THE PHYSICS OF FOAM. Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics. July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter. 1.
|
|
|
- Esmond Day
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation 3. Stability Coarsening Drainage 4. Rheology Linear response Rearrangement & flow Douglas J. DURIAN UCLA Physics & Astronomy Los Angeles, CA
2 Princen-Prud homme model shear a 2D honeycomb, always respecting Plateau s rules deformation is not affine: vertices must rotate to maintain stress, σ slope, G o etc. γ film a γ y strain, γ shear modulus: G o = γ film /Sqrt[3]a yield strain: γ y = 1.2
3 Yes, but Princen-Prud homme is for 2D periodic static dry foam dimensionality? generally expect G ~ Laplace pressure (surface tension/bubble size) wetness? shear modulus must vanish for wet foams dissipation? nonzero strainrate or oscillation frequency? disorder? smaller rearrangement size (not system)? smaller yield strain?
4 small-strain non-affine motion bubble motion is up & down as well as more & less (DJD) compare bonds and displacements (normalized to affine expectation) trends vs polydisersity and wetness width=0.75 width=0.1 φ=0.84 φ=1
5 Frequency dependence, G*(ω) Simplest possibility: Kelvin solid G*(ω) = G 0 + iηω {i.e. G (ω) = G 0 and G (ω) = ηω} But typical data looks much different: G (ω) isn t flat, and increases at high ω G (ω) doesn t vanish at low ω (A. Saint-Jalmes & DJD)
6 High-ω rheology Due to non-affine motion, another term dominates: G*(ω) = G 0 (1 + Sqrt[iω/ω c ]) ** shown by dotted curve for ε=0.08 foam: (A.D. Gopal & DJD) NB: This gives a robust way to extract the shear modulus from G*(ω) vs ω data. Here G o = 2300 dyne/cm 2 [**seen and explained by Liu, Ramaswamy, Mason, Gang, Weitz for compressed emulsion using DWS microrheology]
7 long-τ: rearrangements give exponential decay Short-τ DWS short-τ: thermal interface fluctuations (Y=< r 2 (τ)>) amplitude of fluctuations: microrheology: G o δ = 13± 3 angstroms kbt 1000 ± 300 dyne/cm Rδ 2 2
8 Unjamming vs gas fraction Data for shear modulus: symbols: polydisperse foam solid curve: monodisperse emulsion (Mason & Weitz) dashed curve: polydisperse emulsion (Princen & Kiss) (A. Saint-Jalmes & DJD) Couette cell cone-plate G (dyn/cm 2 ) G / (σ/r) φ polydispersity makes little or no difference! unjammed jammed
9 Behavior near the transition simulation of 2D bubble model (DJD) x20 polydisperse bubbles G width shear modulus Z coordination number better point J statistics by O Hern, Langer, Liu, Nagel 4 3 τ r φ stressrelaxation time τ r appears to diverge at φ rcp ~0.84
10 Unjamming vs time elasticity vanishes at long times stress relaxes as the bubbles coarsen time scale is set by foam age ie how long for size distribution to change not set by the time between coarsening-induced rearrangements (20s) (A.D. Gopal & DJD) Even though this is not a thermally activated mechanism like diffusion or reptation, the rheology is linear G * (ω) and G(t) date are indeed related by Fourier transform
11 Unjamming vs shear make bubbles rearrange & explore packing configurations slow shear: sudden avalanche-like rearrangements of a few bubbles at a time fast shear: rearrangements merge together into continuous smooth flow slow & jerky fast & smooth
12 Rearrangement sizes even the largest are only a few bubbles across picture of a very large event distribution of energy drops (before-after) has a cutoff {but it moves out on approach to φ c point J }
13 NB: shear deformation is uniform uniform shear-band exponential UCLA: direct observation of free surface in Couette cell viscosity and G*(ω) are indep. of sample thickness & cell geometry DWS gives expected decay time in transmission and backscattering viscous fingering morphology Hohler / Cohen-Addad lab (Marne-la-Vallee): multiple light scattering and rheology Dennin lab (UC Irvine): 2D bubble rafts and lipid monolayers Weitz lab (Exxon/Penn/Harvard): Rheology of emulsions Computer simulations: bubble model (DJD-Langer-Liu-Nagel) Surface evolver (Kraynik) 2D (Weaire) vertex model (Kawasaki)
14 important scales notation: τ oq : τ d : γ y : γ c = γ y γ = γ m y τ τ oq d : : time between coarsening - induced rearrangments duration of rearrangement events yield strain whether coarsening - or shear - induced rearrangements dominate whether rearrangements are smooth or avalanche- like values for Foamy: τ oq = 20s τ d = 0.1s γ y = 0.05 γ c = 0.003/ s γ = 0.5 / s m
15 bubble motion via DWS 1 low shear high shear (a) 1 (a) (b) (A.D. Gopal & DJD) g 1 (τ) s -1 g 1 (τ) s s s -1. γ = 0.02 s τ (sec) s -1 g1( τ ) exp 6 L l * τ o = time between rearrangements at each scattering site 2 τ τ o τ s = 30 kl * Ýγ s s -1 γ = 0.02 s τ 2 τ (sec) 2 ) g1( τ ) exp 6 L l * time for adjacent scattering sites to convect apart by λ 2 τ τ s 2
16 DWS times vs strainrate behavior changes at expected strainrate scales (A.D. Gopal & DJD) rate constant (sec -1 ) /τ 0 1/τ s. γ c = γ y /τ 0q. γ m = γ y /τ d strain rate (1/s) discrete rearrangements jammed/solid-like laminar bubble motion unjammed/liquid-like
17 Rheological signature? simplest expectation is Bingham plastic: σ = σ 1 + γτ γ and hence η = σ 1 γ + 1. y ( ) ( γ ) but 1/γ isn t seen in either data or bubble-model: no real signature of γ m in data d y. y (A.D. Gopal & DJD) m
18 Superimpose step-strain! Stress jump and relaxation time both measure elasticity 2 Stress (dyne/cm ) 2 ) Strain Strain G(0) strain rate = 0.01/s γ =0.09 τ R t (s) transient relaxation shear modulus
19 bubble motion vs rheology All measures of elasticity vanish at same point where rearrangements merge together into continuous flow unjamming shear rate = yield strain / event duration G(0,γ) [dyne/cm 2 ] τ R [sec] (c). γ =γ /τ m y d τ 0 τ S -1/2 shear rate [1/sec] This completes the connection between bubble-scale and macroscopic foam behavior
20 We ve now seen three ways to unjam a foam ie for bubbles to rearrange and explore configuration space Jamming vs liquid fraction (gas bubble packing) vs time (as foam coarsens) vs shear Trajectories in the phase diagram? does shear play role of temperature? (A.J. Liu & S.R. Nagel)
21 Three effective temperatures Compressibility & pressure fluctuations κ S 1 = A T Viscosity & shear stress fluctuations Heat capacity & energy fluctuations ( p p )2 η = A T dt σ xy (t)σ xy (0) 0 U T = 1 T 2 (I.K. Ono, C.S O Hern, DJD, S.A. Langer, A.J. Liu, S.R. Nagel) ( U U ) 2 c T s all reduce to (ds/du) -1 for equilibrated thermal systems What is their value & shear rate dependence; are they equal? Difficult to measure, so resort to simulation
22 The three T eff s agree! N=400 bubbles in 2D box at φ=0.90 area fraction T eff approaches constant at zero strain rate T eff increases very slowly with strain rate T bidisperse T p T xy T U T polydisperse γ.
23 also agree with T=(dS/dU) -1 Monte-Carlo results for Ω(U), the probability for a randomly constructed configuration to have energy U 0 log 10 (Ω) S= N= T S T U from shearing runs TU T U =U/0.65N =U/(f/2)N U/N For this system, the effective temperature has all the attributes of a true statistical mechanical temperature.
24 Mini-conclusions Statistical Mechanics works for certain driven athermal systems, unmodified but for an effective temperature When does stat-mech succeed & what sets the value of T eff? Elemental fluidized bed (R.P. Ojha, DJD) upflow of gas: many fast degrees of freedom, constant-temperature reservoir Uniformly sheared foam (I.K. Ono, C.S O Hern, DJD, S.A. Langer, A.J. Liu, S.R. Nagel) neighboring bubbles: many configurations with the same topology In general Perhaps want fluctuations to dominate the dissipation of injected energy? When does stat-mech fail & what to do then? eg anisotropic velocity fluctuations in sheared sand eg P(v)~Exp[-v 3/2 ] in shaken sand eg flocking in self-propelled particles
25 Thank you for your interest in foam! THE END.
Modeling Random Wet 2D Foams with Controlled Polydispersity. Back to the Future?
 Modeling Random Wet 2D Foams with Controlled Polydispersity Back to the Future? Andy Kraynik Sandia National Labs (retired) CEAS, University of Manchester University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Simon Cox Aberystwyth
Modeling Random Wet 2D Foams with Controlled Polydispersity Back to the Future? Andy Kraynik Sandia National Labs (retired) CEAS, University of Manchester University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Simon Cox Aberystwyth
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming
 Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM. Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics. July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter. 1.
 THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
Hysteresis and avalanches in two-dimensional foam rheology simulations
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 59, NUMBER 5 MAY 1999 Hysteresis and avalanches in two-dimensional foam rheology simulations Yi Jiang, 1, * Pieter J. Swart, 1 Avadh Saxena, 1 Marius Asipauskas, 2 and James A.
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 59, NUMBER 5 MAY 1999 Hysteresis and avalanches in two-dimensional foam rheology simulations Yi Jiang, 1, * Pieter J. Swart, 1 Avadh Saxena, 1 Marius Asipauskas, 2 and James A.
The Large Amplitude Oscillatory Strain Response of Aqueous Foam: Strain Localization and Full Stress Fourier Spectrum
 The Large Amplitude Oscillatory Strain Response of Aqueous Foam: Strain Localization and Full Stress Fourier Spectrum By F. Rouyer, S. Cohen-Addad, R. Höhler, P. Sollich, and S.M. Fielding The European
The Large Amplitude Oscillatory Strain Response of Aqueous Foam: Strain Localization and Full Stress Fourier Spectrum By F. Rouyer, S. Cohen-Addad, R. Höhler, P. Sollich, and S.M. Fielding The European
The steady shear of three-dimensional wet polydisperse foams
 J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 92 (2000) 151 166 The steady shear of three-dimensional wet polydisperse foams B.S. Gardiner, B.Z. Dlugogorski, G.J. Jameson Department of Chemical Engineering, The University
J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 92 (2000) 151 166 The steady shear of three-dimensional wet polydisperse foams B.S. Gardiner, B.Z. Dlugogorski, G.J. Jameson Department of Chemical Engineering, The University
Sheared foam as a supercooled liquid?
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 2000 Europhys. Lett., 49 (1), pp. 68 74 (2000) Sheared foam as a supercooled liquid? S. A. Langer 1 and A. J. Liu 2 1 Information Technology Laboratory, NIST - Gaithersburg,
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 2000 Europhys. Lett., 49 (1), pp. 68 74 (2000) Sheared foam as a supercooled liquid? S. A. Langer 1 and A. J. Liu 2 1 Information Technology Laboratory, NIST - Gaithersburg,
Rheology of Soft Materials. Rheology
 Τ Thomas G. Mason Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Department of Physics and Astronomy California NanoSystems Institute Τ γ 26 by Thomas G. Mason All rights reserved. γ (t) τ (t) γ τ Δt 2π t γ
Τ Thomas G. Mason Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Department of Physics and Astronomy California NanoSystems Institute Τ γ 26 by Thomas G. Mason All rights reserved. γ (t) τ (t) γ τ Δt 2π t γ
Interfacial dynamics
 Interfacial dynamics Interfacial dynamics = dynamic processes at fluid interfaces upon their deformation Interfacial rheological properties: elasticity, viscosity, yield stress, Relation between macroscopic
Interfacial dynamics Interfacial dynamics = dynamic processes at fluid interfaces upon their deformation Interfacial rheological properties: elasticity, viscosity, yield stress, Relation between macroscopic
Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids
 Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids Atsushi Ikeda Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University Atsushi Ikeda & Ludovic Berthier Phys. Rev. E 92,
Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids Atsushi Ikeda Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University Atsushi Ikeda & Ludovic Berthier Phys. Rev. E 92,
Flow in two-dimensions: novel fluid behavior at interfaces
 Flow in two-dimensions: novel fluid behavior at interfaces M. Dennin U. C. Irvine Department of Physics and Astronomy and Institute for Surface and Interfacial Science Research Overview Fluid Instabilities
Flow in two-dimensions: novel fluid behavior at interfaces M. Dennin U. C. Irvine Department of Physics and Astronomy and Institute for Surface and Interfacial Science Research Overview Fluid Instabilities
Viscoelasticity. Basic Notions & Examples. Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity. Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies. Non-linear behavior
 Viscoelasticity Basic Notions & Examples Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies Non-linear behavior Viscoelastic Behavior Generic Viscoelasticity: exhibition of both
Viscoelasticity Basic Notions & Examples Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies Non-linear behavior Viscoelastic Behavior Generic Viscoelasticity: exhibition of both
Lecture 7: Rheology and milli microfluidic
 1 and milli microfluidic Introduction In this chapter, we come back to the notion of viscosity, introduced in its simplest form in the chapter 2. We saw that the deformation of a Newtonian fluid under
1 and milli microfluidic Introduction In this chapter, we come back to the notion of viscosity, introduced in its simplest form in the chapter 2. We saw that the deformation of a Newtonian fluid under
Granular materials (Assemblies of particles with dissipation )
 Granular materials (Assemblies of particles with dissipation ) Saturn ring Sand mustard seed Ginkaku-ji temple Sheared granular materials packing fraction : Φ Inhomogeneous flow Gas (Φ = 012) Homogeneous
Granular materials (Assemblies of particles with dissipation ) Saturn ring Sand mustard seed Ginkaku-ji temple Sheared granular materials packing fraction : Φ Inhomogeneous flow Gas (Φ = 012) Homogeneous
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 9, 203 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 203 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 203 Physical Acoustics Session 2pPA: Material Characterization 2pPA. Probing
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 9, 203 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 203 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 203 Physical Acoustics Session 2pPA: Material Characterization 2pPA. Probing
Lecture 4: viscoelasticity and cell mechanics
 Teaser movie: flexible robots! R. Shepherd, Whitesides group, Harvard 1 Lecture 4: viscoelasticity and cell mechanics S-RSI Physics Lectures: Soft Condensed Matter Physics Jacinta C. Conrad University
Teaser movie: flexible robots! R. Shepherd, Whitesides group, Harvard 1 Lecture 4: viscoelasticity and cell mechanics S-RSI Physics Lectures: Soft Condensed Matter Physics Jacinta C. Conrad University
Polymer Dynamics and Rheology
 Polymer Dynamics and Rheology 1 Polymer Dynamics and Rheology Brownian motion Harmonic Oscillator Damped harmonic oscillator Elastic dumbbell model Boltzmann superposition principle Rubber elasticity and
Polymer Dynamics and Rheology 1 Polymer Dynamics and Rheology Brownian motion Harmonic Oscillator Damped harmonic oscillator Elastic dumbbell model Boltzmann superposition principle Rubber elasticity and
Non-linear Viscoelasticity FINITE STRAIN EFFECTS IN SOLIDS
 FINITE STRAIN EFFECTS IN SOLIDS Consider an elastic solid in shear: Shear Stress σ(γ) = Gγ If we apply a shear in the opposite direction: Shear Stress σ( γ) = Gγ = σ(γ) This means that the shear stress
FINITE STRAIN EFFECTS IN SOLIDS Consider an elastic solid in shear: Shear Stress σ(γ) = Gγ If we apply a shear in the opposite direction: Shear Stress σ( γ) = Gγ = σ(γ) This means that the shear stress
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Apr 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Apr 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Apr 2018](/thumbs/83/87308805.jpg) Ideal wet two-dimensional foams and emulsions with finite contact angle S.J. Cox (a), A.M. Kraynik (b,c), D. Weaire (c) and S. Hutzler (c) (a) Department of Mathematics, Aberystwyth University, Aberystwyth
Ideal wet two-dimensional foams and emulsions with finite contact angle S.J. Cox (a), A.M. Kraynik (b,c), D. Weaire (c) and S. Hutzler (c) (a) Department of Mathematics, Aberystwyth University, Aberystwyth
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming
 Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Chapter 6 Molten State
 Chapter 6 Molten State Rheology ( 流變學 ) study of flow and deformation of (liquid) fluids constitutive (stress-strain) relation of fluids shear flow shear rate ~ dγ/dt ~ velocity gradient dv 1 = dx 1 /dt
Chapter 6 Molten State Rheology ( 流變學 ) study of flow and deformation of (liquid) fluids constitutive (stress-strain) relation of fluids shear flow shear rate ~ dγ/dt ~ velocity gradient dv 1 = dx 1 /dt
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
5 The Oldroyd-B fluid
 5 The Oldroyd-B fluid Last time we started from a microscopic dumbbell with a linear entropic spring, and derived the Oldroyd-B equations: A u = u ρ + u u = σ 2 pi + η u + u 3 + u A A u u A = τ Note that
5 The Oldroyd-B fluid Last time we started from a microscopic dumbbell with a linear entropic spring, and derived the Oldroyd-B equations: A u = u ρ + u u = σ 2 pi + η u + u 3 + u A A u u A = τ Note that
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems
 Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
Aging in laponite water suspensions. P. K. Bhattacharyya Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 Aging in laponite water suspensions. P. K. Bhattacharyya Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies Massachusetts Institute of Technology Outline Laponite Basic background. Laponite in suspension Bonn et al.,
Aging in laponite water suspensions. P. K. Bhattacharyya Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies Massachusetts Institute of Technology Outline Laponite Basic background. Laponite in suspension Bonn et al.,
Diffusing-wave-spectroscopy measurements of viscoelasticity of complex fluids
 Mason et al. Vol. 14, No. 1/January 1997/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 139 Diffusing-wave-spectroscopy measurements of viscoelasticity of complex fluids T. G. Mason Department of Chemical Engineering, Johns Hopkins
Mason et al. Vol. 14, No. 1/January 1997/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 139 Diffusing-wave-spectroscopy measurements of viscoelasticity of complex fluids T. G. Mason Department of Chemical Engineering, Johns Hopkins
Rheology of aqueous foams
 Rheology of aqueous foams Benjamin Dollet, Christophe Raufaste To cite this version: Benjamin Dollet, Christophe Raufaste. Rheology of aqueous foams. Comptes rendus de l Académie des sciences. Série IV,
Rheology of aqueous foams Benjamin Dollet, Christophe Raufaste To cite this version: Benjamin Dollet, Christophe Raufaste. Rheology of aqueous foams. Comptes rendus de l Académie des sciences. Série IV,
Rock Rheology GEOL 5700 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth
 Rock Rheology GEOL 5700 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth References: Turcotte and Schubert, Geodynamics, Sections 2.1,-2.4, 2.7, 3.1-3.8, 6.1, 6.2, 6.8, 7.1-7.4. Jaeger and Cook, Fundamentals of
Rock Rheology GEOL 5700 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth References: Turcotte and Schubert, Geodynamics, Sections 2.1,-2.4, 2.7, 3.1-3.8, 6.1, 6.2, 6.8, 7.1-7.4. Jaeger and Cook, Fundamentals of
Jamming and the Anticrystal
 Jamming and the Anticrystal Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Carl Goodrich Corey S. O Hern Leo E. Silbert Vincenzo Vitelli Ning Xu Sidney Nagel UPenn Yale SIUC
Jamming and the Anticrystal Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Carl Goodrich Corey S. O Hern Leo E. Silbert Vincenzo Vitelli Ning Xu Sidney Nagel UPenn Yale SIUC
RHEOLASER LAB MICRORHEOLOGY & END USE PROPERTIES ANALYSIS. MICRORHEOLOGY
 RHEOLASER LAB & END USE PROPERTIES ANALYSIS A NEW RHEOLOGY APPROACH TO CHARACTERISE END-USE PROPERTIES THE FIRST READY TO USE & END-USE PROPERTIES ANALYSER Rheolaser Rheolaser is the first Lab ready-to-use
RHEOLASER LAB & END USE PROPERTIES ANALYSIS A NEW RHEOLOGY APPROACH TO CHARACTERISE END-USE PROPERTIES THE FIRST READY TO USE & END-USE PROPERTIES ANALYSER Rheolaser Rheolaser is the first Lab ready-to-use
Buckling induced jamming in channel flow of particle rafts
 Buckling induced jamming in channel flow of particle rafts Chin-Chang Kuo and Michael Dennin Department of Physics & Astronomy UC Irvine and Institute for Complex Adaptive Matter, Irvine, CA 92697 (Dated:
Buckling induced jamming in channel flow of particle rafts Chin-Chang Kuo and Michael Dennin Department of Physics & Astronomy UC Irvine and Institute for Complex Adaptive Matter, Irvine, CA 92697 (Dated:
Lecture 6: Flow regimes fluid-like
 Granular Flows 1 Lecture 6: Flow regimes fluid-like Quasi-static granular flows have plasticity laws, gaseous granular flows have kinetic theory -- how to model fluid-like flows? Intermediate, dense regime:
Granular Flows 1 Lecture 6: Flow regimes fluid-like Quasi-static granular flows have plasticity laws, gaseous granular flows have kinetic theory -- how to model fluid-like flows? Intermediate, dense regime:
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22836 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Woldhuis, Erik Title: Foam rheology near the jamming transition Issue Date: 2013-12-11
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22836 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Woldhuis, Erik Title: Foam rheology near the jamming transition Issue Date: 2013-12-11
arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 23 Aug 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 23 Aug 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 23 Aug 2017](/thumbs/94/118469267.jpg) 2D foams above the jamming transition: Deformation matters J. Winkelmann a,, F.F. Dunne a, V.J. Langlois b, M.E. Möbius a, D. Weaire a, S. Hutzler a a School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, The University
2D foams above the jamming transition: Deformation matters J. Winkelmann a,, F.F. Dunne a, V.J. Langlois b, M.E. Möbius a, D. Weaire a, S. Hutzler a a School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, The University
Soft glassy rheology & trap models
 Soft glasses, rheology, and trap models Peter Sollich A Barra, M E Cates, S M Fielding, P Hébraud, F Lequeux King s College London Ask me questions before dinner Though I d rather stay here... What s glassy
Soft glasses, rheology, and trap models Peter Sollich A Barra, M E Cates, S M Fielding, P Hébraud, F Lequeux King s College London Ask me questions before dinner Though I d rather stay here... What s glassy
In-depth analysis of viscoelastic properties thanks to Microrheology: non-contact rheology
 In-depth analysis of viscoelastic properties thanks to Microrheology: non-contact rheology Application All domains dealing with soft materials (emulsions, suspensions, gels, foams, polymers, etc ) Objective
In-depth analysis of viscoelastic properties thanks to Microrheology: non-contact rheology Application All domains dealing with soft materials (emulsions, suspensions, gels, foams, polymers, etc ) Objective
RHEOLOGY Principles, Measurements, and Applications. Christopher W. Macosko
 RHEOLOGY Principles, Measurements, and Applications I -56081-5'79~5 1994 VCH Publishers. Inc. New York Part I. CONSTITUTIVE RELATIONS 1 1 l Elastic Solid 5 1.1 Introduction 5 1.2 The Stress Tensor 8 1.2.1
RHEOLOGY Principles, Measurements, and Applications I -56081-5'79~5 1994 VCH Publishers. Inc. New York Part I. CONSTITUTIVE RELATIONS 1 1 l Elastic Solid 5 1.1 Introduction 5 1.2 The Stress Tensor 8 1.2.1
Chapter 6: The Rouse Model. The Bead (friction factor) and Spring (Gaussian entropy) Molecular Model:
 G. R. Strobl, Chapter 6 "The Physics of Polymers, 2'nd Ed." Springer, NY, (1997). R. B. Bird, R. C. Armstrong, O. Hassager, "Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids", Vol. 2, John Wiley and Sons (1977). M. Doi,
G. R. Strobl, Chapter 6 "The Physics of Polymers, 2'nd Ed." Springer, NY, (1997). R. B. Bird, R. C. Armstrong, O. Hassager, "Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids", Vol. 2, John Wiley and Sons (1977). M. Doi,
Strain localization in a shear transformation zone model for amorphous solids
 Strain localization in a shear transformation zone model for amorphous solids M. L. Manning,* J. S. Langer, and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, California
Strain localization in a shear transformation zone model for amorphous solids M. L. Manning,* J. S. Langer, and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, California
Comparison of Low-Amplitude Oscillatory Shear in Experimental and Computational Studies of Model Foams
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Department of Physics Papers Department of Physics 4-20-2009 Comparison of Low-Amplitude Oscillatory Shear in Experimental and Computational Studies of Model
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Department of Physics Papers Department of Physics 4-20-2009 Comparison of Low-Amplitude Oscillatory Shear in Experimental and Computational Studies of Model
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
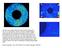 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
Table of Contents. Preface... xiii
 Preface... xiii PART I. ELEMENTS IN FLUID MECHANICS... 1 Chapter 1. Local Equations of Fluid Mechanics... 3 1.1. Forces, stress tensor, and pressure... 4 1.2. Navier Stokes equations in Cartesian coordinates...
Preface... xiii PART I. ELEMENTS IN FLUID MECHANICS... 1 Chapter 1. Local Equations of Fluid Mechanics... 3 1.1. Forces, stress tensor, and pressure... 4 1.2. Navier Stokes equations in Cartesian coordinates...
Flow of Glasses. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Flow of Glasses Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 sec Time scale Liquid!
Flow of Glasses Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 sec Time scale Liquid!
Measurement of Growing Dynamical Lengthscales and Prediction of the Jamming Transition in a Granular Material
 Measurement of Growing Dynamical Lengthscales and Prediction of the Jamming Transition in a Granular Material Aaron S. Keys 1, Adam R. Abate 2, Sharon C. Glotzer 1,3, and Douglas J. Durian 2 1 Department
Measurement of Growing Dynamical Lengthscales and Prediction of the Jamming Transition in a Granular Material Aaron S. Keys 1, Adam R. Abate 2, Sharon C. Glotzer 1,3, and Douglas J. Durian 2 1 Department
Complexity of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media
 1 Complexity of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media Rennes September 16, 2009 Eyvind Aker Morten Grøva Henning Arendt Knudsen Thomas Ramstad Bo-Sture Skagerstam Glenn Tørå Alex Hansen 2 Declining oil production,
1 Complexity of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media Rennes September 16, 2009 Eyvind Aker Morten Grøva Henning Arendt Knudsen Thomas Ramstad Bo-Sture Skagerstam Glenn Tørå Alex Hansen 2 Declining oil production,
Experimental Colloids I (and I)
 Experimental Colloids I (and I) Dave Weitz Harvard http://www.seas.harvard.edu/projects/weitzlab Boulder Summer School 7/24/17 Experimental Colloids I (and I) Dave Weitz Harvard http://www.seas.harvard.edu/projects/weitzlab
Experimental Colloids I (and I) Dave Weitz Harvard http://www.seas.harvard.edu/projects/weitzlab Boulder Summer School 7/24/17 Experimental Colloids I (and I) Dave Weitz Harvard http://www.seas.harvard.edu/projects/weitzlab
The large amplitude oscillatory strain response of aqueous foam: Strain localization and full stress Fourier spectrum
 Eur. Phys. J. E 27, 309 321 (2008) DOI 10.1140/epje/i2008-10382-7 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL E The large amplitude oscillatory strain response of aqueous foam: Strain localization and full stress Fourier
Eur. Phys. J. E 27, 309 321 (2008) DOI 10.1140/epje/i2008-10382-7 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL E The large amplitude oscillatory strain response of aqueous foam: Strain localization and full stress Fourier
Abvanced Lab Course. Dynamical-Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers
 Abvanced Lab Course Dynamical-Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers M211 As od: 9.4.213 Aim: Determination of the mechanical properties of a typical polymer under alternating load in the elastic range
Abvanced Lab Course Dynamical-Mechanical Analysis (DMA) of Polymers M211 As od: 9.4.213 Aim: Determination of the mechanical properties of a typical polymer under alternating load in the elastic range
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29750 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wortel, Geert Title: Granular flows : fluidization and anisotropy Issue Date: 2015-11-19
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29750 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wortel, Geert Title: Granular flows : fluidization and anisotropy Issue Date: 2015-11-19
One- and two-particle microrheology in solutions of actin, fd-virus and inorganic rods
 Microrheology of Biopolymers (ITP Complex Fluids Program 3/05/02) One- and two-particle microrheology in solutions of actin, fd-virus and inorganic rods Christoph Schmidt Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam Collaborators:
Microrheology of Biopolymers (ITP Complex Fluids Program 3/05/02) One- and two-particle microrheology in solutions of actin, fd-virus and inorganic rods Christoph Schmidt Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam Collaborators:
A Thermodynamic Formulation of the STZ Theory of Deformation in Amorphous Solids
 A Thermodynamic Formulation of the STZ Theory of Deformation in Amorphous Solids Michael L. Falk Johns Hopkins University James S. Langer UC Santa Barbara E. Bouchbinder Weizmann Institute Thermodynamics
A Thermodynamic Formulation of the STZ Theory of Deformation in Amorphous Solids Michael L. Falk Johns Hopkins University James S. Langer UC Santa Barbara E. Bouchbinder Weizmann Institute Thermodynamics
GEM4 Summer School OpenCourseWare
 GEM4 Summer School OpenCourseWare http://gem4.educommons.net/ http://www.gem4.org/ Lecture: Microrheology of a Complex Fluid by Dr. Peter So. Given August 10, 2006 during the GEM4 session at MIT in Cambridge,
GEM4 Summer School OpenCourseWare http://gem4.educommons.net/ http://www.gem4.org/ Lecture: Microrheology of a Complex Fluid by Dr. Peter So. Given August 10, 2006 during the GEM4 session at MIT in Cambridge,
cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano
 cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano (Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo) amorphous particulate systems: structure? 2D granular matter close to jamming spontaneous
cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano (Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo) amorphous particulate systems: structure? 2D granular matter close to jamming spontaneous
JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials
 JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials Drienerburght, University of Twente, February 25 - March 1, 2013 Speakers: Dirk van der Ende - Nico Gray - Detlef Lohse - Stefan Luding
JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials Drienerburght, University of Twente, February 25 - March 1, 2013 Speakers: Dirk van der Ende - Nico Gray - Detlef Lohse - Stefan Luding
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES Rheology S.C. BAYNE, 1 J.Y. Thompson 2 1 University of Michigan School of Dentistry, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-1078 sbayne@umich.edu 2 Nova Southeastern College of Dental Medicine, Ft.
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES Rheology S.C. BAYNE, 1 J.Y. Thompson 2 1 University of Michigan School of Dentistry, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-1078 sbayne@umich.edu 2 Nova Southeastern College of Dental Medicine, Ft.
Flow transitions in two-dimensional foams
 Flow transitions in two-dimensional foams Christopher Gilbreth, Scott Sullivan, and Michael Dennin Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California at Irvine, Irvine, California 92697-4575
Flow transitions in two-dimensional foams Christopher Gilbreth, Scott Sullivan, and Michael Dennin Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California at Irvine, Irvine, California 92697-4575
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 30 Mar 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 30 Mar 2017 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 30 Mar 2017](/thumbs/93/112293516.jpg) A viscous froth model adapted to wet foams Denny Vitasari a,b, Simon Cox a, a Institute of Mathematics, Physics and Computer Science, Aberystwyth University, UK b Department of Chemical Engineering, Universitas
A viscous froth model adapted to wet foams Denny Vitasari a,b, Simon Cox a, a Institute of Mathematics, Physics and Computer Science, Aberystwyth University, UK b Department of Chemical Engineering, Universitas
SMR/ Conference on Structure and Dynamics in Soft Matter and Biomolecules: From Single Molecules to Ensembles.
 SMR/1845-16 Conference on Structure and Dynamics in Soft Matter and Biomolecules: From Single Molecules to Ensembles 4-8 June 2007 Structure and dynamics in the physics of foams Denis WEAIRE School of
SMR/1845-16 Conference on Structure and Dynamics in Soft Matter and Biomolecules: From Single Molecules to Ensembles 4-8 June 2007 Structure and dynamics in the physics of foams Denis WEAIRE School of
Steady Couette flows of elastoviscoplastic fluids are non-unique
 Steady Couette flows of elastoviscoplastic fluids are non-unique I. Cheddadi, P. Saramito, and F. Graner 3,4 INRIA Paris - Rocquencourt, BANG team, Domaine de Voluceau, Rocquencourt, B.P. 5, 7853 Le Chesnay,
Steady Couette flows of elastoviscoplastic fluids are non-unique I. Cheddadi, P. Saramito, and F. Graner 3,4 INRIA Paris - Rocquencourt, BANG team, Domaine de Voluceau, Rocquencourt, B.P. 5, 7853 Le Chesnay,
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media
 Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
In-class exercises Day 1
 Physics 4488/6562: Statistical Mechanics http://www.physics.cornell.edu/sethna/teaching/562/ Material for Week 11 Exercises due Mon Apr 16 Last correction at April 16, 2018, 11:19 am c 2018, James Sethna,
Physics 4488/6562: Statistical Mechanics http://www.physics.cornell.edu/sethna/teaching/562/ Material for Week 11 Exercises due Mon Apr 16 Last correction at April 16, 2018, 11:19 am c 2018, James Sethna,
(Polymer rheology Analyzer with Sliplink. Tatsuya Shoji JCII, Doi Project
 Rheology Simulator PASTA (Polymer rheology Analyzer with Sliplink model of entanglement) Tatsuya Shoji JCII, Doi Project 0 sec -3 msec -6 sec -9 nsec -12 psec -15 fsec GOURMET SUSHI PASTA COGNAC MUFFIN
Rheology Simulator PASTA (Polymer rheology Analyzer with Sliplink model of entanglement) Tatsuya Shoji JCII, Doi Project 0 sec -3 msec -6 sec -9 nsec -12 psec -15 fsec GOURMET SUSHI PASTA COGNAC MUFFIN
Supplementary Information. Text S1:
 Supplementary Information Text S1: In order to characterize the change in visco-elastic response in the course of a shear thickening transition in a controlled shear stress flow, on a fresh sample of for
Supplementary Information Text S1: In order to characterize the change in visco-elastic response in the course of a shear thickening transition in a controlled shear stress flow, on a fresh sample of for
Viscoelasticity of Depletion-Induced Gels in Emulsion-Polymer Systems
 1918 Langmuir 1999, 15, 1918-1922 Viscoelasticity of Depletion-Induced Gels in Emulsion-Polymer Systems A. Meller,, T. Gisler,, D. A. Weitz, and J. Stavans*,, Department of Physics of Complex Systems,
1918 Langmuir 1999, 15, 1918-1922 Viscoelasticity of Depletion-Induced Gels in Emulsion-Polymer Systems A. Meller,, T. Gisler,, D. A. Weitz, and J. Stavans*,, Department of Physics of Complex Systems,
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM. Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics. July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter. 1.
 THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 126, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 126, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview. Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore
 Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore UGC-NRCM Summer School on Mechanical Property Characterization- June 2012 Overview of polymer
Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore UGC-NRCM Summer School on Mechanical Property Characterization- June 2012 Overview of polymer
Phys 563 Phase Transition and Renormalization groups Term paper 2010
 Phys 563 Phase Transition and Renormalization groups Term paper 2010 Instructor: Prof. Nigel Goldenfeld Title: Understanding glass-forming and jamming materials in the context of soft colloids Jian Yang
Phys 563 Phase Transition and Renormalization groups Term paper 2010 Instructor: Prof. Nigel Goldenfeld Title: Understanding glass-forming and jamming materials in the context of soft colloids Jian Yang
Rate dependent shear bands in a shear transformation zone model of amorphous solids
 Rate dependent shear bands in a shear transformation zone model of amorphous solids M. L. Manning, E. G. Daub, J. S. Langer, and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara,
Rate dependent shear bands in a shear transformation zone model of amorphous solids M. L. Manning, E. G. Daub, J. S. Langer, and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara,
University Graz / Austria Institut für Chemie Volker Ribitsch
 University Graz / Austria Institut für Chemie Volker Ribitsch 1 Rheology Oscillatory experiments Dynamic experiments Deformation of materials under non-steady conditions in the linear viscoelastic range
University Graz / Austria Institut für Chemie Volker Ribitsch 1 Rheology Oscillatory experiments Dynamic experiments Deformation of materials under non-steady conditions in the linear viscoelastic range
QENS in the Energy Domain: Backscattering and Time-of
 QENS in the Energy Domain: Backscattering and Time-of of-flight Alexei Sokolov Department of Polymer Science, The University of Akron Outline Soft Matter and Neutron Spectroscopy Using elastic scattering
QENS in the Energy Domain: Backscattering and Time-of of-flight Alexei Sokolov Department of Polymer Science, The University of Akron Outline Soft Matter and Neutron Spectroscopy Using elastic scattering
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 20 Apr 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 20 Apr 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 20 Apr 1998](/thumbs/80/81922994.jpg) Rheological constitutive equation for model of soft glassy materials Peter Sollich Department of Physics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EH9 3JZ, U.K., P.Sollich@ed.ac.uk arxiv:cond-mat/97121v2 [cond-mat.soft]
Rheological constitutive equation for model of soft glassy materials Peter Sollich Department of Physics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EH9 3JZ, U.K., P.Sollich@ed.ac.uk arxiv:cond-mat/97121v2 [cond-mat.soft]
Les Houches School of Foam: Rheology of Complex Fluids
 Les Houches School of Foam: Rheology of Complex Fluids Andrew Belmonte The W. G. Pritchard Laboratories Department of Mathematics, Penn State University 1 Fluid Dynamics (tossing a coin) Les Houches Winter
Les Houches School of Foam: Rheology of Complex Fluids Andrew Belmonte The W. G. Pritchard Laboratories Department of Mathematics, Penn State University 1 Fluid Dynamics (tossing a coin) Les Houches Winter
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry. Planetary Surfaces
 Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Aggregates: solid or liquid?
 Aggregates: solid or liquid? François Graner Polarity, Division and Morphogenesis team dir. Yohanns Bellaïche Génétique et Biologie du Développement UMR 3215, CNRS & Institut Curie, Paris, France 2011
Aggregates: solid or liquid? François Graner Polarity, Division and Morphogenesis team dir. Yohanns Bellaïche Génétique et Biologie du Développement UMR 3215, CNRS & Institut Curie, Paris, France 2011
Part III. Polymer Dynamics molecular models
 Part III. Polymer Dynamics molecular models I. Unentangled polymer dynamics I.1 Diffusion of a small colloidal particle I.2 Diffusion of an unentangled polymer chain II. Entangled polymer dynamics II.1.
Part III. Polymer Dynamics molecular models I. Unentangled polymer dynamics I.1 Diffusion of a small colloidal particle I.2 Diffusion of an unentangled polymer chain II. Entangled polymer dynamics II.1.
Stress anisotropy in shear-jammed packings of frictionless disks
 Stress anisotropy in shear-jammed packings of frictionless disks Sheng Chen, 1, 2 Weiwei Jin, 3, 2 Thibault Bertrand, 4 Mark D. Shattuck, 5 6, 7, 8, and Corey S. O Hern 1 Key Laboratory for Thermal Science
Stress anisotropy in shear-jammed packings of frictionless disks Sheng Chen, 1, 2 Weiwei Jin, 3, 2 Thibault Bertrand, 4 Mark D. Shattuck, 5 6, 7, 8, and Corey S. O Hern 1 Key Laboratory for Thermal Science
Rheology. What is rheology? From the root work rheo- Current: flow. Greek: rhein, to flow (river) Like rheostat flow of current
 Rheology What is rheology? From the root work rheo- Current: flow Greek: rhein, to flow (river) Like rheostat flow of current Rheology What physical properties control deformation? - Rock type - Temperature
Rheology What is rheology? From the root work rheo- Current: flow Greek: rhein, to flow (river) Like rheostat flow of current Rheology What physical properties control deformation? - Rock type - Temperature
Indiana University, January T. Witten, University of Chicago
 Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
Pharmaceutics I. Unit 6 Rheology of suspensions
 Pharmaceutics I اينالديصيدلينيات 1 Unit 6 Rheology of suspensions 1 Rheology, the science of the flow or deformation of matter (liquid or soft solid) under the effect of an applied force. It addresses
Pharmaceutics I اينالديصيدلينيات 1 Unit 6 Rheology of suspensions 1 Rheology, the science of the flow or deformation of matter (liquid or soft solid) under the effect of an applied force. It addresses
Subduction II Fundamentals of Mantle Dynamics
 Subduction II Fundamentals of Mantle Dynamics Thorsten W Becker University of Southern California Short course at Universita di Roma TRE April 18 20, 2011 Rheology Elasticity vs. viscous deformation η
Subduction II Fundamentals of Mantle Dynamics Thorsten W Becker University of Southern California Short course at Universita di Roma TRE April 18 20, 2011 Rheology Elasticity vs. viscous deformation η
Non contact measurement of viscoelastic properties of biopolymers
 Non contact measurement of viscoelastic properties of biopolymers Christelle Tisserand, Anton Kotzev, Mathias Fleury, Laurent Brunel, Pascal Bru, Gérard Meunier Formulaction, 10 impasse Borde Basse, 31240
Non contact measurement of viscoelastic properties of biopolymers Christelle Tisserand, Anton Kotzev, Mathias Fleury, Laurent Brunel, Pascal Bru, Gérard Meunier Formulaction, 10 impasse Borde Basse, 31240
Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials
 Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials Anaël Lemaître 1 and Craig Maloney 2 1 Institut Navier France 2 Department of Physics UC Santa Barbara Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 016001 (2004) Phys.
Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials Anaël Lemaître 1 and Craig Maloney 2 1 Institut Navier France 2 Department of Physics UC Santa Barbara Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 016001 (2004) Phys.
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions
 Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids
 Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Structural Signatures of Mobility in Jammed and Glassy Systems
 Lisa Manning Sam Schoenholz Ekin Dogus Cubuk Brad Malone Tim Kaxiras Joerg Rottler Rob Riggleman Jennifer Rieser Doug Durian Daniel Sussman Carl Goodrich Sid Nagel Structural Signatures of Mobility in
Lisa Manning Sam Schoenholz Ekin Dogus Cubuk Brad Malone Tim Kaxiras Joerg Rottler Rob Riggleman Jennifer Rieser Doug Durian Daniel Sussman Carl Goodrich Sid Nagel Structural Signatures of Mobility in
Linear shear of two dimensional foams
 Chapter 2 Linear shear of two dimensional foams In this chapter, we first review recent research on the rheology of two dimensional foams. We then describe experiments to unravel the connection between
Chapter 2 Linear shear of two dimensional foams In this chapter, we first review recent research on the rheology of two dimensional foams. We then describe experiments to unravel the connection between
Foundations of. Colloid Science SECOND EDITION. Robert J. Hunter. School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings. Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney
 Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
FOAMS IN MICROGRAVITY
 FOAMS IN MICROGRAVITY Denis Weaire and Simon Cox Department of Physics, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland dweaire@tcd.ie 1. Introduction Ordinary aqueous foam, which is our main subject in this paper,
FOAMS IN MICROGRAVITY Denis Weaire and Simon Cox Department of Physics, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland dweaire@tcd.ie 1. Introduction Ordinary aqueous foam, which is our main subject in this paper,
Dry granular flows: gas, liquid or solid?
 Dry granular flows: gas, liquid or solid? Figure 1: Forterre & Pouliquen, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mechanics, 2008 1 Characterizing size and size distribution Grains are not uniform (size, shape, ) Statistical
Dry granular flows: gas, liquid or solid? Figure 1: Forterre & Pouliquen, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mechanics, 2008 1 Characterizing size and size distribution Grains are not uniform (size, shape, ) Statistical
Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates
 Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates With MD we can only reproduce the dynamics of the system for 100 ns. Slow thermallyactivated processes, such as diffusion, cannot
Kinetic Monte Carlo: from transition probabilities to transition rates With MD we can only reproduce the dynamics of the system for 100 ns. Slow thermallyactivated processes, such as diffusion, cannot
Local description of the two-dimensional flow of foam through a contraction
 arxiv:97.952v2 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Dec 29 Local description of the two-dimensional flow of foam through a contraction Benjamin Dollet June 13, 213 Abstract The 2D flow of a foam confined in a Hele-Shaw
arxiv:97.952v2 [cond-mat.soft] 24 Dec 29 Local description of the two-dimensional flow of foam through a contraction Benjamin Dollet June 13, 213 Abstract The 2D flow of a foam confined in a Hele-Shaw
Shear rheology of polymer melts
 Shear rheology of polymer melts Dino Ferri dino.ferri@versalis.eni.com Politecnico Alessandria di Milano, 14/06/2002 22 nd October 2014 Outline - Review of some basic rheological concepts (simple shear,
Shear rheology of polymer melts Dino Ferri dino.ferri@versalis.eni.com Politecnico Alessandria di Milano, 14/06/2002 22 nd October 2014 Outline - Review of some basic rheological concepts (simple shear,
MSE 383, Unit 3-3. Joshua U. Otaigbe Iowa State University Materials Science & Engineering Dept.
 Dynamic Mechanical Behavior MSE 383, Unit 3-3 Joshua U. Otaigbe Iowa State University Materials Science & Engineering Dept. Scope Why DMA & TTS? DMA Dynamic Mechanical Behavior (DMA) Superposition Principles
Dynamic Mechanical Behavior MSE 383, Unit 3-3 Joshua U. Otaigbe Iowa State University Materials Science & Engineering Dept. Scope Why DMA & TTS? DMA Dynamic Mechanical Behavior (DMA) Superposition Principles
Experimental study of hydrogel sphere packings close to jamming
 Master Science de la matière Avril-Juillet 2013 Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon Université Claude Bernard Lyon I M2 Physique "Concepts & applications" Experimental study of hydrogel sphere packings close
Master Science de la matière Avril-Juillet 2013 Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon Université Claude Bernard Lyon I M2 Physique "Concepts & applications" Experimental study of hydrogel sphere packings close
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature. Nikolai V. Priezjev
 The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008](/thumbs/86/93817801.jpg) CD2dBS-v2 Convergence dynamics of 2-dimensional isotropic and anisotropic Bak-Sneppen models Burhan Bakar and Ugur Tirnakli Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ege University, 35100 Izmir, Turkey
CD2dBS-v2 Convergence dynamics of 2-dimensional isotropic and anisotropic Bak-Sneppen models Burhan Bakar and Ugur Tirnakli Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ege University, 35100 Izmir, Turkey
FLOWS IN LIQUID FOAMS
 FLOWS IN LIQUID FOAMS A finite element approach A. SAUGEY, E. JANIAUD, W. DRENCKHAN, S. HUTZLER, D. WEAIRE Physics Department,, TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN Facing a problem of fluid flow in a physical system,
FLOWS IN LIQUID FOAMS A finite element approach A. SAUGEY, E. JANIAUD, W. DRENCKHAN, S. HUTZLER, D. WEAIRE Physics Department,, TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN Facing a problem of fluid flow in a physical system,
Lecture 5. Rheology. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 5 Rheology Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton; unless noted otherwise Rheology is... the study of deformation and flow of
Lecture 5 Rheology Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton; unless noted otherwise Rheology is... the study of deformation and flow of
