ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory Spring Quarter Experiment #2: Temperature Measurements and Transient Conduction and Convection
|
|
|
- Penelope Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Lab Page 1 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory Spring Quarter 2010 Experiment #2: Temperature Measurements and Transient Conduction and Convection Objectives a) To calibrate three types of temperature measurement devices, b) to characterize their sensitivity and response times, c) to use them in an experiment in transient heating or cooling, and d) to measure heat transfer coefficients under different conditions. Pre Lab Reading The fundamental concepts behind this lab are the three mechanisms of energy transfer: conduction, free convection, and forced convection. Most of the analysis for this lab and the data reduction relies on lumped capacitance modeling of heat transfer. Whether or not you have studied these topics before, review them in any of the standard textbooks on convective heat transfer (for example: Incropera and Dewitt is a reasonable reference). An overview is presented below, but this lab handout is not a substitute for more extensive background reading. This lab also deals with heat transfer to flowing fluids. Review relevant material from your undergraduate fluid mechanics courses, including the flow field around a sphere as a function of Reynolds number. Read Section 9.2 in Introduction to Engineering Experimentation. Pre Lab Exercises 1. This lab uses three devices to measure temperature thermocouples, thermistors, and resistive thermal devices (RTDs). Briefly explain the physical basis of operation of each. 2. In using a thermocouple, why is it necessary to measure the output voltage relative to that produced by a reference junction placed in an ice bath? 3. Why do RTDs sometimes have three leads? 4. What are the basic assumptions behind the lumped capacitance model for transient heat transfer? Is such a model always valid? 5. Define conduction, forced convection and free convection. How do they differ? Prepare and submit an outline that includes: Calibrations to perform Data sets to collect Possible sources of experimental uncertainty and a plan for quantifying these errors Brief description of the work plan Any equations or physical parameters that may be needed during the laboratory session (See general lab guidelines & print out grading sheet from website).
2 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Lab Page 2 Equipment and Overview Thermocouples (chromel-alumel, so-called type K ) Thermistor Platinum RTD (3-lead) Ohmmeter Millivoltmeter Computer/LabView Thermometer Digital Thermometer Ice Gas stove Aluminum cooking pot with thermocouple well in lid Insulated containers Aluminum sphere with an embedded thermocouple In week one of the lab, you will develop a procedure for calibrating three measurement devices in order to establish a relationship between their output (voltage or resistance) and the temperature. You will also need to establish techniques for measuring or estimating the thermal response time for the three devices. In week two, you will need to use procedures you developed in week one to measure the transient response of the aluminum sphere when subjected to a step change in temperature under different environmental conditions. Theoretical Background 1) Transient energy transfer The key analysis underpinning this laboratory is that of lumped capacitance modeling of transient energy transfer. Consider an object of volume V, density, and surface area A that is initially at a uniform temperature T i and is suddenly exposed to an instantaneous step change in the external temperature to a final value of T. Under suitable assumptions (which you will examine in the prelab exercises), the temperature of the object T(t) is governed by the following differential equation expressing the balance law for energy: (1) with initial condition T(0) = T i. Here c P is the specific heat capacity and h is the heat transfer coefficient. Assuming all the parameters and properties are constant, Equation (1) can be integrated to yield:. (2)
3 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Lab Page 3 Equation (2) may be written equivalently in terms of a dimensionless temperature difference Θ and a relaxation time,, as Θ, (3) which is a very standard result for a process exhibiting first order response. By comparing Equations (3) and (4), one finds that the thermal relaxation time is: 2) The heat transfer coefficient. (4) The heat transfer coefficient depends on the nature and strength of the fluid flow and the geometry of the object. For flow around a sphere, h is often expressed as a dimensionless Nusselt number, Nu: (5) where D the diameter of the sphere, and k is the thermal conductivity of the fluid. Simple relationships exist between the Nusselt number and the flow Reynolds number,, where U is the fluid speed, and the kinematic viscosity. For this experiment: / / (6) where Pr = /k is the Prandtl number of the fluid, which can be found in tables of thermophysical properties. Equation (6) establishes the dependence of the heat transfer coefficient on the fluid that is flowing around a sphere and the speed of the flow. (Note that there are analogous relationships for free convection, but they are more complicated and need not concern us here.) Experimental Procedure WARNING: Please be careful of the boiling water and steam it produces. Severe burns and/or scalding can result from carelessness. Be careful in lighting the stove burners - be sure to have the lighter flame ignited before turning on the gas. Note: This lab involves measuring transient energy transfer, by either heating or cooling of objects following a step change in temperature. Think through whether you are going to heat or cool in terms of which is the safer and easier to do. In any case, do not move the glass thermometer directly from boiling water into the ice bath (or vice versa). Doing so thermally shocks the glass, leading to cracks and eventual breakage of the device.
4 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Lab Page 4 Laboratory: Week One 1) Accuracy of the thermometer The thermometer will be used to calibrate the devices. The calibration will only be as accurate as the thermometer itself, so the purpose here is to establish the degree of uncertainty in the temperature readings of the thermometer. Use the ice bath and boiling water to accomplish this and report thermometer accuracy in terms of +/- o C. 2) Calibration Using water baths of varying temperature, establish a calibration between the outputs of the thermocouple, thermistor, and RTD and temperature (as measured by the thermometer). The thermistor and RTD will be supplied, but you should make your own thermocouple by twisting Cr and Al wires together and crimping with pliers. In commercial thermocouples, the two metals are welded into a small bead, but since we are calibrating our home made thermocouple, that isn t necessary (although we will later make an assumption that our calibration also holds for the thermocouple embedded in the aluminum sphere.) Connect the ends of these two wires to the volt/ohmmeter and interface with the computer using Labview. Be sure to place the cold junction appropriately in the circuit (see prelab question #2.) 3) Sensor response time An important characteristic of a temperature measuring device is its response time. Often the need to have a rapid response (thus a small response time) dictates the type of device chosen for a given application. Estimate the response time of the three devices by subjecting them to a step change in external temperature. 4) Transient heating or cooling of a sphere You are supplied with a large aluminum sphere with an embedded Cr-Al thermocouple. Using Labview, take data on the transient heating (or cooling) of the sphere by subjecting it to a step change in the external temperature and measuring the temperature of the sphere as a function of time. Be sure to record the initial and external temperatures and save T(t) as a data file for later analysis. 5) A simple test of conservation of energy Fill one of the insulated containers with a known volume of water at a known temperature and immerse one of your devices in the water in order to monitor its change in temperature. Heat or cool the large aluminum sphere to a given (different) temperature and then place it in the bath. Using Labview and/or manual data logging, measure the temperature of both the water bath and the sphere as a function of time. Analysis: Between Weeks One and Two Please complete the following tasks, and include these results in your rough draft report/summary. 1) Calibrations, linearity, and sensitivity Analyze your data to obtain calibration curves for the three devices. For each device, plot T vs. measured voltage or resistance. By observing the data, and using a least squares regression
5 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Lab Page 5 analysis, determine the degree to which any of these devices are linear over the range of temperatures studied. Another important property of temperature measuring devices is the sensitivity. This is defined either in terms of the output (voltage or resistance) per unit degree Kelvin or in terms of the percentage change in voltage or resistance per degree Kelvin. Using both definitions, calculate the sensitivity of all three devices. Which is the most sensitive? 2) Response times Estimate the response time for the three devices. Which is the fastest and which is the slowest? Discuss possible reasons for these differences. Using your data on the transient heating (cooling) of the large sphere, determine the degree to which the data are approximated by the exponential form of equation (3). Estimate the thermal response time of the aluminum sphere. (Hint: Use a semi-log plot to simplify the curve fitting). 3) A test of conservation of energy Using the initial and final temperatures of the aluminum sphere and the water in the insulated container, compute the total energy gain (loss) in Joules from the sphere and compare it with the energy loss (gain) to the water in the insulated container. Discuss the degree to which your data support the principle of conservation of energy. Discuss possible reasons for a discrepancy. Laboratory: Week Two 1) Repeat any of the measurements from week one that were not satisfactory. 2) Convective heat transfer Equation (4) expresses the thermal response time as a function of physical properties, the size of the object in question, and the heat transfer coefficient. Measurement of the thermal response time allows the heat transfer coefficient to be determined if all other quantities are known. Measure the temperature response of the large aluminum sphere to a step change in temperature for the following four situations: Sphere in still air Sphere in moving air Sphere in still water Sphere in flowing water (you may have to either stir the water or move the sphere around in a bath in order to accomplish this last one.) Data Analysis: Week Two 1. Use the transient heating (cooling) data from week two to calculate the heat transfer coefficient for the four cases studied. Below is a table of ranges of heat transfer coefficients in air and in water. Compare your data with these ranges. Do they fall within these ranges? If not, can you think of reasons why they might not?
6 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Lab Page 6 Air Water Free convection Forced convection ,000 Table 1. Range of experimental values of the heat transfer coefficient, in W/(m 2 K) 2. The heat transfer coefficient varies with the properties and the speed of the flowing fluid responsible for the convective energy transfer. If this relationship is known, then measurement of the heat transfer coefficient allows one to infer the velocity of the fluid. This is the basis of hot film and hot wire anemometers. In this lab, we built a simple (and relatively crude) anemometer, but we can use the data to illustrate the principle. Using your measured values of h and Equations (5) and (6), estimate the speed of the water and air used in your forced convection experiments. Report Your report should cover the main points of the laboratory work and discusses all the questions raised above. In particular, be sure to: Describe the three devices and how they work Report the properties of the devices including linearity, sensitivity, and response time Test of the predictions of exponential decay of dimensionless temperature and measurement of response times for the large Al sphere. Test of conservation of energy Report the heat transfer coefficients for both free and forced convection in both air and water. Report estimate of air and water velocity in forced convection experiments. As always, your report should clearly state the objectives, give the background theory, and show all the data and results of analysis and curve-fitting using professionally drawn figures and tables. For a detailed description of expectations and requirements, see the general lab guidelines & print out grading sheet from website.
ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory Spring Quarter INTRODUCTION TO TRANSIENT CONDUCTION AND CONVECTION
 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Lab Page 1 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory Spring Quarter 2003 2. INTRODUCTION TO TRANSIENT CONDUCTION AND CONVECTION This set of experiments is designed to provide
ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Lab Page 1 ME 105 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory Spring Quarter 2003 2. INTRODUCTION TO TRANSIENT CONDUCTION AND CONVECTION This set of experiments is designed to provide
EM375 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING EXPERIMENTATION THERMOCOUPLE LABORATORY
 EM375 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING EXPERIMENTATION THERMOCOUPLE LABORATORY PURPOSE The objective of this laboratory is to introduce the student to the manufacture and use of thermocouples. Thermocouples will
EM375 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING EXPERIMENTATION THERMOCOUPLE LABORATORY PURPOSE The objective of this laboratory is to introduce the student to the manufacture and use of thermocouples. Thermocouples will
Thermocouple Calibrations and Heat Transfer Coefficients
 Laboratory Experiment 5: Thermocouple Calibrations and Heat Transfer Coefficients Presented to the University of California, San Diego Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE 170 Prepared
Laboratory Experiment 5: Thermocouple Calibrations and Heat Transfer Coefficients Presented to the University of California, San Diego Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE 170 Prepared
Temperature Measurement
 MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Temperature Measurement Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Introduction Temperature is one of the most
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Temperature Measurement Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Introduction Temperature is one of the most
Understanding Hot-Wire Anemometry
 Thermal Minutes Understanding Hot-Wire Anemometry Introduction Hot-wire anemometry is a technique for measuring the velocity of fluids, and can be used in many different fields. A hot-wire anemometer consists
Thermal Minutes Understanding Hot-Wire Anemometry Introduction Hot-wire anemometry is a technique for measuring the velocity of fluids, and can be used in many different fields. A hot-wire anemometer consists
Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 96. Free and Forced Convection Experiment. Revised: 25 April Introduction
 CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 96 Free and Forced Convection Experiment Revised: 25 April 1994 1. Introduction The term forced convection refers to heat transport
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 96 Free and Forced Convection Experiment Revised: 25 April 1994 1. Introduction The term forced convection refers to heat transport
Lab 1f Boiling Heat Transfer Paradox
 Lab 1f Boiling Heat Transfer Paradox OBJECTIVES Warning: though the experiment has educational objectives (to learn about boiling heat transfer, etc.), these should not be included in your report. - Obtain
Lab 1f Boiling Heat Transfer Paradox OBJECTIVES Warning: though the experiment has educational objectives (to learn about boiling heat transfer, etc.), these should not be included in your report. - Obtain
I m. R s. Digital. R x. OhmmetersxSeries Shunt Digital. R m
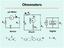 µa Meter I I s I m s E Digital x I Voltmeter x x E µa Meter m Is OhmmetersxSeries Shunt Digital EIx= = ()E sm x mxvi= x Shunt Ohmmeter Shunt s x E µa Meter I m I m V m E ) ( v I E ) ( E v E v E I When
µa Meter I I s I m s E Digital x I Voltmeter x x E µa Meter m Is OhmmetersxSeries Shunt Digital EIx= = ()E sm x mxvi= x Shunt Ohmmeter Shunt s x E µa Meter I m I m V m E ) ( v I E ) ( E v E v E I When
Temperature Measurement and First-Order Dynamic Response *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m13774 1 Temperature Measurement and First-Order Dynamic Response * Luke Graham This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m13774 1 Temperature Measurement and First-Order Dynamic Response * Luke Graham This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer. Week 1
 Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 1 This Lecture Course Organization Introduction Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Application Areas Instructor Information Professor Chang-Da Wen 温昌達» Office: 91713
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 1 This Lecture Course Organization Introduction Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Application Areas Instructor Information Professor Chang-Da Wen 温昌達» Office: 91713
Transient Heat Transfer Experiment. ME 331 Introduction to Heat Transfer. June 1 st, 2017
 Transient Heat Transfer Experiment ME 331 Introduction to Heat Transfer June 1 st, 2017 Abstract The lumped capacitance assumption for transient conduction was tested for three heated spheres; a gold plated
Transient Heat Transfer Experiment ME 331 Introduction to Heat Transfer June 1 st, 2017 Abstract The lumped capacitance assumption for transient conduction was tested for three heated spheres; a gold plated
Measurements & Instrumentation. Module 3: Temperature Sensors
 Measurements & Instrumentation PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit August 2013 Institute of Applied Technology, 2013 Module Objectives Upon successful completion of this module, students should be able
Measurements & Instrumentation PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit August 2013 Institute of Applied Technology, 2013 Module Objectives Upon successful completion of this module, students should be able
I. Introduction and Objectives
 Calibration and Measurement of Temperatures using K, T-Type Thermocouples, and a Thermistor Ben Sandoval 1 8/28/2013 Five K and five T type thermocouples were calibrated using ice water, a hot bath (boiling
Calibration and Measurement of Temperatures using K, T-Type Thermocouples, and a Thermistor Ben Sandoval 1 8/28/2013 Five K and five T type thermocouples were calibrated using ice water, a hot bath (boiling
Harnessing the Power of Arduino for the Advanced Lab
 P P Herbert Jaeger + Harnessing the Power of Arduino for the Advanced Lab (Final Version) ALPhA Immersion Workshop July 27 29, 2017 Department of Physics Indiana University Purdue University Ft. Wayne,
P P Herbert Jaeger + Harnessing the Power of Arduino for the Advanced Lab (Final Version) ALPhA Immersion Workshop July 27 29, 2017 Department of Physics Indiana University Purdue University Ft. Wayne,
Experiment A4 Sensor Calibration Procedure
 Experiment A4 Sensor Calibration Procedure Deliverables: Checked lab notebook, Brief technical memo Safety Note: Heat gloves and lab coats must be worn when dealing with boiling water. Open-toed shoes
Experiment A4 Sensor Calibration Procedure Deliverables: Checked lab notebook, Brief technical memo Safety Note: Heat gloves and lab coats must be worn when dealing with boiling water. Open-toed shoes
Pin Fin Lab Report Example. Names. ME331 Lab
 Pin Fin Lab Report Example Names ME331 Lab 04/12/2017 1. Abstract The purposes of this experiment are to determine pin fin effectiveness and convective heat transfer coefficients for free and forced convection
Pin Fin Lab Report Example Names ME331 Lab 04/12/2017 1. Abstract The purposes of this experiment are to determine pin fin effectiveness and convective heat transfer coefficients for free and forced convection
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 5 FIRST ORDER SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION APPLIED TO TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 5 FIRST ORDER SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION APPLIED TO TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Objectives: In this two week experiment, we will gain familiarity with first order systems by using two
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 5 FIRST ORDER SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION APPLIED TO TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Objectives: In this two week experiment, we will gain familiarity with first order systems by using two
If there is convective heat transfer from outer surface to fluid maintained at T W.
 Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Laboratory 12: Three Thermodynamics Experiments
 Laboratory 12: Three Thermodynamics Experiments Experiment 1: Coefficient of Linear Expansion of Metals The fact that most objects expand when heated is common knowledge. The change in the linear dimensions
Laboratory 12: Three Thermodynamics Experiments Experiment 1: Coefficient of Linear Expansion of Metals The fact that most objects expand when heated is common knowledge. The change in the linear dimensions
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
 Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering g Department MEASURING INSTRUMENTS AND CALIBRATION Lecture (7) Temperature measurement By: Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical
Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering g Department MEASURING INSTRUMENTS AND CALIBRATION Lecture (7) Temperature measurement By: Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical
Temperature Sensors & Measurement
 Temperature Sensors & Measurement E80 Spring 2014 Contents Why measure temperature? Characteristics of interest Types of temperature sensors 1. Thermistor 2. RTD Sensor 3. Thermocouple 4. Integrated Silicon
Temperature Sensors & Measurement E80 Spring 2014 Contents Why measure temperature? Characteristics of interest Types of temperature sensors 1. Thermistor 2. RTD Sensor 3. Thermocouple 4. Integrated Silicon
ASEN 2002 Experimental Laboratory 1: Temperature Measurement and an Blow Dryer Test
 ASEN 2002 Experimental Laboratory 1: Temperature Measurement and an Blow Dryer Test Assigned 6 September 2000 Individual Lab Reports due 3 October 2000 OBJECTIVES Learn the basic concepts and definitions
ASEN 2002 Experimental Laboratory 1: Temperature Measurement and an Blow Dryer Test Assigned 6 September 2000 Individual Lab Reports due 3 October 2000 OBJECTIVES Learn the basic concepts and definitions
SEMICONDUCTOR THERMAL MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
 SEMICONDUCTOR TERMAL MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE The following general procedure is equally applicable to either JEDEC or SEMI thermal measurement standards for integrated circuits and thermal test die. 1. Determine
SEMICONDUCTOR TERMAL MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE The following general procedure is equally applicable to either JEDEC or SEMI thermal measurement standards for integrated circuits and thermal test die. 1. Determine
Sensors and Actuators Sensors Physics
 Sensors and ctuators Sensors Physics Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC SENSORS (Chapter 3.9, 16.4) 3 Thermoelectric effect thermoelectric
Sensors and ctuators Sensors Physics Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC SENSORS (Chapter 3.9, 16.4) 3 Thermoelectric effect thermoelectric
Temperature Scales. Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties. Temperature. Temperature Scale
 Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Temperature Measurements
 Engineering 80 Spring 2015 Temperature Measurements SOURCE: http://www.eng.hmc.edu/newe80/pdfs/vishaythermdatasheet.pdf SOURCE: http://elcodis.com/photos/19/51/195143/to-92-3_standardbody to-226_straightlead.jpg
Engineering 80 Spring 2015 Temperature Measurements SOURCE: http://www.eng.hmc.edu/newe80/pdfs/vishaythermdatasheet.pdf SOURCE: http://elcodis.com/photos/19/51/195143/to-92-3_standardbody to-226_straightlead.jpg
4. Heat and Thermal Energy
 4. Heat and Thermal Energy Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to study cooling and heating by conduction, convection, and radiation. Thermal energy is the energy of random molecular motion.
4. Heat and Thermal Energy Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to study cooling and heating by conduction, convection, and radiation. Thermal energy is the energy of random molecular motion.
Exercise 1: Thermocouple Characteristics
 The Thermocouple Transducer Fundamentals Exercise 1: Thermocouple Characteristics EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to describe and demonstrate the characteristics
The Thermocouple Transducer Fundamentals Exercise 1: Thermocouple Characteristics EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to describe and demonstrate the characteristics
Lecture 11 Temperature Sensing. ECE 5900/6900 Fundamentals of Sensor Design
 EE 4900: Fundamentals of Sensor Design Lecture 11 Temperature Sensing 1 Temperature Sensing Q: What are we measuring? A: Temperature 2 SI Units: Celcius ( C), Kelvin (K) British Units: Fahrenheit ( F)
EE 4900: Fundamentals of Sensor Design Lecture 11 Temperature Sensing 1 Temperature Sensing Q: What are we measuring? A: Temperature 2 SI Units: Celcius ( C), Kelvin (K) British Units: Fahrenheit ( F)
Laboratory 7: Charging and Discharging a Capacitor Prelab
 Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 7: Charging and Discharging a Capacitor Prelab Consider a capacitor with capacitance C connected in series to a resistor with resistance R as shown in Fig. 1. Theory predicts
Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 7: Charging and Discharging a Capacitor Prelab Consider a capacitor with capacitance C connected in series to a resistor with resistance R as shown in Fig. 1. Theory predicts
ECNG3032 Control and Instrumentation I
 sensor ECNG3032 Control and Instrumentation I Lecture 1 Temperature Sensors Sensors The sensor is the first element in the measurement system. Measurand Transducer Principle Excitation Signal Interface
sensor ECNG3032 Control and Instrumentation I Lecture 1 Temperature Sensors Sensors The sensor is the first element in the measurement system. Measurand Transducer Principle Excitation Signal Interface
Sensing, Computing, Actuating
 Sensing, Computing, ctuating Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC EFFECT (Chapter 5.11) 3 Thermocouple cylinder head temperature (thermocouple)
Sensing, Computing, ctuating Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC EFFECT (Chapter 5.11) 3 Thermocouple cylinder head temperature (thermocouple)
Conjugate heat transfer from an electronic module package cooled by air in a rectangular duct
 Conjugate heat transfer from an electronic module package cooled by air in a rectangular duct Hideo Yoshino a, Motoo Fujii b, Xing Zhang b, Takuji Takeuchi a, and Souichi Toyomasu a a) Fujitsu Kyushu System
Conjugate heat transfer from an electronic module package cooled by air in a rectangular duct Hideo Yoshino a, Motoo Fujii b, Xing Zhang b, Takuji Takeuchi a, and Souichi Toyomasu a a) Fujitsu Kyushu System
Florida Institute of Technology College of Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering
 Florida Institute of Technology College of Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering CHE 4115 ChE Process Laboratory II Team Report # 1 Experiment # 3 Experimental Design - Heat Transfer by Convection
Florida Institute of Technology College of Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering CHE 4115 ChE Process Laboratory II Team Report # 1 Experiment # 3 Experimental Design - Heat Transfer by Convection
EA Guidelines on the Calibration of Temperature Indicators and Simulators by Electrical Simulation and Measurement
 Publication Reference EA-10/11 EA Guidelines on the Calibration of Temperature Indicators and Simulators by Electrical PURPOSE This document has been produced by EA as a means of giving advice for calibrating
Publication Reference EA-10/11 EA Guidelines on the Calibration of Temperature Indicators and Simulators by Electrical PURPOSE This document has been produced by EA as a means of giving advice for calibrating
4. Thermometry. Temperature and Heat Flow Temperature Scales Thermometers
 4. Thermometry Measuring temperature by sensation is very imprecise. That is why we need a temperature scale and a thermometer to measure temperature more accurately. Temperature and Heat Flow Temperature
4. Thermometry Measuring temperature by sensation is very imprecise. That is why we need a temperature scale and a thermometer to measure temperature more accurately. Temperature and Heat Flow Temperature
A Demonstration Unit to Enhance Heat Transfer Lectures on Natural and Forced Convection
 A Demonstration Unit to Enhance Heat Transfer Lectures on Natural and Forced Convection Charles H. Forsberg Department of Engineering, Hofstra University, Hempstead, NY 11549 Session 1566 Overview As a
A Demonstration Unit to Enhance Heat Transfer Lectures on Natural and Forced Convection Charles H. Forsberg Department of Engineering, Hofstra University, Hempstead, NY 11549 Session 1566 Overview As a
Veerapong Kanchanawongkul*
 Using LabVIEW to Development of Temperature Measurement System with Thermocouple and Thermistor AIS 08 Veerapong Kanchanawongkul* Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, South-East
Using LabVIEW to Development of Temperature Measurement System with Thermocouple and Thermistor AIS 08 Veerapong Kanchanawongkul* Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, South-East
HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS
 HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS 1. THE ABSOLUTE TEMPERATURE SCALE In the textbook you have been introduced to the concept of temperature, and to the fact that there is a natural zero of temperature, the temperature
HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS 1. THE ABSOLUTE TEMPERATURE SCALE In the textbook you have been introduced to the concept of temperature, and to the fact that there is a natural zero of temperature, the temperature
Energy Conversion in the Peltier Device
 Laboratory exercise 4 Energy Conversion in the Peltier Device Preface The purpose of this exercise is to become familiar with the Peltier effect. Students will observe Peltier device working as a heat
Laboratory exercise 4 Energy Conversion in the Peltier Device Preface The purpose of this exercise is to become familiar with the Peltier effect. Students will observe Peltier device working as a heat
Thermal Process Control Lap 4 Thermal Energy. Notes:
 Thermal Process Control Lap 4 Thermal Energy Notes: 1) Temperature Measurement a) Define temperature i) A measure of the amount of heat contained in a solid, liquid, or gas ii) Result of molecular motion
Thermal Process Control Lap 4 Thermal Energy Notes: 1) Temperature Measurement a) Define temperature i) A measure of the amount of heat contained in a solid, liquid, or gas ii) Result of molecular motion
APPENDIX ELEVEN Open Fire Temperature Measurements
 APPENDIX ELEVEN Open Fire Temperature Measurements Temperatures are usually recorded with alcohol or mercury thermometers, with thermistors or resistance temperature detectors (platinum resistance thermometers),
APPENDIX ELEVEN Open Fire Temperature Measurements Temperatures are usually recorded with alcohol or mercury thermometers, with thermistors or resistance temperature detectors (platinum resistance thermometers),
CHAPTER 4 THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY AND VISCOSITY MEASUREMENTS
 50 CHAPTER 4 THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY AND VISCOSITY MEASUREMENTS 4.1 INTRODUCTION In the development of any energy-efficient heat transfer fluids for enhanced heat transfer performance, in practical applications,
50 CHAPTER 4 THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY AND VISCOSITY MEASUREMENTS 4.1 INTRODUCTION In the development of any energy-efficient heat transfer fluids for enhanced heat transfer performance, in practical applications,
Resistivity vs. Temperature of a Superconductor WARNING
 Resistivity vs. Temperature of a Superconductor 1.0 Expected Learning Outcomes Calibrate a transducer (silicon diode) for low-temperature measurements and measure temperatures down to that of boiling liquid
Resistivity vs. Temperature of a Superconductor 1.0 Expected Learning Outcomes Calibrate a transducer (silicon diode) for low-temperature measurements and measure temperatures down to that of boiling liquid
Experiment 2: THE DENSITY OF A SOLID UNKNOWN AND CALIBRATION WITH DATASTUDIO SOFTWARE
 Experiment 2: THE DENSITY OF A SOLID UNKNOWN AND CALIBRATION WITH DATASTUDIO SOFTWARE Concepts: Density Equipment Calibration Approximate time required: 90 minutes for density 90 minutes for two thermometers
Experiment 2: THE DENSITY OF A SOLID UNKNOWN AND CALIBRATION WITH DATASTUDIO SOFTWARE Concepts: Density Equipment Calibration Approximate time required: 90 minutes for density 90 minutes for two thermometers
(Refer slide Time 1:09)
 Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 2 Lecture - 28 Hot Wire Anemometry and Laser Doppler Velocimetry
Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 2 Lecture - 28 Hot Wire Anemometry and Laser Doppler Velocimetry
Temperature Measurement
 Temperature Measurement Temperature is one of the most common measurements What is Temperature? Intuitively understood as sensation of hot/cold Early Researchers: Galileo (1564-1642) Newton (1642-1727)
Temperature Measurement Temperature is one of the most common measurements What is Temperature? Intuitively understood as sensation of hot/cold Early Researchers: Galileo (1564-1642) Newton (1642-1727)
APPENDIX 1 DESCRIPTION OF HOT WIRE ANEMOMETER
 146 APPENDIX 1 DESCRIPTION OF HOT WIRE ANEMOMETER Basic Principles of CTA Anemometer The hot-wire anemometer was introduced in its original form in the first half of the 0 th century. A major breakthrough
146 APPENDIX 1 DESCRIPTION OF HOT WIRE ANEMOMETER Basic Principles of CTA Anemometer The hot-wire anemometer was introduced in its original form in the first half of the 0 th century. A major breakthrough
CHME 302 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LABOATORY-I EXPERIMENT 302-V FREE AND FORCED CONVECTION
 CHME 302 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LABOATORY-I EXPERIMENT 302-V FREE AND FORCED CONVECTION OBJECTIVE The objective of the experiment is to compare the heat transfer characteristics of free and forced convection.
CHME 302 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LABOATORY-I EXPERIMENT 302-V FREE AND FORCED CONVECTION OBJECTIVE The objective of the experiment is to compare the heat transfer characteristics of free and forced convection.
Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements
 Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements Contents Principle of thermocouples Materials for themocouples Cold junction compensation Compensating wires Selection of thermocouples Illustration of gas temperature
Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements Contents Principle of thermocouples Materials for themocouples Cold junction compensation Compensating wires Selection of thermocouples Illustration of gas temperature
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA ECHE 460 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I Heat Transfer Analysis in Solids Prepared by: M. L. Price, and Professors M. A. Matthews and T. Papathansiou Department of Chemical
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA ECHE 460 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I Heat Transfer Analysis in Solids Prepared by: M. L. Price, and Professors M. A. Matthews and T. Papathansiou Department of Chemical
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer. Week 7
 Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 7 Example Solution Technique Using either finite difference method or finite volume method, we end up with a set of simultaneous algebraic equations in terms
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 7 Example Solution Technique Using either finite difference method or finite volume method, we end up with a set of simultaneous algebraic equations in terms
SEN TRONIC AG 1 A 6 6 / "
 1A 66/" 0!"#$%&'() %"*+", - %"*.", - /01234%( 34.+*!54%& 0*%/# "6#,7857.'.0" - 6#)9.:. &%&;! 0 &????'.&% )&" 8" @&& (++ '() %('.('/(#$!!! ' %! %!& ;!;8 ;!;8 0 &&'&&;! C;!C&(D"@@ &;! 0&&+%&;! C&=;!C&(D"@@
1A 66/" 0!"#$%&'() %"*+", - %"*.", - /01234%( 34.+*!54%& 0*%/# "6#,7857.'.0" - 6#)9.:. &%&;! 0 &????'.&% )&" 8" @&& (++ '() %('.('/(#$!!! ' %! %!& ;!;8 ;!;8 0 &&'&&;! C;!C&(D"@@ &;! 0&&+%&;! C&=;!C&(D"@@
Background Information for Use of Pitot Tube, Manometer, Hot Wires, and Hot Films
 AAE 50 Notes, 9-Jan-04 Page 1 Background Information for Use of Pitot Tube, Manometer, Hot Wires, and Hot Films 1 Background The following is adapted from the handout in AAE333L. 1.1.1 Specific Applications:
AAE 50 Notes, 9-Jan-04 Page 1 Background Information for Use of Pitot Tube, Manometer, Hot Wires, and Hot Films 1 Background The following is adapted from the handout in AAE333L. 1.1.1 Specific Applications:
Core practical 12: Calibrate a thermistor in a potential divider circuit as a thermostat
 Core practical 12 Teacher sheet circuit To determine the temperature variation of a thermistor To design a potential divider circuit that can be used to control temperature Specification links Although
Core practical 12 Teacher sheet circuit To determine the temperature variation of a thermistor To design a potential divider circuit that can be used to control temperature Specification links Although
Section 7. Temperature Measurement
 Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Critical parameters of
 Critical parameters of superconductors 2005-03-30 Why do this experiment? Superconductivity is a very interesting property from both commercial and basic scientific points of view. Superconductors are
Critical parameters of superconductors 2005-03-30 Why do this experiment? Superconductivity is a very interesting property from both commercial and basic scientific points of view. Superconductors are
DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8.
 Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
5. TEMPERATURE AND HEAT
 5. TEMPERATURE AND HEAT You will study the concepts of temperature and heat as they apply to a sample of water and you will measure the specific heat capacity of the sample. The measurement of one property
5. TEMPERATURE AND HEAT You will study the concepts of temperature and heat as they apply to a sample of water and you will measure the specific heat capacity of the sample. The measurement of one property
High Frequency Dielectric Strength Tests
 High Frequency Dielectric Strength Tests Insulation tests at high frequency (HF) need to be done with great care. The mechanism of breakdown is different to normal mains frequency dielectric strength tests
High Frequency Dielectric Strength Tests Insulation tests at high frequency (HF) need to be done with great care. The mechanism of breakdown is different to normal mains frequency dielectric strength tests
Metrology Experiment for Engineering Students: Platinum Resistance Temperature Detector
 Session 1359 Metrology Experiment for Engineering Students: Platinum Resistance Temperature Detector Svetlana Avramov-Zamurovic, Carl Wick, Robert DeMoyer United States Naval Academy Abstract This paper
Session 1359 Metrology Experiment for Engineering Students: Platinum Resistance Temperature Detector Svetlana Avramov-Zamurovic, Carl Wick, Robert DeMoyer United States Naval Academy Abstract This paper
PHYSICAL MECHANISM OF CONVECTION
 Tue 8:54:24 AM Slide Nr. 0 of 33 Slides PHYSICAL MECHANISM OF CONVECTION Heat transfer through a fluid is by convection in the presence of bulk fluid motion and by conduction in the absence of it. Chapter
Tue 8:54:24 AM Slide Nr. 0 of 33 Slides PHYSICAL MECHANISM OF CONVECTION Heat transfer through a fluid is by convection in the presence of bulk fluid motion and by conduction in the absence of it. Chapter
Empirical Co - Relations approach for solving problems of convection 10:06:43
 Empirical Co - Relations approach for solving problems of convection 10:06:43 10:06:44 Empirical Corelations for Free Convection Use T f or T b for getting various properties like Re = VL c / ν β = thermal
Empirical Co - Relations approach for solving problems of convection 10:06:43 10:06:44 Empirical Corelations for Free Convection Use T f or T b for getting various properties like Re = VL c / ν β = thermal
Review: Heat, Temperature, Heat Transfer and Specific Heat Capacity
 Name: Block: Date: IP 614 Review: Heat, Temperature, Heat Transfer and Specific Heat Capacity All these questions are real MCAS questions! 1. In a copper wire, a temperature increase is the result of which
Name: Block: Date: IP 614 Review: Heat, Temperature, Heat Transfer and Specific Heat Capacity All these questions are real MCAS questions! 1. In a copper wire, a temperature increase is the result of which
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY /6.071 Introduction to Electronics, Signals and Measurement Spring 2006
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 22.07/6.07 Introduction to Electronics, Signals and Measurement Spring 2006 Lab6. Resistor Networks 2. Experiment. Power rating of resistors. Power rating is a very
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 22.07/6.07 Introduction to Electronics, Signals and Measurement Spring 2006 Lab6. Resistor Networks 2. Experiment. Power rating of resistors. Power rating is a very
Complete all the identification fields below or 10% of the lab value will be deduced from your final mark for this lab.
 Simple circuits 3 hr Identification page Instructions: Print this page and the following ones before your lab session to prepare your lab report. Staple them together with your graphs at the end. If you
Simple circuits 3 hr Identification page Instructions: Print this page and the following ones before your lab session to prepare your lab report. Staple them together with your graphs at the end. If you
1. Mark the correct statement(s)
 1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
 Since ancient times, people have needed thermal energy (heat) to cook their food and to keep them warm. And since the beginning of time, uncontrolled heat has scorched and spoiled the taste of food and
Since ancient times, people have needed thermal energy (heat) to cook their food and to keep them warm. And since the beginning of time, uncontrolled heat has scorched and spoiled the taste of food and
EXPERIMENT ET: ENERGY TRANSFORMATION & SPECIFIC HEAT
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.01X Fall 2000 EXPERIMENT ET: ENERGY TRANSFORMATION & SPECIFIC HEAT We have introduced different types of energy which help us describe
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.01X Fall 2000 EXPERIMENT ET: ENERGY TRANSFORMATION & SPECIFIC HEAT We have introduced different types of energy which help us describe
Application of Thermocouples in Steady Laminar Flames
 Appendix A Application of Thermocouples in Steady Laminar Flames Despite the simplicity of thermocouple theory [Wright, 1995] and construction, thermocouple thermometry in combustion environments is anything
Appendix A Application of Thermocouples in Steady Laminar Flames Despite the simplicity of thermocouple theory [Wright, 1995] and construction, thermocouple thermometry in combustion environments is anything
Thermal Systems. What and How? Physical Mechanisms and Rate Equations Conservation of Energy Requirement Control Volume Surface Energy Balance
 Introduction to Heat Transfer What and How? Physical Mechanisms and Rate Equations Conservation of Energy Requirement Control Volume Surface Energy Balance Thermal Resistance Thermal Capacitance Thermal
Introduction to Heat Transfer What and How? Physical Mechanisms and Rate Equations Conservation of Energy Requirement Control Volume Surface Energy Balance Thermal Resistance Thermal Capacitance Thermal
Name Partner. Thermal Physics. Part I: Heat of Vaporization of Nitrogen. Introduction:
 Name Partner Thermal Physics Part I: Heat of Vaporization of Nitrogen Introduction: The heat of vaporization of a liquid, L v, is the energy required to vaporize (boil) a unit mass of substance. Thus if
Name Partner Thermal Physics Part I: Heat of Vaporization of Nitrogen Introduction: The heat of vaporization of a liquid, L v, is the energy required to vaporize (boil) a unit mass of substance. Thus if
1. How much heat was needed to raise the bullet to its final temperature?
 Name: Date: Use the following to answer question 1: A 0.0500-kg lead bullet of volume 5.00 10 6 m 3 at 20.0 C hits a block that is made of an ideal thermal insulator and comes to rest at its center. At
Name: Date: Use the following to answer question 1: A 0.0500-kg lead bullet of volume 5.00 10 6 m 3 at 20.0 C hits a block that is made of an ideal thermal insulator and comes to rest at its center. At
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Problems on Heat Transfer
 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
PHYSICAL MECHANISM OF NATURAL CONVECTION
 1 NATURAL CONVECTION In this chapter, we consider natural convection, where any fluid motion occurs by natural means such as buoyancy. The fluid motion in forced convection is quite noticeable, since a
1 NATURAL CONVECTION In this chapter, we consider natural convection, where any fluid motion occurs by natural means such as buoyancy. The fluid motion in forced convection is quite noticeable, since a
EXPERIMENT 9 Superconductivity & Ohm s Law
 Name: Date: Course number: MAKE SURE YOUR TA OR TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START! Lab section: Partner's name(s): Grade: EXPERIMENT 9 Superconductivity & Ohm s Law 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1.
Name: Date: Course number: MAKE SURE YOUR TA OR TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START! Lab section: Partner's name(s): Grade: EXPERIMENT 9 Superconductivity & Ohm s Law 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1.
ECE2019 Sensors, Circuits, and Systems A2015. Lab #2: Temperature Sensing
 ECE2019 Sensors, Circuits, and Systems A2015 Lab #2: Temperature Sensing Introduction This lab investigates the use of a resistor as a temperature sensor. Using the temperature-sensitive resistance as
ECE2019 Sensors, Circuits, and Systems A2015 Lab #2: Temperature Sensing Introduction This lab investigates the use of a resistor as a temperature sensor. Using the temperature-sensitive resistance as
Activity 1: Investigating Temperature
 Contents Activity Overview... 5 Quick Start Guide... 5 Software Installation... 5 Hardware Setup... 6 mytemp Getting Started Program... 10 General Tips and Tricks... 11 Activity 1: Investigating Temperature...
Contents Activity Overview... 5 Quick Start Guide... 5 Software Installation... 5 Hardware Setup... 6 mytemp Getting Started Program... 10 General Tips and Tricks... 11 Activity 1: Investigating Temperature...
PHYS320 ilab (O) Experiment 2 Instructions Conservation of Energy: The Electrical Equivalent of Heat
 PHYS320 ilab (O) Experiment 2 Instructions Conservation of Energy: The Electrical Equivalent of Heat Objective: The purpose of this activity is to determine whether the energy dissipated by a heating resistor
PHYS320 ilab (O) Experiment 2 Instructions Conservation of Energy: The Electrical Equivalent of Heat Objective: The purpose of this activity is to determine whether the energy dissipated by a heating resistor
Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control. The General Control System
 WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
WALJAT COLLEGES OF APPLIED SCIENCES In academic partnership with BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Question Bank Course: Biotechnology Session: 005-006 Subject: BT6008 Process Measurement and Control Semester:
HEAT AND TEMPERATURE Vikasana-Bridge Course 2012
 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE TOPICS Introduction Effects of heat Specific heat Basics of thermodynamics Introduction Heat may be defined as energy in transit from a high temperature region to a lower temperature
HEAT AND TEMPERATURE TOPICS Introduction Effects of heat Specific heat Basics of thermodynamics Introduction Heat may be defined as energy in transit from a high temperature region to a lower temperature
Physics 4C Chapter 18: Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Physics 4C Chapter 18: Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Anyone who has never made a mistake has never tried anything new. Albert Einstein Experience is the name that everyone gives
Physics 4C Chapter 18: Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Anyone who has never made a mistake has never tried anything new. Albert Einstein Experience is the name that everyone gives
University of New Mexico Mechanical Engineering Fall 2012 PhD qualifying examination Heat Transfer
 University of New Mexico Mechanical Engineering Fall 2012 PhD qualifying examination Heat Transfer Closed book. Formula sheet and calculator are allowed, but not cell phones, computers or any other wireless
University of New Mexico Mechanical Engineering Fall 2012 PhD qualifying examination Heat Transfer Closed book. Formula sheet and calculator are allowed, but not cell phones, computers or any other wireless
Heat Transfer II ENGR 7901 Spring, Dr. Y. Muzychka EN 3058
 Heat Transfer II ENGR 7901 Spring, 2010 Dr. Y. Muzychka EN 3058 Course Materials Text: Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Incropera and DeWiP, 6 th EdiRon Course Notes and Handouts Most Course Material on Webpage
Heat Transfer II ENGR 7901 Spring, 2010 Dr. Y. Muzychka EN 3058 Course Materials Text: Fundamentals of Heat Transfer Incropera and DeWiP, 6 th EdiRon Course Notes and Handouts Most Course Material on Webpage
High temperature He is hot
 Lecture 9 What is Temperature and Heat? High temperature He is hot Some important definitions * Two objects are in Thermal contact with each other if energy can be exchanged between them. Thermal equilibrium
Lecture 9 What is Temperature and Heat? High temperature He is hot Some important definitions * Two objects are in Thermal contact with each other if energy can be exchanged between them. Thermal equilibrium
Temperature Measurements
 ME 22.302 Mechanical Lab I Temperature Measurements Dr. Peter Avitabile University of Massachusetts Lowell Temperature - 122601-1 Copyright 2001 A transducer is a device that converts some mechanical quantity
ME 22.302 Mechanical Lab I Temperature Measurements Dr. Peter Avitabile University of Massachusetts Lowell Temperature - 122601-1 Copyright 2001 A transducer is a device that converts some mechanical quantity
Designing a Thermostat Worksheet
 Designing a Thermostat Worksheet Most of us have a thermostat in our homes to control heating and cooling systems of our home. These important devices help us save energy by automatically turning off energy
Designing a Thermostat Worksheet Most of us have a thermostat in our homes to control heating and cooling systems of our home. These important devices help us save energy by automatically turning off energy
CHAPTER 5 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENT
 62 CHAPTER 5 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENT 5.1 INTRODUCTION The primary objective of this work is to investigate the convective heat transfer characteristics of silver/water nanofluid. In order
62 CHAPTER 5 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENT 5.1 INTRODUCTION The primary objective of this work is to investigate the convective heat transfer characteristics of silver/water nanofluid. In order
Comparing the actual value and the experimental value on heat. By conservation of energy
 Topic: Heat 1. Temperature and thermometers a. Temperature: - measure degree of hotness. -measure the average kinetic energy of molecules in random motions. b. Fixed points: -Lower fixed point: temperature
Topic: Heat 1. Temperature and thermometers a. Temperature: - measure degree of hotness. -measure the average kinetic energy of molecules in random motions. b. Fixed points: -Lower fixed point: temperature
Let s Get Digital: A Guide to Unraveling the Tangled World of Digital Thermometers
 Let s Get Digital: A Guide to Unraveling the Tangled World of Digital Thermometers By Maria Knake, Laboratory Assessment Program Manager Posted: November 2011 So, You re Looking to Buy a Digital Thermometer?
Let s Get Digital: A Guide to Unraveling the Tangled World of Digital Thermometers By Maria Knake, Laboratory Assessment Program Manager Posted: November 2011 So, You re Looking to Buy a Digital Thermometer?
Technical Notes. Introduction. PCB (printed circuit board) Design. Issue 1 January 2010
 Technical Notes Introduction Thermal Management for LEDs Poor thermal management can lead to early LED product failure. This Technical Note discusses thermal management techniques and good system design.
Technical Notes Introduction Thermal Management for LEDs Poor thermal management can lead to early LED product failure. This Technical Note discusses thermal management techniques and good system design.
OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 1
 Unit 4: Heat Transfer and Combustion Unit code: K/60/44 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 5 OUTCOME - TUTORIAL Heat transfer coefficients Dimensional analysis: dimensionless groups; Reynolds, Nusselt, Prandtl,
Unit 4: Heat Transfer and Combustion Unit code: K/60/44 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 5 OUTCOME - TUTORIAL Heat transfer coefficients Dimensional analysis: dimensionless groups; Reynolds, Nusselt, Prandtl,
Heat and Temperature Practice Quiz Topic 2 - Measuring Temperature
 Heat and Temperature Practice Quiz Topic 2 - Measuring Temperature 1. Estimating temperature is something that we do automatically. Touching something to see how hot or cold it is is one technique that
Heat and Temperature Practice Quiz Topic 2 - Measuring Temperature 1. Estimating temperature is something that we do automatically. Touching something to see how hot or cold it is is one technique that
Exploring Physics and Math with the CBL System
 Exploring Physics and Math with the CBL System 48 Lab Activities Using CBL and the TI-82 Chris Brueningsen Wesley Krawiec Table of Contents Preface...... 7 Preparing Lab Reports... 8 Experimental Errors...
Exploring Physics and Math with the CBL System 48 Lab Activities Using CBL and the TI-82 Chris Brueningsen Wesley Krawiec Table of Contents Preface...... 7 Preparing Lab Reports... 8 Experimental Errors...
Natural Convection Systems
 C H A P T E R 6 Natural Convection Systems 6.1 Physical Mechanism Of Natural Convection Many familiar heat transfer applications involve natural convection as the primary mechanism of heat transfer. Some
C H A P T E R 6 Natural Convection Systems 6.1 Physical Mechanism Of Natural Convection Many familiar heat transfer applications involve natural convection as the primary mechanism of heat transfer. Some
Heat Transfer F12-ENG Lab #4 Forced convection School of Engineering, UC Merced.
 1 Heat Transfer F12-ENG-135 - Lab #4 Forced convection School of Engineering, UC Merced. October 23, 2012 1 General purpose of the Laboratory To gain a physical understanding of the behavior of the average
1 Heat Transfer F12-ENG-135 - Lab #4 Forced convection School of Engineering, UC Merced. October 23, 2012 1 General purpose of the Laboratory To gain a physical understanding of the behavior of the average
University of Macau Department of Electromechanical Engineering MECH316 Heat Transfer Syllabus 2 nd Semester 2011/2012 Part A Course Outline
 University of Macau Department of Electromechanical Engineering MECH316 Heat Transfer Syllabus 2 nd Semester 2011/2012 Part A Course Outline Compulsory course in Electromechanical Engineering Course description:
University of Macau Department of Electromechanical Engineering MECH316 Heat Transfer Syllabus 2 nd Semester 2011/2012 Part A Course Outline Compulsory course in Electromechanical Engineering Course description:
Temperature. 3
 Temperature In 1848, Sir William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) stated the zero principle of dynamics. This principle enabled him to define thermodynamic temperature and to establish an objective method of measuring
Temperature In 1848, Sir William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) stated the zero principle of dynamics. This principle enabled him to define thermodynamic temperature and to establish an objective method of measuring
Experiment 3. Electrical Energy. Calculate the electrical power dissipated in a resistor.
 Experiment 3 Electrical Energy 3.1 Objectives Calculate the electrical power dissipated in a resistor. Determine the heat added to the water by an immersed heater. Determine if the energy dissipated by
Experiment 3 Electrical Energy 3.1 Objectives Calculate the electrical power dissipated in a resistor. Determine the heat added to the water by an immersed heater. Determine if the energy dissipated by
Physics 248, Spring 2009 Lab 7: Capacitors and RC-Decay
 Name Section Physics 248, Spring 2009 Lab 7: Capacitors and RC-Decay Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete
Name Section Physics 248, Spring 2009 Lab 7: Capacitors and RC-Decay Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete
