Pressure Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
|
|
|
- Donna Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives Identify the data that is acquired through PTA and what it analyzes Identify the types of tests used in PTA and their limitations 1
2 In This Section Pressure Transient Analysis What is it? What data is acquired? What does it analyze? What types of tests are used? What are its objectives? 2
3 What Is Pressure Transient Analysis (PTA)? Input An input rate q(t) is put into a well, either as production or injection It is a function of time Output Pressure P(t) is recorded at the same well or a nearby well P(t) is recorded during: Producing/injection period (drawdown/injectivity test) Shut-in period (buildup/falloff test) and some time before shut-in P(t) is then analyzed What PTA is Not Not a Definite Answer PTA is not a definitive answer to your questions about the inter-well space It is an inverse problem, not a direct problem PTA requires corroboration with: Geology Geophysics 3
4 Data Gathering Valve Closed Tubing Head Pressure Gas Accumulates At Top of Oil Gas Bubbles Rise Flow rate Bottom Hole Pressure Fluid Flows Out WELL TESTING The Diffusivity Equation Record as a function of time: Tubing head pressure (TBH) Bottom hole pressure (BHP) Flow rate Quality Checks: Flow tubing head pressure (FTHP) Flow stable (BSW, GOR, etc. are constant) Flow rate as constant as possible The response of the P(t) from the input of the q(t) follows the Diffusivity Equation, which describes: Flow of a slightly compressible liquid through a porous medium Flow of heat in solids under the influence of a temperature gradient Diffusion of a solute in a solvent under the influence of a concentration gradient Continuity Equation A statement of the law of conservation of matter Darcy s Law Describes the movement of fluid in response to an imposed pressure gradient Equation of State Describes how volume of a slightly compressible liquid changes with pressure 4
5 Hydraulic Diffusivity Equation exp c p u r x b p b k dp dr t u r 2 p 2 r φμct k Hydraulic Diffusivity Equation p t Mass Balance In - Out = Gain bexp c p pb Continuity Equation 2 p 2 r Darcy Equation 1 p. r r φμct k pressure : radius : time p. t Equation of State Where: k effective permeability total porosity μ flowing fluid viscosity c t total compressibility c o S o c g S g c w S w c f Detailed Derivations: OGCI pg. 16-4, Dake (1978) Chapter 5 5
6 This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives Identify the data that is acquired through PTA and what it analyzes Identify the types of tests used in PTA and their limitations 6
7 Learning Objectives Pressure Transient Analysis Core Drawdown Tests, the Concept of Skin, and Drainage Radius This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define drainage radius, radius of investigation, net pay, and skin as used in the diffusivity equation Describe the concept of skin, initially as having no thickness and its relationship to wellbore damage and stimulation Describe the effects of skin, including positive and negative skin Understand that skin has a thickness in order to stimulate through it, if damaged 7
8 In This Section Terminology and Basic Concepts Drainage radius Radius of Investigation Net pay Concept of Skin What is skin? Wellbore damage Skin factor equation Positive skin Negative skin h Damaged Wellbore 8
9 Drawdown Test Terminology p p i, p e p p - p wf p wf What is h? h h r w r r e p i -p wf Units: ft or m Typical values: ft ( m) h 9
10 Radius of Investigation, r inv What part of the reservoir do you see and how fast does a transient move in a reservoir? Field Units Pseudo SI Radius of Investigation q/2 q r inv r inv kt μc 6 t kt μc Parameter Field Units Practical SI Units k md md t hours hours fraction fraction c t psi -1 Pa -1 cp Pa s r ft m t 2q AWTI
11 The Concept of Skin Skin(s) is any phenomenon at the wellbore which results in flowing pressures that are different from radial flow theory. p r w Wellbore Damage Expected flowing pressure Actual flowing pressure r Damaged Wellbore Damage Model p reservoir p skin k a k r a 11
12 Additional Pressure Drop due to Skin Factor p a < 0 p s = 0 p a > 0 k a > k k a < k Distance from axis of wellbore of wellbore Where: k permeability of undisturbed formation, md ka permeability of damaged or stimulated zone near the wellbore, md ra radius of damaged or stimulated altered zone, ft or m pa additional pressure drop due to the presence of the altered zone, psi Kilopascals KP Wellbore Damage (Field Units) Pressure drop across damaged zone Δp d p d r w k a 141.2qB r a k r Δp u ln a 141.2qB ra pu ln kah rw kh rw Additional pressure drop due to damage 141.2qB k r p a s pd pu 1 ln kh k a rw k Pressure drop if no damage r w k r a k Nomenclature (p d ) : pressure drop between (r a ) and (r w ) for a permeability (k a ) (p u ) : pressure drop between (r a ) and (r w ) for a permeability (k) (p s ) : additional pressure drop due to damage 12
13 Skin Factor k r s 1ln a ka rw Where: s skin factor, dimensionless k ka formation permeability, md permeability of altered zone, md ra radius of altered zone, ft rw wellbore radius, ft 13
14 Learning Objectives This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define drainage radius, radius of investigation, net pay, and skin as used in the diffusivity equation Describe the concept of skin, initially as having no thickness, and its relationship to wellbore damage and stimulation Describe the effects of skin, including positive and negative skin Understand that skin has a thickness in order to stimulate through it, if damaged 14
15 Learning Objectives Pressure Transient Analysis Core Buildup Tests and Time Period Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Understand the time periods analyzed in PTA Describe the effects occurring during Early Time Period Analysis and Middle Time Period Analysis Describe the objectives of PTA in each time period analysis Explain how to solve a buildup test problem using the Horner Method 15
16 In This Section Time Periods What they are What is happening in each time period Objectives of each analysis period Buildup Problem Equations needed for example problem Step-by-step instructions Review solution Bottomhole Pressure, psi Late Time Oil Reservoir Well Buildup Horner TIme Ratio Early Time 16
17 Time Period Analysis Let s look at what is important to in each period of a pressure transient test Early Time (ET) Middle Time (MT) Late Time (LT) P ws Wellbore and near wellbore effects Transient or Infinite Acting Period Reservoir parameters log What s Happening in Each Time Period 1 Early Time (ET) Reservoir boundaries Pressure response is controlled by wellbore and near-wellbore phenomena. 2 Middle Time (MT) Pressure response represents infinite-acting radial flow, unaffected by wellbore or reservoir boundaries. 3 Late Time (LT) Pressure response is controlled by reservoir boundaries. 17
18 Objectives of PTA by Analysis Period 1 Early Time (ET) Near-wellbore condition Quantify wellbore damage Evaluate stimulation treatment effectiveness 3 Early Time (ET) Results q 2 Late Time (LT) Reservoir Boundaries Detect presence of reservoir boundaries Identify nature of boundaries Estimate distances to boundaries Estimate drainage area Estimate average drainage area pressure Early Time Middle Time q surface (ET) (MT) Wellbore Theoretical Storage Wellbore Effects Wellbore storage Afterflow Middle Time (MT) Bulk Reservoir Characteristics Estimate in-situ permeability thickness product (kh) Late Time (LT) Theoretical ` Afterflow after Surface Shut In t t q sand face Pressure Draw Down (DD) Pressure Buildup (BU) 18
19 Early Time (ET) Results Pressure Draw Down (DD) q q surface Theoretical t q sand face Wellbore Storage Theoretical ` Pressure Buildup (BU) t Afterflow after Surface Shut In 19
20 Buildup Tests q res 0 p p i, p e p p - p wf p ws Buildup Tests For a Buildup, P ws is recorded at the bottom of the well where P wf was recorded for a drawdown. Buildup requires superposition to the Hydraulic Diffusivity Equation qb t qb = r w r r e p i -p wf + -qb p 0 = + t p t p + t t t p t p +t t p t p +t Horner Result Positive Rate Component Negative Rate Component = + 20
21 Buildup Tests - Equations Transient, S.I. units p p 4k qb ln( t) ln 2 4kh 1.781ctrw i wf 2 s Positive rate component Negative rate component Add: p p i ws qb t ln 4 k h p p p Buildup Tests - Parameters Permeability from slope (k in md): 162.6q o o B m o kh o P skin qb ln( t 4kh 4k t) ln s ct rw i wf p 2 p p 4k qb ln( t) ln 2 4kh 1.781ct rw wf ws 2 t t P 1Hr P wf s m Horner Time Ratio (HTR) Skin: t p t t s k log o 2 o c t r w 3.23 Flow Efficiency P Skin 0.87 ms FlowEfficiency P P P r wf Skin P r P wf 21
22 Buildup Semi-log Graphs Intercept p i 1780 p wsi p 1hr HTR 1hr = (t p +1)/ Horner Time Ratio Permeability and Skin Factor - Liquids SI Units Field Units qb k hm. p1hr pwf k s log m ctrw qb k hm. p1 hr pwf k s log m ctrw HTR 1hr = (t p +1)/1 10 Slope m m in Pa/(log 10 cycle) m in psi/(log 10 cycle) 1 Skin Factor p skin = 0.87ms 22
23 Permeability and Skin Factor Gas m(p) SI Units Field Units k 128.8qT mh m( p1 hr) m( pwf ) k s log m ctrw k 1637qT mh m( p1hr) m( pwf ) k s log m ctrw Radius of Investigation Pressure t = 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 m in Pa/sec / (log 10 cycle) q in m 3 /sec T in degrees Kelvin m in psi 2 /cp / (log 10 cycle) q in Mscfd T in degrees Rankine t 4 Distance from axis of of wellbore r i t 5 t 6 kt 948c t 23
24 Learning Objectives This section has covered the following learning objectives: Understand the time periods analyzed in PTA Describe the effects occurring during Early Time Period Analysis and Middle Time Period Analysis Describe the objectives of PTA in each time period analysis Explain how to solve a buildup test problem using the Horner Method 24
25 Learning Objectives Pressure Transient Analysis Core Late Time Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Understand pressure behavior occurring in late time, from a Horner Time analysis Understand the difference between pseudosteady state and steady state, and their implications to late time Understand what is happening in the late transient period Understand what bounded reservoir behavior is, and that it is equivalent to: Volumetric flow behavior Pseudosteady state Semi-steady state 25
26 In This Section What Happens in Late Time Examples of Horner Plots Pressures Recorded in a Flowing Well Open and Closed Systems 26
27 Open System (full recharge qb) qb r w r w Closed System qb Increasing Time Radius Transient Steady State Increasing Time Transient Steady State Radius qb Pseudo-Steady State (Semi-Steady State) r e No influx r e 27
28 Pressure at the well When do Boundaries Occur? Boundaries None felt Some felt All felt Transient Late Transient Semi-Steady State Late Time Horner Changes Ideal Positive Skin Wellbore Storage Time +t +t +t +t Negative Skin Regular Boundary +t +t +t +t Phase Separation in Tubing ( Gas Hump Fault or Nearby Boundary Naturally Fractured Stratified System 28
29 How Long Does Middle Time Flow Last? Defined by rock and fluid properties for a specific reservoir ct r t 948 k 2 e (field units) Marks the approximate end of transient flow and the beginning of pseudosteady state flow for a well in the center of a circular reservoir Irregular drainage shapes and well locations shorten the time to the end of the transient flow and lengthen the time to the start of pseudosteady state flow 29
30 Learning Objectives This section has covered the following learning objectives: Understand pressure behavior occurring in late time, from a Horner Time analysis Understand the difference between pseudo-steady state and steady state, and their implications to late time Understand what is happening in the late transient period Understand what bounded reservoir behavior is, and that it is equivalent to: Volumetric flow behavior Pseudo-steady state Semi-steady state 30
31 Learning Objectives Pressure Transient Analysis Core Log-Log Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe log-log analysis Explain why log-log analysis may be used to improve over semi-log analysis Describe dimensionless variables, explain why they are used, and explain their importance Discuss how flow regimes are used to identify models, and how they are implicit in model selection 31
32 In This Section Introduction to Log-Log Analysis Problems with semi-log analysis PTA as an inverse problem Dimensionless variables Bounded reservoir behavior Flow Regimes/Models Derivative type curves Example of a log-log plot PTA models that work with bounded reservoirs PTA variations 32
33 Problems with Semi-Log Analysis Semi-log straight line analysis is often difficult Radial flow straight line doesn t exist or cannot be correctly identified, due to: Wellbore effects Reservoir boundaries A flow regime other than radial PTA as an Inverse Problem q Log-Log techniques focus on comparing actual data to solutions for KNOWN theoretical models (the inverse problem) Two Log-Log Techniques Type curve matching by hand or by software Analytical history matching using software Both techniques require the use of dimensionless variables and its derivative, worked simultaneously t Known Input A1, A2, {a 1, a 2, a N } U1, U2, {u 1, u 2, u M }? Unknown Model System p Input: 2, 3 Output: 5, 6 Possible Models: Addition, Multiplication Known Output t 33
34 Dimensionless Variables Field Units Dimensionless variables permit theoretical solutions to be readily converted into dimensional values (time, pressure, rate) for any given set of reservoir conditions. Dimensionless Pressure (P D ) Dimensionless Time (t D ) based on wellbore radius Dimensionless Rate (q D ) Liquid khp 141.2q B kt c 2 t r w 141.2qB khp Bounded Reservoir Behavior Character of bounded reservoir response Pseudopressure khm( p) 1424qT 1424qT khm( p) Recognizing response is more important than analyzing it Many reservoir models produce similar responses Selected model must be consistent with best available geological and geophysical information Boundaries control pressure response after the end of the MT region Pressure Squared 2 khp 1424qzT 1424qzT 2 khp Shape of drawdown pressure response can be understood in terms of flow regimes exhibited 34
35 Derivative Type Curves It is sometimes difficult to identify unique match on standard log-log type curves Derivative functions are included with the pressure change curves p ' D d dp D dp D lnt D dtd Matching two curves simultaneously reduces interpretation ambiguity Is This the Right Model? t D 35
36 Flow Regime Slopes Derivative Curves Give Unique Flow Regime-Identifying Slope The values of the pressure derivative have very specific values for identified flow regimes Therefore, inspection of the log-log derivative type curve allows identification of flow regimes and distance from well The flow regime slope identifies the model If the correct model has been identified the reservoir parameters can be calculated Flow Regime Selection Drives Model Selection Flow Standard Specialized Straight Line Regime/Model Diagnostic Plot Diagnostic Plot Plot Radial 0 t(dp/dt) vs. t p vs. t Linear ½ dp/dt ½ vs. t p vs. t ½ Volumetric 1 dp/dt vs. t p vs. t Spherical ½ dp/dt ½ vs. t p vs. t ½ Bilinear ¼ dp/dt ¼ vs. t p vs. t ¼ Flow Regime/Model Data Needed Slope Gives Intercept Gives Radial h k s Linear k x or w; k w or k x ; L f s g ; s f,ch Volumetric c t C; V p, N J Spherical B, μ, c t, ø k s Bilinear k w f k f s f,ch 36
37 Vertical Well, Infinite-Acting Radial Flow t(dp/dt) vs. t Flow Regimes in Horizontal Wells p w D 1E+03 1E+02 1E+01 1E+00 Early Radial Flow (ERF) Early Hemiradial Flow (EHRF) Early Linear Flow (ELF) Pseudo Radial Flow (PRF) Late Linear Flow (LLF) Pseudo Steady State Flow (PSSF) 1E-01 1E-02 1E-03 1E-06 1E-05 1E-04 1E-03 1E-02 1E-01 1E+00 1E+01 1E+02 1E+03 1E+04 t Lh D 37
38 Learning Objectives This section has covered the following learning objectives: Describe log-log analysis Explain why log-log analysis may be used to improve over semi-log analysis Describe dimensionless variables, explain why they are used, and explain their importance Discuss how flow regimes are used to identify models, and how they are implicit in model selection Key Learning Points 1 PTA involves a q(t) impacting a reservoir and a P(t) analyzed 2 PTA uses the hydraulic diffusivity equation, combining: 3 The continuity equation (mass balance) Darcy s law The equation of state The amount of the reservoir seen is not a function of the rate of production/injection q 4 5 PTA is commonly an inverse problem, without a unique solution, and requires corroboration with geology and geophysics If you know the model, only then can you calculate the parameters, as you did with the buildup problem 38
39 Key Learning Points 6 PTA utility in bounded reservoir management decisions is greater knowing the correct model as opposed to its parameters PTA is analyzed in three distinct connected time periods, having carryover issues to adjoining periods Each PTA time period has different objectives, but these have challenges that impact the analysis in adjoining periods: A. Early Time: Impacted by wellbore storage and near-well reservoir effects B. Middle Time: Impacted by flow regime slope chosen C. Late Time: Impacted by boundaries and well interference Complex well trajectories and production systems, i.e. fractured reservoirs, encounter many more possible flow regimes making them more difficult to analyze PetroAcademy TM Applied Reservoir Engineering Skill Modules Properties Analysis Management This is Reservoir Engineering Core Reservoir Rock Properties Core Reservoir Rock Properties Fundamentals Reservoir Fluid Core Reservoir Fluid Fundamentals Reservoir Flow Properties Core Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Reservoir Fluid Displacement Core Reservoir Fluid Displacement Fundamentals Reservoir Material Balance Core Reservoir Material Balance Fundamentals Decline Curve Analysis and Empirical Approaches Core Decline Curve Analysis and Empirical Approaches Fundamentals Pressure Transient Analysis Core Rate Transient Analysis Core Enhanced Oil Recovery Core Enhanced Oil Recovery Fundamentals Reservoir Simulation Core Reserves and Resources Core Reservoir Surveillance Core Reservoir Surveillance Fundamentals Reservoir Management Core Reservoir Management Fundamentals 39
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals COPYRIGHT. Introduction
 Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
Inflow Performance 1
 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
Rate Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Oil and Gas Well Performance
 Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS
 THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
Dimensionless Wellbore Storage Coefficient: Skin Factor: Notes:
 This problem set considers the "classic" Bourdet example for a pressure buildup test analyzed using derivative type curve analysis. For completeness, the Bourdet, et al. paper is also attached however,
This problem set considers the "classic" Bourdet example for a pressure buildup test analyzed using derivative type curve analysis. For completeness, the Bourdet, et al. paper is also attached however,
Flow equations The basic equation, on which all flow equations are based, is Darcy s Law for radial flow is given by: p
 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Evaluating Productivity Index in a Gas Well Using Regression Analysis Tobuyei Christopher and Osokogwu Uche Department of Petroleum
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Evaluating Productivity Index in a Gas Well Using Regression Analysis Tobuyei Christopher and Osokogwu Uche Department of Petroleum
Introduction to Well Stimulation
 Introduction to Well Stimulation PNGE 691A Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Fall 2018 Ali Takbiri-Borujeni PNGE 691A: Introduction to Well Stimulation 1 / 46 What is well stimulation? Main
Introduction to Well Stimulation PNGE 691A Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Fall 2018 Ali Takbiri-Borujeni PNGE 691A: Introduction to Well Stimulation 1 / 46 What is well stimulation? Main
Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion.
 Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion. T. Marhaendrajana, S. Rachmat, and K. Anam; Institut Teknologi Bandung. I. ABSTRACT Many oil and
Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion. T. Marhaendrajana, S. Rachmat, and K. Anam; Institut Teknologi Bandung. I. ABSTRACT Many oil and
Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS
 Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Well Test Interpretation
 Well Test Interpretation Schlumberger 2002 All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transcribed in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
Well Test Interpretation Schlumberger 2002 All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transcribed in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions
 . Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
. Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance PRACTICE Final Examination (Well "B") 05 May 2003 (08:00-10:00 a.m. RICH 302)
 Protocol: 1. The problems in this exam are to be worked completely and independently. 2. The exam is "CLOSED NOTES," students are limited to the following resources: You are permitted the use of 3 (three)
Protocol: 1. The problems in this exam are to be worked completely and independently. 2. The exam is "CLOSED NOTES," students are limited to the following resources: You are permitted the use of 3 (three)
XYZ COMPANY LTD. Prepared For: JOHN DOE. XYZ et al Knopcik 100/ W5/06 PAS-TRG. Dinosaur Park Formation
 All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
WATER INFLUX. Hassan S. Naji, Professor,
 WATER INFLUX Many reservoirs are bound on a portion or all of their peripheries by water-bearing rocks called aquifers. The aquifer may be so large compared to the reservoir size as to appear infinite,
WATER INFLUX Many reservoirs are bound on a portion or all of their peripheries by water-bearing rocks called aquifers. The aquifer may be so large compared to the reservoir size as to appear infinite,
National Exams May 2016
 National Exams May 2016 98-Pet-A3, Fundamental Reservoir Engineering 3 hours duration NOTES: I. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with tile answer
National Exams May 2016 98-Pet-A3, Fundamental Reservoir Engineering 3 hours duration NOTES: I. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with tile answer
Coalbed Methane Properties
 Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering. Texas A&M University. Lecture 07: Wellbore Phenomena
 Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 07: T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 07: T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Presentation of MSc s Thesis
 Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction
 (Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
(Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildup Test Analysis
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildup Test Analysis
Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well
 UESO #200271 (EXP) [ESO/06/066] Received:? 2006 (November 26, 2006) Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well B.-Z. HSIEH G. V. CHILINGAR Z.-S. LIN QUERY SHEET Q1: Au: Please review your
UESO #200271 (EXP) [ESO/06/066] Received:? 2006 (November 26, 2006) Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well B.-Z. HSIEH G. V. CHILINGAR Z.-S. LIN QUERY SHEET Q1: Au: Please review your
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Lecture:
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Lecture:
Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions
 SPE-185479-MS Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions J. R. Garcia-Pastrana, A. R. Valdes-Perez, and T. A. Blasingame,
SPE-185479-MS Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions J. R. Garcia-Pastrana, A. R. Valdes-Perez, and T. A. Blasingame,
2. Standing's Method for Present IPR
 Koya University College of Engineering School of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department Petroleum Production Engineering II Predicting Present and Future IPRs (Standing Method).
Koya University College of Engineering School of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department Petroleum Production Engineering II Predicting Present and Future IPRs (Standing Method).
Reservoir Management Background OOIP, OGIP Determination and Production Forecast Tool Kit Recovery Factor ( R.F.) Tool Kit
 Reservoir Management Background 1. OOIP, OGIP Determination and Production Forecast Tool Kit A. Volumetrics Drainage radius assumption. B. Material Balance Inaccurate when recovery factor ( R.F.) < 5 to
Reservoir Management Background 1. OOIP, OGIP Determination and Production Forecast Tool Kit A. Volumetrics Drainage radius assumption. B. Material Balance Inaccurate when recovery factor ( R.F.) < 5 to
National yams May Pet-B2, Nahiral Gas Engineering. 3 hours duration NOTES:
 ational yams May 2015 98-Pet-B2, ahiral Gas Engineering 3 hours duration OTES: 1. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with the answer paper, a clear
ational yams May 2015 98-Pet-B2, ahiral Gas Engineering 3 hours duration OTES: 1. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with the answer paper, a clear
Chapter Seven. For ideal gases, the ideal gas law provides a precise relationship between density and pressure:
 Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
READ THIS PAGE COMPLETELY BEFORE STARTING
 READ THIS PAGE COMPLETELY BEFORE STARTING Exam Submission: Step 1: You are to enter your results for Problems 1-10 in e-campus (Dr. SEIDEL will provide instructions). Step 2: You are to submit a scanned
READ THIS PAGE COMPLETELY BEFORE STARTING Exam Submission: Step 1: You are to enter your results for Problems 1-10 in e-campus (Dr. SEIDEL will provide instructions). Step 2: You are to submit a scanned
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR THE RAPID ESTIMATION OF DRAINAGE VOLUME, PRESSURE AND WELL RATES. A Thesis NEHA GUPTA
 A NOVEL APPROACH FOR THE RAPID ESTIMATION OF DRAINAGE VOLUME, PRESSURE AND WELL RATES A Thesis by NEHA GUPTA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR THE RAPID ESTIMATION OF DRAINAGE VOLUME, PRESSURE AND WELL RATES A Thesis by NEHA GUPTA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
Study of early dynamic evaluation methods in complex small fault-block reservoirs
 vailable online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 14 (01) 689 694 Study of early dynamic evaluation methods in complex small fault-block reservoirs Wu Yahong 1 Weng Xingfang Xu Mengya 1 Guo Shengtao
vailable online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 14 (01) 689 694 Study of early dynamic evaluation methods in complex small fault-block reservoirs Wu Yahong 1 Weng Xingfang Xu Mengya 1 Guo Shengtao
Gas Rate Equation. q g C. q g C 1. where. 2πa 1 kh ln(r e /r w ) 0.75 s. T sc p sc T R C C( a 1. =1/(2π 141.2) for field units. =1 for pure SI units
 Section 3 - Well Deliverability 3-1 Gas Rate Equation where q g C 1 dp µ p g B g wf q g C p wf p µ g Z dp C 2πa 1 kh ln(r e /r w ) 0.75 s C C( T sc p sc T R ) a 1 =1/(2π 141.2) for field units a 1 =1 for
Section 3 - Well Deliverability 3-1 Gas Rate Equation where q g C 1 dp µ p g B g wf q g C p wf p µ g Z dp C 2πa 1 kh ln(r e /r w ) 0.75 s C C( T sc p sc T R ) a 1 =1/(2π 141.2) for field units a 1 =1 for
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Analysis
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Analysis
Opportunities in Oil and Gas Fields Questions TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Asset... 3 1. What is the size of the opportunity (size the prize)?... 3 2. Volumetric Evaluation... 3 3. Probabilistic Volume Estimates... 3 4. Material Balance Application... 3 5.
TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Asset... 3 1. What is the size of the opportunity (size the prize)?... 3 2. Volumetric Evaluation... 3 3. Probabilistic Volume Estimates... 3 4. Material Balance Application... 3 5.
Optimization of Plunger Lift Performance in Stripper Gas Wells during the Period 05/15/2001 to 11/30/2002
 Optimization of Plunger Lift Performance in Stripper Gas Wells during the Period 05/15/2001 to 11/30/2002 March 2003 By Erdal Ozkan Colorado School of Mines Work Performed Under Prime Award No. DE-FC26-00NT41025
Optimization of Plunger Lift Performance in Stripper Gas Wells during the Period 05/15/2001 to 11/30/2002 March 2003 By Erdal Ozkan Colorado School of Mines Work Performed Under Prime Award No. DE-FC26-00NT41025
(Page 2 of 7) Reservoir Petrophysics: Introduction to Geology (continued) Be familiar with Reservoir Petrophysics (continued)... Slides Reservoi
 (Page 1 of 7) Introduction to Reservoir Engineering: Be familiar with the World Oil Resources...Slides 3-4 Be familiar with the Reservoir Structure/Depositional Environments... Slide 5 Be familiar with
(Page 1 of 7) Introduction to Reservoir Engineering: Be familiar with the World Oil Resources...Slides 3-4 Be familiar with the Reservoir Structure/Depositional Environments... Slide 5 Be familiar with
SPE Uncertainty in rock and fluid properties.
 SPE 77533 Effects on Well Test Analysis of Pressure and Flowrate Noise R.A. Archer, University of Auckland, M.B. Merad, Schlumberger, T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 2002, Society of Petroleum
SPE 77533 Effects on Well Test Analysis of Pressure and Flowrate Noise R.A. Archer, University of Auckland, M.B. Merad, Schlumberger, T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 2002, Society of Petroleum
GENERALIZED PSEUDOPRESSURE WELL TREATMENT
 GENERALIZED PSEUDOPRESSURE WELL TREATMENT IN RESERVOIR SIMULATION Curtis H. Whitson a,b Øivind Fevang b a Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) b PERA a/s ABSTRACT This paper presents a
GENERALIZED PSEUDOPRESSURE WELL TREATMENT IN RESERVOIR SIMULATION Curtis H. Whitson a,b Øivind Fevang b a Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) b PERA a/s ABSTRACT This paper presents a
Measure Twice Frac Once
 Pre-frac Reservoir Characterization from Perforation Inflow Diagnostic (PID) Testing Measure Twice Frac Once Robert Hawkes Team Leader, Reservoir Services BJ Services Company Canada SPE DISTINGUISHED LECTURER
Pre-frac Reservoir Characterization from Perforation Inflow Diagnostic (PID) Testing Measure Twice Frac Once Robert Hawkes Team Leader, Reservoir Services BJ Services Company Canada SPE DISTINGUISHED LECTURER
Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot
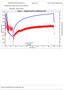 BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
Non-Darcy Skin Effect with a New Boundary Condition
 International Journal of Petroleum and Petrochemical Engineering (IJPPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 46-53 ISSN 2454-7980 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-7980.0301007 www.arcjournals.org
International Journal of Petroleum and Petrochemical Engineering (IJPPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 46-53 ISSN 2454-7980 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-7980.0301007 www.arcjournals.org
Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA)
 PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-031 Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA) N. M. A. RAHMAN Fekete Associates Inc. M. POOLADI-DARVISH University of Calgary
PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-031 Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA) N. M. A. RAHMAN Fekete Associates Inc. M. POOLADI-DARVISH University of Calgary
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Sring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildu Test Analysis Lee
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Sring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildu Test Analysis Lee
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL. A Thesis ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL
 TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Chapter 3 Permeability
 3.2 Darcy s Law In 1856, Darcy investigated the flow of water through sand filters for water purification. His experimental apparatus is shown in Figure 3.11. By empirical observation Figure 3.11 Schematic
3.2 Darcy s Law In 1856, Darcy investigated the flow of water through sand filters for water purification. His experimental apparatus is shown in Figure 3.11. By empirical observation Figure 3.11 Schematic
Production System Analysis
 Production System Analysis Production System Analysis Nodal Analysis An analytical tool used in forecasting the performance of the various elements comprising the completion and production system. This
Production System Analysis Production System Analysis Nodal Analysis An analytical tool used in forecasting the performance of the various elements comprising the completion and production system. This
SPE Copyright 1997, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Inc.
 SPE 3875 Rigorous and Semi-Rigorous Approaches for the Evaluation of Average Reservoir Pressure From Pressure Transient Tests T. Marhaendrajana and T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 1997,
SPE 3875 Rigorous and Semi-Rigorous Approaches for the Evaluation of Average Reservoir Pressure From Pressure Transient Tests T. Marhaendrajana and T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 1997,
WELL/RESERVOIR EVALUATION BY USING PRESSURE TRANSIENT AND MATERIAL BALANCE ANALYSIS OF A GAS WELL IN BANGLADESH. MD.
 WELL/RESERVOIR EVALUATION BY USING PRESSURE TRANSIENT AND MATERIAL BALANCE ANALYSIS OF A GAS WELL IN BANGLADESH. MD. HAFIZUR RAHMAN DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM & MINERAL RESOURCES ENGINEERING BUET, DHAKA,
WELL/RESERVOIR EVALUATION BY USING PRESSURE TRANSIENT AND MATERIAL BALANCE ANALYSIS OF A GAS WELL IN BANGLADESH. MD. HAFIZUR RAHMAN DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM & MINERAL RESOURCES ENGINEERING BUET, DHAKA,
Well Test Interpretation SKM4323 RESERVOIR BOUNDARIES. Azmi Mohd Arshad Department of Petroleum Engineering
 Well Test Interpretation SKM4323 RESERVOIR BOUNDARIES Azmi Mohd Arshad Department of Petroleum Engineering WEEK 08 LINEAR SEALING FAULTS Description Description /2 The boundary condition corresponding
Well Test Interpretation SKM4323 RESERVOIR BOUNDARIES Azmi Mohd Arshad Department of Petroleum Engineering WEEK 08 LINEAR SEALING FAULTS Description Description /2 The boundary condition corresponding
Rate Transient Analysis Theory/Software Course
 Rate Transient Analysis Theory/Software Course RTA Theory / Software Course: Part 1 Introduction Review of Traditional Decline Analysis Techniues Arps Fetkovich Modern Decline Analysis Theory Pseudo S.S.
Rate Transient Analysis Theory/Software Course RTA Theory / Software Course: Part 1 Introduction Review of Traditional Decline Analysis Techniues Arps Fetkovich Modern Decline Analysis Theory Pseudo S.S.
A NEW SERIES OF RATE DECLINE RELATIONS BASED ON THE DIAGNOSIS OF RATE-TIME DATA
 A NEW SERIES OF RATE DECLINE RELATIONS BASED ON THE DIAGNOSIS OF RATE-TIME DATA A Thesis by ANASTASIOS S. BOULIS Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
A NEW SERIES OF RATE DECLINE RELATIONS BASED ON THE DIAGNOSIS OF RATE-TIME DATA A Thesis by ANASTASIOS S. BOULIS Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Production performance analysis of fractured horizontal well in tight oil reservoir
 J Petrol Explor Prod Technol (2018) 8:229 247 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-017-0339-x ORIGINAL PAPER - PRODUCTION ENGINEERING Production performance analysis of fractured horizontal well in tight oil
J Petrol Explor Prod Technol (2018) 8:229 247 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-017-0339-x ORIGINAL PAPER - PRODUCTION ENGINEERING Production performance analysis of fractured horizontal well in tight oil
Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics
 Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume, Number, 29, Pages This paper is available online at http://www.pphmj.com 29 Pushpa Publishing House EVELOPMENT OF SOLUTION TO THE IFFUSIVITY EQUATION WITH
Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume, Number, 29, Pages This paper is available online at http://www.pphmj.com 29 Pushpa Publishing House EVELOPMENT OF SOLUTION TO THE IFFUSIVITY EQUATION WITH
MASTER S THESIS. Faculty of Science and Technology. Study program/ Specialization: Spring semester, Petroleum Engineering/ Reservoir Technology
 Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS Study program/ Specialization: Petroleum Engineering/ Reservoir Technology Spring semester, 2014 Open / Restricted access Writer: Hans Marius Roscher Faculty
Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS Study program/ Specialization: Petroleum Engineering/ Reservoir Technology Spring semester, 2014 Open / Restricted access Writer: Hans Marius Roscher Faculty
A Physics-Based Data-Driven Model for History Matching, Prediction and Characterization of Unconventional Reservoirs*
 A Physics-Based Data-Driven Model for History Matching, Prediction and Characterization of Unconventional Reservoirs* Yanbin Zhang *This work has been submitted to SPEJ and under review for publication
A Physics-Based Data-Driven Model for History Matching, Prediction and Characterization of Unconventional Reservoirs* Yanbin Zhang *This work has been submitted to SPEJ and under review for publication
Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks
 SPE-190841-MS Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks Alex R. Valdes-Perez and Thomas A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University
SPE-190841-MS Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks Alex R. Valdes-Perez and Thomas A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University
The role of capillary pressure curves in reservoir simulation studies.
 The role of capillary pressure curves in reservoir simulation studies. M. salarieh, A. Doroudi, G.A. Sobhi and G.R. Bashiri Research Inistitute of petroleum Industry. Key words: Capillary pressure curve,
The role of capillary pressure curves in reservoir simulation studies. M. salarieh, A. Doroudi, G.A. Sobhi and G.R. Bashiri Research Inistitute of petroleum Industry. Key words: Capillary pressure curve,
The evaluative methods on shale gas productivity using the DFIT
 The evaluative methods on shale gas roductivity using the DFIT 2014. 9. 18 Dr. Sangyu Jang T.H. Kim, G.S. Lee C.H. Shin This is the Eternal Flame Waterfall, on Shale Creek, in Chestnut Ridge Park, near
The evaluative methods on shale gas roductivity using the DFIT 2014. 9. 18 Dr. Sangyu Jang T.H. Kim, G.S. Lee C.H. Shin This is the Eternal Flame Waterfall, on Shale Creek, in Chestnut Ridge Park, near
(Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance. Introduction
 (Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
(Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
SPE Copyright 2003, Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc.
 SPE 84475 Integrating Short-Term Pressure Buildup Testing and Long-Term Production Data Analysis to Evaluate Hydraulically-Fractured Gas Well Performance J.A. Rushing, SPE, Anadarko Petroleum Corp. and
SPE 84475 Integrating Short-Term Pressure Buildup Testing and Long-Term Production Data Analysis to Evaluate Hydraulically-Fractured Gas Well Performance J.A. Rushing, SPE, Anadarko Petroleum Corp. and
MAXIMIZING THE RESERVOIR ACCESS WITH COMPLETION OPTIMIZATION AND EFFECTIVENESS. Luciano Fucello, NCS Multistage Fabio Chiarandini, Gaffney & Cline
 MAXIMIZING THE RESERVOIR ACCESS WITH COMPLETION OPTIMIZATION AND EFFECTIVENESS Luciano Fucello, NCS Multistage Fabio Chiarandini, Gaffney & Cline AGENDA: Completion effectiveness Intro Case Study Completion
MAXIMIZING THE RESERVOIR ACCESS WITH COMPLETION OPTIMIZATION AND EFFECTIVENESS Luciano Fucello, NCS Multistage Fabio Chiarandini, Gaffney & Cline AGENDA: Completion effectiveness Intro Case Study Completion
Petrophysics. Theory and Practice of Measuring. Properties. Reservoir Rock and Fluid Transport. Fourth Edition. Djebbar Tiab. Donaldson. Erie C.
 Petrophysics Theory and Practice of Measuring Reservoir Rock and Fluid Transport Properties Fourth Edition Djebbar Tiab Erie C. Donaldson ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS
Petrophysics Theory and Practice of Measuring Reservoir Rock and Fluid Transport Properties Fourth Edition Djebbar Tiab Erie C. Donaldson ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS
American University of Ras Al Khaimah, United Arab Emirates, Ras Al Khaimah
 Article Open Access DETERMINATION OF INFLOW PERFORMANCE RELATIONSHIP FOR A VERTICAL WELL IN NATU- RALLY FRACTURED OIL RESERVOIRS: NUMERICAL SIMULATION STUDY Reda Abdel Azim, Melissa Ramirez, and Mohammad
Article Open Access DETERMINATION OF INFLOW PERFORMANCE RELATIONSHIP FOR A VERTICAL WELL IN NATU- RALLY FRACTURED OIL RESERVOIRS: NUMERICAL SIMULATION STUDY Reda Abdel Azim, Melissa Ramirez, and Mohammad
SPADES: Swift Production Data Analysis and Diagnostics Engine for Shale Reservoirs
 SPADES: Swift Production Data Analysis and Diagnostics Engine for Shale Reservoirs Xu Xue April 8, 017 Motivation Production data analysis software for shale gas/oil reservoirs Model free analysis of production
SPADES: Swift Production Data Analysis and Diagnostics Engine for Shale Reservoirs Xu Xue April 8, 017 Motivation Production data analysis software for shale gas/oil reservoirs Model free analysis of production
Reservoir Rock Properties COPYRIGHT. Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Learning Objectives Reservoir Rock Properties Core Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability This section will cover the following learning objectives: Explain why petroleum fluids are found in underground
Learning Objectives Reservoir Rock Properties Core Sources and Seals Porosity and Permeability This section will cover the following learning objectives: Explain why petroleum fluids are found in underground
ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE VARIATION OF FLUID IN BOUNDED CIRCULAR RESERVOIRS UNDER THE CONSTANT PRESSURE OUTER BOUNDARY CONDITION
 Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol 36, No 1, January 2017, pp 461 468 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 0331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 wwwnijotechcom
Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol 36, No 1, January 2017, pp 461 468 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 0331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 wwwnijotechcom
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance aily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk ate: Materials overed in lass Today: omment(s): imensionless Parameters: p kh 141.2qB μ Δp t k 0.0002637 t (or Δt)
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance aily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk ate: Materials overed in lass Today: omment(s): imensionless Parameters: p kh 141.2qB μ Δp t k 0.0002637 t (or Δt)
Darcy's Law. Laboratory 2 HWR 531/431
 Darcy's Law Laboratory HWR 531/431-1 Introduction In 1856, Henry Darcy, a French hydraulic engineer, published a report in which he described a series of experiments he had performed in an attempt to quantify
Darcy's Law Laboratory HWR 531/431-1 Introduction In 1856, Henry Darcy, a French hydraulic engineer, published a report in which he described a series of experiments he had performed in an attempt to quantify
COMPARISON OF SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE LINEAR FLOW MODELS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIRS. A Thesis VARTIT TIVAYANONDA
 COMPARISON OF SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE LINEAR FLOW MODELS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIRS A Thesis by VARTIT TIVAYANONDA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
COMPARISON OF SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE LINEAR FLOW MODELS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIRS A Thesis by VARTIT TIVAYANONDA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Imperial College London
 Imperial College London Title Page IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies PREDICTING WHEN CONDENSATE BANKING BECOMES VISIBLE ON BUILD-UP DERIVATIVES
Imperial College London Title Page IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies PREDICTING WHEN CONDENSATE BANKING BECOMES VISIBLE ON BUILD-UP DERIVATIVES
WELL PRODUCTION PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR UNCONVENTIONAL SHALE GAS RESERVOIRS; A CONVENTIONAL APPROACH. FLORIN HATEGAN Devon Canada Corporation
 WELL PRODUCTION PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR UNCONVENTIONAL SHALE GAS RESERVOIRS; A CONVENTIONAL APPROACH FLORIN HATEGAN Devon Canada Corporation BACKGROUND Shale Gas HZ Drilling, Multi-Stage Hydraulic Fracturing:
WELL PRODUCTION PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR UNCONVENTIONAL SHALE GAS RESERVOIRS; A CONVENTIONAL APPROACH FLORIN HATEGAN Devon Canada Corporation BACKGROUND Shale Gas HZ Drilling, Multi-Stage Hydraulic Fracturing:
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi
 A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
Analysis of production and pressure data to characterize the performance of oil and gas reservoirs
 Scholars' Mine Doctoral Dissertations Student Research & Creative Works Fall 2015 Analysis of production and pressure data to characterize the performance of oil and gas reservoirs Abuagila Ramadan Elgmati
Scholars' Mine Doctoral Dissertations Student Research & Creative Works Fall 2015 Analysis of production and pressure data to characterize the performance of oil and gas reservoirs Abuagila Ramadan Elgmati
Predicting Well Performance in Complex Fracture Systems by Slab Source Method Jiajing Lin, SPE, and Ding Zhu, SPE, Texas A&M University
 SPE 5960 Predicting Well Performance in Complex Fracture Systems by Slab Source Method Jiajing Lin, SPE, and Ding Zhu, SPE, Texas A&M University Copyright 0, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was
SPE 5960 Predicting Well Performance in Complex Fracture Systems by Slab Source Method Jiajing Lin, SPE, and Ding Zhu, SPE, Texas A&M University Copyright 0, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was
Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured Reservoirs
 Transport in Porous Media 49: 209 240, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 209 Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured
Transport in Porous Media 49: 209 240, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 209 Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured
PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS: A DENSITY-BASED APPROACH
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School John and Willie Leone Family Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS: A DENSITY-BASED
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School John and Willie Leone Family Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS: A DENSITY-BASED
Calculating Inflow Performance Relationships for Gas Wells
 3rd Annual Appalachian Basin Gas Well Deliquification Seminar Marietta College, Marietta, Ohio Calculating Inflow Performance Relationships for Gas Wells Dr. Robert W. Chase Marietta College Methods for
3rd Annual Appalachian Basin Gas Well Deliquification Seminar Marietta College, Marietta, Ohio Calculating Inflow Performance Relationships for Gas Wells Dr. Robert W. Chase Marietta College Methods for
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. A New Method For Production Data Analysis Using Superposition-Rate. Peter Yue Liang A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method For Production Data Analysis Using Superposition-Rate by Peter Yue Liang A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method For Production Data Analysis Using Superposition-Rate by Peter Yue Liang A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON
 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies Skin Uncertainty in Multi-Layered Commingled Reservoirs with Non- Uniform Formation Damage By Sudhakar Mishra
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies Skin Uncertainty in Multi-Layered Commingled Reservoirs with Non- Uniform Formation Damage By Sudhakar Mishra
GAS DELIVERABILITY USING THE METHOD OF DISTRIBUTED VOLUMETRIC SOURCES. A Thesis XIAOZE JIN
 GAS DELIVERABILITY USING THE METHOD OF DISTRIBUTED VOLUMETRIC SOURCES A Thesis by XIAOZE JIN Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
GAS DELIVERABILITY USING THE METHOD OF DISTRIBUTED VOLUMETRIC SOURCES A Thesis by XIAOZE JIN Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
SPE Comparison of Numerical vs Analytical Models for EUR Calculation and Optimization in Unconventional Reservoirs
 SPE-180209 Comparison of Numerical vs Analytical Models for EUR Calculation and Optimization in Unconventional Reservoirs A. Moinfar, J.C. Erdle, K. Patel, Computer Modelling Group Inc. Motivation Analytical
SPE-180209 Comparison of Numerical vs Analytical Models for EUR Calculation and Optimization in Unconventional Reservoirs A. Moinfar, J.C. Erdle, K. Patel, Computer Modelling Group Inc. Motivation Analytical
AFTER CLOSURE ANALYSIS OF THE LINEAR FLOW REGIME IN A FRACTURE CALIBRATION TEST. A Thesis ZIWENJUE YE
 AFTER CLOSURE ANALYSIS OF THE LINEAR FLOW REGIME IN A FRACTURE CALIBRATION TEST A Thesis by ZIWENJUE YE Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
AFTER CLOSURE ANALYSIS OF THE LINEAR FLOW REGIME IN A FRACTURE CALIBRATION TEST A Thesis by ZIWENJUE YE Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
PORE PRESSURE EVOLUTION AND CORE DAMAGE: A COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS APPROACH
 SCA211-41 1/6 PORE PRESSURE EVOLUTION AND CORE DAMAGE: A COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS APPROACH I. Zubizarreta, M. Byrne, M.A. Jimenez, E. Roas, Y. Sorrentino and M.A. Velazco. Senergy. Aberdeen, United
SCA211-41 1/6 PORE PRESSURE EVOLUTION AND CORE DAMAGE: A COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS APPROACH I. Zubizarreta, M. Byrne, M.A. Jimenez, E. Roas, Y. Sorrentino and M.A. Velazco. Senergy. Aberdeen, United
Applications of Mini Fracs
 Applications of Mini Fracs DFIT - Diagnostic Fracture Injection Test By: Saad Ibrahim, P. Eng. For information: www.petromgt.com 2015 Petro Management Group Quality Petroleum Engineering Consultants Services:
Applications of Mini Fracs DFIT - Diagnostic Fracture Injection Test By: Saad Ibrahim, P. Eng. For information: www.petromgt.com 2015 Petro Management Group Quality Petroleum Engineering Consultants Services:
Condensate banking vs Geological Heterogeneity who wins? Hamidreza Hamdi Mahmoud Jamiolahmady Patrick Corbett SPE
 Condensate banking vs Geological Heterogeneity who wins? Hamidreza Hamdi Mahmoud Jamiolahmady Patrick Corbett SPE 143613 Outline P-T diagram of Gas reservoirs Diffusion equation linearization using gas
Condensate banking vs Geological Heterogeneity who wins? Hamidreza Hamdi Mahmoud Jamiolahmady Patrick Corbett SPE 143613 Outline P-T diagram of Gas reservoirs Diffusion equation linearization using gas
Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques
 1 Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied Geophysics Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques Academic contact during examination: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examination
1 Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied Geophysics Examination paper for TPG4150 Reservoir Recovery Techniques Academic contact during examination: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examination
Sand Control Rock Failure
 Sand Control Rock Failure Why? A bit of Mechanics on rock failure How? Some choices that depend on the rock What is moving? Sand grains? Fines? 3/14/2009 1 Young s Modulus, E Young s Modulus is a material
Sand Control Rock Failure Why? A bit of Mechanics on rock failure How? Some choices that depend on the rock What is moving? Sand grains? Fines? 3/14/2009 1 Young s Modulus, E Young s Modulus is a material
SPE Copyright 2008, Society of Petroleum Engineers
 SPE 119897 Production Analysis and Forecasting of Shale Gas Reservoirs: Case History-Based Approach L. Mattar, B. Gault, K. Morad, Fekete Associates Inc., C.R. Clarkson, EOG Resources, C.M. Freeman, D.
SPE 119897 Production Analysis and Forecasting of Shale Gas Reservoirs: Case History-Based Approach L. Mattar, B. Gault, K. Morad, Fekete Associates Inc., C.R. Clarkson, EOG Resources, C.M. Freeman, D.
GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY
 GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE By Ashish Dabral June
GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE By Ashish Dabral June
Integrated Approach to Drilling Project in Unconventional Reservoir Using Reservoir Simulation
 Integrated Approach to Drilling Project in Unconventional Reservoir Using Reservoir Simulation Jerzy Stopa 1,*, Rafał Wiśniowski 1, Paweł Wojnarowski 1, Damian Janiga 1, and Krzysztof Skrzypaszek 1 1 AGH
Integrated Approach to Drilling Project in Unconventional Reservoir Using Reservoir Simulation Jerzy Stopa 1,*, Rafał Wiśniowski 1, Paweł Wojnarowski 1, Damian Janiga 1, and Krzysztof Skrzypaszek 1 1 AGH
A COUPLED PSEUDO-PRESSURE/DENSITY APPROACH TO DECLINE CURVE ANALYSIS OF NATURAL GAS RESERVOIRS
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School John and Willie Leone Family Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering A COUPLED PSEUDO-PRESSURE/DENSITY APPROACH TO DECLINE CURVE ANALYSIS OF NATURAL
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School John and Willie Leone Family Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering A COUPLED PSEUDO-PRESSURE/DENSITY APPROACH TO DECLINE CURVE ANALYSIS OF NATURAL
GeothermEx, Inc. GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FOR THE SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION HOLE PROGRAM, KILAUEA EAST RIFT ZONE, HAWAII TASK 1 REPORT
 (415) 527 9876 CABLE ADDRESS- GEOTHERMEX TELEX 709152 STEAM UD FAX (415) 527-8164 Geotherm Ex, Inc. RICHMOND. CALIFORNIA 94804-5829 GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FOR THE SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION
(415) 527 9876 CABLE ADDRESS- GEOTHERMEX TELEX 709152 STEAM UD FAX (415) 527-8164 Geotherm Ex, Inc. RICHMOND. CALIFORNIA 94804-5829 GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FOR THE SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION
Unsaturated Flow (brief lecture)
 Physical Hydrogeology Unsaturated Flow (brief lecture) Why study the unsaturated zone? Evapotranspiration Infiltration Toxic Waste Leak Irrigation UNSATURATAED ZONE Aquifer Important to: Agriculture (most
Physical Hydrogeology Unsaturated Flow (brief lecture) Why study the unsaturated zone? Evapotranspiration Infiltration Toxic Waste Leak Irrigation UNSATURATAED ZONE Aquifer Important to: Agriculture (most
Subsurface Maps. K. W. Weissenburger. Isopach. Isochore. Conoco, Inc. Ponca City, Oklahoma, U.S.A.
 Subsurface Maps K. W. Weissenburger Conoco, Inc. Ponca City, Oklahoma, U.S.A. INTRODUCTION Reservoir properties are mapped to promote optimal field development. Subsurface maps dictate well placement and
Subsurface Maps K. W. Weissenburger Conoco, Inc. Ponca City, Oklahoma, U.S.A. INTRODUCTION Reservoir properties are mapped to promote optimal field development. Subsurface maps dictate well placement and
Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering
 Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 70 (2010) 327 333 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/petrol Research
Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 70 (2010) 327 333 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/petrol Research
Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization
 P-408 Summary Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization Asha S. Mishra* and S. K. Mishra 1 The present paper describes the pressure transient
P-408 Summary Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization Asha S. Mishra* and S. K. Mishra 1 The present paper describes the pressure transient
