Section 7. Temperature Measurement
|
|
|
- Augustus Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time, temperature is the second most measured physical unit. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 2 1
2 International Temperature Scale Reference Points triple point of hydrogen C boiling point of oxygen* C boiling point of water* C freezing point of zinc* C freezing point of silver* C freezing point of gold* +1, C (*at atmospheric pressure) T [ K ] T ( C ) T [ C ] T ( F ) 32 T [ F ] T ( C ) 9 5 T [ R ] T ( F ) /25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 3 Common Temperature Measurement Techniques Changes in Physical Dimensions Bimetallic Thermometers Filled-Bulb and Glass-Stem Thermometers Changes in Electrical Properties Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDS) Thermistors Thermocouples Changes in Chemical Phase Quartz Crystal Thermometry Changes in Emitted thermal radiation Radiation and Infrared Pyrometers 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 4 2
3 Bimetal Thermometer Two metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion are bonded together. As temperature changes the unequal expansion of the two metals will cause the bimetal strip to curl or bend. - Bimetal strips can be fabricated into coils, spirals, and disks. - Frequently used in on-off temperature control (thermostats) Range of use: - 65 to 430 C Accuracy varies with range; ± 0.5 to 12 C 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 5 Liquid Expansion Thermometer Volumetric expansion of liquids & solids is used for temperature measurement. - Expansion registered is actually the difference between the liquid & the glass. Mercury filled thermometers Range= -37 to 320 C, Accuracy ± 0.3 C Alcohol filled thermometers. Range =-75 to 120 C, Accuracy ± 0.6 C Upper range determined by boiling point. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 6 3
4 Thermal Expansion Methods liquid-in-glass thermometer bimetallic thermometer capillary tube needle scale scale bimetallic strip bulb containing fluid motion of free end 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 7 Thermocouples 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 8 4
5 Thermocouples: Principle of Operation When two wires composed of dissimilar metals are joined at both ends & one of the ends is heated, an emf is generated. This is referred to as the Seebeck effect. Combined result of two phenomenon, Thomson & Peltier effects: - Thomson observed the existence of an emf due to the contact of two dissimilar metals. - Peltier discovered that an emf is generated when a temperature gradient along a conductor exists. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 9 Seebeck Voltage If this circuit is broken at the center, the net open circuit voltage (the Seebeck voltage) is a function of the junction temperature and the composition of the two metals. Metal A T abs V AB Metal B V AB = T abs For small T 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
6 Temperature Characteristics Thermoelectric Voltage [mv] Chromel-Constantan Chromel-Alumel VT ( ) at at 2 at 3... Platinum/13%Rhodium- Platinum 10 0 Platinum/10%Rhodium- Platinum Temperature [ C] 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 11 Thermocouple System Junctions V 3 J 3 Cu A A V 1 V Cu B B J 1 V 2 J 2 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
7 Law of Intermediate Metals A B C T 1 T 2 T 1 = T 2 =T A C T 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 13 Combined Junctions V 3 J 3 Cu A A V 1 V Cu B B J 1 V 2 J 2 V V V 2 V 1 V 3 T CuB J2 AB T J1 CuA T J3 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
8 Probe Configurations Ungrounded Junction is detached from the probe. Electrical isolation is obtained at the cost of response time. Grounded Junction is physically attached to probe wall. Good heat transfer to junction. Exposed Junction is exposed to the surrounding environment. Best response time. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 15 Law of Intermediate Temperatures T2 T3 T1 T2 If a thermocouple circuit develops: i) a net emf 1-2 when the junctions are placed between temperatures T 1 and T 2, and, ii) a net emf 2-3 when junctions are between temperatures T 2 and T 3. Then the same thermocouple circuit would develop an emf 1-3 when the junctions are at temperatures T 1 and T 3. T3 T1 emf 1-3 = emf 1-2 +emf 2-3 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
9 Isothermal Block Thermistor or IC Temperature Reference V R V Cu Cu T R A B Isothermal Block (same temperature across) A B V1 T1 T R V1 T1 T 1 AB f (V R AB ) T R f (V R ) 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 17 RTD Sensors 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
10 RTD Principle of Operation An RTD is a precision temperature sensing device that utilizes metal conductors (typically a fine platinum wire or thin metallic layer applied to a substrate). Increases in temperature produce positive increases in the resistance, i.e., the sensing element is referred to as having a positive temperature coefficient (PTC). The RTD system error is minimized when the nominal value of the RTD resistance is large. This implies a metallic wire with a high resistivity. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 19 Metal Resistivity Each metal has a specific resistivity, (ohm*m) which varies with temperature. R T o 1 ( T To ) Where: T L A L= metal wire length A=cross-sectional area Temperature Coefficient of resistivity ( o C o C Gold (Au) Aluminum(Al) Copper(C) Platinum (Pt) Tungsten (W) Nickel (Ni) Nichrome Lead (Pb) Iron (Fe) /25/2017 Engineering Measurements
11 RTD Resistance Temperature Curves R R Nickel Copper Platinum Tungsten C Temperature General temperature-dependence RT ( ) R 2 3 0(1 at 1 at 2 at 3...) Linearized temperaturedependence RT ( ) R0(1 at 1 ) 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 21 RTD Platinum Sensor Example The temperature coefficient of resistivity for pure platinum 20ºC is /ºC. A typical platinum RTD has resistance of 100. What is the sensitivity of a typical platinum RTD temperature 20ºC. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
12 RTD Sensor Circuit A V exc + _ calibrated variable resistance D R 4 _ V m R 1 + RTD B R 3 R 2 C 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 23 RTD s Characteristics Low resistance: 100 (most common) to 1000 Wide operating range: -200 C to 850 C High sensitivity: compared to thermocouples High accuracy: ± C to 0.1 C High Repeatability & Stability: Low drift ( C/year) Industrial models drift < 0.1 C/year Slow response time Sensitive to shock and vibration Internal/self-heating: measure resistance by passing current through sensor. Joule Heating = I 2 R 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
13 Thermistors 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 25 Thermistors Thermistors are made from semiconductor materials and in general have a negative temperature coefficient (NTC). So as the temperature increases the resistance of a thermistor decreases (NTC). However, thermistors with a PTC are also available. The resistance-to-temperature relationships for these devices are highly non-linear. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
14 Thermistors Thermistors have resistances from 1 k to 100 k - This high resistance eliminates most issues due to high lead resistance. Highly non-linear resistance-to-temperature relationships. - Thermistors are mostly made from metal oxides and have NTC, but barium and strontium titanate mixtures are models available and have a PTC Small physical size - Fast response time Very high sensitivity and resolution - Up to 1000 times more sensitive than RTD s Thermistors are not sensitive to shock and vibration 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 27 Thermistor Sensor Circuits Vexc (+) R 1 I t R t V Power Dissipation P d =I t V Thermistor 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
15 Infrared Temperature Sensing F F 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 29 Infrared Thermometers What is infrared (IR)? - Thermal energy which spans the wavelength range between 0.7 to 1000 m of the Electromagnetic (E&M) spectrum. - All substances above absolute zero emit thermal energy in the IR range. Infrared thermometers are non-contact devices that are able to estimate an object s temperature (T) by measuring the emitted IR energy. Modern IR instruments can readily measure between 0.7 & 50m due to their low sensitivity outside this wavelength range. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
16 Electromagnetic Spectrum 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 31 Measurement Principles Energy traveling at the speed of light is transmitted as electro-magnetic (E&M) waves or photons. Radiation striking a surface is partially reflected, absorbed, and transmitted. P radiated Pincident Preflected Ptransmitted Pabsorbed P incident Pradiated Pabsorbed P absorbed emissivity absorption P reflected P transmitted Radiative Heat Transfer (Q): q=q/a q=f BA (T A4 -T B4 ) P radiated where the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, = ( x 10-8 W/m 2 K 4 ) 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
17 Thermal Radiation Spectral Radiance [W/m 3 srad] visible K K K K Wavelength [µm] Planck s law: I b 5 2hc e hc kt I b - black body spectral intensity (W/m 3 srad) h = x10-34 (Js); Planck constant c = x 10 8 (m/s); speed of light ~ 0.1 to 1000 m; wavelength k = x (J/K); Boltzmann constant T - absolute temperature [K] 2 1 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 33 Thermal Radiation Heat Source Testpiece Infrared Film or Camera Stefan-Boltzmann law E b 0 I b ( ) d T 4 where E b is the blackbody emissive power and 5.67x10-8 [W/(m 2 K 4 )] 0 E ( ) I b ( ) d T 4 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
18 Thermal Radiation Example The energy emitted from a piece of metal is measured, and assuming an emissivity of 0.82 the temperature is estimated to be 1050 C. It is later found that the true emissivity is only Determine the corrected temperature? 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 35 Overview of IR Thermometers IR thermometers are remote sensing and can measure objects that translate, rotate, or vibrate. They do not damage or contaminate the surface of interest (i.e., food, painted surfaces, or other delicate surfaces). A typical response time is in the millisecond range. However, material emissivity is subject to a great amount of uncertainty because it depends on surface finish, color, oxidation, aging, etc. IR thermometers generally have a low dynamic range and low sensitivity. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
19 Non-Electronic Indicators 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 37 Liquid Crystals Certain cholesteric liquid crystals produce changes in reflectance and hence color as a function of temperature. The range and resolution of liquid crystal thermometers is varied by adjustment of the formulation. Temperature ranges from 0 C to several hundred C are available. Typical temperature resolution is on the order of ~ 0.1 C. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
20 Liquid Crystals Liquid crystals are long chain molecules which exist in a helical type configuration. Due to their thermal sensitivity, the pitch of these helical structures change with temperature, producing a corresponding change in its optical property. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 39 Temperature Sensitive Indicators The maximum temperature of an object can also be detected using various crayons and paints. These devices are produced with pigments dispersed throughout the material, with an approximate melting temperature. As the melting temperature is approached, the color of the pigment deepens due to changes in the light scattering properties of the pigment powder. Temperature sensitive glass tiles work in a similar fashion. 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
21 Temperature Measurement Errors Conduction Convection Radiation Response Time Electrical Noise or Interference Sensor Self-Heating Thermal Gradients in the material being measured Grounding issues and shorts, especially on metal surfaces Calibration stability (static or dynamic) 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements
Temperature Measurement
 MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Temperature Measurement Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Introduction Temperature is one of the most
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Temperature Measurement Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Introduction Temperature is one of the most
Temperature Scales. Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties. Temperature. Temperature Scale
 Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Sensing, Computing, Actuating
 Sensing, Computing, ctuating Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC EFFECT (Chapter 5.11) 3 Thermocouple cylinder head temperature (thermocouple)
Sensing, Computing, ctuating Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC EFFECT (Chapter 5.11) 3 Thermocouple cylinder head temperature (thermocouple)
Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements
 Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements Contents Principle of thermocouples Materials for themocouples Cold junction compensation Compensating wires Selection of thermocouples Illustration of gas temperature
Lecture 36: Temperatue Measurements Contents Principle of thermocouples Materials for themocouples Cold junction compensation Compensating wires Selection of thermocouples Illustration of gas temperature
Sensors and Actuators Sensors Physics
 Sensors and ctuators Sensors Physics Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC SENSORS (Chapter 3.9, 16.4) 3 Thermoelectric effect thermoelectric
Sensors and ctuators Sensors Physics Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems 2 THERMOELECTRIC SENSORS (Chapter 3.9, 16.4) 3 Thermoelectric effect thermoelectric
Module 4 : THERMOELECTRICITY Lecture 21 : Seebeck Effect
 Module 4 : THERMOELECTRICITY Lecture 21 : Seebeck Effect Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Seebeck effect and thermo-emf. Thermoelectric series of metals which can be used to form
Module 4 : THERMOELECTRICITY Lecture 21 : Seebeck Effect Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Seebeck effect and thermo-emf. Thermoelectric series of metals which can be used to form
Temperature Measurement
 Temperature Measurement Dr. Clemens Suter, Prof. Sophia Haussener Laboratory of Renewable Energy Sciences and Engineering Suter Temperature Measurement Mar, 2017 1/58 Motivation Suter Temperature Measurement
Temperature Measurement Dr. Clemens Suter, Prof. Sophia Haussener Laboratory of Renewable Energy Sciences and Engineering Suter Temperature Measurement Mar, 2017 1/58 Motivation Suter Temperature Measurement
Introduction. Measurement of temperature is generally considered to be one of the simplest and most accurate measurements performed in engineering.
 Slide Nr. 0 of 15 Slides Introduction Measurement of temperature is generally considered to be one of the simplest and most accurate measurements performed in engineering. Some important considerations
Slide Nr. 0 of 15 Slides Introduction Measurement of temperature is generally considered to be one of the simplest and most accurate measurements performed in engineering. Some important considerations
SENSORS and TRANSDUCERS
 SENSORS and TRANSDUCERS Tadeusz Stepinski, Signaler och system The Thermal Energy Domain Physics» Seebeck effect» Peltier effect» Thomson effect Thermal effects in semiconductors Thermoelectric sensors
SENSORS and TRANSDUCERS Tadeusz Stepinski, Signaler och system The Thermal Energy Domain Physics» Seebeck effect» Peltier effect» Thomson effect Thermal effects in semiconductors Thermoelectric sensors
1 THE CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE
 1 THE CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE 1 1.1 Historical Perspective, 2 1.2 Early Definitions of Temperature, 9 1.3 A Simple Qualitative Definition of Temperature, 10 1.4 Units of Temperature for Various Temperature
1 THE CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE 1 1.1 Historical Perspective, 2 1.2 Early Definitions of Temperature, 9 1.3 A Simple Qualitative Definition of Temperature, 10 1.4 Units of Temperature for Various Temperature
Temperature Measurement
 Temperature Measurement Temperature is one of the most common measurements What is Temperature? Intuitively understood as sensation of hot/cold Early Researchers: Galileo (1564-1642) Newton (1642-1727)
Temperature Measurement Temperature is one of the most common measurements What is Temperature? Intuitively understood as sensation of hot/cold Early Researchers: Galileo (1564-1642) Newton (1642-1727)
Chapter 6. Fiber Optic Thermometer. Ho Suk Ryou
 Chapter 6. Fiber Optic Thermometer Ho Suk Ryou Properties of Optical Fiber Optical Fiber Composed of rod core surrounded by sheath Core: conducts electromagnetic wave Sheath: contains wave within the core
Chapter 6. Fiber Optic Thermometer Ho Suk Ryou Properties of Optical Fiber Optical Fiber Composed of rod core surrounded by sheath Core: conducts electromagnetic wave Sheath: contains wave within the core
Thermometry. History. History 1/21/18. The art or science of temperature observation
 Thermometry The art or science of temperature observation History No one person credited with the invention of the thermometer; developed over time Avicenna used this principal to show that hotness and
Thermometry The art or science of temperature observation History No one person credited with the invention of the thermometer; developed over time Avicenna used this principal to show that hotness and
Chapter 6 Temperature Measurement (Revision 2.0, 1/12/2009)
 Chapter 6 emperature Measurement (Revision 2.0, /2/2009). Introduction his Chapter looks that various methods of temperature measurement. Historically, there are two temperature measurement scales: he
Chapter 6 emperature Measurement (Revision 2.0, /2/2009). Introduction his Chapter looks that various methods of temperature measurement. Historically, there are two temperature measurement scales: he
Control Engineering BDA30703
 Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Control Engineering BDA30703 Lecture 4: Transducers Prepared by: Ramhuzaini bin Abd. Rahman Expected Outcomes At the end of this lecture, students should be able to; 1) Explain a basic measurement system.
Lecture 11 Temperature Sensing. ECE 5900/6900 Fundamentals of Sensor Design
 EE 4900: Fundamentals of Sensor Design Lecture 11 Temperature Sensing 1 Temperature Sensing Q: What are we measuring? A: Temperature 2 SI Units: Celcius ( C), Kelvin (K) British Units: Fahrenheit ( F)
EE 4900: Fundamentals of Sensor Design Lecture 11 Temperature Sensing 1 Temperature Sensing Q: What are we measuring? A: Temperature 2 SI Units: Celcius ( C), Kelvin (K) British Units: Fahrenheit ( F)
Temperature. Sensors. Measuring technique. Eugene V. Colla. 10/25/2017 Physics 403 1
 Temperature. Sensors. Measuring technique. Eugene V. Colla 10/25/2017 Physics 403 1 Outline Temperature Sensors Measuring equipment and ideas Sensor calibration Temperature scales 10/25/2017 Physics 403
Temperature. Sensors. Measuring technique. Eugene V. Colla 10/25/2017 Physics 403 1 Outline Temperature Sensors Measuring equipment and ideas Sensor calibration Temperature scales 10/25/2017 Physics 403
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
 Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering g Department MEASURING INSTRUMENTS AND CALIBRATION Lecture (7) Temperature measurement By: Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical
Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering g Department MEASURING INSTRUMENTS AND CALIBRATION Lecture (7) Temperature measurement By: Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical
Temperature Measurements
 Engineering 80 Spring 2015 Temperature Measurements SOURCE: http://www.eng.hmc.edu/newe80/pdfs/vishaythermdatasheet.pdf SOURCE: http://elcodis.com/photos/19/51/195143/to-92-3_standardbody to-226_straightlead.jpg
Engineering 80 Spring 2015 Temperature Measurements SOURCE: http://www.eng.hmc.edu/newe80/pdfs/vishaythermdatasheet.pdf SOURCE: http://elcodis.com/photos/19/51/195143/to-92-3_standardbody to-226_straightlead.jpg
Making Contact with Temperature
 Making Contact with Temperature Here is a look at the phenomenon itself, the basic measurement technologies available, and how industry is presently using them. Jesse Yoder, Flow Research Temperature is
Making Contact with Temperature Here is a look at the phenomenon itself, the basic measurement technologies available, and how industry is presently using them. Jesse Yoder, Flow Research Temperature is
Part Number Range Accuracy Printing WP * Probe Special User LDC with Page Logging included Feature Cal Backlight
 Table of Contents Comparison Chart Introduction Temperature Indicators & Controllers Portable Infrared Printing/Logging Page O2 O3 O10 O14 O30 O33 O1 Part Number Range Accuracy Printing WP * Probe Special
Table of Contents Comparison Chart Introduction Temperature Indicators & Controllers Portable Infrared Printing/Logging Page O2 O3 O10 O14 O30 O33 O1 Part Number Range Accuracy Printing WP * Probe Special
Lecture 2: Zero law of thermodynamics
 Lecture 2: Zero law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and temperature scales 2. Thermal contact and thermal equilibrium 3. Zeroth law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and Temperature scales We often associate
Lecture 2: Zero law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and temperature scales 2. Thermal contact and thermal equilibrium 3. Zeroth law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and Temperature scales We often associate
ECNG3032 Control and Instrumentation I
 sensor ECNG3032 Control and Instrumentation I Lecture 1 Temperature Sensors Sensors The sensor is the first element in the measurement system. Measurand Transducer Principle Excitation Signal Interface
sensor ECNG3032 Control and Instrumentation I Lecture 1 Temperature Sensors Sensors The sensor is the first element in the measurement system. Measurand Transducer Principle Excitation Signal Interface
4. Thermometry. Temperature and Heat Flow Temperature Scales Thermometers
 4. Thermometry Measuring temperature by sensation is very imprecise. That is why we need a temperature scale and a thermometer to measure temperature more accurately. Temperature and Heat Flow Temperature
4. Thermometry Measuring temperature by sensation is very imprecise. That is why we need a temperature scale and a thermometer to measure temperature more accurately. Temperature and Heat Flow Temperature
Temperature measurement
 emperature measurement BASICS Interest in emperature measurements appeared definitively later as respect to other quantities. emperature is an intensive quantity (a quantity strictly correlated to temperature
emperature measurement BASICS Interest in emperature measurements appeared definitively later as respect to other quantities. emperature is an intensive quantity (a quantity strictly correlated to temperature
Thermal Process Control Lap 4 Thermal Energy. Notes:
 Thermal Process Control Lap 4 Thermal Energy Notes: 1) Temperature Measurement a) Define temperature i) A measure of the amount of heat contained in a solid, liquid, or gas ii) Result of molecular motion
Thermal Process Control Lap 4 Thermal Energy Notes: 1) Temperature Measurement a) Define temperature i) A measure of the amount of heat contained in a solid, liquid, or gas ii) Result of molecular motion
Mechanical Measurements. Module 2:
 Mechanical Measurements Module : 1. Thermometry Formally we start the study of Mechanical Measurements now! Module will consider the measurement of field quantities like temperature, pressure and fluid
Mechanical Measurements Module : 1. Thermometry Formally we start the study of Mechanical Measurements now! Module will consider the measurement of field quantities like temperature, pressure and fluid
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online tuiton Pakistan Online Tutor Pakistan. Heat
 Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online tuiton Pakistan Online Tutor Pakistan Heat Nature of Heat: Heat is the transfer of energy (every in transit) from one body to another due to the temperature difference
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online tuiton Pakistan Online Tutor Pakistan Heat Nature of Heat: Heat is the transfer of energy (every in transit) from one body to another due to the temperature difference
I m. R s. Digital. R x. OhmmetersxSeries Shunt Digital. R m
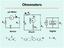 µa Meter I I s I m s E Digital x I Voltmeter x x E µa Meter m Is OhmmetersxSeries Shunt Digital EIx= = ()E sm x mxvi= x Shunt Ohmmeter Shunt s x E µa Meter I m I m V m E ) ( v I E ) ( E v E v E I When
µa Meter I I s I m s E Digital x I Voltmeter x x E µa Meter m Is OhmmetersxSeries Shunt Digital EIx= = ()E sm x mxvi= x Shunt Ohmmeter Shunt s x E µa Meter I m I m V m E ) ( v I E ) ( E v E v E I When
Comparison of sensors for the measurement of temperature with (small) UAV/RPA
 Comparison of sensors for the measurement of temperature with (small) UAV/RPA Norman Wildmann, Jens Bange Center for Applied Geosciences, Eberhard Karls University Tübingen 19 February 2013, Palma de Mallorca
Comparison of sensors for the measurement of temperature with (small) UAV/RPA Norman Wildmann, Jens Bange Center for Applied Geosciences, Eberhard Karls University Tübingen 19 February 2013, Palma de Mallorca
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture 34 Heat Heat transfer Conduction Convection Radiation http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Thermal physics Heat. Specific
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture 34 Heat Heat transfer Conduction Convection Radiation http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Thermal physics Heat. Specific
Real-Time & Embedded 1Systems Physical Coupling. Uwe R. Zimmer - The Australian National University
 Real-Time & Embedded 1Systems 2015 Physical Coupling Uwe R. Zimmer - The Australian National University [ Edler2003 ] Edler et al. Noise temperature measurements for the determination of the thermodynamic
Real-Time & Embedded 1Systems 2015 Physical Coupling Uwe R. Zimmer - The Australian National University [ Edler2003 ] Edler et al. Noise temperature measurements for the determination of the thermodynamic
Introduction to Infrared Radiation.
 Introduction to Infrared Radiation. 1. Starting at the source the Heating Coil. 2. Electrical Issues some basic calculations. 3. The basics of Heat Transfer 4. The Electromagnetic Spectrum 5. Infrared
Introduction to Infrared Radiation. 1. Starting at the source the Heating Coil. 2. Electrical Issues some basic calculations. 3. The basics of Heat Transfer 4. The Electromagnetic Spectrum 5. Infrared
Temperature. 3
 Temperature In 1848, Sir William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) stated the zero principle of dynamics. This principle enabled him to define thermodynamic temperature and to establish an objective method of measuring
Temperature In 1848, Sir William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) stated the zero principle of dynamics. This principle enabled him to define thermodynamic temperature and to establish an objective method of measuring
Chapter 1. Blackbody Radiation. Theory
 Chapter 1 Blackbody Radiation Experiment objectives: explore radiation from objects at certain temperatures, commonly known as blackbody radiation ; make measurements testing the Stefan-Boltzmann law in
Chapter 1 Blackbody Radiation Experiment objectives: explore radiation from objects at certain temperatures, commonly known as blackbody radiation ; make measurements testing the Stefan-Boltzmann law in
Thermal energy. Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules.
 Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
Temperature. Temperature Scales. Temperature (cont d) CHAPTER 14 Heat and Temperature
 Temperature CHAPTER 14 Heat and Temperature The temperature of a substance is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the substance s particles. As the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Temperature CHAPTER 14 Heat and Temperature The temperature of a substance is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the substance s particles. As the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Thermal Sensors and Actuators
 Thermal Sensors and Actuators Part I Fundamentals of heat transfer Heat transfer occurs where there is a temperature gradient until an equilibrium is reached. Four major mechanism Thermal conduction Natural
Thermal Sensors and Actuators Part I Fundamentals of heat transfer Heat transfer occurs where there is a temperature gradient until an equilibrium is reached. Four major mechanism Thermal conduction Natural
[ ] Sensors for Temperature Measurement, and Their Application 2L R 1 1 T 1 T 2
![[ ] Sensors for Temperature Measurement, and Their Application 2L R 1 1 T 1 T 2 [ ] Sensors for Temperature Measurement, and Their Application 2L R 1 1 T 1 T 2](/thumbs/89/97951344.jpg) Sensors for Temperature Measurement, and Their Application In today s market, it is very rare to see electronic equipment that has not undergone extensive thermal evaluation, either by measurement or simulation.
Sensors for Temperature Measurement, and Their Application In today s market, it is very rare to see electronic equipment that has not undergone extensive thermal evaluation, either by measurement or simulation.
THERMOCOUPLE CHARACTERISTICS TRAINER
 THERMOCOUPLE CHARACTERISTICS TRAINER (Model No : ) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
THERMOCOUPLE CHARACTERISTICS TRAINER (Model No : ) User Manual Version 2.0 Technical Clarification /Suggestion : / Technical Support Division, Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd., Plot No :75,Electronics Estate,
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT TWO THERMAL RADIATION
 ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT TWO THERMAL RADIATION Unit Outline 2 Electromagnetic radiation Thermal radiation Blackbody radiation Radiation emitted from a real surface Irradiance Kirchhoff s Law Diffuse and
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT TWO THERMAL RADIATION Unit Outline 2 Electromagnetic radiation Thermal radiation Blackbody radiation Radiation emitted from a real surface Irradiance Kirchhoff s Law Diffuse and
Physical Coupling. Physical Coupling. Physical Coupling. Physical Coupling. Transform physical phenomena into electrical signals.
 231 eal-time & Embedded 1 Systems 2015 Uwe. Zimmer - The Australian National University 233 eal-time Systems Components: Physical coupling Processor Processor Communication Communication munication eal-time
231 eal-time & Embedded 1 Systems 2015 Uwe. Zimmer - The Australian National University 233 eal-time Systems Components: Physical coupling Processor Processor Communication Communication munication eal-time
University of Technology Dr. louay A.Mahdi Department of Machines and Equipments Engineering Branches: General, Refrigeration and Air conditioning,
 1 Introduction: The first recorded temperature measurement was carried out by Galileo at the end of the sixteenth century. His thermometer depended on the expansion of air. Some form of scale was attached
1 Introduction: The first recorded temperature measurement was carried out by Galileo at the end of the sixteenth century. His thermometer depended on the expansion of air. Some form of scale was attached
APPENDIX ELEVEN Open Fire Temperature Measurements
 APPENDIX ELEVEN Open Fire Temperature Measurements Temperatures are usually recorded with alcohol or mercury thermometers, with thermistors or resistance temperature detectors (platinum resistance thermometers),
APPENDIX ELEVEN Open Fire Temperature Measurements Temperatures are usually recorded with alcohol or mercury thermometers, with thermistors or resistance temperature detectors (platinum resistance thermometers),
SEN TRONIC AG 1 A 6 6 / "
 1A 66/" 0!"#$%&'() %"*+", - %"*.", - /01234%( 34.+*!54%& 0*%/# "6#,7857.'.0" - 6#)9.:. &%&;! 0 &????'.&% )&" 8" @&& (++ '() %('.('/(#$!!! ' %! %!& ;!;8 ;!;8 0 &&'&&;! C;!C&(D"@@ &;! 0&&+%&;! C&=;!C&(D"@@
1A 66/" 0!"#$%&'() %"*+", - %"*.", - /01234%( 34.+*!54%& 0*%/# "6#,7857.'.0" - 6#)9.:. &%&;! 0 &????'.&% )&" 8" @&& (++ '() %('.('/(#$!!! ' %! %!& ;!;8 ;!;8 0 &&'&&;! C;!C&(D"@@ &;! 0&&+%&;! C&=;!C&(D"@@
15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have
 105) to convert it to. 15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above. 17. 16. Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have taken from the, is it the same?
105) to convert it to. 15. Compare the result with the value you have taken above. 17. 16. Compare the calculated pressure value with the actual pressure value that you have taken from the, is it the same?
Lecture 22. Temperature and Heat
 Lecture 22 Temperature and Heat Today s Topics: 0 th Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermometers Thermal Expansion Heat, Internal Energy and Work Heat Transfer Temperature and the Zeroth Law
Lecture 22 Temperature and Heat Today s Topics: 0 th Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermometers Thermal Expansion Heat, Internal Energy and Work Heat Transfer Temperature and the Zeroth Law
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6502 -INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION I Regulation 2013
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6502 -INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION I Regulation 2013
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
 Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & Applications 5th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Afshin J. Ghajar McGraw-Hill, 2015 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep
Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & Applications 5th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Afshin J. Ghajar McGraw-Hill, 2015 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep
9/12/2011. Training Course Remote Sensing - Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods September 2011
 Training Course Remote Sensing - Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Introduction to Remote Sensing Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Electro Magnetic (EM)
Training Course Remote Sensing - Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Introduction to Remote Sensing Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl 1 Overview Electro Magnetic (EM)
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5. What is light? What is a wave? Radiation carries information
 Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
TRANSDUCERS transducer Measurand
 TRANSDUCERS Transduction: transformation of one form of energy into another form. Sensing with specificity the input energy from the measurand by means of a "sensing element" and then transforming it into
TRANSDUCERS Transduction: transformation of one form of energy into another form. Sensing with specificity the input energy from the measurand by means of a "sensing element" and then transforming it into
The Stefan-Boltzmann Law
 The Stefan-Boltzmann Law Department of Physics Ryerson University 1 Introduction Thermal radiation is typically considered the starting point in many texts for discussions of old quantum theory and the
The Stefan-Boltzmann Law Department of Physics Ryerson University 1 Introduction Thermal radiation is typically considered the starting point in many texts for discussions of old quantum theory and the
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer. Week 1
 Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 1 This Lecture Course Organization Introduction Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Application Areas Instructor Information Professor Chang-Da Wen 温昌達» Office: 91713
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 1 This Lecture Course Organization Introduction Basic Modes of Heat Transfer Application Areas Instructor Information Professor Chang-Da Wen 温昌達» Office: 91713
1. How much heat was needed to raise the bullet to its final temperature?
 Name: Date: Use the following to answer question 1: A 0.0500-kg lead bullet of volume 5.00 10 6 m 3 at 20.0 C hits a block that is made of an ideal thermal insulator and comes to rest at its center. At
Name: Date: Use the following to answer question 1: A 0.0500-kg lead bullet of volume 5.00 10 6 m 3 at 20.0 C hits a block that is made of an ideal thermal insulator and comes to rest at its center. At
The Kinetic Theory of Matter. Temperature. Temperature. Temperature. Temperature. Chapter 6 HEAT
 The Kinetic Theory of Matter Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 6 HEAT Kinetic Theory of Matter: Matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that are always in
The Kinetic Theory of Matter Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 6 HEAT Kinetic Theory of Matter: Matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that are always in
ABB temperature measurement Radiation thermometry. Measurement made easy. Process temperature measurement practice--non-contacting
 Whitepaper_ WP_T_Non-Contacting_Temperature_Measurement ABB temperature measurement Radiation thermometry Measurement made easy Process temperature measurement practice--non-contacting By Gary Freeman,
Whitepaper_ WP_T_Non-Contacting_Temperature_Measurement ABB temperature measurement Radiation thermometry Measurement made easy Process temperature measurement practice--non-contacting By Gary Freeman,
Using a Mercury itc with thermocouples
 Technical Note Mercury Support Using a Mercury itc with thermocouples Abstract and content description This technical note describes how to make accurate and reliable temperature measurements using an
Technical Note Mercury Support Using a Mercury itc with thermocouples Abstract and content description This technical note describes how to make accurate and reliable temperature measurements using an
Unit 5 Thermodynamics
 Unit 5 Thermodynamics Unit 13: Heat and Temperature Unit 14: Thermal Expansion /Heat Exchange/ Change of Phase Test: Units 13-14 Thermal Energy The total kinetic and potential energy of all the molecules
Unit 5 Thermodynamics Unit 13: Heat and Temperature Unit 14: Thermal Expansion /Heat Exchange/ Change of Phase Test: Units 13-14 Thermal Energy The total kinetic and potential energy of all the molecules
= (fundamental constants c 0, h, k ). (1) k
 Introductory Physics Laboratory, Faculty of Physics and Geosciences, University of Leipzig W 12e Radiation Thermometers Tasks 1 Measure the black temperature T s of a glowing resistance wire at eight different
Introductory Physics Laboratory, Faculty of Physics and Geosciences, University of Leipzig W 12e Radiation Thermometers Tasks 1 Measure the black temperature T s of a glowing resistance wire at eight different
Chapter 17. Temperature. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 17 Temperature Dr. Armen Kocharian Temperature We associate the concept of temperature with how hot or cold an objects feels Our senses provide us with a qualitative indication of temperature Our
Chapter 17 Temperature Dr. Armen Kocharian Temperature We associate the concept of temperature with how hot or cold an objects feels Our senses provide us with a qualitative indication of temperature Our
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE
 I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester. Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE
 INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introduction Photogrammetry: Definition & applications What are we trying to do? Data acquisition systems 3-D viewing of 2-D imagery Automation (matching problem) Necessary tools: Image formation
Chapter 1: Introduction Photogrammetry: Definition & applications What are we trying to do? Data acquisition systems 3-D viewing of 2-D imagery Automation (matching problem) Necessary tools: Image formation
Lecture 6. Rapid Thermal Processing. Reading: Chapter 6
 Lecture 6 Rapid Thermal Processing Reading: Chapter 6 (Chapter 6) Categories: Rapid Thermal Anneal (RTA) Rapid Thermal Oxidation (RTO) Rapid Thermal Nitridation (RTN) (and oxynitrides) Rapid Thermal Diffusion
Lecture 6 Rapid Thermal Processing Reading: Chapter 6 (Chapter 6) Categories: Rapid Thermal Anneal (RTA) Rapid Thermal Oxidation (RTO) Rapid Thermal Nitridation (RTN) (and oxynitrides) Rapid Thermal Diffusion
LASERS. Dr D. Arun Kumar Assistant Professor Department of Physical Sciences Bannari Amman Institute of Technology Sathyamangalam
 LASERS Dr D. Arun Kumar Assistant Professor Department of Physical Sciences Bannari Amman Institute of Technology Sathyamangalam General Objective To understand the principle, characteristics and types
LASERS Dr D. Arun Kumar Assistant Professor Department of Physical Sciences Bannari Amman Institute of Technology Sathyamangalam General Objective To understand the principle, characteristics and types
Measurement in Engineering
 Measurement in Engineering Responsible person for the course: Ing. Martin Novak, Ph.D. Report on the laboratory experiment Measurement of temperature of the 12.10.10 - made by Sebastian Kößler Report on
Measurement in Engineering Responsible person for the course: Ing. Martin Novak, Ph.D. Report on the laboratory experiment Measurement of temperature of the 12.10.10 - made by Sebastian Kößler Report on
* Defining Temperature * Temperature is proportional to the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. * Temperature * Internal energy
 * Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
* Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
High temperature He is hot
 Lecture 9 What is Temperature and Heat? High temperature He is hot Some important definitions * Two objects are in Thermal contact with each other if energy can be exchanged between them. Thermal equilibrium
Lecture 9 What is Temperature and Heat? High temperature He is hot Some important definitions * Two objects are in Thermal contact with each other if energy can be exchanged between them. Thermal equilibrium
We call the characteristic of a system that determines how much its temperature will change heat capacity.
 3/3 Measuring Heat If all we do is add heat to a system its temperature will rise. How much the temperature rises depends on the system. We call the characteristic of a system that determines how much
3/3 Measuring Heat If all we do is add heat to a system its temperature will rise. How much the temperature rises depends on the system. We call the characteristic of a system that determines how much
Chapter 11 FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMAL RADIATION
 Chapter Chapter Fundamentals of Thermal Radiation FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMAL RADIATION Electromagnetic and Thermal Radiation -C Electromagnetic waves are caused by accelerated charges or changing electric
Chapter Chapter Fundamentals of Thermal Radiation FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMAL RADIATION Electromagnetic and Thermal Radiation -C Electromagnetic waves are caused by accelerated charges or changing electric
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS
 Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
WELCOME TO PERIOD 5: THERMAL ENERGY, THE MICROSCOPIC PICTURE. Homework #4 is due today at the beginning of class.
 WELCOME TO PERIOD 5: THERMAL ENERGY, THE MICROSCOPIC PICTURE Homework #4 is due today at the beginning of class. PHYSICS 1104 PERIOD 5 How are temperatures measured? How do atoms and molecules act at different
WELCOME TO PERIOD 5: THERMAL ENERGY, THE MICROSCOPIC PICTURE Homework #4 is due today at the beginning of class. PHYSICS 1104 PERIOD 5 How are temperatures measured? How do atoms and molecules act at different
INTRODUCTION Radiation differs from conduction and convection in that it does not require the presence of a material medium to take place.
 RADIATION INTRODUCTION Radiation differs from conduction and convection in that it does not require the presence of a material medium to take place. Radiation: The energy emitted by matter in the form
RADIATION INTRODUCTION Radiation differs from conduction and convection in that it does not require the presence of a material medium to take place. Radiation: The energy emitted by matter in the form
Chapter 16 Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 16 Temperature and Heat 16-1 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Definition of heat: Heat is the energy transferred between objects because of a temperature difference. Objects are
Chapter 16 Temperature and Heat 16-1 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Definition of heat: Heat is the energy transferred between objects because of a temperature difference. Objects are
1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory.
 Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation
 The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer
 Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics
 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics.. Introduction to kinetic theory of gases... Definition of thermodynamics..3. Thermodynamic systems system, boundary and surroundings closed system open system isolated
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics.. Introduction to kinetic theory of gases... Definition of thermodynamics..3. Thermodynamic systems system, boundary and surroundings closed system open system isolated
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. What is light? Properties of Waves. Waves. The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos What is light? Light is a form of radiant energy Light can act either like a wave or like a particle (photon) Spectrum of the Sun 1 2 Waves
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos What is light? Light is a form of radiant energy Light can act either like a wave or like a particle (photon) Spectrum of the Sun 1 2 Waves
TEMPERATURE. 8. Temperature and Heat 1
 TEMPERATURE Heat is the energy that is transferred between objects because of a temperature difference Terms such as transfer of heat or heat flow from object A to object B simply means that the total
TEMPERATURE Heat is the energy that is transferred between objects because of a temperature difference Terms such as transfer of heat or heat flow from object A to object B simply means that the total
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements
 Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements Third Edition Richard S. Figliola Clemson University Donald E. Beasley Clemson University John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Weinheim / Brisbane
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements Third Edition Richard S. Figliola Clemson University Donald E. Beasley Clemson University John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Weinheim / Brisbane
This book is under copyright to A-level Physics Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit.
 2 This book is under copyright to A-level Physics Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. CONTENTS thermometry what is temperature?, fixed points, Kelvin (Absolute),
2 This book is under copyright to A-level Physics Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. CONTENTS thermometry what is temperature?, fixed points, Kelvin (Absolute),
innovative infrared technology BASIC PRINCIPLES of non-contact temperature measurement
 innovative infrared technology BASIC PRINCIPLES of non-contact temperature measurement Contents Page Physical principles... 2 7 Emissivity and temperature measurement... 8 10..... 1 Physical principles
innovative infrared technology BASIC PRINCIPLES of non-contact temperature measurement Contents Page Physical principles... 2 7 Emissivity and temperature measurement... 8 10..... 1 Physical principles
1. Mark the correct statement(s)
 1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
1. Mark the correct statement(s) Figure to the right shows a mass measurement scale using a spring. 1.1 The span of the scale is a) 16 kg b) 21 kg c) 11 kg d) 5-16 kg 1.2 The range of the scale is a) 16
EXPERIMENT NO. 4. Thermal Radiation: the Stefan-Boltzmann Law
 1 EXPERIMENT NO. 4 Thermal Radiation: the Stefan-Boltzmann Law References: Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Serway and Jewett. Sections 40.1 An Introduction to Thermal Physics, Schroeder, Section
1 EXPERIMENT NO. 4 Thermal Radiation: the Stefan-Boltzmann Law References: Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Serway and Jewett. Sections 40.1 An Introduction to Thermal Physics, Schroeder, Section
Dr. Linlin Ge The University of New South Wales
 GMAT 9600 Principles of Remote Sensing Week2 Electromagnetic Radiation: Definition & Physics Dr. Linlin Ge www.gmat.unsw.edu.au/linlinge Basic radiation quantities Outline Wave and quantum properties Polarization
GMAT 9600 Principles of Remote Sensing Week2 Electromagnetic Radiation: Definition & Physics Dr. Linlin Ge www.gmat.unsw.edu.au/linlinge Basic radiation quantities Outline Wave and quantum properties Polarization
5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS
 5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS TOPIC OUTLINE Section Recommended Time Giancoli Section 5.1 Potential Difference, Current, Resistance 5.2 Electric Circuits 3h 19.1, 19.2 6.2 Electric Field and Force 6.3 Magnetic
5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS TOPIC OUTLINE Section Recommended Time Giancoli Section 5.1 Potential Difference, Current, Resistance 5.2 Electric Circuits 3h 19.1, 19.2 6.2 Electric Field and Force 6.3 Magnetic
Introduction to Blackbody Sources
 Introduction to s This section contains dedicated blackbody sources for low uncertainty calibration of infrared thermometers. A range of portable primary blackbody sources combine high emissivity with
Introduction to s This section contains dedicated blackbody sources for low uncertainty calibration of infrared thermometers. A range of portable primary blackbody sources combine high emissivity with
Heat and temperature are related and often confused, but they are not the same.
 Heat and temperature are related and often confused, but they are not the same. Heat Definition: Heat is energy that is transferred from one body to another as a result of a difference in temperature Symbol:
Heat and temperature are related and often confused, but they are not the same. Heat Definition: Heat is energy that is transferred from one body to another as a result of a difference in temperature Symbol:
Chapters 16 Temperature and Heat
 Chapters 16 Temperature and Heat 1 Overview of Chapter 16 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work Specific Heat Conduction, Convection,
Chapters 16 Temperature and Heat 1 Overview of Chapter 16 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work Specific Heat Conduction, Convection,
Unit 11: Temperature and heat
 Unit 11: Temperature and heat 1. Thermal energy 2. Temperature 3. Heat and thermal equlibrium 4. Effects of heat 5. Transference of heat 6. Conductors and insulators Think and answer a. Is it the same
Unit 11: Temperature and heat 1. Thermal energy 2. Temperature 3. Heat and thermal equlibrium 4. Effects of heat 5. Transference of heat 6. Conductors and insulators Think and answer a. Is it the same
Chapter 11. Energy in Thermal Processes
 Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Chapter 10. Thermal Physics
 Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
Physics 1501 Lecture 35
 Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
Thermal Effects. IGCSE Physics
 Thermal Effects IGCSE Physics Starter What is the difference between heat and temperature? What unit is thermal energy measured in? And what does it depend on? In which direction does heat flow? Heat (Thermal
Thermal Effects IGCSE Physics Starter What is the difference between heat and temperature? What unit is thermal energy measured in? And what does it depend on? In which direction does heat flow? Heat (Thermal
Chapter 14 Heat and Temperature Notes
 Chapter 14 Heat and Temperature Notes Section 1: Temperature The degree of or of an object. Related to the of an object s atoms or molecules What makes something hot? o Particles that make up o They have
Chapter 14 Heat and Temperature Notes Section 1: Temperature The degree of or of an object. Related to the of an object s atoms or molecules What makes something hot? o Particles that make up o They have
Bernoulli s Principle. Application: Lift. Bernoulli s Principle. Main Points 3/13/15. Demo: Blowing on a sheet of paper
 Bernoulli s Principle Demo: Blowing on a sheet of paper Where the speed of a fluid increases, internal pressure in the fluid decreases. Due to continuous flow of a fluid: what goes in must come out! Fluid
Bernoulli s Principle Demo: Blowing on a sheet of paper Where the speed of a fluid increases, internal pressure in the fluid decreases. Due to continuous flow of a fluid: what goes in must come out! Fluid
Overview. Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples
 Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
