The Building Materials Durability Model (BMDM)
|
|
|
- Arnold Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US Army Crps f ngineers Cnstrtin ngineering Researh Labratries USACRL Tehnial Reprt 96/24 Janary 1996 The Bilding Materials Drability Mdel (BMDM) A Cmparative Mdel fr Servie Life Fatrs Affeting Materials Seletin by K.D. Hjelmstad, D.A. Lange, F.V. Lawrene, I.D. Parsns, R.F. Qattrne, J.C. Trvillin, and D.M. Bailey Cnstrtin materials ant fr a majr prtin f bilding sts, affeting the sts f initial nstrtin, ntined maintenane, habitability, and evental demlitin f a bilding. The initial seletin f a nstrtin material may depend n a nmber f mplex and ften intangible fatrs, bt the ttal initial and lng-term sts f sing any bilding material system is ne f the mst imprtant parameters fr U.S. Army planners and bdgeteers. The bjetive f this researh was t investigate the feasibility f sing mdeling and simlatin tehniqes as the basis fr a tl t help Army faility designers and engineers selet materials fr ptimal life-yle enmy and servieability. The researhers develped algrithms representing varis materials drability parameters and envirnmental stimli, and integrated these int a prttype Bilding Materials Drability Mdel (BMDM). This reprt dissses the lgi and assmptins sed in develping BMDM, and desribes the reslts f hypthetial simlatins n tken bilding elements tested in tw different limates. It is nlded that BMDM ld be extended, refined, and sed with Mnte Carl simlatins t reliably prjet and mpare materials drability sts Apprved fr pbli release; distribtin is nlimited.
2 The ntents f this reprt are nt t be sed fr advertising, pbliatin, r prmtinal prpses. Citatin f trade names des nt nstitte an ffiial endrsement r apprval f the se f sh mmerial prdts. The findings f this reprt are nt t be nstred as an ffiial Department f the Army psitin, nless s designated by ther athrized dments. DSTRY THIS RPRT WHN IT IS N LNGR NDD D NT RTURN IT T TH RIGINATR
3 USR VALUATIN F RPRT RFRNC: USACRL Tehnial Reprt 96/24, The Bilding Materials Drability Mdel (BMDM) Please take a few mintes t answer the qestins belw, tear t this sheet, and retrn it t USACRL. As ser f this reprt, yr stmer mments will prvide USACRL with infrmatin essential fr imprving ftre reprts. 1. Des this reprt satisfy a need? (Cmment n prpse, related prjet, r ther area f interest fr whih reprt will be sed.) 2. Hw, speifially, is the reprt being sed? (Infrmatin sre, design data r predre, management predre, sre f ideas, et.). Has the infrmatin in this reprt led t any qantitative savings as far as manhrs/ntrat dllars saved, perating sts avided, effiienies ahieved, et.? If s, please elabrate. 4. What is yr evalatin f this reprt in the fllwing areas? a. Presentatin: b. Cmpleteness:. asy t Understand: d. asy t Implement: e. Adeqate Referene Material: f. Relates t Area f Interest: g. Did the reprt meet yr expetatins? h. Des the reprt raise nanswered qestins?
4 i. General Cmments. (Indiate what y think shld be hanged t make this reprt and ftre reprts f this type mre respnsive t yr needs, mre sable, imprve readability, et.) 5. If y wld like t be ntated by the persnnel wh prepared this reprt t raise speifi qestins r disss the tpi, please fill in the fllwing infrmatin. Name: Telephne Nmber: rganizatin Address: 6. Please mail the mpleted frm t: Department f the Army NSTRUCTIN NGINRING RSARCH LABRATRIS ATTN: CCR-TR-I P.. Bx 9005 Champaign, IL
5 RPRT DCUMNTATIN PAG Frm Apprved MB N Pbli reprting brden fr this lletin f infrmatin is estimated t average 1 hr per respnse, inlding the time fr reviewing Instrtins, searhing existing data sres, gathering and maintaining the data needed, and mpleting and reviewing the lletin f infrmatin. Send mments regarding this brden estimate r any ther aspet f this lletin f infrmatin, inlding sggestins fr reding this brden, t Washingtn Headqarters Servies, Diretrate fr Infrmatin peratins and Reprts, 1215 Jeffersn Davis Highway, Site 1204, Arlingtn, VA , and t the ffie f Management and Bdget, Paperwrk Redtin Prjet ( ), Washingtn, DC AGNCY US NLY (Leave Blank) RPRT DAT Janary RPRT TYP AND DATS VRD Final 4. TITL AND SUBTITL The Bilding Materials Drability Mdel (BMDM): A Cmparative Mdel fr Servie Life Fatrs Affeting Materials Seletin 6. AUTHR(S) K.D. Hjelmstad, D.A. Lange, F.V. Lawrene, I.D. Parsns, R.F. Qattrne, J.C. Trvillin, and D.M. Bailey 5. FUNDING NUMBRS 4A AT41 FM-CM5 7. PRFRMING RGANIZATIN NAM(S) AND ADDRSS(S) U.S. Army Cnstrtin ngineering Researh Labratries (USACRL) P.. Bx 9005 Champaign, IL PRFRMING RGANIZATIN RPRT NUMBR TR 96/24 9. SPNSRING / MNITRING AGNCY NAM(S) AND ADDRSS(S) Headqarters, U.S. Army Crps f ngineers ATTN: CMP-A 20 Massahsetts Ave. NW Washingtn, DC SPNSRING / MNITRING AGNCY RPRT NUMBR 11. SUPPLMNTARY NTS Cpies are available frm the Natinal Tehnial Infrmatin Servie, 5285 Prt Ryal Rad, Springfield, VA a. DISTRIBUTIN / AVAILABILITY STATMNT 12b. DISTRIBUTIN D Apprved fr pbli release; distribtin is nlimited. 1. ABSTRACT (Maximm 200 wrds) Cnstrtin materials ant fr a majr prtin f bilding sts, affeting the sts f initial nstrtin, ntined maintenane, habitability, and evental demlitin f a bilding. The initial seletin f a nstrtin material may depend n a nmber f mplex and ften intangible fatrs, bt the ttal initial and lng-term sts f sing any bilding material system is ne f the mst imprtant parameters fr U.S. Army planners and bdgeteers. The bjetive f this researh was t investigate the feasibility f sing mdeling and simlatin tehniqes as the basis fr a tl t help Army faility designers and engineers selet materials fr ptimal life-yle enmy and servieability. The researhers develped algrithms representing varis materials drability parameters and envirnmental stimli, and integrated these int a prttype Bilding Materials Drability Mdel (BMDM). This reprt dissses the lgi and assmptins sed in develping BMDM, and desribes the reslts f hypthetial simlatins n tken bilding elements tested in tw different limates. It is nlded that BMDM ld be extended, refined, and sed with Mnte Carl simlatins t reliably prjet and mpare materials drability sts. 14. SUBJCT TRMS mdeling simlatin st estimating life-yle sts master planning Army failities 15. NUMBR F PAGS PRIC D 17. SCURITY CLASSIFICATIN F RPRT Unlassified \ISN SCURITY CLASSIFICATIN F THIS PAG Unlassified 19. SCURITY CLASSIFICATIN F ABSTRACT Unlassified 20. LIMITATIN F ABSTRACT SAR Standard Frm 298 (Rev. 2-89) Presribed by ANSI Std
6 USACRL TR 96/24 Frewrd This researh was ndted fr Headqarters, U.S. Army Crps f ngineers nder Prjet 4A162784AT41, "Military Failities ngineering Tehnlgy"; Wrk Unit FM-CM5, "ptimal Materials and Prdts Seletin in Cnrrent ngineering." The tehnial mnitr was Rdger Seeman, CMP-A. The wrk was perfrmed by the Materials Siene and Tehnlgy Divisin (FL-M) f the Failities Tehnlgy Labratry (FL), U.S. Army Cnstrtin ngineering Researh Labratries (USACRL). The USACRL Prinipal Investigatr was Dr. Rbert F. Qattrne. Dr. llen G. Segan is Ating Chief, CCR-FL-M; Dnald F. Frnier is Ating peratins Chief, CCR-FL; and Alvin Smith is Chief, CCR- FL. The USACRL tehnial editr was Grdn L. Chen, Tehnial Resres Center. A prtin f this wrk was perfrmed nder ntrat by Dr. F.V. Lawrene, Dr. K.D. Hjelmstad, Dr. DA. Lange, and Dr. I.D. Parsns f F.V. Lawrene, In. L James T. Stt is Cmmander and Ating Diretr f USACRL, and Dr. Mihael J. 'Cnnr is Tehnial Diretr.
7 USACRL TR 96/24 Cntents SF Frewrd 2 List f Figres and Tables 5 1 Intrdtin 7 Bakgrnd 7 bjetive 8 Apprah 8 Mde f Tehnlgy Transfer 8 Metri Cnversin Fatrs 9 2 Desriptin and Develpment f BMDM 10 Drability Mdel Cnept 10 nvirnmental Stimli 11 General Framewrk fr Damage Mdels 12 Cst Mdeling 15 Mdeling the Drability f a Strtral lement 20 Desriptin f Mdel Prblems 20 Drability Mdel fr a Reinfred Cnrete Beam 22 Drability Mdel fr Steel 27 Drability Mdel fr Wd 1 Drability Mdel fr Alminm 4 Drability Mdel fr FRP 5 4 Mdeling the Drability f a Cladding lement 40 Desriptin f Mdel Prblem 40 Drability Mdel fr Paint 41 Drability Mdel fr IFS 42 Drability Mdel fr Alminm 4 Drability Mdel fr PVC 44 Drability Mdel fr Brik 45 5 Drability Mdel Test Cases 46 Test Case verview 46 Reslts fr Simply Spprted Beam 47
8 USACRL TR 96/24 Reslts fr Cladding 48 Disssin 50 6 Cnlsins and Remmendatins 65 Smmary 65 Remmendatins 65 Referenes 67 Distribtin
9 USACRL TR 96/24 List f Figres and Tables Figres 1 Drability mdel nept 18 2 xpnential grwth eqatins with nstant effiients 19 Plynmial grwth mdel with nstant effiients 19 4 The mdel prblem fr drability f a strtral element 7 5 The mdel prblem fr reinfred nrete 7 6 Measre f reinfrement bar rrsin 7 7 Measre f nrete saling depth 8 8 The mdel prblem fr steel 8 9 Measre f steel rrsin depth 8 10 The mdel prblem fr wd 9 11 Measre f wd deay depth 9 12 Typial trpial envirnmental stimli 51 1 Typial ntinental U.S. envirnmental stimli Behavir f nrete beam sbjeted t trpial envirnmental stimli 5 15 Behavir f nrete beam sbjeted t ntinental U.S. envirn- mental stimli Behavir f steel beam sbjeted t trpial stimli (lw-mainte- nane strategy) 55
10 USACRL TR 96/24 17 Behavir f steel beam sbjeted t trpial stimli (high-maintenane strategy) Behavir f steel beam sbjeted t ntinental U.S. stimli (lw- maintenane strategy) Behavir f the steel beam sbjeted t ntinental U.S. stimli (high-maintenane stragety) Behavir f paint ladding sbjeted t trpial stimli (lw- maintenane strategy) Behavir f paint ladding sbjeted t trpial stimli (high- maintenane strategy) Behavir f paint ladding sbjeted t ntinental U.S. stimli (lw-maintenane strategy) 61 2 Behavir f paint ladding sbjeted t ntinental U.S. stimli (high-maintenane strategy) Behavir f the alminm ladding sbjeted t trpial stimli 6 25 Behavir f alminm ladding sbjeted t ntinental U.S. stimli 64 Tables 1 Drability sts fr reinfred nrete beam (averages frm 10 BMDM simlatins) 47 2 Drability sts fr steel beam (averages frm 10 BMDM simla- tins) 49 Drability sts fr paint ladding (averages frm 10 BMDM simlatins) 49 4 Drability sts fr alminm ladding (averages frm 10 BMDM simlatins) 49
11 USACRL TR 96/24 1 Intrdtin Bakgrnd Cnstrtin materials ant fr a majr prtin f bilding sts, affeting the sts f initial nstrtin, ntined maintenane, habitability, and evental demlitin f a bilding. The initial seletin f a nstrtin material may depend n a nmber f mplex and ften intangible fatrs, bt the ttal initial and lng-term sts f sing any bilding material system is ne f the mst imprtant parameters. Materials with the lwest initial st ften reslt in sh high maintenane sts that any initial st savings an be erased mh earlier than expeted. A key t st redtin thrgh materials seletin is knwledge f the mparative drability f varis bilding materials, and hw their drability affets the ttal bilding's ttal life-yle st. The servie life f a strtre is sally nsidered dring design nly thrgh the speifiatin f the retrn perid f the mst extreme envirnment the strtre is expeted t endre. Fr example, a strtre may be designed t withstand a 100-year earthqake r wind strm. The seletin f materials typially is based n the ntin that, with sme safety fatr bilt in, the strtre will resist the extreme event in a virgin state. A gd engineer nsiders the impliatins f material drability and maintenane in the design f a strtre even thgh rrent Army design reqirements d nt expliitly insist n it. The rrent state f the art in engineering design fr drability is based n rather arse deisin pints sh as "steel rrdes while plasti des nt," r "nrete sales while steel des nt." Sh anedtal knwledge des nt really help the engineer evalate the tradeffs in materials seletins bease it is t sperfiial. The signifiane f materials seletin n verall Army peratinal sts an be seen in rrsin st figres, fr example, whih exeed $00 millin annally (Hahin 1977). Crrsin sts ntrl are ften mst easily reded dring faility design thrgh the seletin f alternative materials. The lak f lng-term experiene with prmising new materials tends t inhibit appliatin f new materials that might signifiantly rede lng-term faility sts. Faility designers and speifiers need a mdel that an predit the drability f varis bilding materials as sed fr a speifi appliatin at a speifi latin. An effetive mdel f this type als wld analyze what rle r pririty materials
12 USACRL TR 96/24 drability shld play in the seletin press. Sh a mdel, when sed dring nept design in a nrrent engineering llabrative deisin envirnment, wld enable engineers t arately and effiiently mpare the life-yle sts f nventinal materials t alternative nes. The mdel ld help the Army maintain the life expetany f strtres at a lwer life-yle st. The U.S. Army Cnstrtin ngineering Researh Labratries was tasked by Headqarters, U.S. Army Crps f ngineers, t develp a Bilding Materials Drability Mdel (BMDM). bjetive The bjetive f this wrk was t investigate nepts fr ptimal seletin f bilding materials, fr pssible inrpratin int a deisin-spprt tl fr faility designers sing an agent-based llabrative design netwrk. Apprah The researhers investigated mdeling tehniqes that nsider preditive, lng-term materials perfrmane in servie, maintenane and repair (M&R) life-yle impliatins, and differing nstrtin envirnments. A prbabalisti mdeling apprah was sed. Damage mdels were develped fr several mmn nstrtin material systems, bth fr strtral elements and ladding elements. The mdel's algrithms were embedded int a spreadsheet sftware prgram fr desktp mpter. Tken bilding elements were sbjeted t differing envirnments fr a nmber f iteratins in a mpter-driven Mnte Carl simlatin, and material perfrmane was evalated. Repair and failre riteria were evalated after eah iteratin, and the amlated st f drability allated. A presentatin frmat fr drability mparisn f different nstrtin materials was develped. Finally, BMDM was applied t fr materials tw strtral materials and tw ladding materials. Drability sts, in terms f net present vale, were allated fr tw different natral envirnments. Mde f Tehnlgy Transfer This wrk will feed int the Arhitet's Assiate prgram, USACRL's nrrent engineering researh initiative. The Arhitet's Assiate tehnlgy transfer plan will
13 USACRL TR 96/24 inlde the frmatin f perative researh and develpment agreements (CRaDAs) fr transfer f appliatins and develpment f an agent llabratin langage. The agent llabratin langage will be prpsed fr inlsin by ANSI and IS* in the Prdt Data xhange Speifiatin (PDS) and the Standard fr the xhange f Prdt Mdel Data (STP). Metri Cnversin Fatrs U.S. standard nits f measre are sed thrght this reprt. A table f metri nversin fatrs is presented belw. 1 in. = 25.4 mm 1 sq in. = mm 2 11b =.78 L F = ( Cx1.8)+2 ANSI is the Amerian Natinal Standards Institte; IS is the Internatinal Standards rganizatin.
14 10 USACRL TR 96/24 2 Desriptin and Develpment f BMDM Drability Mdel Cnept Sppse that it is pssible t simlate the evltin f all envirnmental stimli that are imprtant t the drability f a bilding mpnent. Sppse frther that it is pssible t analytially mdel the damage presses that an r in the bilding mpnent and hypthesize varis repair strategies. Given these assmptins, it wld be pssible t simlate the lifetime fthat bilding mpnent ver time within the framewrk desribed in Figre 1*. In this framewrk the envirnmental stimli T(t), 6(t), and (t) are speified as expliit (pssibly randm) fntins f time. The mpnent inldes a nmber f desriptrs, inlding its material prperties and its gemetri nfigratin. The qantities x represent a lletin f damage variables rerding lss f material, hange in material prperty, lss f aestheti appeal, and ther fatrs that evlve arding t the damage rate fntins f. With an idea f the mpnent's initial st, the riterin h(x)< y an be established t indiate failre r t trigger repair and establish the means t speify a repair strategy and amlate drability st (i.e., initial st pls the sm f the repair sts). Dring eah time perid, the amnt by whih the material servie prperties have degraded is determined arding t the damage mdel. The degraded bilding element is heked fr mpliane with speifi perfrmane and servieability riteria. If the mpnent has failed dring that time perid, its life is ver. The mdel then mptes the mpnent's lifetime and drability sts. If the strtre has nt failed, bt instead a repair has been triggered, then the repair is exeted, the drability st revised, and the element is ready t enter the next time perid. If the element meets all riteria then it simply passes t the next time perid. The simlatin ntines ntil the design life has expired r the mpnent has failed. Clearly, the sess f this drability mdel depends pn hw well the envirnmental fatrs an be simlated and hw well the damage presses an be mdeled and repair strategies defined. Hwever, the paradigm an be implemented with rather primitive envirnmental and damage mdels prviding that mre sphistiated mdels an be pt in plae f the simple nes as they beme available. In this wrk sme Figres are fnd at the end f their rrespnding hapters.
15 USACRL TR 96/24 11 fairly simple mdels f damage are adpted t demnstrate the synergy f the pled apprah. nvirnmental Stimli ver its lifetime, a material mpnent will be sbjeted t many envirnmental fatrs, and these fatrs will generally fltate with time. In this mdel, the BMDM assme that the hanges in these envirnmental stimli ver time are knwn. Three envirnmental effets will be nsidered here: the ambient temperatre T(t), the ambient mistre Q(t) de t hmidity and preipitatin (expressed as a fratin f satratin), and the nentratin f aggressive hemials r agents f deay (t) (expressed as a fratin f the maximm nentratin). Different envirnments an be mdeled by assigning different histries fr these three stimli. Tw hypthetial envirnments will be nsidered: trpial (pssibly indiative f Gam) and ntinental United States (pssibly indiative f Chiag). Temperatre, hmidity, and hemial nentratin generally fltate arding t daily and seasnal hanges. Fr the rrent prpse, the mnthly averages f these stimli are sed. When daily fltatins are imprtant, as they wld be in a freezethaw mdel, they will be anted fr expliitly in damage mdels. Reglar seasnal hanges will be agmented with randm fltatins t simlate the variability f limati effets. The fltatin f temperatre is given by the expressin T(t) = T 0 +ATsin(nt/6)+6Tn(t) [q 1] where T 0 is the average yearly temperatre, AT is half the differene between the highest average mnthly temperatre and the lwest average mnthly temperatre, 6T is the average fltatin in temperatre in 1 mnth, and r\(t) is a nifrmly distribted randm nmber between -1 and 1. The time t is measred in mnths. The ntinental U.S. temperatre mdel has T 0 = 40 F, AT = 50 F, and 6T = 10 F. The trpial mdel has T 0 = 85 F, AT = 10 F, and 6T = 5 F. The fltatin in mistre is given by a similar expressin, 9(t) = 8 0 +A9sin(nt/6)+B6n(t) [q 2] where 8 0 is the average annal mistre ntent, A6 is half the differene between the highest average mnthly mistre ntent and the lwest average mnthly mistre,
16 12 USACRL TR 96/24 80 is the average fltatin in mistre in 1 mnth, and r\(t) is a nifrmly distribted randm nmber between -1 and 1. The ntinental U.S. mistre mdel has 6 0 = 0.5, A6 = 0., and 66 = The trpial mdel has 8 0 = 0.9, A6 = 0.05, and 60 = The hemial envirnment als an vary by seasn, bt fr rrent prpses it is mdeled simply as a nstant average vale with randm fltatins, (t) = 0 +ön(t) [q] where 0 is the average nentratin f aggressive hemials, 6 is the expeted fltatin in that average, and r\(t) is a nifrmly distribted randm nmber between -1 and 1. The ntinental U.S. mdel has 0 = 0.7 and 6= 0.. The trpial mdel has 0 = 0.2 and 6= 0.1. General Framewrk fr Damage Mdels Damage mehanisms fr varis materials are generally determined by fatrs that r at a mirspi sale. Many f these presses are still prly nderstd. It is beynd the spe f the rrent investigatin t attempt t mdel damage at the mirsale. ne might eventally replae eah f the varis damage mdels sed here with mre arate nes, bt fr rrent prpses simple mdels are sed t qalitatively reflet the physial presses that are taking plae. Let p(t) represent a typial damage parameter. Depending pn the mehanism f damage, the evltin f this damage parameter will be gverned by ne f three basi damage mdels: linear grwth, expnential grwth, r plynmial grwth. Linear Grwth Mdel A linear grwth mdel des nt depend n the rrent state f damage, bt has a rate f grwth gverned by sme fntin f the envirnment: ^=fct,0,) at [q4] p(=p
17 USACRL TR 96/24 1 Fr this mdel, if the envirnment is nstant, damage grws linearly with time: p(t) = p 0+ f(t,8,)t [q5] Saling f nrete ased by freeze-thaw yling is an example f linear grwth damage. xpnential Grwth Mdel In an expnential grwth mdel, the rate f hange in the damage parameter depends diretly pn the amnt f damage rrently present (smetimes raised t sme pwer m): ^=fct,8,)p(t) at [q6] P(=P 0 Fr this mdel, if the envirnment is nstant, the damage evlves expnentially with time as fllws: p(t) = P e'ct.e,) t [q7] The sltin t the expnential grwth mdel frp 0 =l and nstant fring fntin f=b is shwn in Figre 2 fr different vales f B. Damage t the srfae prtetin prvided by paint is mdeled as an expnential grwth press. Plynmial Grwth Mdel A plynmial grwth mdel represents a diffsin press. The rate f hange f the damage parameter is inversely prprtinal t the amnt f damage present (ften raised t sme pwer m): dp _ f(t.9.) dt" p(t) [q8] P(=P
18 14 USACRL TR 96/24 Fr this mdel, if the envirnment is nstant, the damage evlves as a plynmial with time as fllws: p(t)=/p f(T,8,)t [q9] ne f the mst imprtant featres f this mdel is that it is sally assiated with failre in a finite amnt f time. The sltin t the expnential grwth mdel fr p 0 =l and nstant fring fntin f=b is shwn in Figre fr different vales f B. Crrsin f steel, deay f wd, and stati fatige f nrete are examples f the diffsin (plynmial grwth) mdel. In eah ase, the envirnmental fntin driving the press will be different. In mst ases a fr-parameter mdel was seleted, with ne tnable parameter fr eah f the three envirnmental effets, and ne t arately represent the verall rate f damage. Sme f these fntinal dependenies me frm first priniples, e.g., Arrhenis's Law (Arrhenis 1907) is sed t haraterize dependene pn temperatre; thers, hwever, are simply plasible heristi mdels, e.g., the expnential mdels ften sed fr mistre and hemial nentratin. A typial example f ne f these fntins is given by: f(t,8,)=d 0 [e(t)] n [1 +(t)] m e - VT(t) [q 1 ] This type f mdel "des the right thing" in the sense that higher mistre ntent drives damage faster, bt there is a premim n mistre ntents near satratin, 8=1, and damage stps if the element dries t. (Nt all mdels have this featre.) Higher nentratins f aggressive hemials speed p the rate f damage, bt damage will r even if n hemials are present. High temperatres speed p damage; lw temperatres nearly stp the damage press. Nmerial Integratin f the Damage Mdels The fntins /(T, 0, ) driving the damage presses will, in general, nt be nstant with time. Ths, the rate eqatins mst be integrated nmerially. Fr rrent prpses the generalized midpint rle is sed. The inremental linear grwth mdel f qatin 4 then takes the frm
19 USACRL TR 96/24 15 p(w=pft)+f(t a,e a, a )At [q11] P(=P where A =i i+i -^, and the envirnmental fatrs are a weighted average f the vales ''i+l at t t and t i+1 as fllws: a = (1-a)(ti)+a(t l+1 ) 9^(1-a)8(t,) + ae(t k1 ) [q 12] T a H(1-a)T(t,) + at(t i+1 ) In general, ne shld se a=0.5, i.e., the trapezidal rle. The ther eqatins are integrated similarly. The expnential grwth mdel has the inremental frm p^^e'^0"'" [q 1] P(=P 0 The plynmial grwth mdel has the inremental frm p(t i+1 )^p 2 (t i ) + 2fCT a,e a, a )At [q 14] P(=P 0 Thrght this wrk details f mptatin are given nly fr exeptins t the abve ases and fr mptatins that help determine the effiients f the mdels. Cst Mdeling The ser an speify an MR strategy in ard with servieability reqirements, safety fatrs, r ther fatrs affeting the perfrmane f eah mpnent. ah
20 16 USACRL TR 96/24 material will be sbjet t different nstraints, bt fr rrent prpses the strategy is mdeled as fllws: the vth repair at sts C v dllars and restres the element prperties, as well as ertain f the mdel parameters, t a fratin q v f the mst reent repaired vale r t a fratin q v f its riginal vale. An element that fails dring a time step mst be replaed it annt be repaired. The qality f a mpnent r a repair jb will depend n many fatrs. Fr example, the qality f a paint jb depends pn the qality f the paint, the qality f srfae preparatin, and the qality f paint appliatin. T simplify this disssin it is hypthesized that the verall qality an be indexed with a single vale based n an assmptin that a persn wh bys the best paint wld als be inlined t d a gd jb preparing the srfae and applying the paint. In ther wrds, this mdel simply annt ant fr a persn ding a slppy jb with gd paint. The qality q will be speified as a nmber between 0 (prest qality) and 1 (best qality). The st assiated with making a repair is als a fntin f the qality fthat repair. Clearly, the best qality repair will st the mst and the wrst qality repair the least. The st f repair is mdeled as C(q) % x [q15] 1-q(1-p) where C 0 is the st f the prest qality repair and p is the rati f the st f the prest qality repair t the st f the best qality repair. The mdel yields a "prgressive tax" n qality as it nears perfetin, bt is relatively insensitive t st at lesser qalities. The ser mst speify the initial st f the mpnent, t failitate mparisn amng materials as well as the st f replaement. In sme mdels ertain things an be repaired while thers annt. In thse ases, the repair strategy applies nly t items that an be repaired. The maintenane sheme reqires the speifiatin f the leastexpensive repair, the mst expensive repair, the initial qality q 0 f the mpnent, and the qality f any sbseqent repair q v (as well as the riteria that determine the time f repair). These speifiatins determine the drability st. The time vale f mney is nsidered by finding the present vale f a ftre amnt arding t the fllwing frmla fr single payment present wrth (SPPW): SPPW=(1+i) n [q16]
21 USACRL TR 96/24 17 where i is the effetive disnt rate per perid (1 mnth fr the rrent simlatins) and n is the nmber f perids. If the st f a repair is C v at the time f repair, then the vale f that repair at time zer is C v =C v (1 + i)-" [q17] where n is the nmber f perids elapsed sine time zer. Fr the amlatin f drability sts, all sts are referred bak t time zer. Therefre, a material reqiring repair in 40 years (fr example) an be nsidered less stly in terms f rrent dllars than a material reqiring repair in 0 years. The time vale f mney that is, the idea that a dllar tday is inherently mre valable than the same dllar next year may play an imprtant rle in mparing a high-maintenane material (sh as steel) with a lw-maintenane bt initially mre expensive material (sh as alminm).
22 18 USACRL TR 96/24 Inpt Parameters Cmpnent Prperties Initial material prperties (e.g. strength, stiffness) Cmpnent gemetry (e.g. beam length, area) Initial sts, repair sts and strategy nvirnmental Stimli T(t) temperatre 6{t) ambient mistre ntent (t) nentratin f aggressive hemials Damage Mdels Metal rrsin, nrete saling (freeie-thaw), paint peeling, viselasti reep, stati fatige,. ^=f{x,t,e,) Design/Perfrmane Criteria lement strength, servieability, aestheti appeal h{x) < y Repair Failre tpt tpt time t failre (r ttal lifetime). tpt ttal drability st Restre prperties in ard with repair strategy. Add repair st t ttal drability st Figre 1. Drability mdel nept.
23 USACRL TR 96/ p Figre 2. xpnential grwth eqatins with nstant effiients. dp _ B 1 B = Figre. Plynmial grwth mdel with nstant effiients.
24 20 USACRL TR 96/24 Mdeling the Drability f a Strtral lement Desriptin f Mdel Prblems As a mdel prblem, nsider the drability f a beam sbjeted t a lading P(t) at its midspan, as shwn in Figre 4. The materials available fr beam nstrtin are reinfred nrete, steel, wd, alminm, r fiber-reinfred plasti (FRP). ver its lifetime, the beam is sbjeted t envirnmental fatrs that fltate with time. As nted in Chapter 2, this prblem fses n three fatrs: ambient temperatre T(t) ambient mistre 0(0 de t hmidity and preipitatin, expressed as a fratin f satratin nentratin f aggressive hemials r agents f deay (t), expressed as a fratin f the maximm nentratin. Fr the simlatins P(t) takes the fllwing frm: P(t)=P 0+ öpn 2 (t) [q18] where P 0 is the expeted lad and bp is the amplitde f the fltatin in the lad. As befre, r\(t) is a nifrmly distribted variate (randm variable). The beam mst ntine t fntin arding t its intended prpse, that is, arry the lading P(t) witht exessive defletin. Fr eah material there are strength and servieability reqirements in terms f rss-setinal prperties like the area A(t) and the mment f inertia I(t), whih are degrading thrgh varis damage mehanisms. Bth the nset f failre (r dysfntin) and the M&R st are nsidered.
25 USACRL TR 96/24 21 Strength Design Criterin It is assmed that the beam is designed t have adeqate bending strength at time =0. The strength f the beam, as a fntin f time, is designated by P^t). The initial strength f the beam is ths Pj/ and meets the design riterin PWexpeted [q19] where (J) 0 is the initial fatr f safety and V apeled is the maximm expeted applied lad. As the prperties f the beam degrade ver time the strength will derease, thereby mprmising the fatr f safety. The rrent design fatr f safety is given by and define the rrent atal fatr f safety is given by P (t) * d(t)h * p(t [q20] P(t) * a (t)-^ [q21] The rrent design fatr f safety will be sed as an index fr repair deisins (e.g., repair if <J) d < 0.8p ) while the rrent atal fatr f safety will be sed t detet failre f the system, i.e., (j) a < 1. Servieability Design Criterin The main servieability design riterin is the gard against exessive defletin. The initial design will have defletin limits fr a variety f reasns, many f whih will have little t d with the lng-term perfrmane f the beam. As a nseqene, a lng-term limit t midspan defletin is simply speified as w lt. The rrent servieability fatr f safety is given as +sw s [q22] The rrent servieability fatr f safety will be sed as an index fr repair deisins (e.g., repair if <J) S > 1) r t detet fntinal failre f the system (e.g., the mpnent is dysfntinal if (J) s > 1.
26 22 USACRL TR 96/24 Drability Mdel fr a Reinfred Cnrete Beam Degradatin f the reinfred nrete beam is ased by rrsin f the reinfrement bars, stati fatige f the mpressive strength, and saling f the tp srfae, as shwn shematially in Figre 5. The strength f the reinfred nrete beam at time t is given by P (t)=^ h(t)-0.59^ä 0 0 (t)b [q2] where Aß) = n s Tz[r 0 - x(t)f is the area f n s steel bars rrded t a depth f x(t), h(t) = h 0 - s(t) is the beam depth saled t a depth s(t), and 0 (t) is the nrete mpressive strength. The yield strength f the steel, f y, and the width f the beam, b, are taken as nstants. Althgh reinfred nrete is sbjet t lng-term reep defletins, they are nt nsidered in this prblem. Crrsin f Reinfrement Bars The beam is reinfred with steel bars f initial radis r 0. De t the histry f temperatre T, mistre 0, and rrding hemials, the bars have a rrent radis f r, reded frm the riginal radis by the amnt x. Figre 6 shws the measre f material lss ased by rrsin. Crrsin f the reinfrement bars will depend n hw mh mistre r ther hemial agents are present. In lie f a mre sphistiated mdel f mistre transprt, it is assmed that the nrete has pre-existing raks that allw envirnmental mistre nimpeded aess t the reinfrement bars. The fllwing rate eqatin desribes the lss f bar radis ased by rrsin: dt " x(t) [q24] The driving fntin takes the frm x(=0 f (T,6,) = D 0 [6(t)] n [1 + (t)] m e -* [q 25]
27 USACRL TR 96/24 2 where Q(t) is the envirnmental mistre ntent as a perentage f satratin, (t) is the nentratin f the hemial envirnment, and T(t) is the temperatre (in degrees Kelvin). The parameters n, m, D 0, and ß are material nstants that will be fit t anedtal data; in ther wrds, all ther fatrs will be held nstant while the pblished variatin ased by a single effet are fit. The sltin t the rate an be btained by nmerial qadratre (sqaring) t give the lss f radis at time t i+i in terms f the lss at time t t agmented by the rrsin that takes plae between thse tw times: xft +1 ) = v/x 2 ft) + 2Atf (T a,e a, a ) [q26] x(=0 The main idea behind this rrsin mdel is as fllws: bease rrsin is mainly the reslt f expsre t mistre, the rate f rrsin shld inrease as the mistre ntent inreases and shld effetively stp in the absene f mistre. Frthermre, nearly dry nditins shld be nsiderably less rrsive than nearly satrated nditins. Therefre, in qatin 25, the expnent n is greater than 1. The greater the expnent, the mre aentated this effet will be. Crrsin is exaerbated by the presene f aggressive hemials, bt it will r even in the absene f hemials. The greater the nentratin f aggressive hemials, the faster the rrsin. Therefre, the expnent m>l. The greater the expnent, the mre aentated this effet will be. Arding t Arrhenis's Law (Arrhenis 1907), the rate f rrsin depends pn the temperatre. The material will rrde faster at a higher temperatre. The effiient ß ntrls the rate f rrsin ased by an inrease in temperatre. Crrsin wld be expeted t drp t arbitrarily lw rates as the temperatre drps belw the freezing pint, and wld r fastest at the tp f the temperatre range being nsidered. The maximm envirnmental temperatre may be designated as T f. If, at any given instant the rate f rrsin at T^ were y times the rate at et^ then the expnent ß mst be given by ß = -J-T,ln Y 1-e [q27]
28 24 USACRL TR 96/24 Fr example, if the rate f rrsin is ne-frth as fast at half the maximm temperatre f 25 K, thenß = 450 K. Stati Fatige in Cnrete At lads that ase the mpressive stress t apprah the strength f nrete, damage is inrred thrgh the mehanism f stati fatige. This phenmenn reslts in a derease in the strength f nrete ver time. Let 0 (t) be the nrete strength and a(t) (psitive mpressive) the applied stress at time t. Assming that the material exhibits elasti behavir, ne an relate the stress t the applied lad thgh the relatinship a(t) = P(t)/S, where S is the setin mdls f the beam. Fr rrent prpses it is hypthesized that the strength degrades arding t a pwer law as fllws *>. -Bö (t) 0 dt - n [q28] 0 ( = where B and n are the parameters desribing the material. Assming that the applied stress remains nstant frm time t t t t i+1, qatin 28 an be integrated t give the strength at the rrent time as 0 (W = 00,)+ [[^-fw'-mn+db^at]"- 1 [q29] This mdel will predit a derease in strength with time, bt it an be rather sensitive. Therefre, ne mst take are t hek fr material failre within a time step. The time t failre, expressed as a fratin f the rrent time inrement, is given as [0,)-0 )r 1 (n-ijbxyat [q0] If x f < 1, then the material has failed dring the rrent time inrement. Bease ne mst mpte time t failre at every step anyway, qatin 29 an be simplified t
29 USACRL TR 96/ (U = (li) + KT f -l)(n + 1)B 0 rf^fl 1 n+1 [q1] ( = The nstants an be fit t data btained frm tests in whih the time t failre is rerded fr nstant stress vales. In sh an instane, failre is defined as a 0 (t f ) = a, and time t failre is given by (n+ijbö-" [q2] Assme that tw tests are available. Let { l, t l ) be the applied stress and time t failre f the first test, and let ( 2,1 2 ) be the applied stress and time t failre f the send test. The expnent f the mdel an be determined frm these tw tests by the fllwing relatinship: nln i( 0-2 ) 2 ( - i) = ln U ~ J M<V 2) [q] After n is determined, B an be determined frm B = (p-pi)"*1 (n + 1)ö 0 ^ r [q4] B = ( 0-2 r 1 (n + 1)ö 0 gt. Fr example, if at a x = 0.9 with t x = and 2 = 0.75 with t 2 = 294 then ne btains n = 5 and B =.5 x 10" 6. Cnrete Saling Saling f a nrete srfae is ased largely by freeze-thaw yling f the envirnment. The mehanism asing material damage frm freeze-thaw yling is extremely
30 26 USACRL TR 96/24 mplex, invlving the mistre ntent at the time f freezing, the rate f freezing, and the pre strtre f the material (whih an als alter the freezing temperatres). T develp a simplified mdel that prves the nept by making qalitatively rret prjetins whih is the present prpse it is neessary t make sme brad assmptins. First it is assmed that the nmber f freeze-thaw yles is related t the average temperatre mltiplied by the time ver whih the temperatre was averaged. (Clearly the mdel will behave best if ne takes time inrements small engh t sense seasnal hanges, bt with this mdel ne des nt need t take them small engh t reslve daily fltatins). Next, it is assmed that the srfae deterirates frm the tside-in, with the amnt f deteriratin dring a time step being given by the nmber f freeze-thaw yles. The depth f saling s(t), shwn in Figre 7, is ths mdeled as ^=f 8 CT,e,) [q5] s(=0 where the driving fntin has the frm f s Cr,e,) = C<T 0 -T(t)>[e(t)] n [1 + (t)f [q 6] and where the parameters C, n, and m affet the rate f saling ased by mistre and nentratin f hemials, mh like the rrsin mdel. The ntatin <x> means that <x>= x if *>0 and <*>= 0 ifx<0. The vale T 0 is the fixed temperatre abve whih n freeze-thaw yling is expeted t r. Fr example, if the average temperatre ver a mnth is 10 F ne might expet daily fltatins t reslt in freeze-thaw yling. While ne might expet less yling fr very ld temperatres, it is assmed fr the rrent prblem that the temperatre f the material is affeted by its ability t absrb the sn's heat. Fr example, blaktp an thaw even if the air temperatre des nt exeed the freezing temperatre fr water. Assming the envirnmental fatrs t be nstant ver the time step, qatin 5 an be integrated t give
31 USACRL TR 96/24 27 s(t M )=s(t j ) + Atf 8 (T a,e a, a ) s(=0 [q7] The mdel parameters an be adjsted t fit anedtal data. The inflene f mistre shld derease rapidly as the mistre level falls belw satratin. Ths, an expnent like n=5 might be reasnable. The inflene f the hemial nentratin might be adeqately refleted by a vale like m=. The vale f C might best be determined by nsidering the time it wld take t sale t a ertain depth in the harshest envirnment. Drability Mdel fr Steel Degradatin f the steel beam is ased by rrsin f the expsed srfaes, as shwn shematially in Figre 8. The strength f the steel beam at time t is given by P «= ^Jh V»W] + 4hb[t,-2x(t)]] [q 8] where all f the plate faes are rrded t a depth f x(t). The strength f the steel f y, the depth f the beam h, and the width f the beam b are taken as nstants. It is assmed that there are n lng-term defletin prblems fr a steel beam. Crrsin f Steel The steel beam has an I-type rss-setin with depth h and flange width b. It has a flange thikness t f and a web thikness t w that, de t the histry f temperatre T, mistre 0, and rrding hemials, have rrded by amnt x n eah fae. Figre 9 shws the measre f material lss ased by rrsin. Crrsin f the steel beam will be mdeled in the same manner as the reinfrement bars were mdeled fr the reinfred nrete beam, bt a mdifiatin mst be made in the envirnmental expsre. Sine steel is almst always painted, a paint mdel is nsidered in njntin with the rrsin mdel. The mistre and nentratin f aggressive hemials in the rrsin mdel will simply be the amnt transprted thrgh the srfaing material.
32 28 USACRL TR 96/24 The fllwing diffsin eqatin desribes the lss f plate thikness ased by rrsin after the vth repair: x ( = 0 dxv f r,e p, p ) dt x v (t) [q9] x v (0=x v - 1 (t;- 1 ) where the vth repair is exeted at time t 0 " = t* 1 with the initial nditin fr the next stage being given by the end nditin f the previs stage. The rss-setin starts in an ndamaged nditin. The rrsin-driving fntin is given by the expressin f (T,e D> D ) = D 0 [8 D (t)ni + D (t)] m e -«"» [q 40] where Q p (t) is the mistre ntent as a perentage f satratin, and p {t) is the nentratin f aggressive hemials transprted thrgh the srfaing material. T(t) is the abslte temperatre (Kelvin). The parameters n, m, D 0, and ß gvern the rate f rrsin. These parameters an be established in exatly the same manner as in the rrsin mdel fr reinfrement bars in the nrete beam mdel. Srfae Prsity Mdel The prsity f the srfae pit) is gverned by a damage mdel that addresses bth ating and sbstrate nditin. The rate f hange in prsity is assmed t be prprtinal t the amnt f prsity, and is driven by a fntin f the envirnmental fatrs as fllws: dp v dt -f D (T,e i,v)p v (t) P v (t V ) = 9 P (qv) [q41] P ( = 1
33 USACRL TR 96/24 29 where the fntin driving the hange in prsity is f D (T,e,,v) = D B tr)f-[i +e f [1 + (t>r [q42] and where T(t) = T(t)-T 0 [q4] is a nrmalized measre f the temperatre. It has been nted that damage t paint generally rs at a greater rate fr very ld temperatres and fr very ht temperatres, bt slws fr intermediate temperatres (Tke 198. Fr this mdel the referene temperatres T g = 00 K and T, = 20 K are sed. Deteriratin speeds p in the presene f mistre and aggressive hemials, bt it will als preed in a dry, hemially netral envirnment. The qality f the srfaing determines the nditin t whih the prsity index retrns. The fntin sed in this mdel is simply taken t be g (qv) = (<U 5 [q44] The parameters n, m, and k are taken t be fntins f the qality f the srfaing (i.e., material sed, srfae preparatin, et.). The ser mst speify the qality q f the initial srfaing and f any sbseqent repair srfaing. The qality q will be speified as a nmber between 0 (prest qality) and 1 (best qality). Then the parameters n and m, at the vth repair, an be speified in ard with the qality f the repair sing the fllwing relatinships i\ = 4/q 1^ = ^ [q45] K, = 1/q The maintenane strategy then nsists f speifying the times and qalities f the resrfaing.
34 0 USACRL TR 96/24 qatin 41 an be nmerially integrated t give the fllwing vale f the prsity at time t i+1 in terms f the prsity at time t t after the vth repair: Pt-P^«41^ P v (0 = g p (q v ) \ f t» 46 l P ( = 1 where A* = t v M - t\, and the envirnmental fatrs, as befre, are the trapezidal averages f vales at t v t and t v i+1. As the prsity index inreases with damage, the resistane f the srfaing material t mistre and hemial transprt dereases. The fllwing simple transprt mdel gives the mistre and hemial nentratin at the srfae f the steel in terms f the envirnmental mistre and hemial nentratin: e p (t) = [i-p v (t)ie(t) [q47] C p (t) = [1-P v (t)](t) The sltin t the rate eqatin fr rrsin an nw be btained by nmerial qadratre t give the lss f plate thikness at time t v M in terms f the lss at time t V i agmented by the rrsin that takes plae between thse tw times: x(c) = /x 2 (0+2Atf CT a,8 pa> pa ) x ( = 0 [q48] x'-x-h where Q pa and pa are evalated in a manner analgs t Q p and p in qatin 12.
35 USACRL TR 96/24 1 Drability Mdel fr Wd Degradatin f the wd beam is ased by deay f the expsed srfaes, as shwn shematially in Figre 10. The strength f the wd beam at time t is given by P (t) = ^[h-2x(l)?lb-2x(t)] L [q49] where all f the beam faes are deayed t a depth f x(t). The mdls f rptre f the wd/", the depth f the beam h, and the width f the beam b are nstants. Deay f Wd The wd beam has a retanglar rss-setin with depth h and width b that, de t the histry f temperatre T, mistre 6, and rrding hemials, have deayed by the amnt x n eah fae. Figre 11 shws the measre f material lss ased by rtting. The fllwing diffsin eqatin desribes the lss f material ased by deay: dx _ Wß) dt x(t) [q50] x(=0 The rss-setin starts in an ndamaged nditin. The deay-driving fntin is given by the expressin f d (T,e) = C d [1-e- l2 ( t»][8(t)r [q51] where T(t) = T(t)-T 0 T, [q52] is a nrmalized measre f the temperatre. It has been nted that deay generally rs nly ver a ertain range f temperatres (Amerian Institte f Timber Cnstrtin 1974). Fr this mdel the referene temperatres are taken as T 0 = 00
36 2 USACRL TR 96/24 K and T t = 20 K. The deteriratin speeds p in the presene f mistre bt will nt take plae in a dry envirnment. The parameters n, m, and k depend n the qality (hardness) f the wd Q, with Q=l being the sftest wd and Q=10 being the hardest wd. The fllwing vales are remmended: n =,/Q [q5] 2 As befre, the sltin t the rate an be btained by nmerial qadratre t give the lss f material at time t M in terms f the lss at time t t agmented by the deay that takes plae between thse tw times: x(u = My + 2Atf d (T ai 8 a ) [q54] x( = 0 where A* = t i+1 - t t and the envirnmental fntins, as befre, are the trapezidal average f vales at t t and t i+1. Creep Defletin f Wd Wd is sbjet t reep defletins ased by lng-term lading. T mdel the lng-term reep behavir a Nrtn expnential reep law (Kahinv 1986) is emplyed. The law is assmed t apply t the mment-rvatre relatinship f the beam as fllws: *(z,t) M^+BM m (z,t) l(t) [q55] where Ü: is the rate f hange f rvatre f the beam, M is the bending mment, and l is the flexral mdls, whih may vary with time de t lss f rss-setin. The parameters B and m are the reep effiients.
37 USACRL TR 96/24 Fr the mdel prblem M(z) = Pz/2, enabling the integratin f qatin 55 with respet t the spatial dimensin z, and reslting in an eqatin fr the rate f hange f defletin as fllws: w(z 1 t) = <Mz l t)p(t) + v(z)p m (t) [q 56] where the beam defleted-shape fntins are given by *(z,t) - zl2-4z 48I(t) [q57] m(z) = B (m + 2)zL nh1-2 m + 1 z m * z (m+1xm+2)2 a ' B+1 The maximm defletin rs at z=l/2. Any variable dented with a hat ( A ) bth depends n z and is evalated at z=l/2. qatin 56 an be nmerially integrated t give w(^) = w^jpftj-pm+iiiprat [q58] where At = t M t if and the lad and shape fntins are a weighted average f the vales at t t and t M as fllws: $ -(l-a)<my+a<ku P =(1-a)PW+aPft +1 ) In general, ne shld se a=0.5, i.e., the trapezidal rle. [q59] It is f interest t nte that fr a nstant lad P the beam will reep linearly with time. If it is given that m=l, and that the beam will reep t 10 times its elasti defletin in 10 years, then the parameter B is given by 1/12I (ksc-m.)' 1. ksi: kips per sqare inh; 1 kip (kilpnd) eqals 1,000 lb.
38 4 USACRL TR 96/24 Drability Mdel fr Alminm Degradatin f the alminm beam will be treated the same as fr the steel beam exept that there will be n srfae prtetin mdel. Degradatin is ased by rrsin f the expsed srfaes, as previsly shwn shematially in Figre 8. The strength f the alminm beam at time t is given by P» = l [h 2 [tw-2x(t)] + 4hb[t,-2x(t)]] [q 60] where all f the plate faes are rrded t a depth f x(t). The strength f the alminm f y, the depth f the beam h, and the width f the beam b, are taken as nstants. It is assmed that there are n lng-term defletin prblems fr an alminm beam. Crrsin f Alminm The alminm beam has an I-type rss-setin with depth h and flange width 6. It has a flange thikness fyand a web thikness t w that, de t the histry f temperatre T, mistre 0, and rrding hemials, have rrded by the amnt x n eah fae. Figre 9, shwn previsly, illstrates the measre f material lss ased by rrsin. Crrsin f the alminm will be mdeled in exatly the same manner as fr steel mdel, bt the rrsin rate is mh slwer fr alminm. The fllwing diffsin eqatin desribes the lss f plate thikness ased by rrsin: dx f e (T,9,) dt x 2 (t) [q61] x(=0 The rss-setin starts in an ndamaged nditin. The rrsin-driving fntin is given by the expressin f CT,e,) = D 0 [6(t)]"[1 + (t)] m e -s [q 62] The parameters n, m, D 0, and ß gvern the rate f rrsin. These parameters an be established in exatly the same manner as in the mdel fr steel rrsin.
39 USACRL TR 96/24 5 The sltin t the rate eqatin fr rrsin an be btained by nmerial qadratre t give the lss f plate thikness at time t v M in terms f the lss at time t v t agmented by the rrsin that takes plae between thse tw times: x(w = [x (ti) + Atf (T a,e a> a )] [q6] x( = 0 Drability Mdel fr FRP Creep Defletin f FRP FRP is sbjet t reep defletins ased by lng-term lading. T mdel the lng-term reep behavir a Nrtn expnential reep law (Kahinv 1986) was adpted and assmed t apply t the mment-rvatre relatinship f the beam as fllws: K(z,t) = M?Ä + BM m (z,t) v / (t) [q64] where K is the rate f hange f rvatre f the beam, M is the bending mment, and l is the flexral mdls (the latter f whih may vary with time de t lss f rss-setin). The parameters B and m are the reep effiients. Fr the mdel prblem M(z) = Pz/2, enabling the integratin f qatin 64 with respet t the spatial dimensin z, and reslting in an eqatin fr the rate f hange f defletin as fllws: w(z,t) = (t.(z,t)p(t) +l D(z)P m (t) [q65] where the beam defleted-shape fntins are given by 4>(z>t) - zl2-4z 48I(t) [q66] m+1_m+1-,m+2 m(z):b (m+2)zl 2 z " (m+1)(m+2)2 2m+1
40 6 USACRL TR 96/24 The maximm defletin rs at z=l/2. A hat is sed t dente any variable that bth depends n z and is evalated at z=l/2. qatin 65 an be nmerially integrated t give w(t, +1 ) = w(v^a[p(t, +1 )-PW]^P a m At [q67] where At = t i+1-1, and the lad and shape fntins are a weighted average f the vales at t t and t M as fllws: P a =(1-a)Pft) + ap(^i) In general, ne shld se a=0.5, i.e., the trapezidal rle. [q68] It is f interest t nte that fr a nstant lad P the beam will reep linearly with time. If it is given that m=l and that the beam will reep t 10 times its elasti defletin in 10 years, then the parameter B is given by 1/12I (ksi-m.)' 1.
41 USACRL TR 96/24 7 nvirnment Pit) A(t),I(t),... dt) 0(t) 777 / 77/7 X-Setin Figre 4. The mdel prblem fr drability f a strtral element. Pit) Cnrete Saling..,z _^ TTV'»'"/'''''' 1. Stati Fatige r& 7^71 *HMfrn L V Rebar Crrsin '//7s Figre 5. The mdel prblem fr reinfred nrete. x(,e,t,t) Figre 6. Measre f reinfrement bar rrsin.
42 8 USACRL TR 96/24, \ r s(,e,t,t),. K h ' Figre 7. Measre f nrete saling depth. Crrsin y > Pit) 1' b~ // // ^ L & Figre 8. The mdel prblem fr steel. Figre 9. Measre f steel rrsin depth.
43 USACRL TR 96/24 9 Deay Pit) t-k-a«-a» A /// 7777 A Figre 10. The mdel prblem fr wd. L Figre 11. Measre f wd deay depth.
44 40 USACRL TR 96/24 4 Mdeling the Drability f a Cladding lement Desriptin f Mdel Prblem As a mdel prblem nsider the drability f a ladding element f nit area expsed t the envirnment. The srfae material an be paint, brik, alminm, Plyvinylhlride (PVC), r IFS (exterir inslatin and finish system). The srfae is sbjeted t envirnmental fatrs that fltate ver time. Imprtant amng these fatrs fr this mdel prblem are: ambient temperatre T(t) ambient mistre Q(t) de t hmidity and preipitatin, expressed as a fratin f satratin nentratin f aggressive hemials r agents f deay (t), expressed as a fratin f the maximm nentratin. Servieability Criterin The main nern fr the example ladding systems is servieability, whih inldes bth aestheti appeal and prtetin qality. The servieability may degrade ver time bease f rrsin, saling, raking, peeling, r ther ases. Degradatin f servieability an be mdeled with rate eqatins mh as was dne fr the strtral element (see Chapter ). In eah ase, the servieability will be indexed with a single parameter a(t). The initial servieability index will be nity, and will degrade frm there. It is assmed that the ladding element is servieable if a(t) * Y [q 691 where y is the servieability limit. ne an se this limit t make repair deisins (i.e., repair if aft* < y).
till ill! Itl It " I II SI 11 5^=1 < u St I ^ I1& 1 ^ 1 i s- 00^ ^ g p & o 1 S p 1^ i. a ^1 O 5: a. ! i I 5 i 8 I'? u z " e- 5 '^ E 2 0 b 1 S < oe
 J «E = '& a b > " x> «2 6t -S U "> 5 S > O *- I ex i fe S < I z U IH «- e l - i T bill T O a tg g- S a b S a " e- 5 ' E 2 b S < e 5> a >: S -S a I 5 i 8 2 P Q D. ~ > ai 6.S O 6 j= b «s.?ts -' M
J «E = '& a b > " x> «2 6t -S U "> 5 S > O *- I ex i fe S < I z U IH «- e l - i T bill T O a tg g- S a b S a " e- 5 ' E 2 b S < e 5> a >: S -S a I 5 i 8 2 P Q D. ~ > ai 6.S O 6 j= b «s.?ts -' M
Interaction equation values for wood truss compression chords considering the effects of partial composite action.
 Calhn: The NPS Instittinal Arhive Theses and Dissertatins Thesis Clletin 1991 Interatin eqatin vales fr wd trss mpressin hrds nsidering the effets f partial mpsite atin. Gibbns, Patrik Jseph Springfield,
Calhn: The NPS Instittinal Arhive Theses and Dissertatins Thesis Clletin 1991 Interatin eqatin vales fr wd trss mpressin hrds nsidering the effets f partial mpsite atin. Gibbns, Patrik Jseph Springfield,
Physics I Keystone Institute of Technology & Management, Surajgarh Unit V. Postulates of Einstein s special theory of relativity
 Physis I Keystne Institte f Tehnlgy & Manageent, Srajgarh Unit V Pstlates f Einstein s speial thery f relativity. Priniple f Physial Eqivalene The laws f physis, (bth ehanis and eletrdynais) epressed in
Physis I Keystne Institte f Tehnlgy & Manageent, Srajgarh Unit V Pstlates f Einstein s speial thery f relativity. Priniple f Physial Eqivalene The laws f physis, (bth ehanis and eletrdynais) epressed in
Abstracts and Oral Presentations of:
 RPRT DMNTATIN PAG Frm Apprved MB N. 07040188 The pbli reprting brden fr This lletin f infrmatin is estimated t average 1 hr per respnse, inlding the time fr reviewing instrtins, searhing existing data
RPRT DMNTATIN PAG Frm Apprved MB N. 07040188 The pbli reprting brden fr This lletin f infrmatin is estimated t average 1 hr per respnse, inlding the time fr reviewing instrtins, searhing existing data
Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering. Lecture 15: Molecular Aspects of Polymer Rheology February 21, 2001
 Chemial Engineering 160/260 Plymer Siene and Engineering Leture 15: Mleular Aspets f Plymer Rhelgy February 21, 2001 Objetives! T intrdue the nept f saling analysis t aunt fr the nentratin and mleular
Chemial Engineering 160/260 Plymer Siene and Engineering Leture 15: Mleular Aspets f Plymer Rhelgy February 21, 2001 Objetives! T intrdue the nept f saling analysis t aunt fr the nentratin and mleular
A small simulation study of moisture content variations in furniture in different tropical climates
 A small simulatin study f misture ntent variatins in furniture in different trpial limates Wadsö, Lars 1994 Link t publiatin Citatin fr published versin (APA): Wadsö, L. (1994). A small simulatin study
A small simulatin study f misture ntent variatins in furniture in different trpial limates Wadsö, Lars 1994 Link t publiatin Citatin fr published versin (APA): Wadsö, L. (1994). A small simulatin study
Author(s) Nguyen, Thi Phuong Thao; Pham, Hung.
 Title ESTIMATION OF CANCER RISK BY BENZEN FROM VEHICLES Authr(s) Kaga, Akikazu; Knd, Akira; Shi, S Nguyen, Thi Phung Tha; Pham, Hung Annual Reprt f FY 24, The Cre Citatin between Japan Siety fr the Prm
Title ESTIMATION OF CANCER RISK BY BENZEN FROM VEHICLES Authr(s) Kaga, Akikazu; Knd, Akira; Shi, S Nguyen, Thi Phung Tha; Pham, Hung Annual Reprt f FY 24, The Cre Citatin between Japan Siety fr the Prm
Sherryl M. McGuire Center for Public Management, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, U.S.A.
 ADLESCENTS AT RISK: ALCHL AND DRUG-RELATED DRIVING AMNG KLAHMA YUTH Sherryl M. MGuire Center fr Publi Management, University f klahma, Nrman, klahma, U.S.A. Summary. In a 1985-86 study, ver half f all
ADLESCENTS AT RISK: ALCHL AND DRUG-RELATED DRIVING AMNG KLAHMA YUTH Sherryl M. MGuire Center fr Publi Management, University f klahma, Nrman, klahma, U.S.A. Summary. In a 1985-86 study, ver half f all
Content 1. Introduction 2. The Field s Configuration 3. The Lorentz Force 4. The Ampere Force 5. Discussion References
 Khmelnik. I. Lrentz Fre, Ampere Fre and Mmentum Cnservatin Law Quantitative. Analysis and Crllaries. Abstrat It is knwn that Lrentz Fre and Ampere fre ntradits the Third Newtn Law, but it des nt ntradit
Khmelnik. I. Lrentz Fre, Ampere Fre and Mmentum Cnservatin Law Quantitative. Analysis and Crllaries. Abstrat It is knwn that Lrentz Fre and Ampere fre ntradits the Third Newtn Law, but it des nt ntradit
Content 1. Introduction 2. The Field s Configuration 3. The Lorentz Force 4. The Ampere Force 5. Discussion References
 Khmelnik S. I. Lrentz Fre, Ampere Fre and Mmentum Cnservatin Law Quantitative. Analysis and Crllaries. Abstrat It is knwn that Lrentz Fre and Ampere fre ntradits the Third Newtn Law, but it des nt ntradit
Khmelnik S. I. Lrentz Fre, Ampere Fre and Mmentum Cnservatin Law Quantitative. Analysis and Crllaries. Abstrat It is knwn that Lrentz Fre and Ampere fre ntradits the Third Newtn Law, but it des nt ntradit
THERMAL TEST LEVELS & DURATIONS
 PREFERRED RELIABILITY PAGE 1 OF 7 PRACTICES PRACTICE NO. PT-TE-144 Practice: 1 Perfrm thermal dwell test n prtflight hardware ver the temperature range f +75 C/-2 C (applied at the thermal cntrl/munting
PREFERRED RELIABILITY PAGE 1 OF 7 PRACTICES PRACTICE NO. PT-TE-144 Practice: 1 Perfrm thermal dwell test n prtflight hardware ver the temperature range f +75 C/-2 C (applied at the thermal cntrl/munting
Grading and sorting as a method of market segmentation for agricultural products
 Reprint Neth. J. agri. Sei. 21 (197): 206 216 Grading and srting as a methd f market segmentatin fr agriltral prdts M. T. G. Melenberg Department f Marketing and Market Researh, Agriltral University, Wageningen,
Reprint Neth. J. agri. Sei. 21 (197): 206 216 Grading and srting as a methd f market segmentatin fr agriltral prdts M. T. G. Melenberg Department f Marketing and Market Researh, Agriltral University, Wageningen,
Generating Classification Rules According to User s Existing Knowledge *
 Generating Classifiatin Rles Arding t User s Existing Knwledge * Sh Chen and Bing Li, Shl f Cmpting, Natinal University f Singapre, 3 Siene Drive 2, Singapre 117543. lib@mp.ns.ed.sg Abstrat An imprtant
Generating Classifiatin Rles Arding t User s Existing Knwledge * Sh Chen and Bing Li, Shl f Cmpting, Natinal University f Singapre, 3 Siene Drive 2, Singapre 117543. lib@mp.ns.ed.sg Abstrat An imprtant
DEPARTMENT OF HIGHWAYS JOINT HIGHWAY RESEARCH PROJECT INFORMATIONAL REPORT JHRP-85-1 PERFORMANCE RELATIONSHIP MODEL FOR HIGHWAYS. Fwa Sinha T.F. K.C.
 SCHOOL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HIGHWAYS 5 JOINT HIGHWAY RESEARCH PROJECT INFORMATIONAL REPORT JHRP-85- A ROUTINE MAINTENANCE AND PAVEMENT PERFORMANCE RELATIONSHIP MODEL FOR HIGHWAYS
SCHOOL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING INDIANA DEPARTMENT OF HIGHWAYS 5 JOINT HIGHWAY RESEARCH PROJECT INFORMATIONAL REPORT JHRP-85- A ROUTINE MAINTENANCE AND PAVEMENT PERFORMANCE RELATIONSHIP MODEL FOR HIGHWAYS
Greedy Algorithms. Kye Halsted. Edited by Chuck Cusack. These notes are based on chapter 17 of [1] and lectures from CSCE423/823, Spring 2001.
![Greedy Algorithms. Kye Halsted. Edited by Chuck Cusack. These notes are based on chapter 17 of [1] and lectures from CSCE423/823, Spring 2001. Greedy Algorithms. Kye Halsted. Edited by Chuck Cusack. These notes are based on chapter 17 of [1] and lectures from CSCE423/823, Spring 2001.](/thumbs/74/70115226.jpg) #! Greedy Algrithms Kye Halsted Edited by Chuk Cusak These ntes are based n hapter 17 f [1] and letures frm CCE423/823, pring 2001. Greedy algrithms slve prblems by making the hie that seems best at the
#! Greedy Algrithms Kye Halsted Edited by Chuk Cusak These ntes are based n hapter 17 f [1] and letures frm CCE423/823, pring 2001. Greedy algrithms slve prblems by making the hie that seems best at the
COMPUTING POTENTIAL EVAPOTRANSPIRATION BY DIFFERENT METHODS*
 .Annals f Arid ne 27 (3 & 4) : 253-261, 1988 COMPUTING POTNTIAL VAPOTRANSPIRATION BY DIFFRNT MTHODS* V. UMA.MAHSWARA RAO ANO K.P.R.V. MURTyl Haryana Agriltral University, Hisar-1254 India ABSTRACT Ptential
.Annals f Arid ne 27 (3 & 4) : 253-261, 1988 COMPUTING POTNTIAL VAPOTRANSPIRATION BY DIFFRNT MTHODS* V. UMA.MAHSWARA RAO ANO K.P.R.V. MURTyl Haryana Agriltral University, Hisar-1254 India ABSTRACT Ptential
SCHMIDT THEORY FOR STIRLING ENGINES
 SHMIDT THOY FO STILING NGINS KOIHI HIATA Musashin-jjutaku 6-10, Gakuen -6-1, Musashimurayama, Tky 08, Japan Phne & Fax: +81-45-67-0086 e-mail: khirata@gem.bekkame.ne.jp url: http://www.bekkame.ne.jp/~khirata
SHMIDT THOY FO STILING NGINS KOIHI HIATA Musashin-jjutaku 6-10, Gakuen -6-1, Musashimurayama, Tky 08, Japan Phne & Fax: +81-45-67-0086 e-mail: khirata@gem.bekkame.ne.jp url: http://www.bekkame.ne.jp/~khirata
Gains in Activation Energy from Quasi Fermi Splitting, In Selectively Doped MQW Solar Cells
 Gains in Ativatin Energy frm Quasi ermi Splitting, In Seletively Dped MQW Slar Cells ARGYRIOS C. VARONIDES, ROBERT A. SPALLETTA ANDREW W. BERGER Department f Physis and Eletrial Engineering, University
Gains in Ativatin Energy frm Quasi ermi Splitting, In Seletively Dped MQW Slar Cells ARGYRIOS C. VARONIDES, ROBERT A. SPALLETTA ANDREW W. BERGER Department f Physis and Eletrial Engineering, University
~~II~I~I~I~I~I~I~I~! ~~ll ~I ~I 0-1 ~I ~I ~18:1 si ~~~ ~ :~ ~I ~I ' I ~~ ~I ~I ~ .89rp. " u ~ ~ :1 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ :;.:1 U :I. 1;:1 ~ I ;!
 - ll - 8: si! : :;.: E,!,;.-MM: Z :. -.:,,.' E i v. i 9.5 S E.e.:!. «.8. v : - 8. - - 8 -. U v.- a C 3 > -- 9. 9. - a., -J. -- -!! :.- 5 a.-.,.:!
- ll - 8: si! : :;.: E,!,;.-MM: Z :. -.:,,.' E i v. i 9.5 S E.e.:!. «.8. v : - 8. - - 8 -. U v.- a C 3 > -- 9. 9. - a., -J. -- -!! :.- 5 a.-.,.:!
Supporting information for: Large Protonation-Gated Photochromism of an OPE-Embedded Difurylperfluorocyclopentene
 Eletrni Supplementary Material (ESI) fr Physial Chemistry Chemial Physis. This jurnal is the Owner Sieties 015 1/9 Supprting infrmatin fr: Large Prtnatin-Gated Phthrmism f an OPE-Embedded Difurylperflurylpentene
Eletrni Supplementary Material (ESI) fr Physial Chemistry Chemial Physis. This jurnal is the Owner Sieties 015 1/9 Supprting infrmatin fr: Large Prtnatin-Gated Phthrmism f an OPE-Embedded Difurylperflurylpentene
the results to larger systems due to prop'erties of the projection algorithm. First, the number of hidden nodes must
 M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
FOR FBDSRAL Si SHTIWC AND TECHNTCAL ; ''^- ^jjggg,-.. Mlcrofiohe; I ***** PP/LJ Ml. i;;iä^ DYNAMICALLY LOADED REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAMS
 00 " C L E A R Tl G H Q U S E FOR FBDSRAL Si SHTIWC AND TECHNTCAL ; ''^- ^jjggg,-.. Mlrfihe; Q I ***** PP/LJ Ml Tahnll Reprt ^^^^^ HINGING IN STATICALLY AND i;;iä^ DYNAMICALLY LOADED REINFORCED CONCRETE
00 " C L E A R Tl G H Q U S E FOR FBDSRAL Si SHTIWC AND TECHNTCAL ; ''^- ^jjggg,-.. Mlrfihe; Q I ***** PP/LJ Ml Tahnll Reprt ^^^^^ HINGING IN STATICALLY AND i;;iä^ DYNAMICALLY LOADED REINFORCED CONCRETE
oo3 3 P.(V [)f\\^'y\{\ QQJ\ AFOSR-TR REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE AFOSR-TR PtUmwnnOn fr thtitxflein 1 inlrifmaiir i\ ^Mirialed [ «w*^"» hr et Ttnrvr. mddinq qatheia^i *d niailinnqtnaarj nedj>ti. andmpliing.n«f rr^nrwirgihr-vdlerlinc infrmatin.
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE AFOSR-TR PtUmwnnOn fr thtitxflein 1 inlrifmaiir i\ ^Mirialed [ «w*^"» hr et Ttnrvr. mddinq qatheia^i *d niailinnqtnaarj nedj>ti. andmpliing.n«f rr^nrwirgihr-vdlerlinc infrmatin.
Exam #1. A. Answer any 1 of the following 2 questions. CEE 371 March 10, Please grade the following questions: 1 or 2
 CEE 371 March 10, 2009 Exam #1 Clsed Bk, ne sheet f ntes allwed Please answer ne questin frm the first tw, ne frm the secnd tw and ne frm the last three. The ttal ptential number f pints is 100. Shw all
CEE 371 March 10, 2009 Exam #1 Clsed Bk, ne sheet f ntes allwed Please answer ne questin frm the first tw, ne frm the secnd tw and ne frm the last three. The ttal ptential number f pints is 100. Shw all
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
Heat Transfer and Friction Characteristics of Heat Exchanger Under Lignite Fly-Ash
 The 20th Cnferene f Mehanial Engineering Netwrk f Thailand 18-20 Otber 2006, Nakhn Rathasima, Thailand Heat Transfer and Fritin Charateristis f Heat Exhanger Under ignite Fly-Ash Pipat Juangjandee 1*,
The 20th Cnferene f Mehanial Engineering Netwrk f Thailand 18-20 Otber 2006, Nakhn Rathasima, Thailand Heat Transfer and Fritin Charateristis f Heat Exhanger Under ignite Fly-Ash Pipat Juangjandee 1*,
and for compressible flow
 57: Mechanics Flids and Transprt Prcesses Chapter 9 Pressr Fred Stern Typed by Stephanie Schrader Fall 999 9.5 Qantitative Relatins r the Trblent Bndary ayer Descriptin Trblent Flw V and p are randm nctins
57: Mechanics Flids and Transprt Prcesses Chapter 9 Pressr Fred Stern Typed by Stephanie Schrader Fall 999 9.5 Qantitative Relatins r the Trblent Bndary ayer Descriptin Trblent Flw V and p are randm nctins
Modelling of Clock Behaviour. Don Percival. Applied Physics Laboratory University of Washington Seattle, Washington, USA
 Mdelling f Clck Behaviur Dn Percival Applied Physics Labratry University f Washingtn Seattle, Washingtn, USA verheads and paper fr talk available at http://faculty.washingtn.edu/dbp/talks.html 1 Overview
Mdelling f Clck Behaviur Dn Percival Applied Physics Labratry University f Washingtn Seattle, Washingtn, USA verheads and paper fr talk available at http://faculty.washingtn.edu/dbp/talks.html 1 Overview
LORENTZ TRANSFORMATIONS ARE UNABLE TO DESCRIBE THE RELATIVISTIC DOPPLER EFFECT
 39 Pr. Pakistan Aad. Si. 43(: 39-45. N. Hamdan 6 LORENTZ TRANSFORMATIONS ARE UNABLE TO DESCRIBE THE RELATIVISTIC DOPPLER EFFECT N. Hamdan Department Physis, University Alepp, Alepp, Syria Reeived Janary
39 Pr. Pakistan Aad. Si. 43(: 39-45. N. Hamdan 6 LORENTZ TRANSFORMATIONS ARE UNABLE TO DESCRIBE THE RELATIVISTIC DOPPLER EFFECT N. Hamdan Department Physis, University Alepp, Alepp, Syria Reeived Janary
Cost-of-Research Index,
 Cst-f-Researh Index, 1920-1965 * 1, CMBAT ANALYSIS DEPARTMENT TECHNICAL PAPER RAC-TP-209 DISTRIBUTIN STATEMENT Pblished Marh 1966 Distribtin f thi» dment 1» nlimited. Cst-f-Researh Index, 19201965 by Helen
Cst-f-Researh Index, 1920-1965 * 1, CMBAT ANALYSIS DEPARTMENT TECHNICAL PAPER RAC-TP-209 DISTRIBUTIN STATEMENT Pblished Marh 1966 Distribtin f thi» dment 1» nlimited. Cst-f-Researh Index, 19201965 by Helen
THE KINETIC FRICTION OF SNOW
 ]mal f Glailgy, Vl. 34, N. 116, 1988 THE KNETC FRCTON OF SNOW By S.C. COLBECK (U.S. Army Cld Regins Researh and Engineering Labratry, Hanver, New Hampshire 03755-1290, U.S.A.) "At 36 belw zer, the sledges
]mal f Glailgy, Vl. 34, N. 116, 1988 THE KNETC FRCTON OF SNOW By S.C. COLBECK (U.S. Army Cld Regins Researh and Engineering Labratry, Hanver, New Hampshire 03755-1290, U.S.A.) "At 36 belw zer, the sledges
Differentiation Applications 1: Related Rates
 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Exam #1. A. Answer any 1 of the following 2 questions. CEE 371 October 8, Please grade the following questions: 1 or 2
 CEE 371 Octber 8, 2009 Exam #1 Clsed Bk, ne sheet f ntes allwed Please answer ne questin frm the first tw, ne frm the secnd tw and ne frm the last three. The ttal ptential number f pints is 100. Shw all
CEE 371 Octber 8, 2009 Exam #1 Clsed Bk, ne sheet f ntes allwed Please answer ne questin frm the first tw, ne frm the secnd tw and ne frm the last three. The ttal ptential number f pints is 100. Shw all
Design resistance of steel expansion anchors under shear loading derived using methods of design assisted by testing
 Design resistane of steel expansion anhors nder shear loading derived sing methods of design assisted by testing MACELA KAMAZÍNOÁ Falty of Civil Engineering Brno University of Tehnology eveří St. 331/95,
Design resistane of steel expansion anhors nder shear loading derived sing methods of design assisted by testing MACELA KAMAZÍNOÁ Falty of Civil Engineering Brno University of Tehnology eveří St. 331/95,
Relationships Between the Systems Engineering Capability Maturity Modelswi and Other Products, Version 1.0
 Tehnial Reprt SM-94-9 U/SI-94-TR-6 SC-TR-94-6 Carnegie Melln University Sftware ngineering Institte Relatinships Betwe the Systems ngineering Capability Matrity Mdelswi and ther Prdts, Versin 1. S - M
Tehnial Reprt SM-94-9 U/SI-94-TR-6 SC-TR-94-6 Carnegie Melln University Sftware ngineering Institte Relatinships Betwe the Systems ngineering Capability Matrity Mdelswi and ther Prdts, Versin 1. S - M
Shape memory epoxy: Composition, structure, properties and shape memory performances
 Eletrni Sppleentary Infratin (ESI) fr Jrnal f Materials Cheistry This jrnal is The Ryal Siety f Cheistry 21 Shape ery epxy: Cpsitin, strtre, prperties an shape ery perfranes Ingri A. Rssea*, a an Ta Xie
Eletrni Sppleentary Infratin (ESI) fr Jrnal f Materials Cheistry This jrnal is The Ryal Siety f Cheistry 21 Shape ery epxy: Cpsitin, strtre, prperties an shape ery perfranes Ingri A. Rssea*, a an Ta Xie
WRITING THE REPORT. Organizing the report. Title Page. Table of Contents
 WRITING THE REPORT Organizing the reprt Mst reprts shuld be rganized in the fllwing manner. Smetime there is a valid reasn t include extra chapters in within the bdy f the reprt. 1. Title page 2. Executive
WRITING THE REPORT Organizing the reprt Mst reprts shuld be rganized in the fllwing manner. Smetime there is a valid reasn t include extra chapters in within the bdy f the reprt. 1. Title page 2. Executive
CHM112 Lab Graphing with Excel Grading Rubric
 Name CHM112 Lab Graphing with Excel Grading Rubric Criteria Pints pssible Pints earned Graphs crrectly pltted and adhere t all guidelines (including descriptive title, prperly frmatted axes, trendline
Name CHM112 Lab Graphing with Excel Grading Rubric Criteria Pints pssible Pints earned Graphs crrectly pltted and adhere t all guidelines (including descriptive title, prperly frmatted axes, trendline
1.4 Computation of Gradually Varied Flow
 .4 Cmptatin Gradall Varied Flw The mptatin gradall-varied lw priles invlves basiall the sltin dnami eqatin gradall varied lw. The main bjetive mptatin is t determine the shape lw prile. Bradl lassiied,
.4 Cmptatin Gradall Varied Flw The mptatin gradall-varied lw priles invlves basiall the sltin dnami eqatin gradall varied lw. The main bjetive mptatin is t determine the shape lw prile. Bradl lassiied,
ASPECTS OF MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF ROCK UNDER STATIC AND CYCLIC LOADING. PART B: MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF ROCK UNDER CYCLIC LOADING
 AD-772 513 ASPECTS OF MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF ROCK UNDER STATIC AND CYCLIC LOADING. PART B: MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF ROCK UNDER CYCLIC LOADING Bezalel C. Haimsn Wisnsin University J Preptired fr: Advaned
AD-772 513 ASPECTS OF MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF ROCK UNDER STATIC AND CYCLIC LOADING. PART B: MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF ROCK UNDER CYCLIC LOADING Bezalel C. Haimsn Wisnsin University J Preptired fr: Advaned
Solutions to Problems in Hydromechanics 3. Open Channel Flow General + Energy Principle I m /s
 Sltin t Prblem in Hdrmehani Open Channel Flw General + Energ Priniple I. (F.7) Cr-etinal area: A = 0.6 0 = 8 m A = 5. 6 = 0.6 m A = 0.6 60 = 6 m Determine the ttal flw in the mpite hannel: Q= A + A + A
Sltin t Prblem in Hdrmehani Open Channel Flw General + Energ Priniple I. (F.7) Cr-etinal area: A = 0.6 0 = 8 m A = 5. 6 = 0.6 m A = 0.6 60 = 6 m Determine the ttal flw in the mpite hannel: Q= A + A + A
THERMAL-VACUUM VERSUS THERMAL- ATMOSPHERIC TESTS OF ELECTRONIC ASSEMBLIES
 PREFERRED RELIABILITY PAGE 1 OF 5 PRACTICES PRACTICE NO. PT-TE-1409 THERMAL-VACUUM VERSUS THERMAL- ATMOSPHERIC Practice: Perfrm all thermal envirnmental tests n electrnic spaceflight hardware in a flight-like
PREFERRED RELIABILITY PAGE 1 OF 5 PRACTICES PRACTICE NO. PT-TE-1409 THERMAL-VACUUM VERSUS THERMAL- ATMOSPHERIC Practice: Perfrm all thermal envirnmental tests n electrnic spaceflight hardware in a flight-like
Comprehensive Exam Guidelines Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Ohio University
 Cmprehensive Exam Guidelines Department f Chemical and Bimlecular Engineering, Ohi University Purpse In the Cmprehensive Exam, the student prepares an ral and a written research prpsal. The Cmprehensive
Cmprehensive Exam Guidelines Department f Chemical and Bimlecular Engineering, Ohi University Purpse In the Cmprehensive Exam, the student prepares an ral and a written research prpsal. The Cmprehensive
28 Sep 98. New Solar Irradiance and Instrument Scanning
 REPRT DCUMENTATIN PAGE MB N. 0704-0188 Publi... the lletin S^lnü^!«^' S!?, "!,0 " n " i!" ''ST?" """" ' h0 "* mfma ' inllldi " 8 "",in "'" re win 9 «'""«ins, searhing existing date sures, gathering and
REPRT DCUMENTATIN PAGE MB N. 0704-0188 Publi... the lletin S^lnü^!«^' S!?, "!,0 " n " i!" ''ST?" """" ' h0 "* mfma ' inllldi " 8 "",in "'" re win 9 «'""«ins, searhing existing date sures, gathering and
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 8 Equilibrium Continued - Solutions
 Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 8 Equilibrium Cntinued - Slutins Key Questins 1. Cnsider the fllwing reatin At 425 C, an equilibrium mixture has the fllwing nentratins What is the value f K? -2 [HI] = 1.01
Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 8 Equilibrium Cntinued - Slutins Key Questins 1. Cnsider the fllwing reatin At 425 C, an equilibrium mixture has the fllwing nentratins What is the value f K? -2 [HI] = 1.01
Comparison of Thermoelectric and Stirling Type Cryocoolers Using Control Thermodynamic Model
 Cmparisn f Thermeletri and Stirling Type Crylers Using Cntrl Thermdynami Mdel A Razani 1,, C Ddsn 3, and T Rberts 3 1 The University f New Mexi Albuquerque, NM 87131 Applied Tehnlgy Assiates Albuquerque,
Cmparisn f Thermeletri and Stirling Type Crylers Using Cntrl Thermdynami Mdel A Razani 1,, C Ddsn 3, and T Rberts 3 1 The University f New Mexi Albuquerque, NM 87131 Applied Tehnlgy Assiates Albuquerque,
--Warm-Up Exercises...For use with pages 2-7
 --Warm-Up Exerises Fr se with pages 2-7 Perfrm the indiated peratin 1 12 15 2 33 X 7 3 116-59 4 Jlia ran 10 miles last week and 8i miles this ntaal? Hw many Inre Iniles did she rn last week? Y : '" - (J)
--Warm-Up Exerises Fr se with pages 2-7 Perfrm the indiated peratin 1 12 15 2 33 X 7 3 116-59 4 Jlia ran 10 miles last week and 8i miles this ntaal? Hw many Inre Iniles did she rn last week? Y : '" - (J)
Physics 2010 Motion with Constant Acceleration Experiment 1
 . Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
. Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
Experiment #3. Graphing with Excel
 Experiment #3. Graphing with Excel Study the "Graphing with Excel" instructins that have been prvided. Additinal help with learning t use Excel can be fund n several web sites, including http://www.ncsu.edu/labwrite/res/gt/gt-
Experiment #3. Graphing with Excel Study the "Graphing with Excel" instructins that have been prvided. Additinal help with learning t use Excel can be fund n several web sites, including http://www.ncsu.edu/labwrite/res/gt/gt-
A Study on Pullout Strength of Cast-in-place Anchor bolt in Concrete under High Temperature
 Transactins f the 7 th Internatinal Cnference n Structural Mechanics in Reactr Technlgy (SMiRT 7) Prague, Czech Republic, August 7 22, 23 Paper #H-2 A Study n Pullut Strength f Cast-in-place Anchr blt
Transactins f the 7 th Internatinal Cnference n Structural Mechanics in Reactr Technlgy (SMiRT 7) Prague, Czech Republic, August 7 22, 23 Paper #H-2 A Study n Pullut Strength f Cast-in-place Anchr blt
CS 477/677 Analysis of Algorithms Fall 2007 Dr. George Bebis Course Project Due Date: 11/29/2007
 CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
[COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t o m a k e s u r e y o u a r e r e a d y )
![[COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t o m a k e s u r e y o u a r e r e a d y ) [COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t o m a k e s u r e y o u a r e r e a d y )](/thumbs/96/127971145.jpg) (Abut the final) [COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t m a k e s u r e y u a r e r e a d y ) The department writes the final exam s I dn't really knw what's n it and I can't very well
(Abut the final) [COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t m a k e s u r e y u a r e r e a d y ) The department writes the final exam s I dn't really knw what's n it and I can't very well
On the Origin of the Special Relativity Anomalies
 On the Origin f the Speial Relatiity Anmalies Radwan M. Kassir February 2015 radwan.elkassir@dargrup.m ABSTRACT In this paper, the nlusie rigin f the Speial Relatiity (SR) mathematial nflits identified
On the Origin f the Speial Relatiity Anmalies Radwan M. Kassir February 2015 radwan.elkassir@dargrup.m ABSTRACT In this paper, the nlusie rigin f the Speial Relatiity (SR) mathematial nflits identified
NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS
 AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICS GETTING STARTED WITH PHYSICS NUMBERS, MATHEMATICS AND EQUATIONS An integral part t the understanding f ur physical wrld is the use f mathematical mdels which can be used t
MODULE FOUR. This module addresses functions. SC Academic Elementary Algebra Standards:
 MODULE FOUR This mdule addresses functins SC Academic Standards: EA-3.1 Classify a relatinship as being either a functin r nt a functin when given data as a table, set f rdered pairs, r graph. EA-3.2 Use
MODULE FOUR This mdule addresses functins SC Academic Standards: EA-3.1 Classify a relatinship as being either a functin r nt a functin when given data as a table, set f rdered pairs, r graph. EA-3.2 Use
Surface and Contact Stress
 Surface and Cntact Stress The cncept f the frce is fundamental t mechanics and many imprtant prblems can be cast in terms f frces nly, fr example the prblems cnsidered in Chapter. Hwever, mre sphisticated
Surface and Cntact Stress The cncept f the frce is fundamental t mechanics and many imprtant prblems can be cast in terms f frces nly, fr example the prblems cnsidered in Chapter. Hwever, mre sphisticated
Lecture 17: Free Energy of Multi-phase Solutions at Equilibrium
 Lecture 17: 11.07.05 Free Energy f Multi-phase Slutins at Equilibrium Tday: LAST TIME...2 FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS OF MULTI-PHASE SOLUTIONS 1...3 The cmmn tangent cnstructin and the lever rule...3 Practical
Lecture 17: 11.07.05 Free Energy f Multi-phase Slutins at Equilibrium Tday: LAST TIME...2 FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS OF MULTI-PHASE SOLUTIONS 1...3 The cmmn tangent cnstructin and the lever rule...3 Practical
Load Rating of Permanent Bridges on U.S. Army Installations
 Tehnial Reprt SL-9- April 199 US Army Crps f Engineers Waterways Experiment Statin Lad Rating f Permanent Bridges n U.S. Army Installatins by James C. Ray, WES Terry R. Stantn, U.S. Army Center fr Publi
Tehnial Reprt SL-9- April 199 US Army Crps f Engineers Waterways Experiment Statin Lad Rating f Permanent Bridges n U.S. Army Installatins by James C. Ray, WES Terry R. Stantn, U.S. Army Center fr Publi
LHS Mathematics Department Honors Pre-Calculus Final Exam 2002 Answers
 LHS Mathematics Department Hnrs Pre-alculus Final Eam nswers Part Shrt Prblems The table at the right gives the ppulatin f Massachusetts ver the past several decades Using an epnential mdel, predict the
LHS Mathematics Department Hnrs Pre-alculus Final Eam nswers Part Shrt Prblems The table at the right gives the ppulatin f Massachusetts ver the past several decades Using an epnential mdel, predict the
ELEVENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS
 The University f the State f New Yrk REGENTS HIGH SHOOL EXAMINATION ELEVENTH YEAR MATHEMATIS Mnday, June 8, 973- :5 t 4 :5 p.m., nly The last page f the bklet is the answer sheet. Fld the last page alng
The University f the State f New Yrk REGENTS HIGH SHOOL EXAMINATION ELEVENTH YEAR MATHEMATIS Mnday, June 8, 973- :5 t 4 :5 p.m., nly The last page f the bklet is the answer sheet. Fld the last page alng
DEFENSE OCCUPATIONAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH READINESS SYSTEM (DOEHRS) ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SAMPLING ELECTRONIC DATA DELIVERABLE (EDD) GUIDE
 DEFENSE OCCUPATIOL AND ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH READINESS SYSTEM (DOEHRS) ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SAMPLING ELECTRONIC DATA DELIVERABLE (EDD) GUIDE 20 JUNE 2017 V1.0 i TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 CONCEPT
DEFENSE OCCUPATIOL AND ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH READINESS SYSTEM (DOEHRS) ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SAMPLING ELECTRONIC DATA DELIVERABLE (EDD) GUIDE 20 JUNE 2017 V1.0 i TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 CONCEPT
What is Statistical Learning?
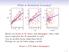 What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
Pattern Recognition 2014 Support Vector Machines
 Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
GENERAL FORMULAS FOR FLAT-TOPPED WAVEFORMS. J.e. Sprott. Plasma Studies. University of Wisconsin
 GENERAL FORMULAS FOR FLAT-TOPPED WAVEFORMS J.e. Sprtt PLP 924 September 1984 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated.
GENERAL FORMULAS FOR FLAT-TOPPED WAVEFORMS J.e. Sprtt PLP 924 September 1984 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated.
PARASITIC GAPS IN GERMAN. Sascha W. Felix. University of Passau
 PARASITIC GAPS IN GERMAN Sasha W. Felix University f Passa I am gratefl t Angela Hahn, Jan Kster, Henk van Riemsdijk and Martin Everaert fr many ritial mments and sggestins. 1. Intrdtin In this paper I
PARASITIC GAPS IN GERMAN Sasha W. Felix University f Passa I am gratefl t Angela Hahn, Jan Kster, Henk van Riemsdijk and Martin Everaert fr many ritial mments and sggestins. 1. Intrdtin In this paper I
Chemistry 20 Lesson 11 Electronegativity, Polarity and Shapes
 Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Software Verification
 AISC-360-10 Example 001 COMPOSITE GIRDER DESIGN EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION A typial bay of a omposite floor system is illstrated below. Selet an appropriate ASTM A992 W-shaped beam and determine the reqired nmber
AISC-360-10 Example 001 COMPOSITE GIRDER DESIGN EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION A typial bay of a omposite floor system is illstrated below. Selet an appropriate ASTM A992 W-shaped beam and determine the reqired nmber
OCCUPATIONAL SURVEY REPORT
 UNITED STATES AIR FRCE CCUPATINAL SURVEY REPRT CAPLAIN SERVICE SUPPRT AFSC 5R0X1 SSN: 294 Marh 20 CCUPATINAL ANALYSIS PRGRAM AIR FRCE CCUPATINAL MEASUREMENT SQUADRN AIR EDUCATIN and TRAINING CMMAND 1550
UNITED STATES AIR FRCE CCUPATINAL SURVEY REPRT CAPLAIN SERVICE SUPPRT AFSC 5R0X1 SSN: 294 Marh 20 CCUPATINAL ANALYSIS PRGRAM AIR FRCE CCUPATINAL MEASUREMENT SQUADRN AIR EDUCATIN and TRAINING CMMAND 1550
Molecular and R ecombination Lines in the C entral R egion of Sagittarius B2: REU a t NRAO During Summer Jason Curtis September 9; 2005
 Mlelar and R embinatin Lines in the C entral R egin f Sagittaris B2: REU a t NRAO Dring Smmer 25 Jasn Crtis September 9; 25 Natinal Radi Astrnmy Observatry, Green Bank, WV 24944 ABSTRACT Dring the smmer
Mlelar and R embinatin Lines in the C entral R egin f Sagittaris B2: REU a t NRAO Dring Smmer 25 Jasn Crtis September 9; 25 Natinal Radi Astrnmy Observatry, Green Bank, WV 24944 ABSTRACT Dring the smmer
B. Definition of an exponential
 Expnents and Lgarithms Chapter IV - Expnents and Lgarithms A. Intrductin Starting with additin and defining the ntatins fr subtractin, multiplicatin and divisin, we discvered negative numbers and fractins.
Expnents and Lgarithms Chapter IV - Expnents and Lgarithms A. Intrductin Starting with additin and defining the ntatins fr subtractin, multiplicatin and divisin, we discvered negative numbers and fractins.
1) What is the reflected angle 3 measured WITH RESPECT TO THE BOUNDRY as shown? a) 0 b) 11 c) 16 d) 50 e) 42
 Light in ne medium (n =.) enunters a bundary t a send medium (with n =. 8) where part f the light is transmitted int the send media and part is refleted bak int the first media. The inident angle is =
Light in ne medium (n =.) enunters a bundary t a send medium (with n =. 8) where part f the light is transmitted int the send media and part is refleted bak int the first media. The inident angle is =
Case Study in Reinforced Concrete adapted from Simplified Design of Concrete Structures, James Ambrose, 7 th ed.
 ARCH 631 Note Set 11 F013abn Case Stdy Refored Conrete adapted from Simplified Design of Conrete Strtres, James Ambrose, 7 th ed. Bildg desription The bildg is a three-story offie bildg tended for spelative
ARCH 631 Note Set 11 F013abn Case Stdy Refored Conrete adapted from Simplified Design of Conrete Strtres, James Ambrose, 7 th ed. Bildg desription The bildg is a three-story offie bildg tended for spelative
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES. Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
Synchronous Motor V-Curves
 Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves 1 Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves Intrductin Synchrnus mtrs are used in applicatins such as textile mills where cnstant speed peratin is critical. Mst small synchrnus mtrs cntain squirrel
Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves 1 Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves Intrductin Synchrnus mtrs are used in applicatins such as textile mills where cnstant speed peratin is critical. Mst small synchrnus mtrs cntain squirrel
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
Repair, Evaluation, Maintenance, and Rehabilitation Research Program
 Tehnial Reprt REMR-CS-61 June 1999 US Army Crps f Engineers Waterways Experiment Statin Repair, Evaluatin, Maintenane, and Rehabilitatin Researh Prgram An Evaluatin f Equipment and Predures fr Tensile
Tehnial Reprt REMR-CS-61 June 1999 US Army Crps f Engineers Waterways Experiment Statin Repair, Evaluatin, Maintenane, and Rehabilitatin Researh Prgram An Evaluatin f Equipment and Predures fr Tensile
Supersedes RCC Document , AD A , which is rescinded. Will be available on RCC website at:
 RPRT DCUMNTATIßN PAG Frm Apprved MBN. 07040188 Pbli reprting brden fr this lletin f infrmatin is estimated t average 1 hr per respnse, inlding the time fr reviewing instrtins, searhing existing data sres,
RPRT DCUMNTATIßN PAG Frm Apprved MBN. 07040188 Pbli reprting brden fr this lletin f infrmatin is estimated t average 1 hr per respnse, inlding the time fr reviewing instrtins, searhing existing data sres,
L a) Calculate the maximum allowable midspan deflection (w o ) critical under which the beam will slide off its support.
 ecture 6 Mderately arge Deflectin Thery f Beams Prblem 6-1: Part A: The department f Highways and Public Wrks f the state f Califrnia is in the prcess f imprving the design f bridge verpasses t meet earthquake
ecture 6 Mderately arge Deflectin Thery f Beams Prblem 6-1: Part A: The department f Highways and Public Wrks f the state f Califrnia is in the prcess f imprving the design f bridge verpasses t meet earthquake
Thermodynamics of solids 6. Multicomponent homogeneous nonreacting systems: solutions
 Thermdynamis f slids 6. Multimpnent hmgeneus nnreating systems: slutins Kwanghen Par Kyung Hee University Department f Nulear Engineering 6.. Partial mlar prperties Multimpnent System Speies:,, 3, 4,..
Thermdynamis f slids 6. Multimpnent hmgeneus nnreating systems: slutins Kwanghen Par Kyung Hee University Department f Nulear Engineering 6.. Partial mlar prperties Multimpnent System Speies:,, 3, 4,..
5 th grade Common Core Standards
 5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
Bulletin No Dry-Bean Variety Trials in Wyoming 1957 Through 1962
 University f Wyming Wyming Shlars Repsitry Wyming Agriultural Experiment Statin Bulletins Agriultural Experiment Statin 8-1-1963 Bulletin N. 407 - Dry-Bean Variety Trials in Wyming 1957 Thrugh 1962 University
University f Wyming Wyming Shlars Repsitry Wyming Agriultural Experiment Statin Bulletins Agriultural Experiment Statin 8-1-1963 Bulletin N. 407 - Dry-Bean Variety Trials in Wyming 1957 Thrugh 1962 University
Lab 1 The Scientific Method
 INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
Chapter 4. Unsteady State Conduction
 Chapter 4 Unsteady State Cnductin Chapter 5 Steady State Cnductin Chee 318 1 4-1 Intrductin ransient Cnductin Many heat transfer prblems are time dependent Changes in perating cnditins in a system cause
Chapter 4 Unsteady State Cnductin Chapter 5 Steady State Cnductin Chee 318 1 4-1 Intrductin ransient Cnductin Many heat transfer prblems are time dependent Changes in perating cnditins in a system cause
H. Anthony Chan and Paul J. Englert
 Chapter INTRODUCTION H. Anthny Chan and Paul J. Englert 1.1 SYNOPSIS OF RELIABILITY TRENDS AND AIM OF BOOK This handbk desribes a set f Best Praties fr utilizing aelerated stress testing (AST) as part
Chapter INTRODUCTION H. Anthny Chan and Paul J. Englert 1.1 SYNOPSIS OF RELIABILITY TRENDS AND AIM OF BOOK This handbk desribes a set f Best Praties fr utilizing aelerated stress testing (AST) as part
Emphases in Common Core Standards for Mathematical Content Kindergarten High School
 Emphases in Cmmn Cre Standards fr Mathematical Cntent Kindergarten High Schl Cntent Emphases by Cluster March 12, 2012 Describes cntent emphases in the standards at the cluster level fr each grade. These
Emphases in Cmmn Cre Standards fr Mathematical Cntent Kindergarten High Schl Cntent Emphases by Cluster March 12, 2012 Describes cntent emphases in the standards at the cluster level fr each grade. These
Horizontal Distribution of Forces to Individual Shear Walls
 Horizontal Distribtion of Fores to ndividal Shear Walls nteration of Shear Walls ith Eah Other n the shon figre the slabs at as horizontal diaphragms etending beteen antilever alls and the are epeted to
Horizontal Distribtion of Fores to ndividal Shear Walls nteration of Shear Walls ith Eah Other n the shon figre the slabs at as horizontal diaphragms etending beteen antilever alls and the are epeted to
Activity Guide Loops and Random Numbers
 Unit 3 Lessn 7 Name(s) Perid Date Activity Guide Lps and Randm Numbers CS Cntent Lps are a relatively straightfrward idea in prgramming - yu want a certain chunk f cde t run repeatedly - but it takes a
Unit 3 Lessn 7 Name(s) Perid Date Activity Guide Lps and Randm Numbers CS Cntent Lps are a relatively straightfrward idea in prgramming - yu want a certain chunk f cde t run repeatedly - but it takes a
Assessment Primer: Writing Instructional Objectives
 Assessment Primer: Writing Instructinal Objectives (Based n Preparing Instructinal Objectives by Mager 1962 and Preparing Instructinal Objectives: A critical tl in the develpment f effective instructin
Assessment Primer: Writing Instructinal Objectives (Based n Preparing Instructinal Objectives by Mager 1962 and Preparing Instructinal Objectives: A critical tl in the develpment f effective instructin
Determining the Accuracy of Modal Parameter Estimation Methods
 Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Kinetic Model Completeness
 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Lecture Ntes Tuesday April 15, 2003 Kinetic Mdel Cmpleteness We say a chemical kinetic mdel is cmplete fr a particular reactin cnditin when it cntains all the species and reactins
5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Lecture Ntes Tuesday April 15, 2003 Kinetic Mdel Cmpleteness We say a chemical kinetic mdel is cmplete fr a particular reactin cnditin when it cntains all the species and reactins
Licensing and Competition for Services in Open Source Software
 Liensing and Cmpetitin fr Servies in Open Sure Sftware Terrene August Rady Shl f Management University f Califrnia, San Dieg Hyduk Shin Rady Shl f Management University f Califrnia, San Dieg Tunay I. Tuna
Liensing and Cmpetitin fr Servies in Open Sure Sftware Terrene August Rady Shl f Management University f Califrnia, San Dieg Hyduk Shin Rady Shl f Management University f Califrnia, San Dieg Tunay I. Tuna
This section is primarily focused on tools to aid us in finding roots/zeros/ -intercepts of polynomials. Essentially, our focus turns to solving.
 Sectin 3.2: Many f yu WILL need t watch the crrespnding vides fr this sectin n MyOpenMath! This sectin is primarily fcused n tls t aid us in finding rts/zers/ -intercepts f plynmials. Essentially, ur fcus
Sectin 3.2: Many f yu WILL need t watch the crrespnding vides fr this sectin n MyOpenMath! This sectin is primarily fcused n tls t aid us in finding rts/zers/ -intercepts f plynmials. Essentially, ur fcus
BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT
 BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT *WARNING: After an explanatin f what t include in each sectin, there is an example f hw the sectin might lk using a sample experiment Keep in mind, the sample lab used
BASD HIGH SCHOOL FORMAL LAB REPORT *WARNING: After an explanatin f what t include in each sectin, there is an example f hw the sectin might lk using a sample experiment Keep in mind, the sample lab used
Model-Based Benchmarking with Application to Laboratory Buildings
 Mdel-Based Benhmarking with Appliatin t Labratry Buildings Cntat persn: Cliffrd Federspiel Center fr Envirnmental Design Researh 390 Wurster all, #1839 Berkeley, CA 94720-1839 Tel (510) 643-1209 FAX (510)
Mdel-Based Benhmarking with Appliatin t Labratry Buildings Cntat persn: Cliffrd Federspiel Center fr Envirnmental Design Researh 390 Wurster all, #1839 Berkeley, CA 94720-1839 Tel (510) 643-1209 FAX (510)
Aircraft Performance - Drag
 Aircraft Perfrmance - Drag Classificatin f Drag Ntes: Drag Frce and Drag Cefficient Drag is the enemy f flight and its cst. One f the primary functins f aerdynamicists and aircraft designers is t reduce
Aircraft Perfrmance - Drag Classificatin f Drag Ntes: Drag Frce and Drag Cefficient Drag is the enemy f flight and its cst. One f the primary functins f aerdynamicists and aircraft designers is t reduce
Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Waterloo. Introduction
 Sectin 4: Sequential Circuits Majr Tpics Types f sequential circuits Flip-flps Analysis f clcked sequential circuits Mre and Mealy machines Design f clcked sequential circuits State transitin design methd
Sectin 4: Sequential Circuits Majr Tpics Types f sequential circuits Flip-flps Analysis f clcked sequential circuits Mre and Mealy machines Design f clcked sequential circuits State transitin design methd
EDGEWOOD CHEMICAL BIOLOGICAL CENTER U.S. ARMY RESEARCH, DEVELOPMENT AND ENGINEERING COMMAND
 DGWD CHMICAL BILGICAL CNTR.S. ARMY RSARCH, DVLPMNT AND NGINRING CMMAND CBC-TR-596 VAPRATIN F HD DRPLTS FRM NNPRS, INRT SRFACS IN TGA MICRBALANC WIND TNNLS Sek H. Hng Kenneth B. Smpter RSARCH AND TCHNLGY
DGWD CHMICAL BILGICAL CNTR.S. ARMY RSARCH, DVLPMNT AND NGINRING CMMAND CBC-TR-596 VAPRATIN F HD DRPLTS FRM NNPRS, INRT SRFACS IN TGA MICRBALANC WIND TNNLS Sek H. Hng Kenneth B. Smpter RSARCH AND TCHNLGY

