|
|
|
- Caitlin Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recurrece reltio & Recursio 9 Chpter 3 Recurrece reltio & Recursio Recurrece reltio : A recurrece is equtio or iequlity tht describes fuctio i term of itself with its smller iputs. T T The problem of size is divided ito subproblems ech of size / d the cost of dividig + combiig the solutio is / T T the cost of dividig + combiig. There re THREE phses : () Divide brek complex problem () Coquer solve recursively. (3) Combie Combied solutios of ll sub problems. Exmples: T If 4T If Or, i geerl, T T f b SP P SP where d b I the bove recurrece the whole problem of iput size is divided ito subproblems of b of dividigs d combiig the solutio is f(). Methods to solve recurrece reltio : () Bckwrd substitutio () Recurrece tree method (3) Mster method (4) Akr Bzzi method. Bckwrd substitutio methods: I this method we reduce vlue of i bckwrd wy utill the size of problem becomes. Let us cosider the followig recurrece. T T We c further expd it s follows: T SP size d the cost
2 30 3 T : : T if T Recurrece Tree Method : Three step process : () Costruct the recurrece tree () Add the cost t ech levels of tree (3) Add the cost of ll levels to get overll cost. e.g. RR give : T T T I bove rr. T T This is free from I, so we ll tret this s root of tree. root Level 0 Recurrece reltio & Recursio T() = T(/) T(/) Level Childre ccordig to the umber of sub-problems here it is sub problem. If we dd both childre d root, we will get the origil R.R. Now we hve to grow this tree. So, we will clculte vlue of child lef d grow it dowwrd. Or, T T u T T cost of dividig 4 Now, this is root c 3 it is free from T. / T(/ ) T(/ ) Now ttch this prtil tree to bove prts tree. T(/) T(/) T(/ ) T(/ ) T(/ ) T(/ ) Similrly : T T 3
3 Recurrece reltio & Recursio 3 / T(/ 3 ) T(/ 3 ) Now combie this prtil tree ito previous. / / / / / / (/ 3 ) (/ 3 ) (/ 3 ) (/ 3 ) (/ 3 ) (/ 3 ) (/ 3 ) (/ 3 )... T() T() T() T() T() T() T() T() T() T() Now we crete recurrece tree we will proceed to ext step : Step - : Add cost of ech level. / / / / / / T() T() T() T() T() T() T() T() Step - 3 : Add ll cost cos... times T t Now, how my times we will dd deped o HEIGHT OF TREE At ech level is divided ito prts i.e i level i At lst level tht is i vlue i Put o both sides we get i i i i
4 3 i = height of the tree =. so, totl cost will be T... times O Mster Method : Mster method is used for the followig recurreces of the form. T T f b the. Cse : If Recurrece reltio & Recursio where d b re costts d f() is symptoticlly positive fuctio f O b for some costt 0 the T b Cse : If f b the T b Cse 3: If f b for some costt 0, the T f Exmples: () T T 9 3 here = 9, b = 3 d f() =. 9 b 3 sice Where 9 f O 3 we c pply cse of mster method d clculte tht T. (b) T T 3 here = b = 3 f ; b 3/ 0 Cse of mster method pplies d thus the solutio to the recurrece reltio is T (c) T 3T 4 We hve 3, b 4; f 3 b O Sice f Where 0. cse 3 pplies s f b c f 4 4 There for by cse of mster theorem: 3 T for 3 c 4 3 4
5 Recurrece reltio & Recursio (d) T T Here =, b = d f b s mster theorem. (e) f is ot polyomilly lrger th. Therefore it does ot follow y cse of T T Sol. Let m d igorig the sig. m m T T m Now let T m S S m S m m the here d f b m m b m m m f m so by cse II of mster method. S m m m m T S m m Akr bzzi Method : If the recurrece hs form With T T f i b Now chgig bck. i i 0 k i 3 k... p p p p p i bi b b b3 bk where, p = row., b i p T du u f u p f f u We will cosider the equtio d fid vlue of P put it i formul, perform itegrtio d the get the vlue. e.g. 3 T T T 4 4 T T T f b b 4 b 3 b 4 i 33
6 34 b p p b 3 p 4 4 p p p 3 p 4 4 u u T du du u u u T e.g. T T T T let T x T f f f,,, 3, 5, 8,... x x x x x x x x x x x x x x 0 Recurrece reltio & Recursio x b b 4c 5 x Solutio is T c c c c T Cocept of Recurrsio: Recursio mes self-referece. A recursive fuctio is fuctio which clls itself durig its executio. It must hve followig properties. () There must be certi criteri, clled bse criteri for which fuctio does ot cll itself. (b) Ech time the fuctio cll itself (directly or idirectly), it must be closer to the bse criteri i.e. it uses the rgumets smller th the oe it ws give. A recursive fuctio with these properties is sid to be well defied. Exmples: () Fctoril fuctio:! d 0!= if 0! if
7 Recurrece reltio & Recursio (b) Computig fctoril by fuctio (Recursive) it fctoril (it ) { If ( = = 0) //Bse criteri. retur ; else retur *fctoril ( ); Iductive step How it executes if = 4. 4! = 4.3!. 3! = 3.! 3.! =.! 4.! =.0! 5. 0!= (Termitio) 6.!=. = 7.! = = 8. 3! = 3 = ! = 4 6 = 4 Fibocci Numbers: A fibocci sequece f 0, f, f, f 3... f is defied s 0,,,, 3, 5, 8, 3,... Tht is f 0 = 0, f =, f = d the subsequet terms re sum of precedig terms. f f f if if Computig th fibocci umber by recurrece. It fib (it ) { If // Bse criteri. retur ; else retur fib ( ) + fib ( ); (Iductive step) fib (5) will be computed s follows: fib(5) 35 fib(4) fib(3) fib(3) fib() fib() fib() fib() fib() fib() fib(0) fib() fib(0) fib() fib(0)
8 36 TOWER OF HANOI PROBLEMS Recurrece reltio & Recursio Iitil cofigurtio of TOH problem is : source peg PegA PegB PegC Source Peg Auxillry Peg Destitio Peg helpig uxiliry peg Fil cofigurtio of TOH problem : destitio peg e.g. For Oe disk : Iitil Stge : 3 p move : A C Fil stge : Whe = umber of movemet = For two disk : 0 p Iitil Stge : Fil stte : Moves : (i) A B (ii) A C (iii) B C So, whe = Number of movemet (3) Gol: All discs re set to Peg C from PegA by movemets of disc i other pegs. (i) Oly oe disc movemet is llowed t time.
9 Recurrece reltio & Recursio (ii) A lrger disc cot be plced over smller disc. Number of movemet of disc i tower of Hoi problem is. T = totl umebr of disc movemet Number of disc = i THP T T T T 37 Recursio or Itertio : A recursive fuctio works through the process of cllig itself util coditio is met. Itertio uses loopig cotrol structure (while, do while, for) to repet sectio of code util coditio is met.recursio is best whe you hve lot of vribles to keep trck of with ech loop, d it s usig divide d coquer type of lgorithm. Recursio helps to trim dow the frme of referece (the portio of the problem you re ow iterested i), very esily.whe we hve few vribles to keep trck of, or the lgorithm is t some type of divide d coquer, the itertive loopig is better.itertio is slightly fster, but tht should ot be the criteri used to choose it. The differece is very smll, d the clrity d shortess of the recursive code, c be quite helpful for debuggig. With itertio it is the sme vrible whose vlue is costtly chged, d you c ccess its vlue t ech stge. With recursio, differet locl vrible (by the sme me) is creted with ech cll. SOLVED PROBLEMS. Let T() be fuctio defied by recurrece [GATE - 005] T T () T (b) T (c) T Sol. T T f So, T Correct optio is () b f b (d) Noe of these. The recurrece reltio [GATE - 996] Sol. () () T T 4 T 3 (b) (c) 3 4 (d) Noe of these 3. For k for some k 0 the recurrece reltio As. T T T () (b) () (c) (d)
10 38 Recurrece reltio & Recursio 4. The ruig time of lgorithm is represeted by the followig recurrece reltio [GATE 009] 3 T T c, otherwise 3 which of the followig represets the complexity of the bove recurrece reltio. Sol. () (b) 3 T T c, otherwise 3 Solve usig mster theorem. T T 3 b 3 f So, b Correct optio is () (c) (d) T T f b 5. The recurrece reltio tht rises with the complexity of biry serch is: [JNUEE-008] Sol. () T T T T k (b) (c) T T (d) T T k For biry serch if we hve umber of elemets. So, first it sorts the rry i scedig or descedig order the divide the rry i hlf of its umber d repet it till we fid out specified umber. T T k Correct optio is (b) 6. Cosider the followig c-code. it j, ; j = ; while (j < ) j = j*; The umbers of comprisio mde i the executio of the loop for y > 0 is [GATE 007] Sol. it j, ; () (b) (c) (d) r j = ; while (j < ) j = j*; For =, J = J =
11 Recurrece reltio & Recursio For =, J = For J =, = 3, J = For J =, J = ; out of loop = 4, J = for J = For J =, J = 4; out of loop Similrly for = 00 It will execute for steps. So, optio () is true. 7. How to fid the complexity of progrm Sol. Complexity is bsic rough estimte complexity is deped o umber of loops for (i =0; i < ; i++) for (j = 0; j < ; j++) 8. Fid out the complexity of progrm. i = ; while (i > 0) { i = i/; Sol. i i i i i i i 9. Fid solutio to the followig recurrece equtio Sol. By usig substitutio method we get followig series: T k k k So put k the we get T O() 0 0. The recurrece reltio As. Sol. 39 T() T, T() [GATE-987 : Mrks] T() = T() = 3T(/4) + Hs the solutio T() equl to () O() (b) O( ) (c) O( 3/4 ) (d) oe of these [GATE-996 : Mrks] () Usig Mster Theorem 4 3 We get
12 40. Let T() be the fuctio defied by T() =, sttemets is true? Recurrece reltio & Recursio T() T for. Which of the followig () T() O( ) (b) T() = O() (c) T() = O( ) (d) oe of these [GATE-997 : Mrks] (b) As. Sol. Use Mster Theorem.. I the followig C fuctios, let m. As. Sol. it gcd (, m) { if (%m = = 0 retur m; = %m; retur gcd (m, ); How my recursive clls re mde by this fuctio? () ( ) (b) () (c) ( ) (d) [GATE-007 : Mrks] () Let T(m, ) be the totl umber of steps. So T(m, 0) = 0, T(m, ) = T(, m mod ) o verge T T(k, ) ; T (T T T ) 0 k 0 T S S (S0S S ) S (S0 S S ) ((S ) S ) S So T ( ) 0() T ( ) 3. Which oe of the followig is the recurrece equtio for the worst cse time complexity of the Quicksort lgorithm for sortig () umbers? I the recurrece equtios give i the optio below, c is costt. As. Sol. () T() T(/) c (b) T() T( ) T() c (c) T() T( ) c (d) T() T(/) c [GATE-05 (Set-) : Mrk] (b) I worst cse the pivot elemet positio my be either first or lst. I tht cse the elemets re lwys divided i : ( ) proportio. The recurrece reltio for such proportiol divisio would be T() T() T( ) O() O( ) () T() T (/) c O( ) (b) T() T( ) T() c O( ) (c) T() T ( ) c O( ) (d) T() T(/) c O()
13 Recurrece reltio & Recursio 4 PRACTICE SET. Cosider the followig recursive fuctio fu(x, y). Wht is the vlue of fu(4, 3) it fu(it x, it y) { if(x == 0) retur y; retur fu(x -, x + y); () 3 (b) (c) 9 (d) 5. Wht does the followig fuctio do? it fu(it x, it y) { if(y == 0) retur 0; retur(x + fu(x, y-)); () x+y (b) x*y (c) x+x*y (d) x^y 3. Output of followig progrm? #iclude<stdio.h> void prit(it ) { if( > 4000) retur; pritf( %d, ); prit(*); pritf( %d, ); it mi() { prit(000); getchr(); retur 0; () (b) (c) (d) Cosider the sme recursive C fuctio tht tkes two rgumets usiged it foo(usiged it, usiged it r) { if( > 0) retur(%r + foo (/r, r )); else retur 0; () 9 (b) 8 (c) 5 (d) 5. Cosider the followig fuctio double f(double x) { if(bs(x*x - 3) < 0.0) retur x; else retur f(x/ +.5/x); Give vlue q (to decimls) such tht f(q) will retur q:. ().73 (b).4 (c) 4. (d) 3.4
14 4 6. T() = T() = T(-) +, evlutes to () + (c) + (b) (d) Recurrece reltio & Recursio 7. Cosider the followig three clims. ( + k) m = Θ( m ), where k d m re costts. + = O( ) 3. + = O( ) Which of these clims re correct? () d (b) d 3 (c) d 3 (d), d 3 8. Wht is the worst cse time complexity of followig implemettio of subset sum problem. // Returs true if there is subset of set[] with sum equl to give sum bool SubsetSum(it set[], it, it sum) { // Bse Cses if(sum == 0) retur true; if( == 0 && sum!= 0) retur flse; // If lst elemet is greter th sum, the igore it if(set[-] > sum) retur issubsetsum(set, -, sum); /* else, check if sum c be obtied by y of the followig () icludig the lst elemet (b) excludig the lst elemet */ retur issubsetsum(set, -, sum) issubsetsum(set, -, sum-set[-]); () O( * ^) (b) O(^) (c) O(^ * ^) (d) O(^) ANSWER KEY. (). (b) 3. (b) 4. (d) 5. () 6. () 7. () 8. (d)
Similar idea to multiplication in N, C. Divide and conquer approach provides unexpected improvements. Naïve matrix multiplication
 Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
Next. Covered bsics of simple desig techique (Divided-coquer) Ch. of the text.. Next, Strsse s lgorithm. Lter: more desig d coquer lgorithms: MergeSort. Solvig recurreces d the Mster Theorem. Similr ide
Merge Sort. Outline and Reading. Divide-and-Conquer. Divide-and-conquer paradigm ( 4.1.1) Merge-sort ( 4.1.1)
 Merge Sort 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 Merge Sort versio 1.3 1 Outlie d Redig Divide-d-coquer prdigm ( 4.1.1 Merge-sort ( 4.1.1 Algorithm Mergig two sorted sequeces Merge-sort tree
Merge Sort 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 Merge Sort versio 1.3 1 Outlie d Redig Divide-d-coquer prdigm ( 4.1.1 Merge-sort ( 4.1.1 Algorithm Mergig two sorted sequeces Merge-sort tree
Section IV.6: The Master Method and Applications
 Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
Sectio IV.6: The Mster Method d Applictios Defiitio IV.6.1: A fuctio f is symptoticlly positive if d oly if there exists rel umer such tht f(x) > for ll x >. A cosequece of this defiitio is tht fuctio
5. Solving recurrences
 5. Solvig recurreces Time Complexity Alysis of Merge Sort T( ) 0 if 1 2T ( / 2) otherwise sortig oth hlves mergig Q. How to prove tht the ru-time of merge sort is O( )? A. 2 Time Complexity Alysis of Merge
5. Solvig recurreces Time Complexity Alysis of Merge Sort T( ) 0 if 1 2T ( / 2) otherwise sortig oth hlves mergig Q. How to prove tht the ru-time of merge sort is O( )? A. 2 Time Complexity Alysis of Merge
Lecture 4 Recursive Algorithm Analysis. Merge Sort Solving Recurrences The Master Theorem
 Lecture 4 Recursive Algorithm Alysis Merge Sort Solvig Recurreces The Mster Theorem Merge Sort MergeSortA, left, right) { if left < right) { mid floorleft right) / 2); MergeSortA, left, mid); MergeSortA,
Lecture 4 Recursive Algorithm Alysis Merge Sort Solvig Recurreces The Mster Theorem Merge Sort MergeSortA, left, right) { if left < right) { mid floorleft right) / 2); MergeSortA, left, mid); MergeSortA,
Lecture 4 Recursive Algorithm Analysis. Merge Sort Solving Recurrences The Master Theorem
 Lecture 4 Recursive Algorithm Alysis Merge Sort Solvig Recurreces The Mster Theorem Merge Sort MergeSortA, left, right) { if left < right) { mid = floorleft + right) / 2); MergeSortA, left, mid); MergeSortA,
Lecture 4 Recursive Algorithm Alysis Merge Sort Solvig Recurreces The Mster Theorem Merge Sort MergeSortA, left, right) { if left < right) { mid = floorleft + right) / 2); MergeSortA, left, mid); MergeSortA,
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES
 PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
Chapter Real Numbers
 Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -,,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls. ex:
Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -,,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls. ex:
MTH 146 Class 16 Notes
 MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
Discrete Mathematics I Tutorial 12
 Discrete Mthemtics I Tutoril Refer to Chpter 4., 4., 4.4. For ech of these sequeces fid recurrece reltio stisfied by this sequece. (The swers re ot uique becuse there re ifiitely my differet recurrece
Discrete Mthemtics I Tutoril Refer to Chpter 4., 4., 4.4. For ech of these sequeces fid recurrece reltio stisfied by this sequece. (The swers re ot uique becuse there re ifiitely my differet recurrece
CS 331 Design and Analysis of Algorithms. -- Divide and Conquer. Dr. Daisy Tang
 CS 33 Desig d Alysis of Algorithms -- Divide d Coquer Dr. Disy Tg Divide-Ad-Coquer Geerl ide: Divide problem ito subproblems of the sme id; solve subproblems usig the sme pproh, d ombie prtil solutios,
CS 33 Desig d Alysis of Algorithms -- Divide d Coquer Dr. Disy Tg Divide-Ad-Coquer Geerl ide: Divide problem ito subproblems of the sme id; solve subproblems usig the sme pproh, d ombie prtil solutios,
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Section 6.3: Geometric Sequences
 40 Chpter 6 Sectio 6.: Geometric Sequeces My jobs offer ul cost-of-livig icrese to keep slries cosistet with ifltio. Suppose, for exmple, recet college grdute fids positio s sles mger erig ul slry of $6,000.
40 Chpter 6 Sectio 6.: Geometric Sequeces My jobs offer ul cost-of-livig icrese to keep slries cosistet with ifltio. Suppose, for exmple, recet college grdute fids positio s sles mger erig ul slry of $6,000.
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
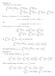 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
INFINITE SERIES. ,... having infinite number of terms is called infinite sequence and its indicated sum, i.e., a 1
 Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
 n. A Very Interesting Example + + = d. + x3. + 5x4. math 131 power series, part ii 7. One of the first power series we examined was. 2!
 mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
The total number of permutations of S is n!. We denote the set of all permutations of S by
 DETERMINNTS. DEFINITIONS Def: Let S {,,, } e the set of itegers from to, rrged i scedig order. rerrgemet jjj j of the elemets of S is clled permuttio of S. S. The totl umer of permuttios of S is!. We deote
DETERMINNTS. DEFINITIONS Def: Let S {,,, } e the set of itegers from to, rrged i scedig order. rerrgemet jjj j of the elemets of S is clled permuttio of S. S. The totl umer of permuttios of S is!. We deote
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, Divide-and-Conquer
 Presettio for use with the textook, Algorithm Desig d Applictios, y M. T. Goodrich d R. Tmssi, Wiley, 25 Divide-d-Coquer Divide-d-Coquer Divide-d coquer is geerl lgorithm desig prdigm: Divide: divide the
Presettio for use with the textook, Algorithm Desig d Applictios, y M. T. Goodrich d R. Tmssi, Wiley, 25 Divide-d-Coquer Divide-d-Coquer Divide-d coquer is geerl lgorithm desig prdigm: Divide: divide the
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
Review of Sections
 Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
is an ordered list of numbers. Each number in a sequence is a term of a sequence. n-1 term
 Mthemticl Ptters. Arithmetic Sequeces. Arithmetic Series. To idetify mthemticl ptters foud sequece. To use formul to fid the th term of sequece. To defie, idetify, d pply rithmetic sequeces. To defie rithmetic
Mthemticl Ptters. Arithmetic Sequeces. Arithmetic Series. To idetify mthemticl ptters foud sequece. To use formul to fid the th term of sequece. To defie, idetify, d pply rithmetic sequeces. To defie rithmetic
Definite Integral. The Left and Right Sums
 Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
INTEGRATION IN THEORY
 CHATER 5 INTEGRATION IN THEORY 5.1 AREA AROXIMATION 5.1.1 SUMMATION NOTATION Fibocci Sequece First, exmple of fmous sequece of umbers. This is commoly ttributed to the mthemtici Fibocci of is, lthough
CHATER 5 INTEGRATION IN THEORY 5.1 AREA AROXIMATION 5.1.1 SUMMATION NOTATION Fibocci Sequece First, exmple of fmous sequece of umbers. This is commoly ttributed to the mthemtici Fibocci of is, lthough
Numbers (Part I) -- Solutions
 Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
Lesson-2 PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES
 Lesso- PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES Arithmetic Progressio: A sequece of terms is sid to be i rithmetic progressio (A.P) whe the differece betwee y term d its preceedig term is fixed costt. This costt is clled
Lesso- PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES Arithmetic Progressio: A sequece of terms is sid to be i rithmetic progressio (A.P) whe the differece betwee y term d its preceedig term is fixed costt. This costt is clled
Numerical Methods (CENG 2002) CHAPTER -III LINEAR ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS. In this chapter, we will deal with the case of determining the values of x 1
 Numericl Methods (CENG 00) CHAPTER -III LINEAR ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS. Itroductio I this chpter, we will del with the cse of determiig the vlues of,,..., tht simulteously stisfy the set of equtios: f f...
Numericl Methods (CENG 00) CHAPTER -III LINEAR ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS. Itroductio I this chpter, we will del with the cse of determiig the vlues of,,..., tht simulteously stisfy the set of equtios: f f...
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
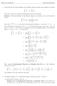 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Chapter 2 Infinite Series Page 1 of 9
 Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
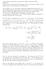 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
Closed Newton-Cotes Integration
 Closed Newto-Cotes Itegrtio Jmes Keeslig This documet will discuss Newto-Cotes Itegrtio. Other methods of umericl itegrtio will be discussed i other posts. The other methods will iclude the Trpezoidl Rule,
Closed Newto-Cotes Itegrtio Jmes Keeslig This documet will discuss Newto-Cotes Itegrtio. Other methods of umericl itegrtio will be discussed i other posts. The other methods will iclude the Trpezoidl Rule,
Chapter System of Equations
 hpter 4.5 System of Equtios After redig th chpter, you should be ble to:. setup simulteous lier equtios i mtrix form d vice-vers,. uderstd the cocept of the iverse of mtrix, 3. kow the differece betwee
hpter 4.5 System of Equtios After redig th chpter, you should be ble to:. setup simulteous lier equtios i mtrix form d vice-vers,. uderstd the cocept of the iverse of mtrix, 3. kow the differece betwee
Approximations of Definite Integrals
 Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
In an algebraic expression of the form (1), like terms are terms with the same power of the variables (in this case
 Chpter : Algebr: A. Bckgroud lgebr: A. Like ters: I lgebric expressio of the for: () x b y c z x y o z d x... p x.. we cosider x, y, z to be vribles d, b, c, d,,, o,.. to be costts. I lgebric expressio
Chpter : Algebr: A. Bckgroud lgebr: A. Like ters: I lgebric expressio of the for: () x b y c z x y o z d x... p x.. we cosider x, y, z to be vribles d, b, c, d,,, o,.. to be costts. I lgebric expressio
THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING
 OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
Chapter Real Numbers
 Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -, 0,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls.
Chpter. - Rel Numbers Itegers: coutig umbers, zero, d the egtive of the coutig umbers. ex: {,-3, -, -, 0,,, 3, } Rtiol Numbers: quotiets of two itegers with ozero deomitor; termitig or repetig decimls.
Lecture 38 (Trapped Particles) Physics Spring 2018 Douglas Fields
 Lecture 38 (Trpped Prticles) Physics 6-01 Sprig 018 Dougls Fields Free Prticle Solutio Schrödiger s Wve Equtio i 1D If motio is restricted to oe-dimesio, the del opertor just becomes the prtil derivtive
Lecture 38 (Trpped Prticles) Physics 6-01 Sprig 018 Dougls Fields Free Prticle Solutio Schrödiger s Wve Equtio i 1D If motio is restricted to oe-dimesio, the del opertor just becomes the prtil derivtive
Merge and Quick Sort
 Merge ad Quick Sort Merge Sort Merge Sort Tree Implemetatio Quick Sort Pivot Item Radomized Quick Sort Adapted from: Goodrich ad Tamassia, Data Structures ad Algorithms i Java, Joh Wiley & So (1998). Ruig
Merge ad Quick Sort Merge Sort Merge Sort Tree Implemetatio Quick Sort Pivot Item Radomized Quick Sort Adapted from: Goodrich ad Tamassia, Data Structures ad Algorithms i Java, Joh Wiley & So (1998). Ruig
MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE
 MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE Prt 1. Let be odd rime d let Z such tht gcd(, 1. Show tht if is qudrtic residue mod, the is qudrtic residue mod for y ositive iteger.
MATH 118 HW 7 KELLY DOUGAN, ANDREW KOMAR, MARIA SIMBIRSKY, BRANDEN LASKE Prt 1. Let be odd rime d let Z such tht gcd(, 1. Show tht if is qudrtic residue mod, the is qudrtic residue mod for y ositive iteger.
SOLUTION OF SYSTEM OF LINEAR EQUATIONS. Lecture 4: (a) Jacobi's method. method (general). (b) Gauss Seidel method.
 SOLUTION OF SYSTEM OF LINEAR EQUATIONS Lecture 4: () Jcobi's method. method (geerl). (b) Guss Seidel method. Jcobi s Method: Crl Gustv Jcob Jcobi (804-85) gve idirect method for fidig the solutio of system
SOLUTION OF SYSTEM OF LINEAR EQUATIONS Lecture 4: () Jcobi's method. method (geerl). (b) Guss Seidel method. Jcobi s Method: Crl Gustv Jcob Jcobi (804-85) gve idirect method for fidig the solutio of system
Unit 1. Extending the Number System. 2 Jordan School District
 Uit Etedig the Number System Jord School District Uit Cluster (N.RN. & N.RN.): Etedig Properties of Epoets Cluster : Etedig properties of epoets.. Defie rtiol epoets d eted the properties of iteger epoets
Uit Etedig the Number System Jord School District Uit Cluster (N.RN. & N.RN.): Etedig Properties of Epoets Cluster : Etedig properties of epoets.. Defie rtiol epoets d eted the properties of iteger epoets
ALGEBRA. Set of Equations. have no solution 1 b1. Dependent system has infinitely many solutions
 Qudrtic Equtios ALGEBRA Remider theorem: If f() is divided b( ), the remider is f(). Fctor theorem: If ( ) is fctor of f(), the f() = 0. Ivolutio d Evlutio ( + b) = + b + b ( b) = + b b ( + b) 3 = 3 +
Qudrtic Equtios ALGEBRA Remider theorem: If f() is divided b( ), the remider is f(). Fctor theorem: If ( ) is fctor of f(), the f() = 0. Ivolutio d Evlutio ( + b) = + b + b ( b) = + b b ( + b) 3 = 3 +
1 Tangent Line Problem
 October 9, 018 MAT18 Week Justi Ko 1 Tget Lie Problem Questio: Give the grph of fuctio f, wht is the slope of the curve t the poit, f? Our strteg is to pproimte the slope b limit of sect lies betwee poits,
October 9, 018 MAT18 Week Justi Ko 1 Tget Lie Problem Questio: Give the grph of fuctio f, wht is the slope of the curve t the poit, f? Our strteg is to pproimte the slope b limit of sect lies betwee poits,
Infinite Series Sequences: terms nth term Listing Terms of a Sequence 2 n recursively defined n+1 Pattern Recognition for Sequences Ex:
 Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Math 2414 Activity 17 (Due with Final Exam) Determine convergence or divergence of the following alternating series: a 3 5 2n 1 2n 1
 Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
 Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
CS583 Lecture 02. Jana Kosecka. some materials here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides
 CS583 Lecture 02 Jaa Kosecka some materials here are based o E. Demaie, D. Luebke slides Previously Sample algorithms Exact ruig time, pseudo-code Approximate ruig time Worst case aalysis Best case aalysis
CS583 Lecture 02 Jaa Kosecka some materials here are based o E. Demaie, D. Luebke slides Previously Sample algorithms Exact ruig time, pseudo-code Approximate ruig time Worst case aalysis Best case aalysis
,... are the terms of the sequence. If the domain consists of the first n positive integers only, the sequence is a finite sequence.
 Chpter 9 & 0 FITZGERALD MAT 50/5 SECTION 9. Sequece Defiitio A ifiite sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. The fuctio vlues,,, 4,...,,... re the terms of the sequece. If the domi
Chpter 9 & 0 FITZGERALD MAT 50/5 SECTION 9. Sequece Defiitio A ifiite sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. The fuctio vlues,,, 4,...,,... re the terms of the sequece. If the domi
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
Relation of BSTs to Quicksort, Analysis of Random BST. Lecture 9
 Reltio o BSTs to Quicsort, Alysis o Rdom BST Lecture 9 Biry-serch-tree sort T Crete empty BST or i = to do TREE-INSERT(T, A[i]) Perorm iorder tree wl o T. Emple: 3 A = [3 8 2 6 7 5] 8 Tree-wl time = O(),
Reltio o BSTs to Quicsort, Alysis o Rdom BST Lecture 9 Biry-serch-tree sort T Crete empty BST or i = to do TREE-INSERT(T, A[i]) Perorm iorder tree wl o T. Emple: 3 A = [3 8 2 6 7 5] 8 Tree-wl time = O(),
Vectors. Vectors in Plane ( 2
 Vectors Vectors i Ple ( ) The ide bout vector is to represet directiol force Tht mes tht every vector should hve two compoets directio (directiol slope) d mgitude (the legth) I the ple we preset vector
Vectors Vectors i Ple ( ) The ide bout vector is to represet directiol force Tht mes tht every vector should hve two compoets directio (directiol slope) d mgitude (the legth) I the ple we preset vector
Lesson 4 Linear Algebra
 Lesso Lier Algebr A fmily of vectors is lierly idepedet if oe of them c be writte s lier combitio of fiitely my other vectors i the collectio. Cosider m lierly idepedet equtios i ukows:, +, +... +, +,
Lesso Lier Algebr A fmily of vectors is lierly idepedet if oe of them c be writte s lier combitio of fiitely my other vectors i the collectio. Cosider m lierly idepedet equtios i ukows:, +, +... +, +,
Laws of Integral Indices
 A Lws of Itegrl Idices A. Positive Itegrl Idices I, is clled the se, is clled the idex lso clled the expoet. mes times.... Exmple Simplify 5 6 c Solutio 8 5 6 c 6 Exmple Simplify Solutio The results i
A Lws of Itegrl Idices A. Positive Itegrl Idices I, is clled the se, is clled the idex lso clled the expoet. mes times.... Exmple Simplify 5 6 c Solutio 8 5 6 c 6 Exmple Simplify Solutio The results i
SM2H. Unit 2 Polynomials, Exponents, Radicals & Complex Numbers Notes. 3.1 Number Theory
 SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
SMH Uit Polyomils, Epoets, Rdicls & Comple Numbers Notes.1 Number Theory .1 Addig, Subtrctig, d Multiplyig Polyomils Notes Moomil: A epressio tht is umber, vrible, or umbers d vribles multiplied together.
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS. Linear Equations. x l ( 3,1 ) _x-axis. Origin ( 0, 0 ) Slope = change in y change in x. Equation for l 1.
 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD
 Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Geometric Sequences. Geometric Sequence. Geometric sequences have a common ratio.
 s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS 2 SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER 11
 UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
ICS141: Discrete Mathematics for Computer Science I
 ICS4: Discrete Mthemtics for Computer Sciece I Dept. Iformtio & Computer Sci., J Stelovsky sed o slides y Dr. Bek d Dr. Still Origils y Dr. M. P. Frk d Dr. J.L. Gross Provided y McGrw-Hill 3- Quiz. gcd(84,96).
ICS4: Discrete Mthemtics for Computer Sciece I Dept. Iformtio & Computer Sci., J Stelovsky sed o slides y Dr. Bek d Dr. Still Origils y Dr. M. P. Frk d Dr. J.L. Gross Provided y McGrw-Hill 3- Quiz. gcd(84,96).
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
Limits and an Introduction to Calculus
 Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
DETERMINANT. = 0. The expression a 1. is called a determinant of the second order, and is denoted by : y + c 1
 NOD6 (\Dt\04\Kot\J-Advced\SMP\Mths\Uit#0\NG\Prt-\0.Determits\0.Theory.p65. INTRODUCTION : If the equtios x + b 0, x + b 0 re stisfied by the sme vlue of x, the b b 0. The expressio b b is clled determit
NOD6 (\Dt\04\Kot\J-Advced\SMP\Mths\Uit#0\NG\Prt-\0.Determits\0.Theory.p65. INTRODUCTION : If the equtios x + b 0, x + b 0 re stisfied by the sme vlue of x, the b b 0. The expressio b b is clled determit
This Lecture. Divide and Conquer. Merge Sort: Algorithm. Merge Sort Algorithm. MergeSort (Example) - 1. MergeSort (Example) - 2
 This Lecture Divide-ad-coquer techique for algorithm desig. Example the merge sort. Writig ad solvig recurreces Divide ad Coquer Divide-ad-coquer method for algorithm desig: Divide: If the iput size is
This Lecture Divide-ad-coquer techique for algorithm desig. Example the merge sort. Writig ad solvig recurreces Divide ad Coquer Divide-ad-coquer method for algorithm desig: Divide: If the iput size is
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
MA123, Chapter 9: Computing some integrals (pp )
 MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
APPLICATION OF DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS TO CERTAIN TRIDIAGONAL MATRICES
 Scietific Reserch of the Istitute of Mthetics d Coputer Sciece 3() 0, 5-0 APPLICATION OF DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS TO CERTAIN TRIDIAGONAL MATRICES Jolt Borows, Le Łcińs, Jowit Rychlews Istitute of Mthetics,
Scietific Reserch of the Istitute of Mthetics d Coputer Sciece 3() 0, 5-0 APPLICATION OF DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS TO CERTAIN TRIDIAGONAL MATRICES Jolt Borows, Le Łcińs, Jowit Rychlews Istitute of Mthetics,
Statistics for Financial Engineering Session 1: Linear Algebra Review March 18 th, 2006
 Sttistics for Ficil Egieerig Sessio : Lier Algebr Review rch 8 th, 6 Topics Itroductio to trices trix opertios Determits d Crmer s rule Eigevlues d Eigevectors Quiz The cotet of Sessio my be fmilir to
Sttistics for Ficil Egieerig Sessio : Lier Algebr Review rch 8 th, 6 Topics Itroductio to trices trix opertios Determits d Crmer s rule Eigevlues d Eigevectors Quiz The cotet of Sessio my be fmilir to
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS 2 SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER 11
 SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER Ifiite Series.5 Altertig Series d Absolute Covergece Next, let us cosider series with both positive d egtive terms. The simplest d most useful is ltertig
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER Ifiite Series.5 Altertig Series d Absolute Covergece Next, let us cosider series with both positive d egtive terms. The simplest d most useful is ltertig
Particle in a Box. and the state function is. In this case, the Hermitian operator. The b.c. restrict us to 0 x a. x A sin for 0 x a, and 0 otherwise
 Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
Prticle i Box We must hve me where = 1,,3 Solvig for E, π h E = = where = 1,,3, m 8m d the stte fuctio is x A si for 0 x, d 0 otherwise x ˆ d KE V. m dx I this cse, the Hermiti opertor 0iside the box The
Math 3B Midterm Review
 Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 643u Office Hours: R 11:00 m - 1:00 pm Lst updted /15/015 Here re some short otes o Sectios 7.1-7.8 i your ebook. The best idictio of wht
Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 643u Office Hours: R 11:00 m - 1:00 pm Lst updted /15/015 Here re some short otes o Sectios 7.1-7.8 i your ebook. The best idictio of wht
Linear Programming. Preliminaries
 Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
BC Calculus Path to a Five Problems
 BC Clculus Pth to Five Problems # Topic Completed U -Substitutio Rule Itegrtio by Prts 3 Prtil Frctios 4 Improper Itegrls 5 Arc Legth 6 Euler s Method 7 Logistic Growth 8 Vectors & Prmetrics 9 Polr Grphig
BC Clculus Pth to Five Problems # Topic Completed U -Substitutio Rule Itegrtio by Prts 3 Prtil Frctios 4 Improper Itegrls 5 Arc Legth 6 Euler s Method 7 Logistic Growth 8 Vectors & Prmetrics 9 Polr Grphig
Error-free compression
 Error-free compressio Useful i pplictio where o loss of iformtio is tolerble. This mybe due to ccurcy requiremets, legl requiremets, or less th perfect qulity of origil imge. Compressio c be chieved by
Error-free compressio Useful i pplictio where o loss of iformtio is tolerble. This mybe due to ccurcy requiremets, legl requiremets, or less th perfect qulity of origil imge. Compressio c be chieved by
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Lectures
 FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
Options: Calculus. O C.1 PG #2, 3b, 4, 5ace O C.2 PG.24 #1 O D PG.28 #2, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG #1, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.
 O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
LEVEL I. ,... if it is known that a 1
 LEVEL I Fid the sum of first terms of the AP, if it is kow tht + 5 + 0 + 5 + 0 + = 5 The iterior gles of polygo re i rithmetic progressio The smllest gle is 0 d the commo differece is 5 Fid the umber of
LEVEL I Fid the sum of first terms of the AP, if it is kow tht + 5 + 0 + 5 + 0 + = 5 The iterior gles of polygo re i rithmetic progressio The smllest gle is 0 d the commo differece is 5 Fid the umber of
10.5 Power Series. In this section, we are going to start talking about power series. A power series is a series of the form
 0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
Linford 1. Kyle Linford. Math 211. Honors Project. Theorems to Analyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of a Function Involving a Radical (A4)
 Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
General properties of definite integrals
 Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
18.01 Calculus Jason Starr Fall 2005
 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
) 2 2(2. Assume that
 lg lg W W W W W W W Assume tht lg log. 0. with for, W W W For ot power of, W 0 W W W for hrd to lyze this cse exctly ecuse of the floors d ceiligs. usig iductio rgumet lie the oe i Ex B.5 i Appedix B,
lg lg W W W W W W W Assume tht lg log. 0. with for, W W W For ot power of, W 0 W W W for hrd to lyze this cse exctly ecuse of the floors d ceiligs. usig iductio rgumet lie the oe i Ex B.5 i Appedix B,
{ } { S n } is monotonically decreasing if Sn
 Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Surds, Indices, and Logarithms Radical
 MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
Advanced Algorithmic Problem Solving Le 6 Math and Search
 Advced Algorithmic Prolem Solvig Le Mth d Serch Fredrik Heitz Dept of Computer d Iformtio Sciece Liköpig Uiversity Outlie Arithmetic (l. d.) Solvig lier equtio systems (l. d.) Chiese remider theorem (l.5
Advced Algorithmic Prolem Solvig Le Mth d Serch Fredrik Heitz Dept of Computer d Iformtio Sciece Liköpig Uiversity Outlie Arithmetic (l. d.) Solvig lier equtio systems (l. d.) Chiese remider theorem (l.5
=> PARALLEL INTERCONNECTION. Basic Properties LTI Systems. The Commutative Property. Convolution. The Commutative Property. The Distributive Property
 Lier Time-Ivrit Bsic Properties LTI The Commuttive Property The Distributive Property The Associtive Property Ti -6.4 / Chpter Covolutio y ] x ] ] x ]* ] x ] ] y] y ( t ) + x( τ ) h( t τ ) dτ x( t) * h(
Lier Time-Ivrit Bsic Properties LTI The Commuttive Property The Distributive Property The Associtive Property Ti -6.4 / Chpter Covolutio y ] x ] ] x ]* ] x ] ] y] y ( t ) + x( τ ) h( t τ ) dτ x( t) * h(
Mathacle. PSet Stats, Concepts In Statistics Level Number Name: Date:
 APPENDEX I. THE RAW ALGEBRA IN STATISTICS A I-1. THE INEQUALITY Exmple A I-1.1. Solve ech iequlity. Write the solutio i the itervl ottio..) 2 p - 6 p -8.) 2x- 3 < 5 Solutio:.). - 4 p -8 p³ 2 or pî[2, +
APPENDEX I. THE RAW ALGEBRA IN STATISTICS A I-1. THE INEQUALITY Exmple A I-1.1. Solve ech iequlity. Write the solutio i the itervl ottio..) 2 p - 6 p -8.) 2x- 3 < 5 Solutio:.). - 4 p -8 p³ 2 or pî[2, +
: : 8.2. Test About a Population Mean. STT 351 Hypotheses Testing Case I: A Normal Population with Known. - null hypothesis states 0
 8.2. Test About Popultio Me. Cse I: A Norml Popultio with Kow. H - ull hypothesis sttes. X1, X 2,..., X - rdom smple of size from the orml popultio. The the smple me X N, / X X Whe H is true. X 8.2.1.
8.2. Test About Popultio Me. Cse I: A Norml Popultio with Kow. H - ull hypothesis sttes. X1, X 2,..., X - rdom smple of size from the orml popultio. The the smple me X N, / X X Whe H is true. X 8.2.1.
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Sect Simplifying Radical Expressions. We can use our properties of exponents to establish two properties of radicals: and
 128 Sect 10.3 - Simplifyig Rdicl Expressios Cocept #1 Multiplictio d Divisio Properties of Rdicls We c use our properties of expoets to estlish two properties of rdicls: () 1/ 1/ 1/ & ( Multiplictio d
128 Sect 10.3 - Simplifyig Rdicl Expressios Cocept #1 Multiplictio d Divisio Properties of Rdicls We c use our properties of expoets to estlish two properties of rdicls: () 1/ 1/ 1/ & ( Multiplictio d
