 (x4 + 2x 2 + ) "3 ' ( = " (("3)(x 4 + 2x 2 + ) -4 (4x 3 + 4x) 2' = (x 4 + 2x 2 + ) -4 (x 3 + x) EXERCISE
2 4. (A) Differentiate F(x) = ln 2x - 3 to see if you get the integrand f(x) = 2x! 3 (B) Wrong; d [ln 2x - 3 ] = 2x! 3 (2) = 2 2x! 3 2x! 3 (C) Let u = 2x - 3, then du = 2 2x! 3 = 2x! = 2 2x! 3 2 = 2 u du = 2 ln u = 2 ln 2x ln2x " 3 ' ( = 2 2x! 3 2 = 2x! (A) Differentiate F(x) = e x4 to see if you get the integrand f(x) = x 3 e x4. (B) Wrong; d [ex4 + c] = e x4 (4x 3 ) = 4x 3 e x4 x 3 e x4 (C) Let u = x 4, then du = 4x 3 x 3 e x4 = 4 4 x3 e x4 = 4 4x 3 e x4 = 4 e u du = 4 eu = 4 ex4 " 4 ex 4 ' = 4 ex4 (4x 3 ) = x 3 e x4 45. (A) Differentiate F(x) = (x2! 2) 2 3x f(x) = 2(x 2-2) 2 (B) Wrong; d (x 2 " 2) 2 3x to see if you get the integrand ( '( = 3x! 2(x2 " 2)(2x) " (x 2 " 2) 2! 3 9x 2 = (x2! 2)[9x 2 + 6] 9x 2 = 9x4! 2x 2! 2 9x 2 = 3x4! 4x 2! 4 3x 2 2(x 2-2) CHAPTER 6 INTEGRATION
3 (C) 2(x 2-2) 2 = 2(x 4-4x 2 + 4) = 2 5 x 5 " 4 3 x3 + 4x ' ( = 2 5 x5-8 3 x3 + 8x 2 5 x 5 " 8 3 x3 + 8x ' ( = 2x4-8x = 2[x 4-4x 2 + 4] = 2(x 2-2) Let u = 3x 2 + 7, then du = 6x. x 3x = (3x 2 + 7) /2 x = (3x 2 + 7) /2 6 6 x = u /2 du = 6 6 u = 9 (3x2 + 7) 3/2 " 9 (3x2 + 7) 3 2 ' =! 3 9 " 2 (3x2 + 7) /2 (6x) = x(3x 2 + 7) /2 49. x(x 3 + 2) 2 = x(x 6 + 4x 3 + 4) = (x 7 + 4x 4 + 4x) 5. x 2 (x 3 + 2) 2 = x x5 + 2x 2 " x x 5 + 2x 2 ' Let u = x 3 + 2, then du = 3x 2. x 2 (x 3 + 2) 2 = x 2 (x 3 + 2) 2 3x 2 ' = x7 + 4x 4 + 4x = x(x 6 + 4x 3 + 4) = x(x 3 + 2) 2 3 = 3 (x 3 + 2) 2 3x 2 = 3 u2 du = 3 u 3 3 = 9 u3 = 9 (x3 + 2) 3 " 9 (x3 + 2) 3 ' = 9 (3)(x3 + 2) 2 (3x 2 ) = x 2 (x 3 + 2) Let u = 2x 4 + 3, then du = 8x 3. x 3 2x = (2x 4 + 3) -/2 x 3 = (2x 4 + 3) -/2 8 8 x3 = u -/2 du = 8 8 u 2 2 = 4 (2x4 + 3) /2 " 4 (2x4 + 3) 2 ' = " '(2x 4 + 3) -/2 (8x 3 ) = 4 2 x 3 (2x 4 + 3) 2 EXERCISE
4 55. Let u = ln x, then du = x. (ln x)3 = u 3 du = u4 (ln x)4 = x 4 4 " (ln x) 4 ' 4 ' = 4 (4)(ln x)3 x 57. Let u =! x = -x-, then du = x 2. x 2 e-/x = e u du = e u = e -/x [e-/x ] = e -/x " ' = 59. = 7t2 (t 3 + 5) 6 x 2 x 2 e-/x = (ln x)3 x Let u = t 3 + 5, then du = 3t 2. x = 7t 2 (t 3 + 5) 6 = 7t 2 (t 3 + 5) 6 = 7(t 3 + 5) t2 = 7 3 u 6 du = 7 3 u 7 7 = 3 (t3 + 5) 7 6. dy = 3t t 2 " 4 Let u = t 2-4, then du = 2t. 3t y = (t 2! 4) 2 = 3 (t 2-4) -/2 t = 3(t 2-4) -/2 2 2 t 63. dp = ex + e!x (e x! e!x ) 2 = 3 2 u-/2 du = 3 2 u 2 Let u = e x - e -x, then du = (e x + e -x ). 2 = 3(t2-4) /2 p = ex + e!x (e x! e!x ) 2 = (e x - e -x ) -2 (e x + e -x ) = u -2 du 65. Let v = au, then dv = a du. e au du = e au a = u!! = -(ex - e -x ) - a du = a e au a du = a e v dv = a ev = a eau " du a eau ' + a eau (a) = e au 374 CHAPTER 6 INTEGRATION
5 67. p'(x) =!6000 (3x + 50) 2 Let u = 3x + 50, then du = 3.!6000 p(x) = (3x + 50) 2 = (3x + 50) -2 = -6000(3x + 50) Given p(50) = 4: = (3! ) 4 = C = 0 Thus, p(x) = x = -2000u -2 u! du = -2000! = x + 50 Now, 2.50 = x (3x + 50) = x + 25 = x = 875 x = 250 Thus, the demand is 250 bottles when the price is C'(x) = x +, x > 0! 500 C(x) = 2 + " x + = (u = x +, du = ) x + = 2x ln(x + ) Now, C(0) = Thus, C(x) = 2x ln(x + ) The average cost is: C (x) = ln(x + ) + x x and C (000) = ln(00) = ln(00) or 7.45 per pair of shoes 7. S'(t) = 0-0e -0.t, 0 t 24 (A) S(t) = (0-0e -0.t ) = 0-0e -0.t = 0t - 0!0. e-0.t = 0t + 00e -0.t Given S(0) = 0: e 0 = 0 00 = 0 C = -00 Total sales at time t: S(t) = 0t + 00e -0.t 00, 0 t 24. EXERCISE
6 (B) S(2) = 0(2) + 00e -0.(2) - 00 = e Total estimated sales for the first twelve months: 50 million. (C) On a graphing utility, solve 0t + 00e -0.t - 00 = 00 or 0t + 00e -0.t = 200 The result is: t 8.4 months. " Q(t) = R(t) = t ' = 00 t = 00 ln(t + ) + 5t Given Q(0) = 0: 0 = 00 ln() + 0 Thus, C = 0 and Q(t) = 00 ln(t + ) + 5t, 0 t 20. Q(9) = 00 ln(9 + ) + 5(9) = 00 ln thousand barrels. 75. W(t) = W(t) = 0.2e 0.t = e 0.t (0.) = 2e 0.t Given W(0) = 2: 2 = 2e 0. Thus, C = 0 and W(t) = 2e 0.t. The weight of the culture after 8 hours is given by: W(8) = 2e 0.(8) = 2e grams. 77. dn = t + t 2, 0 t 0 (A) To find the minimum value of dn, calculate d " dn ' = d2 N 2 = -( + t2 )(2000)! 2000t (2t) ( + t 2 ) 2 = [ " t2 ] ( + t 2 ) 2 = critical value: t = Now dn t=0 = 0 dn t= = -,000 "2000( " t)( + t) ( + t 2 ) 2 dn t=0 =!20, Thus, the minimum value of dn is -,000 bacteria/ml per day. 376 CHAPTER 6 INTEGRATION
7 (B) N =!2,000t + t 2 Let u = + t 2, then du = 2t N =!2,000t + t 2 = -,000 2t + t 2 = -,000 u du = -,000 ln u = -,000 ln( + t 2 ) Given N(0) = 5,000: 5,000 = -,000 ln() = C (ln = 0) Thus, C = 5,000 and N(t) = 5,000 -,000 ln( + t 2 ) Now, N(0) = 5,000 -,000 ln( ) = 5,000 -,000 ln(0) 385 bacteria/ml (C) Set N(t) =,000 and solve for t:,000 = 5,000 -,000 ln( + t 2 ) ln( + t 2 ) = 4 + t 2 = e 4 t 2 = e 4 - t = e 4 " 7.32 days 79. N'(t) = 6e -0.t, 0 t 5 N(t) = N(t) = 6e -0.t = 6e -0.t = 6!0. e -0.t (-0.) = -60e -0.t Given N(0) = 40: 40 = -60e 0 Hence, C = 00 and N(t) = 00-60e -0.t, 0 t 5. The number of words per minute after completing the course is: N(5) = 00-60e -0.(5) = 00-60e words per minute. 8. de = 5000(t + )-3/2, t 0 Let u = t +, then du = E = 5000(t + ) -3/2 = 5000(t + ) -3/2 = 5000u -3/2 du = 5000 u! 2! 2 = -0,000(t + )-/2 = "0,000 t + Given E(0) = 2000: 2000 = "0,000 Hence, C = 2,000 and E(t) = 2,000-0,000 t +. EXERCISE
8 The projected enrollment 5 years from now is: E(5) = 2,000-0,000 0,000 0,000 = 2,000 - = 2, = 9500 students EXERCISE 6-3 Things to remember:. A DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION is an equation that involves an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. The ORDER of a differential equation is the order of the highest derivative of the unknown function. 2. A SLOPE FIELD for a first-order differential equation is obtained by drawing tangent line segments determined by the equation at each point in a grid. 3. EXPONENTIAL GROWTH LAW If dq = rq and Q(0) = Q 0, then Q(t) = Q 0 ert, where Q 0 = Amount at t = 0 r = Relative growth rate (expressed as a decimal) t = Time Q = Quantity at time t 4. COMPARISON OF EXPONENTIAL GROWTH PHENOMENA DESCRIPTION MODEL SOLUTION GRAPH USES Unlimited growth: Rate of growth is proportional to the amount present Exponential decay: Rate of growth is proportional to the amount present Limited growth: Rate of growth is proportional to the difference between the amount present and a fixed limit dy = ky k, t > 0 y(0) = c dy = -ky k, t > 0 y(0) = c dy = k(m - y) k, t > 0 y(0) = 0 y = ce kt y = ce -kt y = M( - e -kt ) c c M y 0 y 0 y 0 t t t Short-term population growth (people, bacteria, etc.) Growth of money at continuous compound interest Price-supply curves Depletion of natural resources Radioactive decay Light absorption in water Price-demand curves Atmospheric pressure (t is altitude) Sales fads (e.g., skateboards) Depreciation of equipment Company growth Learning Logistic growth: Rate of growth is proportional to the amount present and to the difference between the amount present and a fixed limit dy = ky(m - y) k, t > 0 y(0) = M!+!c y = M!-!ce -kmt M y 0 t Long-term population growth Epidemics Sales of new products Rumor spread Company growth 378 CHAPTER 6 INTEGRATION
dy dx dx = 7 1 x dx dy = 7 1 x dx e u du = 1 C = 0
 1. = 6x = 6x = 6 x = 6 x x 2 y = 6 2 + C = 3x2 + C General solution: y = 3x 2 + C 3. = 7 x = 7 1 x = 7 1 x General solution: y = 7 ln x + C. = e.2x = e.2x = e.2x (u =.2x, du =.2) y = e u 1.2 du = 1 e u
1. = 6x = 6x = 6 x = 6 x x 2 y = 6 2 + C = 3x2 + C General solution: y = 3x 2 + C 3. = 7 x = 7 1 x = 7 1 x General solution: y = 7 ln x + C. = e.2x = e.2x = e.2x (u =.2x, du =.2) y = e u 1.2 du = 1 e u
Section 6-1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals
 Name Date Class Section 6-1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals Goal: To find antiderivatives and indefinite integrals of functions using the formulas and properties Theorem 1 Antiderivatives If the
Name Date Class Section 6-1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals Goal: To find antiderivatives and indefinite integrals of functions using the formulas and properties Theorem 1 Antiderivatives If the
1 Differential Equations
 Reading [Simon], Chapter 24, p. 633-657. 1 Differential Equations 1.1 Definition and Examples A differential equation is an equation involving an unknown function (say y = y(t)) and one or more of its
Reading [Simon], Chapter 24, p. 633-657. 1 Differential Equations 1.1 Definition and Examples A differential equation is an equation involving an unknown function (say y = y(t)) and one or more of its
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 2017 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 236 ELAC FALL 207 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) 27 p 3 27 p 3 ) 2) If 9 t 3 4t 9-2t = 3, find t. 2) Solve the equation.
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 207 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) 27 p 3 27 p 3 ) 2) If 9 t 3 4t 9-2t = 3, find t. 2) Solve the equation.
Applications of First Order Differential Equation
 Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 39 Orthogonal Trajectories How to Find Orthogonal Trajectories Growth and Decay
Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 39 Orthogonal Trajectories How to Find Orthogonal Trajectories Growth and Decay
Section 6-1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals
 Name Date Class Section 6- Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals Goal: To find antiderivatives and indefinite integrals of functions using the formulas and properties Theorem Antiderivatives If the
Name Date Class Section 6- Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals Goal: To find antiderivatives and indefinite integrals of functions using the formulas and properties Theorem Antiderivatives If the
UNIT 2 DERIVATIVES 2.1 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION APPLICATIONS. Pre-Class:
 1830 UNIT 2 DERIVATIVES 2.1 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION APPLICATIONS Pre-Class: Take notes on the videos and readings (use the space below). Work and check problem #1 in the 2.1 NOTES section.
1830 UNIT 2 DERIVATIVES 2.1 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION APPLICATIONS Pre-Class: Take notes on the videos and readings (use the space below). Work and check problem #1 in the 2.1 NOTES section.
(C) BOARDWORK: Examples: Solve w/ & w/o calculator (approx vs exact)
 (A Lesson Context BIG PICTURE of this UNIT: How do algebraically & graphically work with growth and decay applications? What are logarithms and how do we invert or undo an exponential function? How do
(A Lesson Context BIG PICTURE of this UNIT: How do algebraically & graphically work with growth and decay applications? What are logarithms and how do we invert or undo an exponential function? How do
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems. (1) Let us consider the circle with equation. (b) Find the center and the radius of the circle given above.
 INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
3. Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve given by 3x y e x+y = 1 + ln x at (1, 1).
 1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications
 34 Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications Recall that exponential functions are one-to-one since every horizontal line passes through at most one point on the graph of y = b x. So, an exponential
34 Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications Recall that exponential functions are one-to-one since every horizontal line passes through at most one point on the graph of y = b x. So, an exponential
Today: 5.4 General log and exp functions (continued) Warm up:
 Today: 5.4 General log and exp functions (continued) Warm up: log a (x) =ln(x)/ ln(a) d dx log a(x) = 1 ln(a)x 1. Evaluate the following functions. log 5 (25) log 7 p 7 log4 8 log 4 2 2. Di erentiate the
Today: 5.4 General log and exp functions (continued) Warm up: log a (x) =ln(x)/ ln(a) d dx log a(x) = 1 ln(a)x 1. Evaluate the following functions. log 5 (25) log 7 p 7 log4 8 log 4 2 2. Di erentiate the
17 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 17 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Concepts: Exponential Functions Power Functions vs. Exponential Functions The Definition of an Exponential Function Graphing Exponential Functions Exponential Growth
17 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Concepts: Exponential Functions Power Functions vs. Exponential Functions The Definition of an Exponential Function Graphing Exponential Functions Exponential Growth
Math 1120, Section 6 Calculus Test 3
 November 15, 2012 Name The total number of points available is 158 Throughout this test, show your work Using a calculator to circumvent ideas discussed in class will generally result in no credit In general
November 15, 2012 Name The total number of points available is 158 Throughout this test, show your work Using a calculator to circumvent ideas discussed in class will generally result in no credit In general
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES 3.8 Exponential Growth and Decay In this section, we will: Use differentiation to solve real-life problems involving exponentially growing quantities. EXPONENTIAL
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES 3.8 Exponential Growth and Decay In this section, we will: Use differentiation to solve real-life problems involving exponentially growing quantities. EXPONENTIAL
2. (10 points) Find an equation for the line tangent to the graph of y = e 2x 3 at the point (3/2, 1). Solution: y = 2(e 2x 3 so m = 2e 2 3
 November 24, 2009 Name The total number of points available is 145 work Throughout this test, show your 1 (10 points) Find an equation for the line tangent to the graph of y = ln(x 2 +1) at the point (1,
November 24, 2009 Name The total number of points available is 145 work Throughout this test, show your 1 (10 points) Find an equation for the line tangent to the graph of y = ln(x 2 +1) at the point (1,
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MAC 1105 Fall 2007 - Final Exam Dr. Schnackenberg If you do not agree with the given answers, answer "E" for "None of the above". MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
MAC 1105 Fall 2007 - Final Exam Dr. Schnackenberg If you do not agree with the given answers, answer "E" for "None of the above". MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
Section 2.3: Logarithmic Functions Lecture 3 MTH 124
 Procedural Skills Learning Objectives 1. Build an exponential function using the correct compounding identifiers (annually, monthly, continuously etc...) 2. Manipulate exponents algebraically. e.g. Solving
Procedural Skills Learning Objectives 1. Build an exponential function using the correct compounding identifiers (annually, monthly, continuously etc...) 2. Manipulate exponents algebraically. e.g. Solving
Chapter 6: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Section 6.1: Algebra and Composition of Functions #1-9: Let f(x) = 2x + 3 and g(x) = 3 x. Find each function. 1) (f + g)(x) 2) (g f)(x) 3) (f/g)(x) 4) ( )( ) 5) ( g/f)(x) 6) ( )( ) 7) ( )( ) 8) (g+f)(x)
Section 6.1: Algebra and Composition of Functions #1-9: Let f(x) = 2x + 3 and g(x) = 3 x. Find each function. 1) (f + g)(x) 2) (g f)(x) 3) (f/g)(x) 4) ( )( ) 5) ( g/f)(x) 6) ( )( ) 7) ( )( ) 8) (g+f)(x)
10 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 10 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Concepts: Rules of Exponents Exponential Functions Power Functions vs. Exponential Functions The Definition of an Exponential Function Graphing Exponential Functions
10 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Concepts: Rules of Exponents Exponential Functions Power Functions vs. Exponential Functions The Definition of an Exponential Function Graphing Exponential Functions
( + ) 3. AP Calculus BC Chapter 6 AP Exam Problems. Antiderivatives. + + x + C. 2. If the second derivative of f is given by f ( x) = 2x cosx
 Chapter 6 AP Eam Problems Antiderivatives. ( ) + d = ( + ) + 5 + + 5 ( + ) 6 ( + ). If the second derivative of f is given by f ( ) = cos, which of the following could be f( )? + cos + cos + + cos + sin
Chapter 6 AP Eam Problems Antiderivatives. ( ) + d = ( + ) + 5 + + 5 ( + ) 6 ( + ). If the second derivative of f is given by f ( ) = cos, which of the following could be f( )? + cos + cos + + cos + sin
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 2014: Lectures Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers. 24x + 72 (x 2 6x + 4) 4
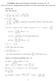 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
INTERNET MAT 117. Solution for the Review Problems. (1) Let us consider the circle with equation. x 2 + 2x + y 2 + 3y = 3 4. (x + 1) 2 + (y + 3 2
 INTERNET MAT 117 Solution for the Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (i) Group
INTERNET MAT 117 Solution for the Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (i) Group
Section 11.3 Rates of Change:
 Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Name Class. 5. Find the particular solution to given the general solution y C cos x and the. x 2 y
 10 Differential Equations Test Form A 1. Find the general solution to the first order differential equation: y 1 yy 0. 1 (a) (b) ln y 1 y ln y 1 C y y C y 1 C y 1 y C. Find the general solution to the
10 Differential Equations Test Form A 1. Find the general solution to the first order differential equation: y 1 yy 0. 1 (a) (b) ln y 1 y ln y 1 C y y C y 1 C y 1 y C. Find the general solution to the
Integration by Partial Fractions
 Integration by Partial Fractions 1. If f(x) = P(x) / Q(x) with P(x) and Q(x) polynomials AND Q(x) a higher order than P(x) AND Q(x) factorable in linear factors then we can rewrite f(x) as a sum of rational
Integration by Partial Fractions 1. If f(x) = P(x) / Q(x) with P(x) and Q(x) polynomials AND Q(x) a higher order than P(x) AND Q(x) factorable in linear factors then we can rewrite f(x) as a sum of rational
1.3 Exponential Functions
 22 Chapter 1 Prerequisites for Calculus 1.3 Exponential Functions What you will learn about... Exponential Growth Exponential Decay Applications The Number e and why... Exponential functions model many
22 Chapter 1 Prerequisites for Calculus 1.3 Exponential Functions What you will learn about... Exponential Growth Exponential Decay Applications The Number e and why... Exponential functions model many
Math RE - Calculus II Differential Equations Page 1 of 9
 Math 201-203-RE - Calculus II Differential Equations Page 1 of 9 Introduction to Differential equation (O.D.E) A differential equation is an equation containing derivatives such as: (1) xy = y 5 (2) d2
Math 201-203-RE - Calculus II Differential Equations Page 1 of 9 Introduction to Differential equation (O.D.E) A differential equation is an equation containing derivatives such as: (1) xy = y 5 (2) d2
Section 6.8 Exponential Models; Newton's Law of Cooling; Logistic Models
 Section 6.8 Exponential Models; Newton's Law of Cooling; Logistic Models 197 Objective #1: Find Equations of Populations that Obey the Law of Uninhibited Growth. In the last section, we saw that when interest
Section 6.8 Exponential Models; Newton's Law of Cooling; Logistic Models 197 Objective #1: Find Equations of Populations that Obey the Law of Uninhibited Growth. In the last section, we saw that when interest
Business and Life Calculus
 Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 2 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 203 / 55
Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 2 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 203 / 55
Chapter 6: Messy Integrals
 Chapter 6: Messy Integrals Review: Solve the following integrals x 4 sec x tan x 0 0 Find the average value of 3 1 x 3 3 Evaluate 4 3 3 ( x 1), then find the area of ( x 1) 4 Section 6.1: Slope Fields
Chapter 6: Messy Integrals Review: Solve the following integrals x 4 sec x tan x 0 0 Find the average value of 3 1 x 3 3 Evaluate 4 3 3 ( x 1), then find the area of ( x 1) 4 Section 6.1: Slope Fields
Homework 3. (33-40) The graph of an exponential function is given. Match each graph to one of the following functions.
 Homework Section 4. (-40) The graph of an exponential function is given. Match each graph to one of the following functions. (a)y = x (b)y = x (c)y = x (d)y = x (e)y = x (f)y = x (g)y = x (h)y = x (46,
Homework Section 4. (-40) The graph of an exponential function is given. Match each graph to one of the following functions. (a)y = x (b)y = x (c)y = x (d)y = x (e)y = x (f)y = x (g)y = x (h)y = x (46,
Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = 3
 Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = g(x) = p x + x We know want to look at two di erent types of functions, called logarithmic functions and exponential functions.
Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = g(x) = p x + x We know want to look at two di erent types of functions, called logarithmic functions and exponential functions.
x C) y = - A) $20000; 14 years B) $28,000; 14 years C) $28,000; 28 years D) $30,000; 15 years
 Dr. Lee - Math 35 - Calculus for Business - Review of 3 - Show Complete Work for Each Problem MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find
Dr. Lee - Math 35 - Calculus for Business - Review of 3 - Show Complete Work for Each Problem MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find
2. (12 points) Find an equation for the line tangent to the graph of f(x) =
 November 23, 2010 Name The total number of points available is 153 Throughout this test, show your work Throughout this test, you are expected to use calculus to solve problems Graphing calculator solutions
November 23, 2010 Name The total number of points available is 153 Throughout this test, show your work Throughout this test, you are expected to use calculus to solve problems Graphing calculator solutions
First Order Differential Equations
 Chapter 2 First Order Differential Equations Introduction Any first order differential equation can be written as F (x, y, y )=0 by moving all nonzero terms to the left hand side of the equation. Of course,
Chapter 2 First Order Differential Equations Introduction Any first order differential equation can be written as F (x, y, y )=0 by moving all nonzero terms to the left hand side of the equation. Of course,
Chapter. Integration. 1. Antidifferentiation: The Indefinite Integral. 2. Integration by Substitution. 3. Introduction to Differential Equations
 Integration Chapter. Antidifferentiation: The Indefinite Integral 2. Integration by Substitution 3. Introduction to Differential Equations 4. Integration by Parts Chapter Summary and Review Problems Antidifferentiation:
Integration Chapter. Antidifferentiation: The Indefinite Integral 2. Integration by Substitution 3. Introduction to Differential Equations 4. Integration by Parts Chapter Summary and Review Problems Antidifferentiation:
AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 6) (Mr. Surowski)
 AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 6) (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Suppose that f is an odd differentiable function. Then (A) f(1); (B) f (1) (C) f(1) f( 1) (D) 0 (E). 1 1 xf (x) =. The
AP Calculus Testbank (Chapter 6) (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Suppose that f is an odd differentiable function. Then (A) f(1); (B) f (1) (C) f(1) f( 1) (D) 0 (E). 1 1 xf (x) =. The
Doug Clark The Learning Center 100 Student Success Center learningcenter.missouri.edu Overview
 Math 1400 Final Exam Review Saturday, December 9 in Ellis Auditorium 1:00 PM 3:00 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part 1: Derivatives and Applications of Derivatives 3:30 PM 5:30 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part
Math 1400 Final Exam Review Saturday, December 9 in Ellis Auditorium 1:00 PM 3:00 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part 1: Derivatives and Applications of Derivatives 3:30 PM 5:30 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29,
 MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
Inverse Functions. Definition 1. The exponential function f with base a is denoted by. f(x) = a x
 Inverse Functions Definition 1. The exponential function f with base a is denoted by f(x) = a x where a > 0, a 1, and x is any real number. Example 1. In the same coordinate plane, sketch the graph of
Inverse Functions Definition 1. The exponential function f with base a is denoted by f(x) = a x where a > 0, a 1, and x is any real number. Example 1. In the same coordinate plane, sketch the graph of
Section Exponential Functions
 121 Section 4.1 - Exponential Functions Exponential functions are extremely important in both economics and science. It allows us to discuss the growth of money in a money market account as well as the
121 Section 4.1 - Exponential Functions Exponential functions are extremely important in both economics and science. It allows us to discuss the growth of money in a money market account as well as the
Practice Questions for Final Exam - Math 1060Q - Fall 2014
 Practice Questions for Final Exam - Math 1060Q - Fall 01 Before anyone asks, the final exam is cumulative. It will consist of about 50% problems on exponential and logarithmic functions, 5% problems on
Practice Questions for Final Exam - Math 1060Q - Fall 01 Before anyone asks, the final exam is cumulative. It will consist of about 50% problems on exponential and logarithmic functions, 5% problems on
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A
 Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
6.1 Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus
 6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus 6. ANTIDERIVATIVES AND SLOPE FIELDS Indefinite Integrals In the previous chapter we dealt with definite integrals. Definite integrals had limits of integration.
6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus 6. ANTIDERIVATIVES AND SLOPE FIELDS Indefinite Integrals In the previous chapter we dealt with definite integrals. Definite integrals had limits of integration.
1 What is a differential equation
 Math 10B - Calculus by Hughes-Hallett, et al. Chapter 11 - Differential Equations Prepared by Jason Gaddis 1 What is a differential equation Remark 1.1. We have seen basic differential equations already
Math 10B - Calculus by Hughes-Hallett, et al. Chapter 11 - Differential Equations Prepared by Jason Gaddis 1 What is a differential equation Remark 1.1. We have seen basic differential equations already
7.1. Calculus of inverse functions. Text Section 7.1 Exercise:
 Contents 7. Inverse functions 1 7.1. Calculus of inverse functions 2 7.2. Derivatives of exponential function 4 7.3. Logarithmic function 6 7.4. Derivatives of logarithmic functions 7 7.5. Exponential
Contents 7. Inverse functions 1 7.1. Calculus of inverse functions 2 7.2. Derivatives of exponential function 4 7.3. Logarithmic function 6 7.4. Derivatives of logarithmic functions 7 7.5. Exponential
Math Want to have fun with chapter 4? Find the derivative. 1) y = 5x2e3x. 2) y = 2xex - 2ex. 3) y = (x2-2x + 3) ex. 9ex 4) y = 2ex + 1
 Math 160 - Want to have fun with chapter 4? Name Find the derivative. 1) y = 52e3 2) y = 2e - 2e 3) y = (2-2 + 3) e 9e 4) y = 2e + 1 5) y = e - + 1 e e 6) y = 32 + 7 7) y = e3-1 5 Use calculus to find
Math 160 - Want to have fun with chapter 4? Name Find the derivative. 1) y = 52e3 2) y = 2e - 2e 3) y = (2-2 + 3) e 9e 4) y = 2e + 1 5) y = e - + 1 e e 6) y = 32 + 7 7) y = e3-1 5 Use calculus to find
Assignment 5 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Assignment 5 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f(x)
Assignment 5 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f(x)
Part 4: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Part 4: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Chapter 5 I. Exponential Functions (5.1) II. The Natural Exponential Function (5.2) III. Logarithmic Functions (5.3) IV. Properties of Logarithms (5.4) V.
Part 4: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Chapter 5 I. Exponential Functions (5.1) II. The Natural Exponential Function (5.2) III. Logarithmic Functions (5.3) IV. Properties of Logarithms (5.4) V.
Name: Partners: PreCalculus. Review 5 Version A
 Name: Partners: PreCalculus Date: Review 5 Version A [A] Circle whether each statement is true or false. 1. 3 log 3 5x = 5x 2. log 2 16 x+3 = 4x + 3 3. ln x 6 + ln x 5 = ln x 30 4. If ln x = 4, then e
Name: Partners: PreCalculus Date: Review 5 Version A [A] Circle whether each statement is true or false. 1. 3 log 3 5x = 5x 2. log 2 16 x+3 = 4x + 3 3. ln x 6 + ln x 5 = ln x 30 4. If ln x = 4, then e
MATH 1040 CP 11 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 1040 CP 11 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Write the equation in its equivalent exponential form. 1) log 5 125 = 3 1) 2) log 2 16
MATH 1040 CP 11 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Write the equation in its equivalent exponential form. 1) log 5 125 = 3 1) 2) log 2 16
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs)
 c01.tex 8/10/2010 22: 55 Page 1 PART A Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Chap. 1 First-Order ODEs Sec. 1.1 Basic Concepts. Modeling To get a good start into this chapter and this section, quickly
c01.tex 8/10/2010 22: 55 Page 1 PART A Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Chap. 1 First-Order ODEs Sec. 1.1 Basic Concepts. Modeling To get a good start into this chapter and this section, quickly
LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 130 LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: A differential equation (DE) is an equation involving an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. A differential
130 LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: A differential equation (DE) is an equation involving an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. A differential
Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs
 Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs Section 5 Exponential Functions Objectives for Section 2.5 Exponential Functions The student will be able to graph and identify the properties of exponential functions. The
Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs Section 5 Exponential Functions Objectives for Section 2.5 Exponential Functions The student will be able to graph and identify the properties of exponential functions. The
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 2017 CA 10 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 36 ELAC FALL 7 CA MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) In a certain country, the rate of increase of the population is proportional
MATH 36 ELAC FALL 7 CA MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) In a certain country, the rate of increase of the population is proportional
Notes for exponential functions The week of March 6. Math 140
 Notes for exponential functions The week of March 6 Math 140 Exponential functions: formulas An exponential function has the formula f (t) = ab t, where b is a positive constant; a is the initial value
Notes for exponential functions The week of March 6 Math 140 Exponential functions: formulas An exponential function has the formula f (t) = ab t, where b is a positive constant; a is the initial value
Study Guide - Part 2
 Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
33. The gas law for an ideal gas at absolute temperature T (in. 34. In a fish farm, a population of fish is introduced into a pond
 SECTION 3.8 EXPONENTIAL GROWTH AND DECAY 2 3 3 29. The cost, in dollars, of producing x yards of a certain fabric is Cx 1200 12x 0.1x 2 0.0005x 3 (a) Find the marginal cost function. (b) Find C200 and
SECTION 3.8 EXPONENTIAL GROWTH AND DECAY 2 3 3 29. The cost, in dollars, of producing x yards of a certain fabric is Cx 1200 12x 0.1x 2 0.0005x 3 (a) Find the marginal cost function. (b) Find C200 and
Exponential Growth (Doubling Time)
 Exponential Growth (Doubling Time) 4 Exponential Growth (Doubling Time) Suppose we start with a single bacterium, which divides every hour. After one hour we have 2 bacteria, after two hours we have 2
Exponential Growth (Doubling Time) 4 Exponential Growth (Doubling Time) Suppose we start with a single bacterium, which divides every hour. After one hour we have 2 bacteria, after two hours we have 2
dx. Ans: y = tan x + x2 + 5x + C
 Chapter 7 Differential Equations and Mathematical Modeling If you know one value of a function, and the rate of change (derivative) of the function, then yu can figure out many things about the function.
Chapter 7 Differential Equations and Mathematical Modeling If you know one value of a function, and the rate of change (derivative) of the function, then yu can figure out many things about the function.
Honors Advanced Algebra Chapter 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions and Relations Target Goals
 Honors Advanced Algebra Chapter 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions and Relations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Graph exponential growth functions. (8.1) Graph exponential
Honors Advanced Algebra Chapter 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions and Relations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Graph exponential growth functions. (8.1) Graph exponential
nt and A = Pe rt to solve. 3) Find the accumulated value of an investment of $10,000 at 4% compounded semiannually for 5 years.
 Exam 4 Review Approximate the number using a calculator. Round your answer to three decimal places. 1) 2 1.7 2) e -1.4 Use the compound interest formulas A = P 1 + r n nt and A = Pe rt to solve. 3) Find
Exam 4 Review Approximate the number using a calculator. Round your answer to three decimal places. 1) 2 1.7 2) e -1.4 Use the compound interest formulas A = P 1 + r n nt and A = Pe rt to solve. 3) Find
Pre-Calculus Exponential/Logarithm Quiz 3A Name Date Period Part 1: Non-Calculator 1. Determine which graph below is the graph of the function.
 Pre-Calculus Exponential/Logarithm Quiz A Name Date Period Part : Non-Calculator. Determine which graph below is the graph of the function. E). Identif the operation that will transform the graph of (
Pre-Calculus Exponential/Logarithm Quiz A Name Date Period Part : Non-Calculator. Determine which graph below is the graph of the function. E). Identif the operation that will transform the graph of (
p351 Section 5.5: Bases Other than e and Applications
 p351 Section 5.5: Bases Other than e and Applications Definition of Exponential Function to Base a If a is a positive real number (a 1) and x is any real number, then the exponential function to the base
p351 Section 5.5: Bases Other than e and Applications Definition of Exponential Function to Base a If a is a positive real number (a 1) and x is any real number, then the exponential function to the base
Part I: Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each) d dx (x3 e 4x ) =
 Part I: Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each) 1. d dx (x3 e 4x ) = (a) 12x 2 e 4x (b) 3x 2 e 4x + 4x 4 e 4x 1 (c) x 3 e 4x + 12x 2 e 4x (d) 3x 2 e 4x + 4x 3 e 4x (e) 4x 3 e 4x 1 2. Suppose f(x) is
Part I: Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each) 1. d dx (x3 e 4x ) = (a) 12x 2 e 4x (b) 3x 2 e 4x + 4x 4 e 4x 1 (c) x 3 e 4x + 12x 2 e 4x (d) 3x 2 e 4x + 4x 3 e 4x (e) 4x 3 e 4x 1 2. Suppose f(x) is
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative
![The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative](/thumbs/96/128959530.jpg) 1 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f
1 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f
Math 110 Final Exam General Review. Edward Yu
 Math 110 Final Exam General Review Edward Yu Da Game Plan Solving Limits Regular limits Indeterminate Form Approach Infinities One sided limits/discontinuity Derivatives Power Rule Product/Quotient Rule
Math 110 Final Exam General Review Edward Yu Da Game Plan Solving Limits Regular limits Indeterminate Form Approach Infinities One sided limits/discontinuity Derivatives Power Rule Product/Quotient Rule
Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes
 Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes Implicit Differentiation and Related Rates Why? We have learned how to take derivatives of functions, and we have seen many applications of this. However
Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes Implicit Differentiation and Related Rates Why? We have learned how to take derivatives of functions, and we have seen many applications of this. However
Exponential Functions Concept Summary See pages Vocabulary and Concept Check.
 Vocabulary and Concept Check Change of Base Formula (p. 548) common logarithm (p. 547) exponential decay (p. 524) exponential equation (p. 526) exponential function (p. 524) exponential growth (p. 524)
Vocabulary and Concept Check Change of Base Formula (p. 548) common logarithm (p. 547) exponential decay (p. 524) exponential equation (p. 526) exponential function (p. 524) exponential growth (p. 524)
( ) = f(x) 6 INTEGRATION. Things to remember: n + 1 EXERCISE A function F is an ANTIDERIVATIVE of f if F'(x) = f(x).
 6 INTEGRATION EXERCISE 6-1 Things to remember: 1. A function F is an ANTIDERIVATIVE of f if F() = f().. THEOREM ON ANTIDERIVATIVES If the derivatives of two functions are equal on an open interval (a,
6 INTEGRATION EXERCISE 6-1 Things to remember: 1. A function F is an ANTIDERIVATIVE of f if F() = f().. THEOREM ON ANTIDERIVATIVES If the derivatives of two functions are equal on an open interval (a,
College Algebra. Word Problems
 College Algebra Word Problems Example 2 (Section P6) The table shows the numbers N (in millions) of subscribers to a cellular telecommunication service in the United States from 2001 through 2010, where
College Algebra Word Problems Example 2 (Section P6) The table shows the numbers N (in millions) of subscribers to a cellular telecommunication service in the United States from 2001 through 2010, where
Math 1120 Calculus Final Exam
 May 4, 2001 Name The first five problems count 7 points each (total 35 points) and rest count as marked. There are 195 points available. Good luck. 1. Consider the function f defined by: { 2x 2 3 if x
May 4, 2001 Name The first five problems count 7 points each (total 35 points) and rest count as marked. There are 195 points available. Good luck. 1. Consider the function f defined by: { 2x 2 3 if x
Population Changes at a Constant Percentage Rate r Each Time Period
 Concepts: population models, constructing exponential population growth models from data, instantaneous exponential growth rate models, logistic growth rate models. Population can mean anything from bacteria
Concepts: population models, constructing exponential population growth models from data, instantaneous exponential growth rate models, logistic growth rate models. Population can mean anything from bacteria
(MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R)
 College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCE University of Toronto FINAL EXAMINATIONS, APRIL 2016 MAT 133Y1Y Calculus and Linear Algebra for Commerce
 FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCE University of Toronto FINAL EXAMINATIONS, APRIL 206 MAT YY Calculus and Linear Algebra for Commerce Duration: Examiners: hours N. Hoell A. Igelfeld D. Reiss L. Shorser J. Tate
FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCE University of Toronto FINAL EXAMINATIONS, APRIL 206 MAT YY Calculus and Linear Algebra for Commerce Duration: Examiners: hours N. Hoell A. Igelfeld D. Reiss L. Shorser J. Tate
Fundamentals of Mathematics (MATH 1510)
 Fundamentals of Mathematics () Instructor: Email: shenlili@yorku.ca Department of Mathematics and Statistics York University February 3-5, 2016 Outline 1 growth (doubling time) Suppose a single bacterium
Fundamentals of Mathematics () Instructor: Email: shenlili@yorku.ca Department of Mathematics and Statistics York University February 3-5, 2016 Outline 1 growth (doubling time) Suppose a single bacterium
5.1 Separable Differential Equations
 5.1 Separable Differential Equations A differential equation is an equation that has one or more derivatives in it. The order of a differential equation is the highest derivative present in the equation.
5.1 Separable Differential Equations A differential equation is an equation that has one or more derivatives in it. The order of a differential equation is the highest derivative present in the equation.
Write the equation of the given line in slope-intercept form and match with the correct alternate form. 10. A
 Slope & y-intercept Class Work Identify the slope and y-intercept for each equation 1. y = 3x 4 2. y = 2x 3. y = 7 m = 3 b = 4 m = 2 b = 0 m = 0 b = 7 4. x = 5 5. y = 0 6. y 3 = 4(x + 6) m = undef b =
Slope & y-intercept Class Work Identify the slope and y-intercept for each equation 1. y = 3x 4 2. y = 2x 3. y = 7 m = 3 b = 4 m = 2 b = 0 m = 0 b = 7 4. x = 5 5. y = 0 6. y 3 = 4(x + 6) m = undef b =
Chapters 8.1 & 8.2 Practice Problems
 EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapters 8.1 & 8. Practice Problems Be able to verify that a given function is a solution to a differential equation. Given a description in words of how some quantity changes in time
EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapters 8.1 & 8. Practice Problems Be able to verify that a given function is a solution to a differential equation. Given a description in words of how some quantity changes in time
The Table of Integrals (pages of the text) and the Formula Page may be used. They will be attached to the nal exam.
 The Table of Integrals (pages 558-559 of the text) and the Formula Page may be used. They will be attached to the nal exam. 1. If f(x; y) =(xy +1) 2 p y 2 x 2,evaluatef( 2; 1). A. 1 B. 1 p 5 C. Not de
The Table of Integrals (pages 558-559 of the text) and the Formula Page may be used. They will be attached to the nal exam. 1. If f(x; y) =(xy +1) 2 p y 2 x 2,evaluatef( 2; 1). A. 1 B. 1 p 5 C. Not de
C.3 First-Order Linear Differential Equations
 A34 APPENDIX C Differential Equations C.3 First-Order Linear Differential Equations Solve first-order linear differential equations. Use first-order linear differential equations to model and solve real-life
A34 APPENDIX C Differential Equations C.3 First-Order Linear Differential Equations Solve first-order linear differential equations. Use first-order linear differential equations to model and solve real-life
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review
 Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
6.0 INTRODUCTION TO DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 6.0 Introduction to Differential Equations Contemporary Calculus 1 6.0 INTRODUCTION TO DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS This chapter is an introduction to differential equations, a major field in applied and theoretical
6.0 Introduction to Differential Equations Contemporary Calculus 1 6.0 INTRODUCTION TO DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS This chapter is an introduction to differential equations, a major field in applied and theoretical
Study guide for the Math 115 final Fall 2012
 Study guide for the Math 115 final Fall 2012 This study guide is designed to help you learn the material covered on the Math 115 final. Problems on the final may differ significantly from these problems
Study guide for the Math 115 final Fall 2012 This study guide is designed to help you learn the material covered on the Math 115 final. Problems on the final may differ significantly from these problems
Write the equation of the given line in slope-intercept form and match with the correct alternate form. 10. A
 Slope & y-intercept Class Work Identify the slope and y-intercept for each equation 1. y = 3x 4 2. y = 2x 3. y = 7 4. x = 5 5. y = 0 6. y 3 = 4(x + 6) 7. y + 2 = 1 (x + 6) 8. 2x + 3y = 9 9. 4x 7y = 14
Slope & y-intercept Class Work Identify the slope and y-intercept for each equation 1. y = 3x 4 2. y = 2x 3. y = 7 4. x = 5 5. y = 0 6. y 3 = 4(x + 6) 7. y + 2 = 1 (x + 6) 8. 2x + 3y = 9 9. 4x 7y = 14
Objectives. Use the number e to write and graph exponential functions representing realworld
 Objectives Use the number e to write and graph exponential functions representing realworld situations. Solve equations and problems involving e or natural logarithms. natural logarithm Vocabulary natural
Objectives Use the number e to write and graph exponential functions representing realworld situations. Solve equations and problems involving e or natural logarithms. natural logarithm Vocabulary natural
Logarithmic Functions
 Logarithmic Functions Definition 1. For x > 0, a > 0, and a 1, y = log a x if and only if x = a y. The function f(x) = log a x is called the logarithmic function with base a. Example 1. Evaluate the following
Logarithmic Functions Definition 1. For x > 0, a > 0, and a 1, y = log a x if and only if x = a y. The function f(x) = log a x is called the logarithmic function with base a. Example 1. Evaluate the following
Chapter 2 Describing Change: Rates
 Chapter Describing Change: Rates Section.1 Change, Percentage Change, and Average Rates of Change 1. 3. $.30 $0.46 per day 5 days = The stock price rose an average of 46 cents per day during the 5-day
Chapter Describing Change: Rates Section.1 Change, Percentage Change, and Average Rates of Change 1. 3. $.30 $0.46 per day 5 days = The stock price rose an average of 46 cents per day during the 5-day
Math 226 Calculus Spring 2016 Practice Exam 1. (1) (10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = f(x) have inverse function x = f 1 (y).
 Math 6 Calculus Spring 016 Practice Exam 1 1) 10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = fx) have inverse function x = f 1 y). a) Write down the formula relating the derivatives f x) and f 1 ) y).
Math 6 Calculus Spring 016 Practice Exam 1 1) 10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = fx) have inverse function x = f 1 y). a) Write down the formula relating the derivatives f x) and f 1 ) y).
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Overview: 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Properties of Logarithms 3.4 Solving Exponential and
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Overview: 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Properties of Logarithms 3.4 Solving Exponential and
Chapter 11 Packet & 11.2 What is a Differential Equation and What are Slope Fields
 Chapter 11 Packet 11.1 & 11. What is a Differential Equation and What are Slope Fields What is a differential equation? An equation that gives information about the rate of change of an unknown function
Chapter 11 Packet 11.1 & 11. What is a Differential Equation and What are Slope Fields What is a differential equation? An equation that gives information about the rate of change of an unknown function
February 03, 2017 WARMUP!!
 WARMUP!! Find the general solution to the logistic differential equation below. Your answer should be in the form P = f(t). Keep in mind that k and L are constants. (Hint: you might need to use partial
WARMUP!! Find the general solution to the logistic differential equation below. Your answer should be in the form P = f(t). Keep in mind that k and L are constants. (Hint: you might need to use partial
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20. ), and f(a + 1).
 Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Purdue University Study Guide for MA for students who plan to obtain credit in MA by examination.
 Purdue University Study Guide for MA 224 for students who plan to obtain credit in MA 224 by examination. Textbook: Applied Calculus For Business, Economics, and the Social and Life Sciences, Expanded
Purdue University Study Guide for MA 224 for students who plan to obtain credit in MA 224 by examination. Textbook: Applied Calculus For Business, Economics, and the Social and Life Sciences, Expanded
Differential Equations
 Differential Equations Big Ideas Slope fields draw a slope field, sketch a particular solution Separation of variables separable differential equations General solution Particular solution Growth decay
Differential Equations Big Ideas Slope fields draw a slope field, sketch a particular solution Separation of variables separable differential equations General solution Particular solution Growth decay
NO CALCULATORS. NO BOOKS. NO NOTES. TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES AND PUT THEM AWAY.
 FINAL EXAM-MATH 3 FALL TERM, R. Blute & A. Novruzi Name(Print LEGIBLY) I.D. Number Instructions- This final examination consists of multiple choice questions worth 3 points each. Your answers to the multiple
FINAL EXAM-MATH 3 FALL TERM, R. Blute & A. Novruzi Name(Print LEGIBLY) I.D. Number Instructions- This final examination consists of multiple choice questions worth 3 points each. Your answers to the multiple
Unit 5: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 71 Rational eponents Unit 5: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions If b is a real number and n and m are positive and have no common factors, then n m m b = b ( b ) m n n Laws of eponents a) b) c) d) e)
71 Rational eponents Unit 5: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions If b is a real number and n and m are positive and have no common factors, then n m m b = b ( b ) m n n Laws of eponents a) b) c) d) e)
Solving Exponential Equations (Applied Problems) Class Work
 Solving Exponential Equations (Applied Problems) Class Work Objective: You will be able to solve problems involving exponential situations. Quick Review: Solve each equation for the variable. A. 2 = 4e
Solving Exponential Equations (Applied Problems) Class Work Objective: You will be able to solve problems involving exponential situations. Quick Review: Solve each equation for the variable. A. 2 = 4e
Unit 8: Exponential & Logarithmic Functions
 Date Period Unit 8: Eponential & Logarithmic Functions DAY TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 1 8.1 Eponential Growth Pg 47 48 #1 15 odd; 6, 54, 55 8.1 Eponential Decay Pg 47 48 #16 all; 5 1 odd; 5, 7 4 all; 45 5 all 4
Date Period Unit 8: Eponential & Logarithmic Functions DAY TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 1 8.1 Eponential Growth Pg 47 48 #1 15 odd; 6, 54, 55 8.1 Eponential Decay Pg 47 48 #16 all; 5 1 odd; 5, 7 4 all; 45 5 all 4
