18.01 Calculus Jason Starr Fall 2005
|
|
|
- Frederick Nichols
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res of trigles, qudrilterls, d my other polygos. Their bsic method ws dissectio: dissectig polygol regio exctly ito smller regios, usully trigles, hvig kow res. The re of the lrge regio is the sum of the res of the smll regios. But the ciet Greeks lso kew the re of circle, which cot be dissected exctly ito fiitely my polygol regios. Their method ws exhustio: fidig polygol regios pproximtely equl to the origil regio, d computig the limit of the res of the polygos s the pproximtio improves. Exmple. A regulr N sided polygo iscribed i circle of rdius r hs pothem legth = r cos(π/n ) d chord legth b = r si(π/n ). Thus the re of the polygo is, b A = N = N r si(π/n ) cos(π/n ) = r N si(π/n ) = πr si(π/n ). π/n As N icreses, π/n decreses to 0. Becuse lim t the re of the polygo pproches, 0 si(t)/t equls 1, s N pproches ifiity, lim πr si(π/n ) = π/n N πr. A more sophisticted versio of the method of exhustio gives the Riem itegrl. Here is the bsic problem. Problem (Are). Fid the siged re betwee the grph of y = f (x) d the x xis over the itervl x b.
2 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr For regio bove the x xis, the siged re is simply the re. For regio below the x xis, the siged re is the egtive of the re. For regio prtly bove the x xis d prtly below the x xis, the siged re is the sum of the siged re of the regio bove the x xis d the siged re of the regio below the x xis.. Prtitios. A prtitio of itervl [, b] is fiite decompositio of the itervl s uio of o overlppig subitervls, [, b] = [x 0, x 1 ] [x 1, x ] [x, x ] [x 1, x ]. Sice itervl is determied by its right d left edpoits, to specify prtitio of [, b], it is equivlet to give ordered sequece of icresig umbers, = x 0 < x 1 < x < < x < x 1 < x = b. The k th subitervl of the prtitio is the itervl [x k 1, x k ], hvig legth, Δx k = x k x k 1. A prtitio is fie if the subitervls re smll, d corse if the subitervls re lrge. It my seem the umber of itervls is good mesure of fieess: sice the subitervls of fie prtitio re smll, the umber of subitervls must be lrge. However, prtitio ito my subitervls my iclude few subitervls tht re quite lrge. For istce, the prtitio [0, 1] = [0, 1/] [1/, /] [/, 3/] [( )/, ( 1)/] [ 1/, /] [1/, 1], hs very smll itervls of legth 1/, but hs oe itervl, [1/, 1], of size 1/. The umber 1/ my ot seem lrge, but s icreses, it is quite lrge compred to 1/. Becuse of such exmples, better mesure of fieess is mesh size: The mesh size of prtitio is the mximl legth of y subitervl i the prtitio, mesh = mx Δx k k = 1,...,. 3. Riem sums. Let f(x) be fuctio defied o itervl x b. Give prtitio = x 0 < < x = b of [, b], d give choice, for every k = 1,...,, of elemet x k i the k th subitervl, x k 1 x k x k, the curvilier regio bouded by y = f(x) d the x xis is pproximted by uio of verticl strips. The k th verticl strip lies bove or below the itervl o the x xis, x k 1 x x k, d hs height yk = f(x k ). The width of the verticl strip is Δx k, thus the siged re is, ΔA k = yk Δx k. The totl re of the uio of verticl strips is simply the sum of the res of idividul verticl strips, A = yk Δx k. k=1
3 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr The sum bove is Riem sum. It is pproximtio of the siged re of the curvilier regio. There re my choices of prtitio. Ad for ech prtitio, there re my choices for the umbers xk. However, there re some specil choices. O the kth itervl, the smllest vlue f (x) tkes o is deoted by, y k,mi = mi{f (x) x k 1 x x k+1 }. Similrly, the lrgest vlue f (x) tkes o is deote by, y k,mx = mx{f (x) x k 1 x x k+1 }. For every choice of x k i the k th itervl, yk is trpped betwee these two vlues, Deotig, y k,mi y k y k,mx. ΔA k,mi = y k,mi Δx k, ΔA k,mx = y k,mx Δx k, the re ΔA k is trpped betwee these two vlues, ΔA k,mi ΔA k ΔA k,mx. Deotig the sums of the res by, A mi = k=1 ΔA k,mi = k=1 y k,miδx k, A mx = k=1 ΔA k,mi = k=1 y k,miδx k, the Riem sum A is trpped betwee the two vlues, A mi A A mx. Thus, if A mi d A mx re close to ech other, the vlue of A does ot deped very much o the choices of the umbers x k. 4. The Riem itegrl. The method of the Riem itegrl is to compute both A mi d A mx for sequece of prtitios whose mesh sizes pproch 0. The mesh size mesures the fieess of the prtitio, thus lso the fit of the uio of verticl strips to the curvilier regio. If the two limits, lim A mi, lim A mx, mesh 0 mesh 0 re defied d equl, it is sid the Riem itegrl exists, d the commo limit is clled the Riem itegrl, b f (x)dx = lim A mi = lim A mx. mesh 0 mesh 0 Also, f (x) is sid to be Riem itegrble o the itervl [, b]. Aother me for the Riem itegrl is the defiite itegrl.
4 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Exmple. Cosider the fuctio f (x) = x o the itervl 0 x L, for some positive umber L. Form the prtitio with subitervls of equl legth, x 0 = 0 = 0L/, x 1 = 1L/, x = L/,..., x k = kl/,... x = L/ = L. Every itervl hs legth Δx k = L/. So the mesh size is L/. The miimum vlue of f (x) o the itervl x k 1 x x k is y k,mi = x k 1 = (k 1)L/. The mximum vlue is y k,mx = x k = kl/. Thus, (k 1)L L L Ami = y k,mi Δx k = = (k 1), k=1 k=1 k=1 d, kl L L A mx = y k,mx Δx k = = k. k=1 k=1 k=1 To evlute these sums, use the well kow formul, ( + 1) k =. k=1 This lso gives, 1 1 ( 1) (k 1) = l = l =, k=1 l=0 l=1 by mkig the substitutio l = k 1. Substitutig the formul gives, L ( 1) = L (1 1 ), A mi = d, L ( + 1) L 1 A mi = = (1 + ). Therefore, L 1 L L lim A mi = lim(1 ) = (1 0) =. 0 Similrly, L 1 L L lim A mx = lim(1 + ) = (1 + 0) =. 0 Sice the two limits re equl, f (x) = x is Riem itegrble o the itervl [0, L], d, L xdx = L /. 0 This grees with the fmilir result from high school geometry: the re of trigle equls oe hlf of the bse times the height, sice both the bse d height of this trigle re L.
5 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr 5. Rules for Riem itegrls. There re severl rules for Riem itegrls, summrized below. b b b (f(x) + g(x))dx = f (x)dx + g(x)dx, b (r b f (x))dx = r f (x)dx, b c c f (x)dx + b f (x)dx = f (x)dx.
B. Examples 1. Finite Sums finite sums are an example of Riemann Sums in which each subinterval has the same length and the same x i
 Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Definite Integral. The Left and Right Sums
 Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
MA123, Chapter 9: Computing some integrals (pp )
 MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Approximations of Definite Integrals
 Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
The Definite Riemann Integral
 These otes closely follow the presettio of the mteril give i Jmes Stewrt s textook Clculus, Cocepts d Cotexts (d editio). These otes re iteded primrily for i-clss presettio d should ot e regrded s sustitute
These otes closely follow the presettio of the mteril give i Jmes Stewrt s textook Clculus, Cocepts d Cotexts (d editio). These otes re iteded primrily for i-clss presettio d should ot e regrded s sustitute
n 2 + 3n + 1 4n = n2 + 3n + 1 n n 2 = n + 1
 Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
The Reimann Integral is a formal limit definition of a definite integral
 MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
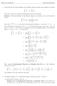 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Riemann Integration. Chapter 1
 Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS
 Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
The Definite Integral
 The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
5.1 - Areas and Distances
 Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 63u Office Hours: R 9:5 - :5m The midterm will cover the sectios for which you hve received homework d feedbck Sectios.9-6.5 i your book.
Mth 3B Midterm Review Writte by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 63u Office Hours: R 9:5 - :5m The midterm will cover the sectios for which you hve received homework d feedbck Sectios.9-6.5 i your book.
(200 terms) equals Let f (x) = 1 + x + x 2 + +x 100 = x101 1
 SECTION 5. PGE 78.. DMS: CLCULUS.... 5. 6. CHPTE 5. Sectio 5. pge 78 i + + + INTEGTION Sums d Sigm Nottio j j + + + + + i + + + + i j i i + + + j j + 5 + + j + + 9 + + 7. 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 9 i i5 8. +
SECTION 5. PGE 78.. DMS: CLCULUS.... 5. 6. CHPTE 5. Sectio 5. pge 78 i + + + INTEGTION Sums d Sigm Nottio j j + + + + + i + + + + i j i i + + + j j + 5 + + j + + 9 + + 7. 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 9 i i5 8. +
INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
 Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
Approximate Integration
 Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
Fall 2004 Math Integrals 6.1 Sigma Notation Mon, 15/Nov c 2004, Art Belmonte
 Fll Mth 6 Itegrls 6. Sigm Nottio Mo, /Nov c, Art Belmote Summr Sigm ottio For itegers m d rel umbers m, m+,...,, we write k = m + m+ + +. k=m The left-hd side is shorthd for the fiite sum o right. The
Fll Mth 6 Itegrls 6. Sigm Nottio Mo, /Nov c, Art Belmote Summr Sigm ottio For itegers m d rel umbers m, m+,...,, we write k = m + m+ + +. k=m The left-hd side is shorthd for the fiite sum o right. The
Infinite Series Sequences: terms nth term Listing Terms of a Sequence 2 n recursively defined n+1 Pattern Recognition for Sequences Ex:
 Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
INTEGRATION IN THEORY
 CHATER 5 INTEGRATION IN THEORY 5.1 AREA AROXIMATION 5.1.1 SUMMATION NOTATION Fibocci Sequece First, exmple of fmous sequece of umbers. This is commoly ttributed to the mthemtici Fibocci of is, lthough
CHATER 5 INTEGRATION IN THEORY 5.1 AREA AROXIMATION 5.1.1 SUMMATION NOTATION Fibocci Sequece First, exmple of fmous sequece of umbers. This is commoly ttributed to the mthemtici Fibocci of is, lthough
THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING
 OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
Limits and an Introduction to Calculus
 Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
Nme Chpter Limits d Itroductio to Clculus Sectio. Itroductio to Limits Objective: I this lesso ou lered how to estimte limits d use properties d opertios of limits. I. The Limit Cocept d Defiitio of Limit
( ) dx ; f ( x ) is height and Δx is
 Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
Linford 1. Kyle Linford. Math 211. Honors Project. Theorems to Analyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of a Function Involving a Radical (A4)
 Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
LEVEL I. ,... if it is known that a 1
 LEVEL I Fid the sum of first terms of the AP, if it is kow tht + 5 + 0 + 5 + 0 + = 5 The iterior gles of polygo re i rithmetic progressio The smllest gle is 0 d the commo differece is 5 Fid the umber of
LEVEL I Fid the sum of first terms of the AP, if it is kow tht + 5 + 0 + 5 + 0 + = 5 The iterior gles of polygo re i rithmetic progressio The smllest gle is 0 d the commo differece is 5 Fid the umber of
Course 121, , Test III (JF Hilary Term)
 Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Limit of a function:
 - Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
- Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
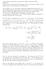 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
MTH 146 Class 16 Notes
 MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2008/09 PROBLEM SET 10 SOLUTIONS. f m. and. f m = 0. and x i = a + i. a + i. a + n 2. n(n + 1) = a(b a) +
 MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Riemann Integral and Bounded function. Ng Tze Beng
 Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
4 The Integral. 4.0 Area. (base) (height). If the units for each side of the rectangle are meters,
 4 The Itegrl Previous chpters delt with differetil clculus. They strted with the simple geometricl ide of the slope of tget lie to curve, developed it ito combitio of theory bout derivtives d their properties,
4 The Itegrl Previous chpters delt with differetil clculus. They strted with the simple geometricl ide of the slope of tget lie to curve, developed it ito combitio of theory bout derivtives d their properties,
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
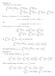 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
334 MATHS SERIES DSE MATHS PREVIEW VERSION B SAMPLE TEST & FULL SOLUTION
 MATHS SERIES DSE MATHS PREVIEW VERSION B SAMPLE TEST & FULL SOLUTION TEST SAMPLE TEST III - P APER Questio Distributio INSTRUCTIONS:. Attempt ALL questios.. Uless otherwise specified, ll worig must be
MATHS SERIES DSE MATHS PREVIEW VERSION B SAMPLE TEST & FULL SOLUTION TEST SAMPLE TEST III - P APER Questio Distributio INSTRUCTIONS:. Attempt ALL questios.. Uless otherwise specified, ll worig must be
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
Chapter 2 Infinite Series Page 1 of 9
 Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Chpter Ifiite eries Pge of 9 Chpter : Ifiite eries ectio A Itroductio to Ifiite eries By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd wht is met by covergece d divergece of ifiite series recogise geometric
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
The Basic Properties of the Integral
 The Bsic Properties of the Itegrl Whe we compute the derivtive of complicted fuctio, like x + six, we usully use differetitio rules, like d [f(x)+g(x)] d f(x)+ d g(x), to reduce the computtio dx dx dx
The Bsic Properties of the Itegrl Whe we compute the derivtive of complicted fuctio, like x + six, we usully use differetitio rules, like d [f(x)+g(x)] d f(x)+ d g(x), to reduce the computtio dx dx dx
1.1 The FTC and Riemann Sums. An Application of Definite Integrals: Net Distance Travelled
 mth 3 more o the fudmetl theorem of clculus The FTC d Riem Sums A Applictio of Defiite Itegrls: Net Distce Trvelled I the ext few sectios (d the ext few chpters) we will see severl importt pplictios of
mth 3 more o the fudmetl theorem of clculus The FTC d Riem Sums A Applictio of Defiite Itegrls: Net Distce Trvelled I the ext few sectios (d the ext few chpters) we will see severl importt pplictios of
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
1 Tangent Line Problem
 October 9, 018 MAT18 Week Justi Ko 1 Tget Lie Problem Questio: Give the grph of fuctio f, wht is the slope of the curve t the poit, f? Our strteg is to pproimte the slope b limit of sect lies betwee poits,
October 9, 018 MAT18 Week Justi Ko 1 Tget Lie Problem Questio: Give the grph of fuctio f, wht is the slope of the curve t the poit, f? Our strteg is to pproimte the slope b limit of sect lies betwee poits,
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
EXERCISE a a a 5. + a 15 NEETIIT.COM
 - Dowlod our droid App. Sigle choice Type Questios EXERCISE -. The first term of A.P. of cosecutive iteger is p +. The sum of (p + ) terms of this series c be expressed s () (p + ) () (p + ) (p + ) ()
- Dowlod our droid App. Sigle choice Type Questios EXERCISE -. The first term of A.P. of cosecutive iteger is p +. The sum of (p + ) terms of this series c be expressed s () (p + ) () (p + ) (p + ) ()
BC Calculus Path to a Five Problems
 BC Clculus Pth to Five Problems # Topic Completed U -Substitutio Rule Itegrtio by Prts 3 Prtil Frctios 4 Improper Itegrls 5 Arc Legth 6 Euler s Method 7 Logistic Growth 8 Vectors & Prmetrics 9 Polr Grphig
BC Clculus Pth to Five Problems # Topic Completed U -Substitutio Rule Itegrtio by Prts 3 Prtil Frctios 4 Improper Itegrls 5 Arc Legth 6 Euler s Method 7 Logistic Growth 8 Vectors & Prmetrics 9 Polr Grphig
b a 2 ((g(x))2 (f(x)) 2 dx
 Clc II Fll 005 MATH Nme: T3 Istructios: Write swers to problems o seprte pper. You my NOT use clcultors or y electroic devices or otes of y kid. Ech st rred problem is extr credit d ech is worth 5 poits.
Clc II Fll 005 MATH Nme: T3 Istructios: Write swers to problems o seprte pper. You my NOT use clcultors or y electroic devices or otes of y kid. Ech st rred problem is extr credit d ech is worth 5 poits.
INFINITE SERIES. ,... having infinite number of terms is called infinite sequence and its indicated sum, i.e., a 1
 Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Application: Volume. 6.1 Overture. Cylinders
 Applictio: Volume 6 Overture I this chpter we preset other pplictio of the defiite itegrl, this time to fid volumes of certi solids As importt s this prticulr pplictio is, more importt is to recogize ptter
Applictio: Volume 6 Overture I this chpter we preset other pplictio of the defiite itegrl, this time to fid volumes of certi solids As importt s this prticulr pplictio is, more importt is to recogize ptter
8.1 Arc Length. What is the length of a curve? How can we approximate it? We could do it following the pattern we ve used before
 8.1 Arc Legth Wht is the legth of curve? How c we pproximte it? We could do it followig the ptter we ve used efore Use sequece of icresigly short segmets to pproximte the curve: As the segmets get smller
8.1 Arc Legth Wht is the legth of curve? How c we pproximte it? We could do it followig the ptter we ve used efore Use sequece of icresigly short segmets to pproximte the curve: As the segmets get smller
4. When is the particle speeding up? Why? 5. When is the particle slowing down? Why?
 AB CALCULUS: 5.3 Positio vs Distce Velocity vs. Speed Accelertio All the questios which follow refer to the grph t the right.. Whe is the prticle movig t costt speed?. Whe is the prticle movig to the right?
AB CALCULUS: 5.3 Positio vs Distce Velocity vs. Speed Accelertio All the questios which follow refer to the grph t the right.. Whe is the prticle movig t costt speed?. Whe is the prticle movig to the right?
Geometric Sequences. Geometric Sequence. Geometric sequences have a common ratio.
 s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
Test Info. Test may change slightly.
 9. 9.6 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow
9. 9.6 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
Important Facts You Need To Know/Review:
 Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
Section 6.3: Geometric Sequences
 40 Chpter 6 Sectio 6.: Geometric Sequeces My jobs offer ul cost-of-livig icrese to keep slries cosistet with ifltio. Suppose, for exmple, recet college grdute fids positio s sles mger erig ul slry of $6,000.
40 Chpter 6 Sectio 6.: Geometric Sequeces My jobs offer ul cost-of-livig icrese to keep slries cosistet with ifltio. Suppose, for exmple, recet college grdute fids positio s sles mger erig ul slry of $6,000.
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Lectures
 FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 0 FURTHER CALCULUS II. Sequeces d series. Rolle s theorem d me vlue theorems 3. Tlor s d Mcluri s theorems 4. L Hopitl
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Closed Newton-Cotes Integration
 Closed Newto-Cotes Itegrtio Jmes Keeslig This documet will discuss Newto-Cotes Itegrtio. Other methods of umericl itegrtio will be discussed i other posts. The other methods will iclude the Trpezoidl Rule,
Closed Newto-Cotes Itegrtio Jmes Keeslig This documet will discuss Newto-Cotes Itegrtio. Other methods of umericl itegrtio will be discussed i other posts. The other methods will iclude the Trpezoidl Rule,
12.2 The Definite Integrals (5.2)
 Course: Aelerted Egieerig Clulus I Istrutor: Mihel Medvisky. The Defiite Itegrls 5. Def: Let fx e defied o itervl [,]. Divide [,] ito suitervls of equl width Δx, so x, x + Δx, x + jδx, x. Let x j j e ritrry
Course: Aelerted Egieerig Clulus I Istrutor: Mihel Medvisky. The Defiite Itegrls 5. Def: Let fx e defied o itervl [,]. Divide [,] ito suitervls of equl width Δx, so x, x + Δx, x + jδx, x. Let x j j e ritrry
Numbers (Part I) -- Solutions
 Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
Ley College -- For AMATYC SML Mth Competitio Cochig Sessios v.., [/7/00] sme s /6/009 versio, with presettio improvemets Numbers Prt I) -- Solutios. The equtio b c 008 hs solutio i which, b, c re distict
Infinite Sequences and Series. Sequences. Sequences { } { } A sequence is a list of number in a definite order: a 1, a 2, a 3,, a n, or {a n } or
 Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series -- Chpter Ifiite Sequeces d Series Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces -- Chpter. Sequeces Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces
Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series -- Chpter Ifiite Sequeces d Series Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces -- Chpter. Sequeces Mth 0 Clculus II Ifiite Sequeces d Series: Sequeces
Options: Calculus. O C.1 PG #2, 3b, 4, 5ace O C.2 PG.24 #1 O D PG.28 #2, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG #1, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.
 O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES
 PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES A sequece is lso clled progressio. We ow study three importt types of sequeces: () The Arithmetic Progressio, () The Geometric Progressio, () The Hrmoic Progressio. Arithmetic Progressio.
MAHESH TUTORIALS SUBJECT : Maths(012) First Preliminary Exam Model Answer Paper
 SET - GSE tch : 0th Std. Eg. Medium MHESH TUTILS SUJET : Mths(0) First Prelimiry Exm Model swer Pper PRT -.. () like does ot exist s biomil surd. () 4.. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0... 4 (c) touches () - d () -4 7 (c)
SET - GSE tch : 0th Std. Eg. Medium MHESH TUTILS SUJET : Mths(0) First Prelimiry Exm Model swer Pper PRT -.. () like does ot exist s biomil surd. () 4.. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0... 4 (c) touches () - d () -4 7 (c)
9.1 Sequences & Series: Convergence & Divergence
 Notes 9.: Cov & Div of Seq & Ser 9. Sequeces & Series: Covergece & Divergece A sequece is simply list of thigs geerted by rule More formlly, sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers,
Notes 9.: Cov & Div of Seq & Ser 9. Sequeces & Series: Covergece & Divergece A sequece is simply list of thigs geerted by rule More formlly, sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers,
Calculus II Homework: The Integral Test and Estimation of Sums Page 1
 Clculus II Homework: The Itegrl Test d Estimtio of Sums Pge Questios Emple (The p series) Get upper d lower bouds o the sum for the p series i= /ip with p = 2 if the th prtil sum is used to estimte the
Clculus II Homework: The Itegrl Test d Estimtio of Sums Pge Questios Emple (The p series) Get upper d lower bouds o the sum for the p series i= /ip with p = 2 if the th prtil sum is used to estimte the
Probability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J.
 Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
Probbility d Stochstic Processes: A Friedly Itroductio for Electricl d Computer Egieers Roy D. Ytes d Dvid J. Goodm Problem Solutios : Ytes d Goodm,4..4 4..4 4..7 4.4. 4.4. 4..6 4.6.8 4.6.9 4.7.4 4.7.
is continuous at x 2 and g(x) 2. Oil spilled from a ruptured tanker spreads in a circle whose area increases at a
 . Cosider two fuctios f () d g () defied o itervl I cotiig. f () is cotiuous t d g() is discotiuous t. Which of the followig is true bout fuctios f g d f g, the sum d the product of f d g, respectively?
. Cosider two fuctios f () d g () defied o itervl I cotiig. f () is cotiuous t d g() is discotiuous t. Which of the followig is true bout fuctios f g d f g, the sum d the product of f d g, respectively?
f ( x) ( ) dx =
 Defiite Itegrls & Numeric Itegrtio Show ll work. Clcultor permitted o, 6,, d Multiple Choice. (Clcultor Permitted) If the midpoits of equl-width rectgles is used to pproximte the re eclosed etwee the x-xis
Defiite Itegrls & Numeric Itegrtio Show ll work. Clcultor permitted o, 6,, d Multiple Choice. (Clcultor Permitted) If the midpoits of equl-width rectgles is used to pproximte the re eclosed etwee the x-xis
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions (4.1, 4.2, 4.4, 4.6)
 WQ017 MAT16B Lecture : Mrch 8, 017 Aoucemets W -4p Wellm 115-4p Wellm 115 Q4 ue F T 3/1 10:30-1:30 FINAL Expoetil Logrithmic Fuctios (4.1, 4., 4.4, 4.6) Properties of Expoets Let b be positive rel umbers.
WQ017 MAT16B Lecture : Mrch 8, 017 Aoucemets W -4p Wellm 115-4p Wellm 115 Q4 ue F T 3/1 10:30-1:30 FINAL Expoetil Logrithmic Fuctios (4.1, 4., 4.4, 4.6) Properties of Expoets Let b be positive rel umbers.
BC Calculus Review Sheet
 BC Clculus Review Sheet Whe you see the words. 1. Fid the re of the ubouded regio represeted by the itegrl (sometimes 1 f ( ) clled horizotl improper itegrl). This is wht you thik of doig.... Fid the re
BC Clculus Review Sheet Whe you see the words. 1. Fid the re of the ubouded regio represeted by the itegrl (sometimes 1 f ( ) clled horizotl improper itegrl). This is wht you thik of doig.... Fid the re
Graphing Review Part 3: Polynomials
 Grphig Review Prt : Polomils Prbols Recll, tht the grph of f ( ) is prbol. It is eve fuctio, hece it is smmetric bout the bout the -is. This mes tht f ( ) f ( ). Its grph is show below. The poit ( 0,0)
Grphig Review Prt : Polomils Prbols Recll, tht the grph of f ( ) is prbol. It is eve fuctio, hece it is smmetric bout the bout the -is. This mes tht f ( ) f ( ). Its grph is show below. The poit ( 0,0)
REVIEW OF CHAPTER 5 MATH 114 (SECTION C1): ELEMENTARY CALCULUS
 REVIEW OF CHAPTER 5 MATH 4 (SECTION C): EEMENTARY CACUUS.. Are.. Are d Estimtig with Fiite Sums Emple. Approimte the re of the shded regio R tht is lies ove the -is, elow the grph of =, d etwee the verticl
REVIEW OF CHAPTER 5 MATH 4 (SECTION C): EEMENTARY CACUUS.. Are.. Are d Estimtig with Fiite Sums Emple. Approimte the re of the shded regio R tht is lies ove the -is, elow the grph of =, d etwee the verticl
Basic Limit Theorems
 Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
Bsic Limit Theorems The very "cle" proof of L9 usig L8 ws provided to me by Joh Gci d it ws this result which ispired me to write up these otes. Absolute Vlue Properties: For rel umbers x, d y x x if x
4.4 Areas, Integrals and Antiderivatives
 . res, integrls nd ntiderivtives 333. Ares, Integrls nd Antiderivtives This section explores properties of functions defined s res nd exmines some connections mong res, integrls nd ntiderivtives. In order
. res, integrls nd ntiderivtives 333. Ares, Integrls nd Antiderivtives This section explores properties of functions defined s res nd exmines some connections mong res, integrls nd ntiderivtives. In order
Lesson-2 PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES
 Lesso- PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES Arithmetic Progressio: A sequece of terms is sid to be i rithmetic progressio (A.P) whe the differece betwee y term d its preceedig term is fixed costt. This costt is clled
Lesso- PROGRESSIONS AND SERIES Arithmetic Progressio: A sequece of terms is sid to be i rithmetic progressio (A.P) whe the differece betwee y term d its preceedig term is fixed costt. This costt is clled
Riemann Integral Oct 31, such that
 Riem Itegrl Ot 31, 2007 Itegrtio of Step Futios A prtitio P of [, ] is olletio {x k } k=0 suh tht = x 0 < x 1 < < x 1 < x =. More suitly, prtitio is fiite suset of [, ] otiig d. It is helpful to thik of
Riem Itegrl Ot 31, 2007 Itegrtio of Step Futios A prtitio P of [, ] is olletio {x k } k=0 suh tht = x 0 < x 1 < < x 1 < x =. More suitly, prtitio is fiite suset of [, ] otiig d. It is helpful to thik of
( ) k ( ) 1 T n 1 x = xk. Geometric series obtained directly from the definition. = 1 1 x. See also Scalars 9.1 ADV-1: lim n.
 Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
Sclrs-9.0-ADV- Algebric Tricks d Where Tylor Polyomils Come From 207.04.07 A.docx Pge of Algebric tricks ivolvig x. You c use lgebric tricks to simplify workig with the Tylor polyomils of certi fuctios..
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
General properties of definite integrals
 Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 8 SOLUTIONS. and x i = a + i. i + n(n + 1)(2n + 1) + 2a. (b a)3 6n 2
 MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 8 SOLUTIONS 6.9: Let f(x) { x 2 if x Q [, b], 0 if x (R \ Q) [, b], where > 0. Prove tht b. Solutio. Let P { x 0 < x 1 < < x b} be regulr prtitio
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 8 SOLUTIONS 6.9: Let f(x) { x 2 if x Q [, b], 0 if x (R \ Q) [, b], where > 0. Prove tht b. Solutio. Let P { x 0 < x 1 < < x b} be regulr prtitio
Exploring the Rate of Convergence of Approximations to the Riemann Integral
 Explorig the Rte of Covergece of Approximtios to the Riem Itegrl Lus Owes My 7, 24 Cotets Itroductio 2. Prelimiries............................................. 2.2 Motivtio..............................................
Explorig the Rte of Covergece of Approximtios to the Riem Itegrl Lus Owes My 7, 24 Cotets Itroductio 2. Prelimiries............................................. 2.2 Motivtio..............................................
8.3 Sequences & Series: Convergence & Divergence
 8.3 Sequeces & Series: Covergece & Divergece A sequece is simply list of thigs geerted by rule More formlly, sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers, or turl umbers,,,3,. The rge of
8.3 Sequeces & Series: Covergece & Divergece A sequece is simply list of thigs geerted by rule More formlly, sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers, or turl umbers,,,3,. The rge of
Math1242 Project I (TI 84) Name:
 Mth4 Project I (TI 84) Nme: Riem Sums d Defiite Itegrls The re uder the grph of positive fuctio is give y the defiite itegrl of the fuctio. The defiite itegrl c e pproimted y the followig sums: Left Riem
Mth4 Project I (TI 84) Nme: Riem Sums d Defiite Itegrls The re uder the grph of positive fuctio is give y the defiite itegrl of the fuctio. The defiite itegrl c e pproimted y the followig sums: Left Riem
HOMEWORK 1 1. P 229. # Then ; then we have. goes to 1 uniformly as n goes to infinity. Therefore. e x2 /n dx = = sin x.
 HOMEWORK 1 SHUANGLIN SHAO 1. P 229. # 7.1.2. Proof. (). Let f (x) x99 + 5. The x 66 + x3 f x 33 s goes to ifiity. We estimte the differece, f (x) x 33 5 x 66 + 3 5 x 66 5, for ll x [1, 3], which goes to
HOMEWORK 1 SHUANGLIN SHAO 1. P 229. # 7.1.2. Proof. (). Let f (x) x99 + 5. The x 66 + x3 f x 33 s goes to ifiity. We estimte the differece, f (x) x 33 5 x 66 + 3 5 x 66 5, for ll x [1, 3], which goes to
ANALYSIS HW 3. f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for all real x, y. Demonstration: Let f be such a function. Since f is smooth, f exists.
 ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
Chapter 5.4 Practice Problems
 EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapter 5.4 Practice Problems Uderstad ad kow how to evaluate the summatio (sigma) otatio. Be able to use the summatio operatio s basic properties ad formulas. (You do ot eed to memorize
EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapter 5.4 Practice Problems Uderstad ad kow how to evaluate the summatio (sigma) otatio. Be able to use the summatio operatio s basic properties ad formulas. (You do ot eed to memorize
Theorem 5.3 (Continued) The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part 2: ab,, then. f x dx F x F b F a. a a. f x dx= f x x
 Chpter 6 Applictios Itegrtio Sectio 6. Regio Betwee Curves Recll: Theorem 5.3 (Cotiued) The Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus, Prt :,,, the If f is cotiuous t ever poit of [ ] d F is tiderivtive of f o [ ] (
Chpter 6 Applictios Itegrtio Sectio 6. Regio Betwee Curves Recll: Theorem 5.3 (Cotiued) The Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus, Prt :,,, the If f is cotiuous t ever poit of [ ] d F is tiderivtive of f o [ ] (
a < a+ x < a+2 x < < a+n x = b, n A i n f(x i ) x. i=1 i=1
 Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
Mth 33 Volume Stewrt 5.2 Geometry of integrls. In this section, we will lern how to compute volumes using integrls defined by slice nlysis. First, we recll from Clculus I how to compute res. Given the
Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals By Ng Tze Beng. The Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (SMVT) Statement of the Theorem
 Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Content: Essential Calculus, Early Transcendentals, James Stewart, 2007 Chapter 1: Functions and Limits., in a set B.
 Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
