Structural Signatures of Mobility in Jammed and Glassy Systems
|
|
|
- Gabriella Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lisa Manning Sam Schoenholz Ekin Dogus Cubuk Brad Malone Tim Kaxiras Joerg Rottler Rob Riggleman Jennifer Rieser Doug Durian Daniel Sussman Carl Goodrich Sid Nagel Structural Signatures of Mobility in Jammed and Glassy Systems Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Syracuse UPenn Harvard Harvard Harvard U British Columbia UPenn UPenn UPenn UPenn UPenn UChicago
2 Free Surfaces T g ( C) thin glassy polymer films experiments see thin mobile layer of about 5-10 particle diameters no structural quantity has been identified with gradients on this length scale h (nm) Courtesy of O. Baumchen et al. PRL (2012)
3 Localized Rearrangements in Disordered Solids 2D binary Lennard-Jones shaving cream Courtesy of DJ Durian sheared glass Aim: identify population of flow defects, analogous to dislocations in crystals, where rearrangements are likely to occur Standard structural quantities fail to predict these supercooled liquid Keys, et al PRX (2011)
4 Starting Point: Vibrations in Sphere Packings ω * /ω 0 Δφ D(ω) 1/2 ω * ω 0 k eff m New class of excitations originates from soft modes at Point J L. E. Silbert, A. J. Liu, S. R. Nagel, PRL 95, ( 05) M. Wyart, S.R. Nagel, T.A. Witten, EPL 72, 486 (05) Related to diverging length scales ll cl/ω* lt ct/ω * α 2 Δφ ( )/2
5 Starting Point: Vibrations in Sphere Packings p=0.01 ω * /ω 0 Δφ 1/2 ω * ω* ω 0 k eff m New class of excitations originates from soft modes at Point J L. E. Silbert, A. J. Liu, S. R. Nagel, PRL 95, ( 05) M. Wyart, S.R. Nagel, T.A. Witten, EPL 72, 486 (05) Related to diverging length scales ll cl/ω* lt ct/ω * α 2 Δφ ( )/2
6 M. Wyart, S.R. Nagel, T.A. Witten, EPL 72, 486 (05) Stability to Boundary Cutting: ll Size of smallest macroscopic rigid cluster for system with a free boundary of any shape or size ll diverges at Point J as expected from scaling argument Goodrich, Ellenbroek, Liu Soft Matter (2013)
7 M. Wyart, S.R. Nagel, T.A. Witten, EPL 72, 486 (05) Stability to Boundary Cutting: ll Size of smallest macroscopic rigid cluster for system with a free boundary of any shape or size ll diverges at Point J as expected from scaling argument Goodrich, Ellenbroek, Liu Soft Matter (2013)
8 Free Surfaces Goodrich, Liu, Nagel, Soft Matter (2013) DHwL L l* cut system bulk system w Daniel Sussman, Carl Goodrich There are zero frequency modes localized to the surface to within particle diameter There are also extra low frequency modes in excess of surface plane wave modes (Rayleigh waves, etc)
9 Free Surfaces Goodrich, Liu, Nagel, Soft Matter (2013) L> l* bulk system cut system Daniel Sussman, Carl Goodrich There are zero frequency modes localized to the surface to within particle diameter There are also extra low frequency modes in excess of surface plane wave modes (Rayleigh waves, etc)
10 Low-Frequency Surface Modes are Localized to Surface Measure polarization vector magnitude vs distance from surface
11 Penetration Depth of Surface Localized Modes e i I II x III Three regimes for decay of polarization vector magnitude Regime I consistent with exponential decay Regime III independent of pressure Extract crossover lengths separating Regimes I & II and II&III
12 Penetration Depth of Surface Localized Modes L p ll lt p Regime I/II crossover scales as lt which diverges at jamming transition as p -1/4 Regime II/III crossover scales as ll which diverges at jamming transition as p -1/2 Consistent with response to local bond perturbations (Lerner, During, Wyart, Soft Matter (2014)) Low frequency surface modes penetrate into system much further than particle diameter. Can this explain glassy thin films?
13 Problem: thin film L> l* bulk bulk system cut system In polymer thin films (or Lennard-Jones glasses), the surface localized modes lie in the same frequency range as the bulk modes so no clean separation of surface from bulk modes But low frequency modes still show high polarization near surface
14 Problem: thin film bulk Jain and de Pablo, J Chem Phys (2004) In polymer thin films (or Lennard-Jones glasses), the surface localized modes lie in the same frequency range as the bulk modes so no clean separation of surface from bulk modes But low frequency modes still show high polarization near surface
15 P(p) Focus on low-participation-ratio modes near ω* cut system uncut system p p c =0.05 p c =0.075 p c =0.1 p c =0.125 p c = Cut system has more low participation-ratio modes than uncut system Low participation ratio modes most prevalent near ω* So look at these modes fraction of modes
16 Polarization Profile in Lennard-Jones Glass e i x/ Regime III has same form as for harmonically-repulsive spheres Regime I/II crossover consistent with lt ct/ω * Regime II/III crossover consistent with ll cl/ω * Polarization vector magnitude decays on scale of 5-10 particle diameters Consistent with observed thickness of mobile layer in thin glassy films High amplitude regions of low-frequency quasi localized modes are structural signature of mobile surface layer D. Sussman, C. P. Goodrich, A. J. Liu, S. R. Nagel
17 Localized Rearrangements in Glasses and Supercooled Liquids 2D binary Lennard-Jones shaving cream Courtesy of DJ Durian sheared glass Aim: identify population of flow defects, analogous to dislocations in crystals, where rearrangements are likely to occur Standard structural quantities fail to predict these supercooled liquid Keys, et al PRX (2011)
18 How Crystals Flow In crystalline packings, localized rearrangements occur at dislocations Courtesy of F Abraham
19 How Crystals Flow In crystalline packings, localized rearrangements occur at dislocations Courtesy of F Abraham
20 How Crystals Pre-Melt Alsayed et al. Science (2005). Premelting also occurs at dislocations and grain boundaries Dislocations vulnerable to rearrangement under mechanical load or temperature
21 Look at Quasilocalized Modes in Crystals Quasilocalized modes localize to flow defects (dislocations and grain boundaries but not vacancies) because these scatter sound most effectively look at quasi localized modes in disordered systems [110] Rottler, Schoenholz, Liu PRE (2014) Chen, Still, Schoenholz, Aptowicz, Schindler, Maggs, Liu, Yodh, PRE 88, (2013)
22 Look at Quasilocalized Modes in Crystals Quasilocalized modes localize to flow defects (dislocations and grain boundaries but not vacancies) because these scatter sound most effectively look at quasi localized modes in disordered systems [110] Rottler, Schoenholz, Liu PRE (2014) Chen, Still, Schoenholz, Aptowicz, Schindler, Maggs, Liu, Yodh, PRE 88, (2013)
23 Anharmonicity Low-frequency quasi-localized modes have the lowest energy barriers to rearrangement Barriers are likely to be lower if rearrangements are localized These are the modes most likely to go unstable due to thermal fluctuations or mechanical load So QLM likely to contain information about flow defects N. Xu, Vi Vitelli, A. J. Liu, S. R. Nagel, EPL 90, (2010). p(ω) Vmax(ω) ω Carl P. Goodrich
24 QLM Method of Identifying Flow Defects M. L. Manning, A. J. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, (2011)
25 QLM Method of Identifying Flow Defects M. L. Manning, A. J. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, (2011)
26 QLM Soft Spots Are Promising, But To identify soft spots, need to know interactions between particles precisely quench system to obtain inherent structures diagonalize dynamical matrix (O(N 3 )) So this method cannot be applied to experimental data and is very slow even for simulation data We want a method for identifying regions vulnerable to rearrangement that relies on local structure alone Problem: all previous attempts have failed
27 Standard Structural Quantities Don t Tell Us Where Soft Spots Are Coordination number M. L. Manning, A. J. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, (2011)
28 Standard Structural Quantities Don t Tell Us Where Soft Spots Are Deviation Coordination BOO from number hexagonal M. L. Manning, A. J. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, (2011)
29 Standard Structural Quantities Don t Tell Us Where Soft Spots Are Deviation Coordination Local shear BOO from modulus number hexagonal M. L. Manning, A. J. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, (2011)
30 Standard Structural Quantities Don t Tell Us Where Soft Spots Are Deviation Log( Coordination Local strain) shear BOO from modulus is number hexagonal M. L. Manning, A. J. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, (2011)
31 Solution Don t just use one quantity to characterize structure Use MANY Introduce two families of functions Sam Schoenholz and Dogus Cubuk
32 Solution Don t just use one quantity to characterize structure Use MANY Introduce two families of functions Sam Schoenholz and Dogus Cubuk
33 Solution Don t just use one quantity to characterize structure Use MANY Introduce two families of functions Sam Schoenholz and Dogus Cubuk
34 Solution Don t just use one quantity to characterize structure Use MANY Introduce two families of functions Sam Schoenholz and Dogus Cubuk
35 Solution Don t just use one quantity to characterize structure Use MANY Introduce two families of functions Sam Schoenholz and Dogus Cubuk
36 Physical Meaning of Structure Functions First family measures density at radius r Radius to probe Particle separation Width of window Second family measures bond anticorrelation at radius r Radius Angular Resolution Alignment/antialignment
37 Classify softness Have a set of structural variables for each particle i (values of S and Q at different values of μ, ξ, λ, ζ Want to categorize each particle as soft (susceptible to rearrangement) or hard Use Support Vector Machines (SVM) Requires a training set with known classification
38 Classifying softness Use D 2 min to find rearrangements D 2 X min(i, t) = j Particle is soft if Dmin 2 >Dmin,0 2 Embed in space where each dimension is a structural variable Find dividing plane with maximum margin h Classify new data with dividing plane [R ij (t + t) min R ij (t)] 2 Soft 2 AA S(μ2) Not Soft h 1 h 2 S(μ1)
39 Classifying softness Use D 2 min to find rearrangements D 2 X min(i, t) = j Particle is soft if Dmin 2 >Dmin,0 2 Embed in space where each dimension is a structural variable Find dividing plane with maximum margin h Classify new data with dividing plane [R ij (t + t) min R ij (t)] 2 Soft 2 AA S(μ2) Not Soft h 1 S(μ1)
40 Classifying softness Use D 2 min to find rearrangements D 2 X min(i, t) = j Particle is soft if Dmin 2 >Dmin,0 2 Embed in space where each dimension is a structural variable Find dividing plane with maximum margin h Classify new data with dividing plane [R ij (t + t) min R ij (t)] 2 Soft 2 AA S(μ2) Not Soft h 1 S(μ1)
41 SVM Method Works better than QLM method Don t need to quench system to obtain inherent structures in fact, method works better because it can be applied to instantaneous snapshots diagonalize dynamical matrix (O(N 3 )) method is O(N) know interactions between particles precisely Apply to experimental system
42 Compressed Granular Pillars Jennifer Rieser, Doug Durian
43
44
45
46
47 PHIn Soft SpotL Compressed Granular Pillars 21% of system captures 80% of rearranging particles D min ês AA
48 Pillar Has Free Surfaces Are There More Soft Particles There? Yes, number of soft particles is higher at surface Soft particles enhanced over range of ~ 5 particle diameters Granular pillars have mobile layer similar to that of glassy films
49 Tests of SVM method (1) Sheared, thermal 2D Lennard-Jones glass 65:35 Kob-Andersen Lennard-Jones mixture apple U(r) =4 r 12 AA = 1.0, AB = 0.88, BB = 0.8, AA = 1.0, AB = 1.5, BB = 0.5. Characterized by Brüning et al. with Tg=0.33 p r 6 T =0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 = 10 4
50 Softness Field
51
52
53 D 2 min,0 Sheared 2D Lennard-Jones glass D 2 min, (a) T=0.1 (b) T= T 0.1 Dmin 2 /( AA 2 ) Dmin 2 /(T AA 2 ) 26% of system captures 73% of rearranging particles Works equally well at all temperatures, even above glass transition Accuracy insensitive to threshold P
54 D 2 min,0 Sheared 2D Lennard-Jones glass D 2 min, (a) T=0.1 (b) T= T 0.1 Dmin 2 /( AA 2 ) Dmin 2 /(T AA 2 ) 26% of system captures 73% of rearranging particles Works equally well at all temperatures, even above glass transition Accuracy insensitive to threshold P
55 D 2 min,0 Sheared 2D Lennard-Jones glass D 2 min, (a) T=0.1 (b) T= T 0.1 Dmin 2 /( AA 2 ) Dmin 2 /(T AA 2 ) 26% of system captures 73% of rearranging particles Works equally well at all temperatures, even above glass transition Accuracy insensitive to threshold P
56 Particle Displacements correlate with softness gradient Rearranging particles tend to move in direction of increasing softness Promising as structural signature of facilitation Keys, et al PRX (2011)
57 Tests of SVM method (2) Quiescent, thermal 3D Lennard-Jones glass 65:35 Kob-Andersen Lennard-Jones mixture apple U(r) =4 r 12 AA = 1.0, AB = 0.88, BB = 0.8, AA = 1.0, AB = 1.5, BB = 0.5. Characterized by Brüning et al. with Tg=0.58 p r T =0.4, 0.5, 0.6 6
58 Rearrangements are localized
59 Softness Field
60 Rearranging Particles are Soft T=0.4 T=0.6 Works well even at high temperatures (Tg=0.58) At T=0.6, 24% of particles capture 72% of rearrangements (kinetic heterogeneities) average softness is high for rearranging particles Accuracy comparable in 2D and 3D T=0.4 T=0.6
61 Softness Lifetime I intermediate scattering function T=0.4 Softness autocorrelation function T=0.6 Softness lifetime is comparable to relaxation time
62 Softness Lifetime II T=0.6 Softness equilibrates over time to approach equilibrium softness distribution
63 Softness Lifetime III T=0.6 soft particles hard particles Softness autocorrelation function Soft particles equilibrate faster than hard particles Softness is promising as structural signature of kinetic heterogeneities
64 Recall structural variables Dividing Surface Contains Physics S measures radial density Q measures relative bond orientation Note g XY (r) = lim SY X (i; r)/2 r so S corresponds to local g(r) N L0 1 NX i=1
65 Soft particles (red) are more liquidlike than system as whole S distinguishes between soft particles and H1 particles but not soft and H0 How are Soft Particles Different? Q distinguishes between soft and H0 but not soft and H1 Need both S and Q (at least) H0 H1 H1 H0
66 Conclusions Quasilocalized modes yields structural signatures of mobility near free surfaces and at flow defects Soft particles are structurally distinct, but in subtle ways that we can pick out using machine learning methods SVM method Promising for identifying particles likely to rearrange under temperature or stress Fast, and only requires positions of particles, not interactions Works on experimental as well as simulation data
67 QLM: Thanks to Lisa Manning Daniel Sussman DOE Carl Goodrich Sid Nagel
68 SVM: Thanks to Sam Schoenholz Brad Malone Dogus Cubuk Tim Kaxiras UPenn MRSEC Jennifer Rieser Joerg Rottler Doug Durian
Efficient determination of soft spots in amorphous solids only using local structural information
 Efficient determination of soft spots in amorphous solids only using local structural information Ekin Dogus Cubuk Samuel Schoenholz, Jennifer Rieser, Brad Malone, Joerg Rottler, Doug Durian, Andrea J
Efficient determination of soft spots in amorphous solids only using local structural information Ekin Dogus Cubuk Samuel Schoenholz, Jennifer Rieser, Brad Malone, Joerg Rottler, Doug Durian, Andrea J
Jamming and the Anticrystal
 Jamming and the Anticrystal Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Carl Goodrich Corey S. O Hern Leo E. Silbert Vincenzo Vitelli Ning Xu Sidney Nagel UPenn Yale SIUC
Jamming and the Anticrystal Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Carl Goodrich Corey S. O Hern Leo E. Silbert Vincenzo Vitelli Ning Xu Sidney Nagel UPenn Yale SIUC
Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 12, 2014
 Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 1, 014 What is role of (dis)order for mechanical behavior? Andrea J. Liu Carl Goodrich Justin
Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 1, 014 What is role of (dis)order for mechanical behavior? Andrea J. Liu Carl Goodrich Justin
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids
 Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming
 Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Indiana University, January T. Witten, University of Chicago
 Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids
 Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids Atsushi Ikeda Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University Atsushi Ikeda & Ludovic Berthier Phys. Rev. E 92,
Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids Atsushi Ikeda Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University Atsushi Ikeda & Ludovic Berthier Phys. Rev. E 92,
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
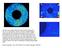 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature. Nikolai V. Priezjev
 The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
Fluctuations in the aging dynamics of structural glasses
 Fluctuations in the aging dynamics of structural glasses Horacio E. Castillo Collaborator: Azita Parsaeian Collaborators in earlier work: Claudio Chamon Leticia F. Cugliandolo José L. Iguain Malcolm P.
Fluctuations in the aging dynamics of structural glasses Horacio E. Castillo Collaborator: Azita Parsaeian Collaborators in earlier work: Claudio Chamon Leticia F. Cugliandolo José L. Iguain Malcolm P.
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming
 Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
Normal modes in model jammed systems in three dimensions
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 79, 238 29 Normal modes in model jammed systems in three dimensions Leonardo E. Silbert, Andrea J. Liu, 2 and Sidney R. Nagel 3 Department of Physics, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 79, 238 29 Normal modes in model jammed systems in three dimensions Leonardo E. Silbert, Andrea J. Liu, 2 and Sidney R. Nagel 3 Department of Physics, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale,
Xiaoming Mao. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania. Collaborators: Tom Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu
 Xiaoing Mao Departent of Physics and Astronoy, University of Pennsylvania Collaborators: To Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu Feb., 009 What is isostaticity? Isostatic systes are at the onset
Xiaoing Mao Departent of Physics and Astronoy, University of Pennsylvania Collaborators: To Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu Feb., 009 What is isostaticity? Isostatic systes are at the onset
Dynamics of Supercooled Liquids The Generic Phase Diagram for Glasses
 Dynamics of Supercooled Liquids The Generic Phase Diagram for Glasses A normal liquid will crystallize at a melting temperature T m as it is cooled via a first-order phase transition (see figure above).
Dynamics of Supercooled Liquids The Generic Phase Diagram for Glasses A normal liquid will crystallize at a melting temperature T m as it is cooled via a first-order phase transition (see figure above).
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016](/thumbs/95/123667841.jpg) Anomalous Stress Fluctuations in Two Dimensional Isotropic Packings of Frictionless Disks Above the Jamming Transition arxiv:1609.09265v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016 Yegang Wu, 1 Kamran Karimi, 2 Craig
Anomalous Stress Fluctuations in Two Dimensional Isotropic Packings of Frictionless Disks Above the Jamming Transition arxiv:1609.09265v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016 Yegang Wu, 1 Kamran Karimi, 2 Craig
Granular materials (Assemblies of particles with dissipation )
 Granular materials (Assemblies of particles with dissipation ) Saturn ring Sand mustard seed Ginkaku-ji temple Sheared granular materials packing fraction : Φ Inhomogeneous flow Gas (Φ = 012) Homogeneous
Granular materials (Assemblies of particles with dissipation ) Saturn ring Sand mustard seed Ginkaku-ji temple Sheared granular materials packing fraction : Φ Inhomogeneous flow Gas (Φ = 012) Homogeneous
Flow of Glasses. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Flow of Glasses Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 sec Time scale Liquid!
Flow of Glasses Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 sec Time scale Liquid!
Microscopic Picture of Aging in SiO 2 : A Computer Simulation
 Microscopic Picture of Aging in SiO 2 : A Computer Simulation Katharina Vollmayr-Lee, Robin Bjorkquist, Landon M. Chambers Bucknell University & Göttingen 7 td tb r n (t) 6 R 5 4 3 2 ti t [ns] waiting
Microscopic Picture of Aging in SiO 2 : A Computer Simulation Katharina Vollmayr-Lee, Robin Bjorkquist, Landon M. Chambers Bucknell University & Göttingen 7 td tb r n (t) 6 R 5 4 3 2 ti t [ns] waiting
Pre-yield non-affine fluctuations and a hidden critical point in strained crystals
 Supplementary Information for: Pre-yield non-affine fluctuations and a hidden critical point in strained crystals Tamoghna Das, a,b Saswati Ganguly, b Surajit Sengupta c and Madan Rao d a Collective Interactions
Supplementary Information for: Pre-yield non-affine fluctuations and a hidden critical point in strained crystals Tamoghna Das, a,b Saswati Ganguly, b Surajit Sengupta c and Madan Rao d a Collective Interactions
Length Scales Related to Alpha and Beta Relaxation in Glass Forming Liquids
 Length Scales Related to Alpha and Beta Relaxation in Glass Forming Liquids Chandan Dasgupta Centre for Condensed Matter Theory Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science With Smarajit Karmakar
Length Scales Related to Alpha and Beta Relaxation in Glass Forming Liquids Chandan Dasgupta Centre for Condensed Matter Theory Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science With Smarajit Karmakar
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
Workshop on Sphere Packing and Amorphous Materials July 2011
 2254-16 Workshop on Sphere Packing and Amorphous Materials 25-29 July 2011 Random Spring Networks vs. Soft Sphere Packings: Jamming Meets Percolation Wouter G. ELLENBROEK Eindhoven Technical University,
2254-16 Workshop on Sphere Packing and Amorphous Materials 25-29 July 2011 Random Spring Networks vs. Soft Sphere Packings: Jamming Meets Percolation Wouter G. ELLENBROEK Eindhoven Technical University,
Phys 563 Phase Transition and Renormalization groups Term paper 2010
 Phys 563 Phase Transition and Renormalization groups Term paper 2010 Instructor: Prof. Nigel Goldenfeld Title: Understanding glass-forming and jamming materials in the context of soft colloids Jian Yang
Phys 563 Phase Transition and Renormalization groups Term paper 2010 Instructor: Prof. Nigel Goldenfeld Title: Understanding glass-forming and jamming materials in the context of soft colloids Jian Yang
T. Egami. Model System of Dense Random Packing (DRP)
 Introduction to Metallic Glasses: How they are different/similar to other glasses T. Egami Model System of Dense Random Packing (DRP) Hard Sphere vs. Soft Sphere Glass transition Universal behavior History:
Introduction to Metallic Glasses: How they are different/similar to other glasses T. Egami Model System of Dense Random Packing (DRP) Hard Sphere vs. Soft Sphere Glass transition Universal behavior History:
Influence of strain on transport in dense Lennard-Jones systems
 Influence of strain on transport in dense Lennard-Jones systems Janka Petravic Citation: The Journal of Chemical Physics 120, 7041 (2004); doi: 10.1063/1.1683073 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1683073
Influence of strain on transport in dense Lennard-Jones systems Janka Petravic Citation: The Journal of Chemical Physics 120, 7041 (2004); doi: 10.1063/1.1683073 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1683073
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10
Experimental Colloids I (and I)
 Experimental Colloids I (and I) Dave Weitz Harvard http://www.seas.harvard.edu/projects/weitzlab Boulder Summer School 7/24/17 Experimental Colloids I (and I) Dave Weitz Harvard http://www.seas.harvard.edu/projects/weitzlab
Experimental Colloids I (and I) Dave Weitz Harvard http://www.seas.harvard.edu/projects/weitzlab Boulder Summer School 7/24/17 Experimental Colloids I (and I) Dave Weitz Harvard http://www.seas.harvard.edu/projects/weitzlab
How Different is the Dynamics of a Lennard-Jones Binary Fluid from One-Component Lennard-Jones Fluid? 1
 How Different is the Dynamics of a Lennard-Jones Binary Fluid from One-Component Lennard-Jones Fluid? Takayuki NARUMI and Michio TOKUYAMA Summary We investigate the dynamics of liquids and supercooled
How Different is the Dynamics of a Lennard-Jones Binary Fluid from One-Component Lennard-Jones Fluid? Takayuki NARUMI and Michio TOKUYAMA Summary We investigate the dynamics of liquids and supercooled
Long-range correlations in glasses and glassy fluids, and their connection to glasses elasticity
 Long-range correlations in glasses and glassy fluids, and their connection to glasses elasticity Grzegorz Szamel Department of Chemistry Colorado State University Ft. Collins, CO 80523, USA Workshop on
Long-range correlations in glasses and glassy fluids, and their connection to glasses elasticity Grzegorz Szamel Department of Chemistry Colorado State University Ft. Collins, CO 80523, USA Workshop on
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011](/thumbs/91/104659018.jpg) arxiv:1006.2365v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011 The jamming scenario an introduction and outlook Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA
arxiv:1006.2365v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011 The jamming scenario an introduction and outlook Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA
Structural signatures of the unjamming transition at zero temperature
 Structural signatures of the unjamming transition at zero temperature Leonardo E. Silbert, 1 Andrea J. Liu, 2 and Sidney R. Nagel 1 1 James Franck Institute, University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois 60637,
Structural signatures of the unjamming transition at zero temperature Leonardo E. Silbert, 1 Andrea J. Liu, 2 and Sidney R. Nagel 1 1 James Franck Institute, University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois 60637,
Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials
 Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials Anaël Lemaître 1 and Craig Maloney 2 1 Institut Navier France 2 Department of Physics UC Santa Barbara Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 016001 (2004) Phys.
Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials Anaël Lemaître 1 and Craig Maloney 2 1 Institut Navier France 2 Department of Physics UC Santa Barbara Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 016001 (2004) Phys.
Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis
 Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis Elastic Networks A family of discrete model networks involving masses connected by springs 1 2 kk( ll)2 Disordered
Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis Elastic Networks A family of discrete model networks involving masses connected by springs 1 2 kk( ll)2 Disordered
The Large Amplitude Oscillatory Strain Response of Aqueous Foam: Strain Localization and Full Stress Fourier Spectrum
 The Large Amplitude Oscillatory Strain Response of Aqueous Foam: Strain Localization and Full Stress Fourier Spectrum By F. Rouyer, S. Cohen-Addad, R. Höhler, P. Sollich, and S.M. Fielding The European
The Large Amplitude Oscillatory Strain Response of Aqueous Foam: Strain Localization and Full Stress Fourier Spectrum By F. Rouyer, S. Cohen-Addad, R. Höhler, P. Sollich, and S.M. Fielding The European
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials
 Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials MARTIN T. DOVE Department ofearth Sciences University of Cambridge OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Observations 1 1.1.1 Microscopic
Structure and Dynamics : An Atomic View of Materials MARTIN T. DOVE Department ofearth Sciences University of Cambridge OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Observations 1 1.1.1 Microscopic
Physics of disordered materials. Gunnar A. Niklasson Solid State Physics Department of Engineering Sciences Uppsala University
 Physics of disordered materials Gunnar A. Niklasson Solid State Physics Department of Engineering Sciences Uppsala University Course plan Familiarity with the basic description of disordered structures
Physics of disordered materials Gunnar A. Niklasson Solid State Physics Department of Engineering Sciences Uppsala University Course plan Familiarity with the basic description of disordered structures
Glass Formation and Thermodynamics of Supercooled Monatomic Liquids
 pubs.acs.org/jpcb Glass Formation and Thermodynamics of Supercooled Monatomic Liquids Vo Van Hoang* Department of Physics, Institute of Technology, National University of HochiMinh City, 268 Ly Thuong
pubs.acs.org/jpcb Glass Formation and Thermodynamics of Supercooled Monatomic Liquids Vo Van Hoang* Department of Physics, Institute of Technology, National University of HochiMinh City, 268 Ly Thuong
Absorbing phase transition on particle trajectories in oscillatory sheared systems near jamming
 Absorbing phase transition on particle trajectories in oscillatory sheared systems near jamming Department of Physics, Nagoya University Takeshi Kawasaki T. Kawasaki and L. Berthier, Phys. Rev. E 94, 022615
Absorbing phase transition on particle trajectories in oscillatory sheared systems near jamming Department of Physics, Nagoya University Takeshi Kawasaki T. Kawasaki and L. Berthier, Phys. Rev. E 94, 022615
Anomalous structural evolution of soft particles: equibrium liquid state theory
 PAPER www.rsc.org/softmatter Soft Matter Anomalous structural evolution of soft particles: equibrium liquid state theory Hugo Jacquin a and Ludovic Berthier* b Received 15th December 2009, Accepted 11th
PAPER www.rsc.org/softmatter Soft Matter Anomalous structural evolution of soft particles: equibrium liquid state theory Hugo Jacquin a and Ludovic Berthier* b Received 15th December 2009, Accepted 11th
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM. Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics. July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter. 1.
 THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano
 cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano (Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo) amorphous particulate systems: structure? 2D granular matter close to jamming spontaneous
cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano (Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo) amorphous particulate systems: structure? 2D granular matter close to jamming spontaneous
Accuracy and transferability of GAP models for tungsten
 Accuracy and transferability of GAP models for tungsten Wojciech J. Szlachta Albert P. Bartók Gábor Csányi Engineering Laboratory University of Cambridge 5 November 214 Motivation Number of atoms 1 1 2
Accuracy and transferability of GAP models for tungsten Wojciech J. Szlachta Albert P. Bartók Gábor Csányi Engineering Laboratory University of Cambridge 5 November 214 Motivation Number of atoms 1 1 2
STRONG CONFIGURATIONAL DEPENDENCE OF ELASTIC PROPERTIES OF A CU-ZR BINARY MODEL METALLIC GLASS
 Chapter 3 STRONG CONFIGURATIONAL DEPENDENCE OF ELASTIC PROPERTIES OF A CU-ZR BINARY MODEL METALLIC GLASS We report the strong dependence of elastic properties on configurational changes in a Cu-Zr binary
Chapter 3 STRONG CONFIGURATIONAL DEPENDENCE OF ELASTIC PROPERTIES OF A CU-ZR BINARY MODEL METALLIC GLASS We report the strong dependence of elastic properties on configurational changes in a Cu-Zr binary
Correlation between local structure and dynamic heterogeneity in a metallic glass-forming liquid
 Correlation between local structure and dynamic heterogeneity in a metallic glass-forming liquid S. P. Pan a,b,*, S. D. Feng c, J. W. Qiao a,b, W. M. Wang d, and J. Y. Qin d a College of Materials Science
Correlation between local structure and dynamic heterogeneity in a metallic glass-forming liquid S. P. Pan a,b,*, S. D. Feng c, J. W. Qiao a,b, W. M. Wang d, and J. Y. Qin d a College of Materials Science
New from Ulf in Berzerkeley
 New from Ulf in Berzerkeley from crystallization to statistics of density fluctuations Ulf Rørbæk Pedersen Department of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeley, USA Roskilde, December 16th, 21 Ulf
New from Ulf in Berzerkeley from crystallization to statistics of density fluctuations Ulf Rørbæk Pedersen Department of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeley, USA Roskilde, December 16th, 21 Ulf
Sheared foam as a supercooled liquid?
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 2000 Europhys. Lett., 49 (1), pp. 68 74 (2000) Sheared foam as a supercooled liquid? S. A. Langer 1 and A. J. Liu 2 1 Information Technology Laboratory, NIST - Gaithersburg,
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 2000 Europhys. Lett., 49 (1), pp. 68 74 (2000) Sheared foam as a supercooled liquid? S. A. Langer 1 and A. J. Liu 2 1 Information Technology Laboratory, NIST - Gaithersburg,
Vibrational properties and phonon transport of amorphous solids
 June 29th (Fri.), 2018 Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Japan Rheology of disordered particles suspensions, glassy and granular materials 10:15-11:05, 40mins. talk and 10mins.
June 29th (Fri.), 2018 Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Japan Rheology of disordered particles suspensions, glassy and granular materials 10:15-11:05, 40mins. talk and 10mins.
Papers Cited >1000X GOOGLE SCHOLAR
 Papers Cited >1000X GOOGLE SCHOLAR March 2019 Citations 60861 15529 h-index 111 57 i10-index 425 206 1. Title: Formation of glasses from liquids and biopolymers Source: Science, 1995 sciencemag.org Abstract
Papers Cited >1000X GOOGLE SCHOLAR March 2019 Citations 60861 15529 h-index 111 57 i10-index 425 206 1. Title: Formation of glasses from liquids and biopolymers Source: Science, 1995 sciencemag.org Abstract
The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain
 The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain Luigi La Ragione and Vanessa Magnanimo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Bari, Italy E-mail: l.laragione@poliba.it;
The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain Luigi La Ragione and Vanessa Magnanimo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Bari, Italy E-mail: l.laragione@poliba.it;
Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview. Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore
 Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore UGC-NRCM Summer School on Mechanical Property Characterization- June 2012 Overview of polymer
Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore UGC-NRCM Summer School on Mechanical Property Characterization- June 2012 Overview of polymer
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Oct 1996
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Oct 1996 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Oct 1996](/thumbs/72/66812395.jpg) December 21, 2013 arxiv:cond-mat/9610066v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Oct 1996 Some Finite Size Effects in Simulations of Glass Dynamics Jürgen Horbach, Walter Kob, Kurt Binder Institut für Physik, Johannes
December 21, 2013 arxiv:cond-mat/9610066v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Oct 1996 Some Finite Size Effects in Simulations of Glass Dynamics Jürgen Horbach, Walter Kob, Kurt Binder Institut für Physik, Johannes
Quantum Annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University
 PY502, Computational Physics, December 12, 2017 Quantum Annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Advancing Research in Basic Science and Mathematics Example:
PY502, Computational Physics, December 12, 2017 Quantum Annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Advancing Research in Basic Science and Mathematics Example:
Slightly off-equilibrium dynamics
 Slightly off-equilibrium dynamics Giorgio Parisi Many progresses have recently done in understanding system who are slightly off-equilibrium because their approach to equilibrium is quite slow. In this
Slightly off-equilibrium dynamics Giorgio Parisi Many progresses have recently done in understanding system who are slightly off-equilibrium because their approach to equilibrium is quite slow. In this
The Structural Origin of Enhanced Dynamics at the Surface of a Glassy Alloy. School of Chemistry, University of Sydney, Sydney NW 2006 Australia
 1 The Structural Origin of Enhanced Dynamics at the Surface of a Glassy Alloy Gang Sun, Shibu Saw, Ian Douglass and Peter Harrowell School of Chemistry, University of Sydney, Sydney NW 006 Australia Abstract
1 The Structural Origin of Enhanced Dynamics at the Surface of a Glassy Alloy Gang Sun, Shibu Saw, Ian Douglass and Peter Harrowell School of Chemistry, University of Sydney, Sydney NW 006 Australia Abstract
collisions inelastic, energy is dissipated and not conserved
 LECTURE 1 - Introduction to Granular Materials Jamming, Random Close Packing, The Isostatic State Granular materials particles only interact when they touch hard cores: rigid, incompressible, particles
LECTURE 1 - Introduction to Granular Materials Jamming, Random Close Packing, The Isostatic State Granular materials particles only interact when they touch hard cores: rigid, incompressible, particles
Kinetic Ising Models and the Glass Transition
 Kinetic Ising Models and the Glass Transition Daniel Sussman May 11, 2010 Abstract The Fredrickson-Andersen model, one of a class of Ising models that introduces constraints on the allowed dynamics of
Kinetic Ising Models and the Glass Transition Daniel Sussman May 11, 2010 Abstract The Fredrickson-Andersen model, one of a class of Ising models that introduces constraints on the allowed dynamics of
Measurement of Growing Dynamical Lengthscales and Prediction of the Jamming Transition in a Granular Material
 Measurement of Growing Dynamical Lengthscales and Prediction of the Jamming Transition in a Granular Material Aaron S. Keys 1, Adam R. Abate 2, Sharon C. Glotzer 1,3, and Douglas J. Durian 2 1 Department
Measurement of Growing Dynamical Lengthscales and Prediction of the Jamming Transition in a Granular Material Aaron S. Keys 1, Adam R. Abate 2, Sharon C. Glotzer 1,3, and Douglas J. Durian 2 1 Department
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings. Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney
 Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
Echoes from anharmonic normal modes in model glasses
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 93, 032905 (2016) Echoes from anharmonic normal modes in model glasses Justin C. Burton * Department of Physics, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia 30322, USA Sidney R. Nagel James Franck
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 93, 032905 (2016) Echoes from anharmonic normal modes in model glasses Justin C. Burton * Department of Physics, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia 30322, USA Sidney R. Nagel James Franck
Glasses and Jamming: lessons from hard disks in a narrow channel
 Glasses and Jamming: lessons from hard disks in a narrow channel Mike Moore School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester, UK June 2014 Co-Author: Mike Godfrey, University of Manchester Mike
Glasses and Jamming: lessons from hard disks in a narrow channel Mike Moore School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester, UK June 2014 Co-Author: Mike Godfrey, University of Manchester Mike
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 19 Apr 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 19 Apr 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 19 Apr 2018](/thumbs/86/94148524.jpg) Slow relaxation dynamics in binary glasses during stress-controlled, tension-compression cyclic loading Nikolai V. Priezjev 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, arxiv:184.7189v1 [cond-mat.soft]
Slow relaxation dynamics in binary glasses during stress-controlled, tension-compression cyclic loading Nikolai V. Priezjev 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, arxiv:184.7189v1 [cond-mat.soft]
Advantages of a Finite Extensible Nonlinear Elastic Potential in Lattice Boltzmann Simulations
 The Hilltop Review Volume 7 Issue 1 Winter 2014 Article 10 December 2014 Advantages of a Finite Extensible Nonlinear Elastic Potential in Lattice Boltzmann Simulations Tai-Hsien Wu Western Michigan University
The Hilltop Review Volume 7 Issue 1 Winter 2014 Article 10 December 2014 Advantages of a Finite Extensible Nonlinear Elastic Potential in Lattice Boltzmann Simulations Tai-Hsien Wu Western Michigan University
Packing grains by thermally cycling
 Packing grains by thermally cycling One of the oldest and most intriguing problems in the handling of materials is how a collection of solid grains packs together. 1 While granular packing is normally
Packing grains by thermally cycling One of the oldest and most intriguing problems in the handling of materials is how a collection of solid grains packs together. 1 While granular packing is normally
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point
 Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
Mal. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol Materials Research Society
 91 MOLECULAR-DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF THIN-FILM GROWTH MATTHIAS SCHNEIDER,* IVAN K. SCHULLER,* AND A. RAHMAN Materials Science Division, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL 60439 Supercomputer Institute,
91 MOLECULAR-DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF THIN-FILM GROWTH MATTHIAS SCHNEIDER,* IVAN K. SCHULLER,* AND A. RAHMAN Materials Science Division, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL 60439 Supercomputer Institute,
Disordered Hyperuniformity: Liquid-like Behaviour in Structural Solids, A New Phase of Matter?
 Disordered Hyperuniformity: Liquid-like Behaviour in Structural Solids, A New Phase of Matter? Kabir Ramola Martin Fisher School of Physics, Brandeis University August 19, 2016 Kabir Ramola Disordered
Disordered Hyperuniformity: Liquid-like Behaviour in Structural Solids, A New Phase of Matter? Kabir Ramola Martin Fisher School of Physics, Brandeis University August 19, 2016 Kabir Ramola Disordered
Spatially heterogeneous dynamics investigated via a time-dependent four-point density correlation function
 JOURAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 119, UMBER 14 8 OCTOBER 2003 Spatially heterogeneous dynamics investigated via a time-dependent four-point density correlation function. Lačević Department of Chemical
JOURAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 119, UMBER 14 8 OCTOBER 2003 Spatially heterogeneous dynamics investigated via a time-dependent four-point density correlation function. Lačević Department of Chemical
The correlation between fragility, density and atomic interaction in glassforming
 The correlation between fragility, density and atomic interaction in glassforming liquids Lijin Wang 1, Pengfei Guan 1*, and W. H. Wang 2 1 Beijing Computational Science Research Center, Beijing, 100193,
The correlation between fragility, density and atomic interaction in glassforming liquids Lijin Wang 1, Pengfei Guan 1*, and W. H. Wang 2 1 Beijing Computational Science Research Center, Beijing, 100193,
Analysis of the simulation
 Analysis of the simulation Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař January 7, 2014 Thermodynamic properties time averages of thermodynamic quantites correspond to ensemble averages (ergodic theorem) some quantities
Analysis of the simulation Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař January 7, 2014 Thermodynamic properties time averages of thermodynamic quantites correspond to ensemble averages (ergodic theorem) some quantities
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 13 Feb 2015
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 13 Feb 2015 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 13 Feb 2015](/thumbs/73/68818601.jpg) Tuning by pruning: exploiting disorder for global response and the principle of bond-level independence Carl P. Goodrich and Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia,
Tuning by pruning: exploiting disorder for global response and the principle of bond-level independence Carl P. Goodrich and Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia,
Origin of Particle Clustering in a Simulated Polymer Nanocomposite and its Impact on Rheology
 Wesleyan University From the SelectedWorks of Francis Starr 2003 Origin of Particle Clustering in a Simulated Polymer Nanocomposite and its Impact on Rheology Francis W. Starr, Wesleyan University J. F.
Wesleyan University From the SelectedWorks of Francis Starr 2003 Origin of Particle Clustering in a Simulated Polymer Nanocomposite and its Impact on Rheology Francis W. Starr, Wesleyan University J. F.
Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors
 Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors L. Staron, F. Radjai & J.-P. Vilotte Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge CB3 0WA, UK. Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie
Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors L. Staron, F. Radjai & J.-P. Vilotte Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge CB3 0WA, UK. Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie
Nonequilibrium dynamics in Coulomb glasses near the metal-insulator transition
 Nonequilibrium dynamics in Coulomb glasses near the metal-insulator transition Dragana Popović National High Magnetic Field Laboratory Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA Boulder 2009 Summer
Nonequilibrium dynamics in Coulomb glasses near the metal-insulator transition Dragana Popović National High Magnetic Field Laboratory Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA Boulder 2009 Summer
Chapter 5: Molecular Scale Models for Macroscopic Dynamic Response. Fluctuation-Dissipation Theorem:
 G. R. Strobl, Chapter 6 "The Physics of Polymers, 2'nd Ed." Springer, NY, (1997). R. B. Bird, R. C. Armstrong, O. Hassager, "Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids", Vol. 2, John Wiley and Sons (1977). M. Doi,
G. R. Strobl, Chapter 6 "The Physics of Polymers, 2'nd Ed." Springer, NY, (1997). R. B. Bird, R. C. Armstrong, O. Hassager, "Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids", Vol. 2, John Wiley and Sons (1977). M. Doi,
Chapter 4. The Effect of Elastic Softening and Cooperativity on the Fragility of
 Chapter 4 The Effect of Elastic Softening and Cooperativity on the Fragility of Glass-Forming Metallic Liquids Key words: Amorphous metals, Shear transformation zones, Ultrasonic measurement, Compression
Chapter 4 The Effect of Elastic Softening and Cooperativity on the Fragility of Glass-Forming Metallic Liquids Key words: Amorphous metals, Shear transformation zones, Ultrasonic measurement, Compression
Dynamical Heterogeneity and Jamming in Glass-Forming Liquids
 J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 19623-19633 19623 Dynamical Heterogeneity and Jamming in Glass-Forming Liquids Naida Lačević, and Sharon C. Glotzer*,, Departments of Chemical Engineering and of Materials Science
J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 19623-19633 19623 Dynamical Heterogeneity and Jamming in Glass-Forming Liquids Naida Lačević, and Sharon C. Glotzer*,, Departments of Chemical Engineering and of Materials Science
Frequency distribution of mechanically stable disk packings
 Frequency distribution of mechanically stable disk packings Guo-Jie Gao, 1 Jerzy Bławzdziewicz, 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
Frequency distribution of mechanically stable disk packings Guo-Jie Gao, 1 Jerzy Bławzdziewicz, 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications
 6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 5: Specific Heat of Lattice Waves Outline Review Lecture 4 3-D Elastic Continuum 3-D Lattice Waves Lattice Density of Modes Specific Heat of Lattice Specific
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 5: Specific Heat of Lattice Waves Outline Review Lecture 4 3-D Elastic Continuum 3-D Lattice Waves Lattice Density of Modes Specific Heat of Lattice Specific
Exploring the energy landscape
 Exploring the energy landscape ChE210D Today's lecture: what are general features of the potential energy surface and how can we locate and characterize minima on it Derivatives of the potential energy
Exploring the energy landscape ChE210D Today's lecture: what are general features of the potential energy surface and how can we locate and characterize minima on it Derivatives of the potential energy
Supplementary Figure 1: Approach to the steady state. Energy vs. cycle for different
 ( = ) -6.9-6.94 (a) N = 8 < y.2 (T = 1).4 (T = 1).6 (T = 1).7 (T = 1) ( = ) -6.94 (b).8 (T = 1).9 (T = 1).12 (T = 1).14 (T = 1).8 (T =.466).9 (T =.466).12 (T =.466).14 (T =.466) > y n * 12 8 (c) N = 8
( = ) -6.9-6.94 (a) N = 8 < y.2 (T = 1).4 (T = 1).6 (T = 1).7 (T = 1) ( = ) -6.94 (b).8 (T = 1).9 (T = 1).12 (T = 1).14 (T = 1).8 (T =.466).9 (T =.466).12 (T =.466).14 (T =.466) > y n * 12 8 (c) N = 8
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 17 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 17 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 17 Jan 2018](/thumbs/96/129174394.jpg) Widom delta of supercritical gas-liquid coexistence Min Young Ha, 1 Tae Jun Yoon, 1 Tsvi Tlusty, 2, 3, Yongseok Jho, 4, and Won Bo Lee 1, 1 School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical
Widom delta of supercritical gas-liquid coexistence Min Young Ha, 1 Tae Jun Yoon, 1 Tsvi Tlusty, 2, 3, Yongseok Jho, 4, and Won Bo Lee 1, 1 School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical
A Quasicontinuum for Complex Crystals
 A Quasicontinuum for Complex Crystals Ellad B. Tadmor Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics University of Minnesota Collaborators: Previous Work: Current Work: U. V. Waghmare, G. S. Smith, N. Bernstein,
A Quasicontinuum for Complex Crystals Ellad B. Tadmor Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics University of Minnesota Collaborators: Previous Work: Current Work: U. V. Waghmare, G. S. Smith, N. Bernstein,
Glassy Dynamics in the Potential Energy Landscape
 Glassy Dynamics in the Potential Energy Landscape Vanessa de Souza University of Granada, Spain University of Cambridge 10ǫAA Glassy Dynamics in the Potential Energy Landscape p. 1/ Overview Introduction
Glassy Dynamics in the Potential Energy Landscape Vanessa de Souza University of Granada, Spain University of Cambridge 10ǫAA Glassy Dynamics in the Potential Energy Landscape p. 1/ Overview Introduction
Is there a de Almeida-Thouless line in finite-dimensional spin glasses? (and why you should care)
 Is there a de Almeida-Thouless line in finite-dimensional spin glasses? (and why you should care) Peter Young Talk at MPIPKS, September 12, 2013 Available on the web at http://physics.ucsc.edu/~peter/talks/mpipks.pdf
Is there a de Almeida-Thouless line in finite-dimensional spin glasses? (and why you should care) Peter Young Talk at MPIPKS, September 12, 2013 Available on the web at http://physics.ucsc.edu/~peter/talks/mpipks.pdf
Linearized Theory: Sound Waves
 Linearized Theory: Sound Waves In the linearized limit, Λ iα becomes δ iα, and the distinction between the reference and target spaces effectively vanishes. K ij (q): Rigidity matrix Note c L = c T in
Linearized Theory: Sound Waves In the linearized limit, Λ iα becomes δ iα, and the distinction between the reference and target spaces effectively vanishes. K ij (q): Rigidity matrix Note c L = c T in
The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3
 The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3 DIETER VOLLHARD T Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Federal Republic of German y PETER WÖLFL E Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany PREFACE
The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3 DIETER VOLLHARD T Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Federal Republic of German y PETER WÖLFL E Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany PREFACE
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems
 Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
CHEM Principles of Chemistry II Chapter 10 - Liquids and Solids
 CHEM 1212 - Principles of Chemistry II Chapter 10 - Liquids and Solids 10.1 Intermolecular Forces recall intramolecular (within the molecule) bonding whereby atoms can form stable units called molecules
CHEM 1212 - Principles of Chemistry II Chapter 10 - Liquids and Solids 10.1 Intermolecular Forces recall intramolecular (within the molecule) bonding whereby atoms can form stable units called molecules
Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering. Lecture 14: Amorphous State February 14, 2001
 Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering Lecture 14: Amorphous State February 14, 2001 Objectives! To provide guidance toward understanding why an amorphous polymer glass may be considered
Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering Lecture 14: Amorphous State February 14, 2001 Objectives! To provide guidance toward understanding why an amorphous polymer glass may be considered
Equilibria in Materials
 009 fall Advanced Physical Metallurgy Phase Equilibria in Materials 10. 13. 009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-71 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Contents for previous
009 fall Advanced Physical Metallurgy Phase Equilibria in Materials 10. 13. 009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-71 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Contents for previous
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004](/thumbs/74/70280953.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0406141v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004 Moving Beyond a Simple Model of Luminescence Rings in Quantum Well Structures D. Snoke 1, S. Denev 1, Y. Liu 1, S. Simon 2, R. Rapaport 2, G. Chen 2,
arxiv:cond-mat/0406141v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004 Moving Beyond a Simple Model of Luminescence Rings in Quantum Well Structures D. Snoke 1, S. Denev 1, Y. Liu 1, S. Simon 2, R. Rapaport 2, G. Chen 2,
Molecular dynamics simulations of sliding friction in a dense granular material
 Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 6 (998) 7 77. Printed in the UK PII: S965-393(98)9635- Molecular dynamics simulations of sliding friction in a dense granular material T Matthey and J P Hansen Department
Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 6 (998) 7 77. Printed in the UK PII: S965-393(98)9635- Molecular dynamics simulations of sliding friction in a dense granular material T Matthey and J P Hansen Department
Commonalities in frequency-dependent viscoelastic damping in glasses in the MHz to THz. regime
 Commonalities in frequency-dependent viscoelastic damping in glasses in the MHz to THz regime Raghavan Ranganathan 1, Yunfeng Shi 1 and Pawel Keblinski 1 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
Commonalities in frequency-dependent viscoelastic damping in glasses in the MHz to THz regime Raghavan Ranganathan 1, Yunfeng Shi 1 and Pawel Keblinski 1 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology
 CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
Temporally Heterogeneous Dynamics in Granular Flows
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Publications Department of Physics 3-25 Temporally Heterogeneous Dynamics in Granular Flows Leo Silbert Southern Illinois University Carbondale, lsilbert@physics.siu.edu
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Publications Department of Physics 3-25 Temporally Heterogeneous Dynamics in Granular Flows Leo Silbert Southern Illinois University Carbondale, lsilbert@physics.siu.edu
Using the Timoshenko Beam Bond Model: Example Problem
 Using the Timoshenko Beam Bond Model: Example Problem Authors: Nick J. BROWN John P. MORRISSEY Jin Y. OOI School of Engineering, University of Edinburgh Jian-Fei CHEN School of Planning, Architecture and
Using the Timoshenko Beam Bond Model: Example Problem Authors: Nick J. BROWN John P. MORRISSEY Jin Y. OOI School of Engineering, University of Edinburgh Jian-Fei CHEN School of Planning, Architecture and
Anomalous phonon scattering and elastic correlations in amorphous solids
 216MacmilanPublishersLimited,partofSpringerNature.Alrightsreserved.SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NMAT4736 Anomalous phonon scattering and elastic correlations in amorphous solids Simon Gelin 1,2,
216MacmilanPublishersLimited,partofSpringerNature.Alrightsreserved.SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NMAT4736 Anomalous phonon scattering and elastic correlations in amorphous solids Simon Gelin 1,2,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007](/thumbs/93/111468426.jpg) Universal Anisotropy in Force Networks under Shear Srdjan Ostojic, 1, Thijs J. H. Vlugt, 2 and Bernard Nienhuis 1 arxiv:cond-mat/0610483v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007 1 Institute for Theoretical Physics,
Universal Anisotropy in Force Networks under Shear Srdjan Ostojic, 1, Thijs J. H. Vlugt, 2 and Bernard Nienhuis 1 arxiv:cond-mat/0610483v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007 1 Institute for Theoretical Physics,
Mechanics of Granular Matter
 Mechanics of Granular Matter Mechanics of Granular Matter Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Published by
Mechanics of Granular Matter Mechanics of Granular Matter Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Published by
