Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions
|
|
|
- Doreen Dawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SPE MS Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids within a Double Porosity Reservoir under Pseudosteady State Interporosity Transfer Conditions J. R. Garcia-Pastrana, A. R. Valdes-Perez, and T. A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 2017, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was prepared for presentation at the SPE Latin America and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference held in Buenos Aires, Argentina, May This paper was selected for presentation by an SPE program committee following review of information contained in an abstract submitted by the author(s). Contents of the paper have not been reviewed by the Society of Petroleum Engineers and are subject to correction by the author(s). The material does not necessarily reflect any position of the Society of Petroleum Engineers, its officers, or members. Electronic reproduction, distribution, or storage of any part of this paper without the written consent of the Society of Petroleum Engineers is prohibited. Permission to reproduce in print is restricted to an abstract of not more than 300 words; illustrations may not be copied. The abstract must contain conspicuous acknowledgment of SPE copyright. Abstract Non-Newtonian fluids have been characterized over the decades, and such characterizations may be used to model a new approach in engineering disciplines. Non-Newtonian fluids are classified as nontime dependent and time-dependent fluids. This paper focuses on the non-time dependent classification, specifically pseudoplastic fluids. The ranges in these fluids allow the proposed model to be validated. The new reservoir model accounts for non-newtonian behavior within a double-porosity reservoir. This model demonstrates an interporosity transfer function for pseudosteady state, based on a new parameter: dimensionless matrix contribution (D). This parameter differentiates our method from previous efforts based on the pseudosteady state interporosity flow for Newtonian fluids introduced in the 1960's. We derive the partial differential equation for a non-newtonian flow within a double porosity reservoir under pseudosteady state interporosity transfer conditions. The solution presented is for an infinite acting reservoir (assuming the corresponding initial, inner and outer conditions). The objective of this paper is to deliver and provide tools that may help to characterize double porosity reservoir under the condition that a non-newtonian fluid is present, and the interporosity transfer conditions between a matrix system and a fracture system are in pseudosteady-state. Introduction The primary purpose of this work is to develop tools to characterize a naturally fractured reservoir (NFR) that produces heavy oil. Non-Newtonian (i.e., shear-thinning) fluids are sometimes injected or produced from petroleum reservoirs. The proposed solution model may assist with characterizing fluids classified as non- Newtonian. However each reservoir has unique properties and should be managed carefully. The literature describes efforts using the diffusivity equation to characterize reservoir properties, such as reservoir size, flow capacity and heterogeneities. Naturally fractured reservoirs are highly heterogeneous systems. Traditionally, they have been idealized as double porosity reservoirs. The governing equation of the fluid for this type of reservoir is modeled considering flow regime and the geometrty of the reservoir. Many double porosity model applications have been published in the literature, but they can be classified as Pseudosteady-state Interporosity Transfer (Barenblatt and Zheltov 1960; Warren and Root 1963), or Transient Interporosity Transfer (Najurieta 1980;
2 2 SPE MS De Swaan, 1978). A third class of double porosity models take the Transient Interporosity Transfer as a basin, and introduce an interporosity skin to reach an apparent Pseudosteady-state Interporosity Transfer condition (Moench 1984; Cinco-Ley et al. 1985). This paper focuses on the Pseudosteady-state Interporosity Transfer, and the Warren and Root (1963) model will be used as reference. The fluid is considered as pseudoplastic within the non-newtonian classification. Therefore, its behavior is described by a power-law function (Chirstopher et al 1965). Within the power law function there is a parameter that describes how non-newtonian a fluid can be. This parameter is the non-newtonian flow behavior index (for pseudoplastic fluids 0 < n < 1). Ikokuet al. (1979) presented a model characterizing homogeneous reservoirs with the presence of a non-newtonian (pseudoplastic) fluid. Two main approaches were performed using the power-law equation in a double porosity reservoir, Escobar et al (2011) and Olarewaju (1992). Escobar modeled the non-newtonian effect at early and late times, but he implicitly assumed a "Newtoniantransference" during the interaction period between matrix and fracture using the terms similar to the Warren and Root interporosity interaction coefficient (λ) and storativity ratio (ω). Olarewaju (1992) modeled the Transient InterporosityTransfer also accounting for the interaction between matrix and fracture as "Newtonian transference". Proposed Model The physical principles used for the model are the law of conservation of mass, a transport equation, and an equation of state. A scheme of the proposed model is shown in Fig.1. Figure 1 Schematic representation of the proposed model.
3 SPE MS 3 Except for the modification in Darcy's law, the typical assumptions for a double porosity reservoir (Warren and Root, 1963)are used. The motion expression used is the one proposed by Christopher et al. (1965) and the fluid of interest is considered tobe pseudoplastic within the classification of the non- Newtonian fluids. The resulting partial differential equation is defined as follows, and the source term, which adds fluids to the fracture system is defined by: During the derivation of eq. 1 and eq.2, a linearization is proposed to obtain the pressure difference between the fracture and the matrix elevated to 1. The validation of eq.1 and eq.2 arises when the fluid is Newtonian (n=1) both equations become the Warren and Root model. The detailed derivation is given in Appendix A. General Solution The solution obtained in the dimensioneless form and in the Laplace domain for an infinite acting reservoir with constant flowrate is defined by, (1) (2) (3) Appendix B shows the development of the solution in more detail. Discussion The Gaver-Stehfest method (Stehfest 1970) is used to invert Eq. 3 numerically, and. the results are presented in the following graphs. Fig. 2 shows the dimensionless pressure derivative with different values of the non- Newtonian flow behavior index (n) ranging from 0.1 to 1. The slope (v) observed at early times is equal to the slope at late times, and its value, which is obtained from a log-log plot, may be used to solve n in Eq. B.5.
4 4 SPE MS Figure 2 Proposed model for several values of the n-parameter. To calculate such parameters, the effective viscosity (μ etf ) has to be known. It is clear that the slope is caused by the effect of the flow behavior index as Ikoku et al (1979) demonstrated. The slope also impacts the interporosity transfer between the matrix and the fracture (valley). This effect is caused by the dimensionless matrix contribution (D), which accounts for the non-newtonian behavior. Notice that when n=1, the model converges to the Warren and Root's (1963) well-known solution for the infinite acting case. The following analysis is based on the variations for the dimensionless matrix contribution (D) ranging from to Figs. 3-5 show the response of this parameter for different values of the non- Newtonian flow behavior index The dimensionless matrix contribution is defined by a ratio between flowrates (matrix to total system) and an area ratio (wellbore to matrix blocks). The numbers assigned to D are intended to show the response in a log-log plot. Figure 3 Dimensionless matrix contribution (n = 0.1).
5 SPE MS 5 Figure 4 Dimensionless matrix contribution (n = 0.5). Figure 5 Dimensionless matrix contribution (n = 0.75). The physical meaning behind this parameter is that when the value is very low, the total flowrate is higher than the matrix flowrate. When the value is very high, the wellbore area is bigger than the matrix blocks. The values of storativity ratio (ω) and the interface interporosity coefficient (λ) are kept constant, and there are no wellbore storage effects. The derivative plots are divided in early, middle and late times. The early time region is when the fracture system is expanding. The middle time region occurs when the pesudosteady state interporosity transfer conditions between the fracture system and the matrix system are in progress (valley). The late time region is when the total system is expanding.
6 6 SPE MS The interface interporosity coefficient, the storativity ratio and the dimensionless matrix characterize the shape and time response of the dip in the log-log plot. The first two are the same parameters defined by Warren and Root (1963), and the third is related to the non-newtonian behavior. Thes three parameters affect either the response or delay for the occurrence of the dip. The model shows a significant change in the slope of the valley following the trend of the early times and the late times. A comparison between Escobar et al (2011) model and the proposed model is shown in Fig.6. The dotted black line represents Escobar's findings ("Newtonian transference") whereas the continuous red line represents the solution of the proposed model. Both models merge to the Warren and Root model infinite acting case when n=1. The difference arises when the effect of the non-newtonian fluid is present in the pseudosteady state interporosity transfer conditions due to the dimensionless matrix. Figure 6 Comparison between Escobar model and the proposed model. The valley in Escobar's derivative response remains as an interporosity within a Newtonian behavior while the model has a significant slope in the valley when the flow behavior index changes its value. This trend is a continuous effect given by the non-newtonian flow behavior index and the dimensionless matrix contribution. These two parameters are closely related. The model demonstrates that a non-newtonian behavior is present in the response at early, middle and late times. Conclusions and Recommendations Conclusions 1. The interporosity transfer depends on the non-newtonian flow behavior index (n). This value depends on the storativity ratio (ω), the interface interporosity parameter (λ) and the dimensionless matrix contribution factor (D). The latter is a function of the non-newtonian flow behavior index (n). 2. The proposed model has two validations first, the model collapses to the Warren-Root solution when the flow behavior index n=1; and second, if ω = 1 and/or λ = 0, then the model collapses into the Ikoku et al (1979) non-newtonian model.
7 SPE MS 7 3. For the matrix contribution factor D, if there is no matrix flow then the parameter is 0, which means that only one system is present (i.e., the fracture). Recommendations 1. A numerical model/solution can be developed to validate the analytical solutions presented in this paper. 2. The non-newtonian interporosity transfer should be considered in other fracture and/or matrix blocks geometries and regimes in the interporosity transfer. Nomenclature D = Dimensionless matrix contribution, dimensionless H = Variable of consistency [Pa s n ] I 0 = Modified Bessel Functions of the first kind, zero order, dimensionless I 1 = Modified Bessel Functions of the first kind, first order, dimensionless I v = Modified Bessel Functions of the first kind, v order, dimensionless K 0 = Modified Bessel Functions of the first kind, zero order, dimensionless = Modified Bessel Functions of the first kind, first order, dimensionless K 1 K v = Modified Bessel Functions of the first kind, v order, dimensionless c o = Fluid compressibility, (M/Lt 2 ) -1 [Pa -1 ] or [psia -1 ] c r = Formation compressibility, M/Lt 2 ) -1 [Pa -1 ] or [psia -1 ] c t = Total compressibility, M/Lt 2 ) -1 [Pa -1 ] or [psia -1 ] h = Net pay thickness, L [m] or [ft]. k = Permeability, L 2 [md] or [m 2 ] k f = Fracture permeability, L 2 [md] or [m 2 ] k m = Matrix permeability, L 2 [md] or [m 2 ] n = Flow behavior index, dimensionless p = Pressure, M/Lt 2 [Pa] or [psi] p f p i p m p fd p md = Pressure in the fracture, M/Lt 2 [Pa] or [psia] = Initial pressure, M/Lt 2 [Pa] or [psia] = Pressure in the matrix, M/Lt 2 [Pa] or [psia] = Dimensionless pressure in the fracture, dimensionless = Dimensionless pressure in the matrix, dimensionless q = Flowrate, L 3 /t [m3/sec] or [ft 3 /s] q m = Matrix flowrate, L 3 /t [m3/sec] or [ft 3 /s] r = Radial distance, L [m] or [ft] r w = Wellbore radius, L [m] or [ft] r ed = Dimensionless external radius drainage, dimensionless r D = Dimensionless radius, dimensionless s = Skin factor, dimensionless t = Time, t [sec] t D = Dimensionless time, dimensionless u, = Laplace transform variable v r = Radial velocity, L/t [m/s] or [ft/s] ΔL = Length, L [m] or [ft] Δp = Pressure differential, M/Lt 2 [Pa] or [psi] = Shear rate, t -1 [s -1 ]
8 8 SPE MS μ eff = Effective viscosity, M/Lt [cp] or [lb m /ft s] λ = Interporosity flow parameter, dimensionless ϕ = Porosity, fraction = Fracture Porosity, fraction ϕ f ϕ m = Matrix Porosity, fraction ρ = Density, M/L 3 [kg/m 3 ] or [lb m /ft 3 ] ρ o = Initial Density, M/L 3 [kg/m 3 ] or [lb m /ft 3 ] ω = Storativity ratio, dimensionless τ = Shear stress M/Lt 2 [N/m 2 ] or [lb f /ft 2 ] References Cinco-Ley, H., Samaniego V., F., and Kucuk, F. (1985). The Pressure Transient Behavior for Naturally Fractured Reservoirs With Multiple Block Size. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi: /14168-MS. Chirstopher, R.H and Middleman S., (1965), Power-Law Flow through a Packed Tube. Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Rochester, N.Y. De Swaan O., A. (1976). Analytic Solutions for Determining Naturally Fractured Reservoir Properties by Well Testing. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi: /5346-PA. Escobar, F. et al Pressure and Pressure Derivative Analysis for Non-Newtonian Pseudoplastic Fluids in DoublePorosity Formations. Ciencia-Teconologia. Colombia. Garcia Jorge R Flow of non-newtonian fluids within a double porosity reservoir under pseudosteady-state interporosity transfer conditions, Master in Science Thesis, Texas A&M University. College Station, TX. Ikoku, C. U., & Ramey, H. J. (1979). Transient Flow of Non-Newtonian Power-Law Fluids in Porous Media. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi: /7139-PA. Moench, A.F Double-Porosity Models for a Fissured Groundwater Reservoir with Fracture Skin. Water Resources Research, Vol. 20, No. 7, Najurieta, H. L. (1980). A Theory for Pressure Transient Analysis in Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi: /6017-PA. Stehfest, H Algorithm Numerical Inversion of Laplace Transforms. Communication, ACM 13 (1): Warren, J. E., & Root, P. J. (1963). The Behavior of Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi: /426-PA Olarewaju, J. S. (1992). A Reservoir Model of Non-Newtonian Fluid Flow. Society of Petroleum Engineers. (SPE MS).
9 SPE MS 9 Appendix A Partial Differential Equation The continuity equation for a "double porosity" reservoir system is given by: Christopher et al. (1965) proposed the following velocity power law equation (A.1) (A.2) Substituting eq. A.2 in eq. A.2, and assuming the permeability and the effective viscosity are constant after expanding the left hand side is given by, (A.3) Assuming that c t = C f + c r, and applying the chain rule on both sides, after expanding and arraying (A.4) Ikoku et al (1979) proposed the following linearization (A.5) Substituting eq A.5 in A.4 (A.6) The volumetric flow coming from the matrix network is defined (A.7) Recalling eq. A.2 but in terms of the pressure differential going from the matrix to the fracture (A.8) After substituting eq A.8 in eq A.7 and arraying terms (A.9) where
10 10 SPE MS (A.10) Notice that eq.a.9 has a pressure difference elevated to a power, which will present a very significant challenge in our quest to find a solution. In order to eliminate this situation, the following linearization is presented After arraying terms and substituting eq. A.11 in eq. A.9, the source term is given by, (A.11) (A.12) Formulation in Terms of Dimensionless Variables To be able to transform eq.a.6 and eq. A.12 into dimensionless form the following dimensionless variables are used, Dimensionless Pressure: Fracture network Dimensionless Pressure: Matrix system Dimensionless Time: (A.13) (A.14) (A.15) Where the total expansion term for the reservoir is given as: Dimensionless Radius: (A.16) (A.17) Solving p f, p m, t and respectively r in order to transform Eqs. A.6 and A.12: (A.18) (A.19) (A.20) (A.21)
11 SPE MS 11 After substituting the dimensionless variables, the dimensionless form of Eq. A.6 and Eq. A.12 is given by, (A.22) and (A.23) Where the storativity ratio (ω), the interface flow coefficient (λ), and the dimensionless matrix contribution (D) are defined as, (A.24) (A.25) respectively. (A.26)
12 12 SPE MS Appendix B Solution Constant Rate Infinite-Acting Reservoir To provide a solution suitable for well test analysis the following initial and boundary conditions are given in dimensionlessvariables. The initial condition, uniform pressure distribution, is given by: The inner boundary condition, constant flow rate, is given by: The outer boundary condition, inifinite acting reservoir, is: Taking the Laplace transform of Eqs. A.22 and A.23, and Eqs. B.1, B.2 and B.3, the general solution in Laplace domain is given by: Where (B.1) (B.2) (B.3) (B.4) (B.5) (B.6) and the interporosity flow function, g is defined by: The constants C1 and C2 depend upon the inner and outer boundary conditions, which for this case, infinite acting reservoir, are defined as: (B.7) (B.8) (B.9) (B.10) Substituting Eq. B.9 and Eq. B.10 in B.4, the solution in Laplace domain for an infinite acting reservoir with constant flowrate at the well is defined by,
13 SPE MS 13 (B.11)
Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks
 SPE-190841-MS Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks Alex R. Valdes-Perez and Thomas A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University
SPE-190841-MS Pressure-Transient Behavior of DoublePorosity Reservoirs with Transient Interporosity Transfer with Fractal Matrix Blocks Alex R. Valdes-Perez and Thomas A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University
Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion.
 Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion. T. Marhaendrajana, S. Rachmat, and K. Anam; Institut Teknologi Bandung. I. ABSTRACT Many oil and
Evaluation and Forecasting Performance of Naturally Fractured Reservoir Using Production Data Inversion. T. Marhaendrajana, S. Rachmat, and K. Anam; Institut Teknologi Bandung. I. ABSTRACT Many oil and
SPE Uncertainty in rock and fluid properties.
 SPE 77533 Effects on Well Test Analysis of Pressure and Flowrate Noise R.A. Archer, University of Auckland, M.B. Merad, Schlumberger, T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 2002, Society of Petroleum
SPE 77533 Effects on Well Test Analysis of Pressure and Flowrate Noise R.A. Archer, University of Auckland, M.B. Merad, Schlumberger, T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 2002, Society of Petroleum
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 29 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance. Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering 324 Reservoir Performance Objectives of Well Tests Review of Petrophysics Review of Fluid Properties 19 January 2007 Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL. A Thesis ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL
 TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
TRANSIENT AND PSEUDOSTEADY-STATE PRODUCTIVITY OF HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED WELL A Thesis by ARDHI HAKIM LUMBAN GAOL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Analysis
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Analysis
Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics
 Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume, Number, 29, Pages This paper is available online at http://www.pphmj.com 29 Pushpa Publishing House EVELOPMENT OF SOLUTION TO THE IFFUSIVITY EQUATION WITH
Far East Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume, Number, 29, Pages This paper is available online at http://www.pphmj.com 29 Pushpa Publishing House EVELOPMENT OF SOLUTION TO THE IFFUSIVITY EQUATION WITH
A Course in Fluid Flow in Petroleum Reservoirs Syllabus Thomas A. Blasingame Petroleum Engineering/Texas A&M University Spring 2005
 Instructor: Thomas A. Blasingame, P.E., Ph.D. Phone: +1.979.845.2292 Department of Petroleum Engineering Fax: +1.979.845.7142 Texas A&M University E-mail: t-blasingame@tamu.edu College Station, TX 77843-3116
Instructor: Thomas A. Blasingame, P.E., Ph.D. Phone: +1.979.845.2292 Department of Petroleum Engineering Fax: +1.979.845.7142 Texas A&M University E-mail: t-blasingame@tamu.edu College Station, TX 77843-3116
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
An approximate analytical solution for non-darcy flow toward a well in fractured media
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 3, 1023, 10.1029/2001WR000713, 2002 An approximate analytical solution for non-arcy flow toward a well in fractured media Yu-Shu Wu Earth Sciences ivision, Lawrence
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 38, NO. 3, 1023, 10.1029/2001WR000713, 2002 An approximate analytical solution for non-arcy flow toward a well in fractured media Yu-Shu Wu Earth Sciences ivision, Lawrence
COMPARISON OF SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE LINEAR FLOW MODELS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIRS. A Thesis VARTIT TIVAYANONDA
 COMPARISON OF SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE LINEAR FLOW MODELS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIRS A Thesis by VARTIT TIVAYANONDA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
COMPARISON OF SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE LINEAR FLOW MODELS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIRS A Thesis by VARTIT TIVAYANONDA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals COPYRIGHT. Introduction
 Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
Reservoir Flow Properties Fundamentals Why This Module is Important Introduction Fundamental understanding of the flow through rocks is extremely important to understand the behavior of the reservoir Permeability
INTEGRATION OF WELL TEST ANALYSIS INTO A NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIR SIMULATION. A Thesis LAURA ELENA PEREZ GARCIA
 INTEGRATION OF WELL TEST ANALYSIS INTO A NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIR SIMULATION A Thesis by LAURA ELENA PEREZ GARCIA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
INTEGRATION OF WELL TEST ANALYSIS INTO A NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIR SIMULATION A Thesis by LAURA ELENA PEREZ GARCIA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS
 THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
THEORETICAL RESERVOIR MODELS TIME EARLY TIME MIDDLE TIME AREA OF INTEREST NEAR WELLBORE RESERVOIR MODELS Wellbore storage and Skin Infinite conductivity vertical fracture Finite conductivity vertical fracture
Pressure Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
Pressure Transient Analysis Core Introduction to Pressure Transient Analysis This section will cover the following learning objectives: Describe pressure transient analysis (PTA) and explain its objectives
Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well
 UESO #200271 (EXP) [ESO/06/066] Received:? 2006 (November 26, 2006) Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well B.-Z. HSIEH G. V. CHILINGAR Z.-S. LIN QUERY SHEET Q1: Au: Please review your
UESO #200271 (EXP) [ESO/06/066] Received:? 2006 (November 26, 2006) Propagation of Radius of Investigation from Producing Well B.-Z. HSIEH G. V. CHILINGAR Z.-S. LIN QUERY SHEET Q1: Au: Please review your
Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization
 P-408 Summary Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization Asha S. Mishra* and S. K. Mishra 1 The present paper describes the pressure transient
P-408 Summary Pressure Transient data Analysis of Fractal Reservoir with Fractional Calculus for Reservoir Characterization Asha S. Mishra* and S. K. Mishra 1 The present paper describes the pressure transient
A NEW SERIES OF RATE DECLINE RELATIONS BASED ON THE DIAGNOSIS OF RATE-TIME DATA
 A NEW SERIES OF RATE DECLINE RELATIONS BASED ON THE DIAGNOSIS OF RATE-TIME DATA A Thesis by ANASTASIOS S. BOULIS Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
A NEW SERIES OF RATE DECLINE RELATIONS BASED ON THE DIAGNOSIS OF RATE-TIME DATA A Thesis by ANASTASIOS S. BOULIS Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Presentation of MSc s Thesis
 Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
Presentation of MSc s Thesis A Framework for Building Transient Well Testing Numerical Models Using Unstructured Grids Mohammed H. Sayyouh Professor in Petroleum Engineering Department FECU Khaled A. Abdel-Fattah
Predicting Well Performance in Complex Fracture Systems by Slab Source Method Jiajing Lin, SPE, and Ding Zhu, SPE, Texas A&M University
 SPE 5960 Predicting Well Performance in Complex Fracture Systems by Slab Source Method Jiajing Lin, SPE, and Ding Zhu, SPE, Texas A&M University Copyright 0, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was
SPE 5960 Predicting Well Performance in Complex Fracture Systems by Slab Source Method Jiajing Lin, SPE, and Ding Zhu, SPE, Texas A&M University Copyright 0, Society of Petroleum Engineers This paper was
Chapter Seven. For ideal gases, the ideal gas law provides a precise relationship between density and pressure:
 Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
Chapter Seven Horizontal, steady-state flow of an ideal gas This case is presented for compressible gases, and their properties, especially density, vary appreciably with pressure. The conditions of the
University of Alberta
 University of Alberta PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF TIGHT HYDROCARBON RESERVOIRS by Shahab Kafeel Siddiqui A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate Studies and Research in partial fulfillment of the
University of Alberta PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF TIGHT HYDROCARBON RESERVOIRS by Shahab Kafeel Siddiqui A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate Studies and Research in partial fulfillment of the
Coalbed Methane Properties
 Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
Coalbed Methane Properties Subtopics: Permeability-Pressure Relationship Coal Compressibility Matrix Shrinkage Seidle and Huitt Palmer and Mansoori Shi and Durucan Constant Exponent Permeability Incline
SPE MS. Copyright 2014, Society of Petroleum Engineers
 SPE-168966-MS Modeling Analysis of Transient Pressure and Flow Behavior at Horizontal Wells with Multi-Stage Hydraulic Fractures in Shale Gas Reservoirs Cong Wang, Colorado School of Mines and Yu-Shu Wu,
SPE-168966-MS Modeling Analysis of Transient Pressure and Flow Behavior at Horizontal Wells with Multi-Stage Hydraulic Fractures in Shale Gas Reservoirs Cong Wang, Colorado School of Mines and Yu-Shu Wu,
Rate Transient Analysis COPYRIGHT. Introduction. This section will cover the following learning objectives:
 Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
Learning Objectives Rate Transient Analysis Core Introduction This section will cover the following learning objectives: Define the rate time analysis Distinguish between traditional pressure transient
TEMPERATURE TRANSIENT ANALYSIS IN NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS
 TEMPERATURE TRANSIENT ANALYSIS IN NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY RESOURCES ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR
TEMPERATURE TRANSIENT ANALYSIS IN NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY RESOURCES ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR
Novel Approaches for the Simulation of Unconventional Reservoirs Bicheng Yan*, John E. Killough*, Yuhe Wang*, Yang Cao*; Texas A&M University
 SPE 168786 / URTeC 1581172 Novel Approaches for the Simulation of Unconventional Reservoirs Bicheng Yan*, John E. Killough*, Yuhe Wang*, Yang Cao*; Texas A&M University Copyright 2013, Unconventional Resources
SPE 168786 / URTeC 1581172 Novel Approaches for the Simulation of Unconventional Reservoirs Bicheng Yan*, John E. Killough*, Yuhe Wang*, Yang Cao*; Texas A&M University Copyright 2013, Unconventional Resources
Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS
 Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
Study program/ Specialization: Faculty of Science and Technology MASTER S THESIS MSc Petroleum Engineering / Reservoir Engineering Spring semester, 2015 Open access Writer: Mahmoud S M Alaassar (Writer
ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE VARIATION OF FLUID IN BOUNDED CIRCULAR RESERVOIRS UNDER THE CONSTANT PRESSURE OUTER BOUNDARY CONDITION
 Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol 36, No 1, January 2017, pp 461 468 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 0331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 wwwnijotechcom
Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol 36, No 1, January 2017, pp 461 468 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 0331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 wwwnijotechcom
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Lecture:
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Petroleum Engineering 324 (2009) Reservoir Performance Lecture:
Factors that affect pressure distribution of horizontal wells in a layered reservoir with simultaneous gas cap and bottom water drive
 Vol. 6(1), pp. 1-9, January, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/JPGE 2013.0180 Article Number: 3C2A1DC50083 ISSN 2I41-2677 Copyright 2015 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jpge
Vol. 6(1), pp. 1-9, January, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/JPGE 2013.0180 Article Number: 3C2A1DC50083 ISSN 2I41-2677 Copyright 2015 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jpge
Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA)
 PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-031 Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA) N. M. A. RAHMAN Fekete Associates Inc. M. POOLADI-DARVISH University of Calgary
PETROLEUM SOCIETY CANADIAN INSTITUTE OF MINING, METALLURGY & PETROLEUM PAPER 2005-031 Perforation Inflow Test Analysis (PITA) N. M. A. RAHMAN Fekete Associates Inc. M. POOLADI-DARVISH University of Calgary
SPE Copyright 1997, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Inc.
 SPE 3875 Rigorous and Semi-Rigorous Approaches for the Evaluation of Average Reservoir Pressure From Pressure Transient Tests T. Marhaendrajana and T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 1997,
SPE 3875 Rigorous and Semi-Rigorous Approaches for the Evaluation of Average Reservoir Pressure From Pressure Transient Tests T. Marhaendrajana and T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M University Copyright 1997,
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildup Test Analysis
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s): Pressure Transient Analysis Pressure Buildup Test Analysis
Introduction to Well Stimulation
 Introduction to Well Stimulation PNGE 691A Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Fall 2018 Ali Takbiri-Borujeni PNGE 691A: Introduction to Well Stimulation 1 / 46 What is well stimulation? Main
Introduction to Well Stimulation PNGE 691A Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Fall 2018 Ali Takbiri-Borujeni PNGE 691A: Introduction to Well Stimulation 1 / 46 What is well stimulation? Main
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. A New Method For Production Data Analysis Using Superposition-Rate. Peter Yue Liang A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method For Production Data Analysis Using Superposition-Rate by Peter Yue Liang A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method For Production Data Analysis Using Superposition-Rate by Peter Yue Liang A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS
SPE A Pseudo-Black-Oil Method for Simulating Gas Condensate Reservoirs S.-W. Wang, SPE, and I. Harmawan, SPE, Unocal Indonesia Co.
 SPE 92828 A Pseudo-Black-Oil Method for Simulating Gas Condensate Reservoirs S.-W. Wang, SPE, and I. Harmawan, SPE, Unocal Indonesia Co. Copyright 2005, Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc. This paper was
SPE 92828 A Pseudo-Black-Oil Method for Simulating Gas Condensate Reservoirs S.-W. Wang, SPE, and I. Harmawan, SPE, Unocal Indonesia Co. Copyright 2005, Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc. This paper was
SPE Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow
 SPE 10262 Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow Prijambodo, R.,U. of Tulsa Raghavan, R., U. of Tulsa Reynolds, A.C., U. of Tulsa 1985 SPEJ Abstract The pressure response
SPE 10262 Well Test Analysis for Wells Producing Layered Reservoirs With Crossflow Prijambodo, R.,U. of Tulsa Raghavan, R., U. of Tulsa Reynolds, A.C., U. of Tulsa 1985 SPEJ Abstract The pressure response
SPE Copyright 2003, Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc.
 SPE 84475 Integrating Short-Term Pressure Buildup Testing and Long-Term Production Data Analysis to Evaluate Hydraulically-Fractured Gas Well Performance J.A. Rushing, SPE, Anadarko Petroleum Corp. and
SPE 84475 Integrating Short-Term Pressure Buildup Testing and Long-Term Production Data Analysis to Evaluate Hydraulically-Fractured Gas Well Performance J.A. Rushing, SPE, Anadarko Petroleum Corp. and
Analysis of flow behavior in fractured lithophysal reservoirs
 Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 62 63 (2003) 189 211 www.elsevier.com/locate/jconhyd Analysis of flow behavior in fractured lithophysal reservoirs Jianchun Liu, G.S. Bodvarsson*, Yu-Shu Wu Earth Sciences
Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 62 63 (2003) 189 211 www.elsevier.com/locate/jconhyd Analysis of flow behavior in fractured lithophysal reservoirs Jianchun Liu, G.S. Bodvarsson*, Yu-Shu Wu Earth Sciences
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Chapter 3 Permeability
 3.2 Darcy s Law In 1856, Darcy investigated the flow of water through sand filters for water purification. His experimental apparatus is shown in Figure 3.11. By empirical observation Figure 3.11 Schematic
3.2 Darcy s Law In 1856, Darcy investigated the flow of water through sand filters for water purification. His experimental apparatus is shown in Figure 3.11. By empirical observation Figure 3.11 Schematic
Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/559655 Radius of Investigation for Reserve Estimation From Pressure Transient Well Tests Article
Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering. Texas A&M University. Lecture 07: Wellbore Phenomena
 Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 07: T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
Petroleum Engineering 613 Natural Gas Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 07: T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116
SPE These in turn can be used to estimate mechanical properties.
 SPE 96112 Pressure Effects on Porosity-Log Responses Using Rock Physics Modeling: Implications on Geophysical and Engineering Models as Reservoir Pressure Decreases Michael Holmes, SPE, Digital Formation,
SPE 96112 Pressure Effects on Porosity-Log Responses Using Rock Physics Modeling: Implications on Geophysical and Engineering Models as Reservoir Pressure Decreases Michael Holmes, SPE, Digital Formation,
PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions
 . Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
. Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR THE RAPID ESTIMATION OF DRAINAGE VOLUME, PRESSURE AND WELL RATES. A Thesis NEHA GUPTA
 A NOVEL APPROACH FOR THE RAPID ESTIMATION OF DRAINAGE VOLUME, PRESSURE AND WELL RATES A Thesis by NEHA GUPTA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR THE RAPID ESTIMATION OF DRAINAGE VOLUME, PRESSURE AND WELL RATES A Thesis by NEHA GUPTA Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of
AFTER CLOSURE ANALYSIS OF THE LINEAR FLOW REGIME IN A FRACTURE CALIBRATION TEST. A Thesis ZIWENJUE YE
 AFTER CLOSURE ANALYSIS OF THE LINEAR FLOW REGIME IN A FRACTURE CALIBRATION TEST A Thesis by ZIWENJUE YE Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
AFTER CLOSURE ANALYSIS OF THE LINEAR FLOW REGIME IN A FRACTURE CALIBRATION TEST A Thesis by ZIWENJUE YE Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction
 (Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
(Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
Multiporosity Flow in Fractured Low-Permeability Rocks
 Multiporosity Flow in Fractured Low-Permeability Rocks arxiv:1502.03067v1 [physics.geo-ph] 19 Jan 2015 Kristopher L. Kuhlman 1, Bwalya Malama 2, Jason E. Heath 3 1 Applied Systems Analysis & Research Dept.,
Multiporosity Flow in Fractured Low-Permeability Rocks arxiv:1502.03067v1 [physics.geo-ph] 19 Jan 2015 Kristopher L. Kuhlman 1, Bwalya Malama 2, Jason E. Heath 3 1 Applied Systems Analysis & Research Dept.,
Dimensionless Wellbore Storage Coefficient: Skin Factor: Notes:
 This problem set considers the "classic" Bourdet example for a pressure buildup test analyzed using derivative type curve analysis. For completeness, the Bourdet, et al. paper is also attached however,
This problem set considers the "classic" Bourdet example for a pressure buildup test analyzed using derivative type curve analysis. For completeness, the Bourdet, et al. paper is also attached however,
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON
 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies Skin Uncertainty in Multi-Layered Commingled Reservoirs with Non- Uniform Formation Damage By Sudhakar Mishra
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies Skin Uncertainty in Multi-Layered Commingled Reservoirs with Non- Uniform Formation Damage By Sudhakar Mishra
Simulation of Pressure Transient Behavior for Asymmetrically Finite-Conductivity Fractured Wells in Coal Reservoirs
 Transp Porous Med (2013) 97:353 372 DOI 10.1007/s11242-013-0128-z Simulation of Pressure Transient Behavior for Asymmetrically Finite-Conductivity Fractured Wells in Coal Reservoirs Lei Wang Xiaodong Wang
Transp Porous Med (2013) 97:353 372 DOI 10.1007/s11242-013-0128-z Simulation of Pressure Transient Behavior for Asymmetrically Finite-Conductivity Fractured Wells in Coal Reservoirs Lei Wang Xiaodong Wang
XYZ COMPANY LTD. Prepared For: JOHN DOE. XYZ et al Knopcik 100/ W5/06 PAS-TRG. Dinosaur Park Formation
 All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
All depths reported in mkb TVD per EUB requirements. All pressures reported in (a) per EUB requirements. 9.01 used as atmospheric pressure adjustment to convert from gauge to absolute pressure. XYZ COMPANY
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance PRACTICE Final Examination (Well "B") 05 May 2003 (08:00-10:00 a.m. RICH 302)
 Protocol: 1. The problems in this exam are to be worked completely and independently. 2. The exam is "CLOSED NOTES," students are limited to the following resources: You are permitted the use of 3 (three)
Protocol: 1. The problems in this exam are to be worked completely and independently. 2. The exam is "CLOSED NOTES," students are limited to the following resources: You are permitted the use of 3 (three)
A NEW TYPE CURVE ANALYSIS FOR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIR PRODUCTION PERFORMANCE WITH DUAL POROSITY LINEAR SYSTEM
 A NEW TYPE CURVE ANALYSIS OR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIR PRODUCTION PERORMANCE WITH DUAL POROSITY LINEAR SYSTEM A Thesis by HAIDER JAAR ABDULAL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University
A NEW TYPE CURVE ANALYSIS OR SHALE GAS/OIL RESERVOIR PRODUCTION PERORMANCE WITH DUAL POROSITY LINEAR SYSTEM A Thesis by HAIDER JAAR ABDULAL Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University
National yams May Pet-B2, Nahiral Gas Engineering. 3 hours duration NOTES:
 ational yams May 2015 98-Pet-B2, ahiral Gas Engineering 3 hours duration OTES: 1. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with the answer paper, a clear
ational yams May 2015 98-Pet-B2, ahiral Gas Engineering 3 hours duration OTES: 1. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with the answer paper, a clear
Non-Darcy Skin Effect with a New Boundary Condition
 International Journal of Petroleum and Petrochemical Engineering (IJPPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 46-53 ISSN 2454-7980 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-7980.0301007 www.arcjournals.org
International Journal of Petroleum and Petrochemical Engineering (IJPPE) Volume 3, Issue 1, 2017, PP 46-53 ISSN 2454-7980 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-7980.0301007 www.arcjournals.org
Naturally Fractured Reservoirs Yet an Unsolved Mystery
 Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 50 (2): 109 114 (2013) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Research Article Naturally
Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 50 (2): 109 114 (2013) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Research Article Naturally
Fracture-matrix transfer function in fractured porous media
 Fluid Structure Interaction VII 109 Fracture-matrix transfer function in fractured porous media A. J. Mahmood Department of Chemical Industries, Al-Anbar Technical Institute, Iraq Abstract One of the mathematical
Fluid Structure Interaction VII 109 Fracture-matrix transfer function in fractured porous media A. J. Mahmood Department of Chemical Industries, Al-Anbar Technical Institute, Iraq Abstract One of the mathematical
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering ANALYSIS OF PRODUCTION DECLINE CHARACTERISTICS OF A MULTI-STAGE HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED HORIZONTAL WELL
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering ANALYSIS OF PRODUCTION DECLINE CHARACTERISTICS OF A MULTI-STAGE HYDRAULICALLY FRACTURED HORIZONTAL WELL
WATER INFLUX. Hassan S. Naji, Professor,
 WATER INFLUX Many reservoirs are bound on a portion or all of their peripheries by water-bearing rocks called aquifers. The aquifer may be so large compared to the reservoir size as to appear infinite,
WATER INFLUX Many reservoirs are bound on a portion or all of their peripheries by water-bearing rocks called aquifers. The aquifer may be so large compared to the reservoir size as to appear infinite,
(Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance. Introduction
 (Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
(Formation Evaluation and the Analysis of Reservoir Performance) Module for: Analysis of Reservoir Performance Introduction T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University
The Effect of High Pressures and High Temperatures on the Properties of Water Based Drilling Fluids
 Energy Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, 2012, pp. 27-33 DOI:10.3968/j.est.1923847920120401.256 ISSN 1923-8460[PRINT] ISSN 1923-8479[ONLINE] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The Effect of High Pressures
Energy Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 1, 2012, pp. 27-33 DOI:10.3968/j.est.1923847920120401.256 ISSN 1923-8460[PRINT] ISSN 1923-8479[ONLINE] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The Effect of High Pressures
GAS DELIVERABILITY USING THE METHOD OF DISTRIBUTED VOLUMETRIC SOURCES. A Thesis XIAOZE JIN
 GAS DELIVERABILITY USING THE METHOD OF DISTRIBUTED VOLUMETRIC SOURCES A Thesis by XIAOZE JIN Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
GAS DELIVERABILITY USING THE METHOD OF DISTRIBUTED VOLUMETRIC SOURCES A Thesis by XIAOZE JIN Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS
 NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials. These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials. These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used
GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY
 GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE By Ashish Dabral June
GREEN WELL TESTING A REPORT SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM ENGINEERING OF STANFORD UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE By Ashish Dabral June
PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS: A DENSITY-BASED APPROACH
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School John and Willie Leone Family Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS: A DENSITY-BASED
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School John and Willie Leone Family Department of Energy and Mineral Engineering PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS: A DENSITY-BASED
The role of capillary pressure curves in reservoir simulation studies.
 The role of capillary pressure curves in reservoir simulation studies. M. salarieh, A. Doroudi, G.A. Sobhi and G.R. Bashiri Research Inistitute of petroleum Industry. Key words: Capillary pressure curve,
The role of capillary pressure curves in reservoir simulation studies. M. salarieh, A. Doroudi, G.A. Sobhi and G.R. Bashiri Research Inistitute of petroleum Industry. Key words: Capillary pressure curve,
THE REAL GAS PSEUDO PRESSURE FOR GEOTHERMAL STEAM -- SUMMARY REPORT
 THE REAL GAS PSEUDO PRESSURE FOR GEOTHERMAL STEAM -- SUMMARY REPORT L. S. Mannon Atlantic Richfield Co. 1860 Lincoln Suite 501 Denver, Colorado 80295 and P. G. Atkinson Union Oil Co. P. 0. Box 6854 2099
THE REAL GAS PSEUDO PRESSURE FOR GEOTHERMAL STEAM -- SUMMARY REPORT L. S. Mannon Atlantic Richfield Co. 1860 Lincoln Suite 501 Denver, Colorado 80295 and P. G. Atkinson Union Oil Co. P. 0. Box 6854 2099
INCORPORATING RIGOROUS HEIGHT DETERMINATION INTO UNIFIED FRACTURE DESIGN. A Thesis TERMPAN PITAKBUNKATE
 INCORPORATING RIGOROUS HEIGHT DETERMINATION INTO UNIFIED FRACTURE DESIGN A Thesis by TERMPAN PITAKBUNKATE Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the
INCORPORATING RIGOROUS HEIGHT DETERMINATION INTO UNIFIED FRACTURE DESIGN A Thesis by TERMPAN PITAKBUNKATE Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the
National Exams May 2016
 National Exams May 2016 98-Pet-A3, Fundamental Reservoir Engineering 3 hours duration NOTES: I. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with tile answer
National Exams May 2016 98-Pet-A3, Fundamental Reservoir Engineering 3 hours duration NOTES: I. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to submit with tile answer
Analysis of stress variations with depth in the Permian Basin Spraberry/Dean/Wolfcamp Shale
 ARMA 15-189 Analysis of stress variations with depth in the Permian Basin Spraberry/Dean/Wolfcamp Shale Xu, Shaochuan and Zoback, M.D. Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA Copyright 2015 ARMA,
ARMA 15-189 Analysis of stress variations with depth in the Permian Basin Spraberry/Dean/Wolfcamp Shale Xu, Shaochuan and Zoback, M.D. Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA Copyright 2015 ARMA,
Oil and Gas Well Performance
 Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
Oil and Gas Well Performance Presented By: Jebraeel Gholinezhad Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Fandamentals 3. Oil Well Performance 4. Gas Well Performance 5. Tubing Flow Performance 6. Artificial Lift Systems
(Page 2 of 7) Reservoir Petrophysics: Introduction to Geology (continued) Be familiar with Reservoir Petrophysics (continued)... Slides Reservoi
 (Page 1 of 7) Introduction to Reservoir Engineering: Be familiar with the World Oil Resources...Slides 3-4 Be familiar with the Reservoir Structure/Depositional Environments... Slide 5 Be familiar with
(Page 1 of 7) Introduction to Reservoir Engineering: Be familiar with the World Oil Resources...Slides 3-4 Be familiar with the Reservoir Structure/Depositional Environments... Slide 5 Be familiar with
Imperial College London
 Imperial College London Title Page IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies PREDICTING WHEN CONDENSATE BANKING BECOMES VISIBLE ON BUILD-UP DERIVATIVES
Imperial College London Title Page IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Department of Earth Science and Engineering Centre for Petroleum Studies PREDICTING WHEN CONDENSATE BANKING BECOMES VISIBLE ON BUILD-UP DERIVATIVES
PVT Concepts (Reservoir Fluids)
 PVT Concepts (Reservoir Fluids) Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116 (USA) +1.979.845.2292 t-blasingame@tamu.edu Orientation
PVT Concepts (Reservoir Fluids) Thomas A. Blasingame, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3116 (USA) +1.979.845.2292 t-blasingame@tamu.edu Orientation
Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured Reservoirs
 Transport in Porous Media 49: 209 240, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 209 Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured
Transport in Porous Media 49: 209 240, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 209 Numerical Simulation of Single-Phase and Multiphase Non-Darcy Flow in Porous and Fractured
Effect of Pressure-Dependent Natural-Fracture Permeability on Shale-Gas Well Production
 Effect of Pressure-Dependent Natural-Fracture Permeability on Shale-Gas Well Production Erdal Ozkan Colorado School of Mines Based on SPE159801, by, Cho, Y., Apaydin, O. G., and Ozkan, E. 1 Motivations
Effect of Pressure-Dependent Natural-Fracture Permeability on Shale-Gas Well Production Erdal Ozkan Colorado School of Mines Based on SPE159801, by, Cho, Y., Apaydin, O. G., and Ozkan, E. 1 Motivations
Inflow Performance 1
 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Radial Flow Equation 3. Straight Line Inflow Performance Relationship 4. Vogel Inflow Performance Relationship 5. Other Inflow Performance Relationship 6. Establishing
Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot
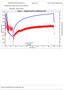 BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
BONAVISTA PETROLEUM LTD. Figure 1 - Gauges Overlay & Difference Plot 10 20700 8 18400 6 16100 4 13800 2 11500 0 9200-2 6900-4 4600-6 2300 0-8 Bottom Gauge Defference Top Gauge 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (hours)
dynamics of f luids in porous media
 dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
Fractional flow in radial flow systems: a study for peripheral waterflood
 J Petrol Expl Prod Technol (2016) 6:441 450 DOI 10.1007/s13202-015-0197-3 ORIGINAL PAPER - PRODUCTION ENGINEERING Fractional flow in radial flow systems: a study f peripheral waterflood Kegang Ling 1 Received:
J Petrol Expl Prod Technol (2016) 6:441 450 DOI 10.1007/s13202-015-0197-3 ORIGINAL PAPER - PRODUCTION ENGINEERING Fractional flow in radial flow systems: a study f peripheral waterflood Kegang Ling 1 Received:
Pre- and Post-Fracturing Analysis of a Hydraulically Stimulated Reservoir
 ARMA 18 503 Pre- and Post-Fracturing Analysis of a Hydraulically Stimulated Reservoir Erfan Sarvaramini Department of Civil and environmental Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada Robert
ARMA 18 503 Pre- and Post-Fracturing Analysis of a Hydraulically Stimulated Reservoir Erfan Sarvaramini Department of Civil and environmental Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada Robert
Shale Gas Reservoir Simulation in Eclipse
 PNG 512- Project Report Shale Gas Reservoir Simulation in Eclipse Submitted By: Priyank Srivastava Thought by: Dr. Turgay Ertekin Spring-2017 Model Description From Given Eclipse File Reservoir dimensions
PNG 512- Project Report Shale Gas Reservoir Simulation in Eclipse Submitted By: Priyank Srivastava Thought by: Dr. Turgay Ertekin Spring-2017 Model Description From Given Eclipse File Reservoir dimensions
Nhan Hoang Thinh 1, Nguyen Huu Trương 2, Nguyen Van Hung 3, Luong Hai Linh 4, Vu The Quang 5 Petrovietnam University (PVU)
 Study on Proppant Selection for Hydraulic Fracturing Design in Lower Oligocene Reservoir Nhan Hoang Thinh 1, Nguyen Huu Trương 2, Nguyen Van Hung 3, Luong Hai Linh 4, Vu The Quang 5 Petrovietnam University
Study on Proppant Selection for Hydraulic Fracturing Design in Lower Oligocene Reservoir Nhan Hoang Thinh 1, Nguyen Huu Trương 2, Nguyen Van Hung 3, Luong Hai Linh 4, Vu The Quang 5 Petrovietnam University
Modeling two-phase flow in strongly heterogeneous porous media
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2010 China COMSOL 2010 I«^rc Modeling two-phase flow in strongly heterogeneous porous media Zhaoqin Huang Research Center for Oil & Gas Flow in Reservoir, School of Petroleum
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2010 China COMSOL 2010 I«^rc Modeling two-phase flow in strongly heterogeneous porous media Zhaoqin Huang Research Center for Oil & Gas Flow in Reservoir, School of Petroleum
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer
 CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance Daily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk. Date: Materials Covered in Class Today: Comment(s):
 Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance aily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk ate: Materials overed in lass Today: omment(s): imensionless Parameters: p kh 141.2qB μ Δp t k 0.0002637 t (or Δt)
Petroleum Engineering 324 Well Performance aily Summary Sheet Spring 2009 Blasingame/Ilk ate: Materials overed in lass Today: omment(s): imensionless Parameters: p kh 141.2qB μ Δp t k 0.0002637 t (or Δt)
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS
 NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used for
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used for
A Numerical Estimate of Flexible Short-Tube Flow and Deformation with R-134a and R-410a
 For personal use only. Additional reproduction, distribution, or transmission SL-08-043 A Numerical Estimate of Flexible Short-Tube Flow and Deformation with R-134a and R-410a Ramadan Bassiouny, PhD Dennis
For personal use only. Additional reproduction, distribution, or transmission SL-08-043 A Numerical Estimate of Flexible Short-Tube Flow and Deformation with R-134a and R-410a Ramadan Bassiouny, PhD Dennis
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi
 A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
A modern concept simplifying the interpretation of pumping tests M. Stundner, G. Zangl & F. Komlosi Austria E-mail: listen+talk(a),magnet.at Abstract A thorough analysis of hydrologic pumping tests requires
This paper was prepared for presentation at the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference held in San Antonio, Texas, USA, 1-3 August 2016.
 URTeC: 2444366 Using Depletion-Zone Microseismicity to Understand Producing Volumes Jonathan P. McKenna*, Michael H. Grealy, Michael S. Blaz and Nathan M. Toohey, MicroSeismic, Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
URTeC: 2444366 Using Depletion-Zone Microseismicity to Understand Producing Volumes Jonathan P. McKenna*, Michael H. Grealy, Michael S. Blaz and Nathan M. Toohey, MicroSeismic, Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
INTERPRETATION OF PSEUDOTRANSIENT LINEAR FLOW IN PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF TIGHT, NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS
 INTERPRETATION OF PSEUDOTRANSIENT LINEAR FLOW IN PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF TIGHT, NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS by Wisam J. Assiri A thesis submitted to the Faculty and the Board of Trustees of the
INTERPRETATION OF PSEUDOTRANSIENT LINEAR FLOW IN PRODUCTION DATA ANALYSIS OF TIGHT, NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS by Wisam J. Assiri A thesis submitted to the Faculty and the Board of Trustees of the
Calculating Inflow Performance Relationships for Gas Wells
 3rd Annual Appalachian Basin Gas Well Deliquification Seminar Marietta College, Marietta, Ohio Calculating Inflow Performance Relationships for Gas Wells Dr. Robert W. Chase Marietta College Methods for
3rd Annual Appalachian Basin Gas Well Deliquification Seminar Marietta College, Marietta, Ohio Calculating Inflow Performance Relationships for Gas Wells Dr. Robert W. Chase Marietta College Methods for
SPE Direct Estimation of Gas Reserves Using Production Data. I.M. Buba, Texas A&M U. T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U.
 SPE 77550 Direct Estimation of Gas Reserves Using Production Data I.M. Buba, Texas A&M U. T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Contact: Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station,
SPE 77550 Direct Estimation of Gas Reserves Using Production Data I.M. Buba, Texas A&M U. T.A. Blasingame, Texas A&M U. Contact: Department of Petroleum Engineering Texas A&M University College Station,
Jim Lambers ENERGY 281 Spring Quarter Homework Assignment 3 Solution. 2 Ei r2 D., 4t D and the late time approximation to this solution,
 Jim Lambers ENERGY 8 Spring Quarter 7-8 Homework Assignment 3 Solution Plot the exponential integral solution p D (r D,t D ) = ) ( Ei r D, 4t D and the late time approximation to this solution, p D (r
Jim Lambers ENERGY 8 Spring Quarter 7-8 Homework Assignment 3 Solution Plot the exponential integral solution p D (r D,t D ) = ) ( Ei r D, 4t D and the late time approximation to this solution, p D (r
Fluid Mechanics Introduction
 Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
Fluid Mechanics Introduction Fluid mechanics study the fluid under all conditions of rest and motion. Its approach is analytical, mathematical, and empirical (experimental and observation). Fluid can be
CONF SLUG TESTING IN WELLS WITH FINITE-THICKNESS SKIN A.F. Moench and P.A. Hsieh. U.S. Geological Survey Menlo Park, CA 94025
 .'PROCEEDINGS, Tenth Workahop on Ceothernal Rescrvuir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 22-24. 1985 SGP-TR-84 CONF-850107-29 SLUG TESTING IN WELLS WITH FINITE-THICKNESS SKIN
.'PROCEEDINGS, Tenth Workahop on Ceothernal Rescrvuir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 22-24. 1985 SGP-TR-84 CONF-850107-29 SLUG TESTING IN WELLS WITH FINITE-THICKNESS SKIN
