Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis
|
|
|
- Valentine Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis
2 Elastic Networks A family of discrete model networks involving masses connected by springs 1 2 kk( ll)2 Disordered Interactions Central force springs Angle bending stiffness 1 2 κκ( θθ)2 Ordered Simple, good for: Analytic calculations Numerical simulations In any dimension
3 Why Elastic Networks Why we want to use elastic networks models ( as opposed to continuum elasticity?) Because many soft matter systems are marginal solids (both solid and liquid characteristics). Elastic networks help understand the microscopic origin of different classes of marginal solids Elastic networks also provide ideas of making new metamaterials with novel properties Topological Mechanics
4 Experimental Systems as Elastic Networks Elastic networks capture the essential physics of many interesting systems Glasses (silica, TEM image, Huang et al, Science 2013) Granular matter Colloids and Emulsion (E. Weeks group, Emory) Biopolymer networks (collagen, Ovaska et al, 2017)
5 Experimental Systems as Elastic Networks Elastic networks capture the essential physics of many interesting systems Protein rigidity/function (Chubynsky et al, 2008) Mechanical metamaterials design (J. Greer s group, Caltech) Structural phase transitions in crystals (α-β transition of cristobalites)
6 Why Elastic Network Models Are Useful? With generalization, elastic networks can also be used to study: Foams (D. Durian s group, Penn) Biological tissues (Bi et al, Nat. Phys. 2015) Origami & Kirigami (Evans et al, PRE 2015) and many more!
7 How to Understand Elastic Networks? First Step: Mechanical Stability Floppy mode Vs. Floppy How to find out? Mechanically Stable
8 Maxwell s Counting # of zero modes (normal modes cost 0 elastic energy) NN 0 = NN dd.oo.ff NN CC Degrees of freedom Constraints Central force bonds between point-like particles NN dd NN bb # of particles * spatial dimension Bonds # of floppy modes (excluding trivial modes) NN mm = NN 0 dd(dd+1) 2 Trivial translations and rotations of the whole system NN 0 = = 4 NN 0 = = 3 NN mm = 4 3 = 1 Floppy mode Vs. NN mm = 3 3 = 0 Floppy Mechanically Stable J. C. Maxwell, Phil. Mag. 27, 598 (1864).
9 Maxwell s Counting on Infinitely Large Systems # of zero modes (normal modes cost 0 elastic energy) NN 0 = NN dd.oo.ff NN CC Degrees of freedom Constraints Central force bonds between point-like particles NN dd NN bb # of particles * spatial dimension Bonds # of floppy modes (excluding trivial modes) NN mm = NN 0 dd(dd+1) 2 of O(1) and can be dropped for large system Trivial translations and rotations of the whole system NN mm = NN dd NN bb = NN dd NN zz /2 In order to have mechanical stability zz : average coordination number e.g. zz = 5 particle zz 2222 for stability J. C. Maxwell, Phil. Mag. 27, 598 (1864).
10 Periodic Lattices Critical condition for mechanical stability: zz = 2222 (assuming only NN central force interactions) z = 3 < 2d z = 2d z = 6 > 2d Floppy Extensive # of floppy modes Maxwell Lattices How many floppy modes? Over-constrained No floppy modes
11 Mechanical Critical Systems With zz = 2dd Critical condition for mechanical stability: zz = 2222 Example 1: Rigidity percolation on a central-force lattice Randomly take off bonds zz = 6pp When does it lose rigidity? pp < 1 pp = 1 pp cc /3 pp Numerical value Using (meanfield) counting rule zz = 2222 Feng and Sen, PRL 52, 216 (1984). Feng and Thorpe, PRB 31, 276 (1985). Feng, Sen, Halperin, and Lobb, PRB 30, 5386 (1984).
12 Mechanical Critical Systems With zz = 2dd Critical condition for mechanical stability: zz = 2222 Example 2: Jamming of frictionless particles (contact repulsive interactions) Non-overlapped liquid Overlapped solid Increasing density J φ C φ Random close packing Isostaticity zz = zz CC = 2222 A. J. Liu and S. R. Nagel, Nature 396 N6706, 21 (1998). C. S. O Hern, et al., Phys. Rev. E 68, (2003).
13 Classification of Systems at zz = 2dd? Both rigidity percolation and jamming: zz = 2222 Different universality classes (correlation length scaling, elastic moduli scaling, etc ) Are there other universality classes of rigidity transitions at zz = 2222? Elastic network models can help us understand this Main Reference of my lectures: Lubensky, T. C., et al. "Phonons and elasticity in critically coordinated lattices." Reports on Progress in Physics 78.7 (2015):
14 Rich Physics of Critical Mechanical Structures Interesting fundamental questions: e.g.: Cut a finite piece of Maxwell lattice (zz = 2222) Deficit of constraints on the boundary # of floppy modes Size of boundary But where are these modes located? Control of floppy modes Program mechanical Response
15 Where Are The Floppy Modes? Case I. Floppy modes localized at where you cut Example: twisted kagome Floppy modes on all edges Described by conformal transformations Periodic BC in x K. Sun, A. Souslov, X. Mao, and T. C. Lubensky, PNAS 109, (2012).
16 Where Are The Floppy Modes? Case II. Floppy modes are plane waves Example: regular kagome regular square Periodic BC in x
17 Where Are The Floppy Modes? Case III. Floppy modes are topologically protected edge modes on one side Example: deformed kagome (arrows show a pair of modes) Soft edge Topological polarization RR TT Hard edge Periodic BC in x C. L. Kane and T. C. Lubensky, Nat. Phys. 10, 39 (2014).
18 Where Are The Floppy Modes? Case IV. Floppy modes are topologically protected Weyl modes in the bulk Example: deformed square (4 site per cell) (arrows show a Weyl mode) Rocklin, Chen, Falk, Vitelli & Lubensky, PRL, 116, (2016)
19 Nonlinear Floppy Modes: Mechanisms What if an elastic network has NN 0 > 0? Finite systems: A more interesting example: Floppy mode Following the floppy mode to nonlinear order: Mechanism Theo Jansen s walking mechanism and Strandbeest (wind powered robot using this mechanism) Critical mechanical structures : structures close to mechanical instability and exhibit a small number of floppy modes
20 Second Lecture Slides
21 Topological 1D Chain 1D Rotor Chain C. L. Kane and T. C. Lubensky, Nat. Phys. 10, 39 (2014). Chen, Upadhyaya and Vitelli, PNAS 111, (2014).
22 Topological 1D Chain: Soliton 1D Rotor Chain: floppy mode beyond linear order topological soliton C. L. Kane and T. C. Lubensky, Nat. Phys. 10, 39 (2014). Chen, Upadhyaya and Vitelli, PNAS 111, (2014).
23 2D Lattices: Topological Kagome Lattice Soft edge Topological polarization RR TT Hard edge Periodic BC in x C. L. Kane and T. C. Lubensky, Nat. Phys. 10, 39 (2014).
24 Reconfigure Topological Kagome Using Soft Strain All Maxwell lattices have at least one macroscopic soft deformation: θθ Does it change the topological structures of the phonons? Non-polarized RR TT RR TT Non-polarized θθ 1 θθ 2 θθ 3 θθ aa 2 aa 1 θθ What happens at the topological transitions θθ 1, θθ 2, θθ 3? Rocklin, Zhou, Sun, and Mao, Nat Comm, 8, (2017)
25 What happens at the transition? Evolution of a pair of floppy edge modes (determined by topological polarization RR TT ) a b Metallic state c Soft edge Insulating states with different topologies θθ < θθ 1 d 1 Hard edge θθ = θθ 1 RR TT Hard edge θθ > θθ 1 Edge Stiffness Soft edge θθ Transformable mechanical metamaterial Rocklin, Zhou, Sun, and Mao, Nat Comm, 8, (2017)
26 Rigid connector Hinge Webpage of video: /research/ttmm/ttmm.html
27 Brandeis Page 1 Tuesday, May 30, :03 AM
28 Brandeis Page 2
29 Brandeis Page 3
30 Brandeis Page 4
31 Brandeis Page 5
32 Brandeis Page 6
33 Brandeis Page 7
Frames near Mechanical Collapse
 Frames near Mechanical Collapse Xiaming Mao (Umich) Kai Sun (Umich) Charlie Kane (Penn) Anton Souslov (Ga Tech) Olaf Stenull (Penn) Zeb Rocklin (Umich) Bryan Chen (Leiden) Vincenzo Vitelli (Leiden) James
Frames near Mechanical Collapse Xiaming Mao (Umich) Kai Sun (Umich) Charlie Kane (Penn) Anton Souslov (Ga Tech) Olaf Stenull (Penn) Zeb Rocklin (Umich) Bryan Chen (Leiden) Vincenzo Vitelli (Leiden) James
Xiaoming Mao. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania. Collaborators: Tom Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu
 Xiaoing Mao Departent of Physics and Astronoy, University of Pennsylvania Collaborators: To Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu Feb., 009 What is isostaticity? Isostatic systes are at the onset
Xiaoing Mao Departent of Physics and Astronoy, University of Pennsylvania Collaborators: To Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu Feb., 009 What is isostaticity? Isostatic systes are at the onset
Jamming and the Anticrystal
 Jamming and the Anticrystal Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Carl Goodrich Corey S. O Hern Leo E. Silbert Vincenzo Vitelli Ning Xu Sidney Nagel UPenn Yale SIUC
Jamming and the Anticrystal Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Carl Goodrich Corey S. O Hern Leo E. Silbert Vincenzo Vitelli Ning Xu Sidney Nagel UPenn Yale SIUC
Workshop on Sphere Packing and Amorphous Materials July 2011
 2254-16 Workshop on Sphere Packing and Amorphous Materials 25-29 July 2011 Random Spring Networks vs. Soft Sphere Packings: Jamming Meets Percolation Wouter G. ELLENBROEK Eindhoven Technical University,
2254-16 Workshop on Sphere Packing and Amorphous Materials 25-29 July 2011 Random Spring Networks vs. Soft Sphere Packings: Jamming Meets Percolation Wouter G. ELLENBROEK Eindhoven Technical University,
Topological Phonons, Edge States, and Guest Modes. 5/17/2016 Zanjan School
 Topological Phonons, Edge States, and Guest Modes Topological Defects Closed path in real space Path in order parameter space: topological invariant Periodic Brillouin Zone Function on torus Torus It no
Topological Phonons, Edge States, and Guest Modes Topological Defects Closed path in real space Path in order parameter space: topological invariant Periodic Brillouin Zone Function on torus Torus It no
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids
 Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 12, 2014
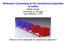 Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 1, 014 What is role of (dis)order for mechanical behavior? Andrea J. Liu Carl Goodrich Justin
Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 1, 014 What is role of (dis)order for mechanical behavior? Andrea J. Liu Carl Goodrich Justin
The bulk modulus of covalent random networks
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9 (1997) 1983 1994. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(97)77754-3 The bulk modulus of covalent random networks B R Djordjević and M F Thorpe Department of Physics and Astronomy
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9 (1997) 1983 1994. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(97)77754-3 The bulk modulus of covalent random networks B R Djordjević and M F Thorpe Department of Physics and Astronomy
Phonons and elasticity in critically coordinated lattices
 REVIEW ARTICLE Phonons and elasticity in critically coordinated lattices Contents T C Lubensky 1, C L Kane 1, Xiaoming Mao 2, A Souslov 3 and Kai Sun 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
REVIEW ARTICLE Phonons and elasticity in critically coordinated lattices Contents T C Lubensky 1, C L Kane 1, Xiaoming Mao 2, A Souslov 3 and Kai Sun 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
Review of Last Class 1
 Review of Last Class 1 X-Ray diffraction of crystals: the Bragg formulation Condition of diffraction peak: 2dd sin θθ = nnλλ Review of Last Class 2 X-Ray diffraction of crystals: the Von Laue formulation
Review of Last Class 1 X-Ray diffraction of crystals: the Bragg formulation Condition of diffraction peak: 2dd sin θθ = nnλλ Review of Last Class 2 X-Ray diffraction of crystals: the Von Laue formulation
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 8 Feb 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 8 Feb 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 8 Feb 2018](/thumbs/79/79710473.jpg) Folding mechanisms at finite temperature arxiv:180.0704v1 [cond-mat.soft] 8 Feb 018 D. Zeb Rocklin, 1,, 3 Vincenzo Vitelli, 4, 5, 6 and Xiaoming Mao 1 1 Department of Physics, University of Michigan, 450
Folding mechanisms at finite temperature arxiv:180.0704v1 [cond-mat.soft] 8 Feb 018 D. Zeb Rocklin, 1,, 3 Vincenzo Vitelli, 4, 5, 6 and Xiaoming Mao 1 1 Department of Physics, University of Michigan, 450
Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids
 Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids Atsushi Ikeda Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University Atsushi Ikeda & Ludovic Berthier Phys. Rev. E 92,
Thermal fluctuations, mechanical response, and hyperuniformity in jammed solids Atsushi Ikeda Fukui Institute for Fundamental Chemistry, Kyoto University Atsushi Ikeda & Ludovic Berthier Phys. Rev. E 92,
Active Stresses and Self-organization in Cytoskeletal Networks
 Active Stresses and Self-organization in Cytoskeletal Networks Cytoskeleton: rich mechanics, dynamics and activity Mechanics: nonlinear elasticity, stiffening, anomalous stresses Active stresses and non-equilibrium
Active Stresses and Self-organization in Cytoskeletal Networks Cytoskeleton: rich mechanics, dynamics and activity Mechanics: nonlinear elasticity, stiffening, anomalous stresses Active stresses and non-equilibrium
Mechanics of Granular Matter
 Mechanics of Granular Matter Mechanics of Granular Matter Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Published by
Mechanics of Granular Matter Mechanics of Granular Matter Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Published by
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 13 Feb 2015
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 13 Feb 2015 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 13 Feb 2015](/thumbs/73/68818601.jpg) Tuning by pruning: exploiting disorder for global response and the principle of bond-level independence Carl P. Goodrich and Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia,
Tuning by pruning: exploiting disorder for global response and the principle of bond-level independence Carl P. Goodrich and Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia,
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
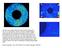 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
Structural Signatures of Mobility in Jammed and Glassy Systems
 Lisa Manning Sam Schoenholz Ekin Dogus Cubuk Brad Malone Tim Kaxiras Joerg Rottler Rob Riggleman Jennifer Rieser Doug Durian Daniel Sussman Carl Goodrich Sid Nagel Structural Signatures of Mobility in
Lisa Manning Sam Schoenholz Ekin Dogus Cubuk Brad Malone Tim Kaxiras Joerg Rottler Rob Riggleman Jennifer Rieser Doug Durian Daniel Sussman Carl Goodrich Sid Nagel Structural Signatures of Mobility in
Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Different ways to increase the internal energy of system: 2 Joule s apparatus
Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Different ways to increase the internal energy of system: 2 Joule s apparatus
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 7 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 7 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 7 Nov 2016](/thumbs/72/66748703.jpg) Criticality and mechanical enhancement in composite fibre networks Jan Maarten van Doorn, Luuk Lageschaar, Joris Sprakel, and Jasper van der Gucht arxiv:1611.01991v1 [cond-mat.soft] 7 Nov 2016 Physical
Criticality and mechanical enhancement in composite fibre networks Jan Maarten van Doorn, Luuk Lageschaar, Joris Sprakel, and Jasper van der Gucht arxiv:1611.01991v1 [cond-mat.soft] 7 Nov 2016 Physical
JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials
 JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials Drienerburght, University of Twente, February 25 - March 1, 2013 Speakers: Dirk van der Ende - Nico Gray - Detlef Lohse - Stefan Luding
JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials Drienerburght, University of Twente, February 25 - March 1, 2013 Speakers: Dirk van der Ende - Nico Gray - Detlef Lohse - Stefan Luding
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications
 6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 29: Electron-phonon Scattering Outline Bloch Electron Scattering Deformation Potential Scattering LCAO Estimation of Deformation Potential Matrix Element
6.730 Physics for Solid State Applications Lecture 29: Electron-phonon Scattering Outline Bloch Electron Scattering Deformation Potential Scattering LCAO Estimation of Deformation Potential Matrix Element
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011](/thumbs/91/104659018.jpg) arxiv:1006.2365v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011 The jamming scenario an introduction and outlook Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA
arxiv:1006.2365v2 [cond-mat.soft] 27 Jan 2011 The jamming scenario an introduction and outlook Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov 2013
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov 2013 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov 2013](/thumbs/84/91227656.jpg) Topological Boundary Modes in Isostatic Lattices C. L. Kane and T. C. Lubensky Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 1914 arxiv:138.554v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov
Topological Boundary Modes in Isostatic Lattices C. L. Kane and T. C. Lubensky Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 1914 arxiv:138.554v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov
Modeling athermal sub-isostatic fiber networks
 Chapter 2 Modeling athermal sub-isostatic fiber networks A.J. Licup, A. Sharma, and F.C. MacKintosh. Elastic regimes of sub-isostatic athermal fiber networks. Physical Review E 93(1):012407, 2016. 15 Chapter
Chapter 2 Modeling athermal sub-isostatic fiber networks A.J. Licup, A. Sharma, and F.C. MacKintosh. Elastic regimes of sub-isostatic athermal fiber networks. Physical Review E 93(1):012407, 2016. 15 Chapter
collisions inelastic, energy is dissipated and not conserved
 LECTURE 1 - Introduction to Granular Materials Jamming, Random Close Packing, The Isostatic State Granular materials particles only interact when they touch hard cores: rigid, incompressible, particles
LECTURE 1 - Introduction to Granular Materials Jamming, Random Close Packing, The Isostatic State Granular materials particles only interact when they touch hard cores: rigid, incompressible, particles
Symmetry Protected Topological Insulators and Semimetals
 Symmetry Protected Topological Insulators and Semimetals I. Introduction : Many examples of topological band phenomena II. Recent developments : - Line node semimetal Kim, Wieder, Kane, Rappe, PRL 115,
Symmetry Protected Topological Insulators and Semimetals I. Introduction : Many examples of topological band phenomena II. Recent developments : - Line node semimetal Kim, Wieder, Kane, Rappe, PRL 115,
Linearized Theory: Sound Waves
 Linearized Theory: Sound Waves In the linearized limit, Λ iα becomes δ iα, and the distinction between the reference and target spaces effectively vanishes. K ij (q): Rigidity matrix Note c L = c T in
Linearized Theory: Sound Waves In the linearized limit, Λ iα becomes δ iα, and the distinction between the reference and target spaces effectively vanishes. K ij (q): Rigidity matrix Note c L = c T in
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties
 2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 5 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 5 Aug 2015 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 5 Aug 2015](/thumbs/73/68168064.jpg) Selective buckling via states of self-stress in topological metamaterials Jayson Paulose, Anne S. Meeussen, and Vincenzo Vitelli Instituut-Lorentz, Universiteit Leiden, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands
Selective buckling via states of self-stress in topological metamaterials Jayson Paulose, Anne S. Meeussen, and Vincenzo Vitelli Instituut-Lorentz, Universiteit Leiden, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands
Breakdown of Elasticity Theory for Jammed Hard-Particle Packings: Conical Nonlinear Constitutive Theory
 Breakdown of Elasticity Theory for Jammed Hard-Particle Packings: Conical Nonlinear Constitutive Theory S. Torquato, 1,2 A. Donev 2,3, and F. H. Stillinger 1 Department of Chemistry, 1 Princeton Materials
Breakdown of Elasticity Theory for Jammed Hard-Particle Packings: Conical Nonlinear Constitutive Theory S. Torquato, 1,2 A. Donev 2,3, and F. H. Stillinger 1 Department of Chemistry, 1 Princeton Materials
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 11 Jul 2014
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 11 Jul 2014 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 11 Jul 2014](/thumbs/71/65765159.jpg) Topological mechanisms as classical spinor fields Vincenzo Vitelli, Nitin Upadhyaya, and Bryan Gin-ge Chen Instituut-Lorentz, Universiteit Leiden, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands A mechanism is a zero-energy
Topological mechanisms as classical spinor fields Vincenzo Vitelli, Nitin Upadhyaya, and Bryan Gin-ge Chen Instituut-Lorentz, Universiteit Leiden, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands A mechanism is a zero-energy
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings. Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney
 Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
Module 6 (Lecture 22) LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE
 Module 6 (Lecture ) LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE 1.1 LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE DUE TO SURCHARGE 1. ACTIVE PRESSURE FOR WALL ROTATION ABOUT TOP- BRACED CUT 1.3 ACTIVE EARTH PRESSURE FOR TRANSLATION OF RETAINING
Module 6 (Lecture ) LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE 1.1 LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE DUE TO SURCHARGE 1. ACTIVE PRESSURE FOR WALL ROTATION ABOUT TOP- BRACED CUT 1.3 ACTIVE EARTH PRESSURE FOR TRANSLATION OF RETAINING
Physical Pendulum, Torsion Pendulum
 [International Campus Lab] Physical Pendulum, Torsion Pendulum Objective Investigate the motions of physical pendulums and torsion pendulums. Theory ----------------------------- Reference --------------------------
[International Campus Lab] Physical Pendulum, Torsion Pendulum Objective Investigate the motions of physical pendulums and torsion pendulums. Theory ----------------------------- Reference --------------------------
Lecture No. 1 Introduction to Method of Weighted Residuals. Solve the differential equation L (u) = p(x) in V where L is a differential operator
 Lecture No. 1 Introduction to Method of Weighted Residuals Solve the differential equation L (u) = p(x) in V where L is a differential operator with boundary conditions S(u) = g(x) on Γ where S is a differential
Lecture No. 1 Introduction to Method of Weighted Residuals Solve the differential equation L (u) = p(x) in V where L is a differential operator with boundary conditions S(u) = g(x) on Γ where S is a differential
REVIEW : INTERATOMIC BONDING : THE LENNARD-JONES POTENTIAL & RUBBER ELASTICITY I DERIVATION OF STRESS VERSUS STRAIN LAWS FOR RUBBER ELASTICITY
 LECTURE #3 : 3.11 MECHANICS O MATERIALS 03 INSTRUCTOR : Professor Christine Ortiz OICE : 13-40 PHONE : 45-3084 WWW : http://web.mit.edu/cortiz/www REVIEW : INTERATOMIC BONDING : THE LENNARD-JONES POTENTIAL
LECTURE #3 : 3.11 MECHANICS O MATERIALS 03 INSTRUCTOR : Professor Christine Ortiz OICE : 13-40 PHONE : 45-3084 WWW : http://web.mit.edu/cortiz/www REVIEW : INTERATOMIC BONDING : THE LENNARD-JONES POTENTIAL
4/14/11. Chapter 12 Static equilibrium and Elasticity Lecture 2. Condition for static equilibrium. Stability An object is in equilibrium:
 About Midterm Exam 3 When and where Thurs April 21 th, 5:45-7:00 pm Rooms: Same as Exam I and II, See course webpage. Your TA will give a brief review during the discussion session. Coverage: Chapts 9
About Midterm Exam 3 When and where Thurs April 21 th, 5:45-7:00 pm Rooms: Same as Exam I and II, See course webpage. Your TA will give a brief review during the discussion session. Coverage: Chapts 9
On the Collapse of Locally Isostatic Networks
 On the Collapse of Locally Isostatic Networks By Vitaliy Kapko 1, M.M.J. Treacy 1, M.F. Thorpe 1, S.D. Guest 2 1 Arizona State University, Department of Physics and Astronomy, P.O. Box 871504, Tempe, AZ,
On the Collapse of Locally Isostatic Networks By Vitaliy Kapko 1, M.M.J. Treacy 1, M.F. Thorpe 1, S.D. Guest 2 1 Arizona State University, Department of Physics and Astronomy, P.O. Box 871504, Tempe, AZ,
Vibrational properties and phonon transport of amorphous solids
 June 29th (Fri.), 2018 Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Japan Rheology of disordered particles suspensions, glassy and granular materials 10:15-11:05, 40mins. talk and 10mins.
June 29th (Fri.), 2018 Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Japan Rheology of disordered particles suspensions, glassy and granular materials 10:15-11:05, 40mins. talk and 10mins.
Two-dimensional Phosphorus Carbide as Promising Anode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Two-dimensional Phosphorus Carbide as Promising
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Two-dimensional Phosphorus Carbide as Promising
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Elasticity of biological gels
 Seminar II Elasticity of biological gels Author: Gašper Gregorič Mentor: assoc. prof. Primož Ziherl Ljubljana, February 2014 Abstract In the seminar we discuss the elastic behavior of biological gels,
Seminar II Elasticity of biological gels Author: Gašper Gregorič Mentor: assoc. prof. Primož Ziherl Ljubljana, February 2014 Abstract In the seminar we discuss the elastic behavior of biological gels,
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming
 Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
Advantages of a Finite Extensible Nonlinear Elastic Potential in Lattice Boltzmann Simulations
 The Hilltop Review Volume 7 Issue 1 Winter 2014 Article 10 December 2014 Advantages of a Finite Extensible Nonlinear Elastic Potential in Lattice Boltzmann Simulations Tai-Hsien Wu Western Michigan University
The Hilltop Review Volume 7 Issue 1 Winter 2014 Article 10 December 2014 Advantages of a Finite Extensible Nonlinear Elastic Potential in Lattice Boltzmann Simulations Tai-Hsien Wu Western Michigan University
Indiana University, January T. Witten, University of Chicago
 Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
Structure 1. Glass formation in chalcogenide system Structure models
 Structure 1 Glass formation in chalcogenide system Structure models 1 Explaining glass formation? As for glass formation in the chalcogenide system, there are theories, concepts, criteria, semi-empirical
Structure 1 Glass formation in chalcogenide system Structure models 1 Explaining glass formation? As for glass formation in the chalcogenide system, there are theories, concepts, criteria, semi-empirical
LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display. May, protests. Fashion school is in top-3 in USA. Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA
 LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display May, 4 1970 protests Fashion school is in top-3 in USA Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA Topological insulators driven by electron spin Maxim Dzero Kent
LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display May, 4 1970 protests Fashion school is in top-3 in USA Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA Topological insulators driven by electron spin Maxim Dzero Kent
Mechanical behavior of Tendon and Skin 1. The nonlinear mechanical behavior of tendon. 2. The extensibility of skin.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.523J: Cell-Matrix Mechanics Prof. Ioannis Yannas Mechanical behavior of Tendon and Skin 1. The nonlinear mechanical behavior of tendon. 2. The
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.523J: Cell-Matrix Mechanics Prof. Ioannis Yannas Mechanical behavior of Tendon and Skin 1. The nonlinear mechanical behavior of tendon. 2. The
Emergent Frontiers in Quantum Materials:
 Emergent Frontiers in Quantum Materials: High Temperature superconductivity and Topological Phases Jiun-Haw Chu University of Washington The nature of the problem in Condensed Matter Physics Consider a
Emergent Frontiers in Quantum Materials: High Temperature superconductivity and Topological Phases Jiun-Haw Chu University of Washington The nature of the problem in Condensed Matter Physics Consider a
Quantum spin systems - models and computational methods
 Summer School on Computational Statistical Physics August 4-11, 2010, NCCU, Taipei, Taiwan Quantum spin systems - models and computational methods Anders W. Sandvik, Boston University Lecture outline Introduction
Summer School on Computational Statistical Physics August 4-11, 2010, NCCU, Taipei, Taiwan Quantum spin systems - models and computational methods Anders W. Sandvik, Boston University Lecture outline Introduction
20.GEM GEM4 Summer School: Cell and Molecular Biomechanics in Medicine: Cancer Summer 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 20.GEM GEM4 Summer School: Cell and Molecular Biomechanics in Medicine: Cancer Summer 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 20.GEM GEM4 Summer School: Cell and Molecular Biomechanics in Medicine: Cancer Summer 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
Quantitative Mappings from Symmetry to Topology
 Z. Song, Z. Fang and CF, PRL 119, 246402 (2017) CF and L. Fu, arxiv:1709.01929 Z. Song, T. Zhang, Z. Fang and CF arxiv:1711.11049 Z. Song, T. Zhang and CF arxiv:1711.11050 Quantitative Mappings from Symmetry
Z. Song, Z. Fang and CF, PRL 119, 246402 (2017) CF and L. Fu, arxiv:1709.01929 Z. Song, T. Zhang, Z. Fang and CF arxiv:1711.11049 Z. Song, T. Zhang and CF arxiv:1711.11050 Quantitative Mappings from Symmetry
Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups
 Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups Haruki Watanabe University of Tokyo [Noninteracting] Sci Adv (2016) PRL (2016) Nat Commun (2017) (New) arxiv:1707.01903 [Interacting]
Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups Haruki Watanabe University of Tokyo [Noninteracting] Sci Adv (2016) PRL (2016) Nat Commun (2017) (New) arxiv:1707.01903 [Interacting]
Lecture 3 Transport in Semiconductors
 EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 3 Transport in Semiconductors Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken,
EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 3 Transport in Semiconductors Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 2015](/thumbs/92/110516249.jpg) Mechanical Weyl Modes in Topological Maxwell Lattices arxiv:151.497v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 215 D. Zeb Rocklin, 1 Bryan Gin ge Chen, 2, Martin Falk, 3 Vincenzo Vitelli, 2 and T. C. Lubensky 4 1 Department
Mechanical Weyl Modes in Topological Maxwell Lattices arxiv:151.497v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 215 D. Zeb Rocklin, 1 Bryan Gin ge Chen, 2, Martin Falk, 3 Vincenzo Vitelli, 2 and T. C. Lubensky 4 1 Department
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature. Nikolai V. Priezjev
 The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
From Atoms to Materials: Predictive Theory and Simulations
 From Atoms to Materials: Predictive Theory and Simulations Week 3 Lecture 4 Potentials for metals and semiconductors Ale Strachan strachan@purdue.edu School of Materials Engineering & Birck anotechnology
From Atoms to Materials: Predictive Theory and Simulations Week 3 Lecture 4 Potentials for metals and semiconductors Ale Strachan strachan@purdue.edu School of Materials Engineering & Birck anotechnology
Manipulator Dynamics (1) Read Chapter 6
 Manipulator Dynamics (1) Read Capter 6 Wat is dynamics? Study te force (torque) required to cause te motion of robots just like engine power required to drive a automobile Most familiar formula: f = ma
Manipulator Dynamics (1) Read Capter 6 Wat is dynamics? Study te force (torque) required to cause te motion of robots just like engine power required to drive a automobile Most familiar formula: f = ma
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems
 Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
Sculptural Form finding with bending action
 Sculptural Form finding with bending action Jens Olsson 1, Mats Ander 2, Al Fisher 3, Chris J K Williams 4 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Dept. of Architecture, 412 96 Göteborg, jens.gustav.olsson@gmail.com
Sculptural Form finding with bending action Jens Olsson 1, Mats Ander 2, Al Fisher 3, Chris J K Williams 4 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Dept. of Architecture, 412 96 Göteborg, jens.gustav.olsson@gmail.com
Work, Energy, and Power. Chapter 6 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Work, Energy, and Power Chapter 6 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 With the knowledge we got so far, we can handle the situation on the left but not the one on the right.
Work, Energy, and Power Chapter 6 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 With the knowledge we got so far, we can handle the situation on the left but not the one on the right.
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming
 Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Structure 1. Glass formation in chalcogenide system Structural models
 Structure 1 Glass formation in chalcogenide system Structural models 1 Explaining glass formation? As for glass formation in the chalcogenide system, there are theories, concepts, criteria, semi-empirical
Structure 1 Glass formation in chalcogenide system Structural models 1 Explaining glass formation? As for glass formation in the chalcogenide system, there are theories, concepts, criteria, semi-empirical
Lecture 6. Notes on Linear Algebra. Perceptron
 Lecture 6. Notes on Linear Algebra. Perceptron COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Andrey Kan Copyright: University of Melbourne This lecture Notes on linear algebra Vectors
Lecture 6. Notes on Linear Algebra. Perceptron COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Andrey Kan Copyright: University of Melbourne This lecture Notes on linear algebra Vectors
Introduction to Computer Simulations of Soft Matter Methodologies and Applications Boulder July, 19-20, 2012
 Introduction to Computer Simulations of Soft Matter Methodologies and Applications Boulder July, 19-20, 2012 K. Kremer Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research, Mainz Overview Simulations, general considerations
Introduction to Computer Simulations of Soft Matter Methodologies and Applications Boulder July, 19-20, 2012 K. Kremer Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research, Mainz Overview Simulations, general considerations
Modelling and numerical simulation of the wrinkling evolution for thermo-mechanical loading cases
 Modelling and numerical simulation of the wrinkling evolution for thermo-mechanical loading cases Georg Haasemann Conrad Kloß 1 AIMCAL Conference 2016 MOTIVATION Wrinkles in web handling system Loss of
Modelling and numerical simulation of the wrinkling evolution for thermo-mechanical loading cases Georg Haasemann Conrad Kloß 1 AIMCAL Conference 2016 MOTIVATION Wrinkles in web handling system Loss of
Frictional Jamming & MRJ/RLP crossover
 Frictional Jamming & MRJ/RLP crossover Stefanos Papanikolaou (Yale University) Ref: SP, C. S. O Hern, M. D. Shattuck, arxiv:1207.6010 (2012) Outline Isostaticity in Jamming, Friction and the failure of
Frictional Jamming & MRJ/RLP crossover Stefanos Papanikolaou (Yale University) Ref: SP, C. S. O Hern, M. D. Shattuck, arxiv:1207.6010 (2012) Outline Isostaticity in Jamming, Friction and the failure of
Defect-Driven Structures for Self-Assembly
 Defect-Driven Structures for Self-Assembly ICTP, Trieste May 13, 2011 Mark Bowick Syracuse University MJB and L. Giomi, Adv. Phys. 58, 449-563 (2009) (arxiv:0812.3064) Introduction Among soft and biological
Defect-Driven Structures for Self-Assembly ICTP, Trieste May 13, 2011 Mark Bowick Syracuse University MJB and L. Giomi, Adv. Phys. 58, 449-563 (2009) (arxiv:0812.3064) Introduction Among soft and biological
Lecture 10. Rigid Body Transformation & C-Space Obstacles. CS 460/560 Introduction to Computational Robotics Fall 2017, Rutgers University
 CS 460/560 Introduction to Computational Robotics Fall 017, Rutgers University Lecture 10 Rigid Body Transformation & C-Space Obstacles Instructor: Jingjin Yu Outline Rigid body, links, and joints Task
CS 460/560 Introduction to Computational Robotics Fall 017, Rutgers University Lecture 10 Rigid Body Transformation & C-Space Obstacles Instructor: Jingjin Yu Outline Rigid body, links, and joints Task
Lecture 4: viscoelasticity and cell mechanics
 Teaser movie: flexible robots! R. Shepherd, Whitesides group, Harvard 1 Lecture 4: viscoelasticity and cell mechanics S-RSI Physics Lectures: Soft Condensed Matter Physics Jacinta C. Conrad University
Teaser movie: flexible robots! R. Shepherd, Whitesides group, Harvard 1 Lecture 4: viscoelasticity and cell mechanics S-RSI Physics Lectures: Soft Condensed Matter Physics Jacinta C. Conrad University
Floppy modes and the free energy: Rigidity and connectivity percolation on Bethe lattices
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 1999 Floppy modes and the free energy: Rigidity and connectivity percolation on Bethe lattices P. M. Duxbury, D. J. Jacobs, and M. F. Thorpe Department of
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 59, NUMBER 2 FEBRUARY 1999 Floppy modes and the free energy: Rigidity and connectivity percolation on Bethe lattices P. M. Duxbury, D. J. Jacobs, and M. F. Thorpe Department of
Dirac fermions in condensed matters
 Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 5 Dec 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 5 Dec 2011 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 5 Dec 2011](/thumbs/88/114657689.jpg) Isostaticity, auxetic response, surface modes, and conformal invariance in twisted kagome lattices Kai Sun, Anton Souslov, Xiaoming Mao, and T.C. Lubensky Condensed Matter Theory Center and Joint Quantum
Isostaticity, auxetic response, surface modes, and conformal invariance in twisted kagome lattices Kai Sun, Anton Souslov, Xiaoming Mao, and T.C. Lubensky Condensed Matter Theory Center and Joint Quantum
REVIEW : INTRODUCTION TO THE MOLECULAR ORIGINS OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES QUANTITATIVE TREATMENT OF INTERATOMIC BONDING : THE LENNARD-JONES POTENTIAL
 LECTURE #19 : 3.11 MECANICS OF MATERIALS F3 INSTRUCTOR : Professor Christine Ortiz OFFICE : 13-422 PONE : 452-384 WWW : http://web.mit.edu/cortiz/www REVIEW : INTRODUCTION TO TE MOLECULAR ORIGINS OF MECANICAL
LECTURE #19 : 3.11 MECANICS OF MATERIALS F3 INSTRUCTOR : Professor Christine Ortiz OFFICE : 13-422 PONE : 452-384 WWW : http://web.mit.edu/cortiz/www REVIEW : INTRODUCTION TO TE MOLECULAR ORIGINS OF MECANICAL
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter
 Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Dimerized & frustrated spin chains. Application to copper-germanate
 Dimerized & frustrated spin chains Application to copper-germanate Outline CuGeO & basic microscopic models Excitation spectrum Confront theory to experiments Doping Spin-Peierls chains A typical S=1/2
Dimerized & frustrated spin chains Application to copper-germanate Outline CuGeO & basic microscopic models Excitation spectrum Confront theory to experiments Doping Spin-Peierls chains A typical S=1/2
Cold atoms in optical lattices
 Cold atoms in optical lattices www.lens.unifi.it Tarruel, Nature Esslinger group Optical lattices the big picture We have a textbook model, which is basically exact, describing how a large collection of
Cold atoms in optical lattices www.lens.unifi.it Tarruel, Nature Esslinger group Optical lattices the big picture We have a textbook model, which is basically exact, describing how a large collection of
Cenke Xu. Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem 许岑珂
 Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem Cenke Xu 许岑珂 University of California, Santa Barbara Quantum Phase Transitions between bosonic Symmetry
Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem Cenke Xu 许岑珂 University of California, Santa Barbara Quantum Phase Transitions between bosonic Symmetry
The Gutzwiller Density Functional Theory
 The Gutzwiller Density Functional Theory Jörg Bünemann, BTU Cottbus I) Introduction 1. Model for an H 2 -molecule 2. Transition metals and their compounds II) Gutzwiller variational theory 1. Gutzwiller
The Gutzwiller Density Functional Theory Jörg Bünemann, BTU Cottbus I) Introduction 1. Model for an H 2 -molecule 2. Transition metals and their compounds II) Gutzwiller variational theory 1. Gutzwiller
Dynamics of Solitary Waves Induced by Shock Impulses in a Linear Atomic Chain*
 Dynamics of Solitary Waves Induced by Shock Impulses in a Linear Atomic Chain* PHUOC X. TRAN, DONALD W. BRENNER, and C. T. WHITE Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC 20375-5000 Abstract The propagation
Dynamics of Solitary Waves Induced by Shock Impulses in a Linear Atomic Chain* PHUOC X. TRAN, DONALD W. BRENNER, and C. T. WHITE Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC 20375-5000 Abstract The propagation
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix. Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed
 Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
, to obtain a way to calculate stress from the energy function U(r).
 BIOEN 36 014 LECTURE : MOLECULAR BASIS OF ELASTICITY Estimating Young s Modulus from Bond Energies and Structures First we consider solids, which include mostly nonbiological materials, such as metals,
BIOEN 36 014 LECTURE : MOLECULAR BASIS OF ELASTICITY Estimating Young s Modulus from Bond Energies and Structures First we consider solids, which include mostly nonbiological materials, such as metals,
Modeling Random Wet 2D Foams with Controlled Polydispersity. Back to the Future?
 Modeling Random Wet 2D Foams with Controlled Polydispersity Back to the Future? Andy Kraynik Sandia National Labs (retired) CEAS, University of Manchester University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Simon Cox Aberystwyth
Modeling Random Wet 2D Foams with Controlled Polydispersity Back to the Future? Andy Kraynik Sandia National Labs (retired) CEAS, University of Manchester University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Simon Cox Aberystwyth
Announcements. Homework 3 (Klaus Schulten s Lecture): Due Wednesday at noon. Next homework assigned. Due Wednesday March 1.
 Announcements Homework 3 (Klaus Schulten s Lecture): Due Wednesday at noon. Next homework assigned. Due Wednesday March 1. No lecture next Monday, Feb. 27 th! (Homework is a bit longer.) Marco will have
Announcements Homework 3 (Klaus Schulten s Lecture): Due Wednesday at noon. Next homework assigned. Due Wednesday March 1. No lecture next Monday, Feb. 27 th! (Homework is a bit longer.) Marco will have
Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets
 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets theory and application to YbMgGaO 4 Yukawa Institute, Kyoto, November 2017 Itamar Kimchi I.K., Adam Nahum, T. Senthil, arxiv:1710.06860 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum
Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets theory and application to YbMgGaO 4 Yukawa Institute, Kyoto, November 2017 Itamar Kimchi I.K., Adam Nahum, T. Senthil, arxiv:1710.06860 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum
Theory of Force Transmission and Rigidity in Granular Aggregates. A Different kind of NonEquilibrium System
 Theory of Force Transmission and Rigidity in Granular Aggregates A Different kind of NonEquilibrium System Dapeng Bi Sumantra Sarkar Kabir Ramola Jetin Thomas Bob Behringer, Jie Ren Dong Wang Jeff Morris
Theory of Force Transmission and Rigidity in Granular Aggregates A Different kind of NonEquilibrium System Dapeng Bi Sumantra Sarkar Kabir Ramola Jetin Thomas Bob Behringer, Jie Ren Dong Wang Jeff Morris
548 Advances of Computational Mechanics in Australia
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2016-07-25 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 846, pp 547-552 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.846.547 2016 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Geometric bounds for buckling-induced
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2016-07-25 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 846, pp 547-552 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.846.547 2016 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Geometric bounds for buckling-induced
The Elasticity of Quantum Spacetime Fabric. Viorel Laurentiu Cartas
 The Elasticity of Quantum Spacetime Fabric Viorel Laurentiu Cartas The notion of gravitational force is replaced by the curvature of the spacetime fabric. The mass tells to spacetime how to curve and the
The Elasticity of Quantum Spacetime Fabric Viorel Laurentiu Cartas The notion of gravitational force is replaced by the curvature of the spacetime fabric. The mass tells to spacetime how to curve and the
Ultrafast study of Dirac fermions in out of equilibrium Topological Insulators
 Ultrafast study of Dirac fermions in out of equilibrium Topological Insulators Marino Marsi Laboratoire de Physique des Solides CNRS Univ. Paris-Sud - Université Paris-Saclay IMPACT, Cargèse, August 26
Ultrafast study of Dirac fermions in out of equilibrium Topological Insulators Marino Marsi Laboratoire de Physique des Solides CNRS Univ. Paris-Sud - Université Paris-Saclay IMPACT, Cargèse, August 26
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6. Tetsuya Takimoto
 Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
T. Egami. Model System of Dense Random Packing (DRP)
 Introduction to Metallic Glasses: How they are different/similar to other glasses T. Egami Model System of Dense Random Packing (DRP) Hard Sphere vs. Soft Sphere Glass transition Universal behavior History:
Introduction to Metallic Glasses: How they are different/similar to other glasses T. Egami Model System of Dense Random Packing (DRP) Hard Sphere vs. Soft Sphere Glass transition Universal behavior History:
DECRIRE LA TRANSITION VITREUSE: Simulations moléculaires et approches topologiques. Matthieu Micoulaut, LPTMC, Paris Sorbonne Universités UPMC
 DECRIRE LA TRANSITION VITREUSE: Simulations moléculaires et approches topologiques Matthieu Micoulaut, LPTMC, Paris Sorbonne Universités UPMC C. Yildrim, O. Laurent, B. Mantisi, M. Bauchy «Chasseurs d
DECRIRE LA TRANSITION VITREUSE: Simulations moléculaires et approches topologiques Matthieu Micoulaut, LPTMC, Paris Sorbonne Universités UPMC C. Yildrim, O. Laurent, B. Mantisi, M. Bauchy «Chasseurs d
Multimedia : Fibronectin and Titin unfolding simulation movies.
 I LECTURE 21: SINGLE CHAIN ELASTICITY OF BIOMACROMOLECULES: THE GIANT PROTEIN TITIN AND DNA Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #2 : EXTENSIBLE FJC AND WLC... 2 STRUCTURE OF MUSCLE AND TITIN... 3 SINGLE MOLECULE
I LECTURE 21: SINGLE CHAIN ELASTICITY OF BIOMACROMOLECULES: THE GIANT PROTEIN TITIN AND DNA Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #2 : EXTENSIBLE FJC AND WLC... 2 STRUCTURE OF MUSCLE AND TITIN... 3 SINGLE MOLECULE
Materials & Advanced Manufacturing (M&AM)
 Modeling of Shear Thickening Fluids for Analysis of Energy Absorption Under Impulse Loading Alyssa Bennett (University of Michigan) Nick Vlahopoulos, PhD (University of Michigan) Weiran Jiang, PhD (Research
Modeling of Shear Thickening Fluids for Analysis of Energy Absorption Under Impulse Loading Alyssa Bennett (University of Michigan) Nick Vlahopoulos, PhD (University of Michigan) Weiran Jiang, PhD (Research
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
Equilibrium. the linear momentum,, of the center of mass is constant
 Equilibrium is the state of an object where: Equilibrium the linear momentum,, of the center of mass is constant Feb. 19, 2018 the angular momentum,, about the its center of mass, or any other point, is
Equilibrium is the state of an object where: Equilibrium the linear momentum,, of the center of mass is constant Feb. 19, 2018 the angular momentum,, about the its center of mass, or any other point, is
Origins of Mechanical and Rheological Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites. Venkat Ganesan
 Department of Chemical Engineering University of Texas@Austin Origins of Mechanical and Rheological Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites Venkat Ganesan $$$: NSF DMR, Welch Foundation Megha Surve, Victor
Department of Chemical Engineering University of Texas@Austin Origins of Mechanical and Rheological Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites Venkat Ganesan $$$: NSF DMR, Welch Foundation Megha Surve, Victor
Adaptive algorithm for saddle point problem for Phase Field model
 Adaptive algorithm for saddle point problem for Phase Field model Jian Zhang Supercomputing Center, CNIC,CAS Collaborators: Qiang Du(PSU), Jingyan Zhang(PSU), Xiaoqiang Wang(FSU), Jiangwei Zhao(SCCAS),
Adaptive algorithm for saddle point problem for Phase Field model Jian Zhang Supercomputing Center, CNIC,CAS Collaborators: Qiang Du(PSU), Jingyan Zhang(PSU), Xiaoqiang Wang(FSU), Jiangwei Zhao(SCCAS),
Welcome to Physics 460 Introduction to Solid State Physics
 Welcome to Physics 460 Introduction to Solid State Physics Scanning Tunneling Microscope image of atoms placed on a surface, and confined quantum electron waves D. Eigler IBM Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 1
Welcome to Physics 460 Introduction to Solid State Physics Scanning Tunneling Microscope image of atoms placed on a surface, and confined quantum electron waves D. Eigler IBM Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 1
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
