Math 104: Final exam solutions
|
|
|
- Augustus McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there exists K such tht k > K implies s k s < 1, d hece for k > K, s k < s + 1. Suppose tht (s ) is ot bouded bove. The there exists N such tht s N > s + 1, d sice it is icresig sequece, s > s + 1 for ll > N. Choosig k such tht k > K d k > N gives s k < s + 1 d s k > s + 1 which is cotrdictio. Hece (s ) is bouded bove, d sice it is icresig it coverges.
2 x 2. () Let f (x) = be fuctios defied o R, for ll 2 N. By usig the Weierstrß 2 (1+x 2 ) M-test, or otherwise, prove tht  f coverges uiformly o R. Aswer: If x < 1, the f (x) < 1 2 (1 + x 2 ) pple 1 2 = 1 2. If x 1 the f (x) pple x 2 (x 2 ) pple 1 2 (x) pple 1 2. Hece f (x) < 1 / 2 for ll x 2 R. Sice  1 / 2 coverges, it follows tht  f coverges by the Weierstrß M-test. (b) Cosider the sequece of fuctios defied o R s g (x) = 1/ for 1 pple x <, otherwise, for ll 2 N. Defie M = sup{ g (x) : x 2 R}. Prove tht  g coverges uiformly to limit g, but tht  M diverges. Sketch g(x) for pple x < 5. Aswer: From the defiitio, it c be see tht M = 1 /, d hece  M diverges. Cosider x 2 [ 1, ) for some 2 N. The  f (x) = 1 /. Sice f k (x) = for ll k > it follows tht  f (x) = 1 /. Thus  g coverges poitwise to 1/m if x 2 [m 1, m) for some m 2 N, g(x) = otherwise. To show tht covergece is uiform, cosider y e >. By the Archimede property, there exists N 2 N such tht 1 /N < e. For > N, ote tht g(x) 1/m if x 2 [m 1, m) for some m 2 N with m >,  g k (x) = otherwise, d thus g(x)  g k(x) < 1 / < e, so the covergece is uiform. The fuctio g is plotted i Fig. 1.
3 3. Cosider the sequece defied recursively ccordig to s 1 = 1 /3 d s +1 = ls (1 s ) for 2 N, where l is rel costt. () Prove tht (s ) coverges for l = 1. Aswer: Suppose tht s 2 (, 1). The s +1 = s (1 s ) < s d s +1 >, so s +1 2 (, s ). Sice s 1 = 1 /3 it follows by iductio tht (s ) is decresig sequece tht is bouded below by, so it coverges. (b) Prove tht (s ) hs coverget subsequece for l = 4. Aswer: First, ote tht s +1 = 4(s s 2 )=4 1 4! s = 1 4 s. 2 2 Suppose tht s 2 [, 1]. The s 1/2 2 [ 1/2, 1 /2], so 4(s 1/2) 2 2 [, 1], d hece s +1 2 [, 1]. Sice s 1 2 [, 1] it follows by mthemticl iductio tht s 2 [, 1] for ll 2 N. Thus the sequece is bouded, so it hs coverget subsequece vi the Bolzo Weierstrß theorem. (c) Prove tht (s ) diverges for l = 12. Aswer: Now suppose tht for 2, s > 2 1. The s +1 = 12 s 1 s > (2 1 1) > = 2. so s +1 > 2 (+1) 1. Sice s 2 = 8 /3 > 2 it follows by mthemticl iductio tht s > 2 1 for ll 2 N with > 2. Sice 2! s!, it follows tht s is ubouded d hece diverges.
4 4. A rel-vlued fuctio f defied o set S is defied to be Lipschitz cotiuous if there exists K > such tht for ll x, y 2 S, f (x) f (y) pplek x y. () Prove tht if f is Lipschitz cotiuous o S, the it is uiformly cotiuous o S. Aswer: Choose e >. The set d = e K. If x, y 2 S such tht x y < d, the d hece f is uiformly cotiuous. f (x) f (y) pplek x y < Kd = e (b) Cosider the fuctio f (x) = p x o the itervl [, ). Prove tht it is uiformly cotiuous, but ot Lipschitz cotiuous. Aswer: To show tht f is uiformly cotiuous, choose e >, d ote tht f (x) f (y) = p x p y = ( p x p y)( p x + p y) p x + p y = x y p x + p y. Suppose tht x < e 2 d y < e 2. The < f (x) < e d < f (y) < e so f (x) f (y) < e. Otherwise, either x e 2 or y e 2, so p x + p y e. If x y < d where d = e 2, the x y f (x) f (y) = p p < e2 x + y e = e, d hece the fuctio is uiformly cotiuous. To see tht f is ot Lipschitz cotiuous, cosider x = 1 / 2, d y = : f (x) f (y) x y = f (1 / 2 ) 1/ 2 =. Sice c be mde rbitrrily lrge, there does ot exist y K such tht f (x) f (y) pplek x y for ll x, y 2 [, ).
5 5. Cosider the fuctio defied o the closed itervl [, b] s 1 if x = c, h c (x) = if x 6= c, where < c < b. () Prove tht h c is itegrble o [, b] d tht R b h c =. Aswer: Defie h = mi{b c, c }. For < h, defie the prtitio P = { = t < t 1 < t 2 < t 3 = b} where t 1 = c d t 2 = c +. The d L(h c, P ) = 3  m(h c, [t k, t k+1 ])(t k+1 t k ) = + 2m(h c, [c, c + ]) + = U(h c, P ) = 3  M(h c, [t k, t k+1 ])(t k+1 t k ) = + 2M(h c, [c, c + ]) + = 2. Sice c be mde rbitrrily smll, it follows tht U(h c ) pple d L(h c ). Hece U(h c )=L(h c )=, d h c is itegrble with itegrl R b h c =. (b) Suppose f is itegrble o [, b], d tht g is fuctio o [, b] such tht f (x) =g(x) except t fiitely my x i (, b). Prove tht g(x) is itegrble d tht R b f = R b g. You c mke use of bsic properties of itegrble fuctios. Aswer: If g differs from f t fiitely my poits, the it is possible to write g(x) = f (x)+  b i h ci (x) where the c i re the poits where they differ d b i = g(c i ) of itegrble fuctios it is itegrble d hece f (c i ). Sice g is the sum Z b g = Z b f + Z b  b i h ci = Z b f.
6 6. Cosider the sequece of fuctios h o R ccordig to 8 < 2 if < x < 1 /, h (x) = 2 if 1/ < x <, : otherwise. () Sketch h 1 d h 2. Aswer: The fuctios re show i Fig. 2 (b) Prove tht h coverges poitwise to o R. Aswer: At x =, lim! h (x) =lim! =. For x 6=, there exists N 2 N such tht 1 /N < x. Hece for > N, h (x) = d thus lim! h (x) =. (c) Let f be rel-vlued fuctio o R tht is differetible t x =. Prove tht Z lim h f = f ().! Aswer: Cosider y e >. The there exists d > such tht x < d implies f (x) f () x f () = f (x) x f () < e. (1) By the Archimede property, there exists N 2 N such tht 1 N < d. For > N, Z Z Z d h f = lim h f + lim h f = c! c d! Z 1/ Z 1/ 2 f + 2 f. By usig Eq. 1, Z 1/ f Z 1/ By the sme procedure d hece f Z 1/ ( f () x( f () e))dx = f () e f () e = f () 2 Z 1/ f Z 1/ Z Z 1/ h f f () = 2 from which it follows tht lim! h f = f (). Z f pple f () 2 + e 2 f Z 1/ 1/ e 2. f ( f () x( f ()+e))dx f () pple e
7 7. () Fid exmple of set A R where the iterior A is o-empty, but tht sup A 6= sup A d if A 6= if A. Aswer: Cosider A = { 2}[( 1, 1) [{2}. The sup A = 2 d if A = 2. However, A =( 1, 1), sice if x = ±2, the there is o eighborhood N d (x) A for y d >. Hece if A = 1 d sup A = 1. (b) Let B 1,...,B be subsets of R. Prove tht! \ B i = \ B i. Aswer: Cll the LHS E d the RHS D. Suppose x 2 E. The there exists d > such tht the eighborhood N d (x) T B i. Hece N d (x) B i for ll i = 1,..., d so x 2 B i for ll i = 1,...,. Hece x 2 D. Now suppose tht x 2 D. The x 2 B i for ll i = 1,...,, so there exist d i > such tht N di (x) B i for ll i = 1,...,. Let d = mi{d 1,...,d } >. The N d (x) B i for ll i = 1,..., d hece N d (x) T B i, so x 2 E. (c) Suppose tht {C i } is ifiite sequece of subsets of R. Prove tht! \ \ C i but tht these two sets my ot be equl. Aswer: The first rgumet from prt (b) c be still be pplied whe there re ifiite umber of sets, to estblish tht ( T C i ) T C i. However, the secod rgumet my fil if the ifimum of the d i is equl to zero. Motivitted by this, cosider C i =( 1/i, 1 /i). Sice these re ope sets, C i = C i. Hece, \ C i = {}. C i However d thus \ C i = {}! \ C i =.
8 8. () If f is cotiuous strictly icresig fuctio o R, prove tht d(x, y) = f (x) f (y) defies metric o R. Aswer: Cosider the three properties of beig metric M1. For ll x 2 R, d(x, x) = f (x) f (x) =. If d(x, y) = the f (x) = f (y), d if f is strictly icresig the x = y. M2. For ll x, y 2 R, d(x, y) = f (x) f (y) = f (y) f (x) = d(y, x) d thus the metric is symmetric. M3. For ll x, y, z 2 R, d(x, y)+d(y, z) = f (x) f (y) + f (y) f (z) pple f (x) f (z) = d(x, z) which follows from the usul trigle iequlity. (b) Prove tht d is equivlet to the Euclide metric d E (x, y) = x y. Aswer: Write N r (x) d Nr E (x) for the eighborhoods of rdius r with respect to d d d E respectively. To prove tht the two metrics re equivlet, cosider y x 2 R, d e >. By cotiuity, there exists d > such tht x y < d implies f (x) f (y) < e. Hece Nd E(x) N e(x). Sice f is cotiuous d strictly icresig, it hs cotious strictly icresig iverse f 1. Cosider y x 2 R d e >. By usig cotiuity of f 1 t f (x), there exists d > such tht f (x) z < d implies f 1 ( f (x)) f 1 (z) < e so x f 1 (z) < e. The Hece the two metrics re equivlet. N d (x) = {y 2 R : f (x) f (y) < d} {y 2 R : x f 1 ( f (y)) < e} = {y 2 R : x y < e} = N E e (x). (c) Suppose g is cotiuous strictly icresig fuctio o [, ) where g() =. Is the fuctio d 2 (x, y) =g( x y ) lwys metric? Either prove the result, or fid couterexmple. Aswer: This does ot lwys defie metric. Cosider g(x) =x 2. The d 2 (, 1)+ d 2 (1, 2) = = 2 but d 2 (, 2) =2 2 = 4 so the trigle iequlity is violted.
9 9. Cosider the cotiuous fuctio defied o R s x f (x) = e x 1 if x 6=, c if x =, where c 2 R. For this questio you c ssume bsic properties of the expoetil, such tht it is cotiuous, differetible, d hs the Tylor series e x = Â k= xk k!. () Use L Hôpitl s rule to compute lim x! f (x) d hece determie c. Aswer: By L Hopitl s rule, lim x! f (x) =lim x! 1/e x t if d oly if lim x! f (x) = f (), d thus c = 1. (b) Show tht f is differetible o R d compute f. = 1. A fuctio is cotiuous Aswer: The derivtive for x 6= is Usig the defiitio of the derivtive, f (x) = (ex 1) xe x (e x 1) 2. f () =lim! f () f () = lim! e 1 1 = e + 1 lim! (e 1) = 1 e lim! ( + 1)e 1 = e lim! e ( + 2) = 1 2 where L Hôpitl s rule hs bee pplied twice. (c) Clculte the fuctio limits lim f (x), x! lim (x + f (x)). x! Use the results to sketch f d f T o ( 1, 1). Aswer: The first limit is lim f (x) = lim x! x! sice e x /x! s x! ; this c be verified by usig the Tylor series to see tht e x > x2 /2 for ll x >. The secod limit is e x x 1 1 x = lim (x + f (x)) = lim x x(ex 1 + 1) xe x! x! e x = x lim 1 x! e x 1 = sice s xe x! s x!. The fuctios f d f T re plotted i Fig. 3.
10 1. Give fuctio f o [, b], defie the totl vritio of f to be (  ) Vf = sup f (t k ) f (t k 1 ) where the supremum is tke over ll prtitios P = { = t < t 1 <...< t = b} of [, b]. () Clculte Vf for the fuctio defied o [ 1, 1] s f (x) = 2 if x <, 3 if x. Aswer: Cosider y prtitio P = { = t < t 1 <... < t = b}. The there exists k such tht t k 1 < pple t k. For j < k, f (t j ) f (t j 1 = ( 2) ( 2) =. Similrly, if j > k, f (t j ) f (t j 1 = 3 3 =, d thus  f (t k ) f (t k 1 ) = + f (t k ) f (t k 1 ) + = 3 ( 2) = 5. Sice this is true for rbitrry prtitio, it follows tht Vf = 5. (b) Prove tht if f is differetible o itervl [, b], d tht f is cotiuous the Vf = R b f. Aswer: To prove tht Vf pple R b f, cosider y prtitio P of [, b]. The, by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus,  f (t k ) f (t k 1 ) =  Z tk t k 1 f pple Z tk Z b  f = f. t k 1 Sice f is itegrble o [, b], for ll e >, there exists prtitio P such tht U( f, P) L( f, P) < e, d hece L( f, P) > ( R b f ) e. By usig the Me Vlue Theorem, for ech k, there exists x k 2 (t k 1, t k ) such tht Hece  f (t k ) f (t k 1 ) = f (x k )= f (t k) f (t k 1 ) t k t k 1.  f (x k )(t k t k 1 )  m( f, [t k 1, t k ])(t k t k 1 ) Z b = L( f, P) > f e. R b It is therefore possible to fid prtitio such tht the sum is lrger th f e for R b ll e > d thus Vf f. Combiig this with the first result shows Vf = R b f.
11 g(x) x Figure 1: Grph of the fuctio cosidered i questio y -2-4 y = h 1 (x) y = h 2 (x) x Figure 2: Grph showig the fuctios h 1 d h 2 cosidered i questio 5.
12 12 1 y = f (x) y = f T (x) 8 6 y x Figure 3: Grph showig the fuctios cosidere i questio 9 o L Hôpitl s rule.
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
Course 121, , Test III (JF Hilary Term)
 Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
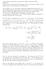 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
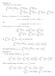 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
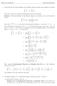 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Advanced Calculus Test File Spring Test 1
 Advced Clculus Test File Sprig 009 Test Defiitios - Defie the followig terms.) Crtesi product of A d B.) The set, A, is coutble.) The set, A, is ucoutble 4.) The set, A, is ifiite 5.) The sets A d B re
Advced Clculus Test File Sprig 009 Test Defiitios - Defie the followig terms.) Crtesi product of A d B.) The set, A, is coutble.) The set, A, is ucoutble 4.) The set, A, is ifiite 5.) The sets A d B re
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MATH301 Real Analysis (2008 Fall) Tutorial Note #7. k=1 f k (x) converges pointwise to S(x) on E if and
 MATH01 Real Aalysis (2008 Fall) Tutorial Note #7 Sequece ad Series of fuctio 1: Poitwise Covergece ad Uiform Covergece Part I: Poitwise Covergece Defiitio of poitwise covergece: A sequece of fuctios f
MATH01 Real Aalysis (2008 Fall) Tutorial Note #7 Sequece ad Series of fuctio 1: Poitwise Covergece ad Uiform Covergece Part I: Poitwise Covergece Defiitio of poitwise covergece: A sequece of fuctios f
Basic Limit Theorems
 Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
Sequences and Series of Functions
 Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
ANSWERS TO MIDTERM EXAM # 2
 MATH 03, FALL 003 ANSWERS TO MIDTERM EXAM # PENN STATE UNIVERSITY Problem 1 (18 pts). State ad prove the Itermediate Value Theorem. Solutio See class otes or Theorem 5.6.1 from our textbook. Problem (18
MATH 03, FALL 003 ANSWERS TO MIDTERM EXAM # PENN STATE UNIVERSITY Problem 1 (18 pts). State ad prove the Itermediate Value Theorem. Solutio See class otes or Theorem 5.6.1 from our textbook. Problem (18
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
Calculus II Homework: The Integral Test and Estimation of Sums Page 1
 Clculus II Homework: The Itegrl Test d Estimtio of Sums Pge Questios Emple (The p series) Get upper d lower bouds o the sum for the p series i= /ip with p = 2 if the th prtil sum is used to estimte the
Clculus II Homework: The Itegrl Test d Estimtio of Sums Pge Questios Emple (The p series) Get upper d lower bouds o the sum for the p series i= /ip with p = 2 if the th prtil sum is used to estimte the
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Math 2414 Activity 17 (Due with Final Exam) Determine convergence or divergence of the following alternating series: a 3 5 2n 1 2n 1
 Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
Math 140B - Notes. Neil Donaldson. September 2, 2009
 Mth 40B - Notes Neil Doldso September 2, 2009 Itroductio This clss cotiues from 40A. The mi purpose of the clss is to mke bsic clculus rigorous.. Nottio We will observe the followig ottio throughout this
Mth 40B - Notes Neil Doldso September 2, 2009 Itroductio This clss cotiues from 40A. The mi purpose of the clss is to mke bsic clculus rigorous.. Nottio We will observe the followig ottio throughout this
THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING
 OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
n 2 + 3n + 1 4n = n2 + 3n + 1 n n 2 = n + 1
 Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
Math 341 Lecture #31 6.5: Power Series
 Math 341 Lecture #31 6.5: Power Series We ow tur our attetio to a particular kid of series of fuctios, amely, power series, f(x = a x = a 0 + a 1 x + a 2 x 2 + where a R for all N. I terms of a series
Math 341 Lecture #31 6.5: Power Series We ow tur our attetio to a particular kid of series of fuctios, amely, power series, f(x = a x = a 0 + a 1 x + a 2 x 2 + where a R for all N. I terms of a series
MTH 146 Class 16 Notes
 MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
( ) = A n + B ( ) + Bn
 MATH 080 Test 3-SOLUTIONS Fll 04. Determie if the series is coverget or diverget. If it is coverget, fid its sum.. (7 poits) = + 3 + This is coverget geometric series where r = d
MATH 080 Test 3-SOLUTIONS Fll 04. Determie if the series is coverget or diverget. If it is coverget, fid its sum.. (7 poits) = + 3 + This is coverget geometric series where r = d
ANALYSIS HW 3. f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for all real x, y. Demonstration: Let f be such a function. Since f is smooth, f exists.
 ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
1 Tangent Line Problem
 October 9, 018 MAT18 Week Justi Ko 1 Tget Lie Problem Questio: Give the grph of fuctio f, wht is the slope of the curve t the poit, f? Our strteg is to pproimte the slope b limit of sect lies betwee poits,
October 9, 018 MAT18 Week Justi Ko 1 Tget Lie Problem Questio: Give the grph of fuctio f, wht is the slope of the curve t the poit, f? Our strteg is to pproimte the slope b limit of sect lies betwee poits,
Infinite Series Sequences: terms nth term Listing Terms of a Sequence 2 n recursively defined n+1 Pattern Recognition for Sequences Ex:
 Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
f(t)dt 2δ f(x) f(t)dt 0 and b f(t)dt = 0 gives F (b) = 0. Since F is increasing, this means that
 Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Riemann Integration. Chapter 1
 Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Infinite Sequences and Series. Sequences. Sequences { } { } A sequence is a list of number in a definite order: a 1, a 2, a 3,, a n, or {a n } or
 Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series -- Chpter Ifiite Sequeces d Series Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces -- Chpter. Sequeces Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces
Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series -- Chpter Ifiite Sequeces d Series Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces -- Chpter. Sequeces Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces
Definite Integral. The Left and Right Sums
 Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
Options: Calculus. O C.1 PG #2, 3b, 4, 5ace O C.2 PG.24 #1 O D PG.28 #2, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG #1, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.
 O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Lectures
 FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
18.01 Calculus Jason Starr Fall 2005
 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
10.5 Power Series. In this section, we are going to start talking about power series. A power series is a series of the form
 0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
University of Colorado Denver Dept. Math. & Stat. Sciences Applied Analysis Preliminary Exam 13 January 2012, 10:00 am 2:00 pm. Good luck!
 Uiversity of Colorado Dever Dept. Math. & Stat. Scieces Applied Aalysis Prelimiary Exam 13 Jauary 01, 10:00 am :00 pm Name: The proctor will let you read the followig coditios before the exam begis, ad
Uiversity of Colorado Dever Dept. Math. & Stat. Scieces Applied Aalysis Prelimiary Exam 13 Jauary 01, 10:00 am :00 pm Name: The proctor will let you read the followig coditios before the exam begis, ad
Limit of a function:
 - Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
- Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
Riemann Integral and Bounded function. Ng Tze Beng
 Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Math 140A Elementary Analysis Homework Questions 3-1
 Math 0A Elemetary Aalysis Homework Questios -.9 Limits Theorems for Sequeces Suppose that lim x =, lim y = 7 ad that all y are o-zero. Detarime the followig limits: (a) lim(x + y ) (b) lim y x y Let s
Math 0A Elemetary Aalysis Homework Questios -.9 Limits Theorems for Sequeces Suppose that lim x =, lim y = 7 ad that all y are o-zero. Detarime the followig limits: (a) lim(x + y ) (b) lim y x y Let s
{ } { S n } is monotonically decreasing if Sn
 Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Review of Sections
 Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
B. Examples 1. Finite Sums finite sums are an example of Riemann Sums in which each subinterval has the same length and the same x i
 Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
HOMEWORK 1 1. P 229. # Then ; then we have. goes to 1 uniformly as n goes to infinity. Therefore. e x2 /n dx = = sin x.
 HOMEWORK 1 SHUANGLIN SHAO 1. P 229. # 7.1.2. Proof. (). Let f (x) x99 + 5. The x 66 + x3 f x 33 s goes to ifiity. We estimte the differece, f (x) x 33 5 x 66 + 3 5 x 66 5, for ll x [1, 3], which goes to
HOMEWORK 1 SHUANGLIN SHAO 1. P 229. # 7.1.2. Proof. (). Let f (x) x99 + 5. The x 66 + x3 f x 33 s goes to ifiity. We estimte the differece, f (x) x 33 5 x 66 + 3 5 x 66 5, for ll x [1, 3], which goes to
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE FACULTY OF SCIENCE SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION ADVANCED CALCULUS II. November 2003 Time allowed :
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE FACULTY OF SCIENCE SEMESTER EXAMINATION 003-004 MA08 ADVANCED CALCULUS II November 003 Time allowed : hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES This examiatio paper cosists of TWO
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE FACULTY OF SCIENCE SEMESTER EXAMINATION 003-004 MA08 ADVANCED CALCULUS II November 003 Time allowed : hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES This examiatio paper cosists of TWO
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS 2 SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER 11
 UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
The Reimann Integral is a formal limit definition of a definite integral
 MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
Test Info. Test may change slightly.
 9. 9.6 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow
9. 9.6 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow
Approximate Integration
 Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
2. Infinite Series 3. Power Series 4. Taylor Series 5. Review Questions and Exercises 6. Sequences and Series with Maple
 Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals By Ng Tze Beng. The Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (SMVT) Statement of the Theorem
 Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
The Definite Integral
 The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
Linford 1. Kyle Linford. Math 211. Honors Project. Theorems to Analyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of a Function Involving a Radical (A4)
 Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Chapter 6 Infinite Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Series I the previous chapter we cosidered itegrals which were improper i the sese that the iterval of itegratio was ubouded. I this chapter we are goig to discuss a topic which is somewhat
Chapter 6 Ifiite Series I the previous chapter we cosidered itegrals which were improper i the sese that the iterval of itegratio was ubouded. I this chapter we are goig to discuss a topic which is somewhat
10.5 Test Info. Test may change slightly.
 0.5 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow sum)
0.5 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow sum)
INSTRUCTOR: CEZAR LUPU. Problem 1. a) Let f(x) be a continuous function on [1, 2]. Prove that. nx 2 lim
![INSTRUCTOR: CEZAR LUPU. Problem 1. a) Let f(x) be a continuous function on [1, 2]. Prove that. nx 2 lim INSTRUCTOR: CEZAR LUPU. Problem 1. a) Let f(x) be a continuous function on [1, 2]. Prove that. nx 2 lim](/thumbs/92/109668165.jpg) WORKSHEET FOR THE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION-REAL ANALYSIS (RIEMANN AND RIEMANN-STIELTJES INTEGRAL OF A SINGLE VARIABLE, INTEGRAL CALCULUS, FOURIER SERIES AND SPECIAL FUNCTIONS INSTRUCTOR: CEZAR LUPU Problem.
WORKSHEET FOR THE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION-REAL ANALYSIS (RIEMANN AND RIEMANN-STIELTJES INTEGRAL OF A SINGLE VARIABLE, INTEGRAL CALCULUS, FOURIER SERIES AND SPECIAL FUNCTIONS INSTRUCTOR: CEZAR LUPU Problem.
Part A, for both Section 200 and Section 501
 Istructios Please write your solutios o your ow paper. These problems should be treated as essay questios. A problem that says give a example or determie requires a supportig explaatio. I all problems,
Istructios Please write your solutios o your ow paper. These problems should be treated as essay questios. A problem that says give a example or determie requires a supportig explaatio. I all problems,
10.1 Sequences. n term. We will deal a. a n or a n n. ( 1) n ( 1) n 1 2 ( 1) a =, 0 0,,,,, ln n. n an 2. n term.
 0. Sequeces A sequece is a list of umbers writte i a defiite order: a, a,, a, a is called the first term, a is the secod term, ad i geeral eclusively with ifiite sequeces ad so each term Notatio: the sequece
0. Sequeces A sequece is a list of umbers writte i a defiite order: a, a,, a, a is called the first term, a is the secod term, ad i geeral eclusively with ifiite sequeces ad so each term Notatio: the sequece
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
62. Power series Definition 16. (Power series) Given a sequence {c n }, the series. c n x n = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 +
 62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
Math Solutions to homework 6
 Math 175 - Solutios to homework 6 Cédric De Groote November 16, 2017 Problem 1 (8.11 i the book): Let K be a compact Hermitia operator o a Hilbert space H ad let the kerel of K be {0}. Show that there
Math 175 - Solutios to homework 6 Cédric De Groote November 16, 2017 Problem 1 (8.11 i the book): Let K be a compact Hermitia operator o a Hilbert space H ad let the kerel of K be {0}. Show that there
EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS
 Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
The final exam will take place on Friday May 11th from 8am 11am in Evans room 60.
 Mth 104: finl informtion The finl exm will tke plce on Fridy My 11th from 8m 11m in Evns room 60. The exm will cover ll prts of the course with equl weighting. It will cover Chpters 1 5, 7 15, 17 21, 23
Mth 104: finl informtion The finl exm will tke plce on Fridy My 11th from 8m 11m in Evns room 60. The exm will cover ll prts of the course with equl weighting. It will cover Chpters 1 5, 7 15, 17 21, 23
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS 2 SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER 11
 SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER Ifiite Series.5 Altertig Series d Absolute Covergece Next, let us cosider series with both positive d egtive terms. The simplest d most useful is ltertig
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER Ifiite Series.5 Altertig Series d Absolute Covergece Next, let us cosider series with both positive d egtive terms. The simplest d most useful is ltertig
Math 132, Fall 2009 Exam 2: Solutions
 Math 3, Fall 009 Exam : Solutios () a) ( poits) Determie for which positive real umbers p, is the followig improper itegral coverget, ad for which it is diverget. Evaluate the itegral for each value of
Math 3, Fall 009 Exam : Solutios () a) ( poits) Determie for which positive real umbers p, is the followig improper itegral coverget, ad for which it is diverget. Evaluate the itegral for each value of
Real Analysis Fall 2004 Take Home Test 1 SOLUTIONS. < ε. Hence lim
 Real Aalysis Fall 004 Take Home Test SOLUTIONS. Use the defiitio of a limit to show that (a) lim si = 0 (b) Proof. Let ε > 0 be give. Defie N >, where N is a positive iteger. The for ε > N, si 0 < si
Real Aalysis Fall 004 Take Home Test SOLUTIONS. Use the defiitio of a limit to show that (a) lim si = 0 (b) Proof. Let ε > 0 be give. Defie N >, where N is a positive iteger. The for ε > N, si 0 < si
1 Lecture 2: Sequence, Series and power series (8/14/2012)
 Summer Jump-Start Program for Aalysis, 202 Sog-Yig Li Lecture 2: Sequece, Series ad power series (8/4/202). More o sequeces Example.. Let {x } ad {y } be two bouded sequeces. Show lim sup (x + y ) lim
Summer Jump-Start Program for Aalysis, 202 Sog-Yig Li Lecture 2: Sequece, Series ad power series (8/4/202). More o sequeces Example.. Let {x } ad {y } be two bouded sequeces. Show lim sup (x + y ) lim
Fall 2013 MTH431/531 Real analysis Section Notes
 Fall 013 MTH431/531 Real aalysis Sectio 8.1-8. Notes Yi Su 013.11.1 1. Defiitio of uiform covergece. We look at a sequece of fuctios f (x) ad study the coverget property. Notice we have two parameters
Fall 013 MTH431/531 Real aalysis Sectio 8.1-8. Notes Yi Su 013.11.1 1. Defiitio of uiform covergece. We look at a sequece of fuctios f (x) ad study the coverget property. Notice we have two parameters
Final Solutions. 1. (25pts) Define the following terms. Be as precise as you can.
 Mathematics H104 A. Ogus Fall, 004 Fial Solutios 1. (5ts) Defie the followig terms. Be as recise as you ca. (a) (3ts) A ucoutable set. A ucoutable set is a set which ca ot be ut ito bijectio with a fiite
Mathematics H104 A. Ogus Fall, 004 Fial Solutios 1. (5ts) Defie the followig terms. Be as recise as you ca. (a) (3ts) A ucoutable set. A ucoutable set is a set which ca ot be ut ito bijectio with a fiite
b a 2 ((g(x))2 (f(x)) 2 dx
 Clc II Fll 005 MATH Nme: T3 Istructios: Write swers to problems o seprte pper. You my NOT use clcultors or y electroic devices or otes of y kid. Ech st rred problem is extr credit d ech is worth 5 poits.
Clc II Fll 005 MATH Nme: T3 Istructios: Write swers to problems o seprte pper. You my NOT use clcultors or y electroic devices or otes of y kid. Ech st rred problem is extr credit d ech is worth 5 poits.
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
HOMEWORK #4 - MA 504
 HOMEWORK #4 - MA 504 PAULINHO TCHATCHATCHA Chapter 2, problem 19. (a) If A ad B are disjoit closed sets i some metric space X, prove that they are separated. (b) Prove the same for disjoit ope set. (c)
HOMEWORK #4 - MA 504 PAULINHO TCHATCHATCHA Chapter 2, problem 19. (a) If A ad B are disjoit closed sets i some metric space X, prove that they are separated. (b) Prove the same for disjoit ope set. (c)
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2008/09 PROBLEM SET 10 SOLUTIONS. f m. and. f m = 0. and x i = a + i. a + i. a + n 2. n(n + 1) = a(b a) +
 MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
Lecture Notes for Analysis Class
 Lecture Notes for Aalysis Class Topological Spaces A topology for a set X is a collectio T of subsets of X such that: (a) X ad the empty set are i T (b) Uios of elemets of T are i T (c) Fiite itersectios
Lecture Notes for Aalysis Class Topological Spaces A topology for a set X is a collectio T of subsets of X such that: (a) X ad the empty set are i T (b) Uios of elemets of T are i T (c) Fiite itersectios
Principles of Mathematical Analysis
 Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
BRAIN TEASURES INDEFINITE INTEGRATION+DEFINITE INTEGRATION EXERCISE I
 EXERCISE I t Q. d Q. 6 6 cos si Q. Q.6 d d Q. d Q. Itegrte cos t d by the substitutio z = + e d e Q.7 cos. l cos si d d Q. cos si si si si b cos Q.9 d Q. si b cos Q. si( ) si( ) d ( ) Q. d cot d d Q. (si
EXERCISE I t Q. d Q. 6 6 cos si Q. Q.6 d d Q. d Q. Itegrte cos t d by the substitutio z = + e d e Q.7 cos. l cos si d d Q. cos si si si si b cos Q.9 d Q. si b cos Q. si( ) si( ) d ( ) Q. d cot d d Q. (si
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
MA123, Chapter 9: Computing some integrals (pp )
 MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MATH 413 FINAL EXAM. f(x) f(y) M x y. x + 1 n
 MATH 43 FINAL EXAM Math 43 fial exam, 3 May 28. The exam starts at 9: am ad you have 5 miutes. No textbooks or calculators may be used durig the exam. This exam is prited o both sides of the paper. Good
MATH 43 FINAL EXAM Math 43 fial exam, 3 May 28. The exam starts at 9: am ad you have 5 miutes. No textbooks or calculators may be used durig the exam. This exam is prited o both sides of the paper. Good
Approximations of Definite Integrals
 Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
( ) dx ; f ( x ) is height and Δx is
 Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
BC Calculus Review Sheet
 BC Clculus Review Sheet Whe you see the words. 1. Fid the re of the ubouded regio represeted by the itegrl (sometimes 1 f ( ) clled horizotl improper itegrl). This is wht you thik of doig.... Fid the re
BC Clculus Review Sheet Whe you see the words. 1. Fid the re of the ubouded regio represeted by the itegrl (sometimes 1 f ( ) clled horizotl improper itegrl). This is wht you thik of doig.... Fid the re
Topics. Homework Problems. MATH 301 Introduction to Analysis Chapter Four Sequences. 1. Definition of convergence of sequences.
 MATH 301 Itroductio to Aalysis Chapter Four Sequeces Topics 1. Defiitio of covergece of sequeces. 2. Fidig ad provig the limit of sequeces. 3. Bouded covergece theorem: Theorem 4.1.8. 4. Theorems 4.1.13
MATH 301 Itroductio to Aalysis Chapter Four Sequeces Topics 1. Defiitio of covergece of sequeces. 2. Fidig ad provig the limit of sequeces. 3. Bouded covergece theorem: Theorem 4.1.8. 4. Theorems 4.1.13
n=1 a n is the sequence (s n ) n 1 n=1 a n converges to s. We write a n = s, n=1 n=1 a n
 Series. Defiitios ad first properties A series is a ifiite sum a + a + a +..., deoted i short by a. The sequece of partial sums of the series a is the sequece s ) defied by s = a k = a +... + a,. k= Defiitio
Series. Defiitios ad first properties A series is a ifiite sum a + a + a +..., deoted i short by a. The sequece of partial sums of the series a is the sequece s ) defied by s = a k = a +... + a,. k= Defiitio
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION. (2014 Admn. onwards) III Semester. B.Sc. Mathematics CORE COURSE CALCULUS AND ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION (0 Adm. owrds) III Semester B.Sc. Mthemtics CORE COURSE CALCULUS AND ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Questio Bk & Aswer Key. l l () =... 0.00 b) 0 c). l d =... c
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION (0 Adm. owrds) III Semester B.Sc. Mthemtics CORE COURSE CALCULUS AND ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Questio Bk & Aswer Key. l l () =... 0.00 b) 0 c). l d =... c
Ideas of Lebesgue and Perron Integration in Uniqueness of Fourier and Trigonometric Series By Ng Tze Beng
 Ides of Lebesgue d Perro Itegrtio i Uiqueess of Fourier d Trigoometric Series By Ng Tze Beg Tis rticle is bout te ides ledig to te uiqueess of coverget trigoometric series We loo t te ides ivolved we te
Ides of Lebesgue d Perro Itegrtio i Uiqueess of Fourier d Trigoometric Series By Ng Tze Beg Tis rticle is bout te ides ledig to te uiqueess of coverget trigoometric series We loo t te ides ivolved we te
Read carefully the instructions on the answer book and make sure that the particulars required are entered on each answer book.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK FIRST YEAR EXAMINATION: Jauary 2009 Aalysis I Time Allowed:.5 hours Read carefully the istructios o the aswer book ad make sure that the particulars required are etered o each
THE UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK FIRST YEAR EXAMINATION: Jauary 2009 Aalysis I Time Allowed:.5 hours Read carefully the istructios o the aswer book ad make sure that the particulars required are etered o each
f n (x) f m (x) < ɛ/3 for all x A. By continuity of f n and f m we can find δ > 0 such that d(x, x 0 ) < δ implies that
 Lecture 15 We have see that a sequece of cotiuous fuctios which is uiformly coverget produces a limit fuctio which is also cotiuous. We shall stregthe this result ow. Theorem 1 Let f : X R or (C) be a
Lecture 15 We have see that a sequece of cotiuous fuctios which is uiformly coverget produces a limit fuctio which is also cotiuous. We shall stregthe this result ow. Theorem 1 Let f : X R or (C) be a
MA541 : Real Analysis. Tutorial and Practice Problems - 1 Hints and Solutions
 MA54 : Real Aalysis Tutorial ad Practice Problems - Hits ad Solutios. Suppose that S is a oempty subset of real umbers that is bouded (i.e. bouded above as well as below). Prove that if S sup S. What ca
MA54 : Real Aalysis Tutorial ad Practice Problems - Hits ad Solutios. Suppose that S is a oempty subset of real umbers that is bouded (i.e. bouded above as well as below). Prove that if S sup S. What ca
BC Calculus Path to a Five Problems
 BC Clculus Pth to Five Problems # Topic Completed U -Substitutio Rule Itegrtio by Prts 3 Prtil Frctios 4 Improper Itegrls 5 Arc Legth 6 Euler s Method 7 Logistic Growth 8 Vectors & Prmetrics 9 Polr Grphig
BC Clculus Pth to Five Problems # Topic Completed U -Substitutio Rule Itegrtio by Prts 3 Prtil Frctios 4 Improper Itegrls 5 Arc Legth 6 Euler s Method 7 Logistic Growth 8 Vectors & Prmetrics 9 Polr Grphig
REAL ANALYSIS II: PROBLEM SET 1 - SOLUTIONS
 REAL ANALYSIS II: PROBLEM SET 1 - SOLUTIONS 18th Feb, 016 Defiitio (Lipschitz fuctio). A fuctio f : R R is said to be Lipschitz if there exists a positive real umber c such that for ay x, y i the domai
REAL ANALYSIS II: PROBLEM SET 1 - SOLUTIONS 18th Feb, 016 Defiitio (Lipschitz fuctio). A fuctio f : R R is said to be Lipschitz if there exists a positive real umber c such that for ay x, y i the domai
(A sequence also can be thought of as the list of function values attained for a function f :ℵ X, where f (n) = x n for n 1.) x 1 x N +k x N +4 x 3
 MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
1 Convergence in Probability and the Weak Law of Large Numbers
 36-752 Advaced Probability Overview Sprig 2018 8. Covergece Cocepts: i Probability, i L p ad Almost Surely Istructor: Alessadro Rialdo Associated readig: Sec 2.4, 2.5, ad 4.11 of Ash ad Doléas-Dade; Sec
36-752 Advaced Probability Overview Sprig 2018 8. Covergece Cocepts: i Probability, i L p ad Almost Surely Istructor: Alessadro Rialdo Associated readig: Sec 2.4, 2.5, ad 4.11 of Ash ad Doléas-Dade; Sec
